3.6 - Immunology IV and cancer cells
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
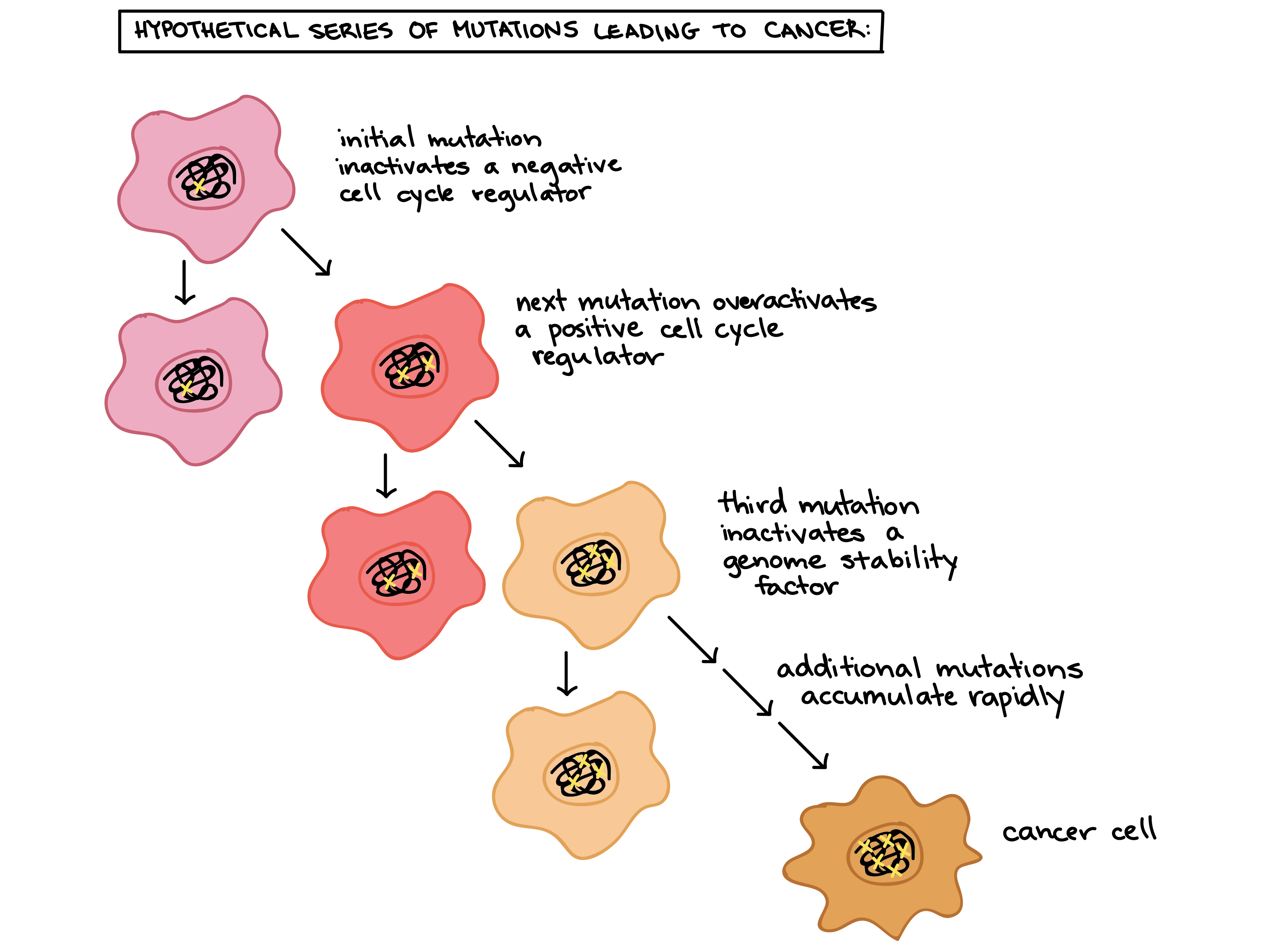

What have cells experienced to become cancerous?
(accumulation of) mutations
When mutations of cancerous cells impact the genes that regulate cell division, what can the response be?
unchecked cellular division
unchecked cellular division is a ______
tumor
What’s an outcome of cancer involving proteins?
synthesizes mutated proteins (immune system recognizes as antigens)
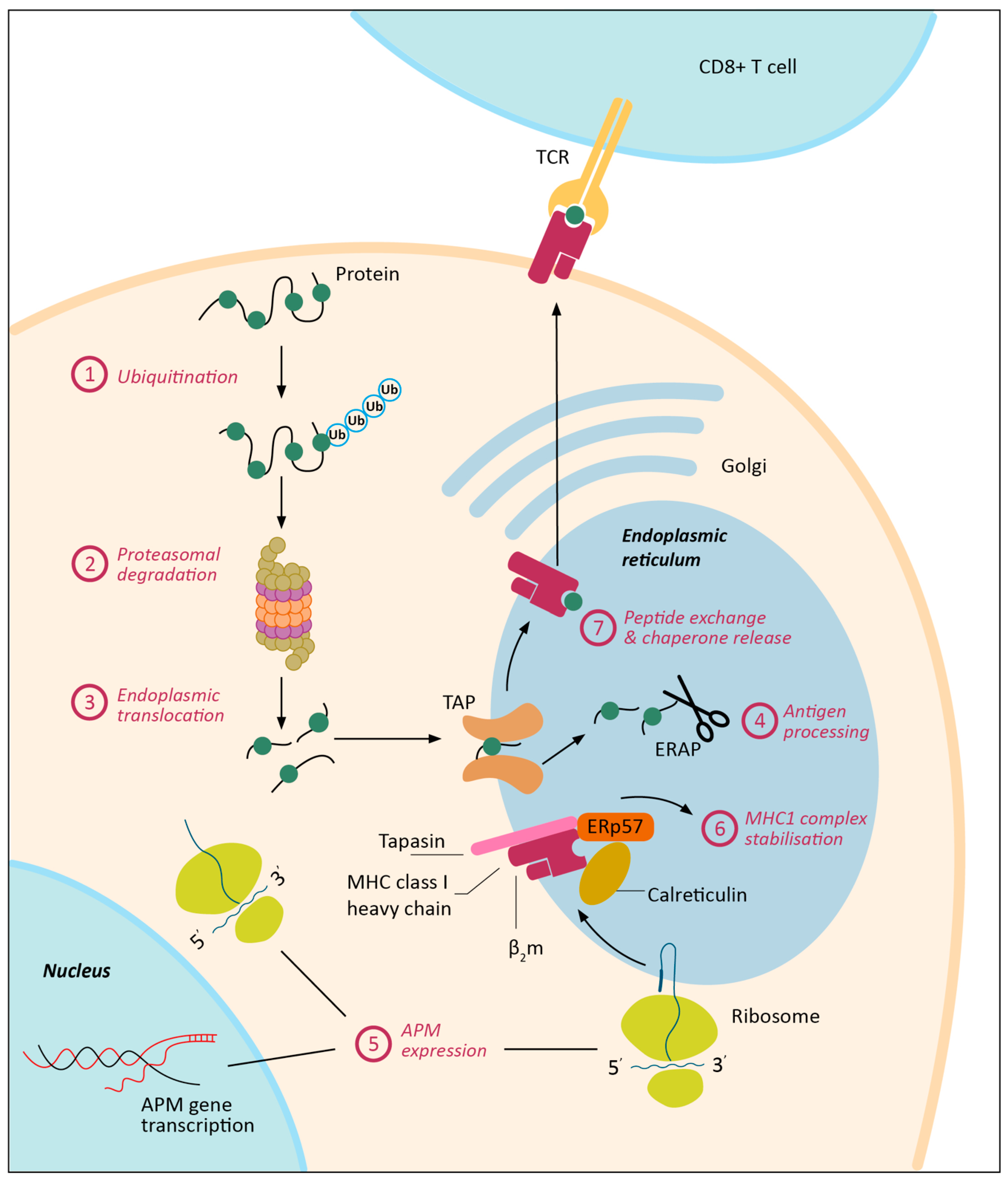
How are the proteins displayed in cancerous cells?
as antigens displayed in MHC I
What else can cancerous cells do regarding genes?
turn on genes that shouldn’t be on
Ex. of a gene that gets turned on/expressed by cancer cells?
fetal proteins
What does the immune system see fetal proteins as?
antigenic (will trigger immune response)
What can identify cancer antigens (proteins) in MHC I?
cytotoxic t-cells
What type of cell are Natural Killer Cells?
lymphocytes
Where are Natural Killer cells stationed?
tissues

What do the NK cells patrol for?
abnormal behaviors on surface of cells
What are 2 abnormal behaviors on the surface of cells?
lack of MHC I, weird surface patterns
Since all cells with a nucleus SHOULD have MHC I, the lack of MHC I would cause the NK cell to think …
what are you hiding? (suspicious, they know it’s a cancer cell)
Do NK cells require TH permission to kill cells?
no (act autonomously)
What are residual B-cells (regarding immunity)? (2)
(long-lived) plasma cells and memory B cells
Define Immunity
after exposure, residual B and TH cells (sometimes TC army if applicable) provide immunity, resulting in mild-no symptoms upon re-exposure
For primary exposure of a virus, there will be a delay in _____ production.
antibody
Once secondary exposure occurs, the antigens will be ready, causing them to _____ in numbers quickly, destorying the virus before you even feel it.
increase
Immunity is ______-specific
antigen
Do memory cells last forever?
no (they die off)
more antigens correlates to?
more memory cells
so _____ allows the secondary exposure to produce more antibodies getting rid of the virus much faster.
immunity
What’s the goal of vaccination/immunization?
generate memory cell production from antigen exposure without the full disease
What’s in a “Whole Cell/Virus” vaccine? (2)
contains entire pathogen, but it’s dead (gets injected into person)
What’s a pro of the whole cell/virus vaccine?
easy
What’s a con of the whole cell/virus vaccine? (2)
fixed antigen levels (because pathogen is dead), so less memory cells produced
What type of immunity would be used from the whole cell/virus vaccine?
humoral
What does the Subunit Vaccine contain?
antigenic components of pathogen (only spikes/proteins)
What’s the pro of a subunit vaccine? (2)
has more antigens of various pathogens, so stimulates more memory cells
What’s a con of subunit vaccines?
antigen levels are fixed
What type of immunity does the Subunit Vaccine trigger?
humoral
What’s within the Live, attenuated vaccines?
weakened strains of viruses
So does the live, attenuated vaccine have pathogens that are still alive?
yes (but modified to be weak to not actually get you sick)
Example of a vaccine that uses Live, attenuated?
Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR) vaccine
What are some pros of the live, attenuated vaccine?
replication occurs providing more antigens, so more memory cells
What type of immunity occurs with Live, attenuated vaccines? (2)
humoral and cell-mediated
What’s a con of the live, attenuated vaccine?
risk factor for immunocompromised (since they’re alive, you could get sick)
How is the mRNA vaccine created? (COVID specif.)
took a mRNA strand that only coded for the covid spike (antigen)
So, the mRNA that codes for the covid spike get injected into your cells and causes the mRNA to make the virus within. BUT, it only could create ____ ____.
covid spikes
What did the spikes end up being displayed as?
MHC-I
What type of immunity does the mRNA vaccine allow for? (2)
humoral and cell-mediated
What’s a pro of the mRNA vaccine? (2)
your own cells produce the antigens (higher antigen = more memory cells); no risk of actual infection (b/c not actually getting a pathogen into your body)
What’s the most common type of vaccine?
Subunit vaccine
What’s a booster shot do?
An additional vaccine dose to restore immunity by maintaining antibody levels and memory cells