Ch. 9: Hearing and Language
1/45
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Adequate Stimulus
The energy form for which a receptor is specialized.
Agraphia
The inability to write due to brain damage.
Alexia
The inability to read due to brain damage.
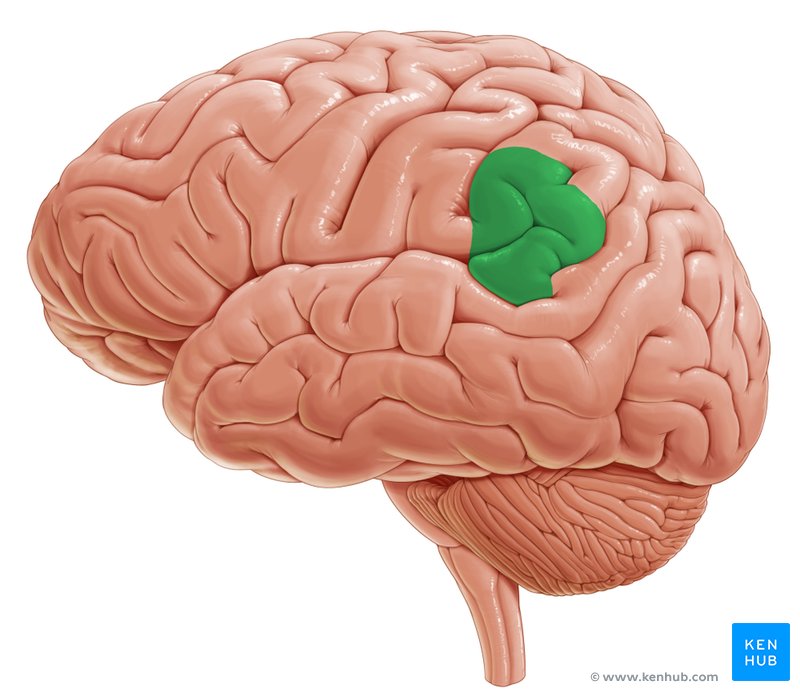
Angular Gyrus
A gyrus at the border of the parietal and occipital lobes containing pathways that connect the visual area with auditory, visual, and somatosensory association areas.
Aphasia
Language impairment caused by damage to the brain.
Auditory Object
A sound that we recognize as having an identity that is distinct from other sounds.
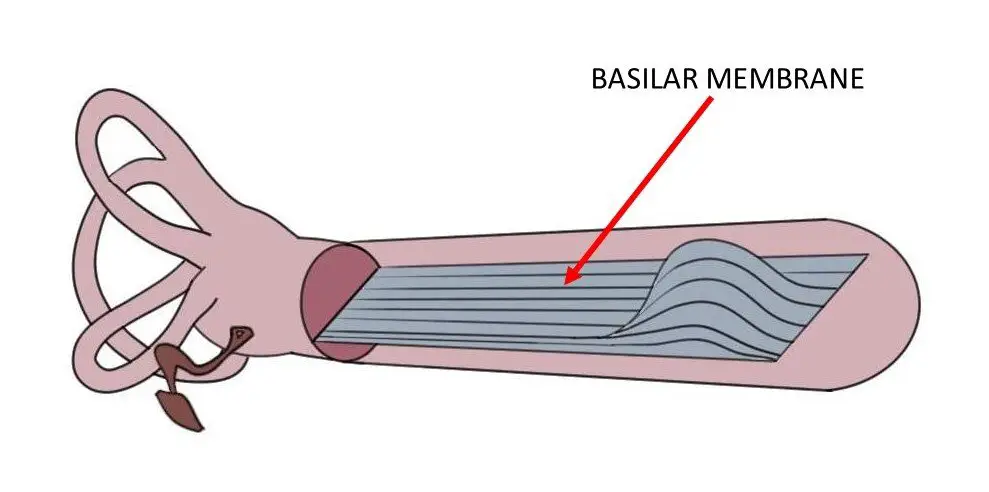
Basilar Membrane
The membrane in the cochlea that separates the cochlear canal from the tympanic canal.
Broca’s Aphasia
Language impairment caused by damage to Broca’s area and surrounding cortical and subcortical areas.
Cochlea
The snail-shaped structure where the ear’s sound-analyzing structures are located.
Cochlear Canal
The middle canal in the cochlea, which contains the organ of Corti.
Cocktail Party Effect
The ability to sort out meaningful auditory messages from a complex background of sounds.
Coincidence Detectors
Neurons that fire most when they receive input from both ears at the same time.
Complex Sound
A sound composed of more than one pure tone.
Dyslexia
An impairment of reading, which can be developmental or acquired through brain damage.
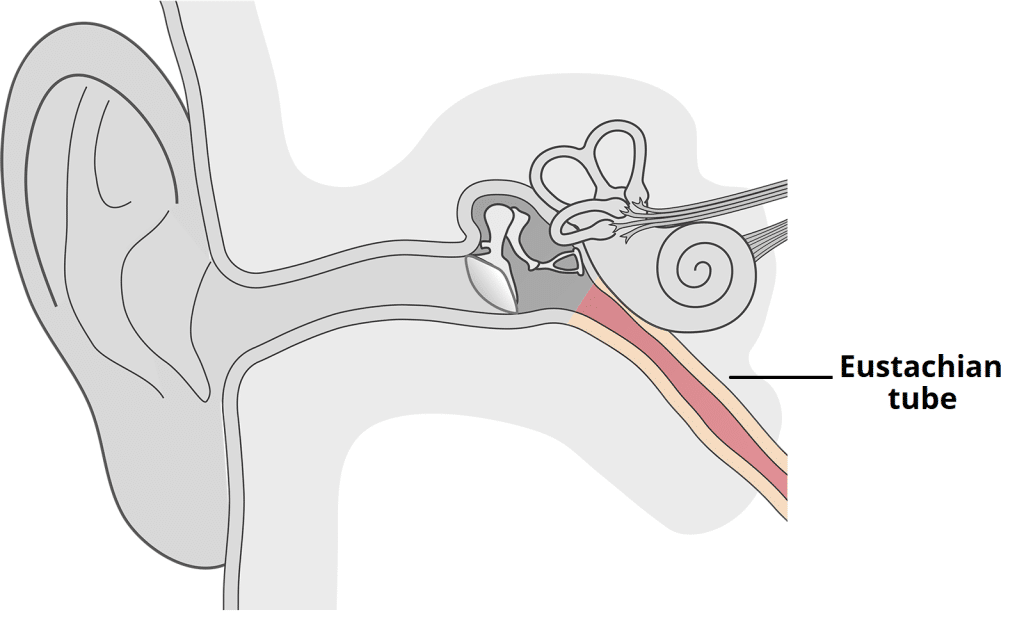
Eustachian Tube
The connection between the middle ear and the oral cavity, equalizing air pressure differences.
Frequency
The number of cycles or waves of alternating compression and decompression of sound in a second.
Frequency-Place Theory
The hypothesis that frequency discrimination is based on neuron activity and the place of greatest activity on the basilar membrane.
Frequency Theory
Hypotheses that state the frequency of a sound is represented in the firing rate of auditory neurons.
Grammar
The consistent set of rules of a particular language.
Head-Related Transfer Function (HRTF)
Spectral frequency alterations to a sound as it passes through the head, aiding sound localization.
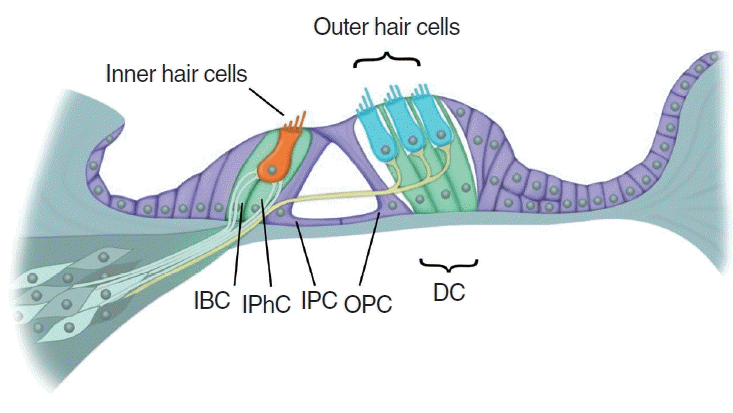
Inner Hair Cells
About 3,500 hair cells on the basilar membrane that produce most of the auditory signal.
Intensity
The physical energy in sound; the sound’s amplitude.
Interaural Level Difference
A binaural cue to sound location based on the sound shadow created by the head.
Interaural Timing Difference (ITD)
A binaural cue to sound location due to the time sound takes to travel between ears.
Language
A structured system of communication with a common set of rules.
Language Acquisition Device
A hypothesized part of the brain dedicated to language learning.
Loudness
Our experience of sound intensity.
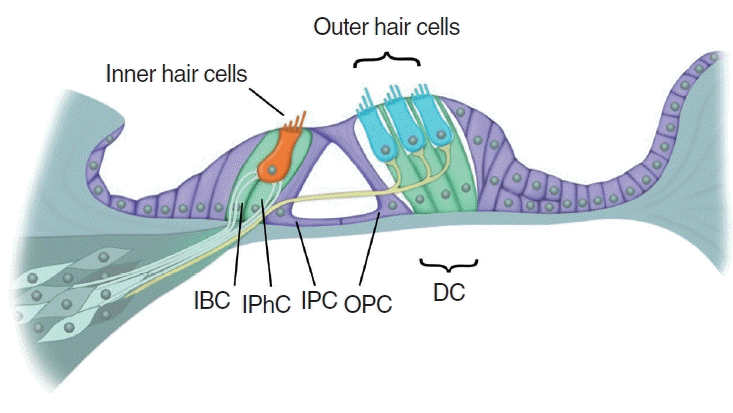
Organ of Corti
The sound-analyzing structure on the basilar membrane of the cochlea.
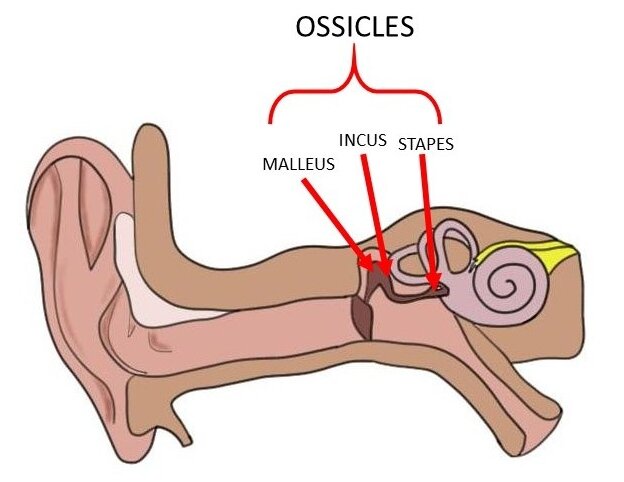
Ossicles
Tiny bones in the middle ear that transfer vibration from the tympanic membrane to the cochlea.
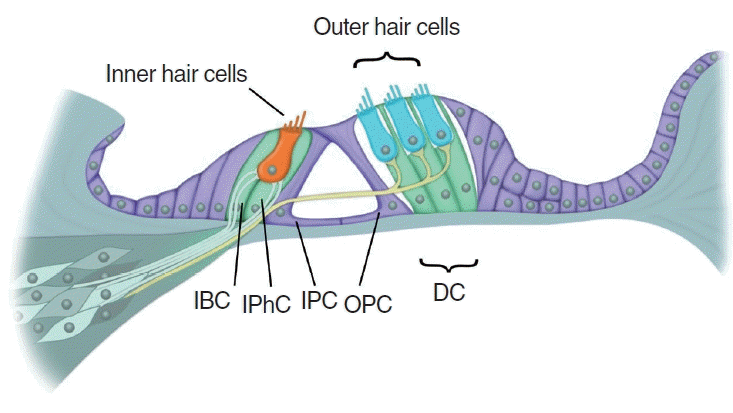
Outer Hair Cells
Three rows of cells in the cochlea that amplify sound output and sharpen frequency tuning.
Perception
The interpretation of sensory information.
Phonological Hypothesis
The idea that dyslexia's fundamental problem is impaired phoneme processing.
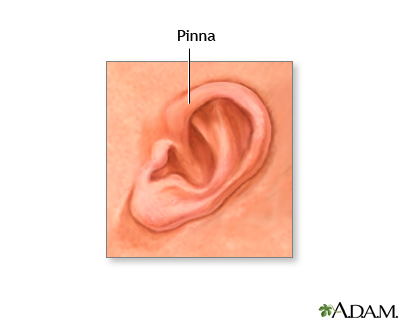
Pinna
The ear flap on each side of the head.
Pitch
The experience of the frequency of a sound.
Place Theory
The theory that frequency is identified by the location of maximal vibration on the basilar membrane.
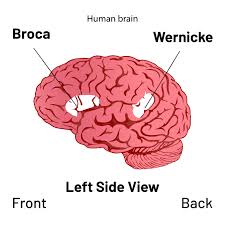
Planum Temporale
The area in each temporal lobe where Wernicke’s area is located.
Prosody
The use of intonation, emphasis, and rhythm in speech.
Pure Tone
A sound consisting of a single frequency.
Receptor
A cell that responds to a particular form of energy.
Sensation
The acquisition of sensory information.
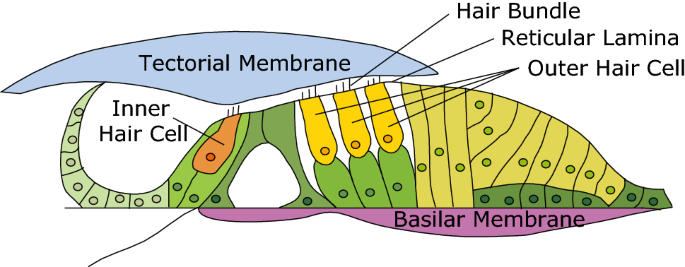
Tectorial Membrane
A shelf-like membrane overlying the hair cells in the cochlea.
Telephone Theory
A theory stating that auditory neurons transmit actual sound frequencies to the cortex.
Tonotopically Organized
Neurons from adjacent receptor locations project to adjacent cells in the auditory cortex.
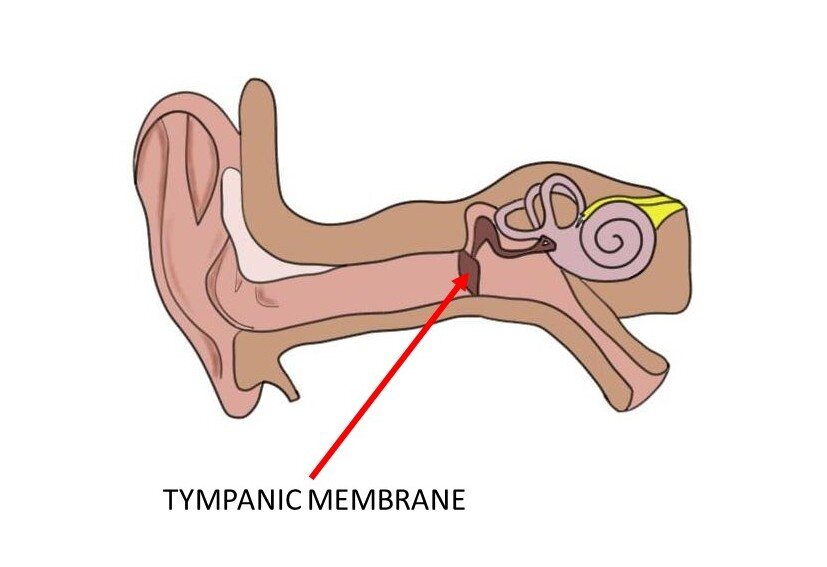
Tympanic Membrane
The eardrum; its vibration transmits sound energy to the ossicles.
Volley Theory
A hypothesis that states groups of neurons follow the sound frequency when it exceeds a neuron's firing rate.
Wernicke’s Aphasia
Language impairment resulting from damage to Wernicke’s area.