Human Geo Unit 6 Exam Prep
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
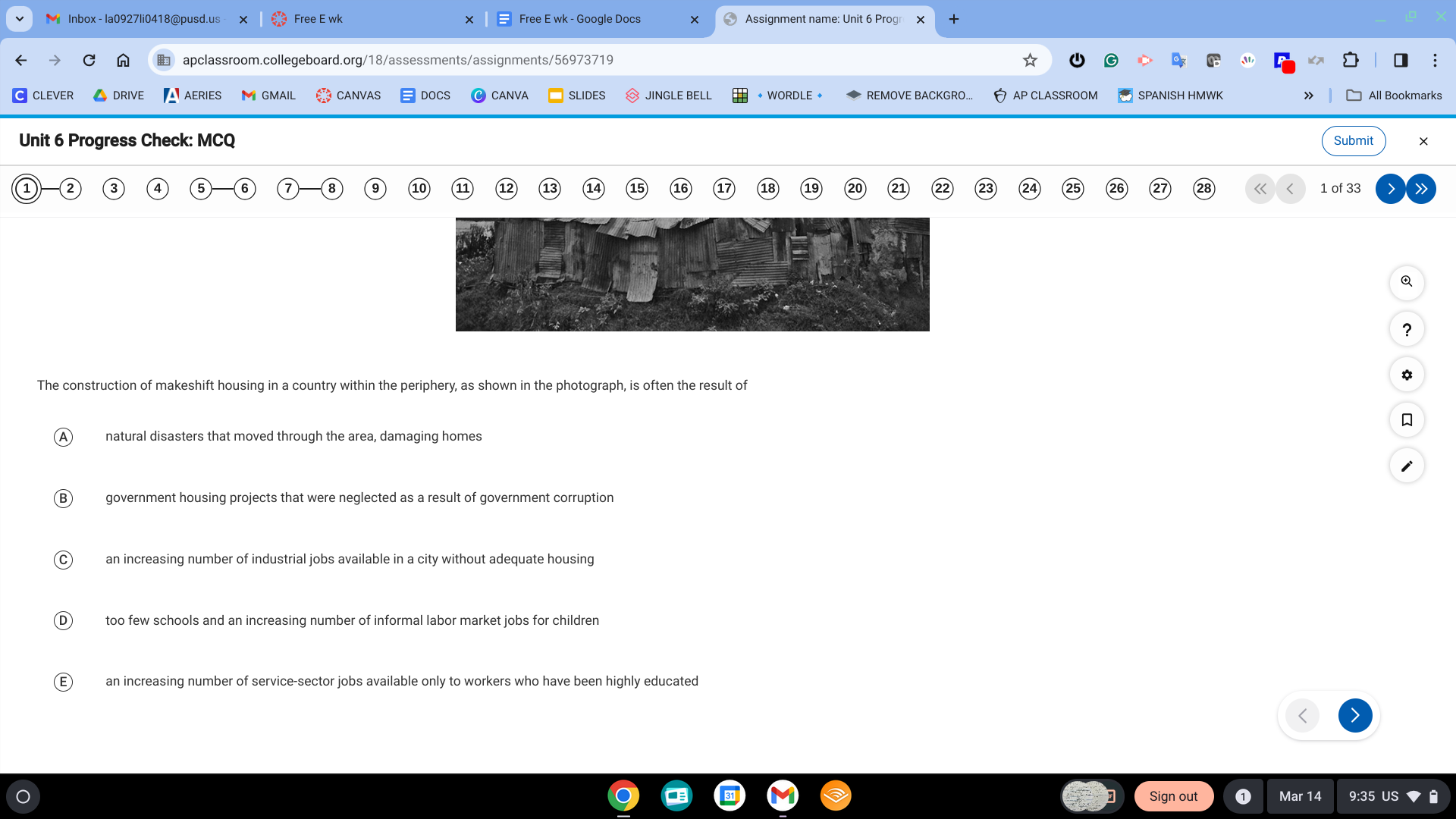
C. an increasing number of industrial jobs available in a city without adequate housing
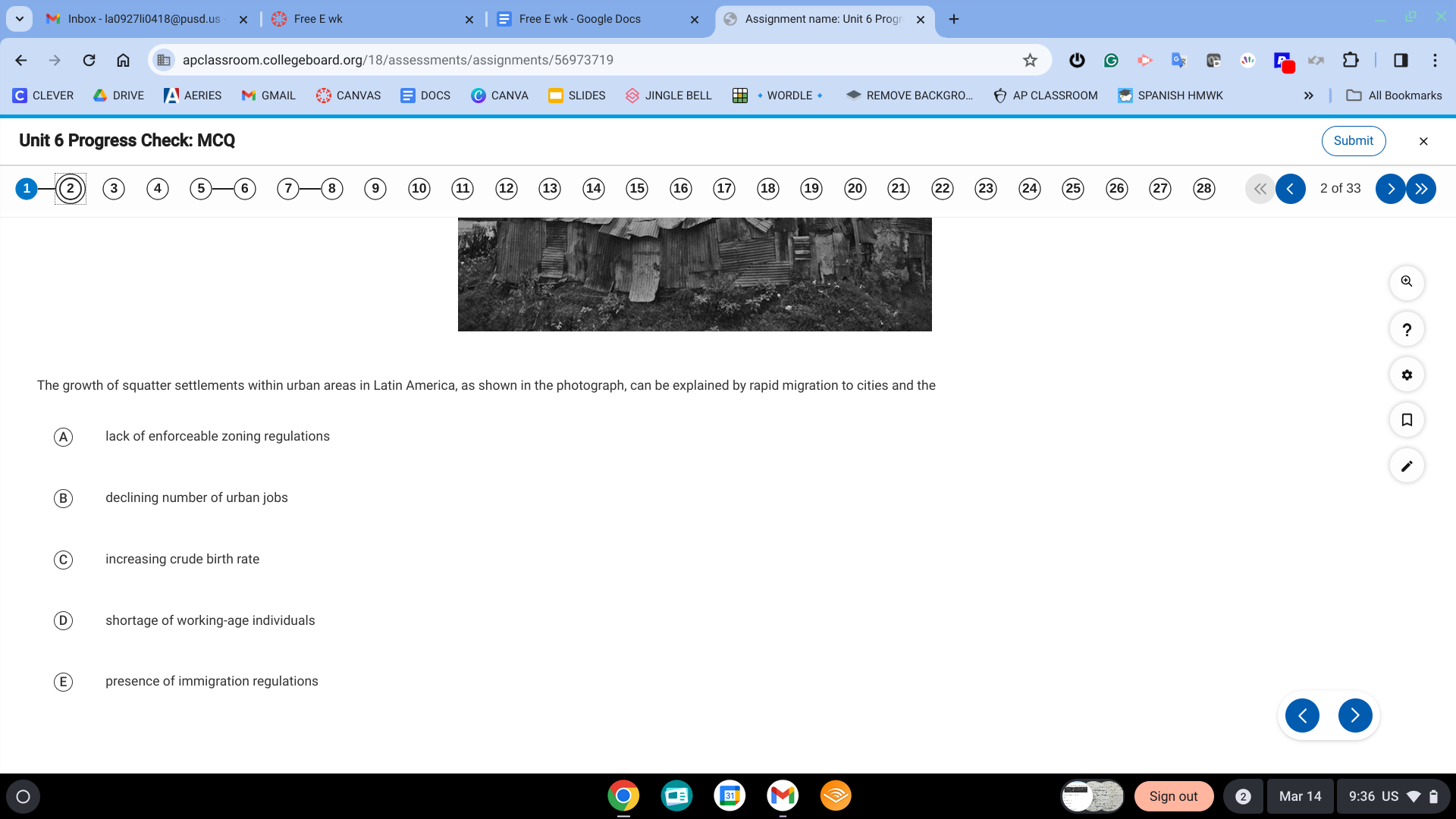
A. lack of enforceable zoning regulations
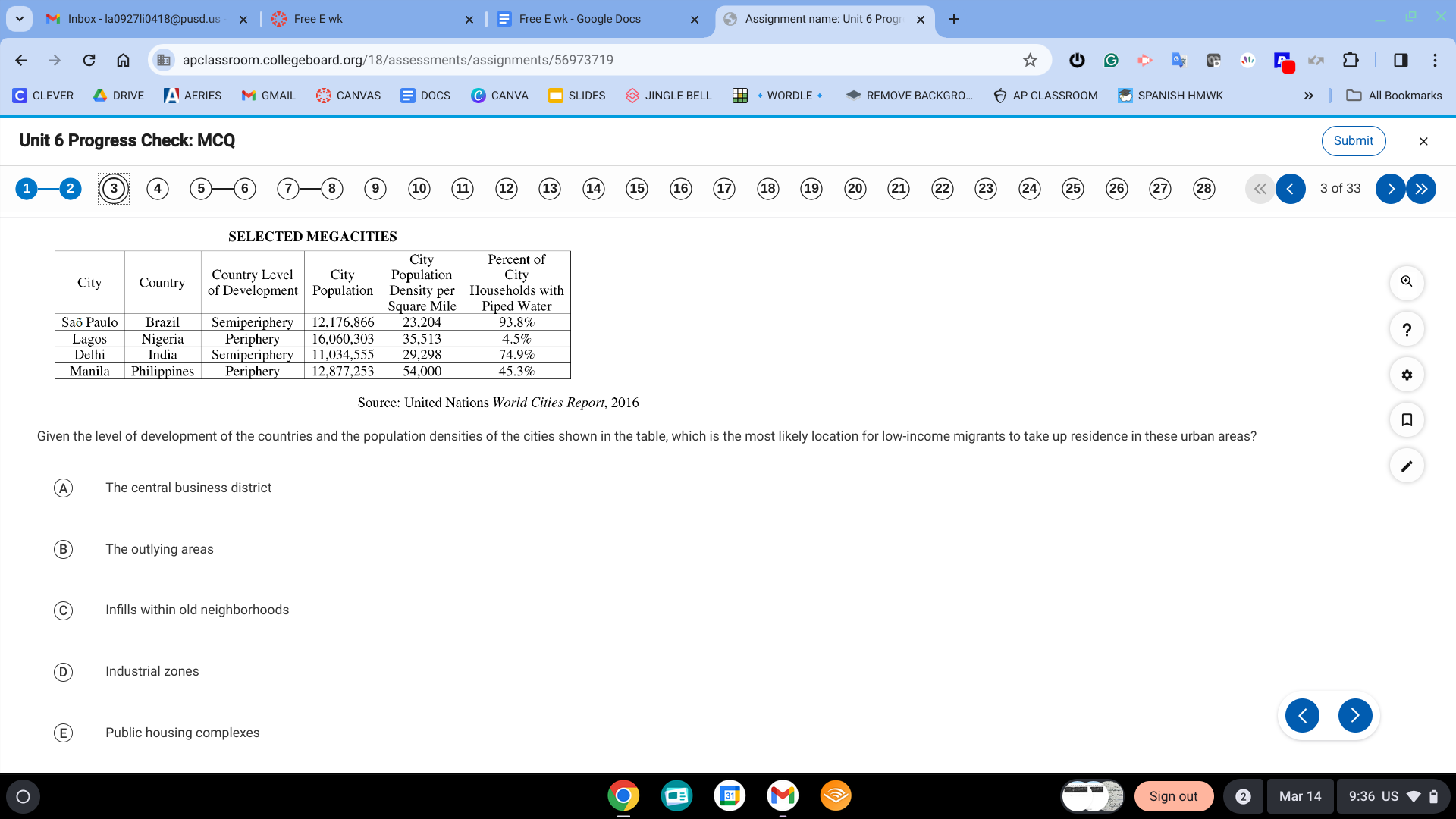
B. The outlying areas
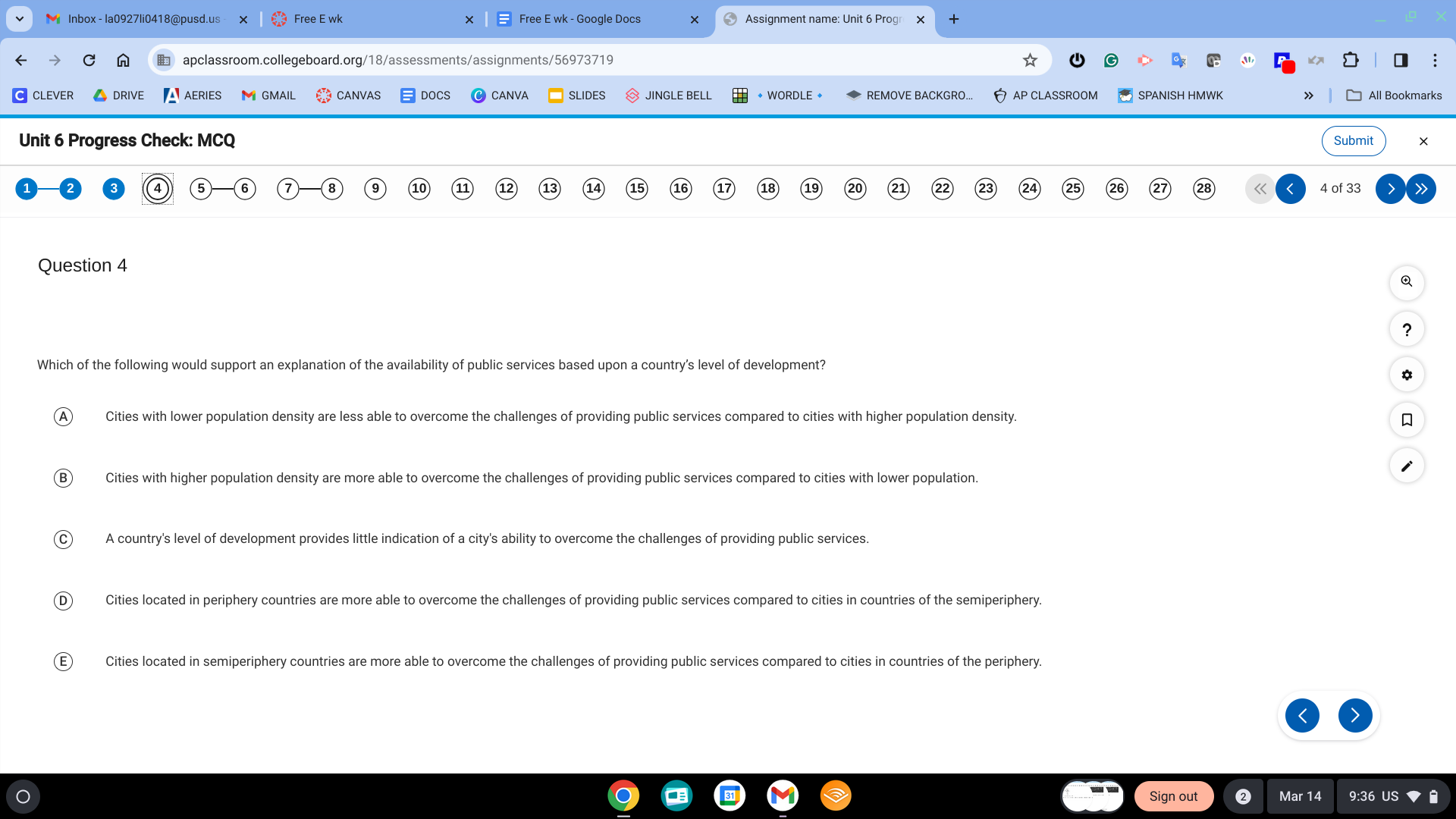
Cities located in semiperiphery countries are more able to overcome the challenges of providing public services compared to cities in countries of the periphery.
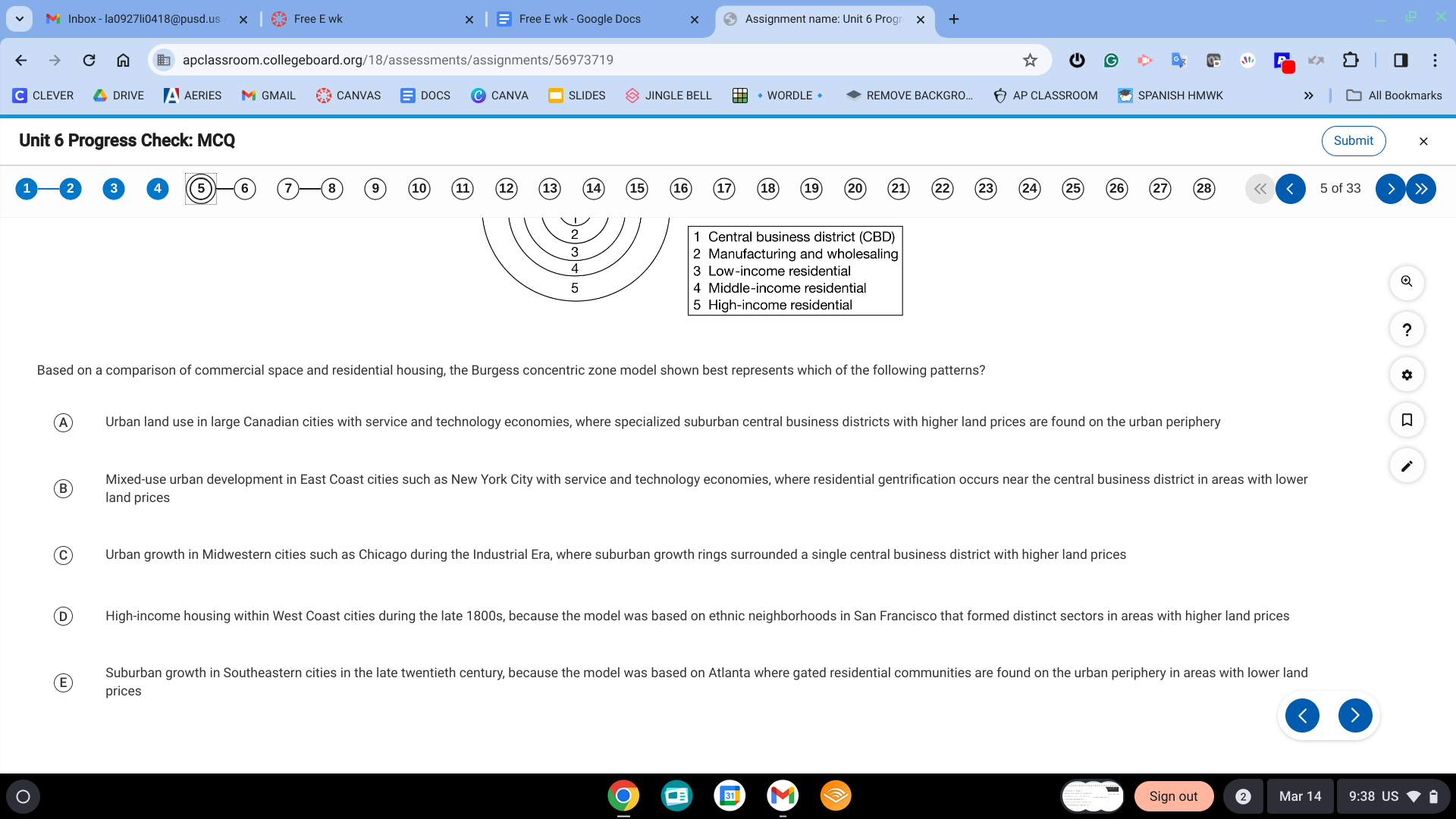
C. urban growth in midwestern cities such as Chicago during the Industrial Era, where suburban growth rings surrounded a single central business district with higher land prices.
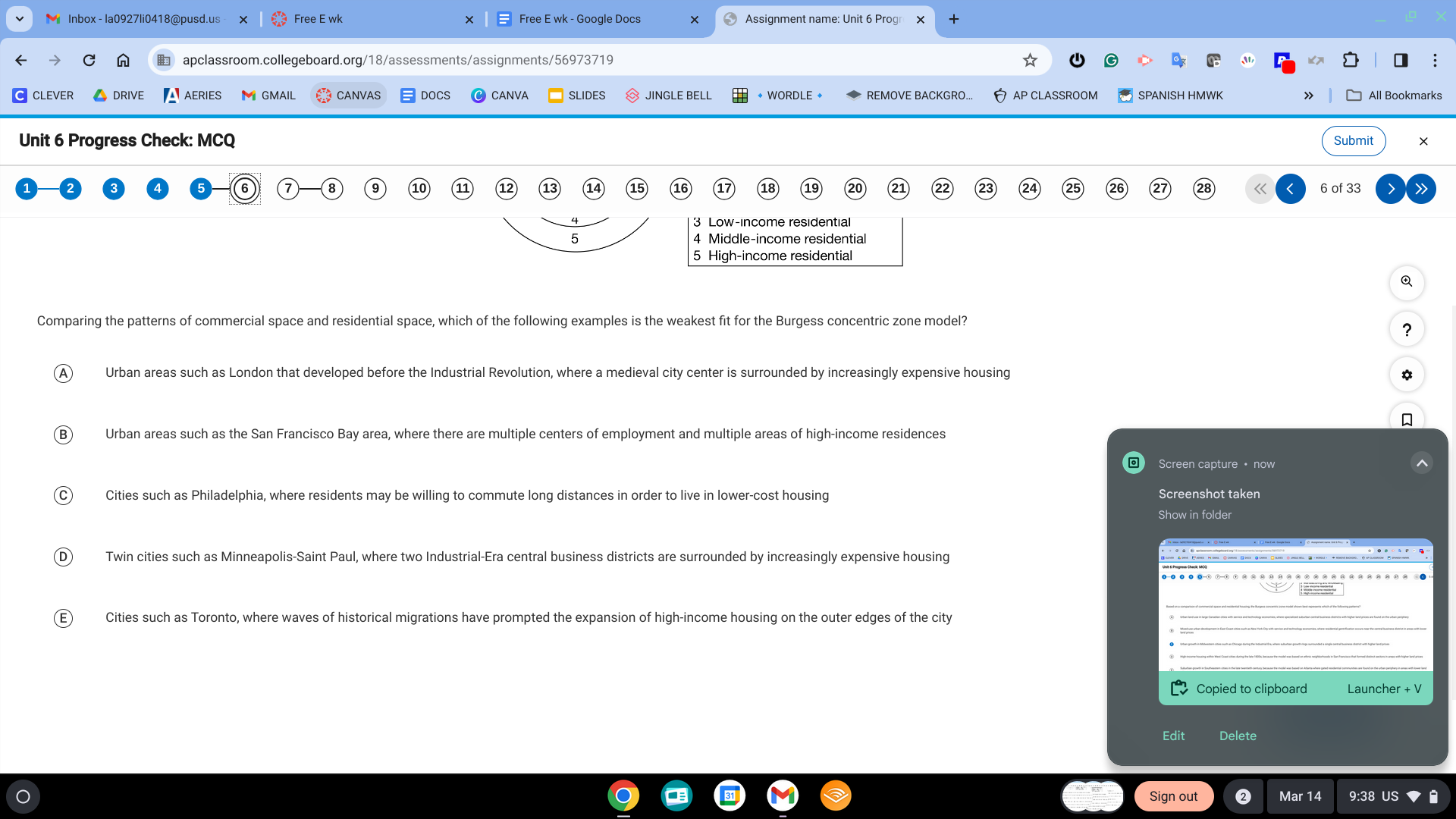
B. Urban areas such as the San Francisco Bay area, where there are multiple centers of employment and multiple areas of high-income residences
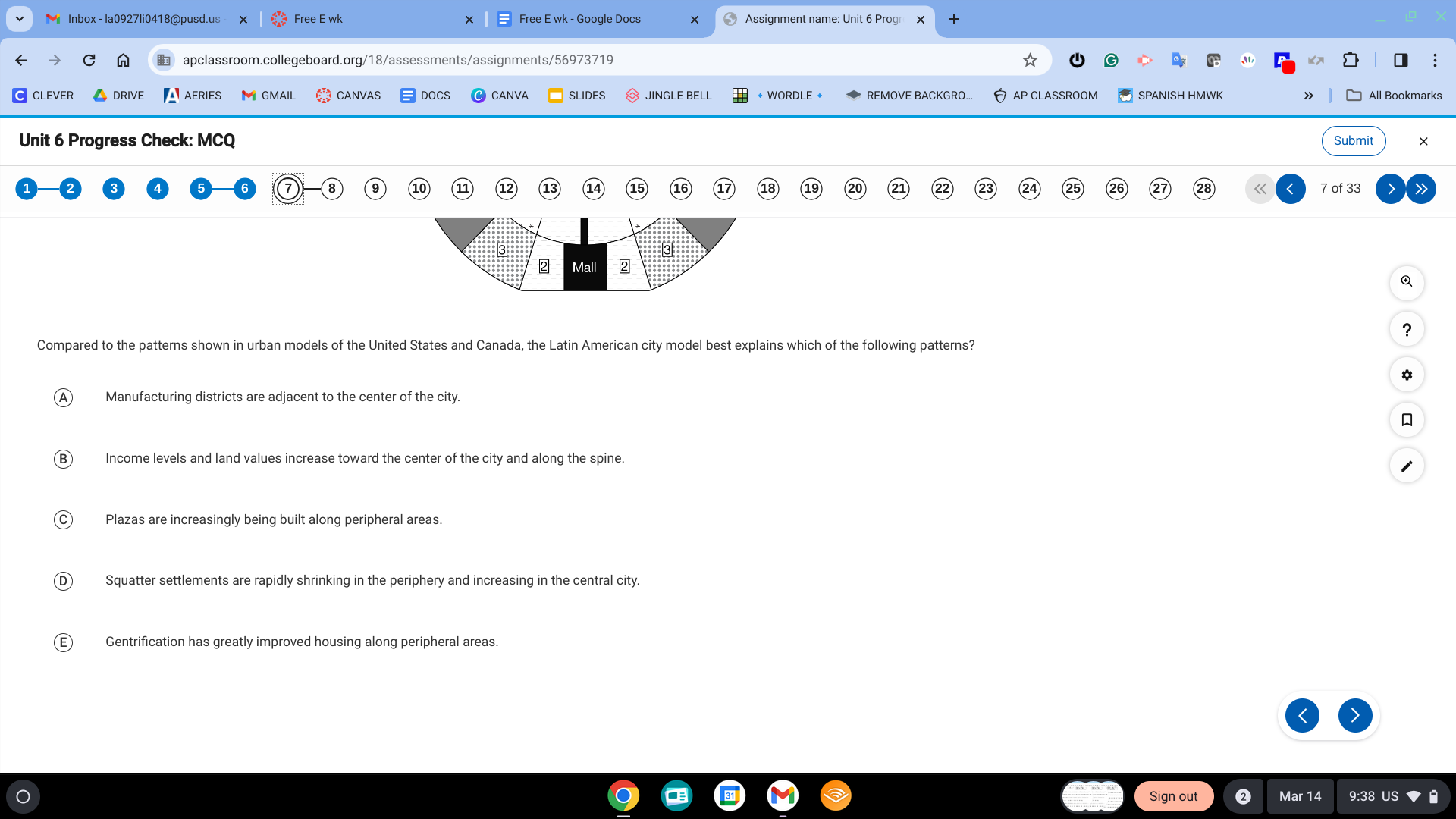
B. Income levels and land values increase toward the center of the city and along the spine
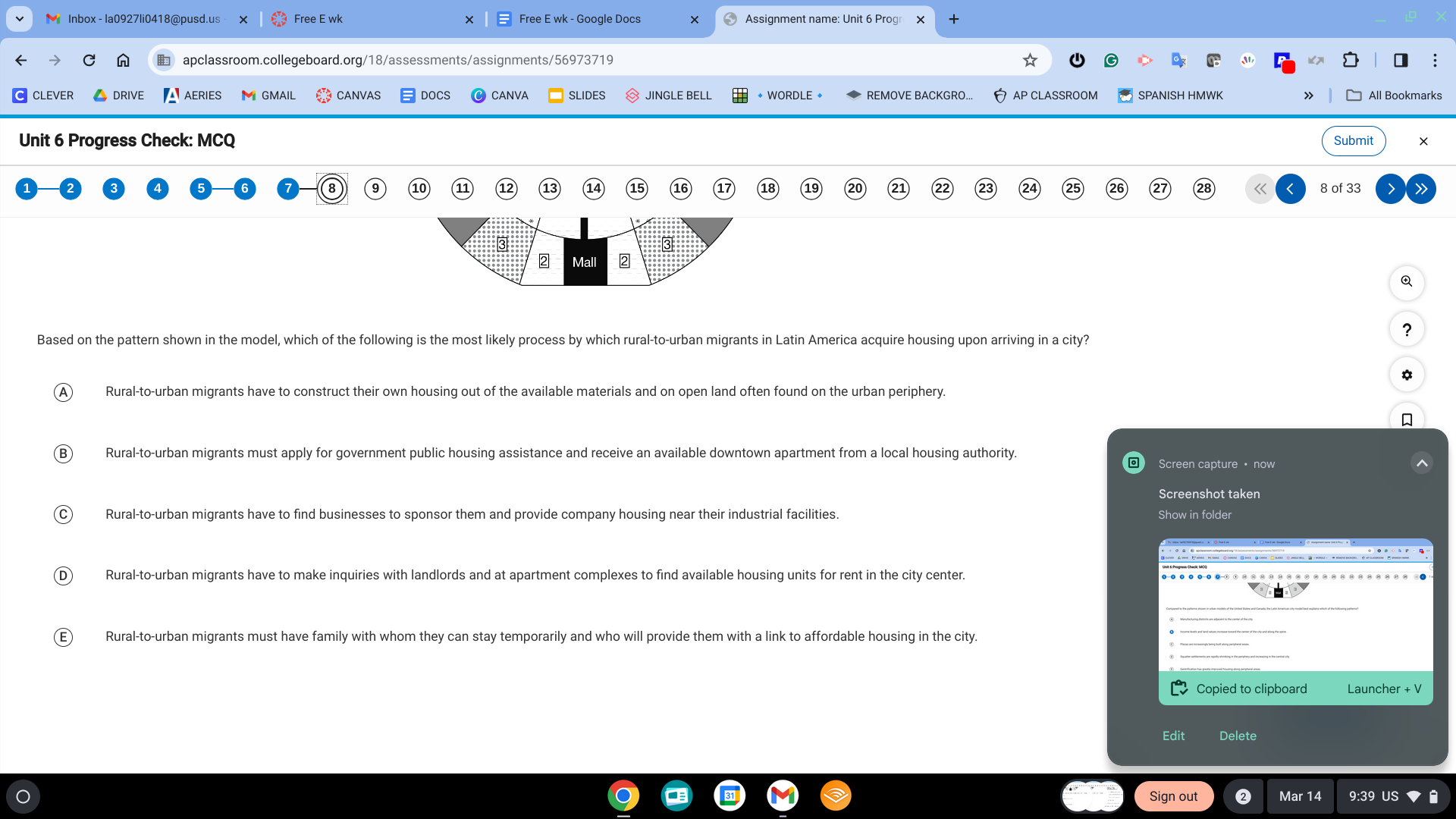
A. rural-to-urban migrants have to construct their own housing out of the available materials and on open land often found on the urban periphery
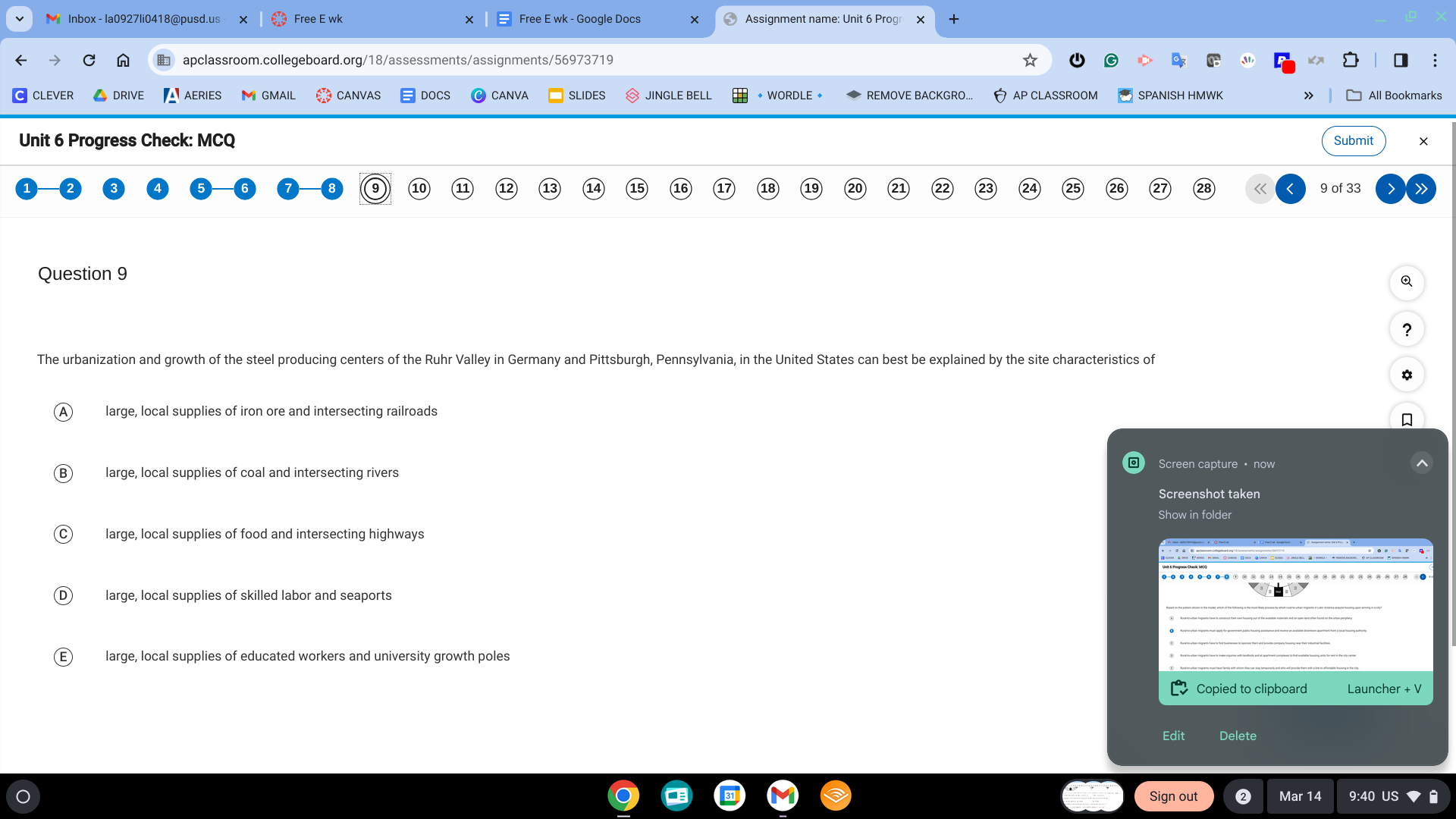
B. large, local supplies of coal and intersecting rivers
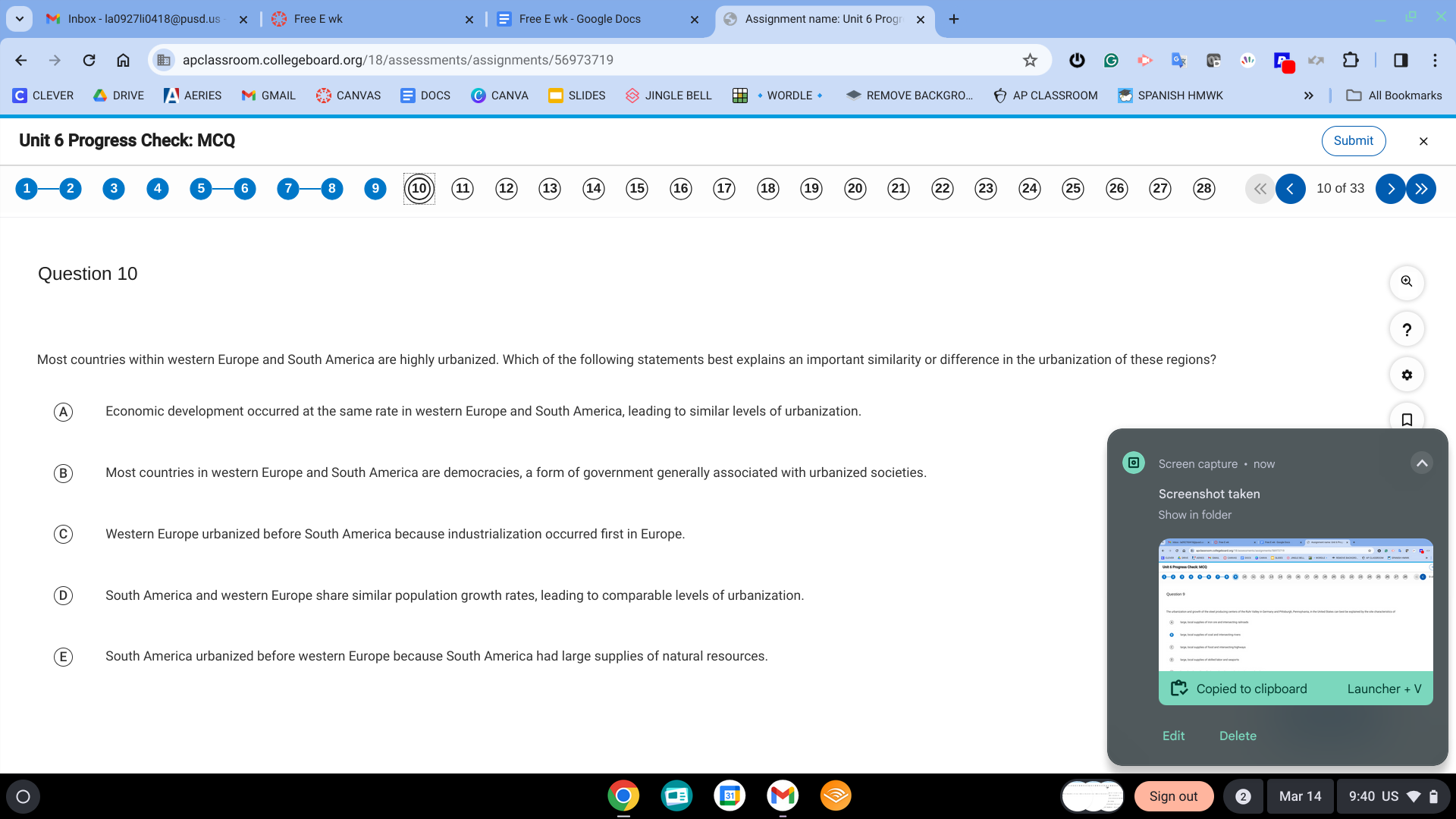
C. western Europe urbanized before South America because industrialization occurred first in Europe
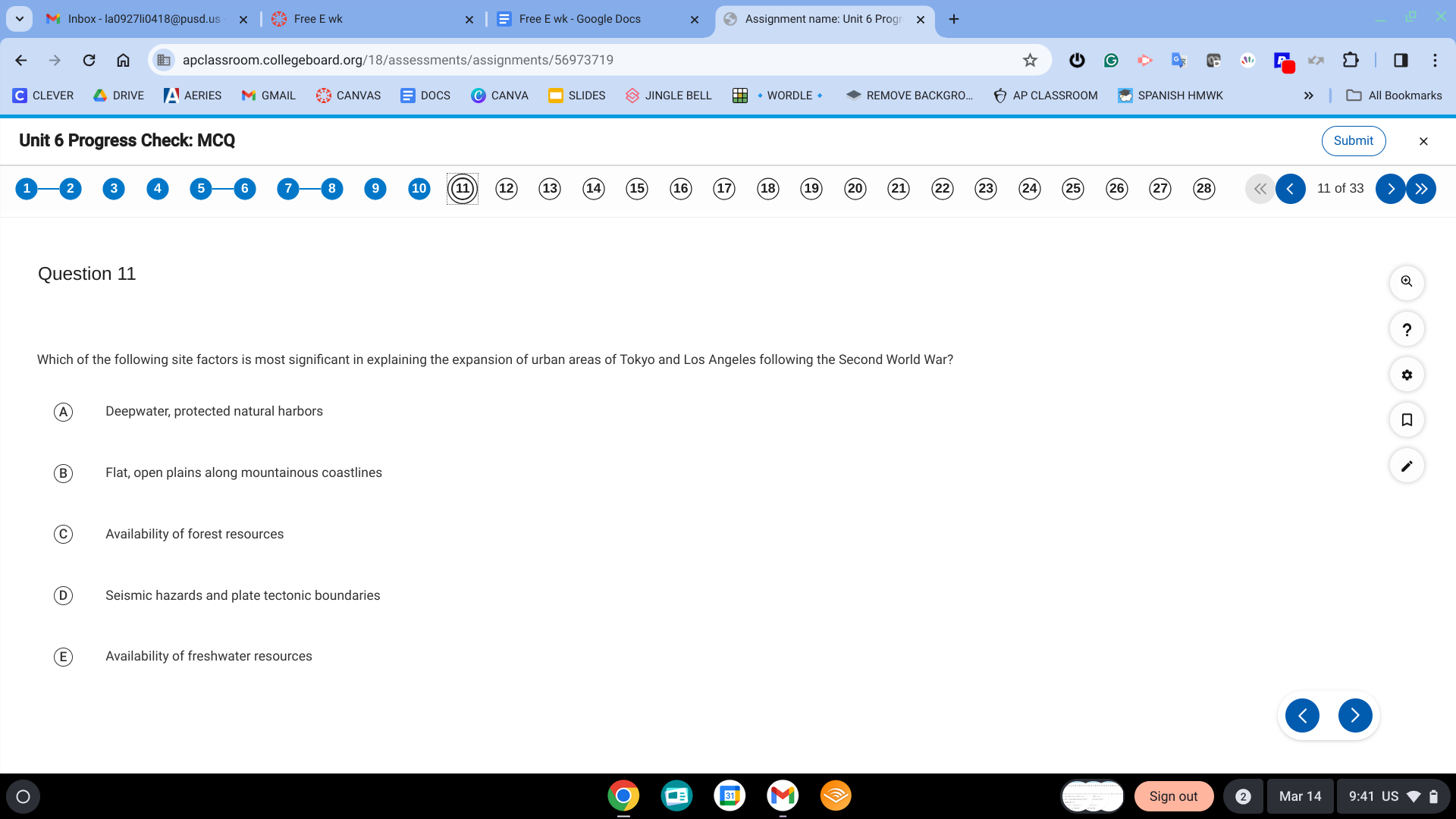
B. Flat, open plains on mountainous coastlines
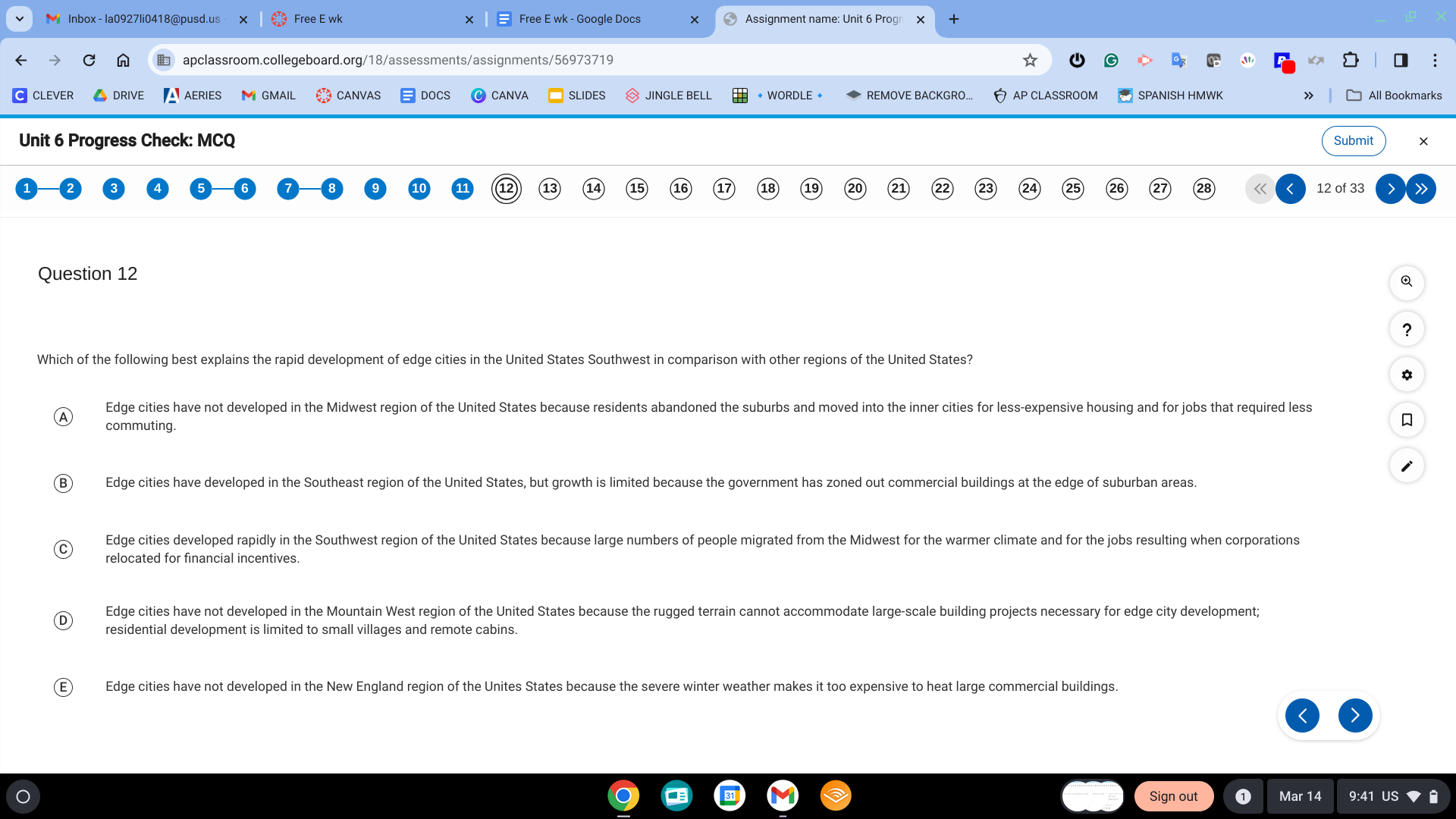
C. Edge cities developed rapidly in the southwest region of the united states because large numbers of people migrated from the midwest for the warmer climate and for the jobs resulting when corporations relocated for financial incentives
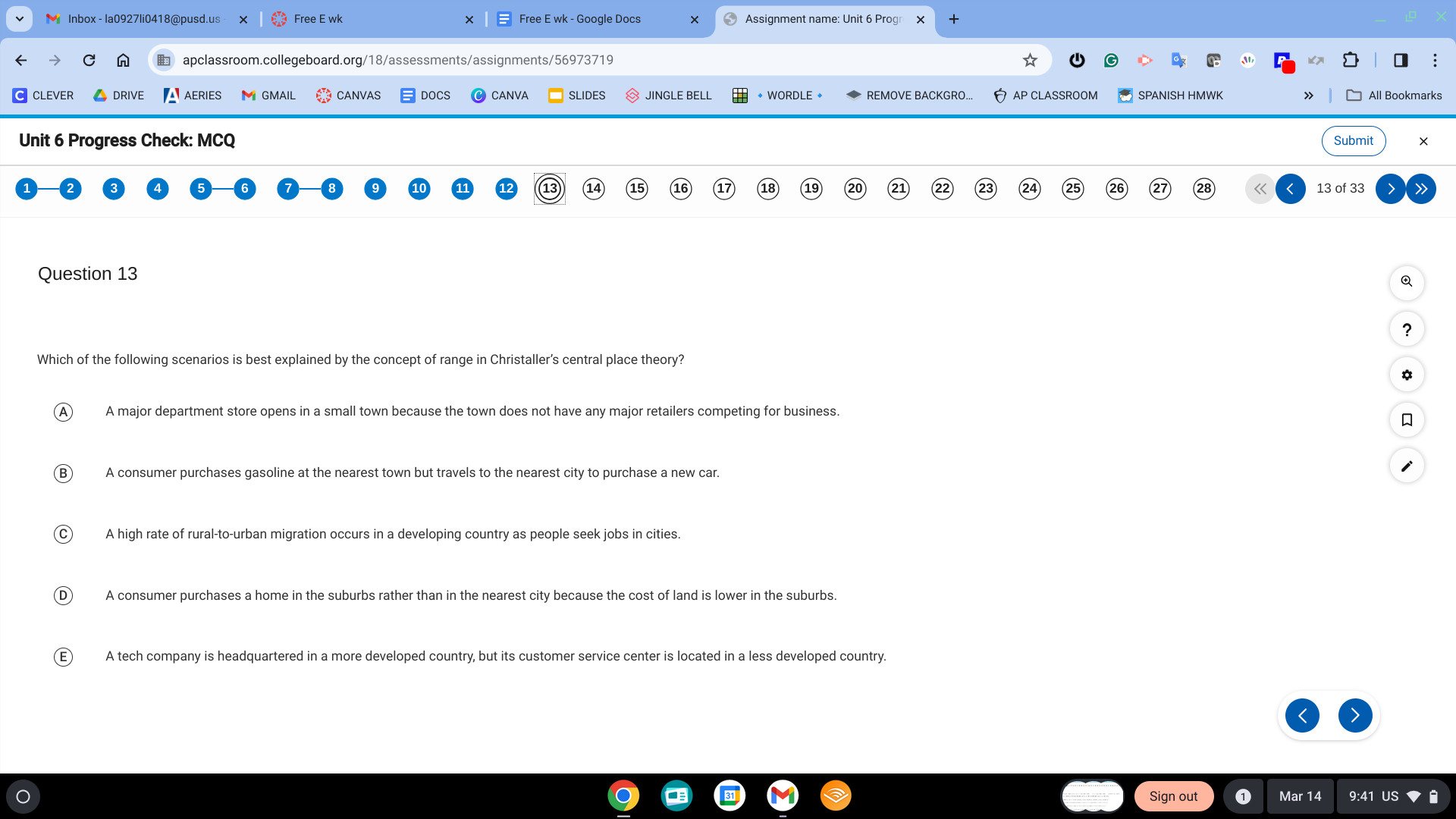
B. A consumer purchases gasoline at the nearest town but travels to the nearest city to purchase a new car
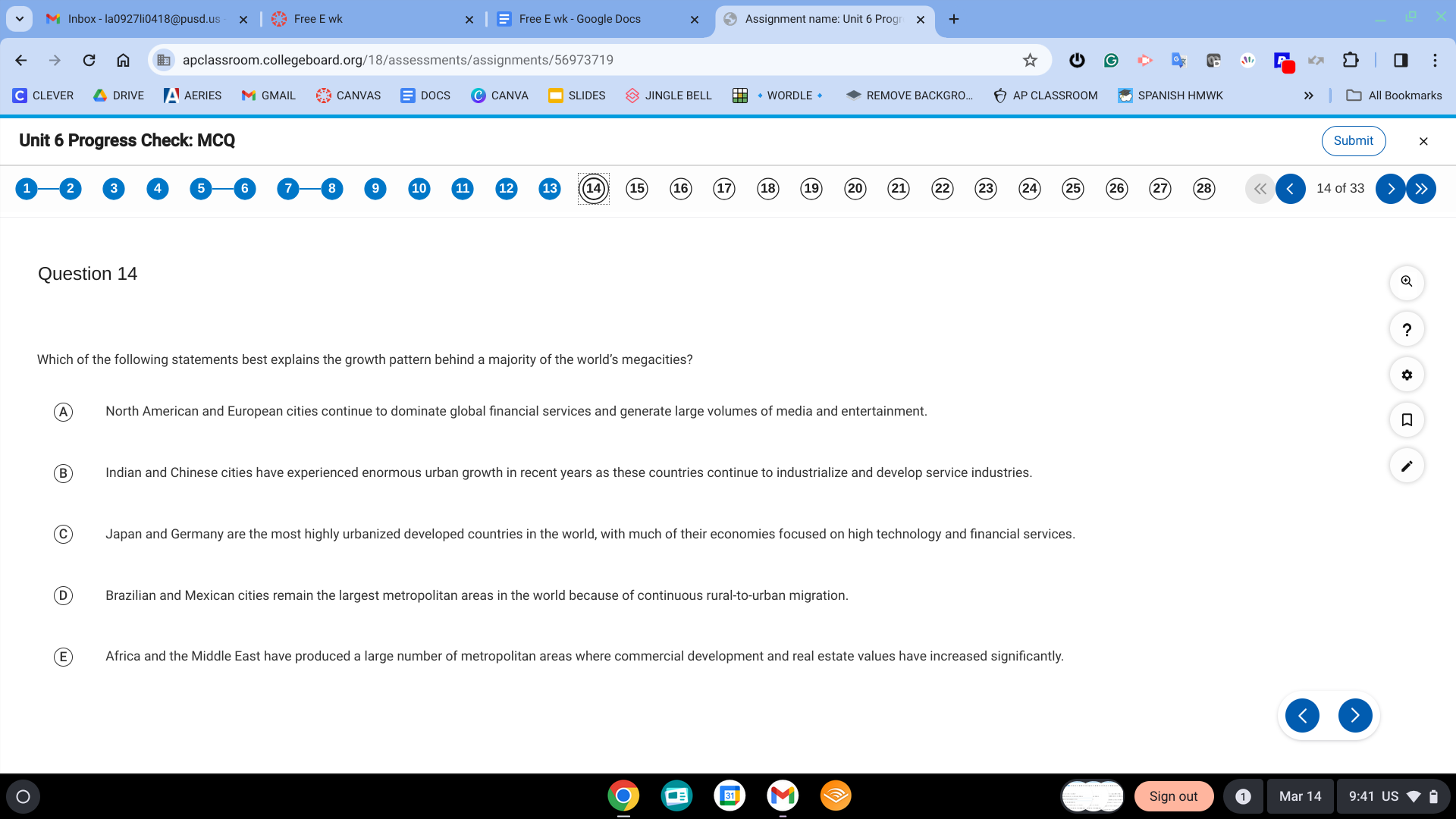
B. Indian and Chinese cities have experienced enormous urban growth in recent years as these countries continue to industrialize and develop service industries.
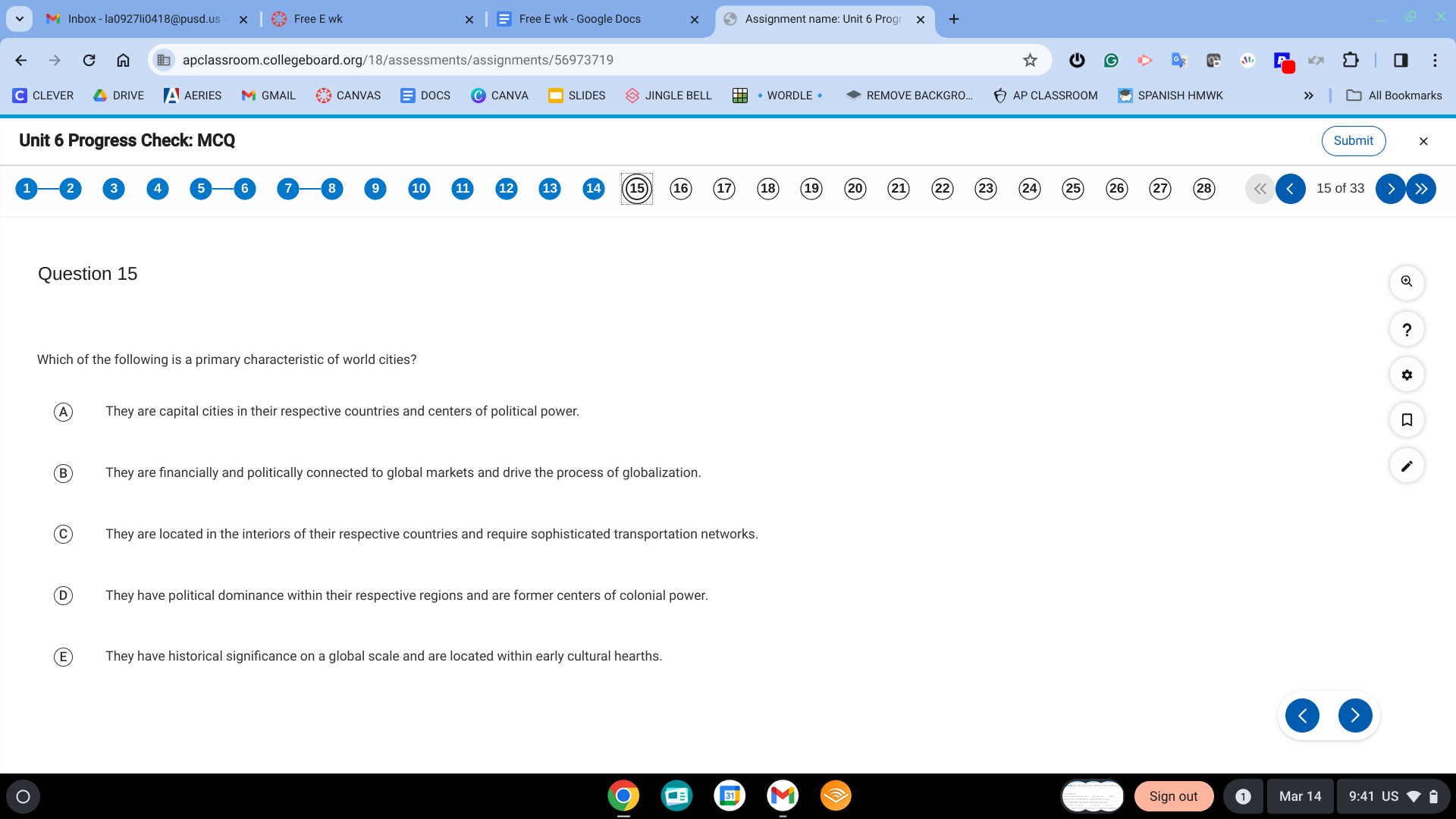
B. They are financially and politically connected to global markets and drive the process of globalization
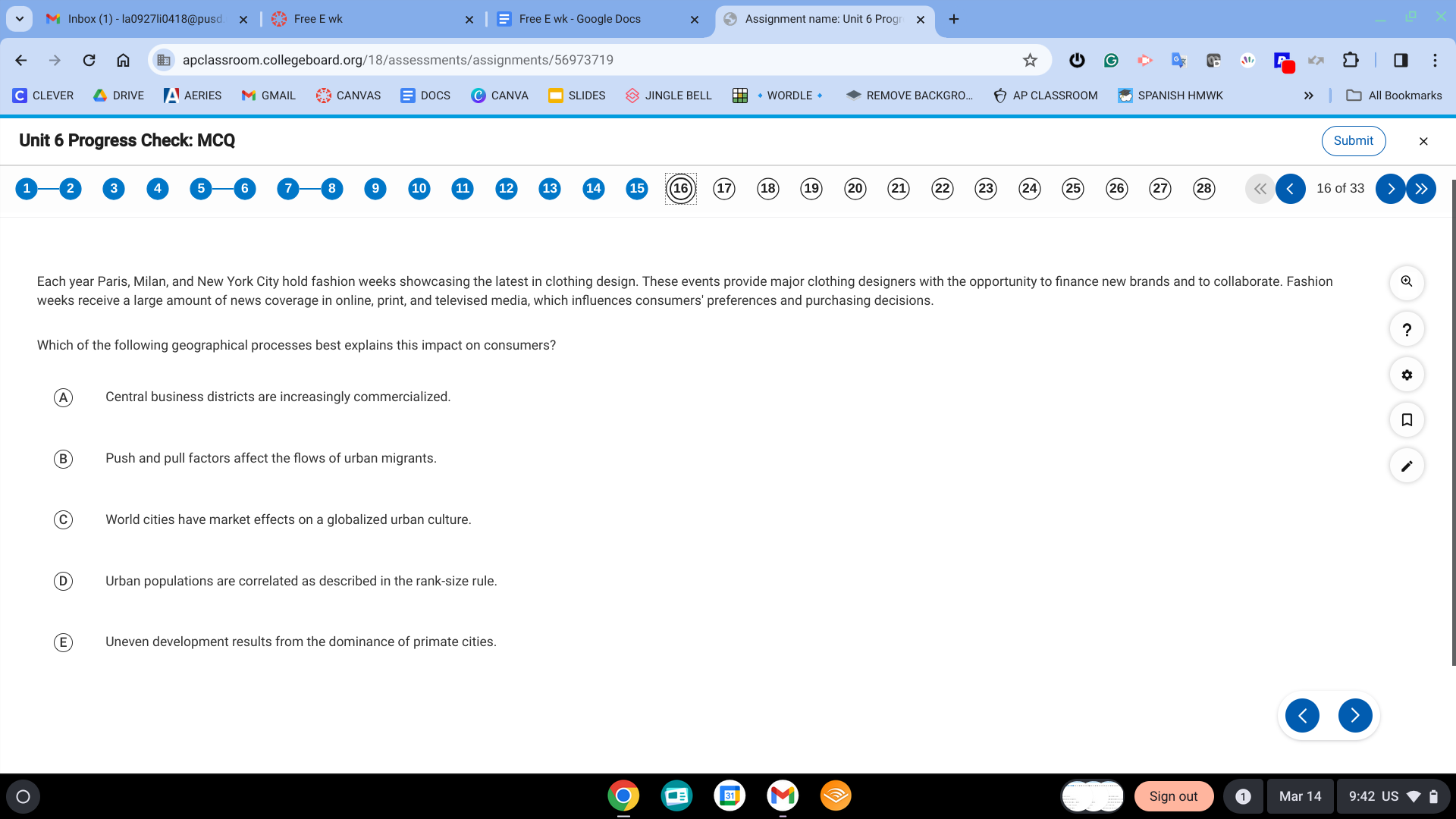
C. World cities have market effects on globalized urban culture
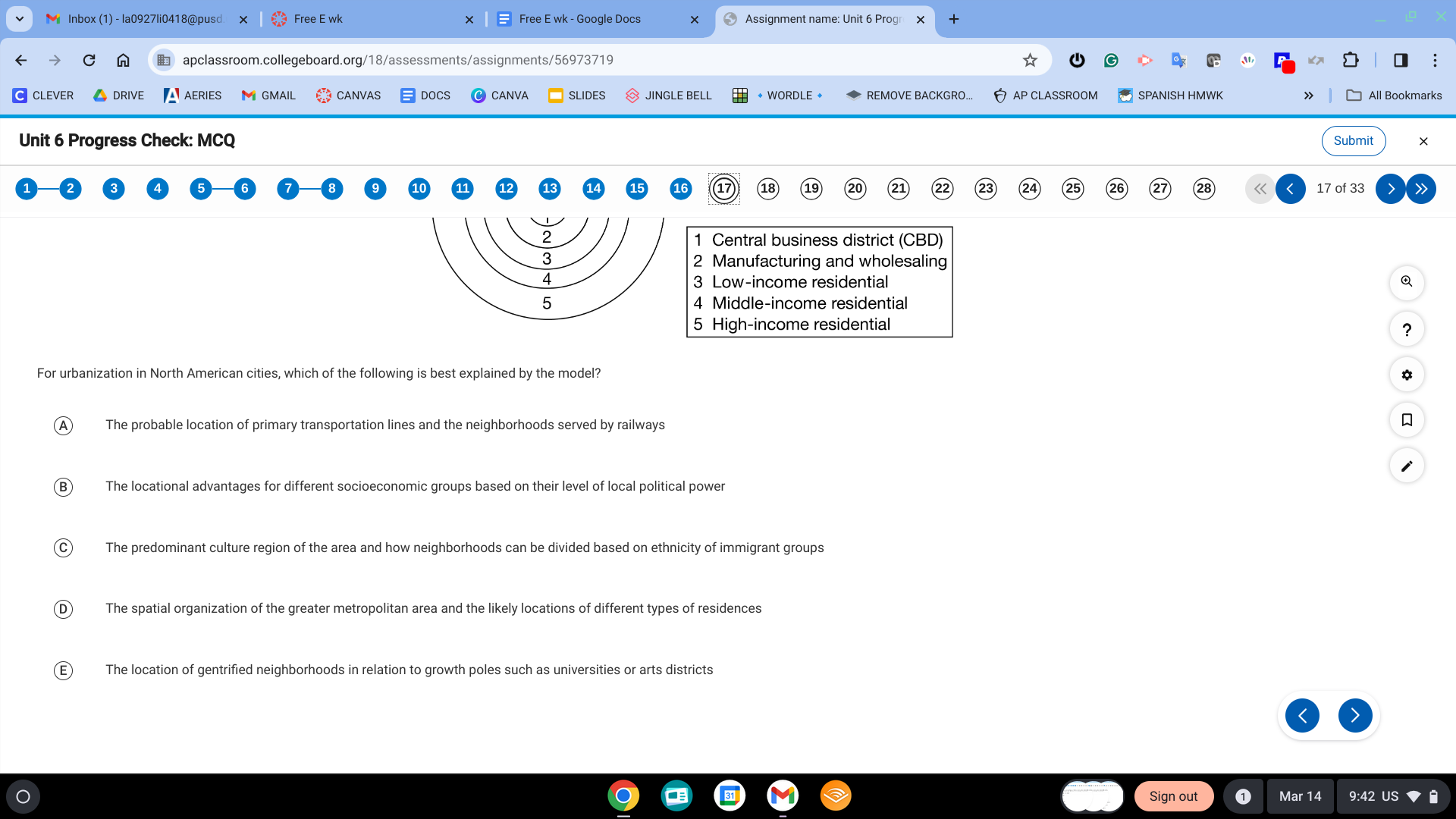
D. The spatial organization of the greater metropolitan area and the likely locations of different types of residences
E. Seoul serves as the economic, political, and cultural center of South Korea
B. The government could significantly expand the availability and use of more environmentally friendly mass transit that utilizes renewable resources.
E. Slow growth cities, which emphasize long standing cultural traditions
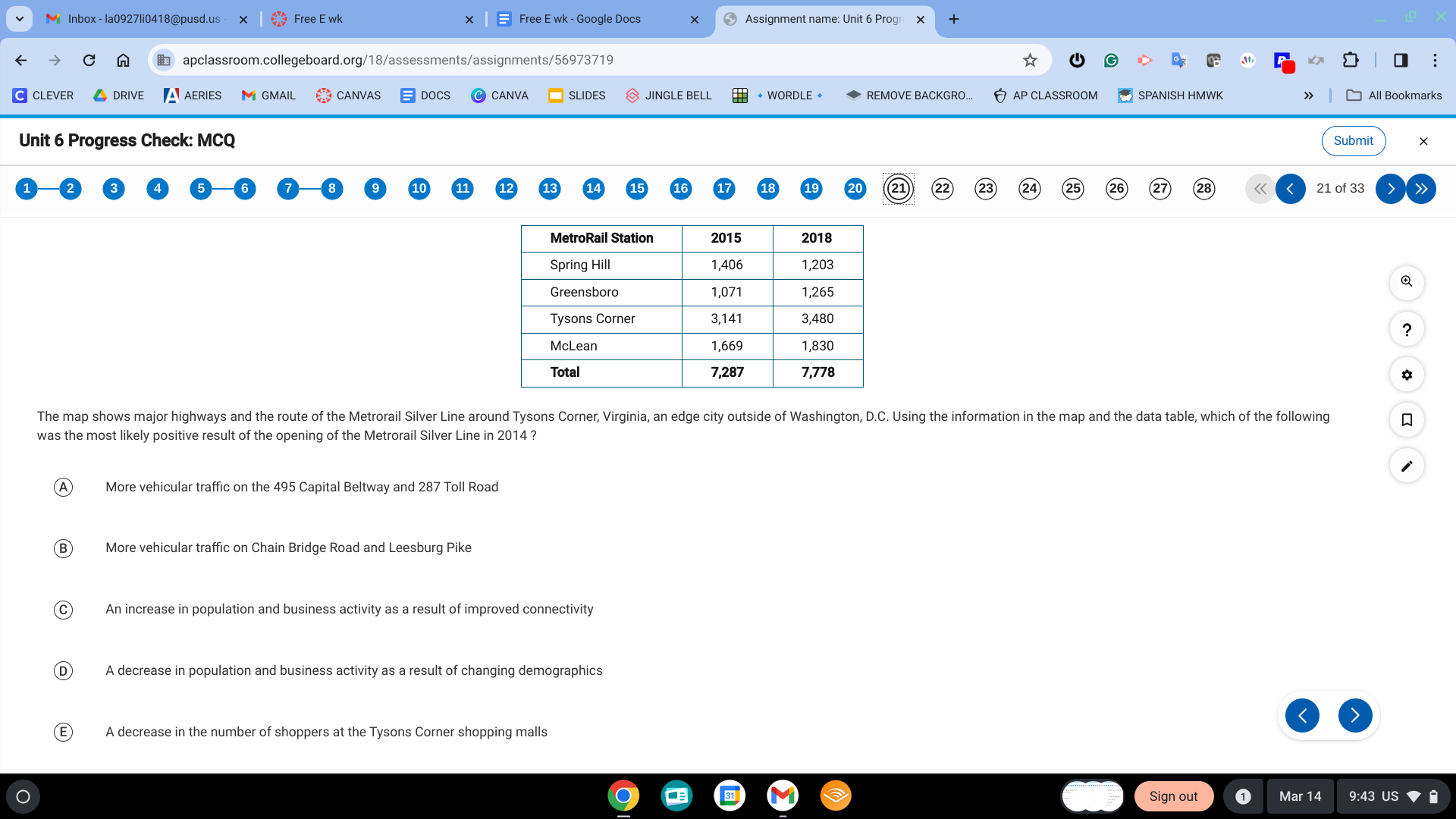
C. An increase in population and business activity as a result of improved connectivity
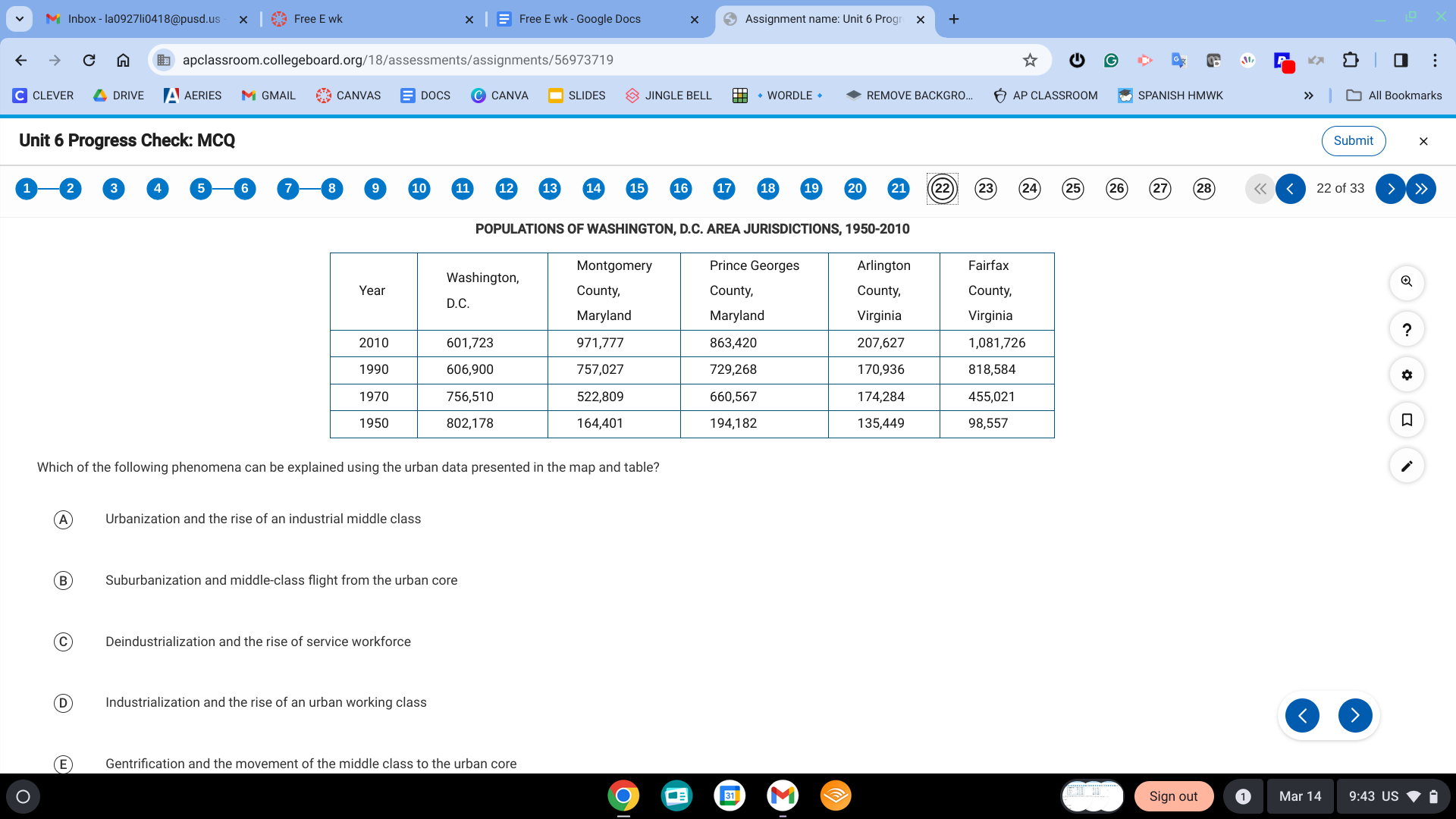
B. Suburbanization and the middle class fight from the urban core
C. The redevelopment of brownfields enables the reuse of abandoned areas that are often located in urban centers and have existing infrastructure.
A. An increase in mixed land-use development, which improves the walkability of neighborhoods
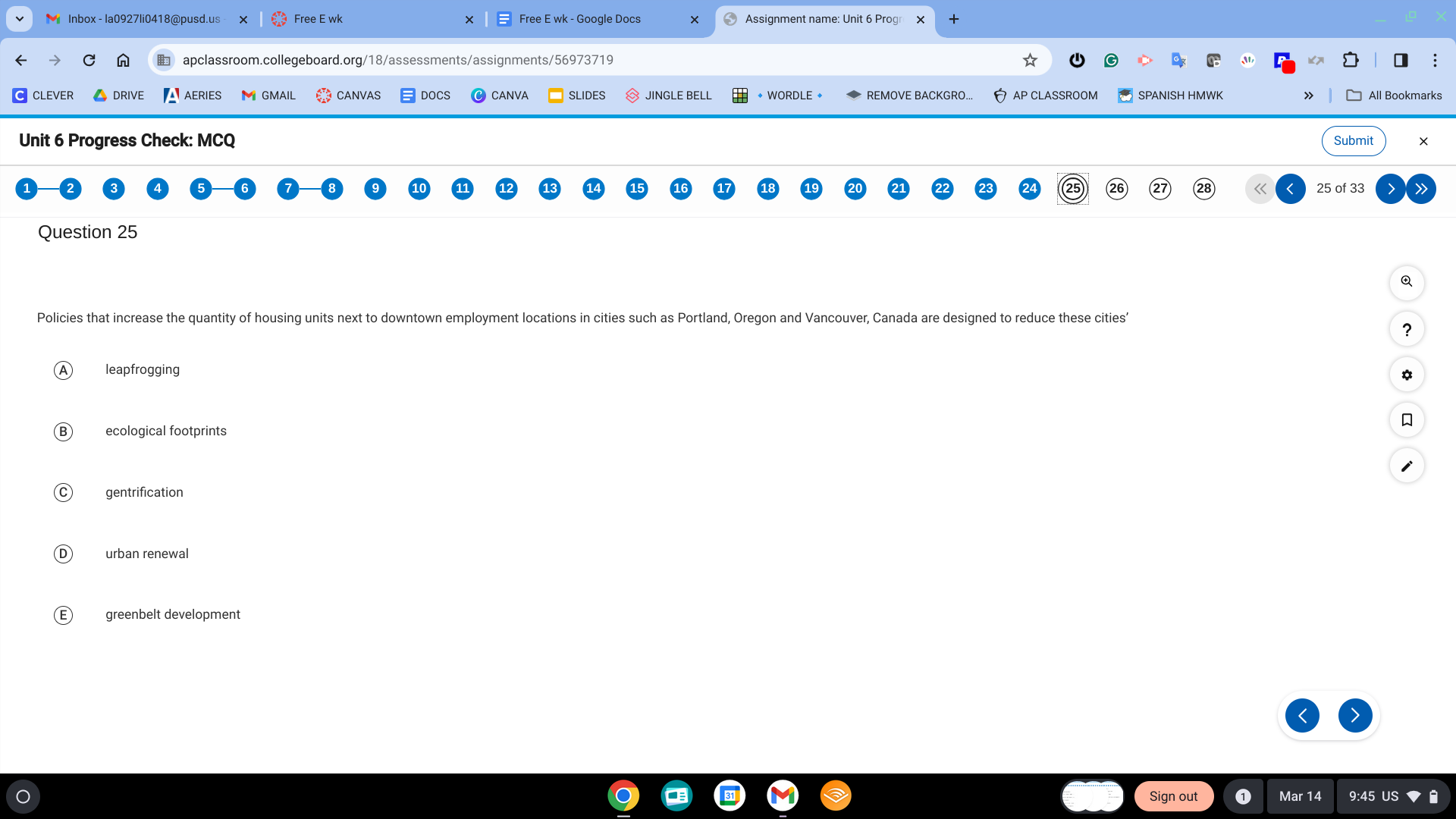
ecological footprints
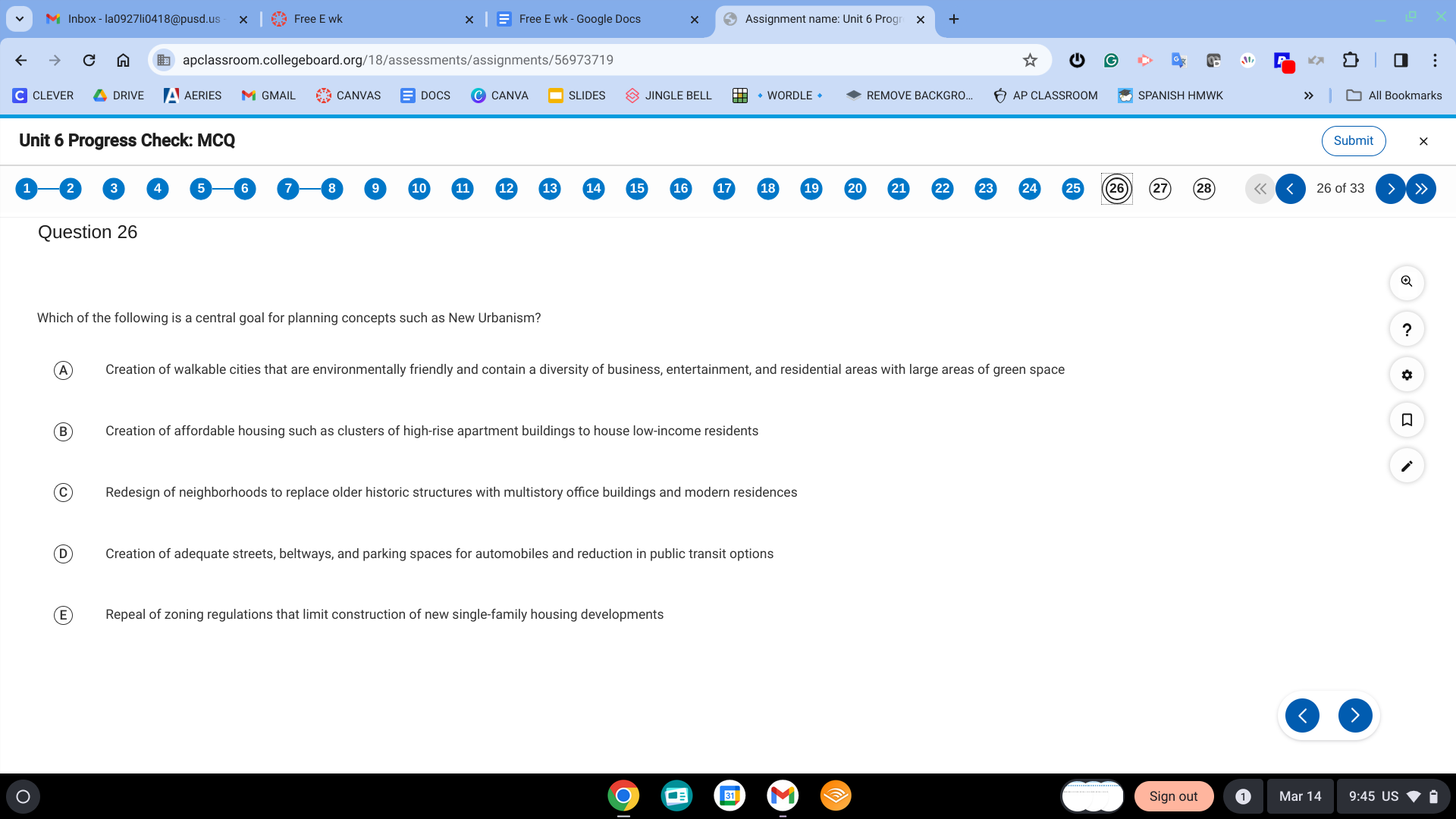
A. Creation of walkable cities that are environmentally friendly and contain a diversity of business, entertainment, and residential areas with large areas of green space
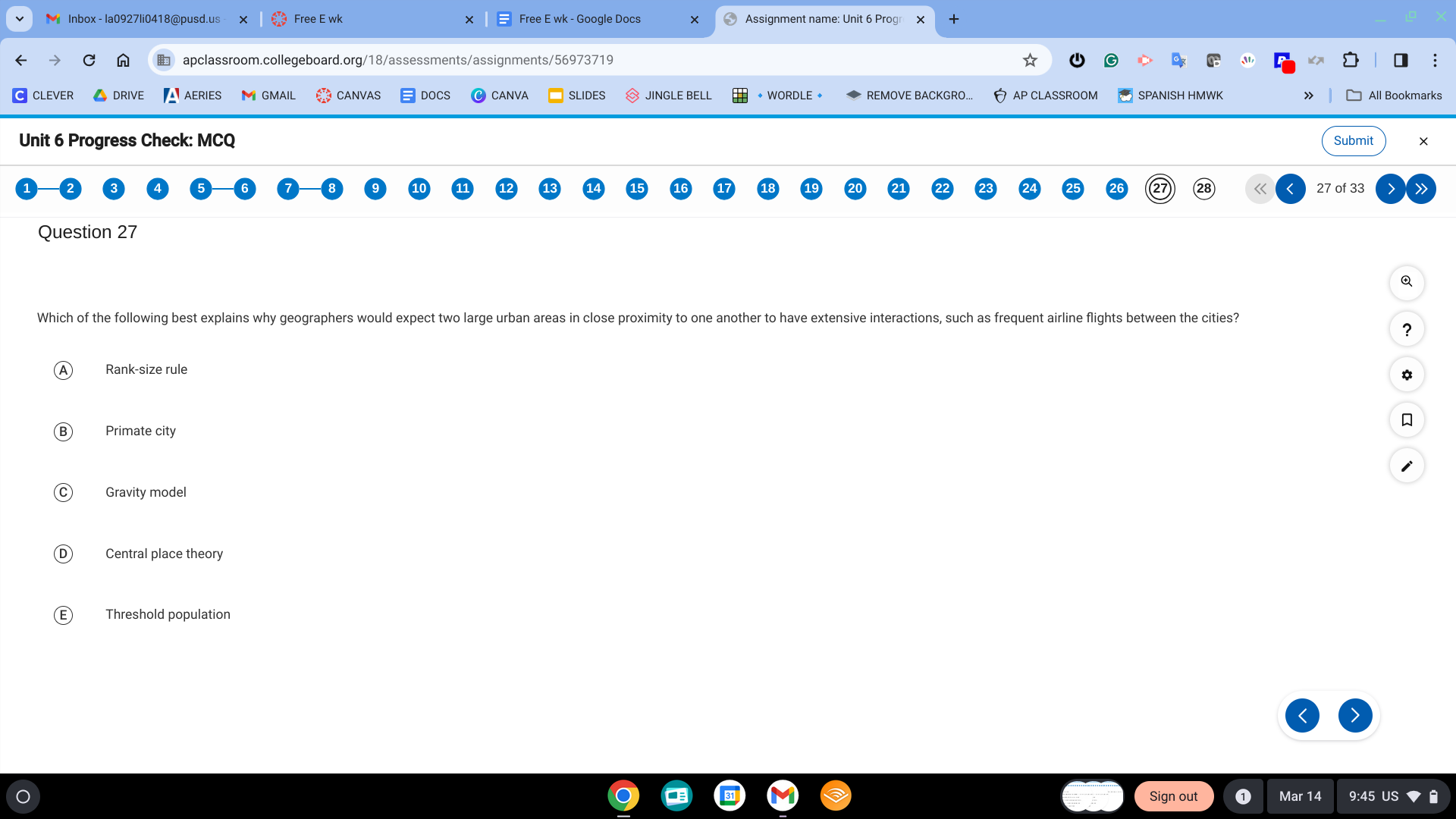
C. Gravity Model
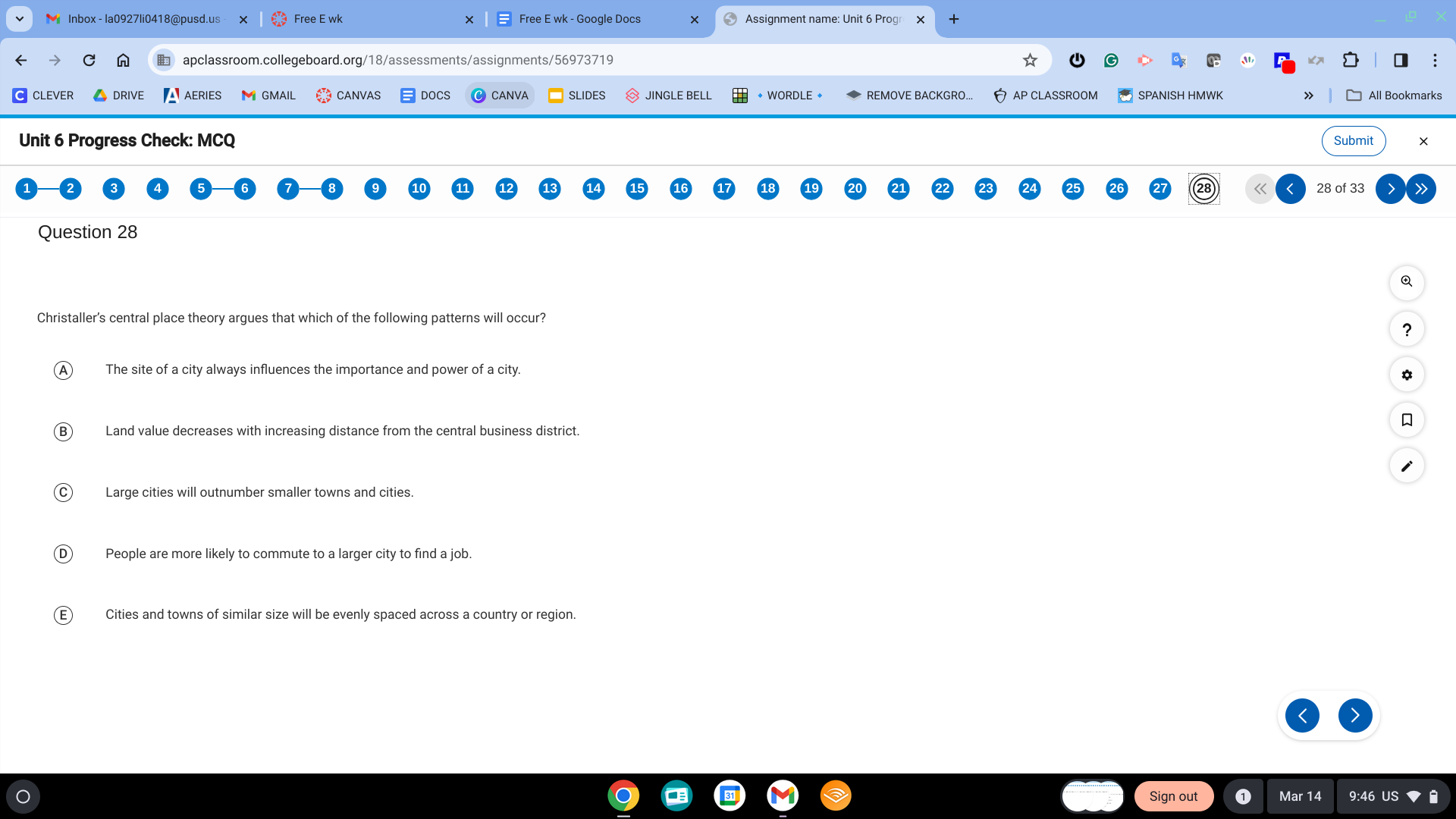
E. Cities and towns of similar size will be evenly spaced across a country or region.
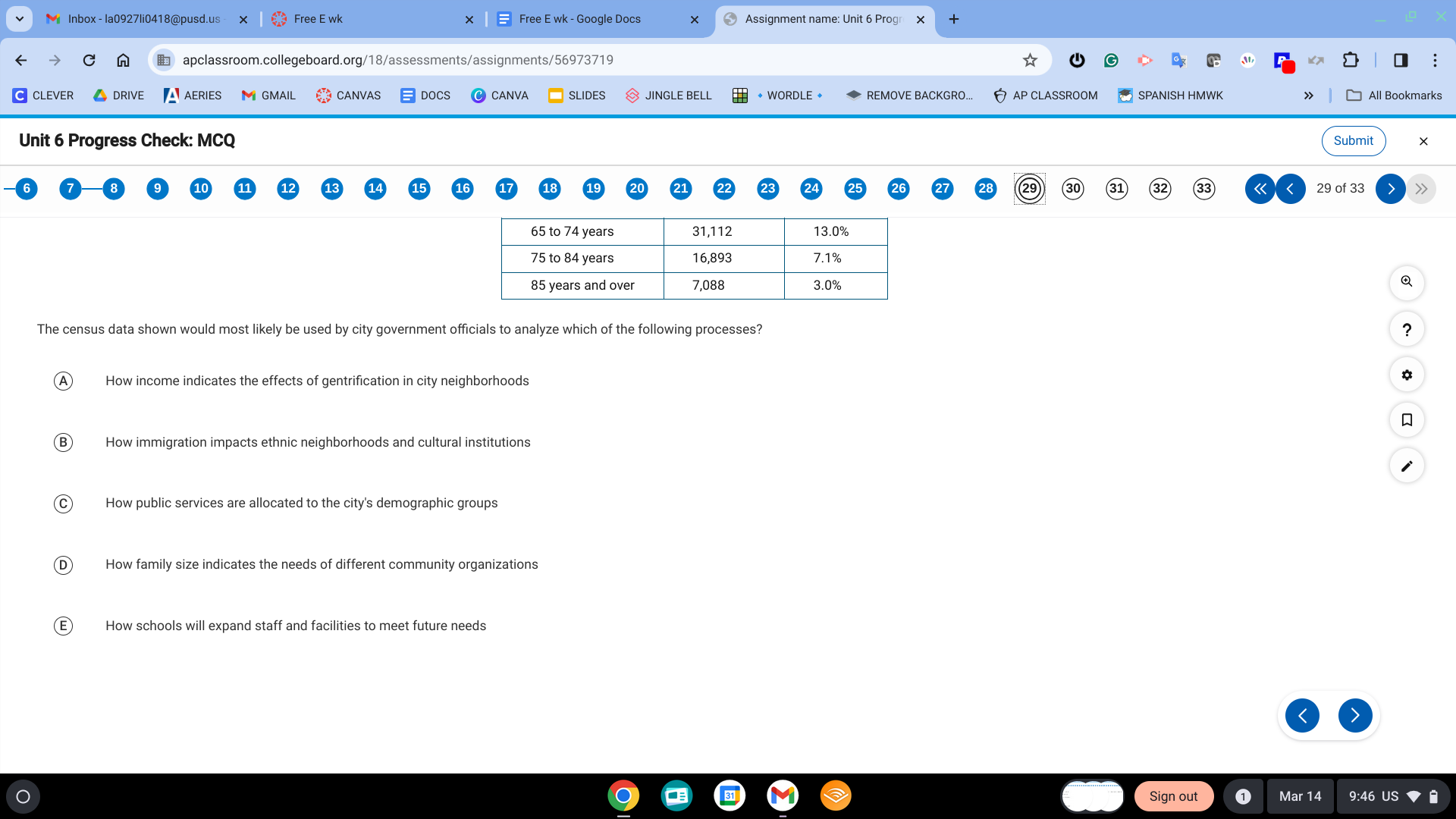
C. How public services are allocated to the city's demographic groups
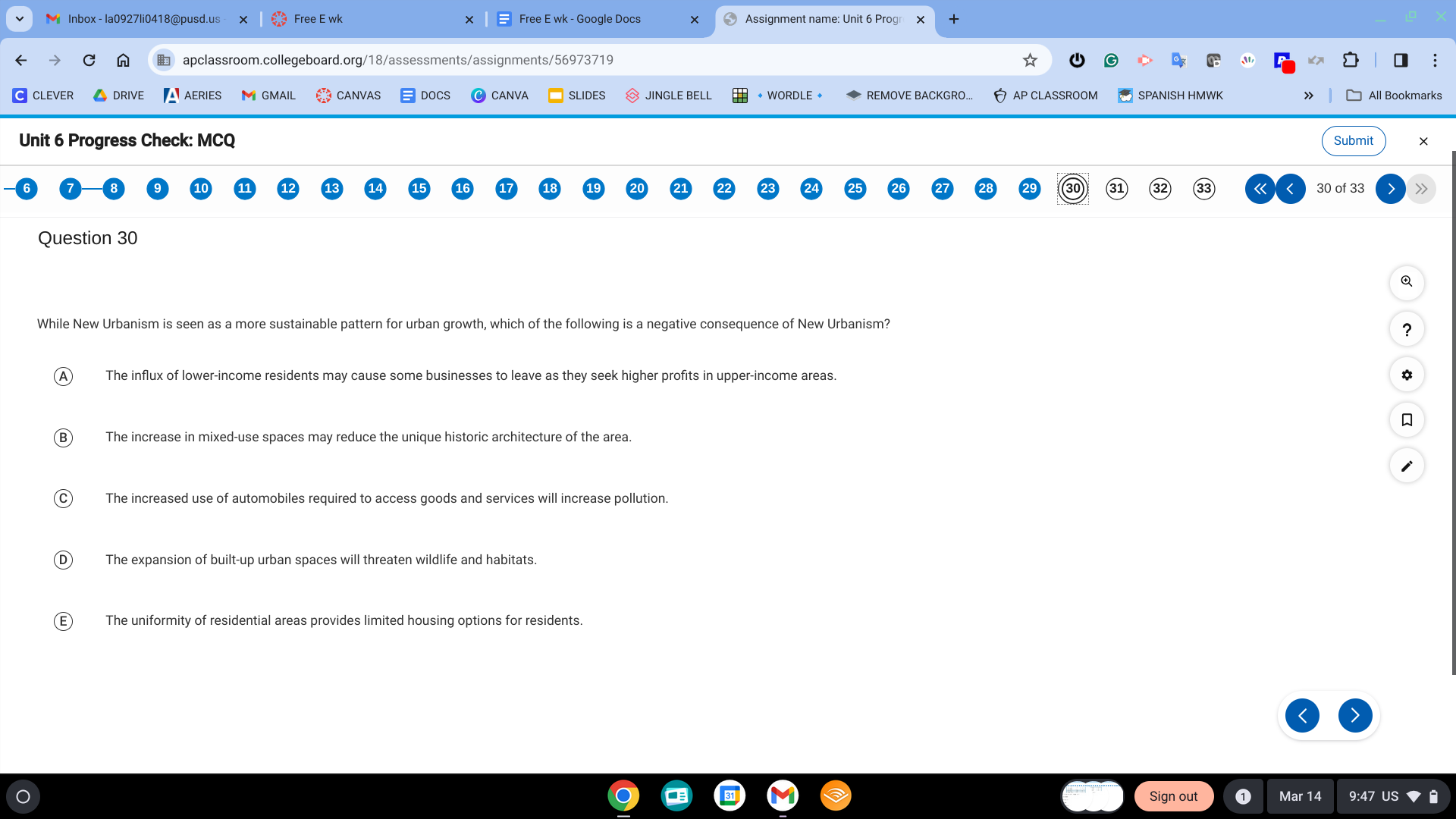
B. The increase in mixed-use spaces may reduce the unique historic architecture of the area
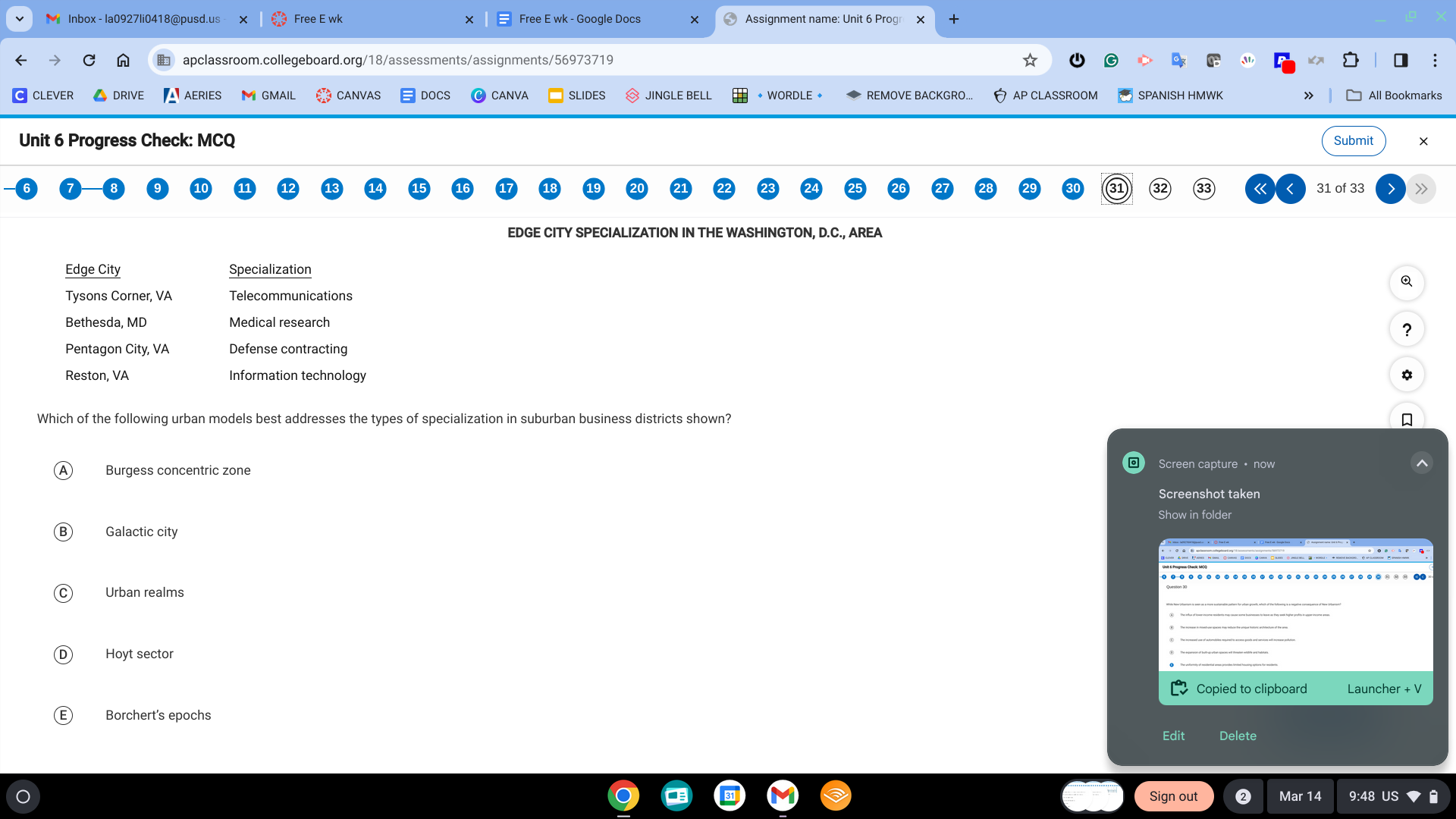
B. Galactic city
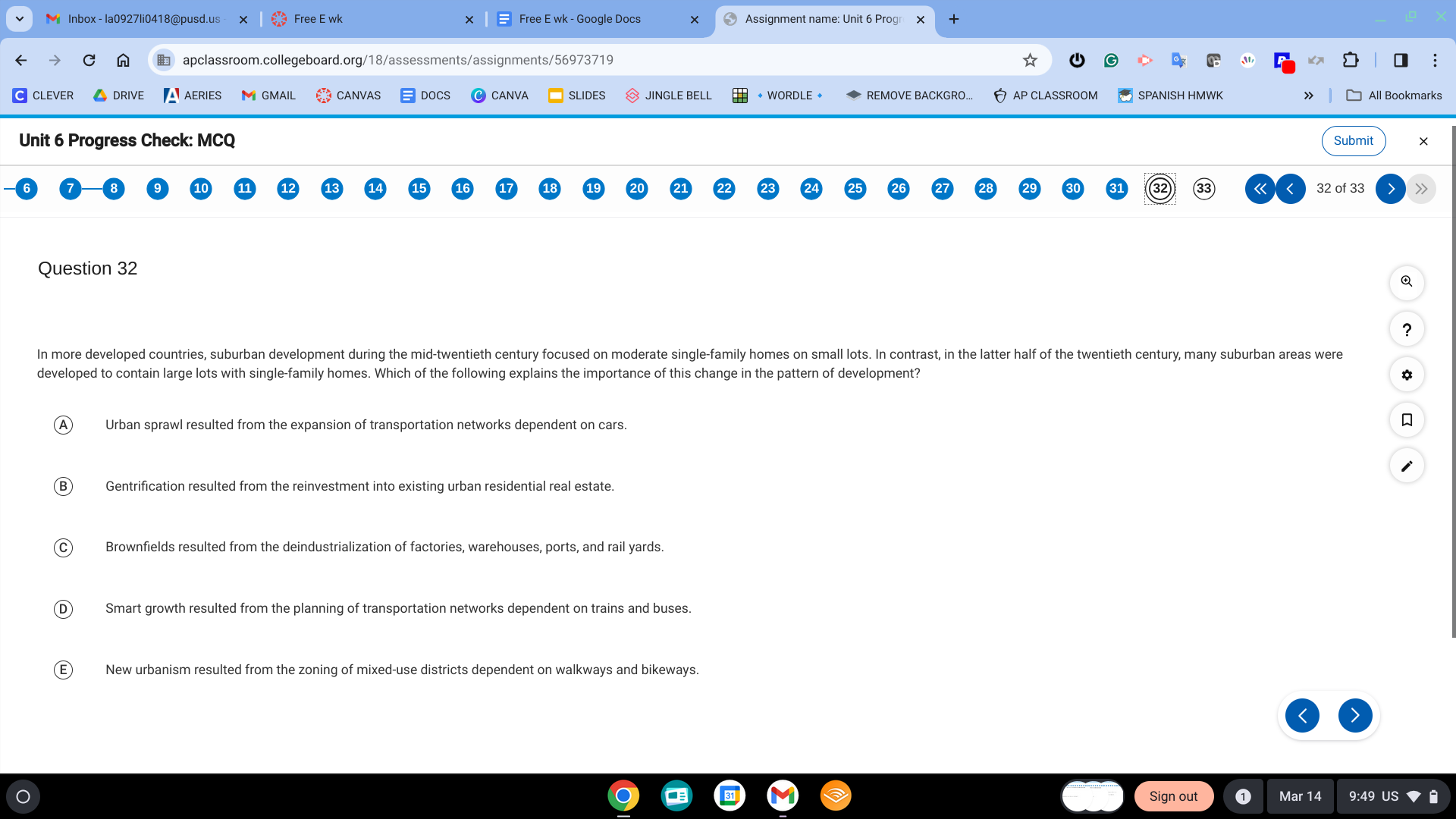
A. Urban sprawl resulted from the expansion of transportation networks dependent on cars.
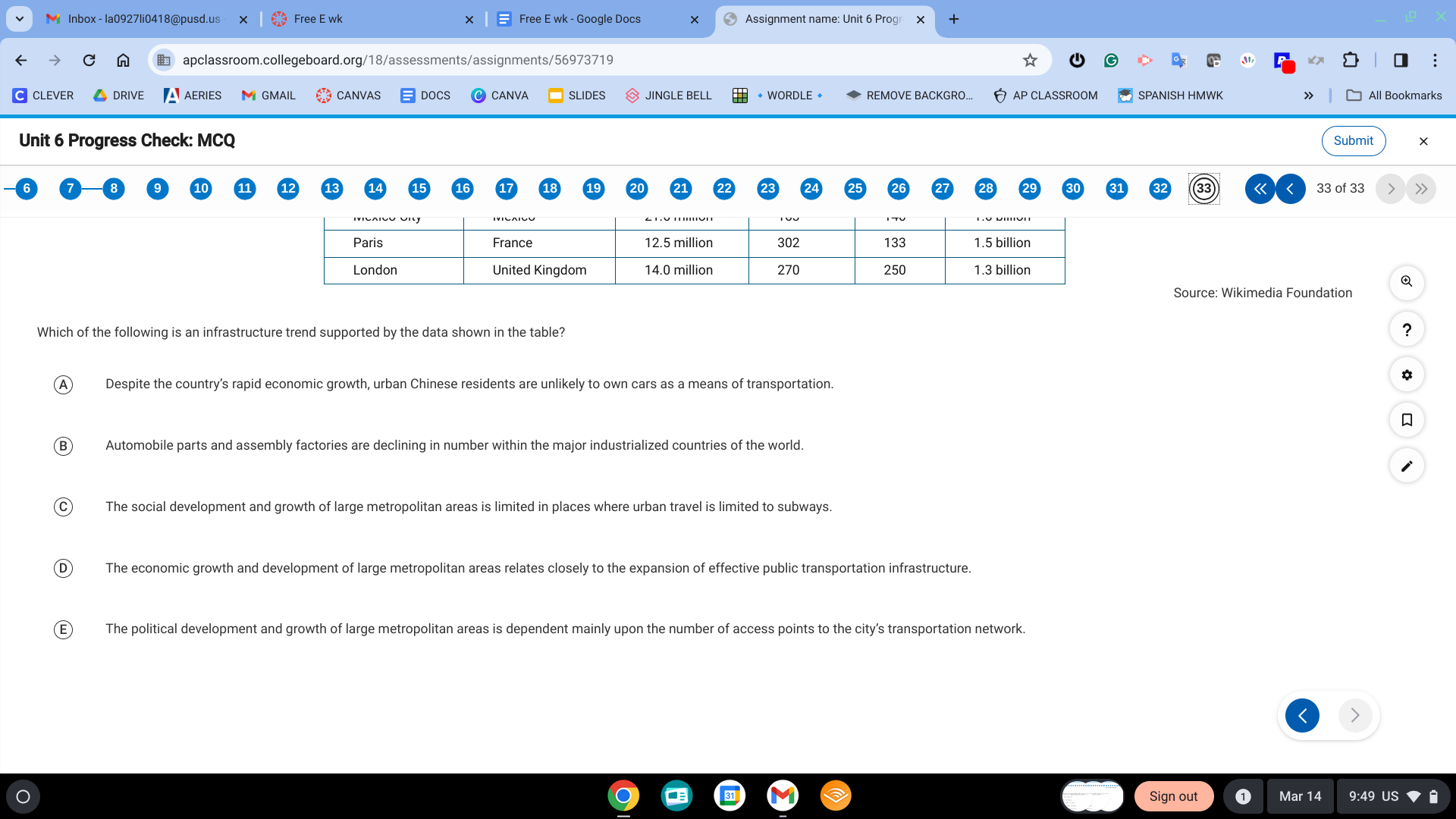
D. The economic growth and development of large metropolitan areas relates closely to the expansion of effective public transportation infrastructure.