Homeostasis/Biological Molecules
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Homeostasis
presence of a stable environment (unchanging+ stable)
Parts of a homeostasis loop
Receptor, Control center, Effector
Receptor
Sensitive to a particular environmental change/stimulus
Control center
Receives and processes information from receptor and sends out commands
Effector
responds to command opposing the stimulus
set point
desired value
ex- Thermometer
receptor
ex-Thermostat
Control center
ex-Air condition
Effector
What is negative feedback
An effector activated by the control center opposes the original stimulus
What is feedback
Occurs when receptor stimulation leads to a response that changes the environment at the receptor
Key notes of negative feedback
Try’s to minimize change
Brings us back to homeostasis by combatting with a response
long term control
Positive feedback
an initial stimulus signals a response that exaggerates or enhances the change/stimulus in the original conditions
key notes of positive feedback
extreme responses
dangerous or stressful process is to be done quickly before returning to homeostasis
Short term
Childbirth
Positive feedback
shivering occurs
Negative feedback
Sweating increases
Negative feedback
Blood clotting
Positive feedback
Blood pressure falling
Negative feedback
Suckling milk
Positive feedback
insulin release to blood sugar
negative feedback
Blood vessel
Receptor
Platelets
Control center
Chemicals released
Effector
What is work
Movement of an objct
What is energy
Capacity to perform work
What is kinetic energy
Energy that can transfer to another object to perform work
What is potential energy
energy stored that has the potential to perform work
What is true about energy
energy is not 100% efficient
energy is lost as heat
What is activation energy
The amount of energy required to start a reaction
What are enzymes
A protein that lowers activation energy to promote chemical reactions by denaturing
What is a catalyst
Compounds that speed up a chemical reaction
What are organic compounds
Compounds that always contain carbon and hydrogen as their primary structural ingredient
Example of organic compound
Carbs, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids
What are inorganic compounds
Compounds that don’t contain carbon or hydrogen as their primary structural ingredient
what are examples of an inorganic compound
CO2, H2O, O2, H+, OH-, and NaCl
What are macromolecules
large molecules made of monomer sub units (complex)
What are monomers
molecules that can be bonded to form a polymer
H2O properties
Lubrication, Chemical rxn, high heat capacity, solvent
What is a cation
positive charged ion (ex- Na)
What is an anion
negative charged ion (ex- Cl)
is H2O polar or non-polar
polar
What is an electrolyte
a soluble inorganic compound who’s ions will conduct an electrical current in solution (ex- NaCl)
What is pH
Hydrogen ion (H+) concentration in body fluids which ranges from acidic to basic
What is an acidic solution
A solution that has a pH below 7 —> more H+ than OH- (limes)
What is a basic solution
A solution above a pH of 7 —> more OH- than H+ (ex- bleach)
What is a neutral solution
A solution that has a pH of 7 —> equal parts OH- and H+ (ex- Water)
What is a buffer
Compounds that stabilize the pH solutions by removing or replacing H+ —> helps maintain pH within normal limits
What is carbohydrate
an organic molecule that contains C,H,O in a 1:2:1 ratio
What are monosaccharides
A simple sugar containing 3-7 carbon atoms (glucose, fructose)
What are disaccharides
Two monosaccharides formed together via dehydration synthesis (sucrose)
What are polysaccharides
More complex carbohydrates adding mono/di saccharides to a structure (glycogen)
sterioids
large lipid molecules that share a distinctive carbon-ring framework
Cholesterol
important for plasma membrane and cell growth/division
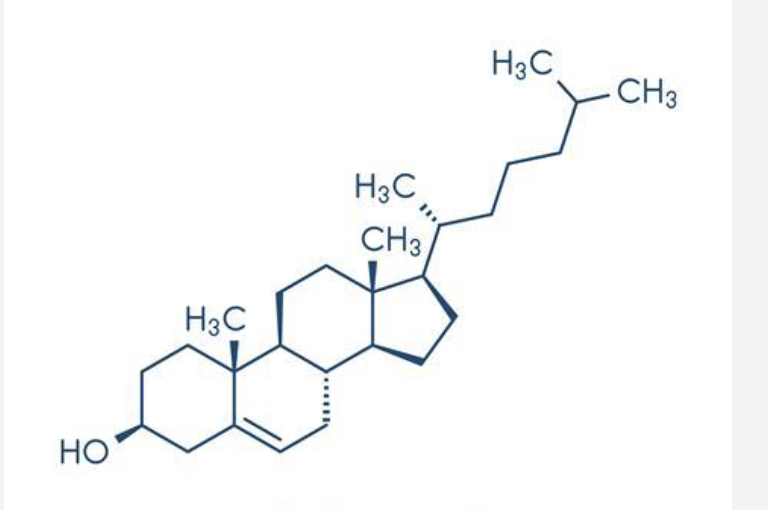
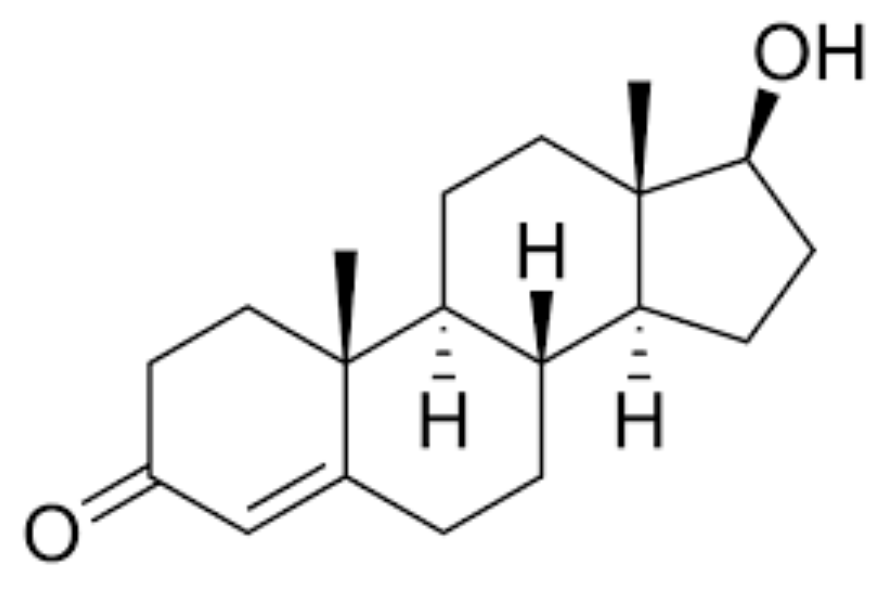
testosterone
steroid hormone which regulates sexual functions
Phospholipid
Phosphate group
non-lipid group
glycerol
fatty acid
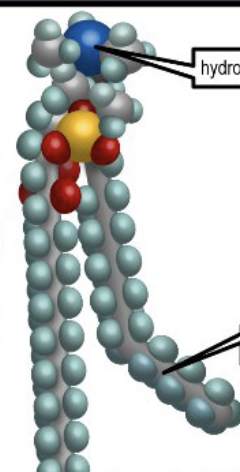
Glycolipid
Carbohydrate
Glycerol
Fatty acid
Glycerides
The result of a fatty acid attachment