synovial fluid
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
synovivla fluid is
an ultra filtrate of plasma- Meaning no high MW molecules
therfore G and uric acid levels are equal to that of plasma, while protein is still < that of plasma
From blank, synovial membrane cellls secrete blank, making the fluid blank
From synonviocytes, they secrete hyaluronic acid, making the fluid thick and stringy
Functions of synovial fluid
Lubricates the joints
lessens shock
transport medium for delivery of O2 and nutrients and removal of CO2 and cellular waste
What are the categoried of joint effusion
Non-inflammatory
inflammatory
septic
hemorrhagic
Non-inflammatory artirtis pathologic significance
Degenerative joint dz
Inflammatory arthritis pathologic significance
Crystal-induced arthritis (gout & pseudogout
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), reactive arthritis,
psoriatic arthritis, Lyme arthritisLupus erythematosus (SLE),
septic arthiritis pathologic significance
microbial infection
joint effusion is collected into 3 different tubes via
arthrocentesis
must collect in liquid additive bc it would interfere with crystal studies
What is the order of the tubes for synovial fluid
CHem and sero
Hemat and cyto
Microbio
what si the RR for synovial fluid volume
<3.5
>3.5 = effusion
what does the synovial fluid color say about the condition
non-inflammatory- yellow, clear
inflammatory- cloudy, turbid
crystals- milky, cloudy
sepsis- yellow- green, cloudy
hemorrhagic or traumatic tap - pinl-red brown, cloudy
where does the viscosity of synvoial fluid come from
due to the polymerization of hyaluronic acid
string test- 4-6 cm long
low visc- indicates inflammatory or septic process
what are the three different inclusions
lipid droplete- crush injuries
ochronotic shards- black debris from joint prosthesis- pigmented cartilage from alkaptonuria
Rice bodies- collagen and fibrin- RA
Hematology in synovial fluid
most common test
may need to thin w/ hyaluronidase
wbc differential- from smear prepared by cytocentrifuge
An increase in neutrophils indicates
bacterial septic
An increase in lymphocytes indicates
non-septic inflammatory and viral
An increase in eosinophils indicate
allergies, lyme dz, parasitic infection
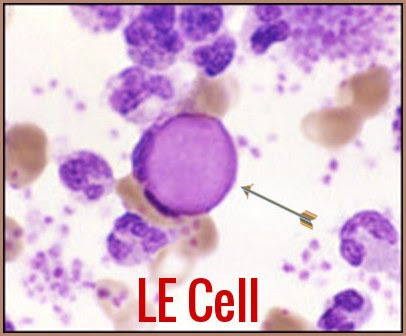
what are LE cells
neutrophils or macrophages w/phagocytosed nucleus of another cell, indicates lupus
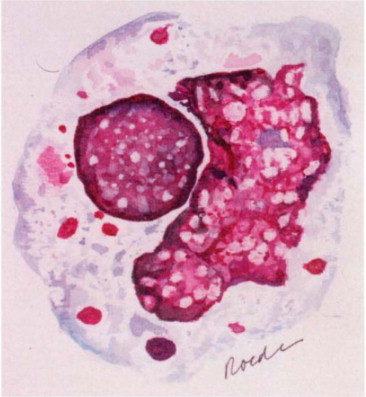
What are Tart cells
monocytes or macrophages that have engulfed some nuclear material, not significant
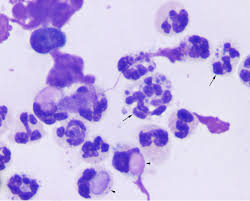
what are ragocytes
Neutrophils w/ precipiated RF, indicates RA
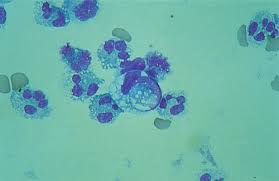
What are reiter cells/neutrophages
vacuolated macrophages w/ ingested neutrophils, indicates autoimmine DZ
1st birefringent crystals are screens w
polarized light microscopy
if positive- they use red compensator filter
if a crystal appears yellow when parallel to this arrow
it is negatively birefrigence
if blue, its positive
what is monosodium urate
needle shaped and yellow when parallel to arrow- strong( - ) BR
indicates gout
What is calcium pyrophosphate
rhombic shaped and blue when parallel to arrow- weak ( + ) BR
indicates pseudogout
total protein is increased in
inflammatory and hemorrhagic D/Os
a decrease in G levels indicate
septic (bacterial)artirtis
an increase in lactic acid indicates
septic
an increase in uric acid indicates
gout
RF indicates
RA`
What are the most common autoimmune cases of arthritis
RA and SLE
test for RF and ANA
Lyme disease
Arthritis is a frequent complication, test serum for borrelia burgdorferi antibodies