ppcm- health screening
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Varieties of Screening
Pt with referral and dx from physician
Pt with referral, no MD dx
Pt without a referral
In search of particular dx or risk factor (Primary prevention)
Why Are We Screening?
Shifts in Practice Setting
Practitioner of Choice
Health Promotion/Disease Prevention
Better Patient Care!
Why Are We Screening for Mental Health?
Outcomes
Co-Morbidities
QOL
what are we screening for?
Undiagnosed
Existing Stable/Unstable
Masqueraders
PT Screening: Diabetes Complications
Heart Dx
Stroke
Blindness
Peripheral Neuropathy
Kidney Failure
Amputations
Screening as an Ongoing Process
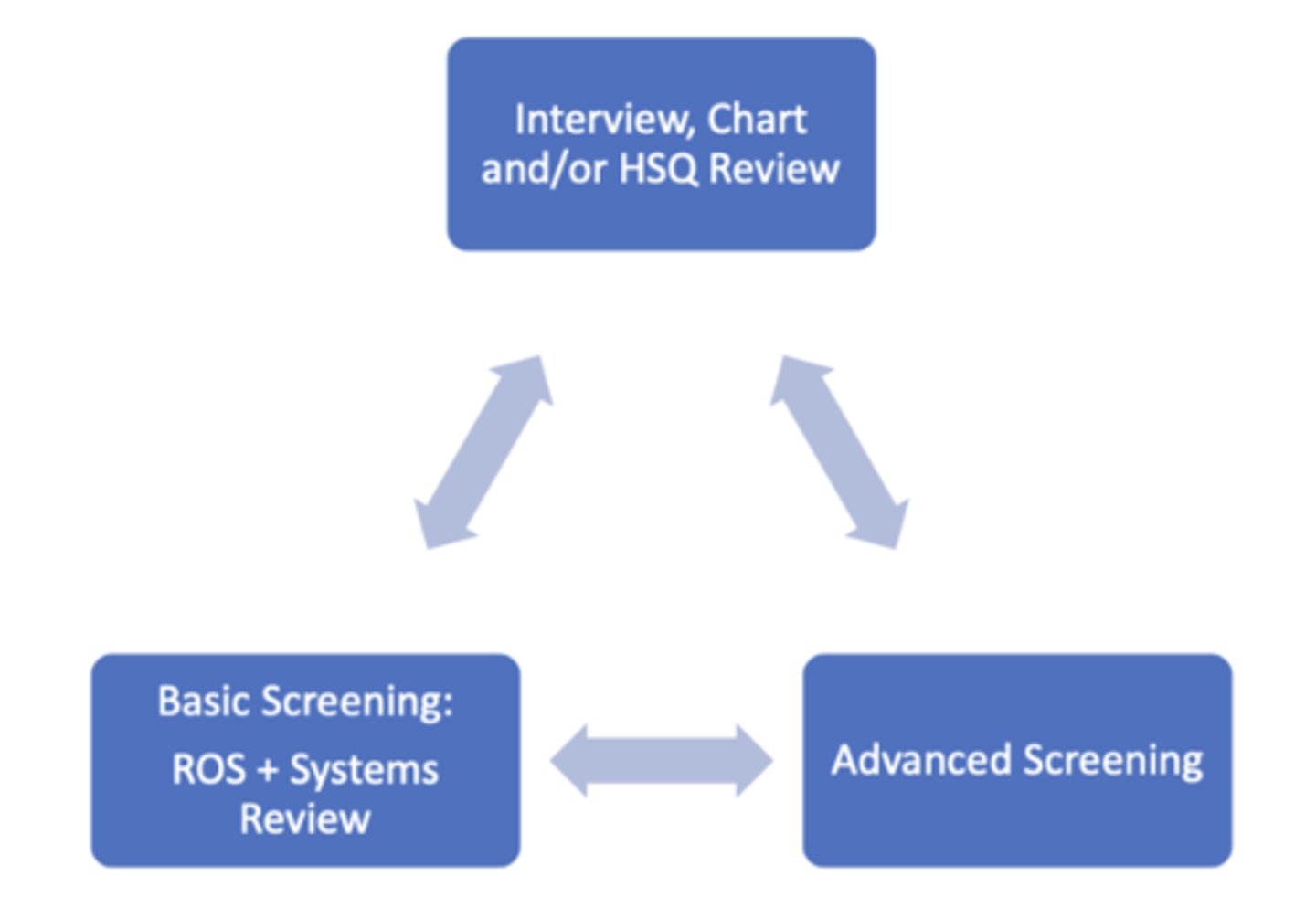
Basic Screening: Review of Systems and Systems Review
Gross Screen, Every patient regardless of health condition, Every setting
Hands on and Observational
Baseline pt status
Quick and efficient
Advanced Screening
Subset of patients
Based on documentation,hx, ROS and Systems Review
Review of Systems Goals
Obtain info relevant to all bodysystems through observation, and questioning (screening).
Determine if the pt requires referral to another HCP
Is it urgent? Emergent?
Tx, Refer and Tx, Refer
Basic Screening: Review of Systems
Seek information relevant tomajor body systems through observation and questioning to help determine whether there are symptoms that suggest the need for referral for additional medical evaluation
Review of Systems
Cardiovascular system
Pulmonary system
Endocrine system
Eyes, ears, nose, and throat
Gastrointestinal system•
Genitourinary/reproductive systems• Hematologic/lymphaticsystems
Immune system
Integumentary system
Nervous system
Musculoskeletal system
Overall physical and psychological condition,such as unexplained weight change, fatigue, lethargy, and malaise; cognitive well-being; and emotional well-being, such as anxiety and feelings of hopelessness
Screening Goals
To Identify S&S within and outside of PT scope of practice
Determine Treat, Refer, Refer and Treat
Focus the examination, tests, and measures
Advanced Screening: Subset of Pts
When selecting screening tools, always consider:
Population for whom the screening is intended
Condition that the screen is intended to detec
When you are doing patient history what is it improtant to remember?
Psychological Wellbeing
Health Habits/Behavioral Risks
Social History: Culture/Religion/Spirituality, Live Alone/Socialization/Resources, Access to Care• Safety
Components of the Decision-Making Process: Focus on Screening
Pt/client history
RF Assessment
Pain Pattern and Type
Associated signs and symptoms of systemic disease
General Risk Factors
Age
Prior Personal or Family History
Race/Ethnicity
BMI
Etoh, Tobacco, Substanse Use
Sedentary Lifestyle
PT diagnosis is a
label encompassing a cluster of signs and symptoms commonly associated with a disorder or syndrome or category of impairments in body structures and function, activity limitations, or participation restrictions.
PT diagnosis is
ACTION oriented
Organize data into defined clusters to determine appropriate intervention strategies
Red flags...
are signs and symptoms found in the history and physical examination that suggest the presence of a serious pathology
Tx, Refer, Refer and T
Cautionary
prompts DPT to : "slow down"
Assess pain-associated psychological distress
Screen multiple system including psychological factors
signs for stroke
B: Balance difficulties
E: Eyesight changes
Face: Smile and see if one side of the face droops.•
Arms: Raise both arms. Does one arm drop?
Speech: Say a short phrase and check for slurred or strange speech.
Time: If the answer to any of these is yes, call 911 right away and write down the time when symptoms started
Signs & Symptoms Help Identify Pathological Conditions Detection Process
Perform screening process
Look for symptoms grouped together
Conduct a risk factor assessment
Primary and secondary prevention of disease Look for associated signs and symptoms
Categories of Red Flags
PMH• Risk Factors
Clinical Presentation
Pain Pattern
Associated signs/symptoms
Indicators of Systemic illness
Gradual onset with no known cause
Gradual, progressive, cyclical onset
Constant
Intense
Symptoms unrelieved by rest or change in position
Bilateral symptoms
Constitutional symptoms*
Bilateral symptoms that are indicators of systemic illness
Pigmentation changes
Edema
Rash
Clubbing/nail bed changes
Weakness
Numbness/tingling
Burning
Common Constitutional Symptoms
Fatigue
Malaise
Weakness
Headaches/Dizzy/Faint
Fever/Chills
Unexplained Weight Loss/Gain
Early Satiety
Nausea/Vomit
Bowel & Bladder Function
Numbness/Paresthesia
Constitutional Symptoms are
Potential Flags: In Context!
1.Fever
2. Diaphoresis (unexplained perspiration)
3. Night sweats (can occur during the day)
4. Nausea
5. Vomiting
6. Diarrhea
7. Pallor
8. Dizziness/Syncope (fainting)
9. Fatigue
10. Weight Loss
key POTENTIAL red/yellow flags
unexpected patterns
suspicious lymph nodes
trauma
recent infection
travel
multiple sexual patterns
severe constant night pain
recurrent colds/flu
the interview clinicans
Listen Well
Build on Pt Responses
Detect Confusion
Are Pt Centered
Shared Decision Making
Interview Goals
Rapport Building
Identify barriers
Establish the patient's goals
Determining the severity, irritability, nature, stage and stability of the patient's condition
Establish an early hypothesis regarding the source of symptoms
Interview Technique
Open-Ended
Close-Ended
Funnel Sequence
Paraphrasing
Open-ended questions
Responses: are not yes/no answers
Helps Clarify Details
Minimizes Grey Areas:Allows for Elaboration
Methods to Limit Excessive Elaboration: Redirect, Summarize, Circle Back to Core Issue
paraphrasing
Litmus Test
Repeat/rephrase
Bolsters Accuracy
What Constitutes GOOD MEDICAL History Taking?
HP
Thorough PMH: Use of systematic method, screening tools
Thorough PSH
Meds
Associated Signs and Symptoms
Medical History Taking HPI
OLDCARTS
Recurrent problem or new?
Seen any other provider?
Any treatments?
Imaging
Recent illnesses/infections
Medical History Taking PMH
When diagnosed?
How treated?
How managed?
MD Follow up
Stable/Unstable
Always Ask/Verify
Cardiac Dx
Hypertension,CVA, Neuro dx
Pulmonary Dx
DM
CA
PSH
Meds (Prescribed, OTC etc)
Trauma
Med History Taking PSH
Reason for surgery
Dates and Type of Surgery
Complications
Precautions
Impact
Questions to ask about medications
Prescribed: Taken as prescribed?Helping? Side effects?
MD Follow up
OTC: Taken as prescribed? Helping?MD aware?
Supplements: Recommendeddosage? MD aware
Alternative rxs: MD aware?