Cofactors, coenzymes and prosthetic groups
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/6
Last updated 10:52 PM on 12/18/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
1
New cards
What are cofactors?
Inorganic enzyme helpers
* Transfer atoms or groups from one reaction to another
Or
* Form part of the active site
* Transfer atoms or groups from one reaction to another
Or
* Form part of the active site
2
New cards
Where are cofactors obtained?
* Via diet as minerals (Fe, Ca, Cl, Zn ions)
* Eg - amylase has a Cl ion for a correct AS
* Eg - amylase has a Cl ion for a correct AS
3
New cards
What are coenzymes?
Organic cofactors
* A non-protein organic molecule, not permanently attached to an enzyme, but needed to allow the enzyme to function.
* A non-protein organic molecule, not permanently attached to an enzyme, but needed to allow the enzyme to function.
4
New cards
Where are coenzymes derived from?
Vitamins
* Eg - vitamin B3 synthesises NAD, coenzyme responsible for transferring H atoms between respiration molecules
* NADP is derived from B3 and has a similar role in photosynthesis
* Eg - vitamin B3 synthesises NAD, coenzyme responsible for transferring H atoms between respiration molecules
* NADP is derived from B3 and has a similar role in photosynthesis
5
New cards
What is a prosthetic group?
* A cofactor that forms a permanent part of a functioning protein molecule
* Eg - Zn ions form a part of carbonic anhydrase (metabolism of CO2)
* Eg - Zn ions form a part of carbonic anhydrase (metabolism of CO2)
6
New cards
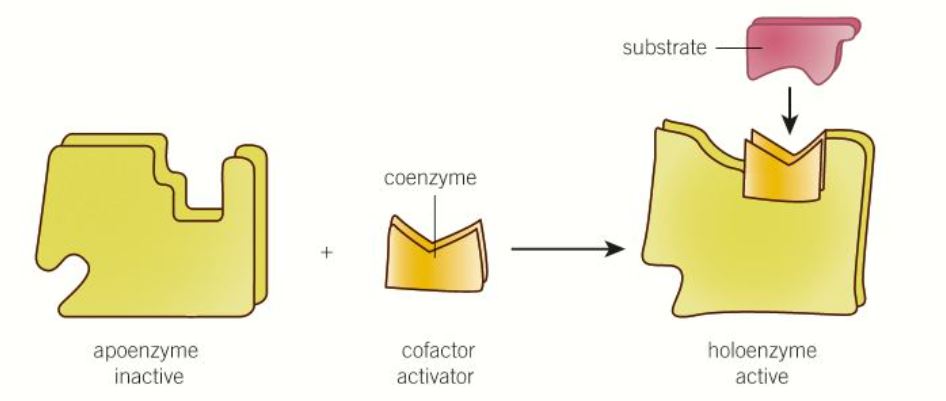
What is precursor activation?
* Where an enzyme must be activated to begin its function
* Need to have its 3• changed by adding a cofactor
* Before it's added the precursor is apoenzyme
* After it's added it is a holoenzyme
* Need to have its 3• changed by adding a cofactor
* Before it's added the precursor is apoenzyme
* After it's added it is a holoenzyme
7
New cards
How can the tertiary structure of an enzyme be changed for precursors?
* An enzyme split bonds in the molecule
* Changes in temp and pH (zymogens or proenzymes)
* Changes in temp and pH (zymogens or proenzymes)