coastal landscapes 2
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
The littoral zone
a series of sub-zones to represent the features of the wider coastline from sea to land
offshore, nearshore, foreshore and backshore
This zone reaches dynamic equilibrium where there is a balance between inputs and outputs
high energy coastline
Destructive waves, long fetches, high rates of erosion, caves, arches, stacks and stumps, cliffs and wave-cut platforms.
low energy coastline
Constructive waves, shorter fetches, higher rates of deposition, spits and bars, beaches, sand dunes and salt marshes
concordant coastline
alternating bands of hard and soft rock parallel to the coast.

discordant coastlines
have alternating bands of hard and soft rock at 90o to the coast.
Erosional landforms are more common on discordant coastlines because erosion happens at different rates along their length.
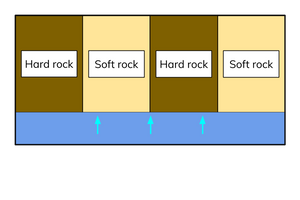
coastal morphology
the shape of the coastline is continually changing
bays and headlands
On discordant coastlines, the retreating, less resistant rock and the exposed resistant rocks cause a change in the shape of the coastline. This leads to wave refraction.
This change in the way in which waves approach the coastline can cause an increase in the rate of erosion on the headlands.
This leads to the formation of headland features like caves, arches, stacks and stumps.
Dalmation coastline
formed as a result of tectonic forces and sea level rise
series of islands which run parallel to the coast
e.g croatia
Haff coastline
Along the southern Baltic coastine
Large amounts of sand and gravel deposited offshore during the glacial period
a feature of a low energy coastline
geological structure
Strata - layers of rock
Bedding planes - horizontal cracks created by pauses in rock formation
Joints - vertical cracks caused by tectonic movement or contraction
Folds - the result of pressure during tectonic movement causing the rock strata to fold
Faults - the result of stress or pressure causing it to fracture
Dip - the angle of the rock strata
Cliff profiles
The angle and height of the cliff face
features such as wave cut platforms
what affects cliff profiles
lithology
Hydraulic action and abrasion
Subaerial processes
Wave type
what is coastal recession due to
Erosion
Sea level rise
Submergence
Mineral composition
Rock classification
Structure
Mineral composition
Some minerals are more reactive than others
This affects the rate of chemical weathering for example:
Calcite is reactive and so easily chemically weathered
Sedimentary rocks
form as a result of compaction and cementation of sediment called lithification
shales, sandstone, and limestone
Sedimentary rocks:
Erode and weather more rapidly than other types of rock
Form in layers
They are clastic which means they are made of clasts (sediment particles)
metamorphic rock
form when sedimentary and igneous rocks are altered through heat and pressure, but do not melt in the process
slate and marble
Metamorphic rocks:
Have a crystalline structure
Are often folded and faulted
Are more resistant than sedimentary rock and less resistant than igneous rocks
Igneous rock
form when molten rock from the Earth's mantle cools and hardens
granite and basalt
Igneous rocks:
Erode and weather very slowly
Can be categorised into two types:
Intrusive igneous rock - forms within the ground, cools slowly, and has large course crystals
Differential erosion
the changing rates of erosion
Leads to complex cliff profiles
Influences rates of recession
Role of vegetation
Help stabilise coastlines- The plant roots help to bind the soil/sand together reducing the impact of erosion
infiltration- improve soil structure
regulate climate
pioneer species
The fist plants to grow in the harsh coastal environment
help stabilise sediment
trap sediment
Sand dune succession
The changes in an ecosystem, over time, of the species that occupy it
An example of pioneer species
Sandy beaches usually have sand dunes at their rear, because of strong onshore winds transporting dried, exposed sand
Sand grains are trapped and deposited against any obstacle (rubbish, rocks, driftwood etc) and begin to form embryo dunes
It is the interaction of winds and vegetation that helps form sand dunes
Formation of a sand dune
Windblown sand is deposited against an obstruction: Pebbles or driftwood
As more sand particles are caught, the dunes grow in size, forming rows at right angles to the prevailing wind
Over time, the ridges of the dunes will be colonized and fixed by vegetation in a process called succession