Ag Econ Exam 3
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
1
New cards
perfect
mr/mc for the _____ competitor
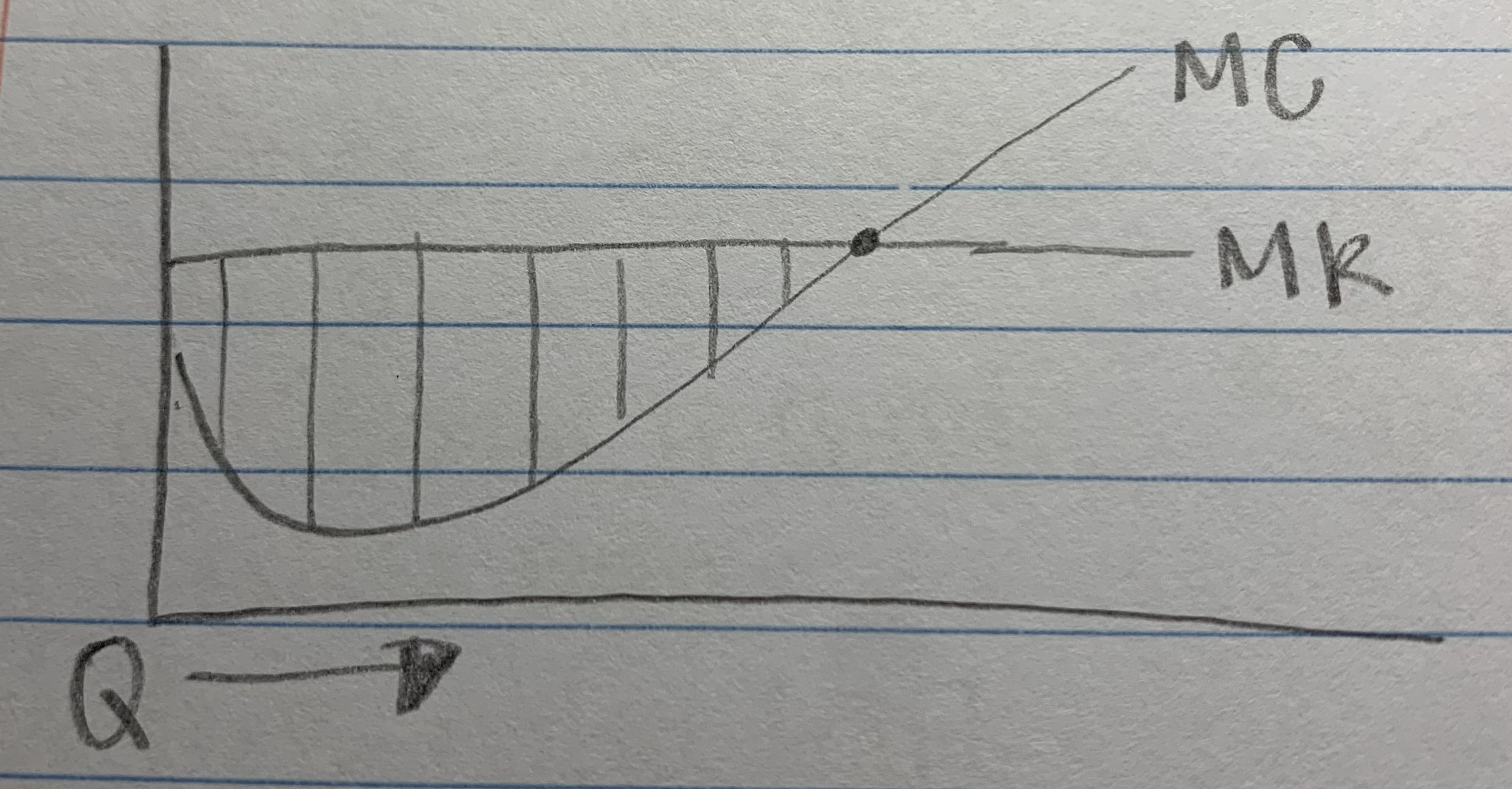
2
New cards
firms?; small town businesses; no fee for entry
monopolist
3
New cards
monopoly power is lasting and won't go away
monopoly vs. "monopoly power"
4
New cards
monopolist
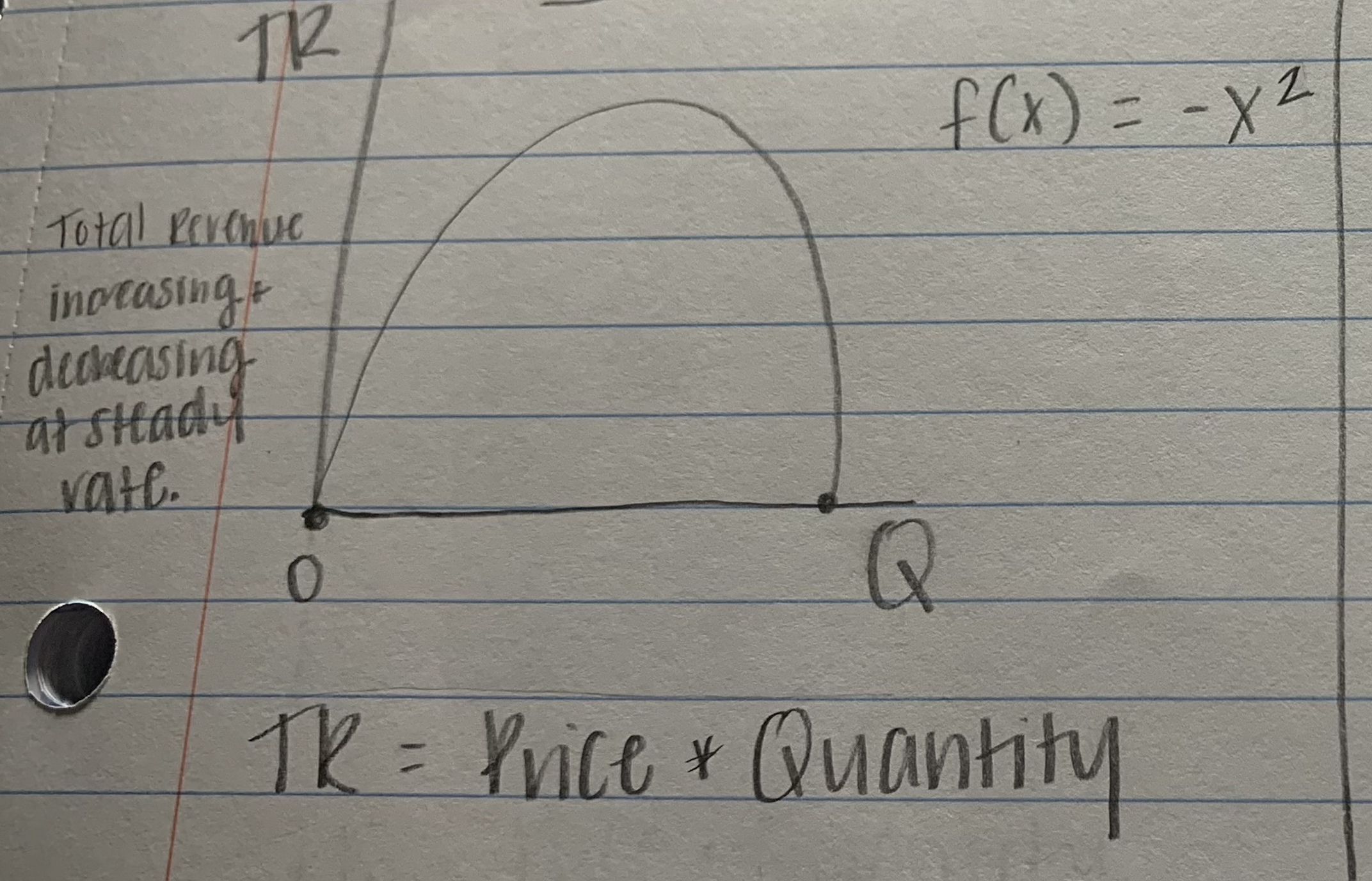
5
New cards
competitor
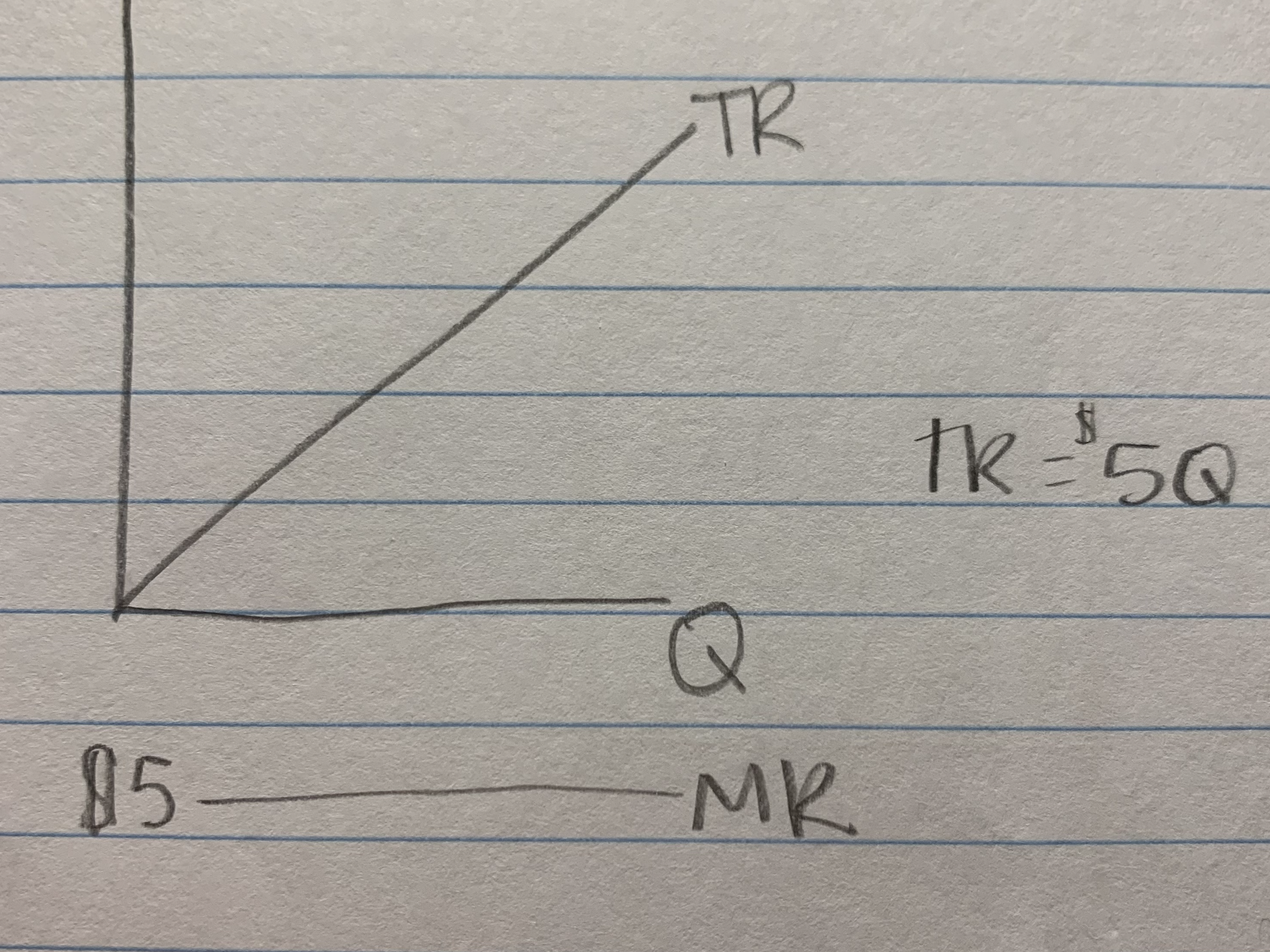
6
New cards
outputs
monopolist restrict
7
New cards
perfect competition
most monopolistic company
- many buyers and sellers
-ID products
- no barriers to entry
- perfect info
- free entry/exit (no market power)
- no long run economic power
- many buyers and sellers
-ID products
- no barriers to entry
- perfect info
- free entry/exit (no market power)
- no long run economic power
8
New cards
oligopoly
middle monopolistic company
- few firms (sellers)
- no barriers
- perfect info
- free entry/exit
- market power
9
New cards
monopoly
least monopolistic company
- one seller
-barriers to entry
- market power
- long rune economic profit
10
New cards
product differentiation
- making a product "different"
- no matter what's on the can, all beer tastes the same.
ex/ advil vs ibuphrofen
ex/ lays (more uniform chips than off brand)
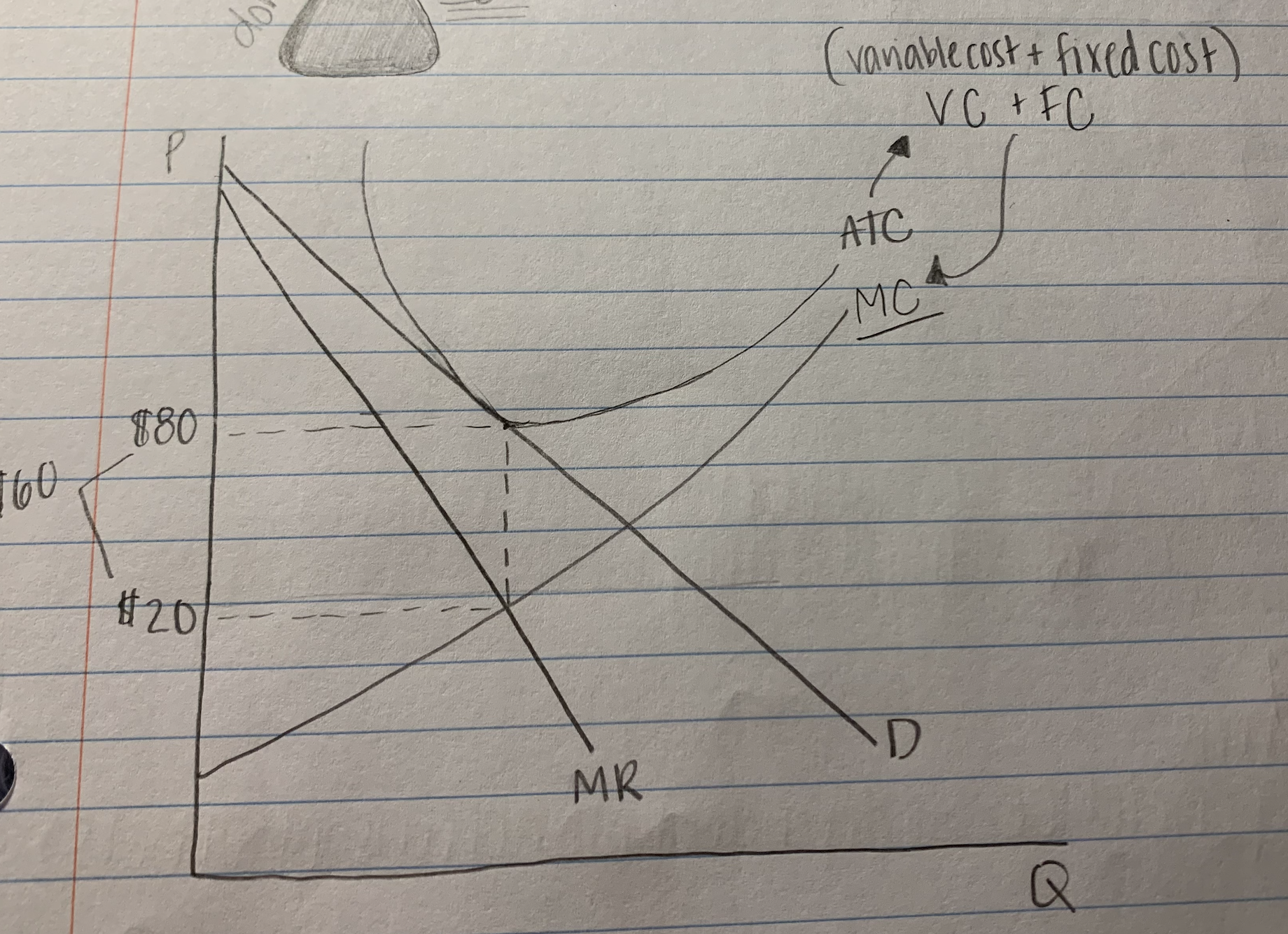
11
New cards
oligopoly
- few firms
- interdependence (dependent on actions of others)
12
New cards
5
How many models of oligopoly's are there?
13
New cards
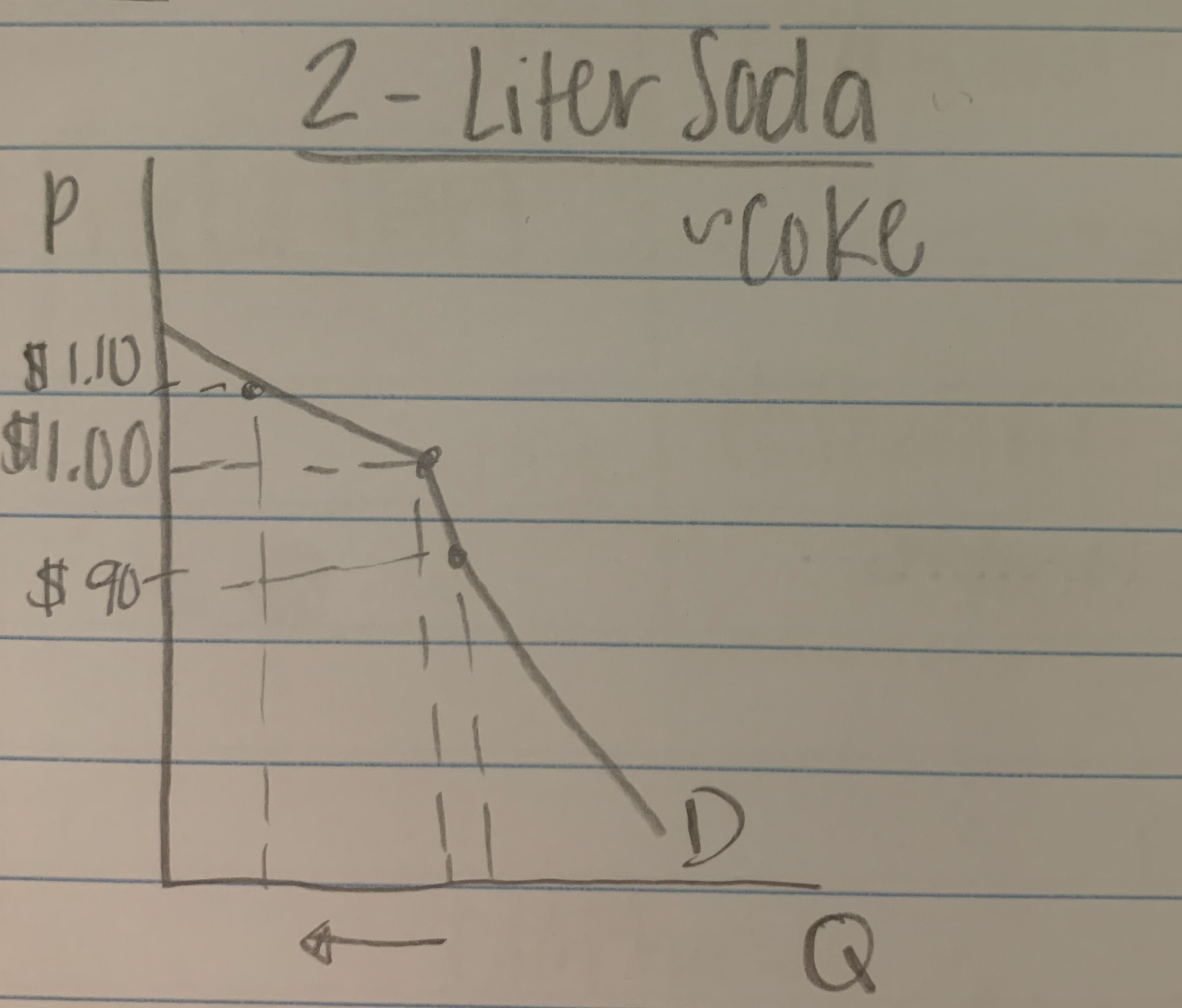
kinked demand curve model
- For products in this market, price stays the same as it’s the sole (or only significant) determinant of demand.
- model of oligopoly
- model of oligopoly
14
New cards
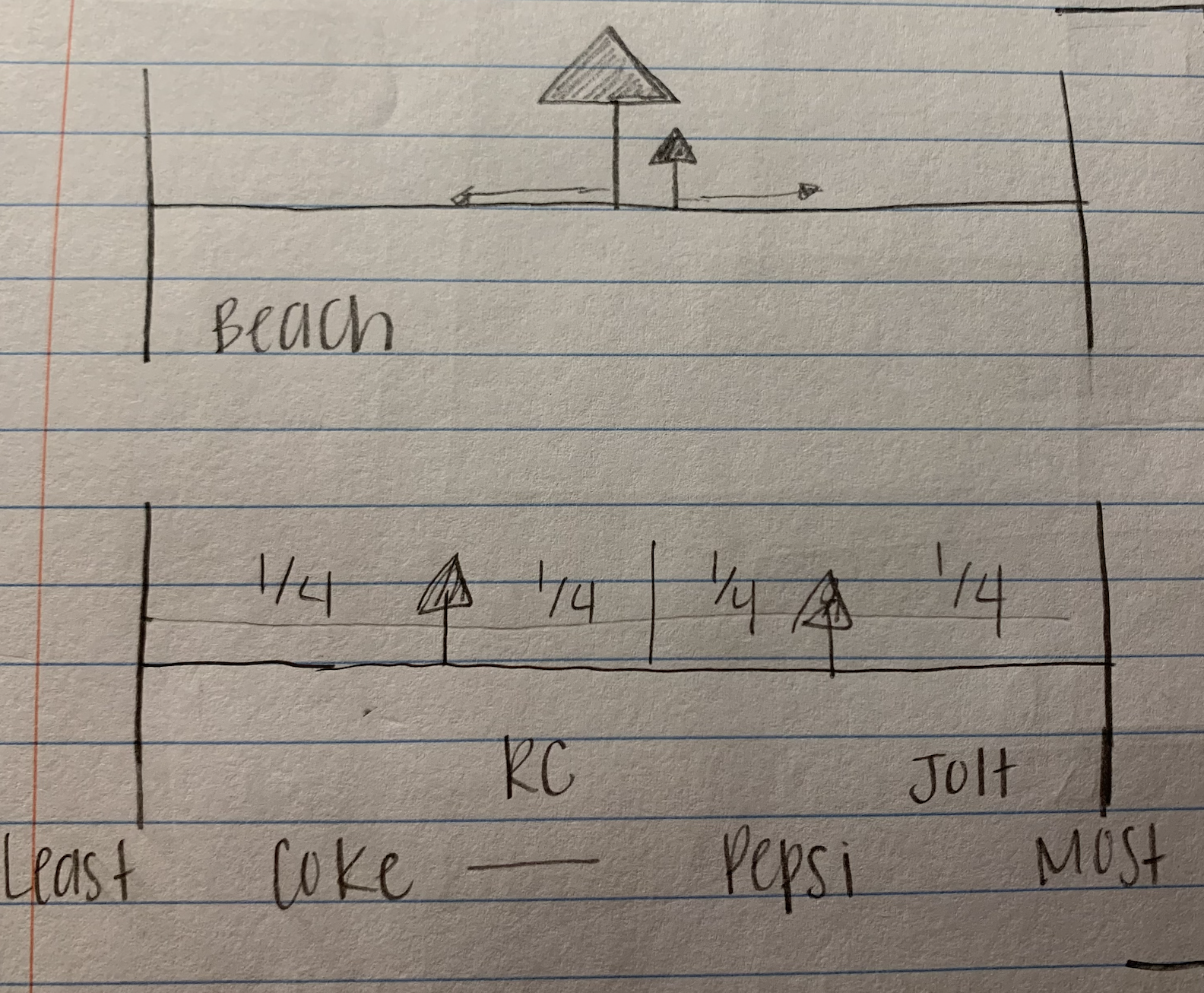
salop's line
- If you go to the beach and set up a refreshment stand in the middle, it minimizes the beachgoer’s implicit cost of buying stuff from you (in this case, the distance traveled)
- The next day, a stand pops up directly next to you in order to segment your market, rinse and repeat.
- model of oligopoly
- The next day, a stand pops up directly next to you in order to segment your market, rinse and repeat.
- model of oligopoly
15
New cards
Cournot-Nash
- As the number of firms increases, market production will gradually approach equilibrium
- model of oligopoly
- "n" firms
- model of oligopoly
- "n" firms

16
New cards
stackelberg
- leader/follower dichotomy
- the leader is the firm with the lower marginal cost
- model of oligopoly
17
New cards
market failure
- anytime market efficiency is hindered
- persistant shortages or surpluses
- persistant shortages or surpluses
18
New cards
externality
when SOMEONE ELSE is effected in a market
--> a "third party"
--> a "third party"
19
New cards
4 types of externalities
positive and negative production
positive and negative consumption
positive and negative consumption
20
New cards
economic impact or apple farmer with his orchard set up near a beekeeper.
example of positive production externality
21
New cards
pollution or mining coal has been linked to adverse health effects, same with burning it.
example of negative production externality
22
New cards
higher education
example of positive consumption externality
23
New cards
ryan and his egg salad sandwich or Fertilizer used to produce crops leaches into groundwater, pesticide use has been linked to public health issues
example of negative consumption externality
24
New cards
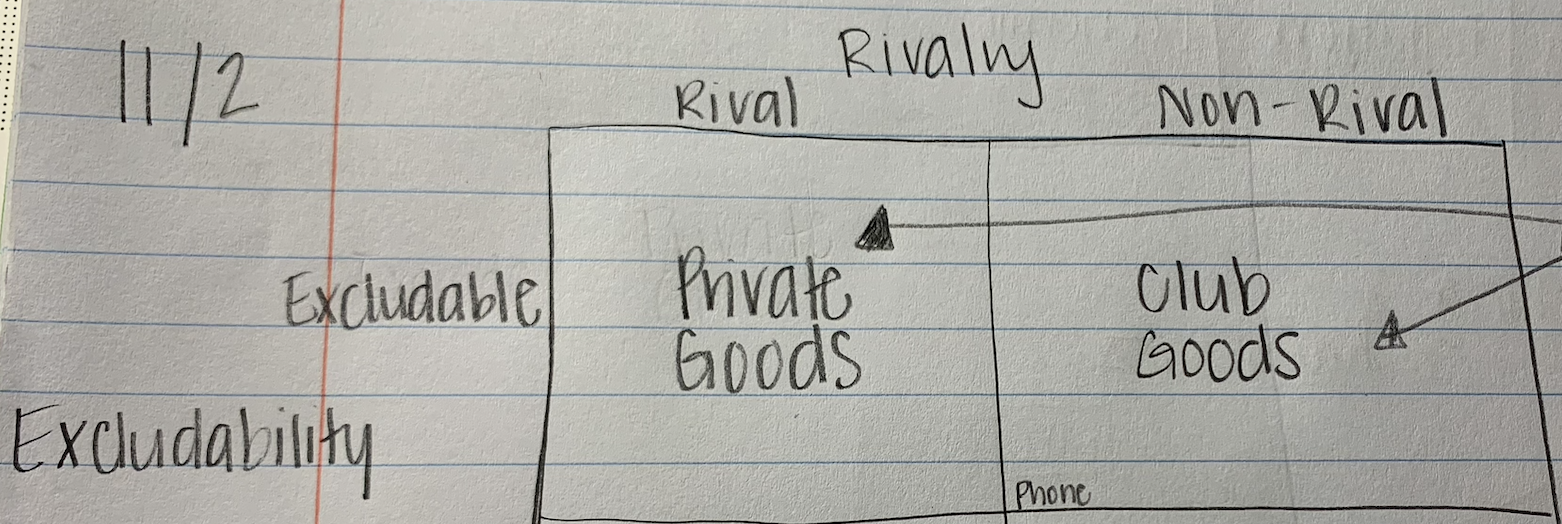
private and club goods
government does not need to provide these
25
New cards
public resources and public goods
government enforces these

26
New cards
tragedy of the commons
- public resource
- no personal incentive to reserve resources
- theory that individuals tend to exploit communal resources
ex/ overgrazing
- no personal incentive to reserve resources
- theory that individuals tend to exploit communal resources
ex/ overgrazing
27
New cards
private, club, public resources, and public goods
what are the 4 types of goods?
28
New cards
short run agrigate supply (SRAS)
supply of everything for everyone
29
New cards
agrigate demand (AD)
demand of everything for everyone
30
New cards
inflation
average level of prices rising
31
New cards
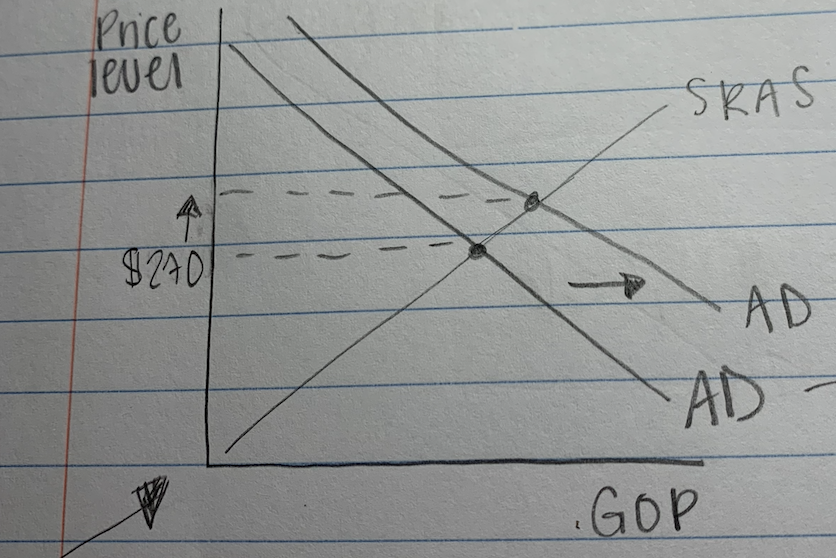
demand pull inflation
- increase in demand for everyone
- (kind of good)
- (kind of good)
32
New cards
cost push inflation (supply shock)
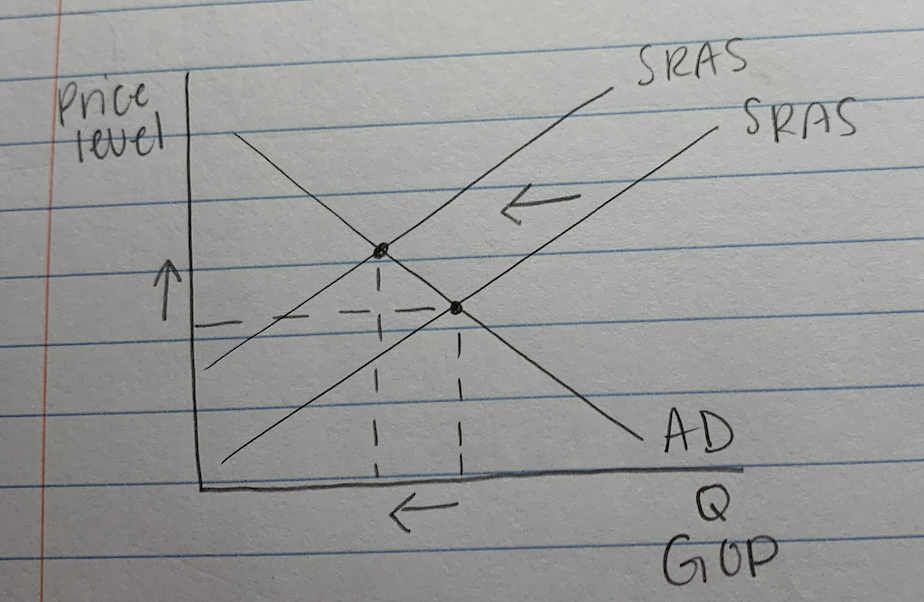
- (bad inflation)
33
New cards
rule of 72
- time to double = 72 (inflation/interest rates)
- if you notice inflation, it is a problem
- if you notice inflation, it is a problem
34
New cards
command interest formula
fu = pu x (lti)^n
fu - future
pu - present
lti - interest
n - years
fu - future
pu - present
lti - interest
n - years
35
New cards
bertrand
competitors who can only compete with price
36
New cards
game theory
- study of interdependence
- (meaning of interdependence: the dependence of two or more people or things on each other)
- (meaning of interdependence: the dependence of two or more people or things on each other)
37
New cards
price floors/ceilings
- a minimum (or maximum) cap on a good
38
New cards
example of an (extreme) price ceiling
-rent control
-If the “ceiling” is below the actual market equilibrium, it will affect the market.
-If the “ceiling” is below the actual market equilibrium, it will affect the market.
39
New cards
example of a price floor
- minimum wage
- if this is "binding" then the "floor" is a price over the market equilibrium
- if this is "binding" then the "floor" is a price over the market equilibrium
40
New cards
consumption externalities
- when consuming a commodity affects an unknown third party
41
New cards
negative consumption externality
when consuming a commodity HARMS the third party
42
New cards
positive consumption externality
when consuming a commodity BENEFITS the third party
43
New cards
private benefit/private cost
what's weighed by the decision maker
44
New cards
consumption externalities
when consuming a commodity affects an unknown third party
45
New cards
production externalities
when producing a commodity affects an unknown third party
46
New cards
negative production externality
when producing a commodity HARMS the third party
47
New cards
positive production externality
when producing a commodity BENEFITS the third party
48
New cards
subsidy
direct payment to someone for consuming or producing a particular commodity
ex: scholarships/financial aid
ex: out of state tuition is the FULL cost of letting you attend school for a year, in-state tuition is that MINUS the subsidy.
ex: scholarships/financial aid
ex: out of state tuition is the FULL cost of letting you attend school for a year, in-state tuition is that MINUS the subsidy.
49
New cards
free rider problem
arises when individuals are allowed to consumer more of public goods than their fair share