12 Economics - Unit 3.1
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Closed Economy
If the economy does not engage with the foreign sector
Open Economy
When an economy opens itself up to international trade through engaging with the foreign sector
Factor Endowment
The supply of the factors of production that exist within a country.
Exchange Rate
The value of the currency of a nation expressed in terms of the currency of another nation.
Standard of Living
A measure of lifestyle standards based on material and quantitative indicators.
Absolute Advantage
The ability of a nation to produce commodities more efficiently than another nation. A term coined by Adam Smith in his book, the Wealth of Nations.
Assumptions of PPC’s representing Absolute Advantage
Resources are perfectly mobile
There are only two countires and two commodities
Both countires ahve equal quantities of resources, but not the same quality
If trade takes place there are no transfer costs
Comparative Advantage
The ability of a nation to produce a product at a lower opportunity cost of production than another nation. - Coined by David Ricardo
Competitive Advantage
Trade advantage obtained through the capacity of a nations industries to innovate and upgrade. - Coined by Michael Porter in 1990
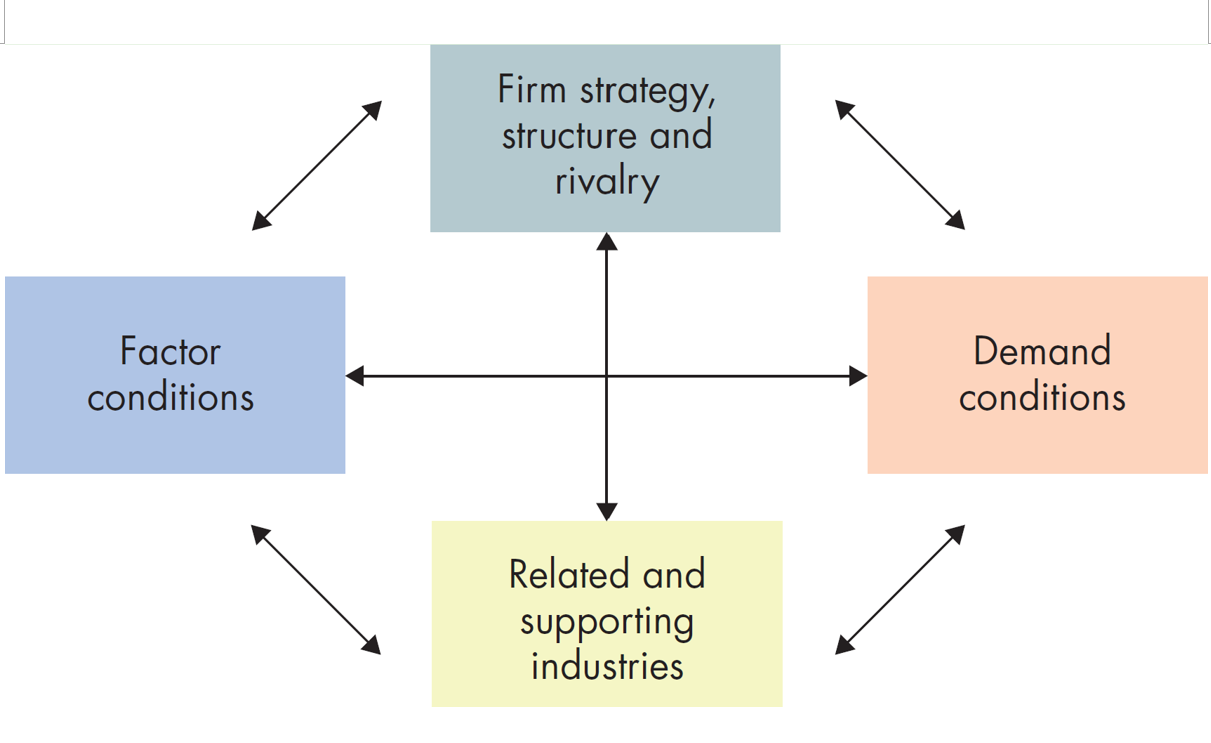
Factor Conditions of Competitive Advantage
The nation must have an advantage in factors of production. They can be created through investment for infrastructure and highly specialised training of the workforce
Demand Conditions
The nation can benefit from having a clear view of consumer demand by first developing a domestic market to help anticipate international market needs.
Related and Supporting Industries
A nation can gain an advantage by having efficient and internationally competitive supplier industries.
Firm Structure, Strategy, and Rivalry
Conditions governing company creation, organisation and management, and domestic rivalry need to be disciplined, flexible and supportive of innovation.
Self-Sufficiency
Refers to the ability of a nation to produce sufficient products to meet its own needs for domestic sources.
Exchange Rate
The value of the currency of a nation expressed in terms of the currency of another nation.
Law of one price
Identical goods should have the same price in different markets when adjusted for currency exchange rates and transport costs.
Purchasing Power Parity
Exchange rates should eventually adjust so that an identical basket of goods and services costs the same in any two countries.
Currency Appreciation
An increase in the value of a currency relative to other currencies under a floating exchange regime.
Currency Depreciation
A decrease in the value of a currency relative to other currencies under a floating exchange regime.
Fixed Exchange Rate
The value of a currency that is determined by the government fixing it to the value of another currency at a certain level, and guaranteeing to maintain it at that level.
Floating Exchange Rate
The value of a currency determined by the forces of supply and demand in the foreign market.
Managed Exchange Rate
A floating rate with some government intervention in currency value to keep it in a certain range.
Currency Revaluation
A deliberate upward adjustment to the value of country’s currency relative to the value of a country’s currency.
Currency Devaluation
A deliberate downward adjustment to the value of country’s currency relative to the value of a country’s currency.
Money Supply
Represents the amount of money in circulation at a given time.
Determinants of Demand - Exchange Rates
Exports of goods and services
Incomes received
Capital inflow - referring to Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Speculation - People who purchase currency as an investment
Determinants of Suppy
Speculation - People who purchase currency as an investment
Capital outflow
Incomes payable
Imports of goods and services
When representing supply on an exchange rate demand and supply graph…
It is not a representation of how much money exists, but rather how willing the different people who own the currency are to sell it.
Porter’s diamond
The Balance of Payments
The summary of a nation’s payments to, and receipts from, the rest of the world over a year.
The Current Account
The record of day-to-day financial transactions involving the trade of goods and services between a nation and the rest of the world
Balance of Trade
Is the difference between the value of imports and the value of exports. Formula = Total Value of Exports - Total value of Imports
Terms of Trade
The ratio of export prices to import prices. Formula = (Index of Export Prices / Index of Import Prices) x 100.
Sub Accounts within the Current Account
The balance of trade.
Net primary income - earnings derived from our foreign investments or paid to foreigners for their investment in Australia.
Net current transfers - movement of funds in which there is no reciprocal activity, e.g. migration, foreign aid, insurance payments.
The Capital Account
A record that includes capital transfers and the acquisition / disposal of non-produced, non-financial assets between residents and non-residents.
The Financial Account
Tracks transactions and financial assets and liabilities between economic entities.
Direct Investment
Transaction s related to long-term capital investment in a business where the investor has significant voting power in the business.
Portfolio Investment
The purchase of equity or debt in a business. In contrast to direct investment, portfolio investment occurs when the investor does not have an influence in the operation of the business.
Financial Derivatives
The purchase or sale of financial derivatives. These transactions involve the exchange of risk between parties, rather than funds.
Reserve Assets
The purchases or sale of reserve assets held by the Reserve Bank. These reserves are assets controlled by the Reserve Bank to meet policy objectives such as intervention in the foreign exchange market and to assist the Australian Government in Meeting its commitments to the IMF.
Other investments
Transactions that do not fit into any one of the Financial Account categories.
Double Entry Accounting
The current account minus the capital and financial accounts should equal 0.
Credits
Payments received by a nation from the rest of the world.
Debits
Payments by a nation to the rest of the world.
Intra-Industry Trade
When countries trade similar / the same good.
Intra-Company Trade
Trade between affiliates of the one organisation; for example, between a home-based subsidiary and a foreign-based subsidiary of the same company.
Transfer Price
The price charged for goods by one subsidiary of a multinational corporation to another subsidiary of the same company in another company.
Value of FDI
Economic Growth and Employment
Productive Capacity
Technological Advancement
Foreign Exchange Access
Market Access.
Problems of FDI
Loss of Ownership and Control
Increased External Debt and Servicing Costs
Profit Repatriation
Foreign Investment Review Board (FIRB)
Established in 1976. Acts as an advisory body to the Treasurer and the government on Australia’s foreign investment policy.
The FIRB has three main functions:
To examine investment proposals
To provide advice regarding policy on foreign investment
To foster awareness and understanding of foreign investment
Foreign Debt
A debt owned by a nation to the rest of the world
Gross Foreign Debt
The total of Australia’s overseas borrowings (what we owe)
Net Foreign Debts
Gross foreign debt less Australian lending to overseas residents (what we owe minus what we are owed).
Private Foreign Debt
The part of debt owed by private residence
Public Foreign Debt
The part of debt owed by the government.