Stage 1 - Forensic Psychology
1/29
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Forensic Psychology
A scientific field of study that applies psychological theories and skills to the legal and criminal justice system.
Polygraph machine
informally known as lie-detectors that measures physiological responses such as blood pressure, heart rate, breathing rate, and galvanic skin response (sweating).
How reliable are polygraphs?
Mostly unreliable because there are many factors that can affect polygraphs such as an innocent person acting fearful and anxious, a guilty person shows no remorse for their actions, and a person may manipulate their response to relevant questions.
What is the difference between the control question test and the guilty knowledge test?
The control question test involves questions that aren't related to the incident being investigated but rather to create an emotional response whereas the guilty knowledge test involves multiple-choice questions that has information from the incident which, one is correct.
What are two factors that affect eyewitness testimony?
Psychological factors where testimony can be influenced by other memories, prejudices, beliefs, and expectations.
Environmental factors can be distorted and shaped by the context and other aspects of the event.
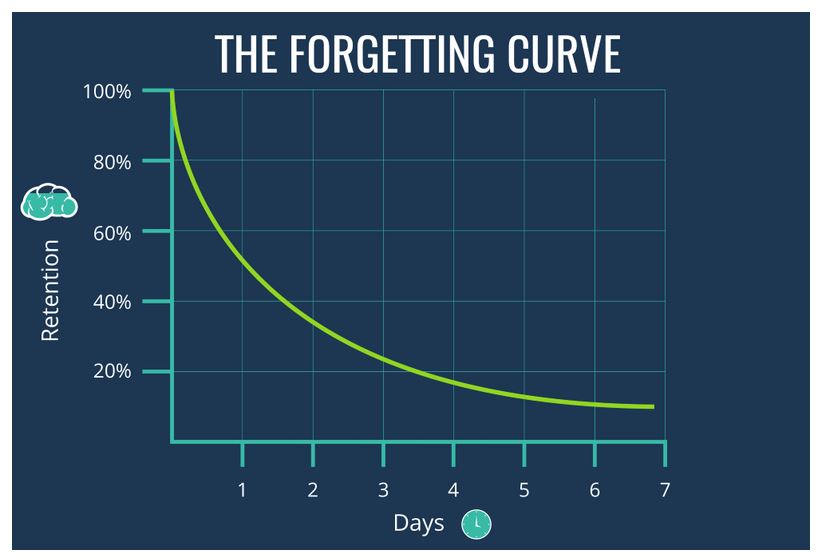
What does Ebbinghaus state about forgetting?
According to Ebbinghaus, memory drops to below 50% after just one hour and will gradually drop if information is not rehearsed.
What are the three main problems with encoding?
Reconstructive memory - When memories are shaped by our own beliefs and expectations of what we expect to occur, this could lead to false memories and unreliable eyewitness testimonies.
Weapon focus - In a scenario involving a weapon, most witnesses focus on the weapon rather than the culprit which will distract them from key details in the crime.
Violence distraction - Research has shown that people have better memory for non-violent events than for violent events.
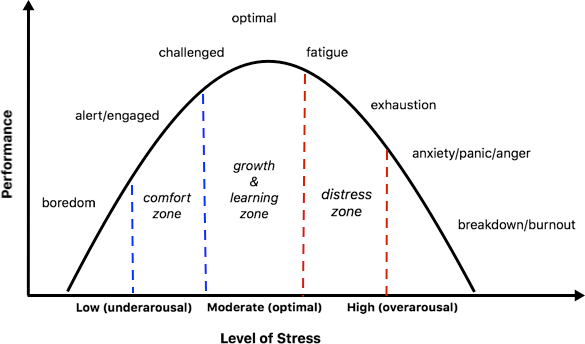
What does the Yerkes-Dodson Law state?
The Yerkes-Dodson Law states there should be an optimal level of arousal for the best performance but if there are high levels of arousal, it could lead to stress whereas if there are low levels of arousal, it could lead to laziness.
What is the Schema Theory?
The theory that our memory systems take advantage of the reoccurring patterns by forming and using schemata that provides a framework for remembering new information.
How does a cognitive interview differ from a traditional police interview?
Unlike a traditional police interview that typically involves just asking the eyewitness how much they can remember; cognitive interviews employ four main techniques such as;
Help the eyewitness mentally reconstruct the physical (external) and personal (internal) contexts which existed at the time of the crime.
Ask the witness to report everything.
Ask for recall from a variety of perspectives.
Ask the eyewitness to make retrieval attempts from different starting points.
Physiological Arousal
A state of heightened activity within the autonomic nervous system that awaken the sense organs to respond to stimuli.
What is the difference between sympathetic (SNS) and parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS)?
Sympathetic system activates the “fight-or-flight” response in dangerous and stressful situations or when you’re physically active whereas parasympathetic system activates the “rest-or-digest” response to control your body’s response during times of rest.
How does the sympathetic nervous system respond to physiological arousal?
Eyes: Pupil enlarges to let more light in and improve vision.
Heart: Heart rate increases to improve delivery of oxygen throughout the body.
Lungs: Relax your airway muscles to improve oxygen delivery to the lungs.
Digestive tract: Slow down digestion so its energy is diverted to other areas of your body.
Liver: Activate energy stores in your liver to energy that can be used quickly.
How does the parasympathetic nervous system respond to physiological arousal?
Eyes: Pupils get smaller to limit how much light enters your eyes, improve close-up vision, and causes tear production in your eyes.
Nose and mouth: It makes glands produce saliva (mouth) and mucus (nose) to help with digestion and slow down breathing.
Lungs: It tightens airway muscles and ultimately reduces the amount of work your lungs do during rest.
Heart: It lowers heart rate and the pumping force of your heart.
Digestive tract: It increases rate of digestion and tells your pancreases to make and release insulin to break down sugar into usable energy for cells.
How do integrators look for signs of lying?
Subjective Experience - How we feel.
Physiological Arousal - How our body reacts to stimuli.
Expressive Behaviour - What others can see.
What are the biological causes for someone to commit crimes?
Natural selection (mostly unreliable).
Genetics (parents are criminals).
What is the difference between twin studies and adoption studies?
Twin studies involve comparing criminal behaviour between monozygotic (individual twins) and dizygotic (non-identical twins) whereas adoption studies are comparing biological/adoptive parents with their children.
What are the psychological causes for someone to commit crimes?
Nurture (e.g. children living in a family of criminals).
Operant conditioning.
Low self-esteem.
Self-fulfilling prophecy
An expectation or prediction that influence’s one’s behaviour due to stereotyped beliefs.
What is the difference between organised and disorganised criminals?
Organised criminals typically commit premediated crimes and leave little to no evidence behind whereas disorganised criminals typically commit non-premediated crimes and leave behind a lot of evidence.
What are the six stages of criminal profiling?
Input
Decision Process Models
Crime Assessment
Criminal Profile
Investigation
Apprehension
Stage 1: Input
The first stage involves collecting as much information and evidence about the crime.
The profiler’s job is to do a complete background check of the victim to help determine their behaviour during the crime.
Stage 2: Decision Process Models
The second stage involves organising and classifying data to be used to look for patterns and form a basis for the profile of the crime.
The profilers classify the crime, determine motives of offender, and determine risk level of the victim prior to the crime.
What are two aspects of a offender’s signature?
Signature aspect - Emotional or psychological needs of the offender which is the motivation behind the crime.
Signature behaviours - Acts committed by the offender during the crime like leaving a symbol or using particular equipment.
Stage 3: Crime Assessment
The third stage involves the profiler completing the crime reconstruction based on the behaviour of the victim and criminal.
This is used to provide clues on who committed the crime and looking for a pattern in terms of tools, weapons of choice, or preference of victims.
Stage 4: Criminal Profile
The fourth stage involves developing a description of the suspect. This typically involves the suspect’s potential race, sex, physical characteristics, and personality traits.
Once the profile is complete, it must be compared with the decision process models and the reconstruction of the crime to ensure it matches the data.
Stage 5: Investigation
The fifth stage begins with the profiler adding a written report to the information investigators have already gathered.
During an investigation, suspects matching the profiler’s description is evaluated which will help narrow it down, if no further evidence is bought forward.
However, if another crime of the same nature with the same MO and signature is committed or if there is no suspect identified, the process will restart.
Stage 6: Apprehension
The final stage where the suspect is arrested from either a confession or the physical evidence links the suspect to the crime.
What is the difference between the top-down approach and bottom-up approach?
Top-down approach focuses on individual behaviour and looking at the individual through cases studies and crime scenes whereas bottom-up approach looks at bunch of statistics from different cases and the characteristics of different types of people and see who are most likely to commit those crimes.
Biopsychosocial Model
Model of behaviour analysis that examines the biological, psychological, and social factors that influence criminal behaviour.