FAR - Chapter 9 - Intangible assets
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What is the definition of an intangible asset according to IAS38?
‘an intangible asset is an identifiable nonmonetary asset without physical substance’
What does identifiable mean?
capable of separate disposal
or
arising from contractual or other legal rights.
What are 9 examples of intangible assets?
Patents & copyrights
Technology platforms
Licences
Trademarks
Customer lists
Brand names
Publishing titles
Franchises
Development costs
Does internally generated good will fall under the IAS38 definition of an intangible asset?
No as it cannot be disposed of individually
How is the IAS38 definition of an intangible asset stricter than the Conceptual Framework’s?
. It requires future economic benefits to be expected, whereas the Conceptual Framework only requires potential.
What are the 2 necessary conditions for an intangible asset to be recognised under IAS 38?
it is probable that future economic benefits will flow to the entity,
AND
the cost of the asset can be reliably measured.
How should the separate acquisition of an intangible asset be treated?
If a company purchases an intangible asset, the purchase price is an indication that future economic benefits are probable.
The cost can be measured as price paid.
Therefore an intangible asset should be recognised.
How does IAS 38 define research with regards to research expenditure?
‘research is original and planned investigation undertaken with the prospect of gaining new scientific or technical knowledge and understanding
What is the accounting treatment for research costs?
Research costs do not meet the recognition criteria as research is too distant from commercial production for an inflow of economic benefits to be probable.
Therefore, research costs should be written off to the statement of profit or loss as incurred.
DR Expense X
CR Cash/payable X
How does IAS 38 define development with regards to development expenditure?
‘development is the application of research findings or other knowledge to a plan or design for the production of new or substantially improved materials, devices, products, processes, systems or services before the start of commercial production or use
What 6 criteria must be met for development costs to be capitalised under IAS38?
Probable flow of economic benefit from the asset, whether through sale or internal cost savings
Intention is to complete and use or sell the asset
Reliable measure of development cost
Adequate resource is available to complete the asset
Technical feasibility of completing the intangible asset so that it will be available for use or sale
Expected to be profitable, i.e. the costs of the project will be exceeded by the benefits generated
Which expenditure can be recognised?
only expenditure incurred after the recognition criteria have been met which should be recognised as an asset
Can expenditure be capitalised once it has been expensed?
NO
If PPE is used in the development process, can the depreciation on the PPE is capitalised to the development costs?
Yes, the depreciation on the PPE is capitalised to the development costs in intangible assets during the period the project meets the development criteria.
When will the depreciation is capitalised as part of the intangible asset as the benefit from the use of the PPE be realised?
It’s only realised when the development project is complete and production is underway.
The expense will be recognised in the statement of profit or loss as amortisation
Can internally generated brands be capitalised?
costs of developing the brand cannot be identified separately from the cost of developing the business as a whole. Write off expenditure to the statement of profit or loss (SPL) as incurred.
Can staff training costs be capitalised and if so why?
Staff training costs can NEVER be capitalised as staff cannot be controlled and can leave at any time
What 2 things may a company acquire when they purchase another company? What value will they be recognised at?
intangible assets recognised on the acquired company’s statement of financial position
intangible assets not recognised by the acquired company.
These will be recognised in consolidated financial statements initially at fair value
What is a digital asset? Give 5 examples
any item stored digitally that can be uniquely identified and used by organisations to gain value. Examples include digital documents, audio, videos, software and cryptocurrency.
What are cryptocurrencies?
A cryptocurrency is a type of digital asset that can be used to buy things and save value. It works on a network of computers that is not controlled by any central authority, such as a bank. Cryptocurrencies use blockchain technology to keep everything secure and transparent
What did the IFRS Interpretations Committee state that cryptocurrencies should be treated as, in 2019?
as intangible assets, as they most closely meet the definition in accordance with IAS 38.
What should a cryptocurrency be treated as under IAS 2 if it is meant to be sold as part of normal business activities?
it should be treated as inventory in accordance with IAS 2.
What is the initial measurement for intangible assets?
Where an intangible asset meets the recognition criteria, it should be measured initially at cost PLUS directly attributable costs e.g. legal fees.
What is the subsequent measurement for intangible assets?
Valued at either:
Cost MINUS accumulated amortisation and impairment losses
Revalued amount MINUS accumulated amortisation and impairment losses
When only can an intangible asset be revalued?
if the fair value can be determined by reference to an active market
What is the IFRS 13 definition of an active market?
A market in which transactions for the asset or liability take place with sufficient frequency and volume to provide pricing information on an ongoing basis
→ Buyers and sellers should be able to be found at any time
What does the nature of most intangible assets mean?
that they are not homogenous (identical).
However, markets of identical items may exist for assets such as some licences, quotas or cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin.
What should happen if an item is revalued?
, all assets of its class should also be revalued
How should we treat intangible assets with a finite useful life?
Amortise the asset over its useful life, starting when the asset is available for use.
(Development expenditure is deemed to be available for use when commercial production of the product being developed begins.)
Amortisation should reflect the pattern of use of the asset
What should we assume about the residual value of an intangible asset with a finite useful life?
Residual value is zero unless:
a third party has agreed to buy the asset at the end of the useful life
there is an active second-hand market which can be used to measure a residual value
How should we treat intangible assets with an indefinite useful life?
Do not amortise, instead test for impairment annually.
Review the useful life each accounting period. If the asset now has a finite useful life, it should be amortised
What does indefinite mean when talking about useful lives?
There’s no foreseeable limit to the period over which an asset is expected to generate net cash flows
How do you calculate the profit or loss of an intangible asset on its disposal?
Proceeds - Carrying amount = Profit/ (loss)
Where should a revaluation reserve be transferred if an asset was held under the revaluation model and a revaluation reserve exists?
To retained earnings
Does IFRS require development costs meeting the criteria to be capitalised?
YES
What does UK GAAP allow, regarding development costs?
UK GAAP allows a choice between capitalisation and expensing the development costs as incurred.
Does IFRS allow intangible assets with indefinite useful lives & if so how do we deal with them?
Yes, it does
These assets will not be amortised but should be tested annually for impairment.
If at any point a useful life can be ascertained the asset should be amortised over the remainder of that life.
What is the limit on useful life for an intangible asset under UK GAAP?
that no intangible asset will have a useful life exceeding ten years
What 4 disclosures must be made regarding intangible assets in addition to the ones in IAS 16 PPE?
if the asset has a finite or indefinite useful life
for assets with indefinite lives, their carrying amount and why they have an indefinite life
individual assets if they are material
amount of research and development expensed during the period.
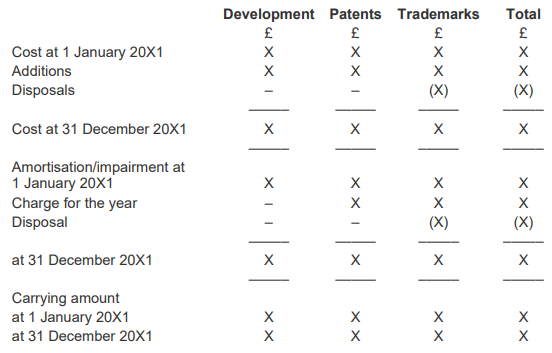
What may a IAS38 Intangible Asset reconciliation note look like?
B/f Cost X
Additions X
Disposals (X)
C/f Cost X
Amortisation/impairment b/f X
Charge for year X
Disposal (X)
Amortisation/impairment c/f X
Carrying amount b/f X
Carrying amount c/f X