AP Chemistry Unit 7: Equillbrium
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ALMOST THERE 7/9!!!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Equilibrium expression
[Products]] / [Reactants]
![<p>[Products]] / [Reactants]</p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b820e848-0453-4d63-8fe1-f47253ec160c.png)
characteristics of EQ expression
Includes only gaseous/aqueous molecules
DOES NOT include solids and pure liquids (e.g. H2O)
rate of forward reaction = reverse reaction
Equilibrium constant Kc
The ratio of reactants to products at equilibrium
Kc > 1 → more products than reactants (thermodynamically favorable = non spontaneous)
Kc < 1 → more reactants than products (thermodynamically unfavorable = spontaneous)
Keq when reaction is reversed
1/Keq (reciprocal of original)
Keq when reaction is multiplied by a coefficient C
KC (raise power by the coefficient)
Keq when 2 reactions are added
KEQ1 x KEQ2 → Multiply the equilibrium constants
Reaction Quotient (Qc, Qp)
relative concentrations/partial pressures of reacting species AT ANY TIME
DOES NOT include solids and pure liquids (represented as 1)
tends towards KEQ
if Q > KEQ → too many products → more reverse reaction
if Q < KEQ → too many reactants → more forward reaction
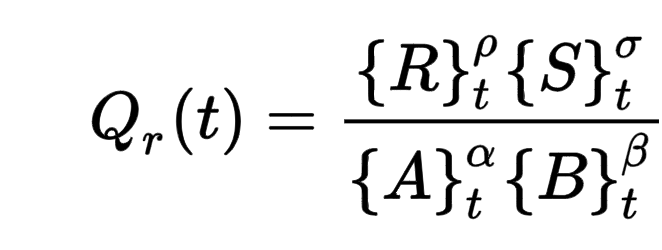
Le Châtelier’s Principle
systems at equilibrium respond to external stresses by shifting the equilibrium to offset its effects
leftward shift of EQ → more reverse reactions
rightward shift of EQ → more forwards reactions
examples of external stresses
addition or removal of chemical species
change in temperature
change in pressure/volume
dilution of a reaction system
effect of addition/removal of chemical species
removal of products → more fwd rxn
addition of products → more reverse rxn
change in temperature effect on EQ
Higher Temp:
Endothermic reaction → EQ shifts right (to use up heat)
Exo → EQ shifts left
Lower Temp
Endothermic reaction → EQ shifts left
Exo → EQ shifts right (to release more heat)
treat heat as a reactant/product
change in volume/pressure effect on EQ
(Only in gas equation)
V↑ P↓ → more space = increase in number of molecules(shift to the side with less molecules)
V↓ P↑ → less space = decrease in number of molecules (shift to the side with more molecules)
dilution effect on EQ
dilution → decrease concentration of all dissolved species → EQ shifts towards more aqueous molecules
change in KEQ
can change from a change in temperature
since heat = energy, change in energy in the system can change the stable ratio of reactants and products
a disturbance/stress to a system at EQ causes Q to differ from K
Solubility-product constant Ksp
can describe the dissolution of a salt
type of equilibrium constant
greater Ksp = better the salt dissolves (solubility)
when Ksp «1 → insoluble
when Ksp »1 → soluble
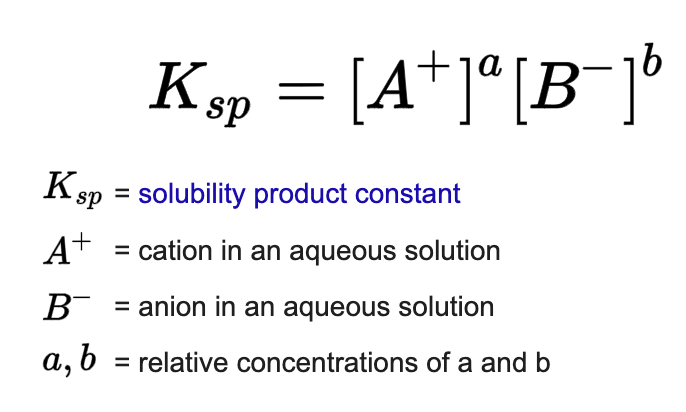
molar solubility
amount of solute that can be dissolved to make one liter of a saturated solution
increases with rising temperatures
higher temp = more energy to force the water molecules apart and make room for the solute ions
Common-Ion Effect
The solubility of a salt decreases when it is dissolved into a solution that already has one of the ions present in the salt
the amount of the ion dissolved from the salt decreases
pH and Solubility
pH affects solubility of a salt if one of its ions is a weak acid/base
Free Energy Change (Gibbs Free Energy) (ΔGo)
ΔG°diss = ΔH°diss - TΔS°diss
Determines the spontaneity of a reaction
uses change in enthalpy and entropy in
the breaking of intermolecular forces of solutes
preparation of solvent to receive solute
solvation (interaction of solute and solvent)
ΔG° > 1 → thermodynamically favorable (soluble)
ΔG° < 1 → thermodynamically unfavorable (insoluble)