Week 6
1/287
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
288 Terms
Midbrain, Pons, and medulla
What makes up the brainstem?
Cerebrum and diencephalon
What makes up the forebrain?
Cortex, basal ganglia, and the limbic system
What are the three major sections of the cerebrum?
Frontal, Parietal, occipital and temporal
What are the four lobes of the cortex?
Higher cognitive and motor functions (planning, problem-solving, decision making, and social behavior)
What is the function of the frontal lobe?
Processing and coordination
What is the function of the parietal lobe?
Visual processing
What is the function of the occipital lobe?
Auditory processing and memory emotions
what is the function of the temporal lobe?
Motor control and muscle tone
What is the function of the basal ganglia of the cortex?
Amygdala, Hippocampus and nucleus accumbens
What are the components of the limbic system?
Emotional processing
What is the function of the amygdala?
Memory
What is the function of the hippocampus?
Motivation and reward
What is the function of the nucleus accumbens?
Thalamus, hypothalamus, and pineal gland
What are the sections of the diencephalon?
Relay station and filter for sensory information
What is the function of the thalamus?
Control center for NS, Control body temp, sleep, hunger, and satiety
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
Circadian (melatonin)
What is the function of the pineal gland?
Passage of motor signals from and signals to the diencephalon/cortices and control of movement incl eyes
What is the function of the midbrain?
Passage of motor and sensory information, Respiratory control centers, and CN V
What is the function of the pons?
Passage for motor and sensory information, vital control center (HR, BP, respiration and GIT), CN Vl and Xll
What is the function of the medulla?
Fine-tunes movement, coordinates posture balance and gait
What is the function of the cerebellum?
Excite the motor system
The cerebellar cortex inhibits deep cerebellar structures. These deep structures do what?
ARAS
What functional unit of the brain can filter out distracting stimuli?
Cortex
Where would the ARAS functional unit project sensory information to?
Pain, touch, temperature, itch and proprioception
What are examples of somatic senses located everywhere in the body?
Vision, hearing, balance, taste, smell
What are the special senses?
Osmolarity, blood pressure and body temperature
What are some visceral senses?
Primitive beings
Crude awareness is defined as sensation reaching the thalamic area/ARAS with subconscious awareness. What types of organisms is this important for?
Free nerve ending, encapsulated, and sensory receptor cells
What are the three ways sensory nerves can be embedded?
Transduction
What term refers to incoming energy translation into electrical energy?
higher
The stronger the stimulus the (lower or higher) the AP frequency.
Mechanoreceptor
What is the most common type of sensory receptor class?
Trigger zone
Where do graded potentials initiate action potentials in the first order sensory neurons?
Ascending tracts
Sensory neurons form what in the spinal cord?
CN ganglion outside the brain
Cranial nerve sensory cell bodies are located where?
Glutamate
What is the neurotransmitter that conveys sound?
Special sense receptor cell
What is the carrier of touch, taste or smell to the first order neuron in the head?
Third order neuron
What part of the 3-order neuron chain is important because its terminal portion location will decide what is perceived?
Signals from a specific part of the body are always projected to the same location within its sensory cortex.
How does the brain know which body part was stimulated?
Head
What area of the body occupy the largest portion of the ARAS cortex?
Star-nosed mole and the eimers organ
What organ is the most powerful sensory organ in the whole animal kingdom and which animal does it belong to?
Hypothalamus
What area of the brain is considered the temperature control center?
Enzymatic and temperature sensitive functions
By keeping the body at the optimal temperature, it ensures that what is safeguarded ?
Vasodilation in skin, sweating or panting, metabolic rate reduction via thyroid gland, appetite reduction, and behavioral changes
What are some heat-loosing mechanisms?
Vasoconstriction, muscle shivering, brown fat, metabolic rate and appetite inc, and behavioral changes
What are some heat-conserving mechanisms?
Behavioral changes
What mechanism for heat conservation is most important for ectotherms and animals with low metabolism?
Pyrogens (bacterial toxins, interleukins etc)
What will cause fever?
PGE2
What main molecule will influence the body temperature set point?
Chill phase
During a fever, pyrogens are released (like PGE2) which will inc the set temperature inducing the hypothalamus to conserve heat in which phase?
Fever phase
What phase of the fever is characterized by a new body temperature set point being reached?
Pyrogens
The removal of what will lower the set point back to normal inducing the hypothalamus to lose heat in the crisis phase?
Pit organ
What organ of snakes contains thermoreceptors and is sensitive to infrared radiation?
Neuropathy
A disease or dysfunction of one or more peripheral nerves is termed what?
Myelopathy
A disease of the spinal cord is termed what?
Encephalopathy
General term for disease affecting the brain is termed what?
Neuritis
Inflammation of a nerve is termed what?
Anisocoria
Different sized pupils is termed what?
Mydriasis
Dilation of pupils is termed what?
Miosis
Constriction of pupils is termed what?
Opisthotonus
An abnormal dorsiflexion of the head/neck is termed what?
Decerebrate rigidity
An abnormal recumbency with opisthotonus and rigid extension of all 4 limbs is termed what?
Decerebellate rigidity
An abnormal position where there is opisthotonus and rigid thoracic limb extension and flexed pelvic limbs is termed what?
Schiff-Sherington posture
Parapalegia with extended thoracic limbs is termed what?
Astrocytosis
Increased size and number of astrocytes is termed what?
Axonotmesis
Axonial injury of a peripheral nerve in which there is degeneration of the part distal to the site of trauma, leaving the supporting framework intact and allowing for improved potential for regeneration and effective reinnervation is termed what?
Brain edema
Increases in tissue water within the brain resulting in an increase in brain volume is termed what?
Brain swelling
Marked and rapidly increasing blood volume in the brain is termed what?
Central chromatolysis
The dissolution of cytoplasmic Nissl substance in the central part of the neuronal body that results from injury to the neuron. Swollen cell body and nucleus is often displaced peripherally. This is termed what?
Cranium bifidum
A dorsal midline cranial defect through which meninges alone or meninges and brian tissue may protrude into a sac covered by skin is termed what?
Dysraphism
An abnormal seam or closure of the neuronal tube during development is termed what?
Ganglionitis
Inflammation of the peripheral ganglia is termed what?
Gemistocyte
A reactive, hypertrophied astrocyte that develops in areas of necrosis of CNS is termed what?
Gitter cells
What are macrophages that accumulate in areas of necrosis in the CNS termed?
Distended cytoplasm abundant with lipid containing material, peripherally placed nuclei.
What do gitter cells look like?
Hydranencephaly
A large fluid filled cavity in the area normally occupied by CNS resulting from abnormal development is termed what?
Hydrocephalus
Accumulation of excess CSF resulting from obstruction within the ventricular system associated with enlargement of any or all of the following: lateral ventricles, third ventricle, mesencephalic aqueduct, and fourth ventricle is termed what?
Leukoencephalitis
Inflammation of the white matter of the brain is termed what?
Malacia
Grossly detectable softening of CNS usually result of necrosis is termed what?
Meningomyelocele
A form of spina bifida in which meninges and spinal cord herniate through a defect in the vertebral column into a sac covered by skin is termed what?
Microglia
A resident macrophage of the CNS that arise from mesodermal stem cells of the yolk sac is termed what?
Endorphins
What are naturally occurring chemical s in the brain that help to reduce pain and improve mood by acting as natural painkillers?
Parasthesia
Abnormal sensations in the skin, often described as tingling, itching, or pins and needles is termed what?
Wind-up
A phenomenon where repeated, low-level pain stimuli can lead to an exaggerated response, due to the CNS becoming sensitized is termed what?
Internal Ophthalmoplegia
Which disease is characterized by iris sphincter muscle dysfunction and the inability to move pupil?
CN lll and aniscoria
What cranial nerve is affected and what clinical sign will be aparent?
External Ophthalmoplegia and CN lll
Which disease is characterized by the inability to move the eyes and what nerve is often associated?
Strabismus
The misalignment of eyes or abnormal eye position is termed what?
Oculomotor
Ventrolateral strabismus is associated with which cranial nerve?
Abducent
Medial strabismus is associated with which cranial nerve dysfunction?
Medial strabismus and abducens
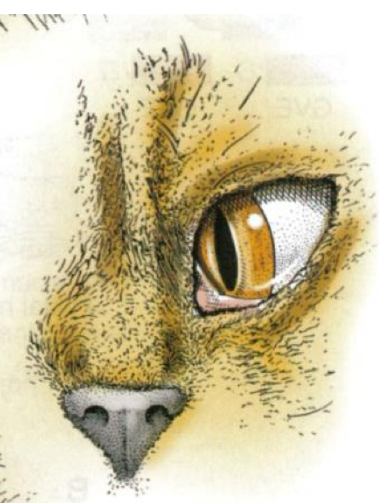
What is this and what nerve is affected?
4th nerve palsy and trochlear
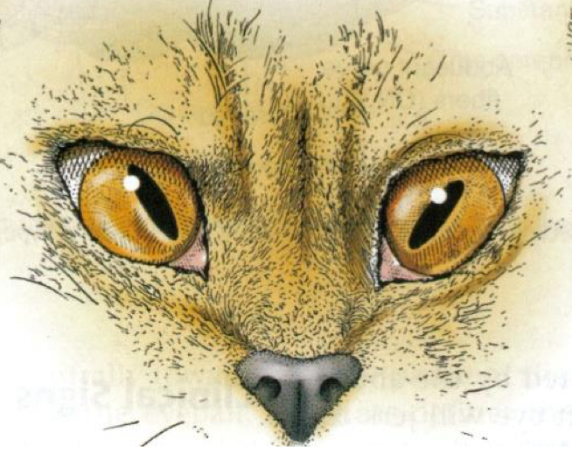

What is this and what cranial nerve is affected?
Ventrolateral strabismus and CN lll
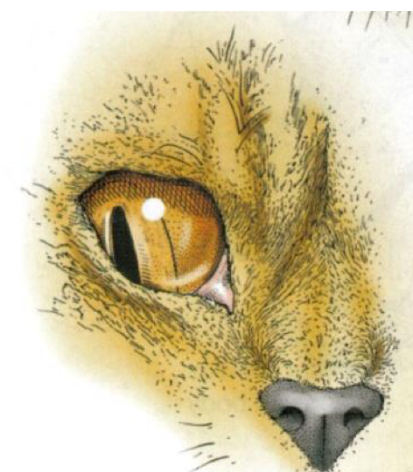

What is occurring here and which nerve is affacted?
Red is dead
When neuronal cells turn red, what can be deduced?
Degen and fragmentation of axon and myelin
Removal of axonal and myelin debris by phagocytosis
Regeneration of the axon if the endoneurium is intact
Remyelinization by schwann
What is the sequence of wallerian degeneration in the PNS?
Microgliosis and neuronophagia
How do microglia cells respond to cell injury?
Regulate blood brain barrier, provide structural and metabolic support to neurons, maintain neurotransmitter homeostasis, modulate synaptic formation and function, guide axon growth during development and form a glial scar after injury
What is the function of the astrocyte?
Act as brains primary resident immune cells and perform immune surveillance and phagocytosis
What is the function of the microglial cells?
Form barriers that regulate cerebrospinal fluid composition and flow.
What is the function of ependymal cells?
Make up the choroid plexus within the brain ventricles which produces the CSF
What is the function of the choroid plexus cells?
What neuronal change would