Overview of Cancer and Treatments and Therapies - CHEMOTHERAPY
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Chemotherapeutic drugs are designed to target where?
various aspects of all the cell cycle
What does Chemotherapeutic drugs mainly affect?
mitosis, but some target S-phase processes, while others directly damage DNA
What do Chemotherapeutic drugs do not specifically recognize what?
neoplastic cells (what cancer is/isn't)
Majority of cells in many tissues are non-cycling, so cancer cells in these tissues are favorably targeted why?
to their HIGH rate of mitosis
What tissues what have high turnover?
GI tract, hair follicles, and germ cells
What is essential for producing healthy daughter cells?
mitosis
What are the 5 distinct phases of mitosis?
1. Prophase
2. Metaphase
3. Anaphase
4. Telophase
5. Cytogenesis
What are mitotic inhibitors?
Drugs that kill cells as the process of mitosis begins
What are the 2 mitotic inhibitors?
1. Vinca Alkaloids
2. Taxanes
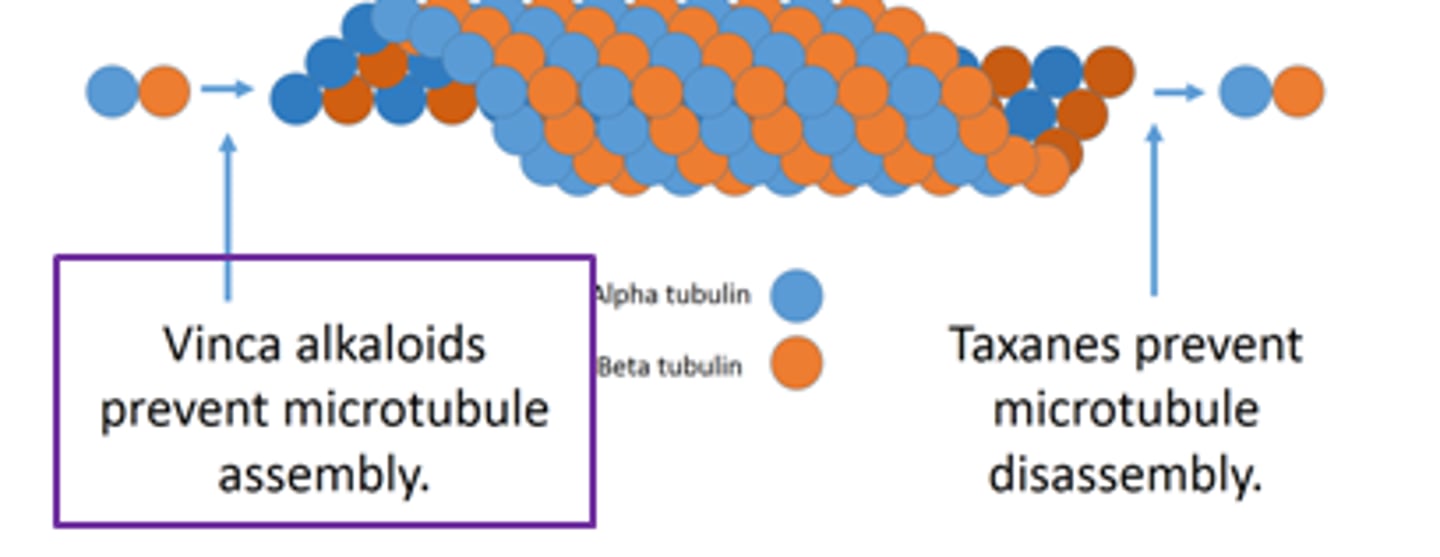
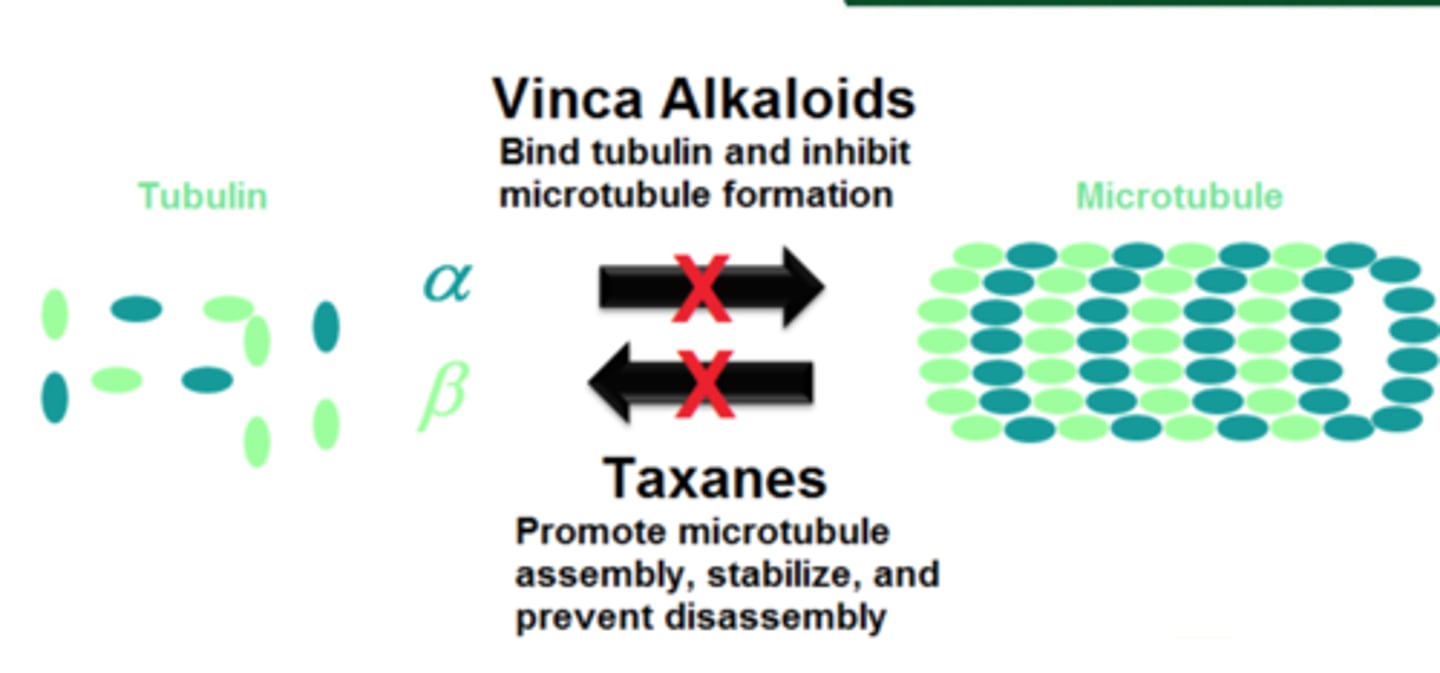
Vinca Alkaloids (mitotic inhibitor)
microtubule destabilizers and inhibit their growth
- binds to free tubulin dimers, preventing them from being incorporated into microtubule polymers
- NO GROWTH
What are examples of Vinca Alkaloids?
vincristine and vinblastine
What are Vinca Alkaloids used to treat?
breast cancers, lung cancer, myelomas, lymphomas, and leukemias
Taxanes (mitotic inhibitor)
microtubule stablizers
- bind to the cap on the plus end of the microtubule and prevent GTP to GDP conversion, INHIBITING the shrinkage of the microtubule
- NO SHRINK
What are examples of taxanes?
Paclitaxel and Docetaxel
Anti-Metabolites
1. Methotrexate
2. Fluorouracil
Methotrexate (Anti-Metabolites)
analogue of folic acid
What does Methotrexate inhibit?
DHFR
When methotrexate inhibits DHFR, what does this mean?
no synthesis of thymidine
Fluorouracil - 5-FU (Anti-Metabolites)
prevents the synthesis of thymidine
What are Anti-Metabolites commonly used to treat?
leukemias, breast, overian, and GI cancers
Why do both Anti-Metabolite drugs result in Thymineless death of cells?
its due to the absence of dTTPs and inability to replicate DNA
What does DNA Damaging agents have?
cytotoxic activity
DNA Damaging agents cytotoxic activity is due to what?
the induction of DNA damage
What are 3 examples of DNA Damaging agents?
1. Doxorubicin
2. Dactinomycin (actinomycin D)
3. Alkylating Agents
Doxorubicin (DNA Damaging Agents)
induces free radical species
Dactinomycin (DNA Damaging Agents)
intercalates into the minor groove of the DNA double helix structure
Alklaying Agents (DNA Damaging Agents)
can also be used to induce DNA damage
- Streptozocin
- Busulfan