Corneal Dystrophies
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
What are corneal dystrophies?
group of slow progressive bilateral corneal opacification conditions
What is true of ALL corneal dystrophies?
they are non-inflammatory therefore they do not have redness (all have white eyes)
Where do corneal dystrophies affect?
start out in the center of the cornea and migrate to the periphery
What are the epithelial-subepithelial corneal dystrophies?*
Epithelial Basement Membrane Dystrophy (EBMD)
Meesman epithelial dystrophy
What are the epithelial-stromal corneal dystrophies?*
Reis-Buckler and Theil-Behnke
Lattice Dystrophy
Granular Dystrophy
What are the stromal corneal dystrophies?*
macular dystrophy
Schnyder (Crystalline) dystrophy
What are the endothelial corneal dystrophies?
Fuch's Corneal dystrophy
Posterior Polymorphous dystrophy (PPMD)
What is the most common corneal dystrophy?
EBMD, Epithelial Basement Membrane Dystrophy (also known as map-dot-fingerprint or Cogan)
What is the onset for EBMD?
20s
What is the epidemiology for EBMD?
females
no clear inheritance pattern *Unique
What is the pathophysiology of EBMD?
production of abnormal basement membrane resulting in faulty adhesions + elevated epithelial tissue
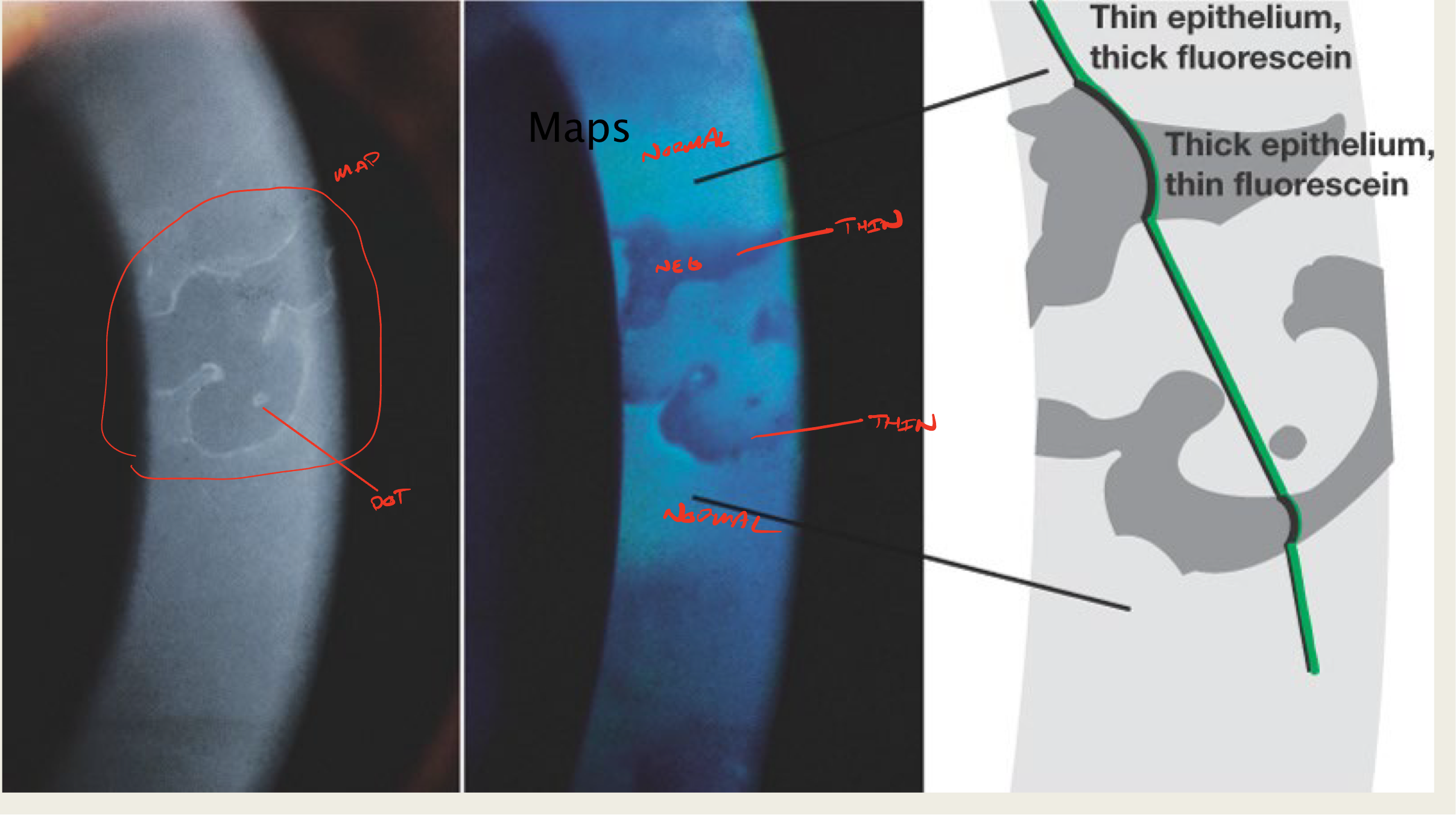
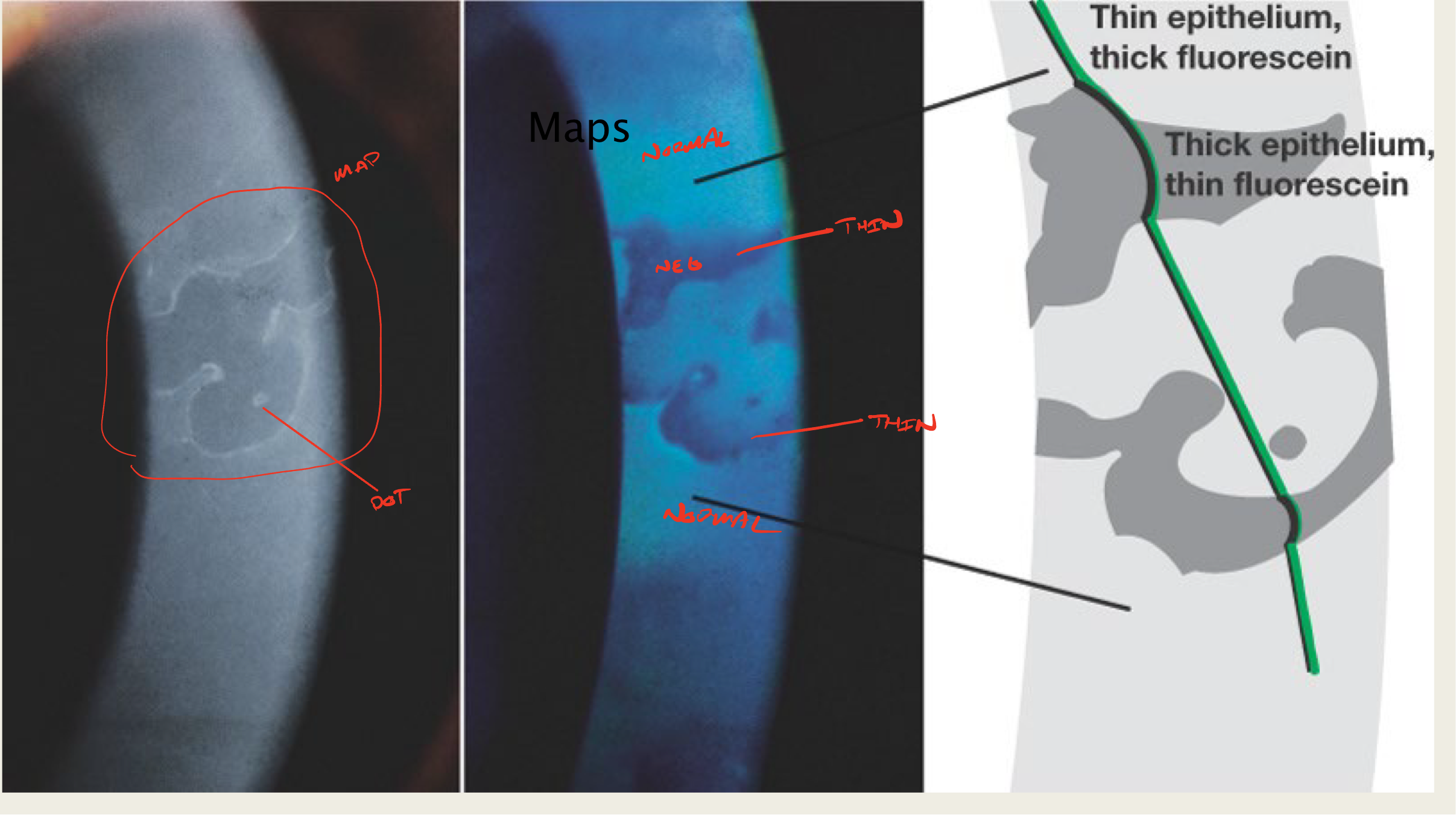
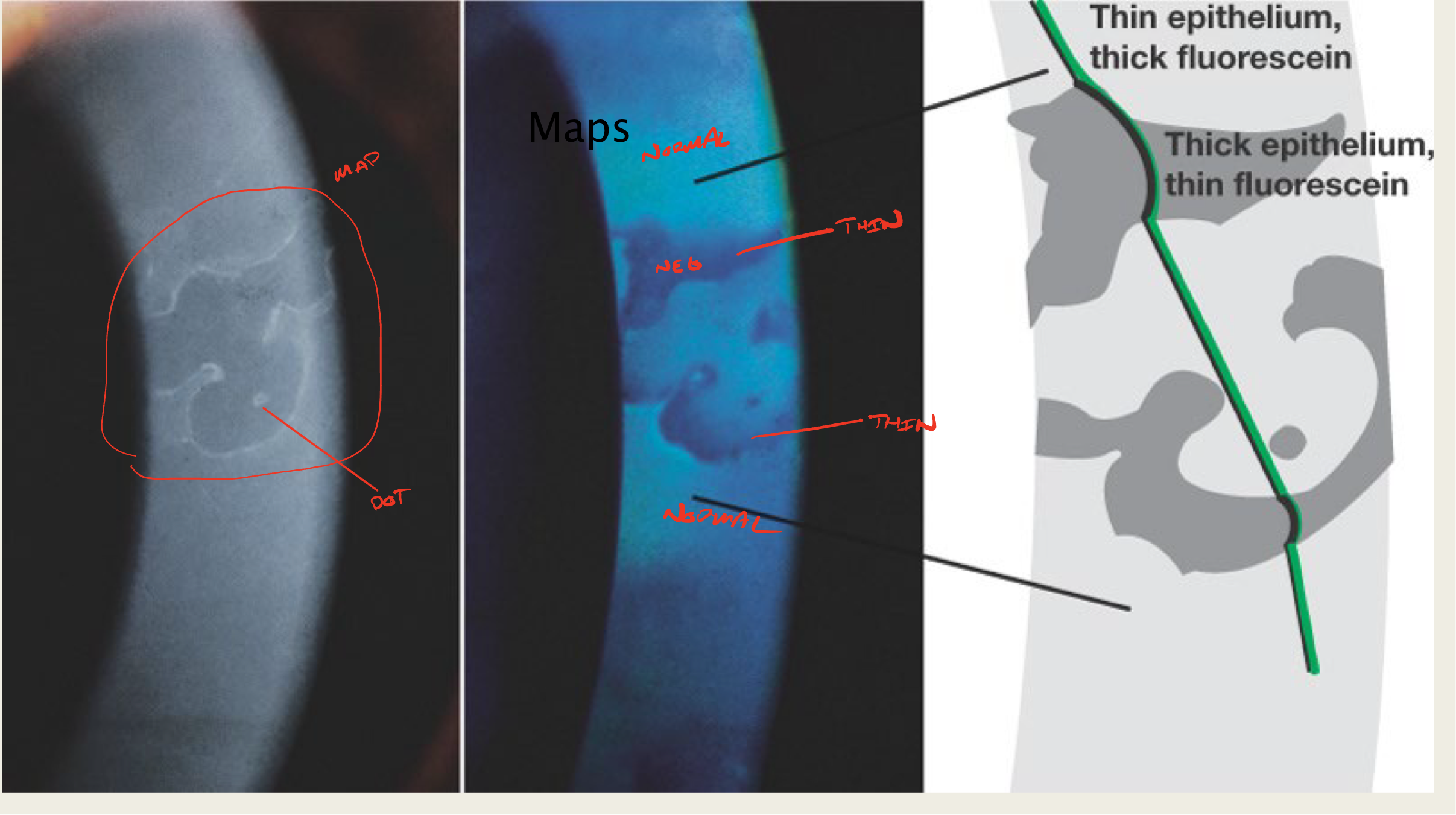
What is creating the "map" sign in EBMD?
elevated epithelial tissue
negative staining
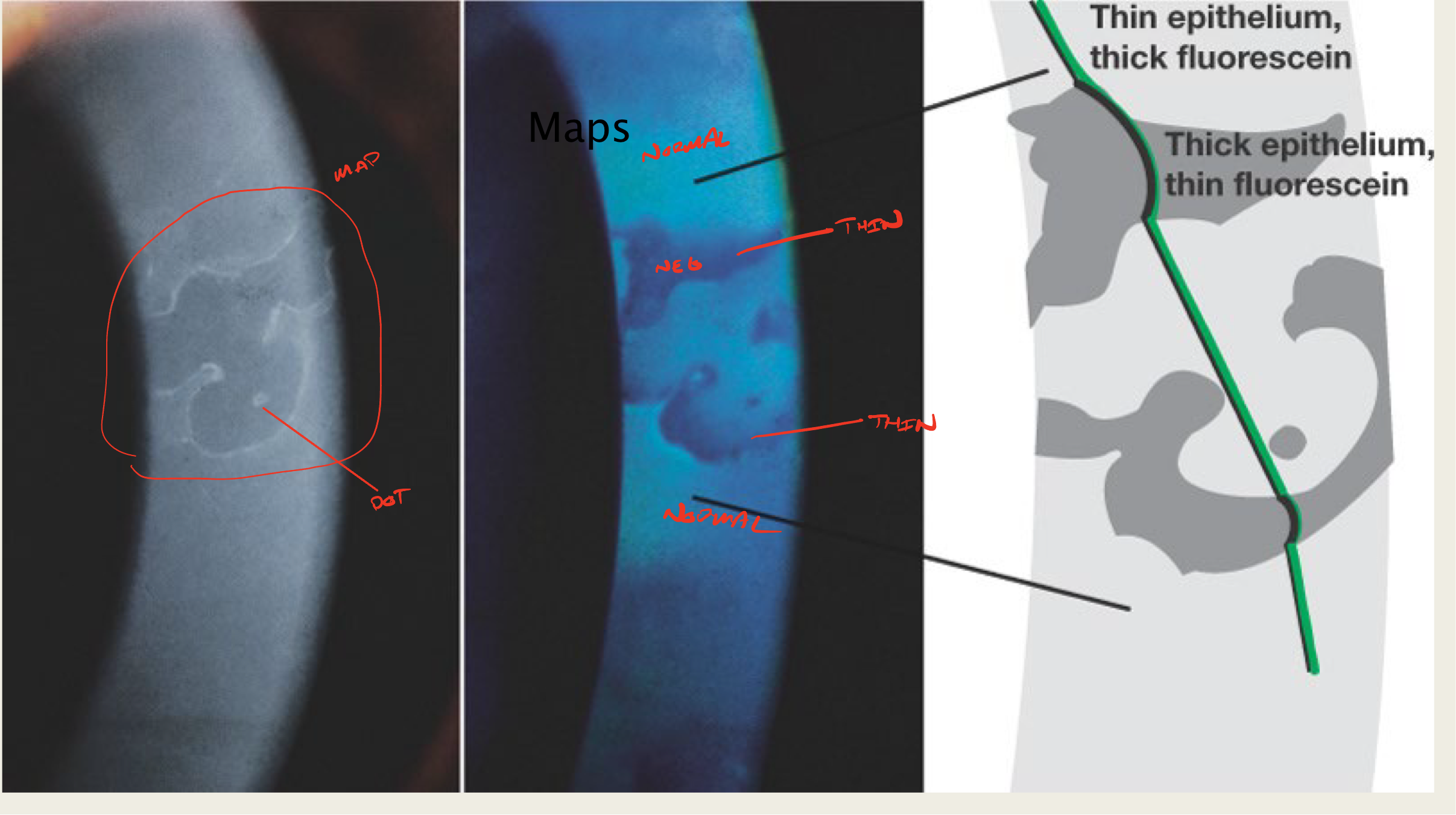
What is creating the "dot" sign in EBMD?
trapped cellular material within
Which presentation of EBMD is seen in isolation?
Fingerprint

What is creating the "fingerprint" sign in EBMD?
adjacent rows of thickened + elevated epithelium

What are the symptoms of EBMD?
majority asymptomatic
dry eye symptoms
What is the presentation of EBMD?
maps
dots
fingerprints
negative staining
What do maps look like?
large geographic lesion
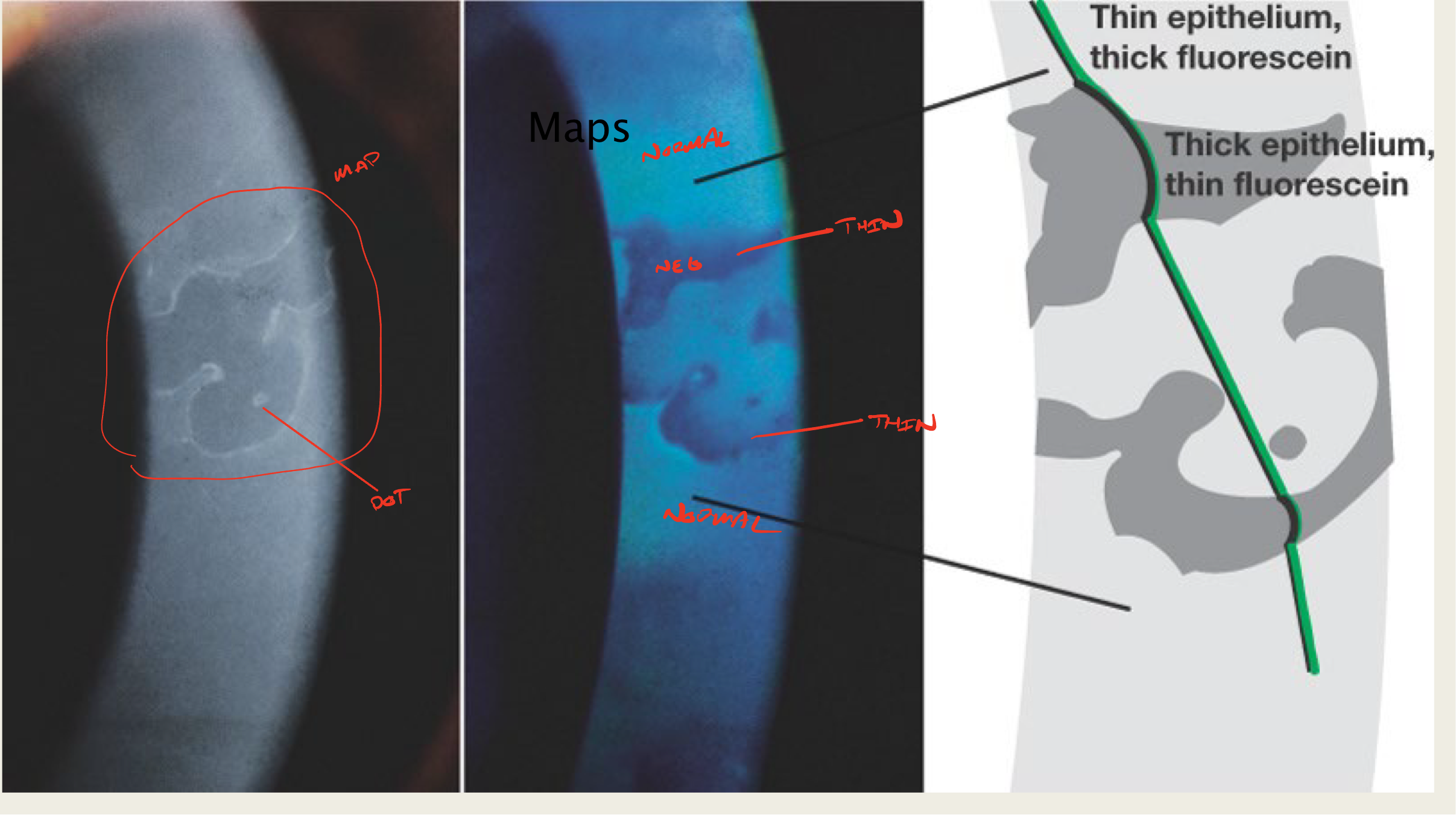
What do "dots" in EBMD look like?
little translucent dots
commonly seen with maps
What do "fingerprints" in EBMD look like?
wave lines

When are maps, dots, and fingerprints in EBMD seen?
map + dots are seen together
fingerprints are isolated
What are the complications of EBMD?
Recurrent corneal erosions (RCE)
When do RCEs appear in EBMD?
30s
What are the symptoms of an RCE?
severe pain, especially upon waking
Etiology of Recurrent Corneal Erosion
Hemidesmosomes unable to anchor epithelium to anterior stroma
What is the presentation of an RCE?
epithelial defect that stains with fluorescein
Where are the RCEs located with EBMD?
inferior 1/3 of cornea (resting eyelid)
What is the treatment for asymptomatic patients with EBMD?
nothing (maybe AFT)
Treatment for EBMD patients with Dry Eye
Prophylactic AFT
What is the treatment for mild cases/RCE prevention of EBMD?
hypertonic salt solution
oral tetra/doxycyclines
topical steroids
What is the number one treatment for RCE?
hypertonic salt solution
What is the treatment for moderate to severe EBMD WITH an active RCE(RCE treatment)?
debridement with Q tip
stromal puncture
(optional for card)
bandage CL
phototherapeutic keratectomy

What is the treatment for moderate to severe EBMD with or without active RCE (RCE treatment)?
bandage CL
phototherapeutic keratectomy
What is the inheritance pattern for Messmann epithelial dystrophy?
Autosomal Dominant
(mutation in gene responsible for producing epithelial keratin)
What is the onset of Messmann epithelial dystrophy??
first year of life
Epithelial-subepithelial dystrophy whose onset is first year of life?
Meesmann epithelial dystrophy
What are the symptoms of Meesmann epithelial dystrophy after 1st decade?
blurred vision (d/t corneal opacification)
What is the cause of symptoms of Meesmann epithelial dystrophy that occur in life?
Intraepithelial cysts and vesicles (opacify and burst)
What are the symptoms of Meesmann epithelial dystrophy that occur later in life?
glare, light sensitivity, discomfort
What causes glare and light sensitivity in Meesmann epithelial dystrophy
Cysts that opacify
What is the presentation of Messmann epithelial dystrophy??
intraepithelial cysts
Intraepithealial cysts
cysts start clear and become opaque with age
there is a clear space surrounding the cysts
What is Messmann epithelial dystrophy also called?
juvenile hereditary epithelial dystrophy
What are unique characteristics of the presentation of Messmann epithelial dystrophy??
cysts are smaller than EBMD dots
there is a clear space surrounding the cysts
Where is the location of the cysts seen with Messmann epithelial dystrophy??
concentrated central + interpalpebral, but extend toward limbus
What is the complication of Messmann epithelial dystrophy?
RCE
What is the treatment for asymptomatic Messmann epithelial dystrophy??
nothing
What is the treatment for mild/moderate Messmann epithelial dystrophy?
lubrication if cysts rupture
RCE treatment
What are the treatments for recurrent corneal erosions (RCEs)?
hypertonic salt solution
bandage CL
debridement
stromal puncture
phototherapeutic keratectomy
What is the treatment for severe Messmann epithelial dystrophy?
lamellar keratoplasty
What two dystrophies are variants of eachother?
Reis-Buckler and Theil-Benhke
Where does Reis-Buckler and Theil-Benhke affect?
bilateral
epithelial-stromal
What is the inheritance pattern of Reis-Buckler and Theil-Benhke?
Autosomal Dominant
What is the onset of Reis-Buckler and Theil-Benhke??
first decade
What are the symptoms of Reis-Buckler and Theil-Benhke?
visual complaints: blurred vision, photophobia, diplopia
foreign body sensation and pain
What problem does Reis-Bückler cause?
bowmans layer is replaced by connective tissue
What is the presentation of Reis-Bückler?
grey-white rod-like subepithelial opacities that are more dense central
irregular astigmatism
cornea gets increasingly hazy with age
What is unique about Reis-Bückler??
corneal sensitivity will be reduced
increased central corneal thickness
irregular astigmatism
Between Reis-Bückler and Theil-Benhke, which is more severe?
Reis-Bückler
What is the presentation of Theil-Benhke?
curly opacities in central cornea
opacities for a ring or honeycomb pattern
What is the difference in presentation of opacities in Reis-Bückler and Theil-Benhke?
Reis-Bückler: rod like opacities
Thiel-Benhke: curly opacities, in ring/honeycomb pattern, opacities are less defined than in Reis-Bückler
What is unique about Thiel-Behnke?
will not have corneal irregularities (irregular astigmatism), thickened cornea, or decreased corneal sensation
What are the complications of Reis-Bückler and Theil-Benhke?
RCEs in early childhood
Corneal opacifications (Reis-Bückler worse)
What is unique about the complications of Reis-Bückler and Theil-Benhke??
The RCEs will be present in early childhood
What is the treatment for mild/moderate Reis-Bückler and Theil-Benhke??
Observation
RCE treatment
What is the treatment for severe Reis-Bückler and Theil-Benhke??
Lamellar Keratoplasty if severe corneal involvement (reduced VA)
What is the most common epithelial-stromal dystrophies?
lattice dystrophy
What is the inheritance pattern of lattice dystrophy ?
AD
What systemic condition has signs of lattice dystrophy?
Systemic amyloidosis
What is the pathophysiology of lattice dystrophy?
amyloid deposits accumulated between epithelial basement membrane + bowmans + ant stroma
What are the symptoms of lattice dystrophy?
blurred vision
pain
What is the presentation of lattice dystrophy?
amyloid deposits in anterior stroma
refractive dots and crossing lines
opacification of stroma
reduced corneal sensitivity
Where is lattice dystrophy found?
anterior central cornea
What are the complications of lattice dystrophy?
RCE
blurred vision due to cornea haze
What is the treatment for mild/moderate lattice dystrophy?
observation
RCE treatment
What is the treatment for severe lattice dystrophy?
lamellar keratoplasty
What is the inheritance pattern of granular dystrophy?
AD
When is the onset of granular dystrophy 1?
first decade
When is the onset of granular dystrophy 2?
second decade
What are the two types of granular dystrophy?
granular 1
granular 2
What is granular dystrophy?
hyaline deposition
What are the symptoms of granular dystrophy 1?
asymptomatic early on
blurred vision, photophobia, glare
pain
What is the presentation of granular dystrophy 1?
First:
small, well defined opacities in anterior stroma
clear space between opacities
reduced corneal sensitivity
As disease progressesL
opacities extend posterior
opacities confluence, decreasing clear space between deposits
What are the complications of granular dystrophy?
RCE
What is the treatment for mild-moderate granular dystrophy 1?
Observation
RCE treatment
What is the treatment for severe granular dystrophy 1??
lamellar keratoplasty
phototherapeutic keratectomy
What is unique about the treatment for granular dystrophy 1?
reoccurrence can occur in the graft
What is granular dystrophy 2?
combination of granular dystrophy 1 and lattice dystrophy
What are the symptoms of granular dystrophy 2?
blurred vision
pain
What is the presentation of granular dystrophy 2??
grey-whtite thorn, ring, or stellate opacities in anterior stroma
white lines that dont cross in posterior stroma
What is the treatment of granular dystrophy 2??
observation
RCE treatment
What is the only AR dystrophy?
macular dystrophy
What is the onset of macular dystrophy?
first decade
What is the inheritance pattern of macular dystrophy?
AR
What are the symptoms of macular dystrophy?
blurred vision, significant in 2nd/3rd decade
pain
What is the presentation of macular dystrophy?
ill-defined grey-white deposits that start central and migrate to the limbus
entire cornea appears cloudy
eventual corneal thinning
decreased corneal sensitivity
cornea edema later on'
What is unique about the presentation of macular dystrophy?
has more limbal involvement than any other dystrophy
entire cornea will be cloudy
corneal thinning
Where are the deposits located in macular dystrophy?
anterior and posterior stroma
What are the deposits made up of in macular dystrophy?
mucopolysaccharides