Animal Nutrition Exam 1 - Protein Nutrition
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
Proteins
What is the most abundant biological macromolecule?
Protein
_____ are the most abundant biological macromolecules. Present in all cells and all parts of cells.
Great variety, ranging in size and biological diversity
Name is derived from the Greek language, “proto” meaning FIRST
expensive
Protein is often the most ____ dietary ingredient → therefore it is socially and economically important
Amino Acids
______ = The “Building Blocks” of Protein
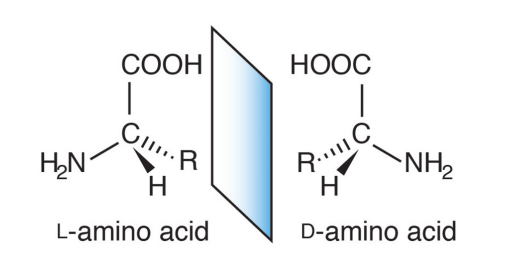
Stereoisomers
Amino Acid Structure
______ (Isomeric Molecules)
Groups of isomers in which the atoms are linked in the same order but differ in spatial arrangement.
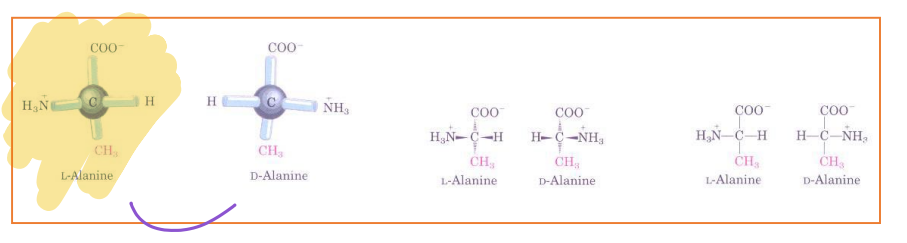
L-Form
Enantiomers are Mirror Images. When we synthesize proteins you get L and D forms of Amino Acids, which one is present/use in biological proteins?
L-Amino Acids
L vs D Amino Acids
______
Most abundant form of amino acids and is found in all proteins in plants and animals
D-Amino Acids
L vs D Amino Acids
______
Amino Acids that are not commonly seen in animal or plant protein.
May come from microbial population → are of microbial origin (produced during microbial protein synthesis in the GIT)
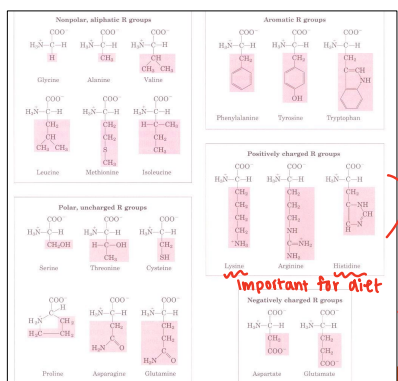
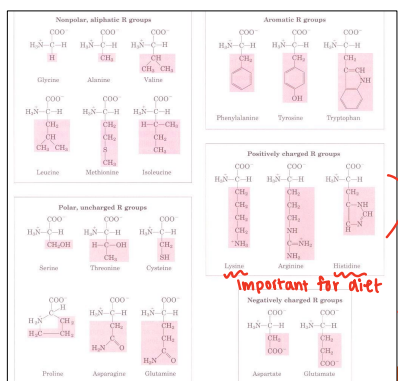
Hydrophobic
Chemical Characteristics of Amino Acids
_____
Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups
Aromatic R groups
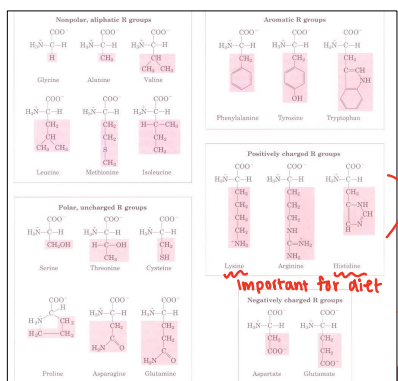
Hyrdrophilic
Chemical Characteristics of Amino Acids
_____
Polar, uncharged R groups
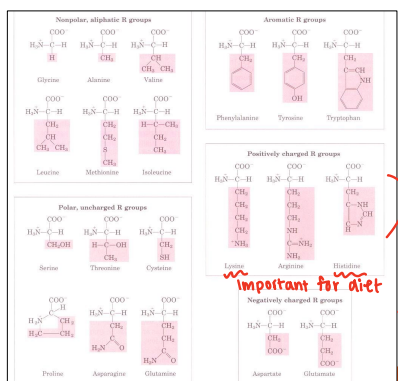
Very Hydrophilic
Chemical Characteristics of Amino Acids
______
Positively & Negatively charged R groups
Chemical Characteristics
Amino acids with similar ______ are more inclined to compete for similar sites of absorption within the small intestine
Absorption
If you feed similar amino acids in excess they will compete for _____
Biologically
_______ Essential Amino Acids
Amino Acids that are required for specific biological pathways to function within the body
Essential Amino Acids
Biologically Essential Amino Acids Include:
_______
Amino Acids that are produced in an inadequate supply in the body. Therefore, they must be supplemented in the diet.
Nonessential Amino Acids
Biologically Essential Amino Acids Include:
________
Amino acids that are produced in adequate amounts by the body.
Do not need to consume them
Quality
Protein ____
Determined by a combination of both AA sequence and AA digestibility
Type of amino acids present in protein
Nutritionally Essential
Biologically Essential Amino Acids → all have biological functions in the body: some of them are ________ because the does not produce enough to meet the requirements

Protein Synthesis
Limiting Amino Acids
1st Limiting Amino Acids: amino acid that limits ________
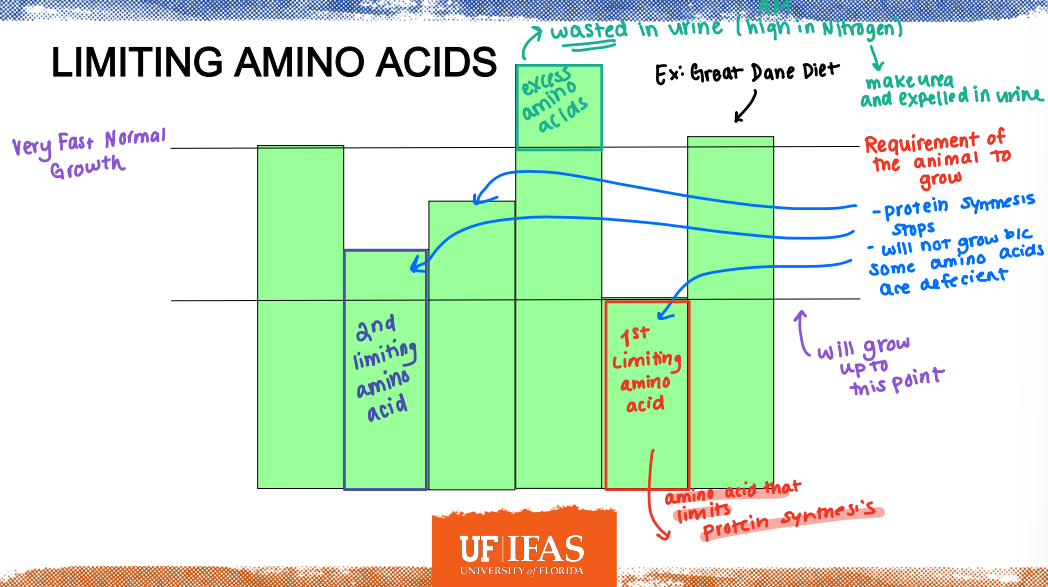
Defecient
Limiting Amino Acids
Protein synthesis stops
Will not grow because some amino acids are ____
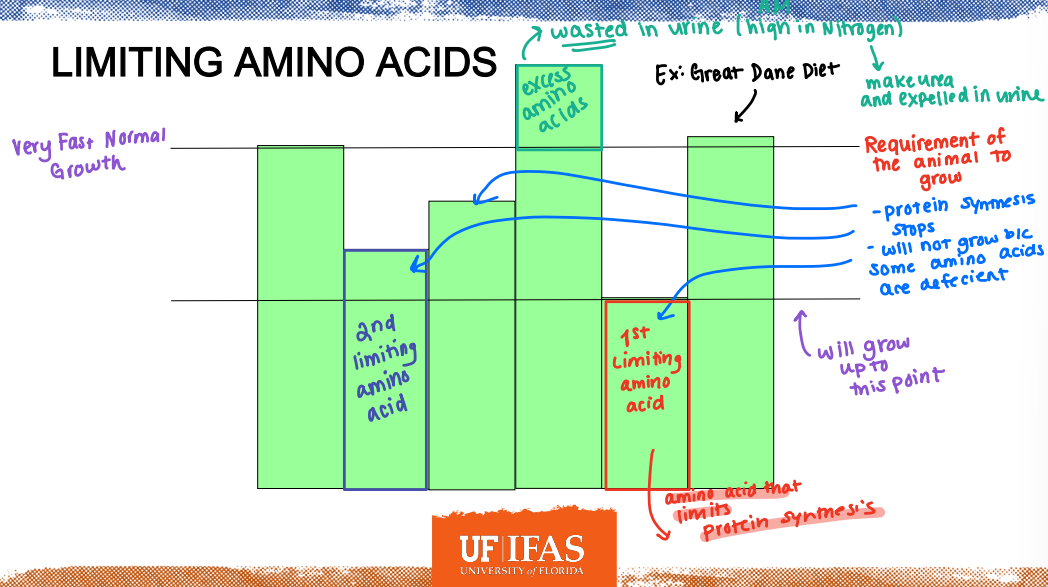
Urine
Limiting Amino Acids
Excess Amino Acids: wasted in _____ (high in Nitrogen)
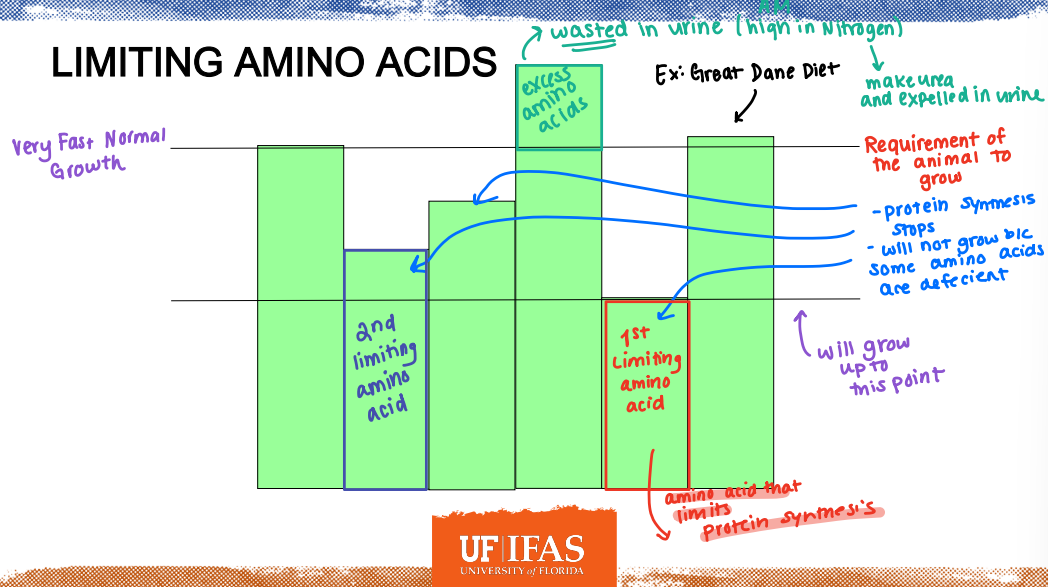
Limiting Amino Acids
______: An amino acid that is first to limit protein synthesis. It varies among species, physiological stage, and dietary conditions.
Amino Acids
Animals have specific requirements for _____, not proteins
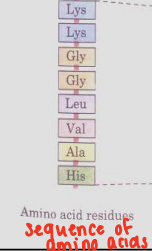
Primary Structure
Protein Structures
Secondary Structure
Protein Structures
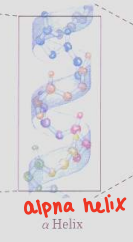
Tertiary Structure
Protein Strcutures

Quaternary Structure
Protein Structures
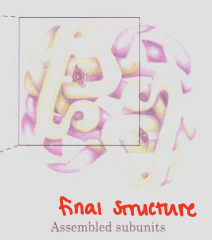
Configuration
Modification of Protein
*Changing the ______of proteins
Denature by heat: ex → egg yolks turning from clear to white
Changing the chemical properties of the protein
Review
Review
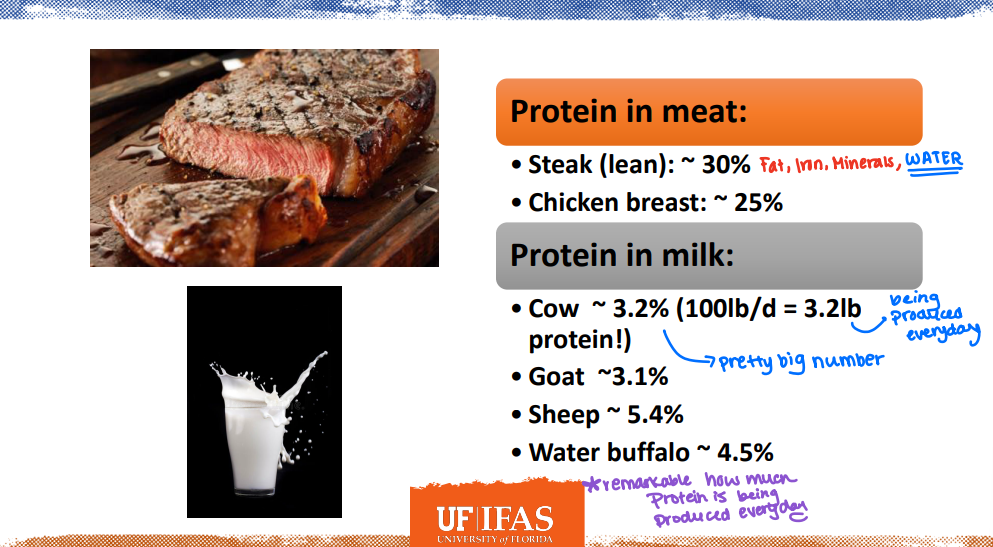
It is remarkable how much protein is being produced everyday
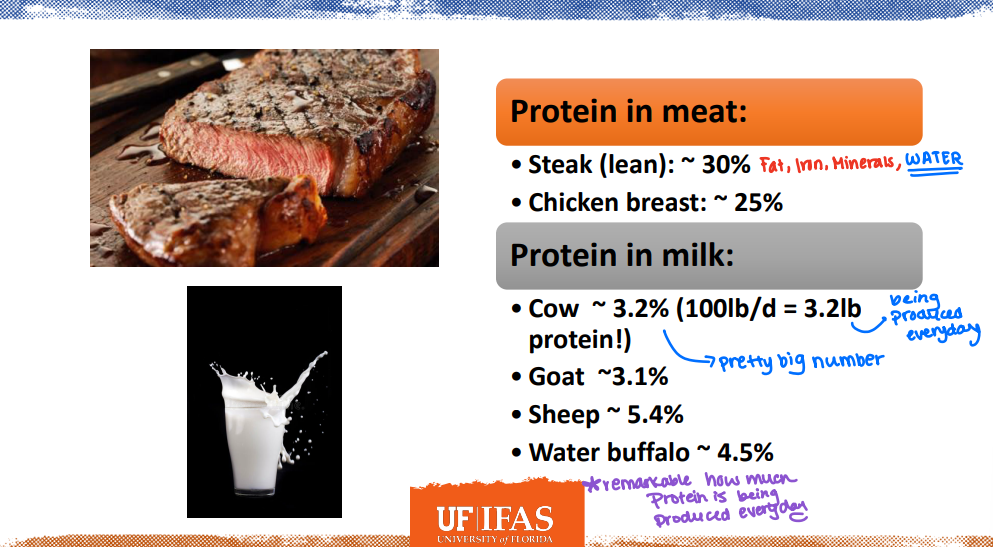
Crude Protein (CP)
_______
A crude way to estimate protein content of a material based on Nitrogen alone.
Nitrogen only comes for protein.
Nitrogen
Crude Protein
An estimation of protein within a sample based on _____ content
6.25
Crude Protein = Nitrogen content x _____
Crude Protein
Most proteins contain 16% nitrogen. Therefore if you multiply the N content by 6.25 you will get the ____ value.

Review
Review


Review
Review
*Tip: If given a specific N content of a specific protein in a sample, you will more than likely be required to calculate the actual conversion factor of said protein

Protein
Crude Protein is not 100% accurate because not all proteins have the same Nitrogen content. In addition to this, there are also components that have Nitrogen but are not ____ (ex. NPN)
Amino Acids → want to know exact amino acid profile and quantity
Different amino acids have different internal concentrations of amino acids
If you wanted a better entity (term) to describe protein content over Crude Protein, what would it be?
Diets
Crude Protein is not 100% accurate
However….
CP is simple to calculate
CP is widely used
Easy to compare _____, even though you really don’t know the amino acid composition
Non Protein Nitrogen (NPN)
_______ is the portion of nitrogen within a sample that does not come from protein
Urea
For milk, urine, and livestock feed ____ is the most abundant component of Non Protein Nitrogen
Urea
_____
Found in fertilizer
Found in urine (main source of the excertion of Nitrogen)
Nitrogen
Dog urine contains urea with too much ____ for the grass → Kills the grass but fertilizes the soil around it (causing grass to grow)
Protein
Nonprotein Nitrogen (NPN)
However, it is important to recognize that other molecules such as free amino acids, peptides, nitrate, amides, creatine and creatinine can be present (ARE NOT ______)
Mitochondria - Urea Cycle
Where in the body do we make urea?
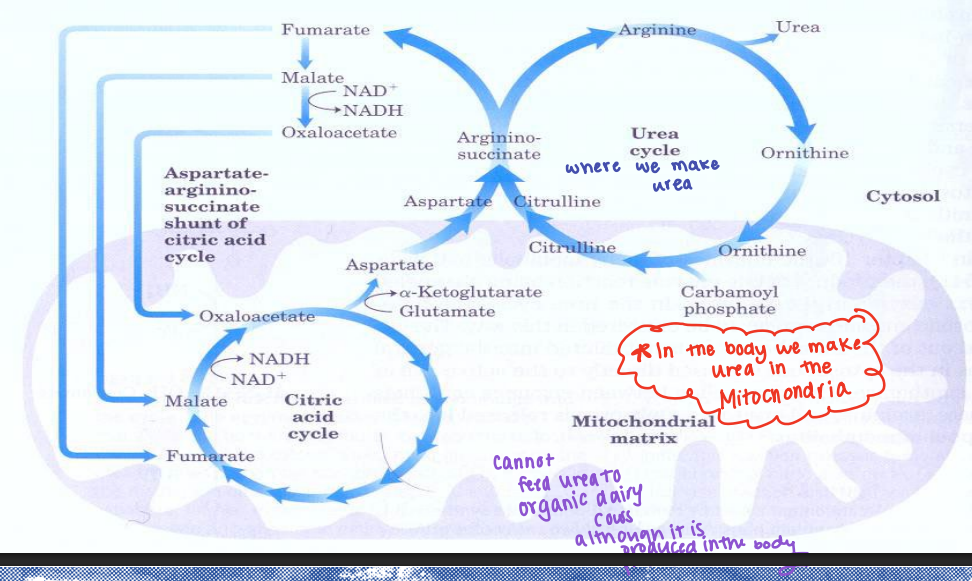
Body
You cannot feed urea to dairy cows although it is produced in the ____
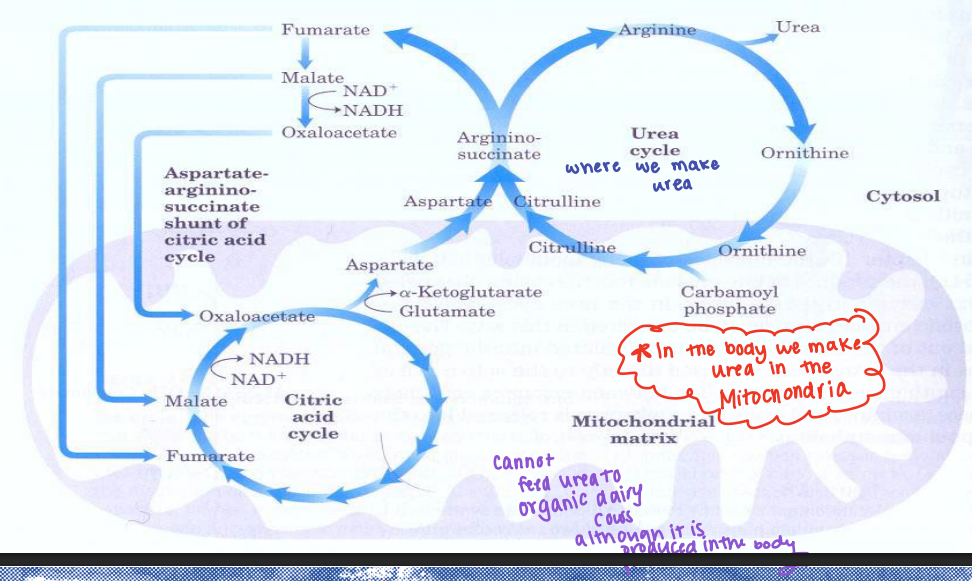
Rumen
Urea Utilization
Urea is degraded in the ____ by microbial urease (enzyme) forming NH3 (ammonia) and CO2 (carbon dioxide)
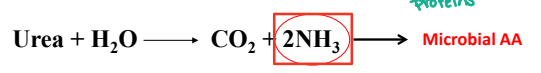
Rumen
Where is urea degraded?
Urease
What microbial enzyme degrades urea forming NH3 and CO2?
Amino Acids
Urea Utilization
Microbial populations within the rumen then utilize NH3 (ammonia) to synthesize microbial _____
NH3
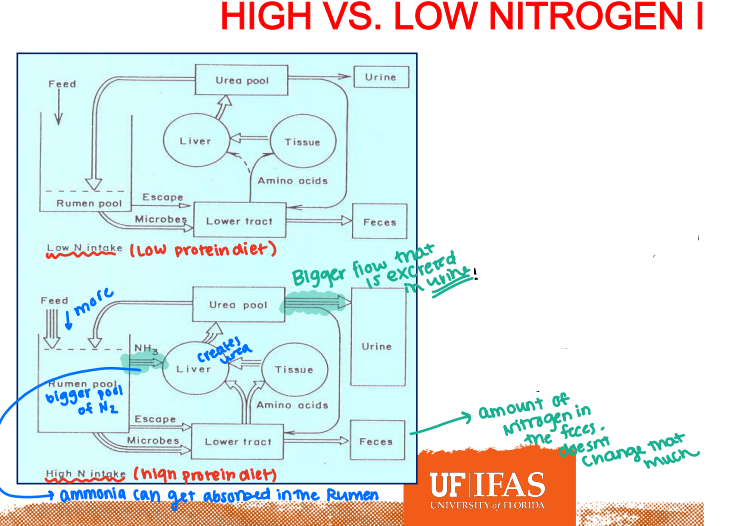
High vs. Low Nitrogen Intake
Within ruminants, increased intake of Nitrogen from the feed with result in an increased concentration of ____ being absorbed through the rumen epithelium
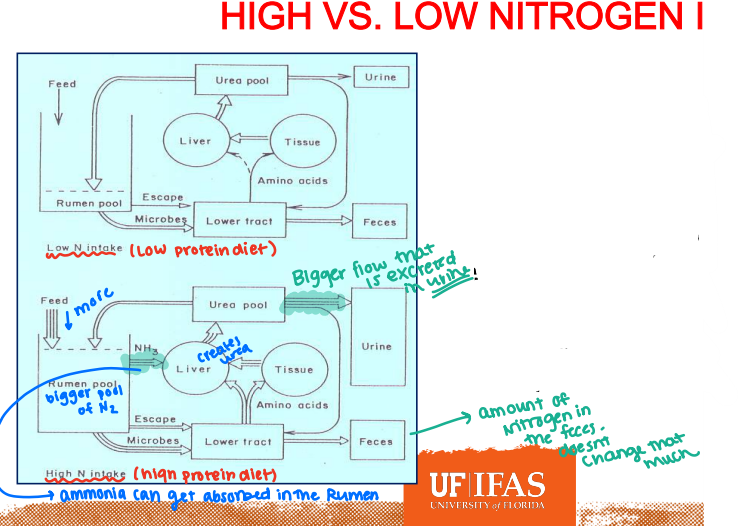
Flow
High vs. Low Nitrogen Intake
As you increase Nitrogen intake, the size of the pools (except the urine) does not change. Instead, the ___ of Nitrogen throughout various organs changes
This is seen in changes in the amount of urine produced and excreted
Ex: the amount of nitrogen in the feces doesn’t change that much
Protein
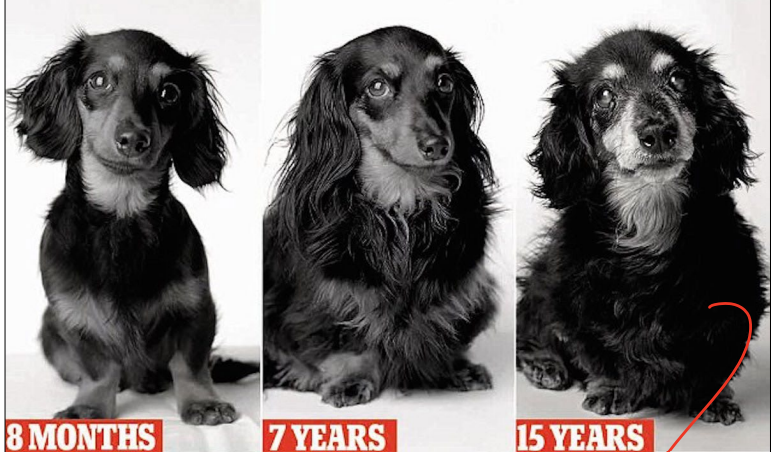
Young animals require more ____ because they are still growing

Urea
Older animals no longer require growth, thus if you overfeed (such as feeding puppy food) protein, the flow of _____increases and puts strain on the liver and kidneys
The liver produces urea
Urea
What organ produces urea?
Ammonia
Urea is a normal component of bodily fluids and is not toxic. However, ____ is, especially in high concentrations
Nonruminants
You should not feed urea to _______
Urea
Microbes can use ____ to make microbial amino acids
Blood pH
Under the circumstances that no organic acids are available, which can be seen in low starch diets NH3 builds up in the blood → This causes an increase in ____ which can result in death if not treated. (need to aclimate animals when feeding urea)
Ammonia (pH = 9)
Consume
You want to make NOT ____ urea if you are not a ruminant
Small Amounts
Urea Toxicity
Horses, pigs, and other monogastrics can tolerate ______ of urea
Crude Protein
Urea Toxicity
Cattle can tolerate up to ~25% of their _____ as urea (~1/2% urea in the total diet), all essential amino acids can be formed in the rumen if sulfur, phosphorus, and iron are present.
Symptoms
Urea Toxicity
_____ of Toxicity
Convulsions, Excess salivation, and death → Means ammonia is already in the blood

Acid Infusion
Urea Toxicity
What to do if toxicity symptoms appear?
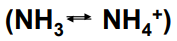
_______ (50% vinegar solution) to prevent ammonia absorption
Acidifies the rumen and converts NH3 to NH4+ → slower absorption through rumen wall trapping NItrogen in Rumen thus slowing the amount of NH3 reaching the bloodstream
Urease
Urea Toxicity
What to do if toxicity symptoms appear?
Cold water also reduces ____ activity → enzyme that breaks down urea into ammonia, reducing ammonia concentration
Protein Digestibility
_________: The amount of protein that can be converted into a form that can be absorbed by an animal
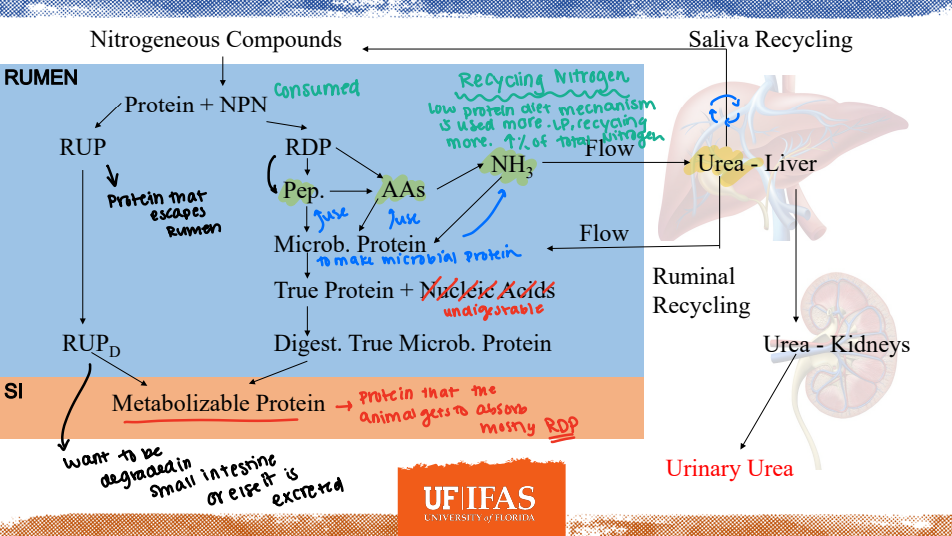
Rumen Undegraded Protein (RUP)
____________: Dietary protein fraction that is not degraded in the rumen. (escape vs. bypass protein)
The more the animal eats the greater this fraction.
Protein from diet not degraded in the rumen, micobes will not have access to it as microbes are in the rumen
Rumen Degraded Protein (RDP)
____________: Dietary fraction that is degraded in the rumen.
We want this unless we are feeding TOP NOTCH proteins → as we want specific amino acids and not microbial amino acids
In Situ
RDP and RUP Measurements
_______
Live animals experiments with cannulated animals. Mobile bag technique → put food in tea bag, put inside animal
In Vitro
RDP and RUP Measurements
______ (in the glass)
Experimental laboratorial approaches

Computer Models
RDP and RUP Measurements
______
Combination of all experimental approaches (combines data from multiple experiments)
In Vivo
RDP and RUP Measurements
______ (live animals) THE BEST***
Live animal experiments with cannulated animals
takes a long time
Very expensive
Labor intensive
Large number of animals
Degraded
In Situ Limitations
Assumes that proteins, peptiles and AA in the soluble fraction are completely _______
Leaving the bag does not inherently mean it was degraded could just be soluble
Physical Restrictions
In Situ Limitations
Reduced access to feed by the microbial populations due to __________ imposed by the use of mobile bags
Contamination
In Situ Limitations
Imprecise quantification of microbial contamination of the undigested residues
Presence of microbes within the bag itself, ____ of sample.
Liquids
____ go faster through the GI tract
Protein Solubility
_________
How well a particular protein mixes with water in the rumen
Protein Degradability
_______
How much of particular protein is broken down in the rumen.
Urea is immediately degraded
Strach is degraded slowly to provide more energy for a longer period of time → it eventually becomes sugar in tthe blood (longer lasting energy slower degradable)
Soybean Meal
What is the most common protein source in the United States?
For HIGH PRODUCING ANIMALS
Slow digestion to stay longer in the GI tract, more opportunities for it to be digested.
TQ: When would you want something to be highly degradable but not highly soluble?
The more soluble, the quicker it passes through the GI tract
Review
Review
Passage Rate
Factors Affecting Protein Digestion
_____
Inversely related to retention time. → goes fast through the GI tract → less digested (not as much time for the enzymes)
With increased Kp overall digestibility will decrease → Retention time is slower if you eat too much : will pass through your body faster
Diet
Factors Affecting Protein Digestion
_____(Forage vs. Grain)
Grains help improve microbes allowing the animal to better digest cellulose
Less
**The more you consume the ___ chance for digestion as it leads to a lower retention time and faster passage rate
Synchronization
Factors Affecting Protein Digestion
Carbohydrate and Nitrogen _______
Necessary to provide microbes with necessary energy source to digest protein
Dry Matter Intake
Factors Affecting Protein Digestion
_______ Intake (DMI)
Increase in DMI leads to a decrease in overall digestibility
Increased consumption → decreased digestibility
Diet Processing
Factors Affecting Protein Digestion
________
Examples:
Maillard Reaction
Tannins
Formaldehyde
Acid Treatment
Rumen Protected Amino Acids
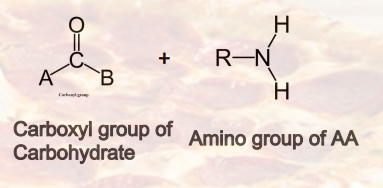
Maillard Reaction
Diet Processing
_________ (Browning Reacting) → Toast, Heat Reaction
Named after French chemist Louis-Camille Maillard, in 1912 while attempting to reproduce biological protein synthesis. The reactive carboxyl group of the carbohydrates reacts with the nucelophilic amino group of AA, and forms a complex mixture of molecules responsible for a range of odors and flavors.
Tannins
Diet Processing
______ (Reduce Digestibility)
Polyohenolic compounds that bind and precipitate proteins and AA.
Hydroxyls and carboxyls groups form strong bonds with proteins and AA
Combined with plants that are usually highly degradable in the rumen → protects protein
Binds with proteins and makes proteins less digestible
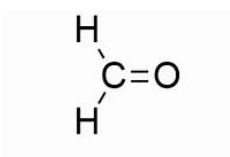
Formaldehyde
Diet Processing
___________ (add in tiny amounts to preserve cells)
preserves tissues or cells by cross linking primary amino groups in proteins with other nearby nitrogen atoms in protein ot DNA through alpha CH2 linkages.
Acid Treatment
Diet Processing
______
Variety of reactions that denature (structural change) protein
Citric acid: common additive to food
Protected Amino Acids
Diet Processing
________
pH, temperature, or physical sensitive
Protection of AA from microbial attacks to ensure the essential Amino Acids are absorbed in the small intestine
Trypsin Inhibitors
Diet Processing
__________(Reduces digestibility)
Decrease the activity of protein hydrolyzing enzymes in the small intestine (trypsin and chymotrypsin)
Decreases protein digestibility
Heat treat will also destroy inhibitors (this is why we feed roasted soybeans to destroy inhibitors)
Commonly found in soybean protein

Trypsin
Enzyme is small intestine that digests protein
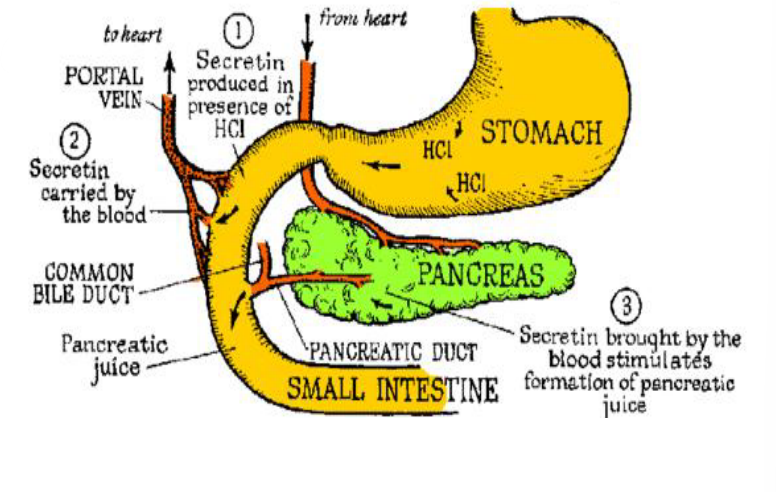
Stomach
Protein Digestion
No chemical digestion takes place in the mouth, it begins in the _______
Pepsin
Protein Digestion (Stomach)
Monogastrics: Hydrochloric acid denatures protein and also converts pepsinogen (produced in walls of the stomach) to _____
Peptides
Protein Digestion
Pepsin breaks the protein down into ____ of various lengths and some amino acids
Trypsinogen
Chymotrypsinogen
Protein Digestion
In response to a drop in pH (due to release of HCl in the stomach), the pancreas makes ______ and ______ (zymogen)
This signals that the protein has arrived within the small intestine
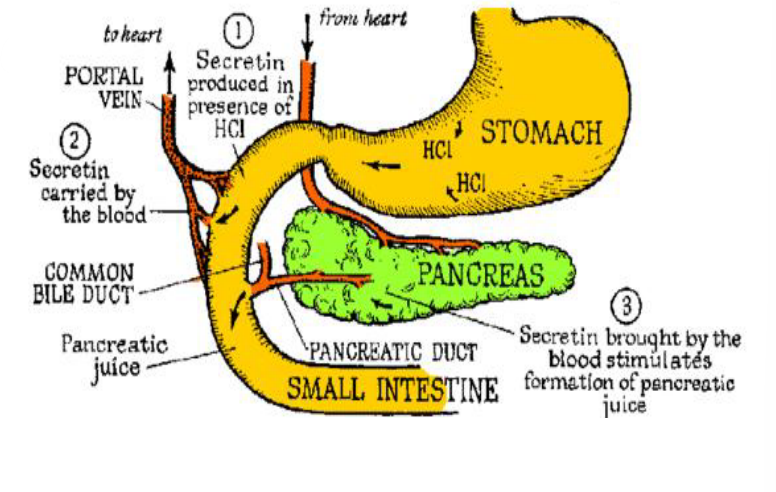
Small Intestine
Protein Digestion
These zymogens will be activiated (by some form of cleavage) and be secreted into the _________ in the for of trypsin and chymotrypsin
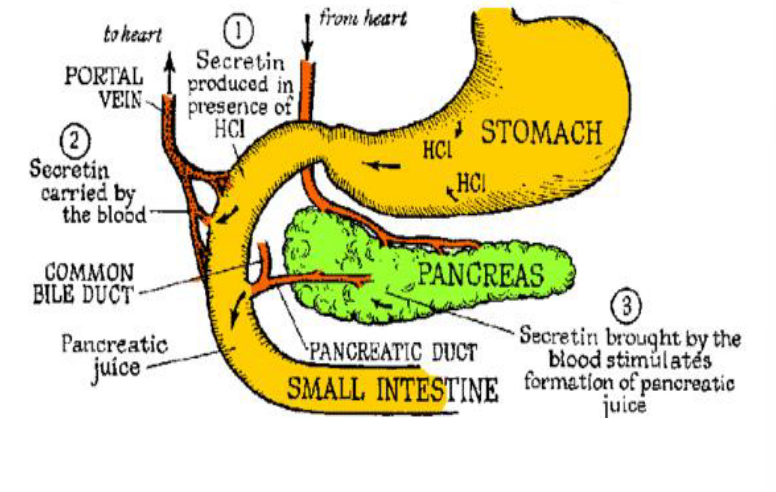
Peptides
Protein Digestion
These proteases break down polypeptides into smaller ______ (very few peptides have to be broken down at this stage)
Small Intestine
What is the main site of digestion and absorption?