Biology: Atomic Structure, Chemical Bonds, and Cell Membranes
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Proton
Positively charged subatomic particle located in the nucleus of an atom.
Neutron
Neutrally charged subatomic particle located in the nucleus of an atom.
Electron
Negatively charged subatomic particle found in orbitals around the nucleus.
Ionic bond
Bond formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another, resulting in oppositely charged ions.
Covalent bond
Bond formed by the sharing of one or more pairs of electrons between atoms.
Ionic vs covalent
Ionic bonds transfer electrons and form ions; covalent bonds share electrons and form molecules.
Molecule
Two or more atoms chemically bonded together, can be same or different elements.
Compound
A substance composed of two or more different elements chemically bonded in fixed proportions.
Hydrogen bond
Weak attraction between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an electronegative atom and another electronegative atom.
Solubility
The ability of a substance (solute) to dissolve in a solvent, forming a homogeneous solution.
Dissociation
The separation of an ionic compound into its constituent ions when dissolved in water.
Electrolyte
A substance that dissociates into ions in solution and conducts an electric current.
Nonelectrolyte
A substance that dissolves in water without dissociating into ions and does not conduct electricity.
Dehydration synthesis
Reaction that joins monomers by removing a water molecule to form a covalent bond.
Hydrolysis
Reaction that breaks covalent bonds in polymers by adding water, yielding smaller subunits.
Carbohydrates
Biomolecules of C, H, O; include sugars and starches; function in energy storage and structural support.
Lipids
Hydrophobic biomolecules (fats, phospholipids, steroids); function in energy storage, membrane structure, and signaling.
Proteins
Polymers of amino acids folded into specific 3D structures; function as enzymes, structural components, transporters, and regulators.
Nucleic acids
Polymers of nucleotides (DNA, RNA); function in storing and transferring genetic information and energy (ATP).
DNA
Double-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid helix that stores the hereditary blueprint of an organism.
RNA
Single-stranded ribonucleic acid involved in protein synthesis and gene regulation.
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate; the primary energy currency of the cell, fuels biochemical reactions.
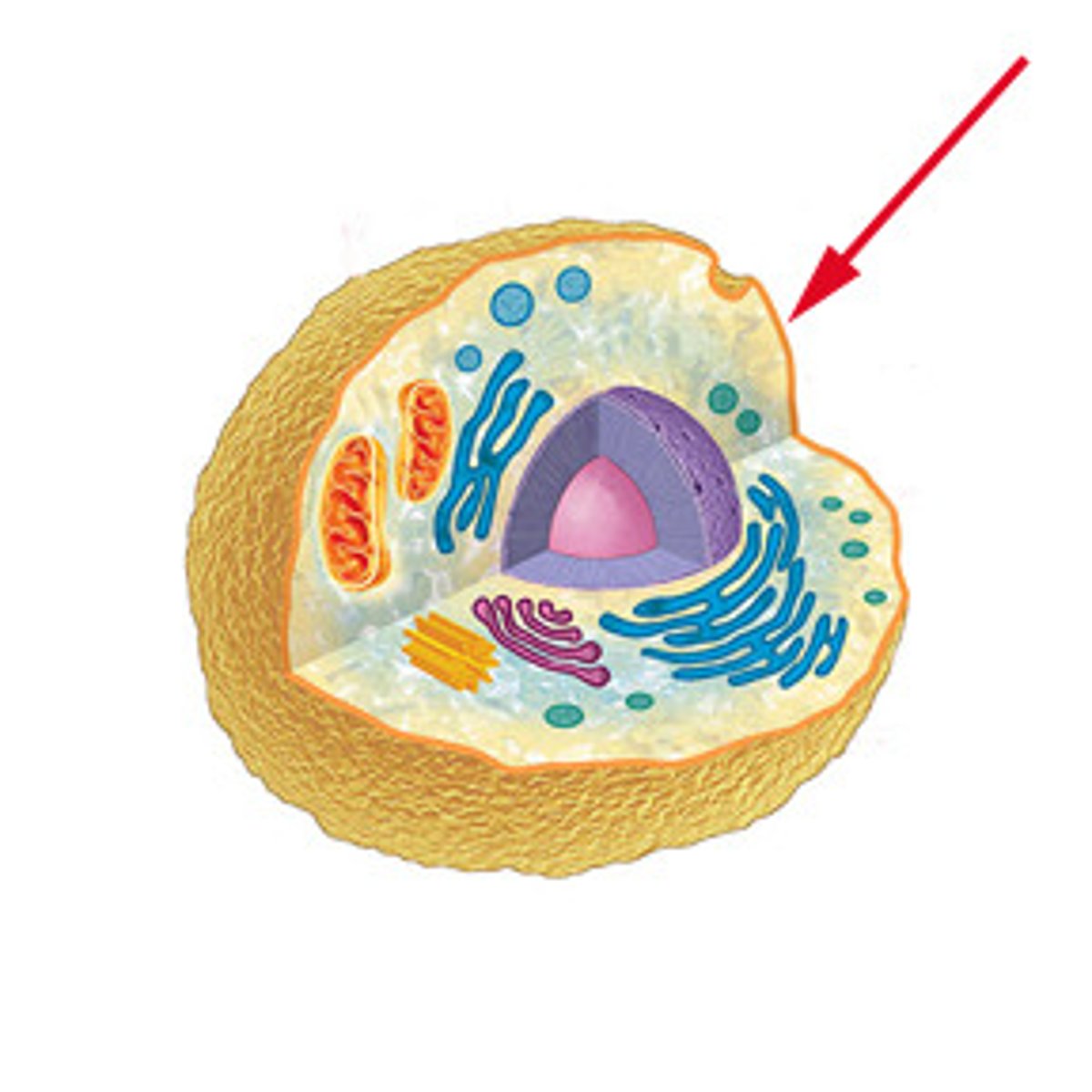
General parts of a cell
Plasma membrane, cytoplasm (cytosol and organelles), nucleus (in eukaryotes), and cytoskeleton.
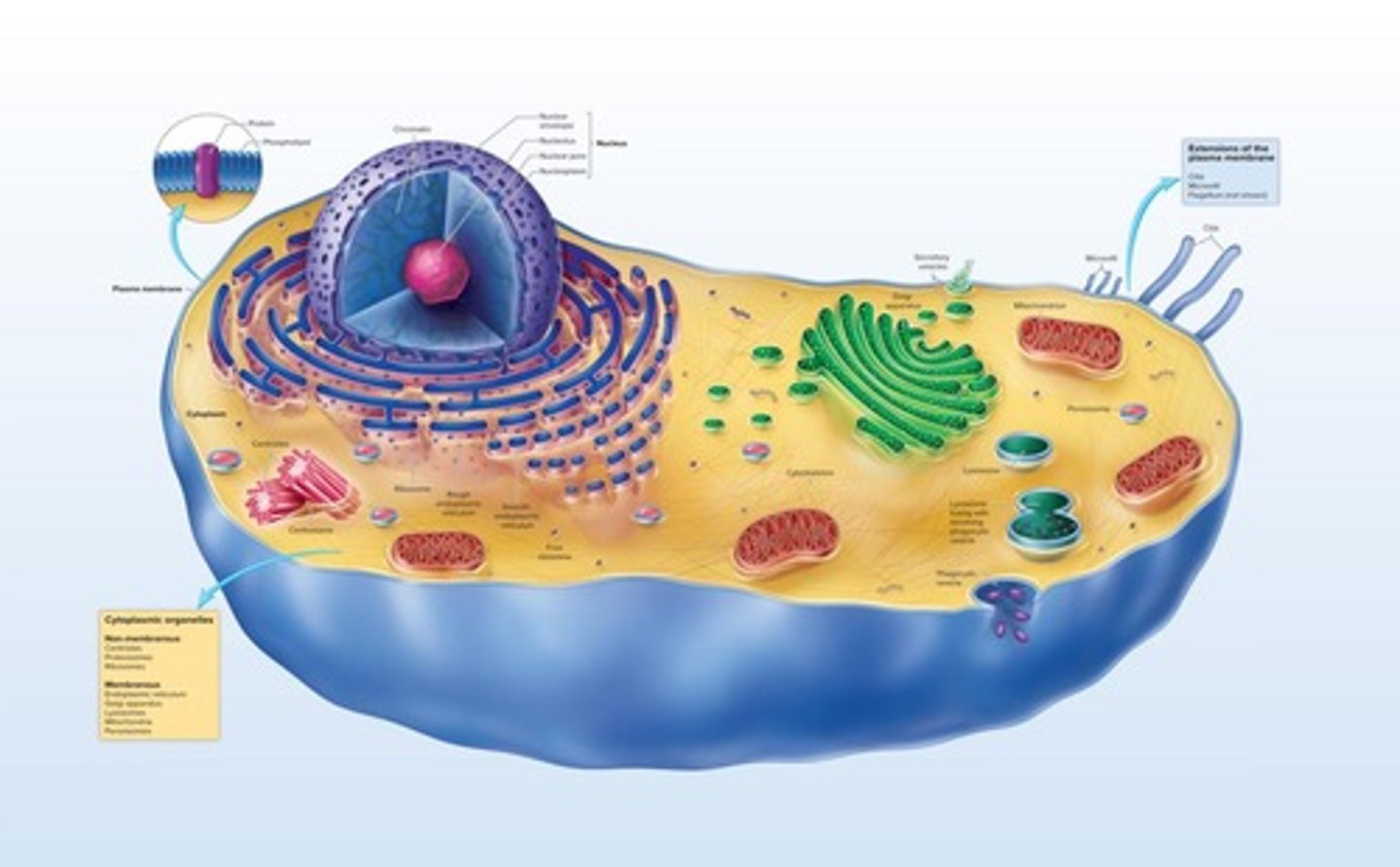
Plasma membrane
Phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins and cholesterol; regulates passage of materials and cell signaling.
Membrane potential
Electrical potential difference across the plasma membrane due to uneven distribution of ions.
Phospholipids
Amphipathic lipids with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails that form the membrane bilayer.
Cholesterol
Steroid lipid interspersed in the bilayer that modulates fluidity and stability of the membrane.
Glycolipids
Lipids with attached carbohydrate chains on the extracellular surface for cell recognition and stability.
Fluid mosaic model
Description of the membrane as a fluid lipid bilayer with proteins that move laterally like a mosaic.
Membrane proteins
Integral and peripheral proteins serving as transporters, receptors, enzymes, and structural anchors.
Transport proteins
Integral proteins that facilitate the movement of specific ions or molecules across the membrane.
Selective permeability
The property of the plasma membrane to allow certain substances to cross while excluding others.
Simple diffusion
Passive movement of solutes down their concentration gradient directly through the lipid bilayer.
Facilitated diffusion
Passive transport of solutes down their gradient via specific carrier or channel proteins without energy.
Active transport
Energy-dependent movement of solutes against their concentration gradient via transport proteins.
Diffusion
Net movement of molecules from regions of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration.
Osmosis
Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane toward higher solute concentration.
Osmotic pressure
Pressure required to halt the net movement of water during osmosis.
Hypotonic solution
Solution with lower solute concentration than the cell's cytosol; water enters cells, causing swelling.
Isotonic solution
Solution with equal solute concentration to the cell's cytosol; no net water movement, cell shape remains constant.
Hypertonic solution
Solution with higher solute concentration than the cell's cytosol; water leaves cells, causing shrinkage.
Mediated transport
Movement of substances across the membrane via specific carrier or channel proteins; can be passive or active.
Primary active transport
Use of ATP directly by transport proteins (pumps) to move ions or molecules against their gradient.
Secondary active transport
Transport driven by the energy stored in an ion's electrochemical gradient established by primary active transport.
Endocrine signaling
Long-distance cell communication via hormones secreted into the bloodstream to reach target cells.
Paracrine signaling
Local cell communication where signaling molecules affect nearby target cells.
Autocrine signaling
Cells respond to signaling molecules that they themselves secrete.
Juxtacrine signaling (contact-dependent)
Direct cell-cell communication via membrane-bound signals requiring physical contact.
Internal receptors
Cytoplasmic or nuclear receptors that bind lipophilic ligands capable of crossing the plasma membrane.
Cell-surface receptors
Transmembrane proteins that bind hydrophilic ligands and transduce signals to the cell interior.
Ligand structure vs mechanism
Ligand polarity determines whether it binds surface receptors (hydrophilic) or internal receptors (lipophilic).
Ligand binding initiation
Ligand binding induces receptor conformational change, triggering an intracellular signaling cascade.
Phosphorylation
Addition of phosphate groups by kinases to activate or deactivate proteins in signaling pathways.
Second messengers
Small intracellular molecules (e.g., cAMP, Ca²⁺, IP₃) that amplify and distribute signals within the cell.
Signal pathways and cell functions
Signaling cascades activate transcription factors and enzymes to regulate gene expression, metabolism, and growth.
Protein kinase C (PKC)
Kinase activated by diacylglycerol and Ca²⁺ that phosphorylates proteins in key signaling pathways.
Cellular hierarchy
Cells form tissues, tissues form organs, organs form organ systems in multicellular organisms.
Skin organization
Epidermis: stratified epithelial tissue; Dermis: connective tissue layer containing collagen and elastin.
Cell theory
All living organisms are composed of cells; cells are the basic unit of life; all cells arise from preexisting cells.
Basic cell attributes
Characteristics include metabolism, growth, reproduction, responsiveness, and homeostasis.
Prokaryotic vs eukaryotic
Prokaryotes lack a nucleus and organelles and are generally smaller; eukaryotes have a nucleus, organelles, and complex cytoskeleton.
Cytoskeletal filaments
Intermediate filaments provide support, microtubules enable transport and division, microfilaments (actin) drive movement.
Motor proteins
Kinesin transports cargo toward the plus end of microtubules; dynein moves cargo toward the minus end.
Desmosomes
Junctions that anchor adjacent cells together, providing mechanical strength.
Hemidesmosomes
Junctions that anchor epithelial cells to the basement membrane.
Gap junctions
Channels (connexons) that allow direct communication and ion exchange between adjacent cells.
Adherens junctions
Junctions that connect actin cytoskeletons of neighboring cells to maintain tissue integrity.
Tight junctions
Seals between cells that prevent the passage of molecules through the intercellular space.
Integrins
Transmembrane receptors that mediate cell-extracellular matrix adhesion and bidirectional signaling.
Selectins
Cell adhesion molecules that bind carbohydrate ligands and mediate leukocyte-endothelial interactions.
microfilaments
Diameter ~7 nm; F-actin double helix of G-actin monomers; distinct plus/minus ends; rapid assembly/disassembly; functions: cell cortex support, lamellipodia/filopodia, muscle contraction (actin-myosin), cytokinesis, vesicle transport (myosin motors)
intermediate filaments
Diameter ~10 nm; rope-like polymers of cell-specific proteins (e.g., keratins, vimentin, neurofilaments; lamins in nucleus); nonpolar, stable filaments; functions: tensile strength, mechanical resilience, desmosome/hemidesmosome anchoring, nuclear envelope support
microtubules
Diameter ~25 nm; hollow tubes of 13 protofilaments from α/β-tubulin heterodimers; plus end (dynamic GTP-cap growth) and minus end (MTOC anchored); dynamic instability (growth/shrinkage); functions: intracellular transport (kinesin toward plus, dynein toward minus), mitotic spindle/chromosome segregation, cilia/flagella structure, organelle positioning