Chapter 7: Patterns of movement
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Distribution patterns
➢ Information from hunting records, survey ships, strandings
➢ From passive acoustics, e.g. Tracking of single blue whale 3000km across mid Atlantic
➢ Population characteristics, e.g. Parasite infections, morphological features, genetic markers, coloration,
and diet components (stomach, fatty acids...)
Movement of individuals
➢Branding or discovery markings
➢ID through natural markings:
shows migration patterns site fidelity to feeding / breeding groundschanges in feeding distribution
➢Photo-ID method
➢Genetic tagging: tissue samples / DNA to identify individuals, resampling, sex determination. But sampling is usually invasive and can disturb behaviour/movement of animals!
➢Non-invasive: faeces samples («Tucker» - 400m away) Distinguishing the Impacts of Inadequate Prey and Vessel Traffic on an Endangered Killer Whale (Orcinus orca) Population
➢Telemetry (D-tags, satellite tags, neck collars..) but invasive!
Foraging
➢Areas of high productivity - banks, canyons edge of continental shelf, slopes, transient oceanographic features mesoscale frontal systems or polar fronts
➢Re-sightings of individuals in specific feeding areas ➢Preference for specific prey
e.g. Orcas in Canada: transients and residents groups
Size, gender and reproduction
➢Harbour seals - foraging range positively correlates with body size - greater in males than females
➢Migration differences between males and females: Sperm whales, Belugas and Elephant seal ➢Female otariids nurse pups several months & are restricted to breeding grounds
(but may travel 900km to feed)
Tidal/diurnal factors
➢Some dolphins swim with dial cycle from open water to coastal areas due to prey movement
➢Often prey moves to surface in evening, e.g. Herring / Killer whales, Squid / Pilot whales
➢Seals need tidal areas for haul out sites: rest during low tide when rocks are out of the water and hunt when
high tide
Seasonal movements
➢Cycles of reproduction & feeding, feeding areas can change due to prey abundance!
Example: Herring changed overwintering grounds from Tysfjord to the north of Tromso!
➢Site fidelity to breeding areas high for Pinnipeds: need to haul out for birth and nursing / mating follows / fasting during breeding. Breeding and feeding sites often far away, e.g. Elephant seals
➢Humpback, Grey & Right whales travel to specific breeding sites, far away from feeding sites
➢For many other species breeding and feeding areas are close
Moult
Specific haul out areas, e.g. elephant seals 1000km away from feeding grounds
➢Beluga whales - fresh water river mouths for moult
➢Hooded seals swim > 1000km from moult to haul out
places in 47 days!
Pinnipeds - fault out
➢Need to spend a lot of time on haul out areas on landca. 40% of their time, away from feeding / breeding areas
➢Thermal regulation, predator avoidance, rest (reduced metabolic rate), social interaction and parasite reduction
➢Short forage trips 2-5 days from haul out place
➢Elephant seals don't haul out during foraging, rest in water
Thermoregulation manatees
Warms up in warmer areas, e.g. power plants or just warmer water areas
Migration - routes
Winter & Summer grounds, normally north-south (polar - equatorial) migration
-> Philopatry feeding grounds 90% (Humpback whales) - learned through maternal association in first year!
Example Humpback whale migration from Norway to Caribbean through Photo-ID
Distance
➢Long travel (round trips 15.-25.000 km Grey whales, 18.600 km Humpback whales, 6.000 km Elephant seals)
➢Short or no travel (Humpback whales in Indian Ocean or Arabian Sea, breeding female Sperm whales, Bryde whales and Omura whales in tropics)
Individual travel / cross ocean transects
Humpback Whales: Japan to British Columbia, Canada Male Humpback Whale sets new record with 13,000km Journey from South America to Africa!
Long distance travel
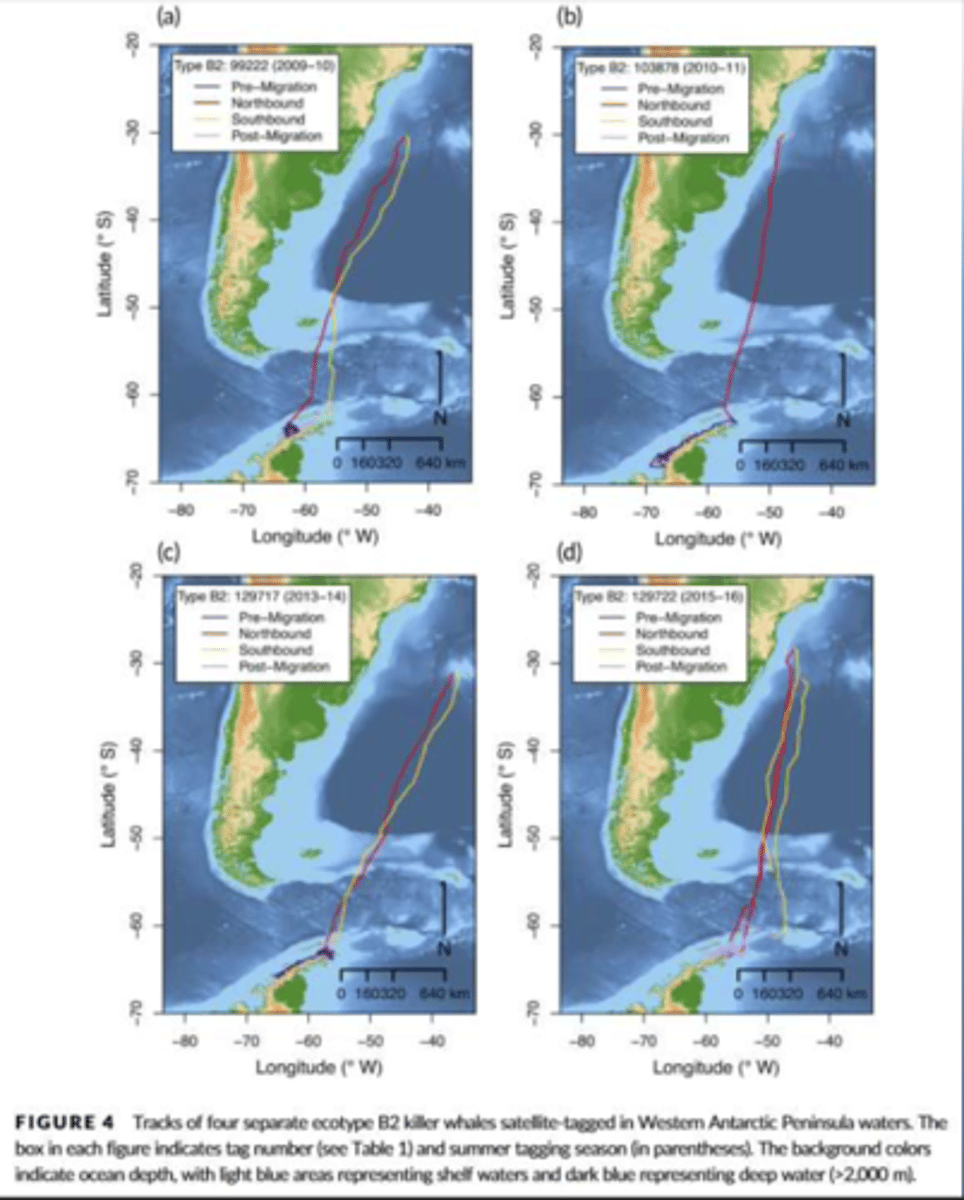
Killer Whales for epidermal moulting:
Antarctica - Brazil (10.000km) (Pitman et al., 2019)
Alaska – Azores (5.400-km with top speed of 252km a day
Intraspecific differences
(age, sex or reproductive stage)
➢Sexual dimorphism - longer feeding migrations for males
Sperm whales (Azores - Arctic)
Walruses (Svalbard -Franz Josef Land)
Belugas (Canada)
Elephant seals (continental shelf)
But: northern Right Whales only females with calves migrate south!
➢Individuals: Juveniles may take different migration routes
some individuals stay in feeding grounds and do not migrate every year! e.g. older male sperm whales in northern Norway
➢Females with calves arrive last in feeding grounds but migrate first to breeding grounds
Exploration routes
➢Phocid seals: weaned pups must explore environment e.g. Harp seals pups,or hooded seals with long migration routes
➢Necessary to find new food patches!
➢But also adult individuals explore
Orientation
Orientation (recognizing and maintaining direction)
Navigation (identifying the direction of a given point in space)
➢Underwater & land topography: sight & hearing e.g. seals often use land marks, association with seabed topography
But: Gray whales use direct path, not topography
Navigation
➢Sun & stars: harbour seals can use the star sky to navigate!
➢Currents / other oceanographic features such as water masses, currents, frontal systems, temperature, salinity, turbidity etc.
➢Geomagnetism: passive electrolocation has been demonstrated in the Guiana dolphin and Bottlenose dolphins - may detect Earths magnetic field for large-scale orientation
➢Polarized light? Not proven
Strandings and anthropogenic impacts
➢Wrong navigation?
➢Sand banks
➢Starvation & Illness (e.g. Pilot Whales in New Zealand/Australia)
➢Ocean Noise Pollution
➢Seismic exploration
➢Military Sonar ➢Disease / Parasites ➢Sunspot activities ➢Unknown causes ...
Antropogenic impacts
-> Too much Garbage, Fishing gear - Bycatch & Entanglements, Chemical & Plastic Pollution Oil & Gas extraction, Transport, Recreation & Tourism
-> Aquaculture, Military actions ...
-> Climate change!