COPD, Cystic Fibrosis, Bronchiectasis
1/71
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
COPD (GOLD definition)
Heterogenous lung disease with chronic respiratory symptoms due to abnormalities of airway and/or alveoli that cause persistent progressive airflow obstruction
Chronic bronchitis, Emphysema
Types of COPD
Only during acute exacerbations and goes back to baseline
Are chronic bronchitis and emphysema reversible?
Male, Smoking, environmental exposure (smoke, dust, chemicals, recurrent respiratory infection), air pollution, biomass fuels, genetic factors
Risk factors of COPD
Emphysema
The destruction of alveolar walls and capillaries that results in large air spaces, impaired gas exchange, and air trapping on expiration are signs of?
Chronic bronchitis
Fibrosis and thickening of the bronchiolar walls that result in narrow airways are signs of?
Infection (viral more common)
Most common trigger for COPD exacerbations
Antibiotics (Augmentin, azithromycin, Doxy, moxifloxacin, levofloxacin)
With any COPD exacerbation, what are we giving them prophylactically?
Chronic, persistent productive cough, SOB, dyspnea worse on exertion
Clinical findings of COPD
Loss of air space, loss of recoil, Easy to get air in but not out, acinus
Emphysema is characterized by
In the large air ways mucus hypersecretion, inflammation; Small airways peribrochiolar fibrosis, airway obstruction, edema, cyanotic picture
Chronic bronchitis is characterized by
Mucupurlent
What does the mucus look like in blue bloaters?
cyanosis, pulmonary HTN, and peripheral edema
What clinical symptoms are specific to chronic bronchitis?
Respiratory acidosis with metabolic alkalosis comp (high CO2, high Bicarb)
How’s your blood gas look with COPD exacerbation
Hemoglobin/Hematocrit elevated (maybe)
How’s your CBC look with a COPD excerbation?
TLC elevated, FVC normal (unless severe), Decreased FEV1/FVC
How’s that spirometry look in COPD (Hint: its obstructive)?
Chest CT
What’s the imaging of choice of COPD?
Hyperinflation, flattened diaphragm, vertically oriented cardiomegaly
On an AP view CXR positive for COPD what are our red flags?
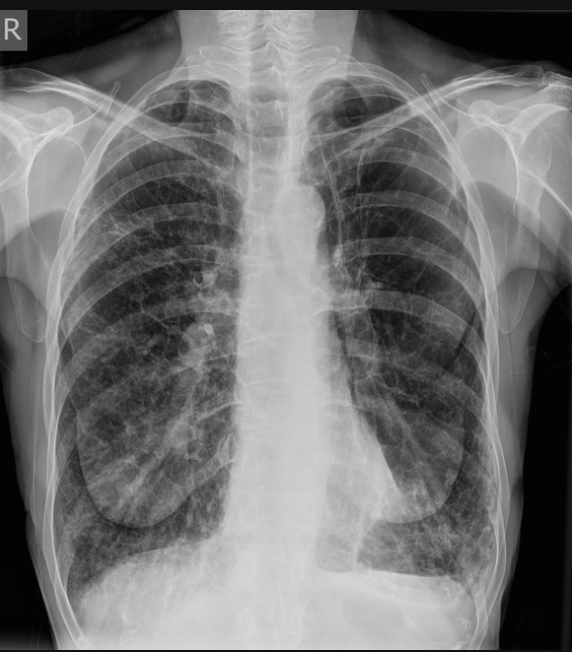
Barrel chest, increased retrosternal space, increased AP diameter, bronchovesicular markings
On a lateral view CXR positive for COPD what are some red flags?
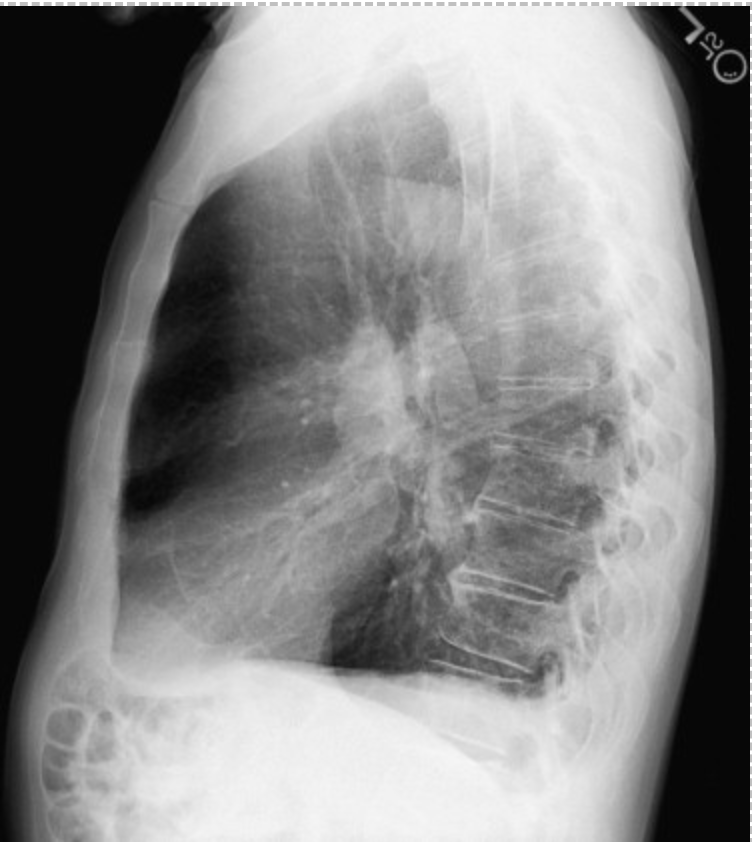
bronchial wall thickening, scarring, increased broncovesicular markings
What does a CT chest show in chronic bronchitis?
alveolar destruction, airspace enlargement
What does a CT chest show in emphysema?
Chronic bronchitis (leads to P pulmonale)
In what type of COPD would it be useful to get a Doppler echocardiogram?
Asthma, URI, pneumonia, bronchiectasis, CHF, AMI
Differentials for COPD
ABE, mMRC, COPD assessment test (CAT)
What are some assessment tools we can use to stage COPD (not in exacerbations)
Mild (GOLD I)
What stage has an FEV1 greater than or equal to 80%?
Moderate (GOLD II)
What stage has an FEV1 between 50 and 80%?
Severe (GOLD III)
What stage has an FEV1 between 30 and 50%?
Very severe (Gold IV)
What stage has an FEV1 lower than 30%?
SEVERE (E)
If a COPD patient has had 2+ moderate exacerbation or has been hospitalized in the past year, that is a straight shot to which GOLD group?
ICS-LAMA-LABA, SABA PRN
If your severe (GOLD Group E) COPD homie has been hospitalized or has high eosinophils what’s our treatment plan?
LAMA-LABA, SABA PRN
If your severe (GOLD Group E) COPD homie has NOT been hospitalized and does NOT have elevated eosinophils what’s our treatment plan?
oxygen therapy
What is the only COPD intervention with evidence of actually improving resting hypoxemia, leads to prolonged survival, decreased hospitalizations, and increased QOL?
Tiotropium (LAMA)
1st line treatment for COPD
ICS-LABA
What combination therapy can reduce COPD exacerbations?
ICS
What treatment modality decreases symptoms in COPD but has no effect on mortality
Oral/IV steroids
What medication can we use ONLY for COPD exacerbation?
Theophylline
4th line for COPD (LAST RESORT)
Supplemental O2 (probs BiPAP maybe CPAP) → ABCs
71 y/o male presents to the ER for increased SOB over the past week. History is positive for COPD and CKD. Patient also reports yellowish-brown sputum. Denies chest pain, LE swelling, fever, and chills. Vitals are stable with an exception of RR 27 and SPO2 at 78%. What is step one in treating this patient?
EKG, CBC, CMP, ABG, VBG, CXR
So we got our COPD patient on supplemental oxygen, what are some next steps?
SABA-SAMA, systemic steroids and antibiotics
Okay so homie is definitely having an COPD exacerbation what meds are we getting on board?
Admit the patient
Okay so we go check on our COPD homie, he has failed the walk of life and has gone from A&O4 to A&O2. He lives alone and has a history of poor compliance. What is the next step?
Lung volume reduction surgery, transplant
What surgeries can provide modest (TBH they’re not great) improvements in the treatment of COPD?
Palliative care (survival ~ 4 yrs)
If our COPD patient’s FEV1 is less than 1L who should we probably get on board?
young patients (under 50 think alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency), frequent exacerbations, severe/rapid progression, symptoms are worse than severity, home oxygen therapy, comorbidities
When do we refer for COPD
pneumonias, atrial dysrhythmias, PEs, cor pulmonale, spontaneous pneumo
Complications of COPD
Quit smoking (a pack a day?), avoid irritants
Prevention of COPD
Cystic fibrosis (CF)
A white people disease that it the result of an abnormally functioning chloride channel leading to altered CL- and H2O movement across apical membranes and is autosomal recessive.
Dried mucus in all exocrine glands
What leads to the systemic dysfunction in CF?
obstruction of small and medium airways, medium for bacterial growth
What issues does the mucus of CF lead to in the lungs?
Hx of chronic lung disease (bronchiectasis), pancreatitis, infertility
Patients with ______, ______ and _________ should get screen for CF
sweat test
A patient presents to the clinic with a cough with sputum production and blood. They say they can’t exercise like they use to and are constantly on medications for chronic sinusitis and abdominal pain. Vitals are stable with the exception of a low BMI. On a physical exam you note digital clubbing, increased AP chest diameter, apical rales and hyperresonance to percussion. What diagnostic test is 1st line for what we’re all thinking
hypoxemia, Comp respiratory acidosis
As CF progresses, how’s that blood gas gonna look?
Low FVC, Low FEV1, Low FEV1/FVC
How’s our PFTs/spirometry look in CF?
Chest CT
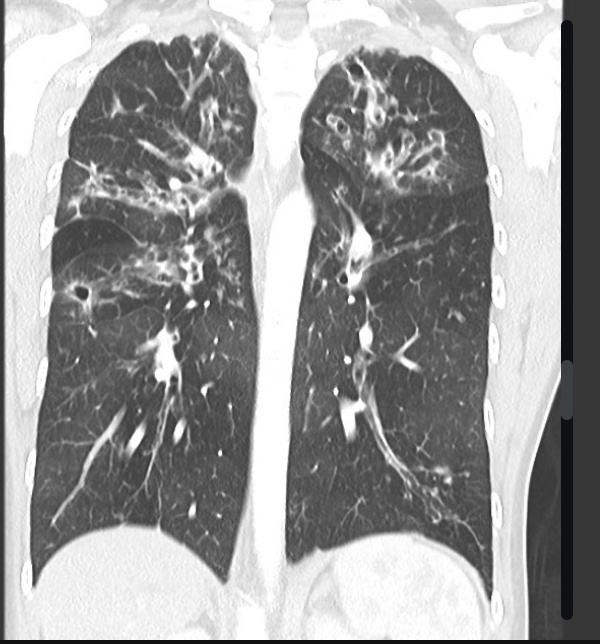
What is the imaging of choice for CF?
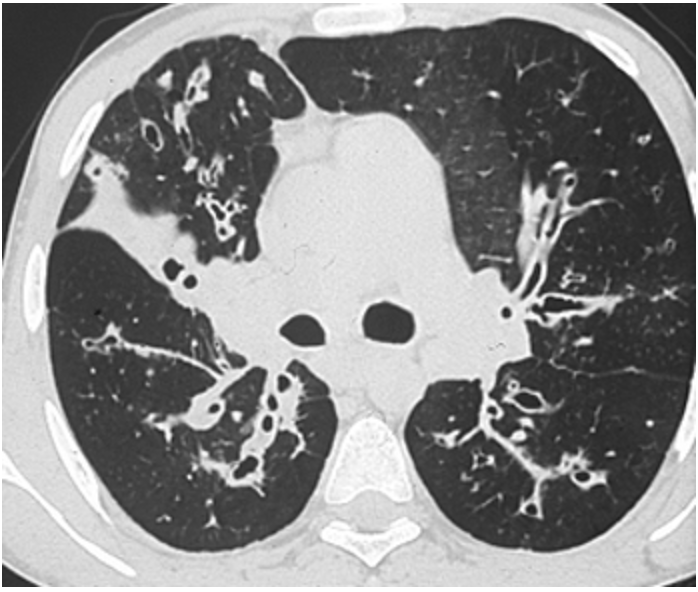
hyperinflation, peribronchial thickening, mucus plugging, small rounded peripheral opacities, focal atelectasis, large airway dilations
What’s a chest CT going to show cystic fibrosis?
2 positive sweat test on 2 different days (if negative get genetic testing)
To diagnose CF what do you need?
Refer to CF center, CFTR modulators, Airway clearance, inhaled hypertonic solutions, Abx, inhaled bronchodilators
How are you treating CF?
Median expected age is 50, lung transplant is the only option
Prognosis for CF
Bronchiectasis
The PERMANENT dilation of the bronchi due to persistent inflammation, most common complications of chronic bronchitis and is associated with bronchiolectasis (dilation of the broncioli)
release of enz from bacteria/leukocytes, mechanical pressure
What causes the inflammation that leads to dilation of the airways in bronchiectasis/bronchiolectasis?
saccular/cystic dilation
How do the larger bronchi look in bronchiectasis
Cylindrical dilation
How do the smaller bronchi look in bronchiectasis
bronchiectasis
A 55 y/o female presents to the ER with a chronic cough with copious purulent and bloody sputum. She reports that she has loss 20 lbs without trying and pleuritic chest pain. On a physical exam you note her breath STANK and crackles/rales in the bases of the lungs. Labs are stable with the exception of a decreased HGB/HCT. What are we thinking team?
CT chest
What is the diagnostic test of choice for bronchiectasis?
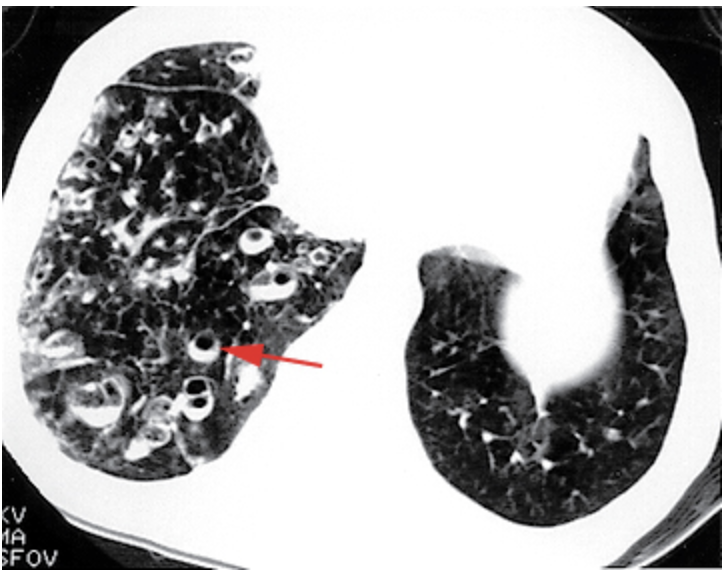
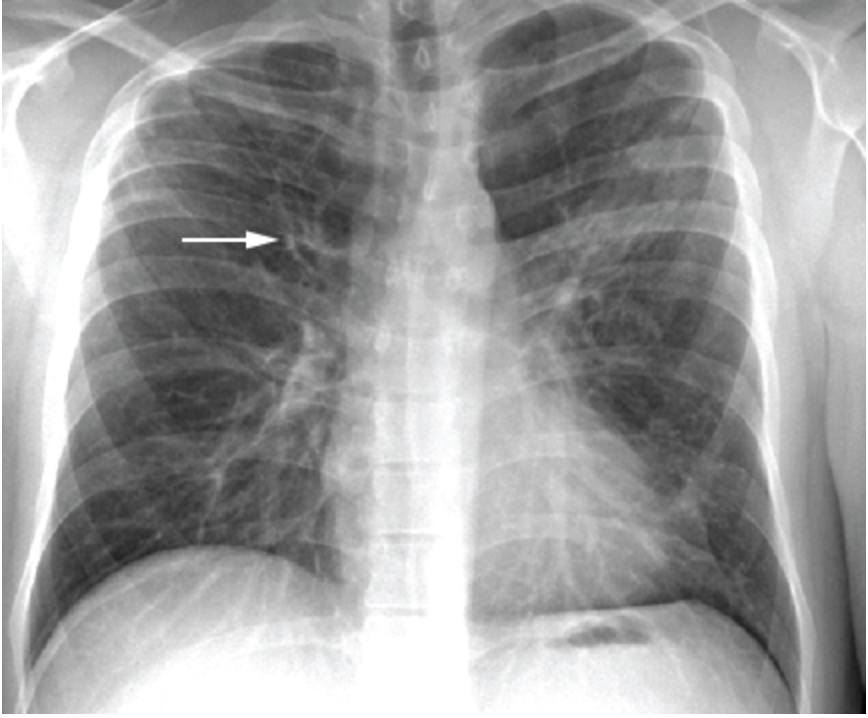
dilated and thickened bronchi, “tram tracks”
What might you see on a CXR for bronchiectasis
H. influenza (others are Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Strep pneimonia, staph A)
Most common bacterial infection of bronchiectasis
Pseudomonas
Which type of bronchiectasis is more severe
control active infections, decrease microbial load, improve secretion clearance
Goals in managing bronchiectasis
Antibiotics (amoxicillin, augmentin, doxy, azithromycin, fluoroquinolone)
Treatment plan for bronchiectasis → to control infections and reduce microbial load
chest physiotherapy, postural drainage, chest percussion, inhaled bronchodilators
Treatment plan for bronchiectasis → to improve secretion clearance
Chest bronchoscopy (get up in there), surgical resection
Other ways to treat bronchiectasis
hemoptysis, cor pulmonale, visceral abscesses due to bacterial seeding
Complications of bronchiectasis