Zoology Test 3 Study
1/343
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
344 Terms
ectodermal placodes
platelike ectodermal thickenings that appear on either side of the neural tube
hox genes
series of genes that controls the differentiation of cells and tissues in an embryo
Myxini
hagfish
- 70 species
- marine
Petromyzontida
lampreys
- anadromous
- vestiges as eyes
chemosensory
respond to external chemicals and molecules released by damaged cells
- barbels around mouth
anadromous
A life cycle in which creatures are hatched in fresh water, migrate to salt water as adults, and then go back to fresh water in order to reproduce
catadromous
fishes that migrate from fresh water to spawn in the ocean
ammocoetes
petromyzontida larva
placodermi
armored fish
acanthodii
spiny sharks
- multiple paired pelvic fins
chondrichthyes
cartilaginous fish
- covered in scales (placoid type)
- lateral line system
osteichthyes
bony fish
tetrapoda
four-limbed vertebrates
lift
an upward force
drag
resistance by friction from air or water moving over a surface
maneuverability
results from drag, drag needed to change direction
If drag is greater than lift, then
it is not efficient because there is a trade-off between speed and maneuverability
Elasmobranchii
sharks, skates, rays
- 1,000 extant species
- ampullae of lorenzini
Holocephali
chimaeras and ratfishes
- 30 extant species
heterocercal
possessing a tail with the upper lobe larger than the lower and with the vertebral column prolonged into the upper lobe
oviparous
egg laying
ovoviviparous
producing living young from eggs that hatch within the body
viviparous
producing living young (not eggs)
Body design of Class Insecta
- head, thorax, abdomen
- have wings as unique structures
general rules for body design
head: sensory organs
thorax: locomotory structures
abdomen: reproductive structures
hemocoel
The primary body cavity of most invertebrates contains circulatory fluid known as hemolymph
- disperses nutrients and hormones
Functional unit of Class Insecta
ommatidium
Sensilla
these tiny hairs give insects their senses of touch, balance, hearing, smell, taste and temperature
What are the 4 major mouthparts?
- mandibles, maxillae, labium, labrum
Ametabolous
no metamorphosis
- Juveniles resemble miniature adults
Hemimetabolous
incomplete metamorphosis, aquatic
- Juveniles look different from adults but have no pupal stage
Paurometabolous
partial metamorphosis, terrestrial
- Juveniles look different from adults but have no pupal stage
Holometabolous
complete metamorphosis
- Juveniles look very different as immatures, have a pupal stage
Class Protura
Proturans
Class Diplura
Diplurans
What does molecular evidence suggest how arthropods evolved
- several different times independently
- from Myriapod-like ancestor
What subgenus in Celoeptera is the fastest?
Rivacindela
Important Coleoptera species that transmit diseases to trees
- elm bark beetle
- Emerald ash borer
How can butterflies be distinguished from moths?
by their antennae
- thread-like/feathery in moths
Order Lepidoptera genetics
male: homogametic sex (ZZ)
female: heterogametic (ZW)
- bilateral gynandromorphs
chrysalis
pupa of a moth or butterfly enclosed in a cocoon
Order Lepidoptera legs
- 3 pairs of thoracic legs
- 5 pairs of abdominal prolegs
Order Hymenoptera stingers are modifications of
reproductive apparatus
Apocrita
bees, wasps, ants
- have distinct constriction between the first and second abdominal segments
Apis mellifera
European honey bee
- dependent on for pollination of food production
Halteres
Highly modified wings used for balance rather than flight. Usually are club- shaped structures; found on the metathorax of true flies (Diptera).
Nematocera
wings can fold directly over body

Brachycera
wings tent over the body

Hessian fly
major pest of what
- of economic and medical importance
- Order Diptera

Examples of flys that are major vectors of human diseases
- black, deer, horse, tsetse flies
Chaetotaxy
arrangement of bristles
forensic entomology
The study of insects to determine such matters as a person's time of death.
Ensifera
Crickets and Katydids with long, thin antennae
Order Neuroptera
lacewings, antlions
- heavily veined wings, tent like over body
Order Hemiptera
true bugs
- contain hemielytra
- killed Charles Darwin = Chagas disease
hemielytra
The half leathery, half membranous wings of true bugs like stink bugs.
Order Odonata
dragonflies and damselflies
- 2 pairs of long wings (identical)
Order Thysanoptera
Thrips
- heavy infestations can damage plants
Order Trichoptera
Caddisflies
- wings covered w/ scales
Vertebrate evolutionary characteristics
1. More developed endoskeleton
- cartilage/bone
2. Skeleton provides anchor points for segmented muscles
- skull = 3 units
3. Changes is physiological systems
- gills, digestive tract, kidneys
Ostracoderms
heavily armored jawless fishes, mostly small
- during Silurian and Devonian
Subphylum Hexapoda
all are six-legged
Class insecta
- over 50% of animal species
- over 1 million species
Agnatha
jawless fish
- 120 species
Gnathostomata
jawed fishes
- 60,000 species
Tetrapoda
amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals
The class Insecta has Malphighian tubules which is a
a system that removes nitrogen-waste from the blood without losing water
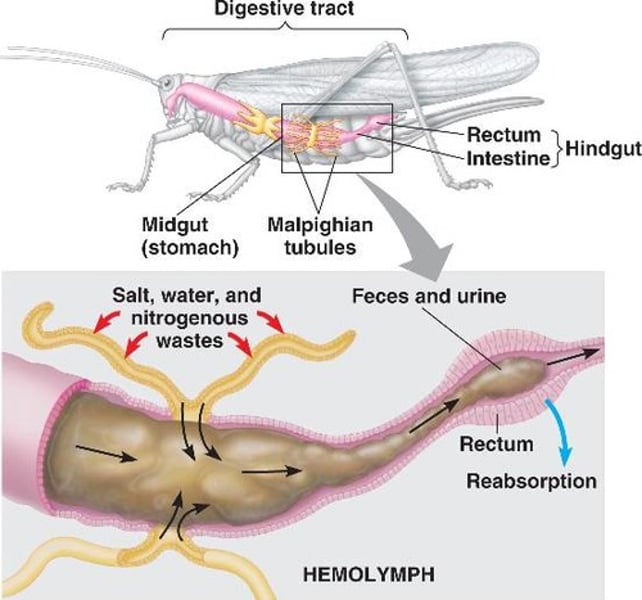
Examples of Insect borne diseases
- Malaria (Anopheles)
- Epidemic typhus
- African sleeping sickness
Class Collembola
Springtails
instar
stage between molts
Order Coleoptera lives where
live anywhere except regions with permanent ice
elytra
a beetle's hardened forewings

What is the second most diverse insect order?
Lepidoptera
Flies have ____ wings, while wasps have ________.
2 wings, 4 wings
Hymenoptera have _______ mouthparts, while Diptera have _________.
chewing, piercing
Order Hymenoptera females cannot breed because
they are supposed to be workers
Order Orthoptera
grasshoppers and crickets
- large hind legs used for jumping
tegmina
leathery forewings
Tympana
the ears of crickets, katydids and grasshoppers that are not on their heads, but are on their legs or abdomen
Caelifera
short-horned grasshoppers
ootheca
A protective structure many female insects construct around their eggs.
All living deuterostomes are
coelomates
Lepidoptera
butterflies and moths
What is the largest Insecta order?
order Coleoptera
Phylum Chaetognatha
- arrow worms
- have bristles (teeth) around the mouth, aid in prey capture
- postanal tail
- 100 species known
Phylum Echinodermata
starfish, sea stars, brittle stars
- went from bilateral symmetry to radial symmetry over time
- around 7,000 species
bipinnaria larva
the first stage in larva development of most starfish, followed by the brachiolaria stage
- bilateral symmetry
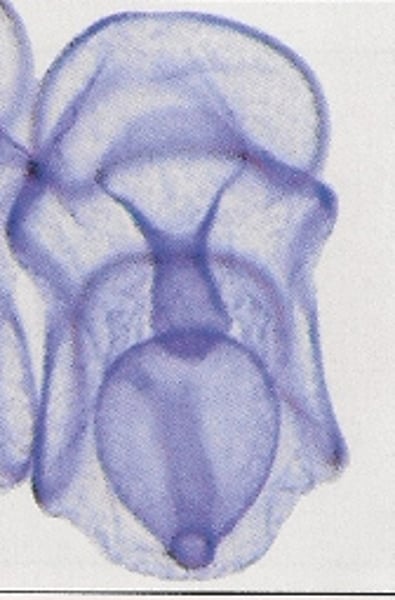
ossicles
bone pieces
water vascular system
A network of hydraulic canals unique to echinoderms that branches into extensions called tube feet, which function in locomotion, feeding, and gas exchange
- can over power other organisms without using muscles
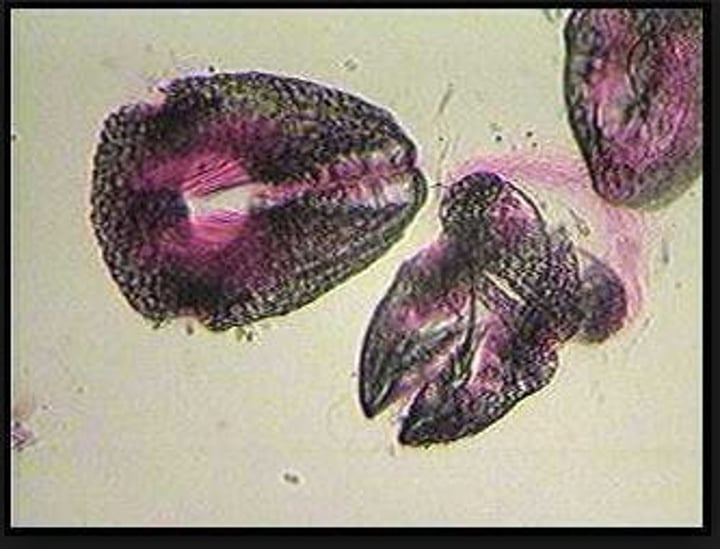
pedicellarie
numerous tiny pincers that surrounds the spines
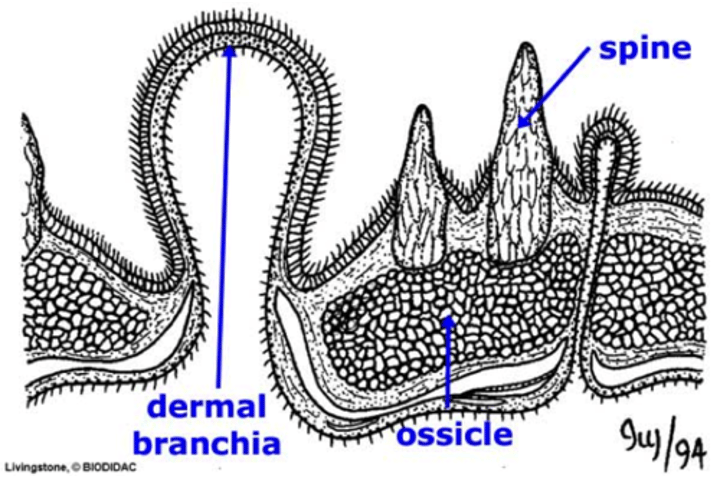
dermal branchiae
skin gills
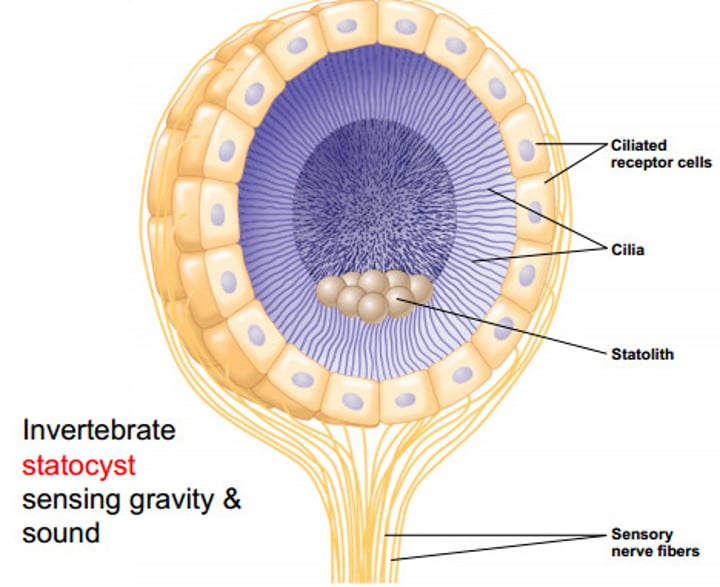
statocysts
a small organ of balance and orientation in some aquatic invertebrates, consisting of a sensory vesicle or cell containing statoliths.
bursae
flattened fibrous sacs lined with synovial membrane and containing a thin film of synovial fluid
The simpler your anatomy, _______
the easier it is to do asexual reproduction
sea cucumbers are unique in that
they can regenerate their internal organs
Asteroidea
sea stars
- 1,500 species
Ophiuroidea
brittle stars, basket stars
- 1,600 species
Echinoidea
sea urchins, sand dollars
- 1,000 species
- fused ossicles
Radial symmetry makes sense when organisms
are stationary and can't move
ampullae
the bulb that squeezes water into the tube foot