Glandular Epithelium
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
merocrine
mode of secretion in which the secretory product is delivered to the apical domain of the cell within vesicles, which release their contents via exocytosis
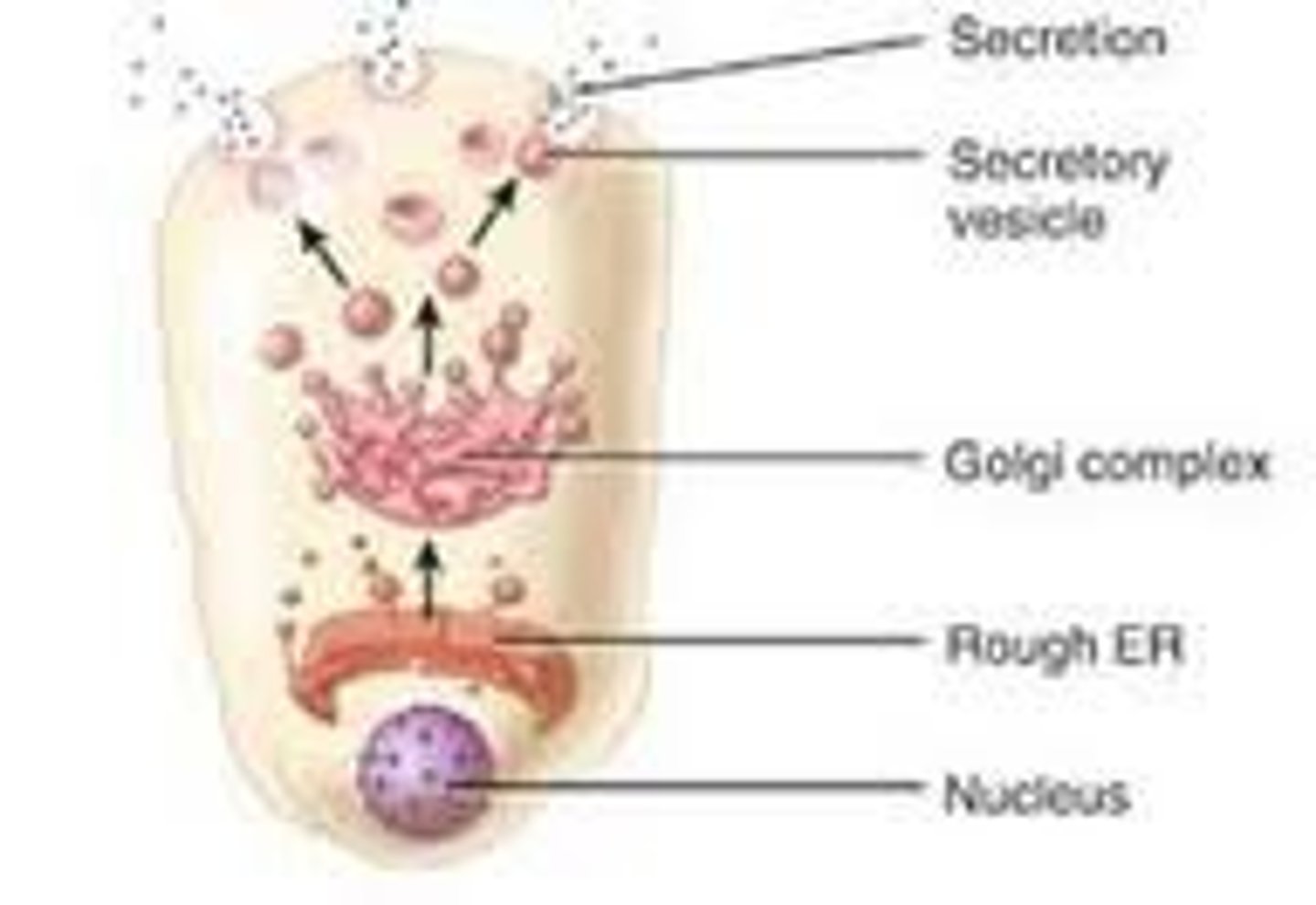
true
True or false: With merocrine secretion, none of the cell itself is lost or part of the secretion.
apocrine
mode of secretion in which the secretory product accumulates in the apical portion of the cell (in vesicles) and the tip of the cell is lost during secretion
false
(the tip of the cell becomes part of the secretion)
True or false: With apocrine secretion, none of the cell itself is lost or part of the secretion.
holocrine
mode of secretion in which the entire secreting cell, along with its accumulated secretory product, forms the secreted matter of the gland
false
(the WHOLE cell is the secretion)
True or false: With holocrine secretion, none of the cell itself is lost or part of the secretion.
unicellular
refers to a gland in which single secretory cells are distributed in a covering epithelium among other non-secretory cells; always secrete directly onto a surface, never into a duct
**main example is goblet cells
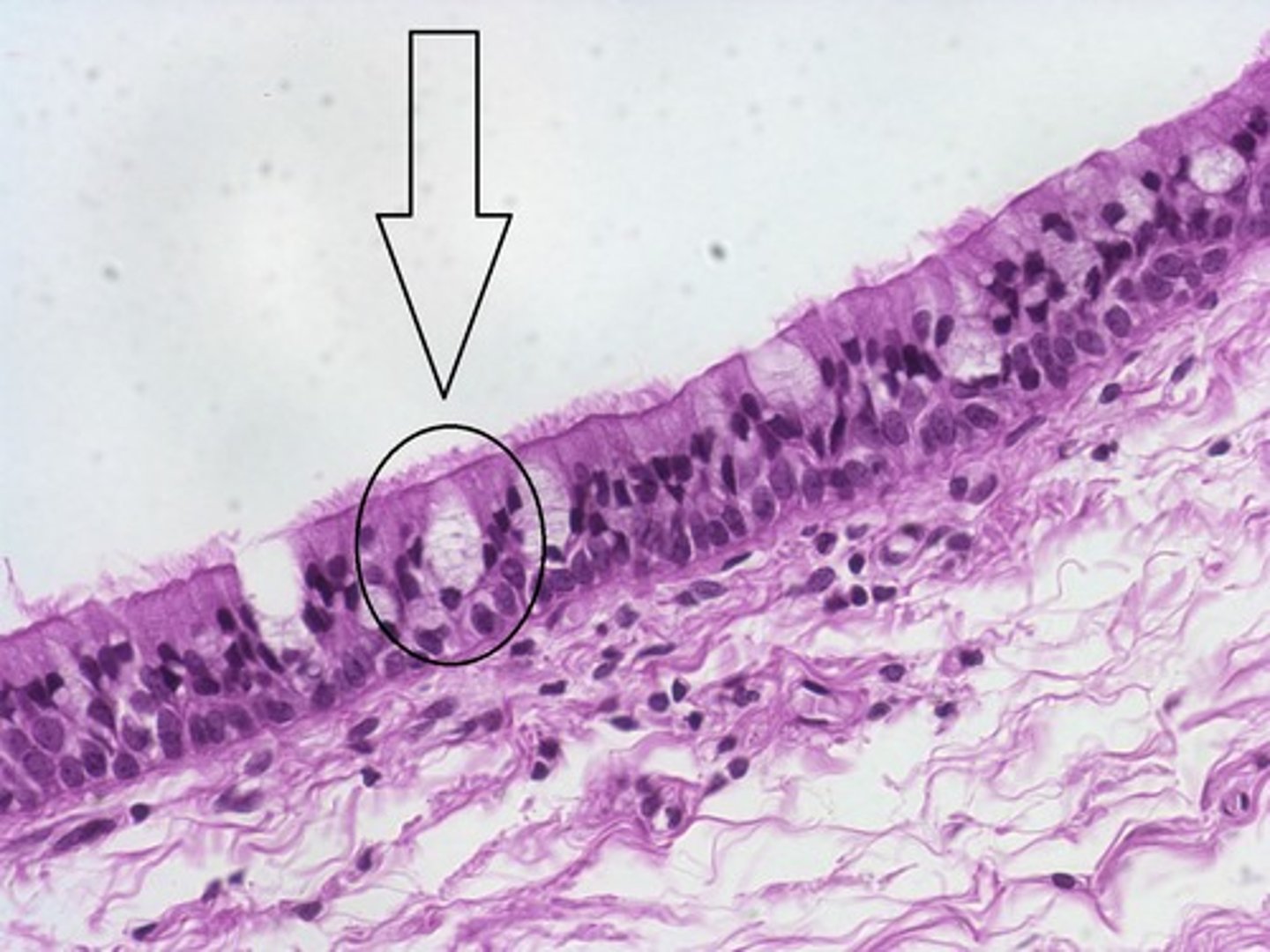
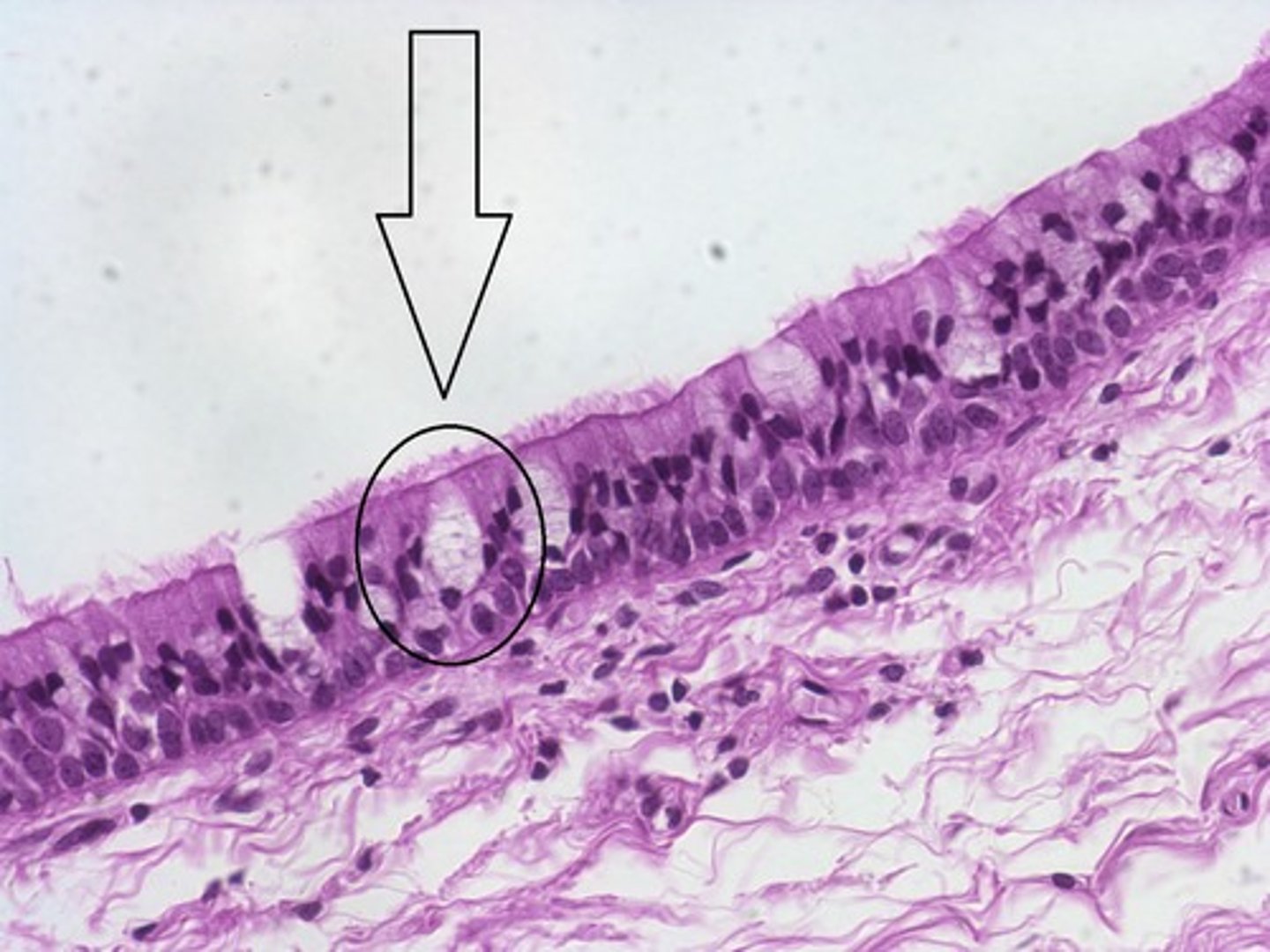
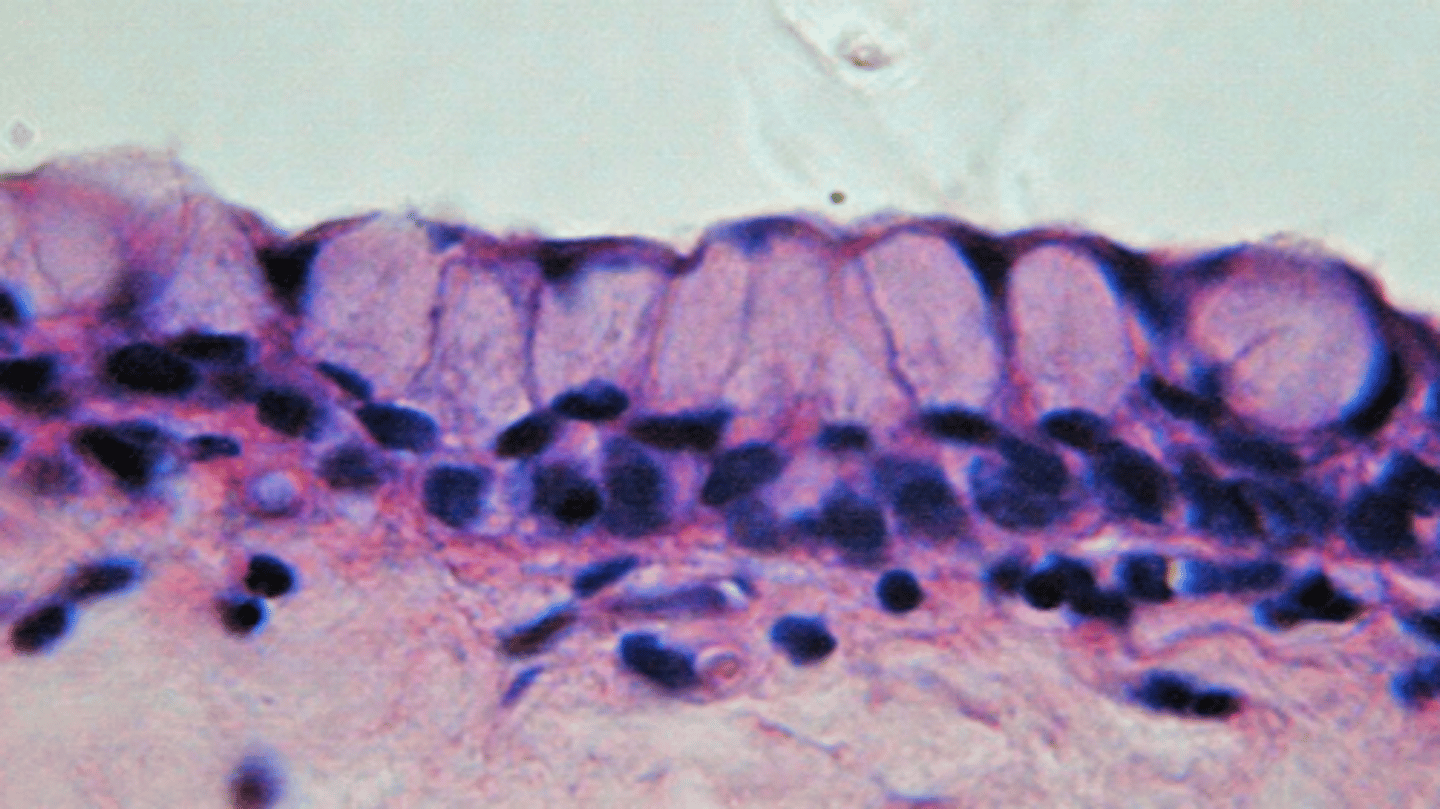
goblet cell
columnar-shaped, mucus-secreting cell that is always positioned among other columnar epithelial cells (either simple, pseudostratified, or stratified)
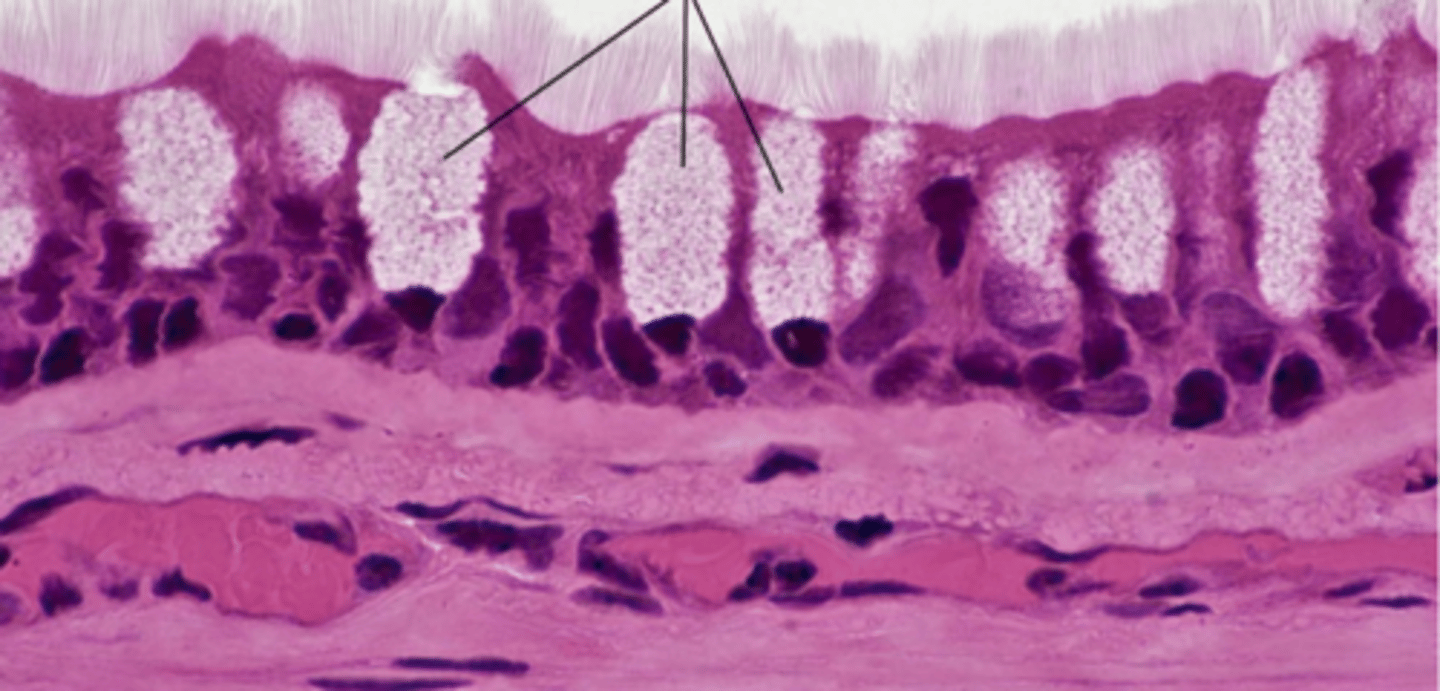
goblet cells
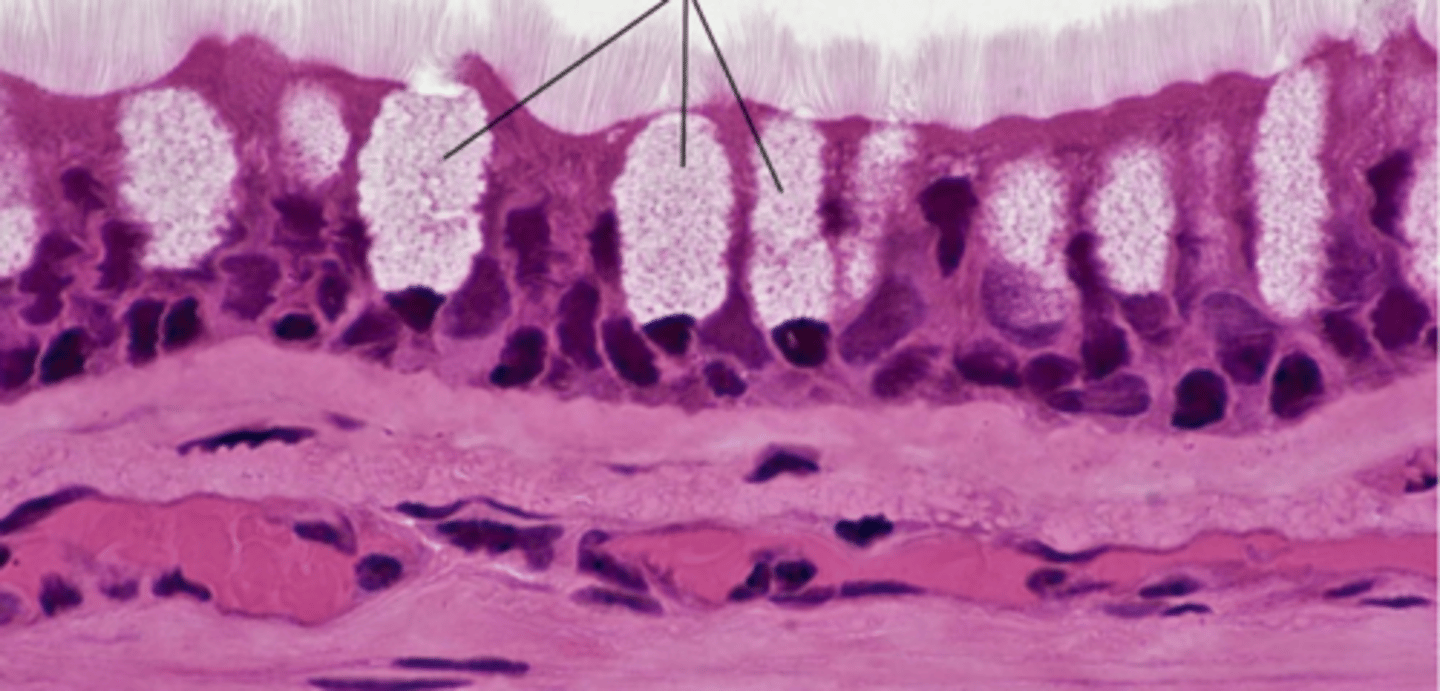
goblet cells
goblet cells
goblet cells
columnar
In what SHAPE of epithelial cells are goblet cells found?
mucus
What do goblet cells produce?
PAS
With regular H&E staining, mucus is not stained very well and goblet cells look empty. Therefore, what can we use to stain mucus bright red?
conjunctiva in/near the fornix, intestines, parts of respiratory tract
Where are goblet cells found in the body?
stratified columnar
Goblet cells in the eye are specifically found in the portions of conjunctiva that consist of what classification of epithelium?
makes mucin layer of tear film
Why are goblet cells so important for the eye?
merocrine
What kind of secretion do goblet cells use under baseline conditions?
apocrine
What kind of secretion do goblet cells use during times of accelerated secretion?
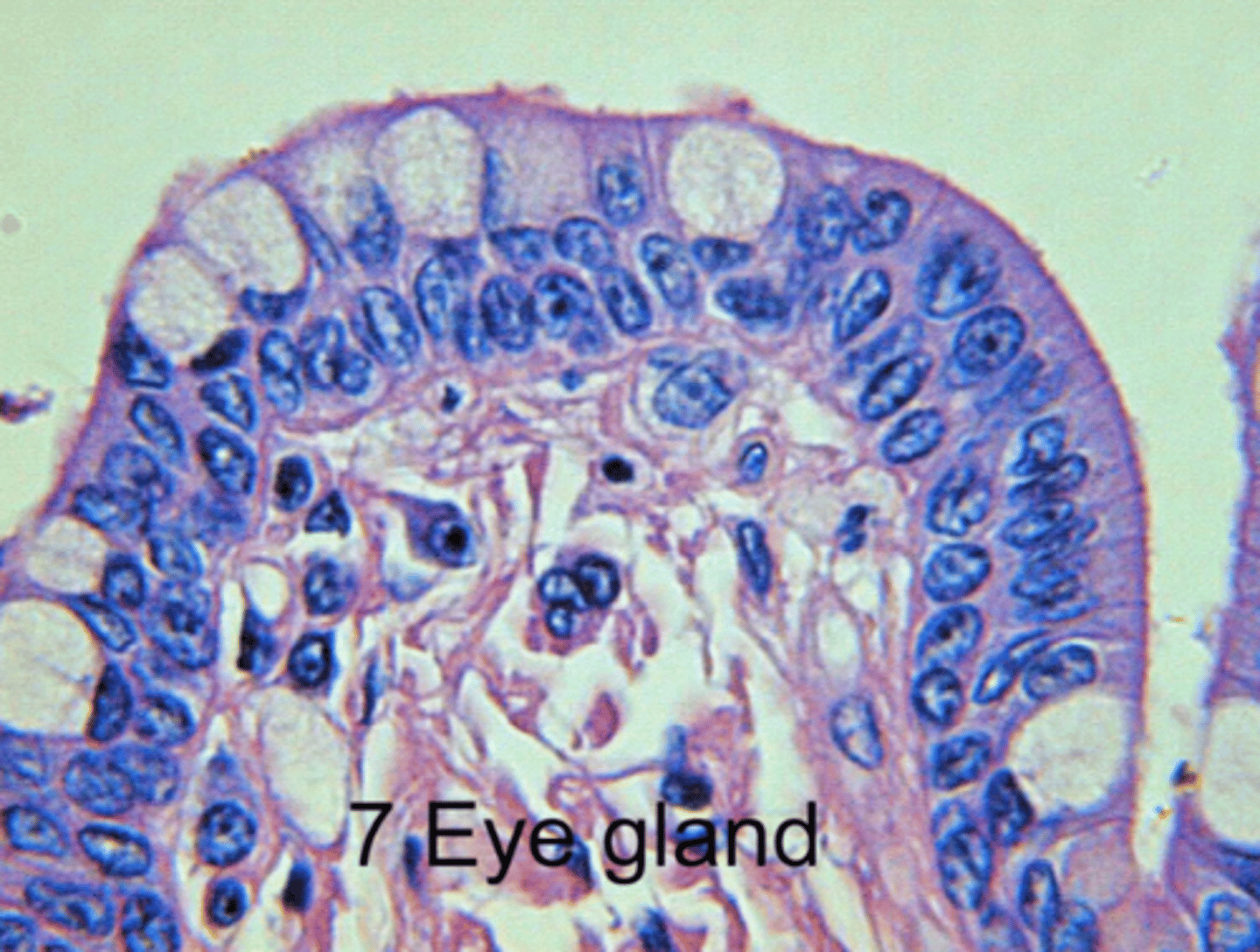
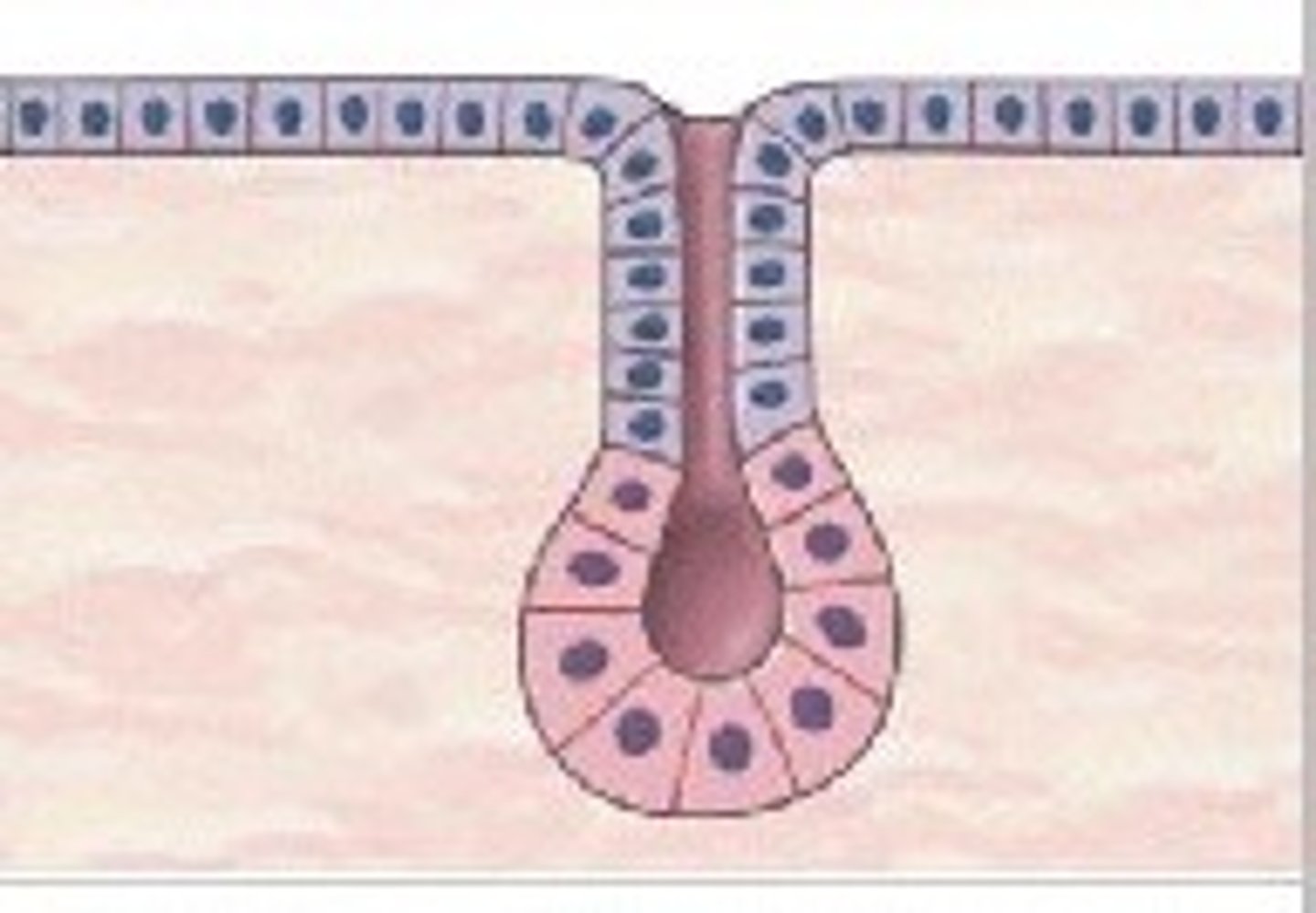
multicellular
refers to a gland that is composed of more than one secretory cell (usually lots); they usually, but don't always, secrete into a duct
stroma
connective tissue that supports an organ/gland; usually contains larger blood vessels
capsule
part of the stroma of most organs that surrounds the outside and basically holds the organ together
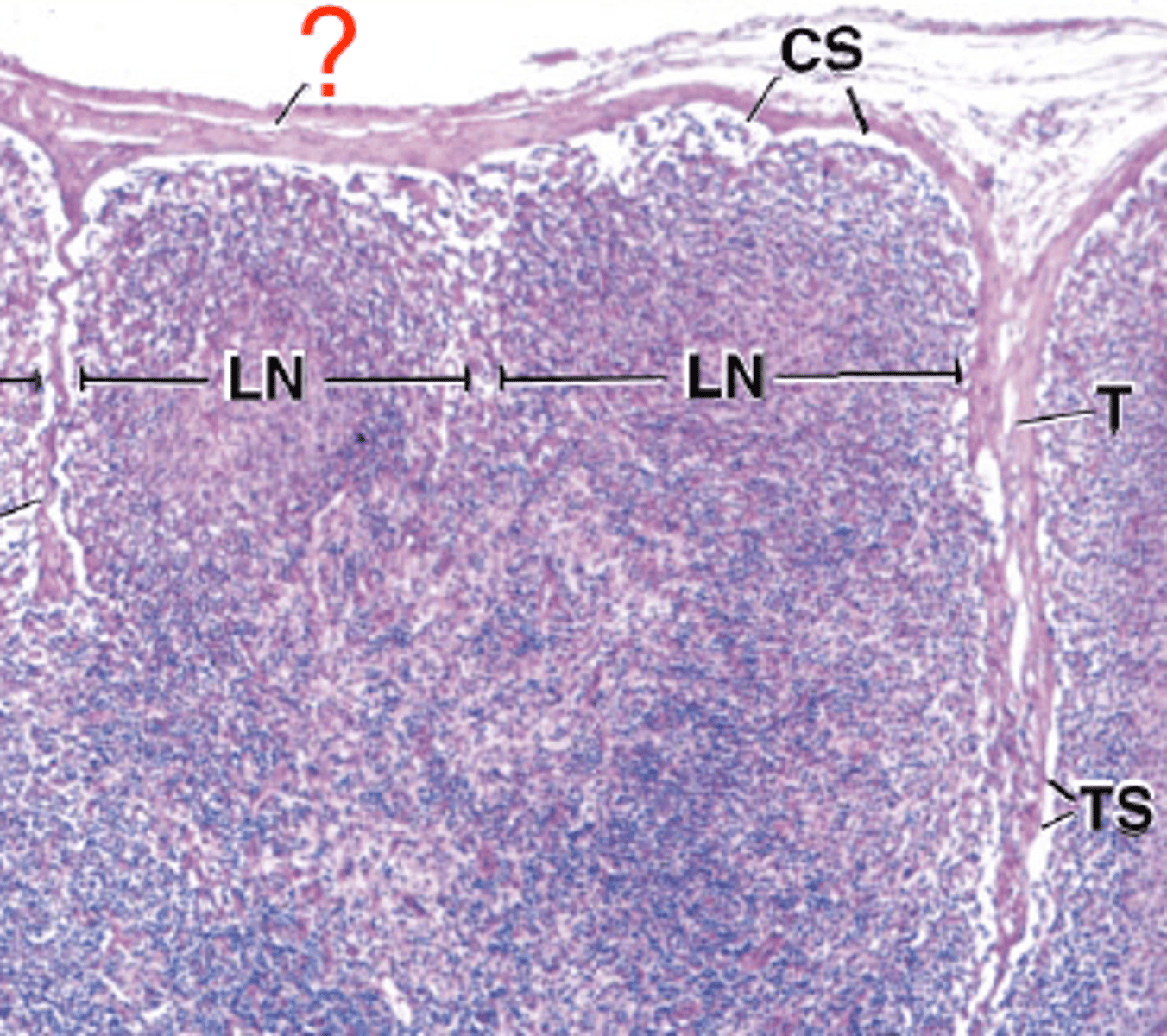
septa
connective tissue structures that extend into the interior of an organ/gland from the capsule and separates the parenchyma into lobules
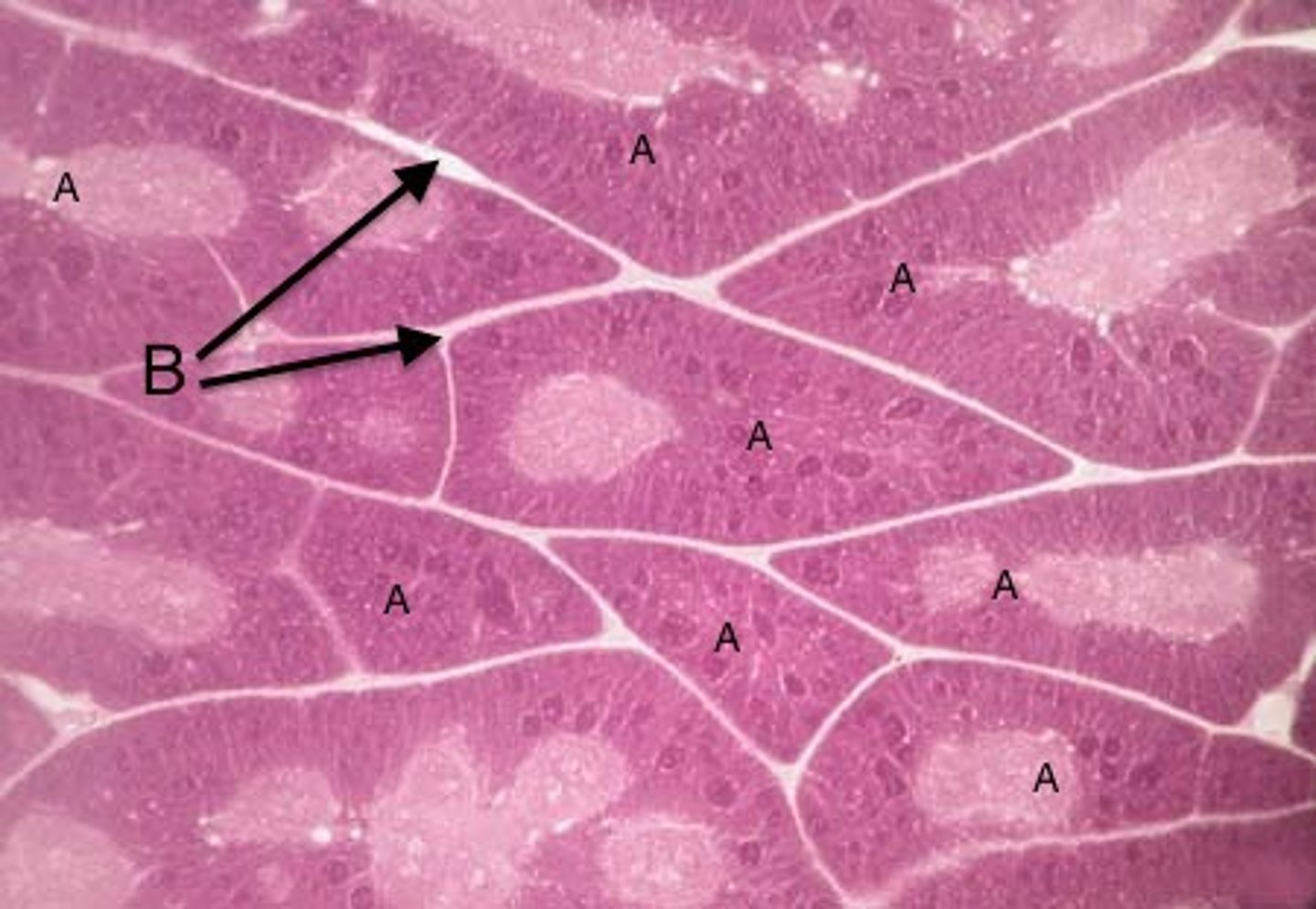
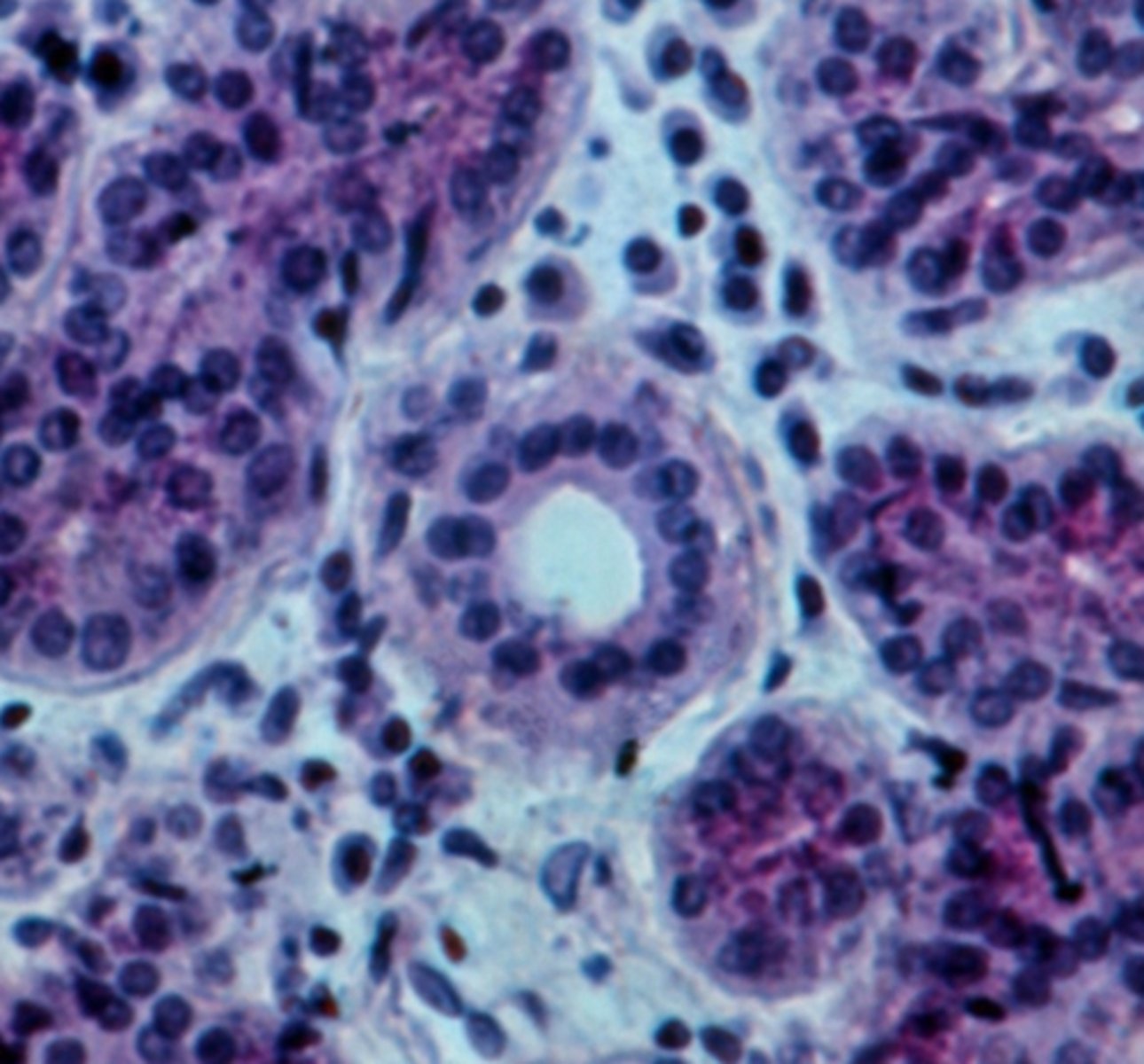
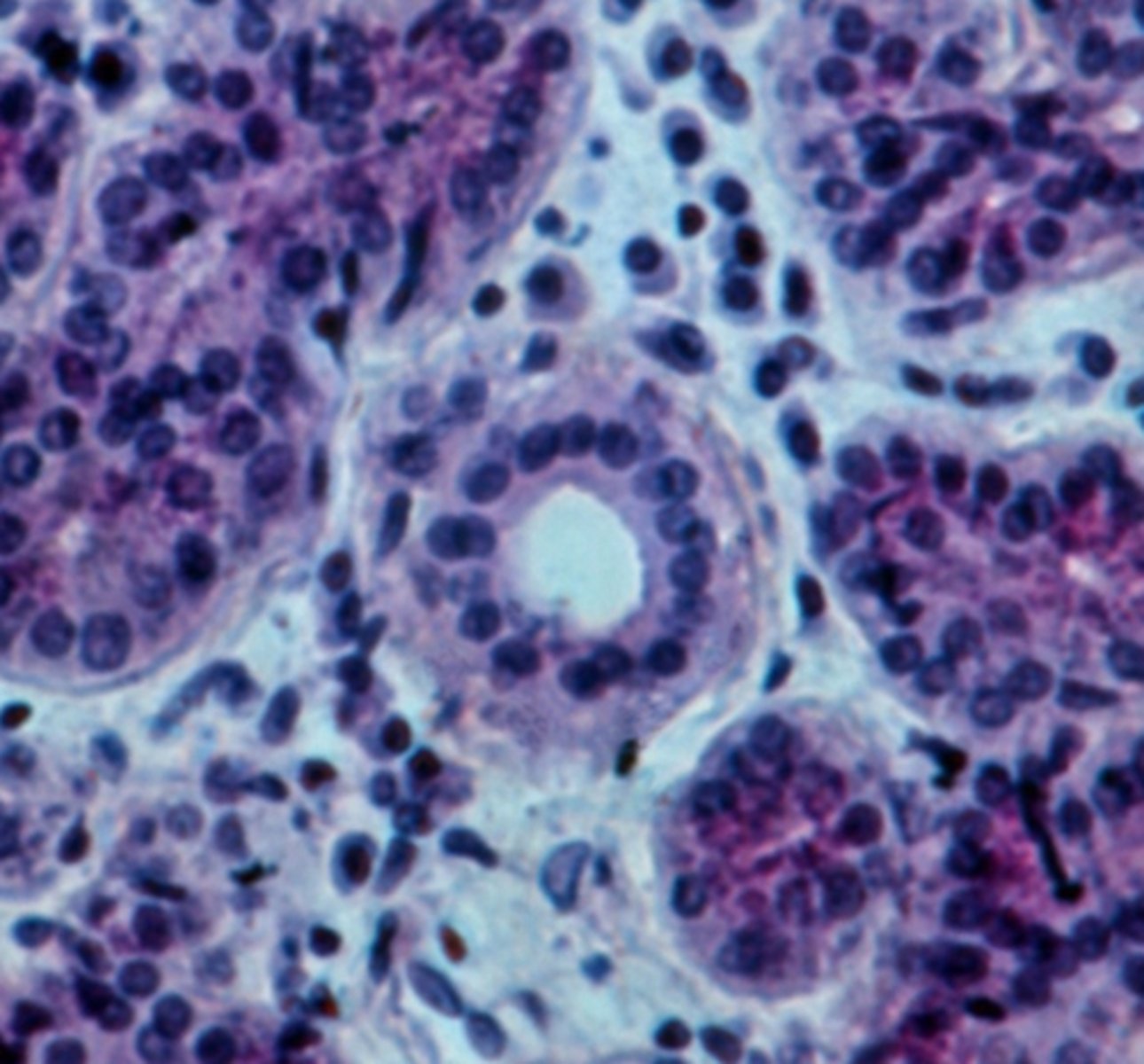
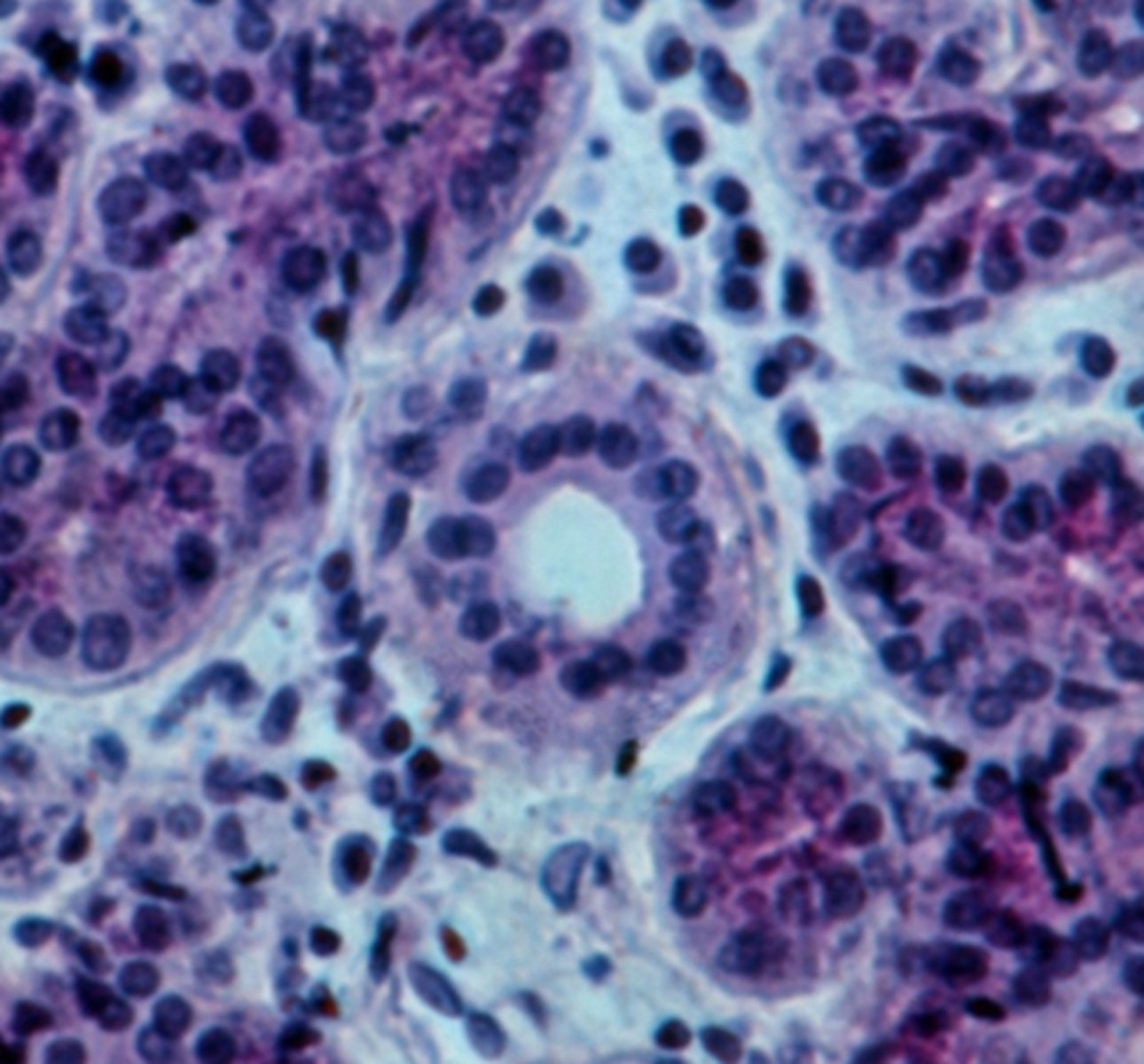
intercalated ducts
ducts that are the beginning of the duct system in parenchyma of exocrine glands; attach directly to the secretory elements
true
True or false: Intercalated ducts attach directly to the secretory elements.
simple cuboidal
The walls of intercalated ducts usually consist of what classification of epithelium?
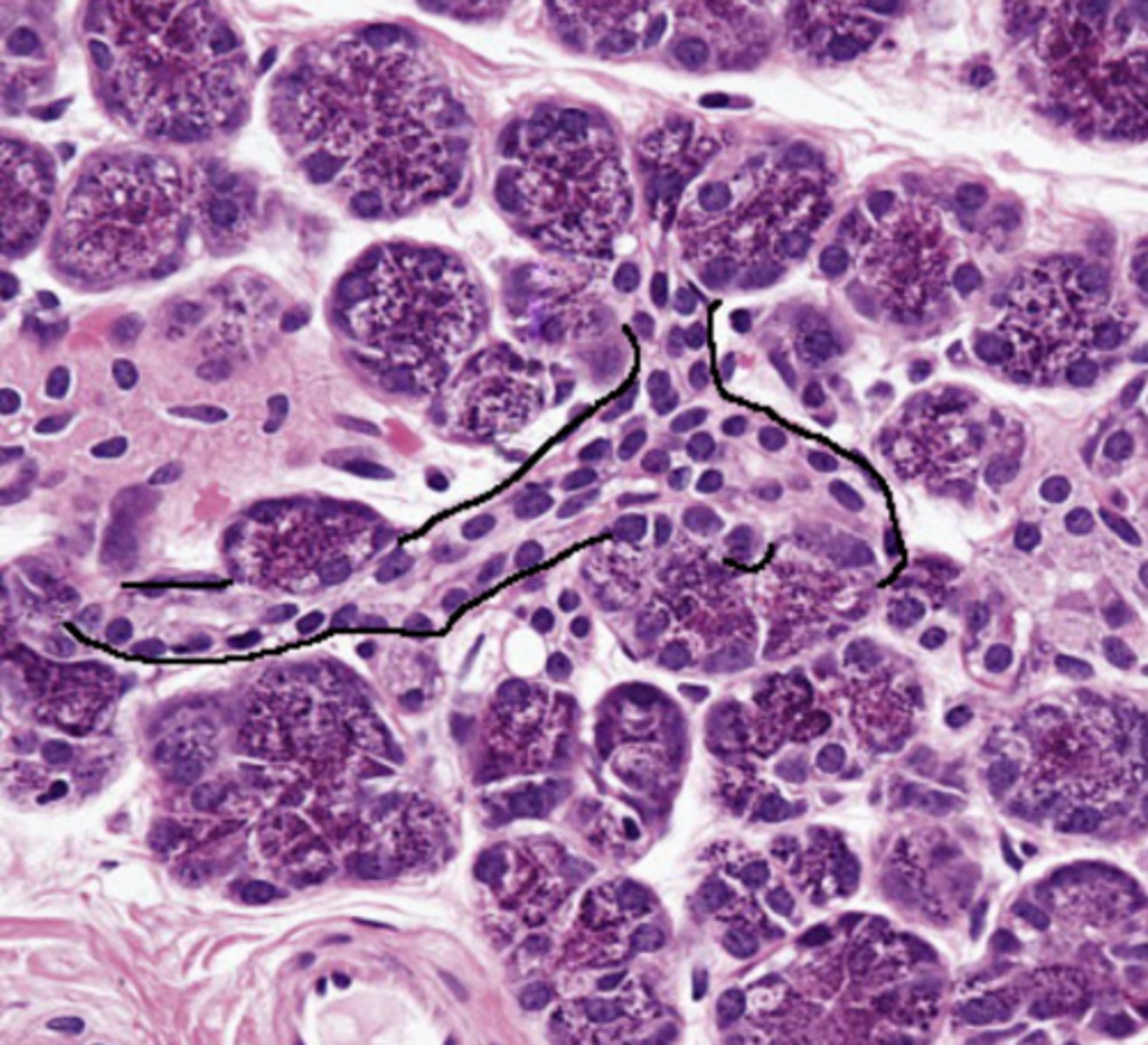
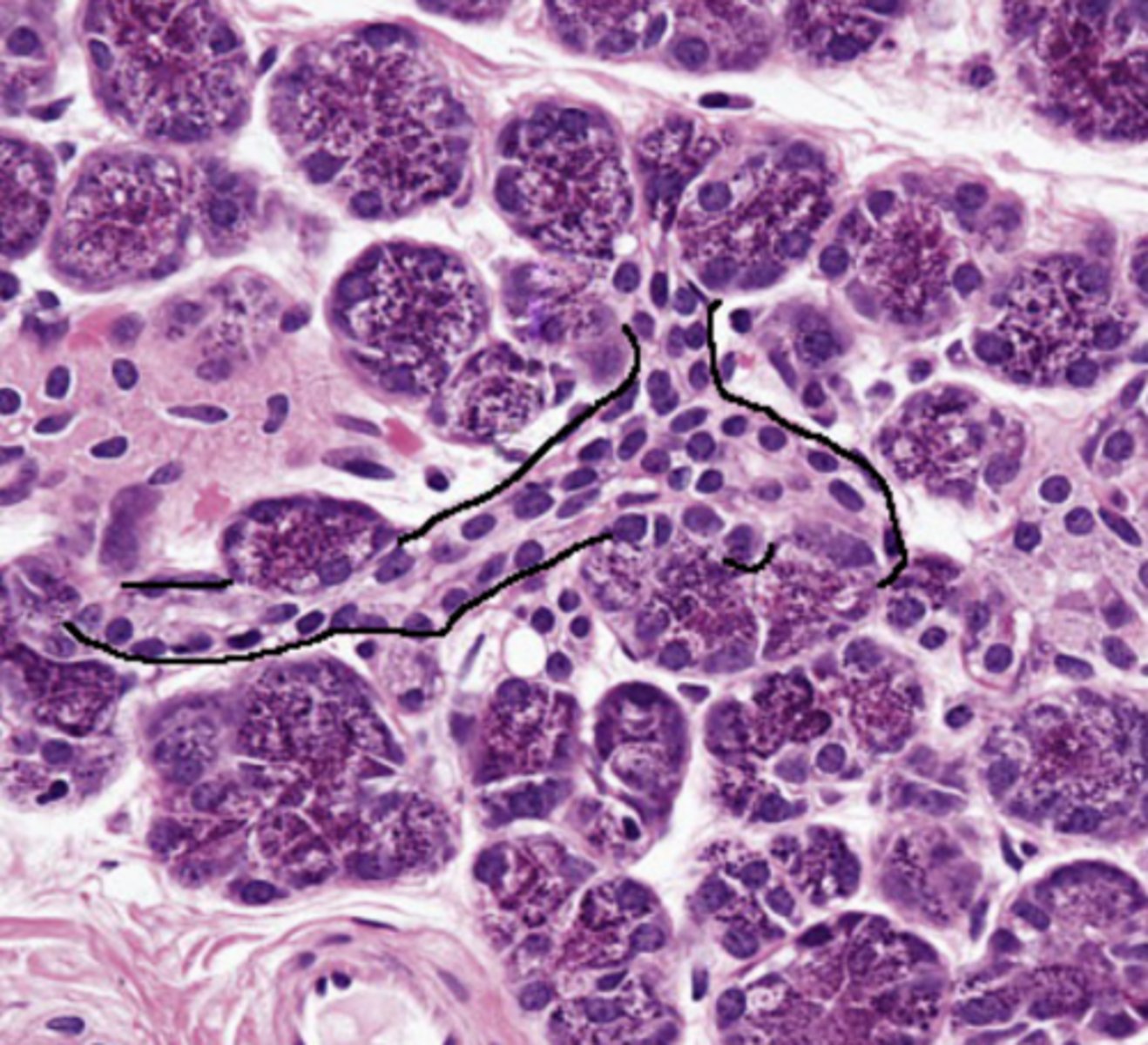
intercalated duct, simple cuboidal
type of duct + classification of epithelium
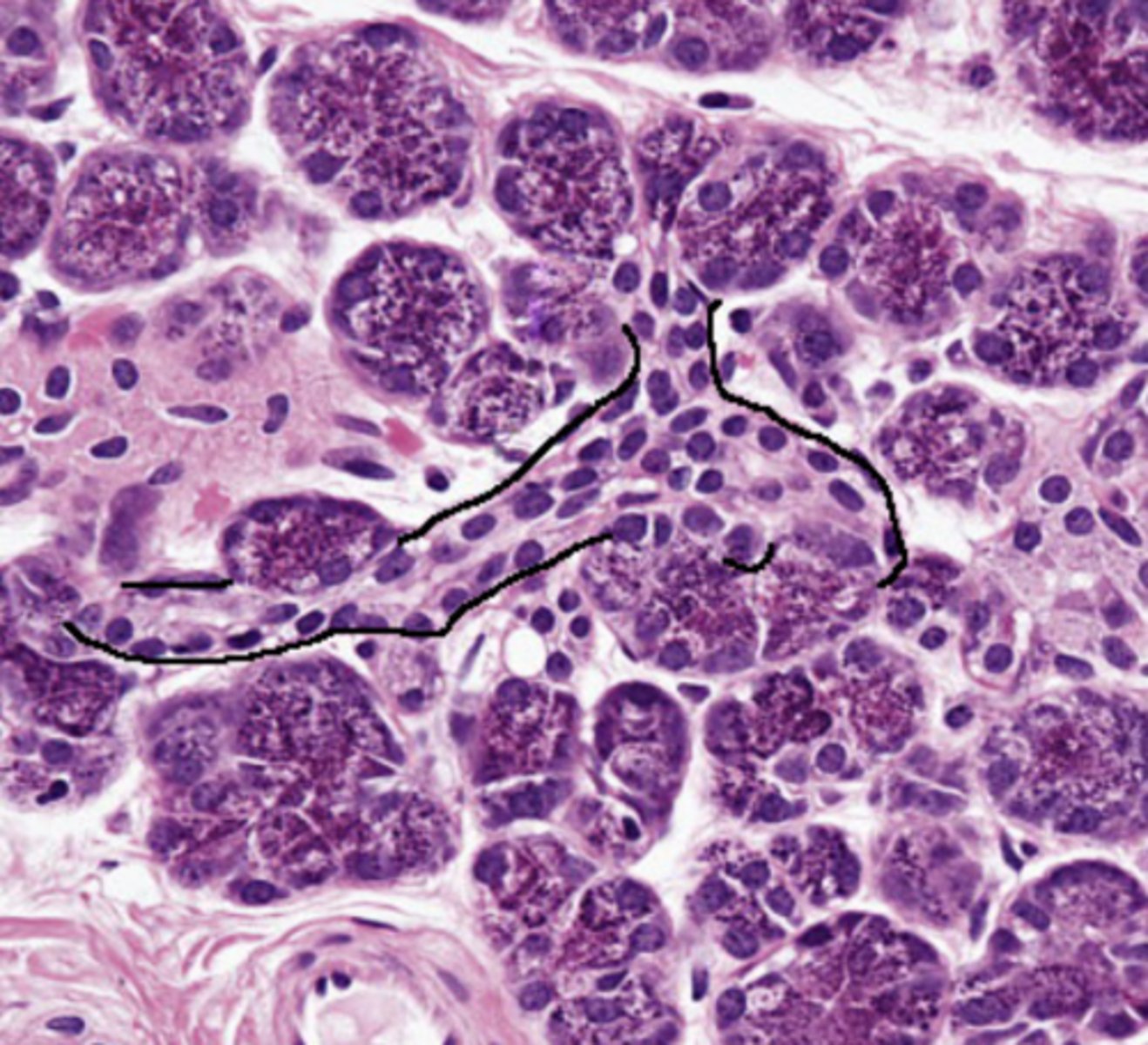
intercalated duct, simple cuboidal
type of duct + classification of epithelium
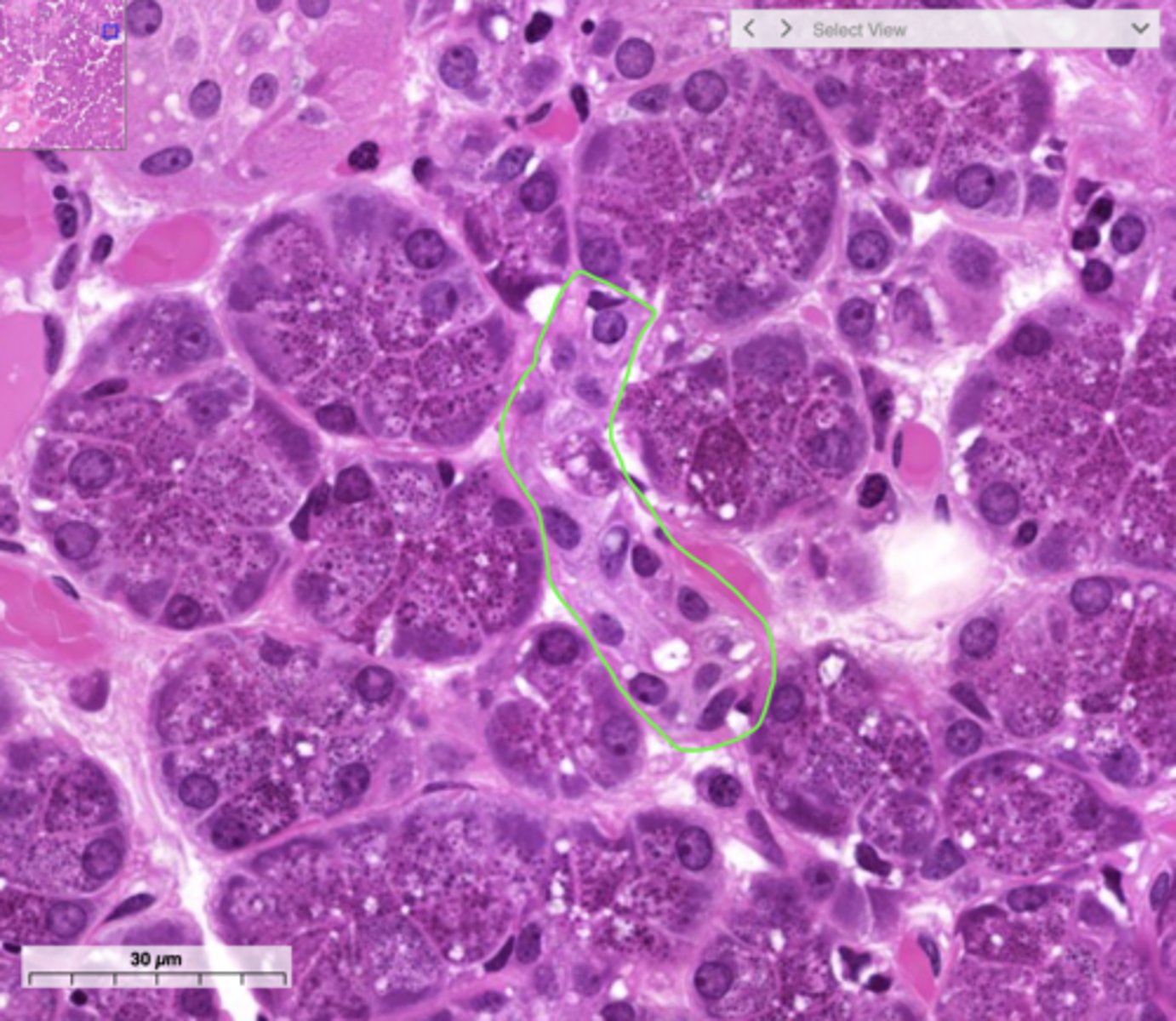
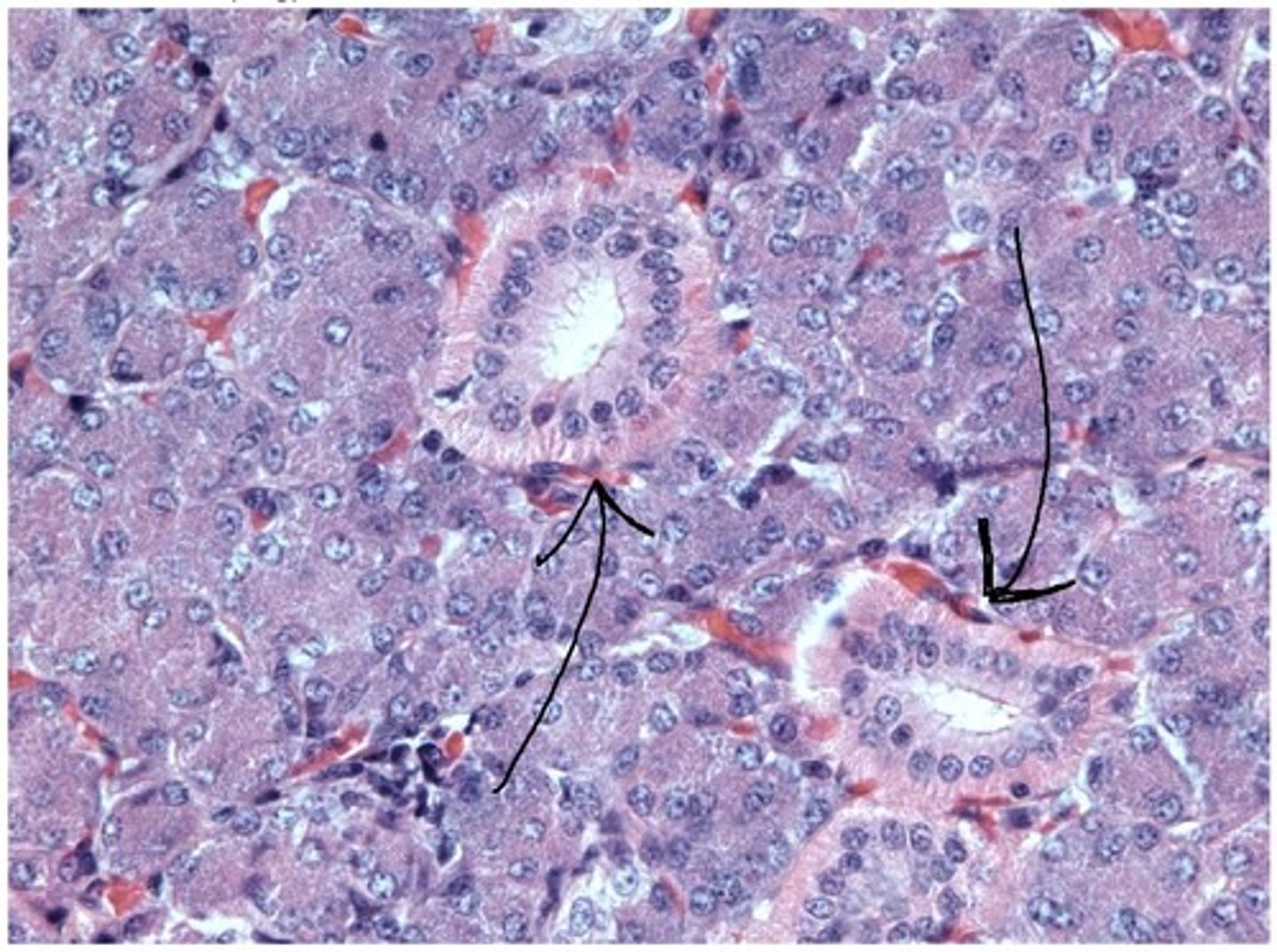
intralobular ducts
ducts formed by the union of several intercalated ducts; found within a single lobule but NOT directly attached to the secretory elements
false
True or false: Intralobular ducts attach directly to the secretory elements.
simple columnar
The walls of intralobular ducts usually consist of what classification of epithelium?
intralobular duct, simple columnar
type of duct + classification of epithelium
intralobular duct, simple columnar
type of duct + classification of epithelium
interlobular ducts
ducts that are formed by the union of several intralobular ducts, found in the septa between lobules
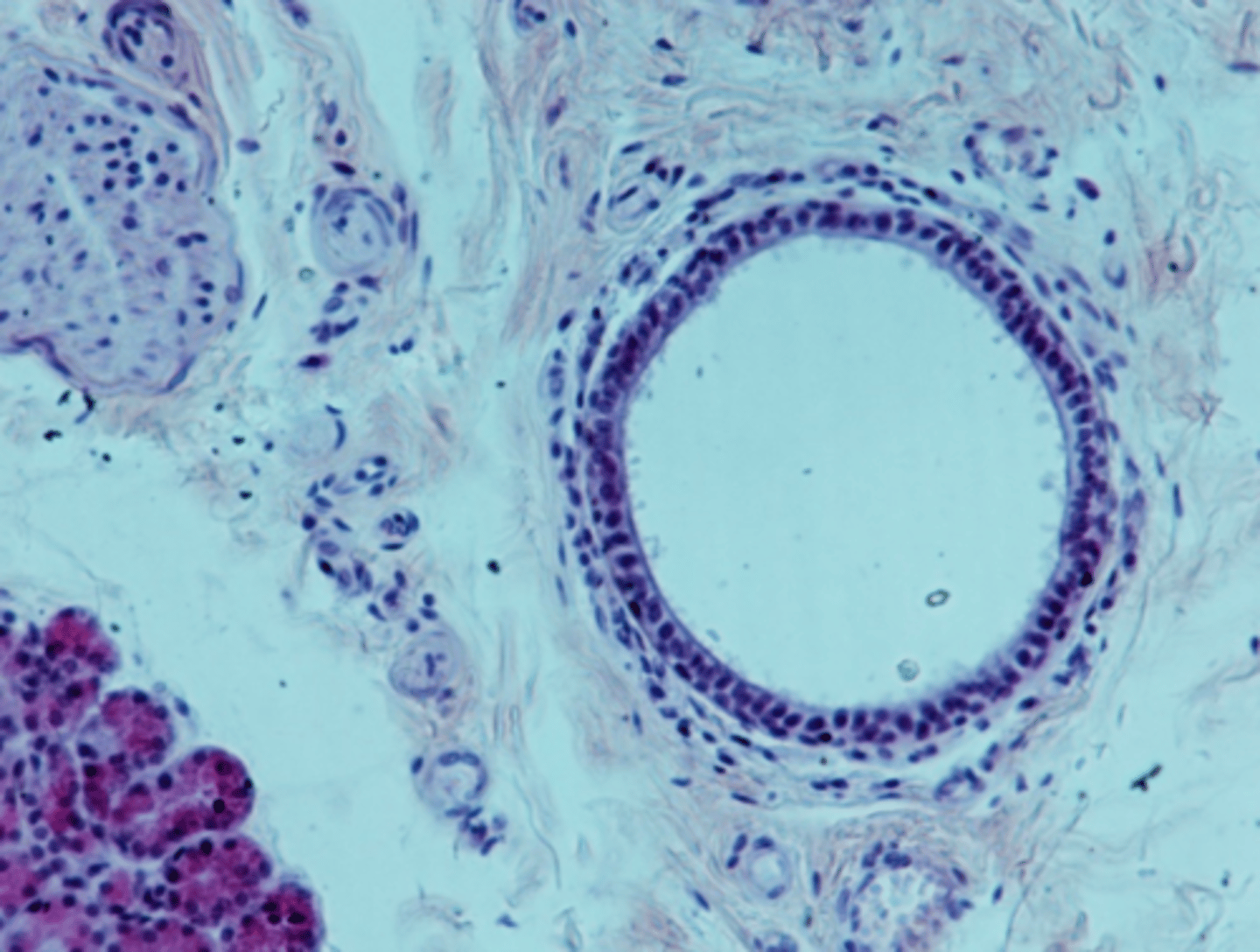
stratified cuboidal
The walls of interlobular ducts usually consist of what classification of epithelium?
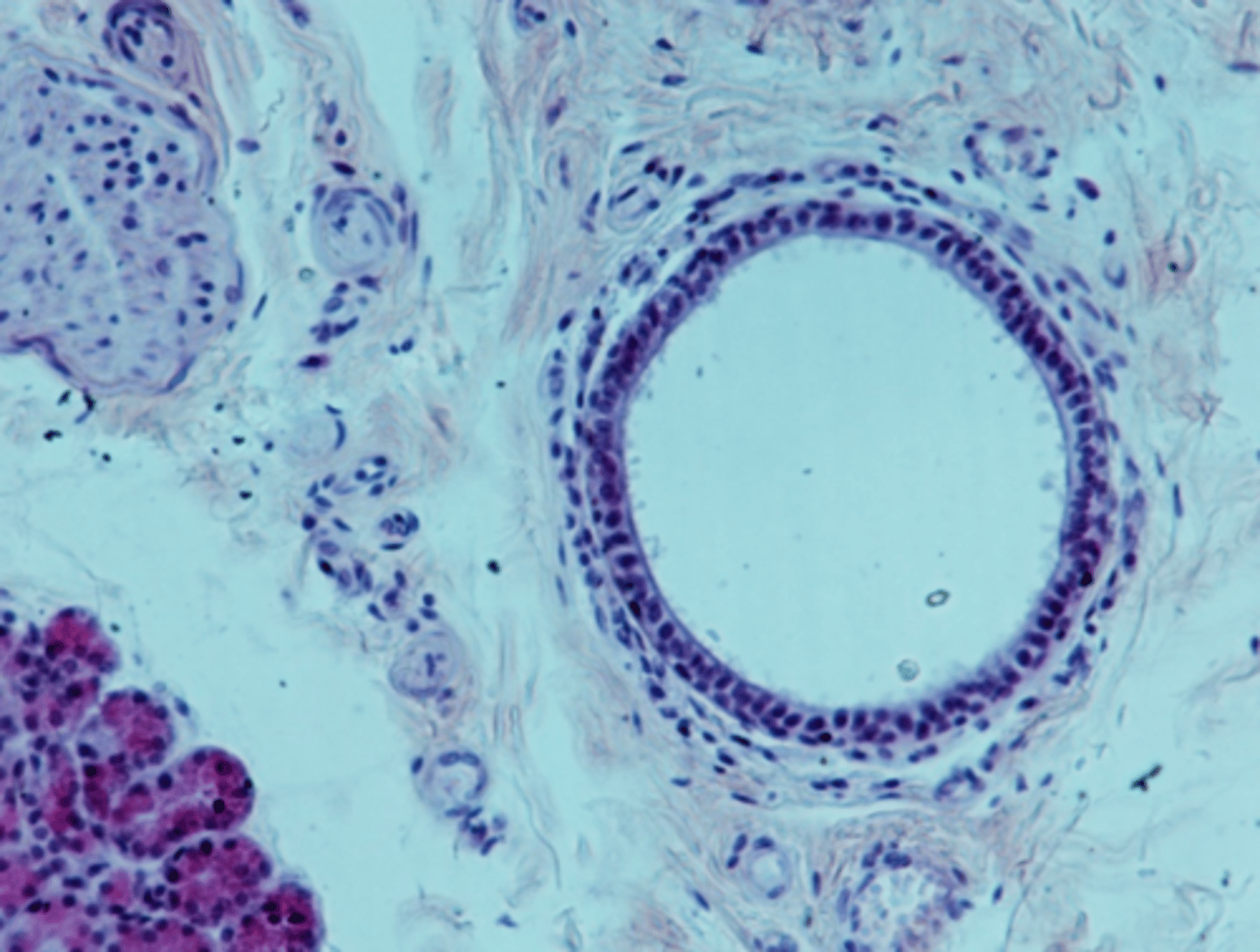
interlobular duct, stratified cuboidal
type of duct + classification of epithelium
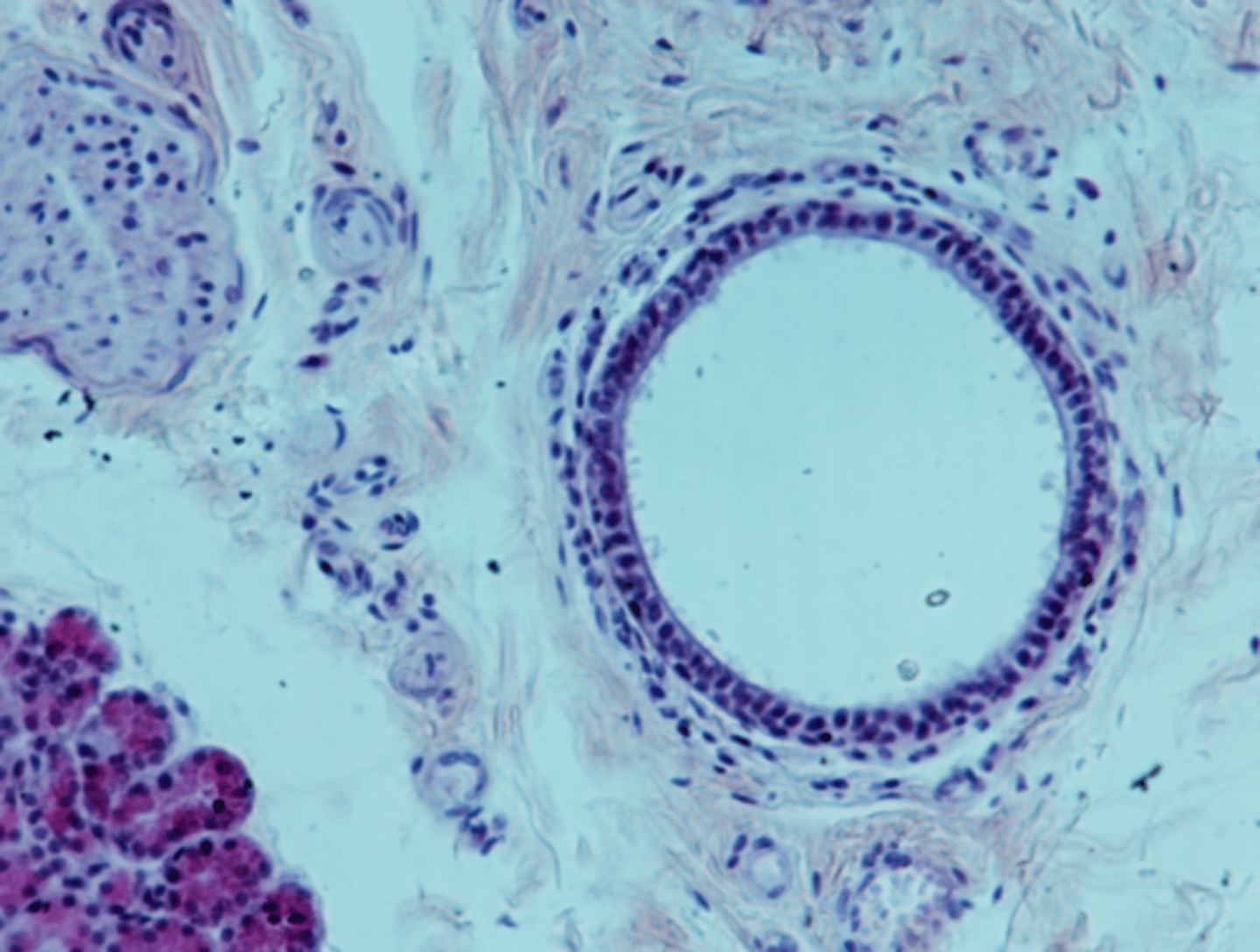
main ducts
ducts (at least one in each gland) that leave the gland and take the secretory product to where it needs to go to be useful for the body; formed by the unions of interlobular ducts
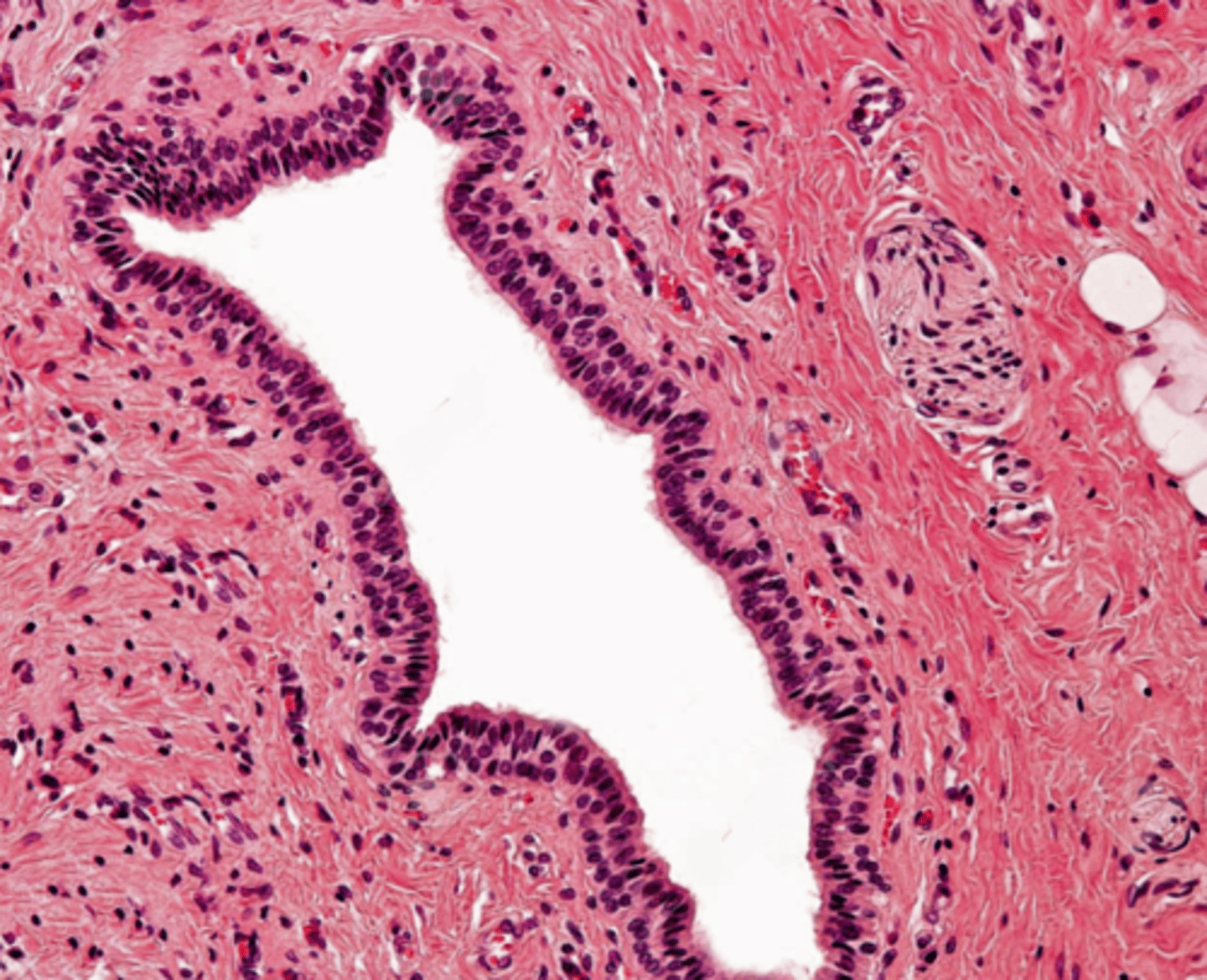
stratified columnar
The walls of main ducts usually consist of what classification of epithelium?
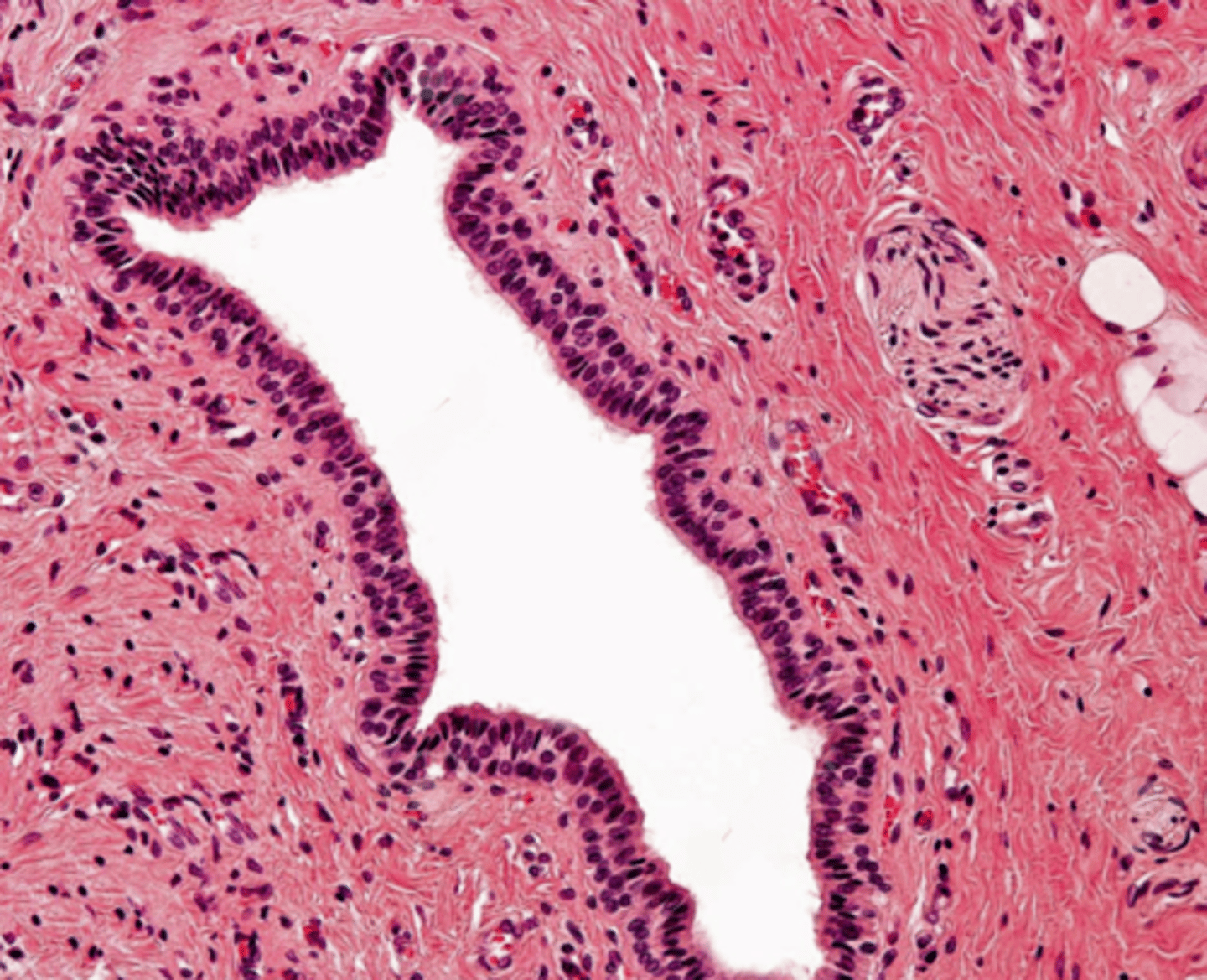
main duct, stratified columnar
type of duct + classification of epithelium
sebaceous glands
(so called because they produce sebum, aka oil)
oil glands associated with the hairs of the body, including the eyebrows (NOT eyelashes)
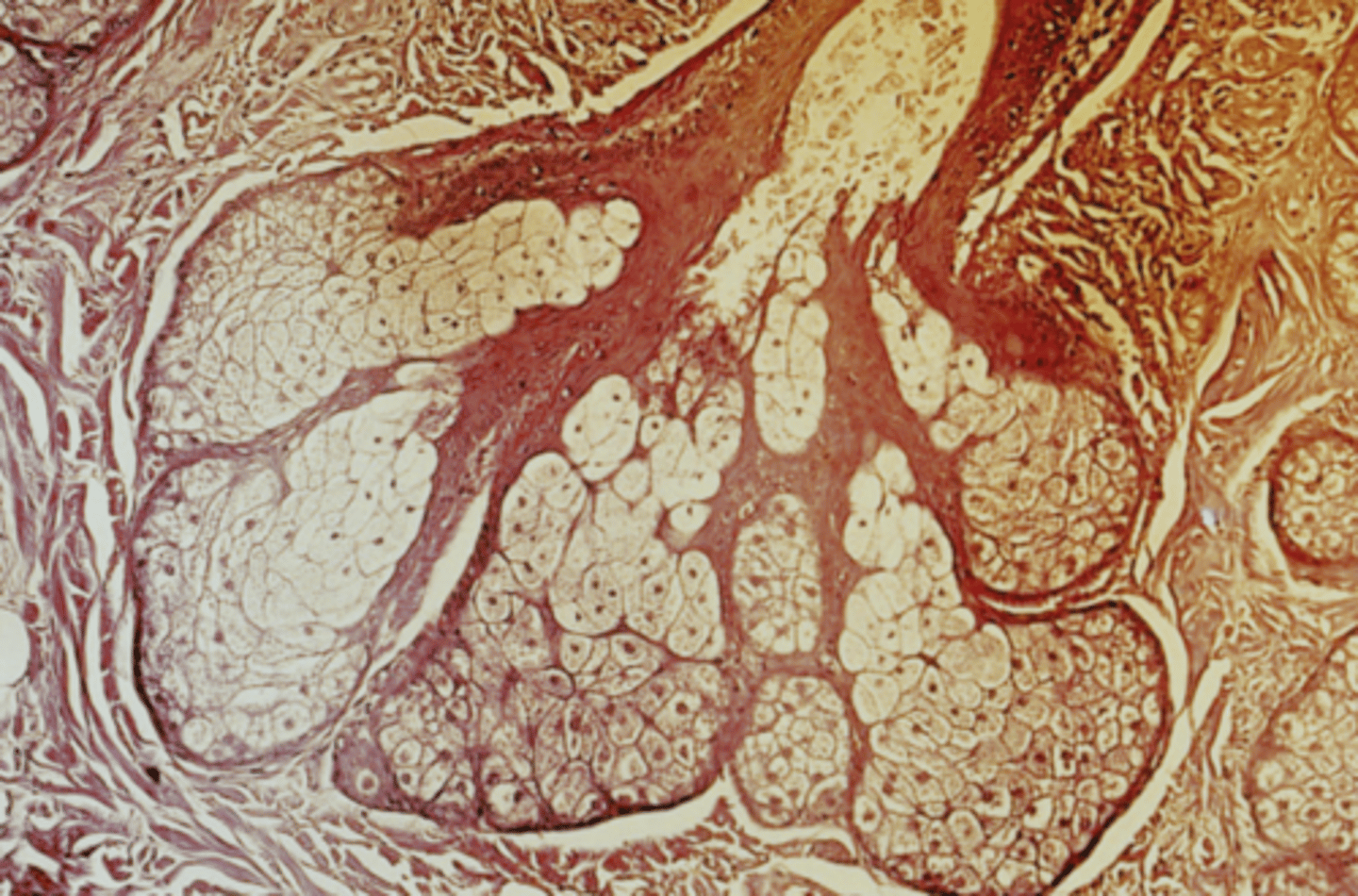
sebum (oil)
What is the main secretory product of sebaceous glands?
rounded cells, pale lipid filled vacuoles, round/central nucleus
How do sebaceous glands appear?
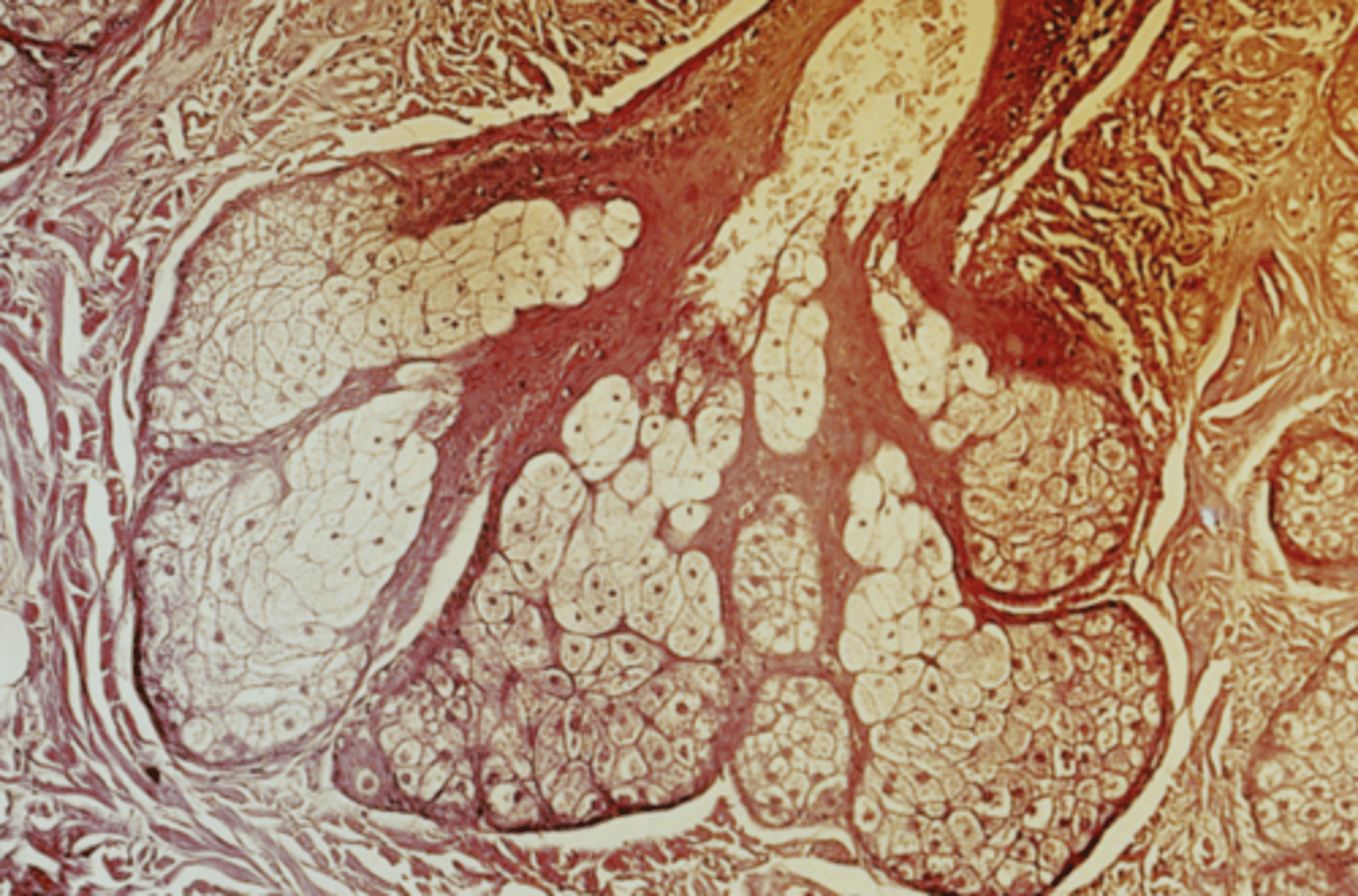
hair follicles
What do the ducts of sebaceous glands open into?
holocrine
What is the mode of secretion of sebaceous glands?
true
True or false: Sebaceous glands are associated with hair follicles.
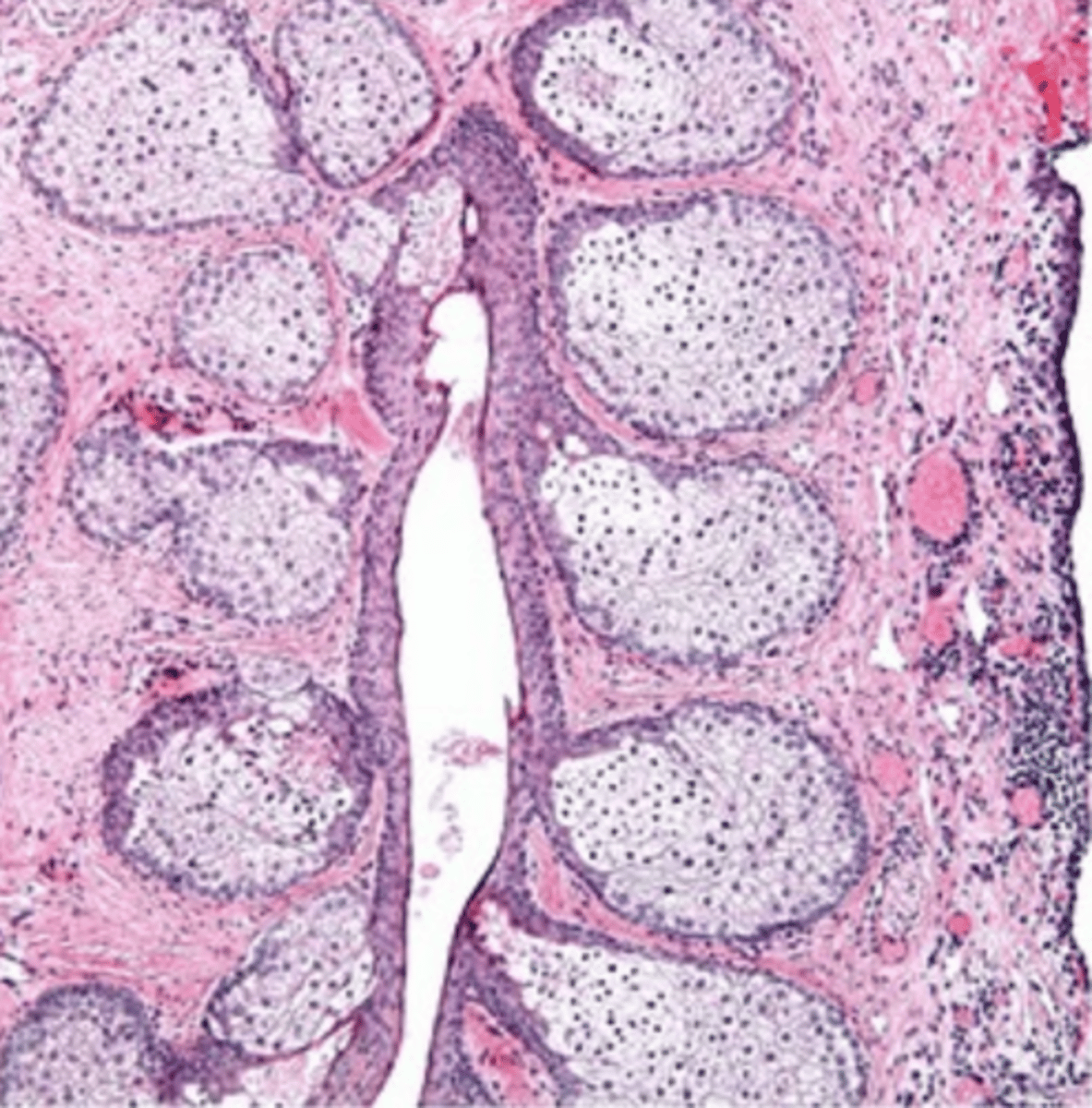
meibomian (tarsal) glands
eyelid modified sebaceous glands that are vertically oriented and embedded in the tarsal plates of the eyelids
sebaceous gland
type of eyelid gland
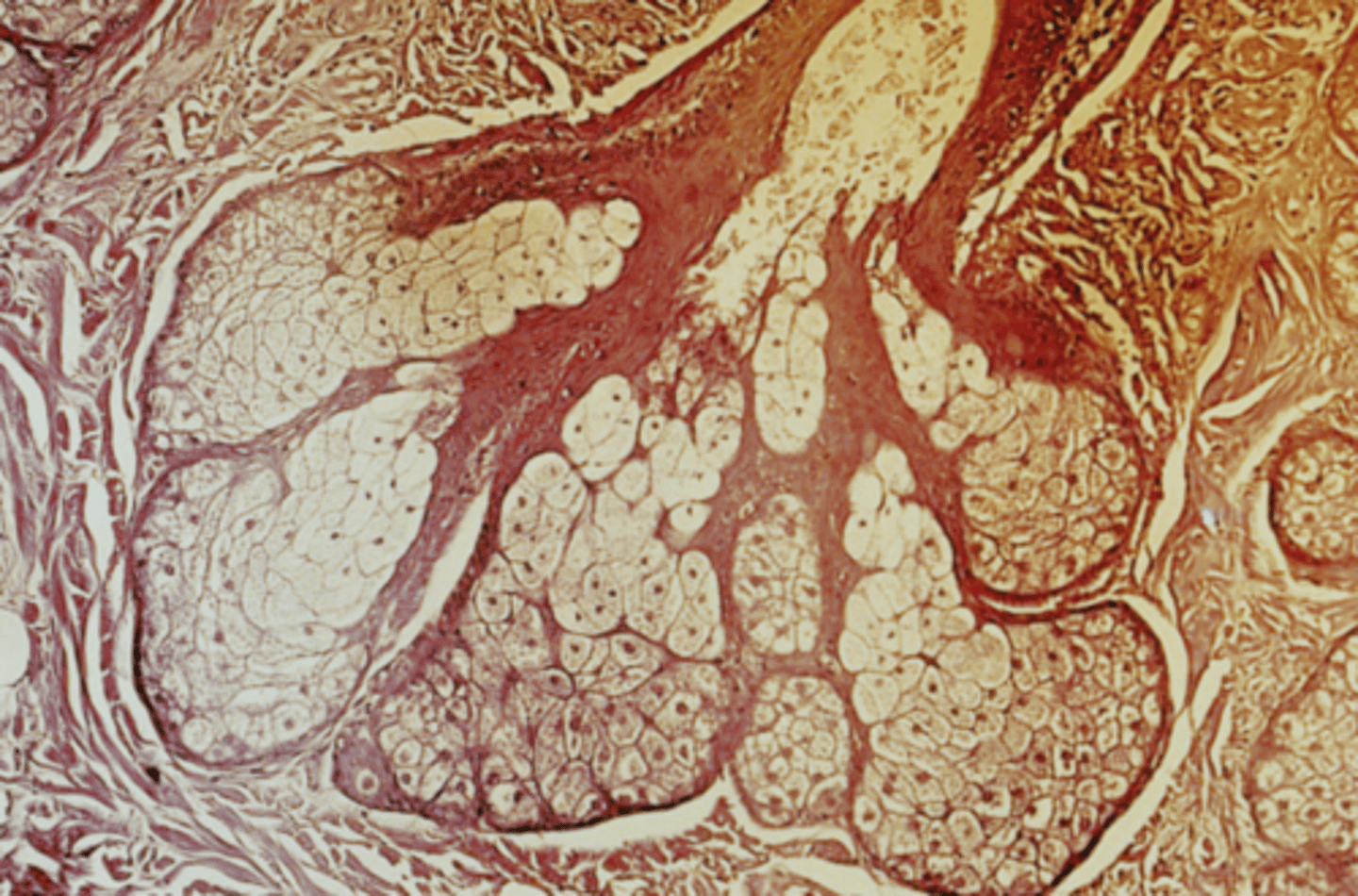
false
True or false: Meibomian glands are associated with hair follicles.
lipid layer of tears
What is the main secretory product of meibomian (tarsal) glands?
pale, central nucleus, duct opens onto eyelid surface
How do meibomian (tarsal) glands appear?
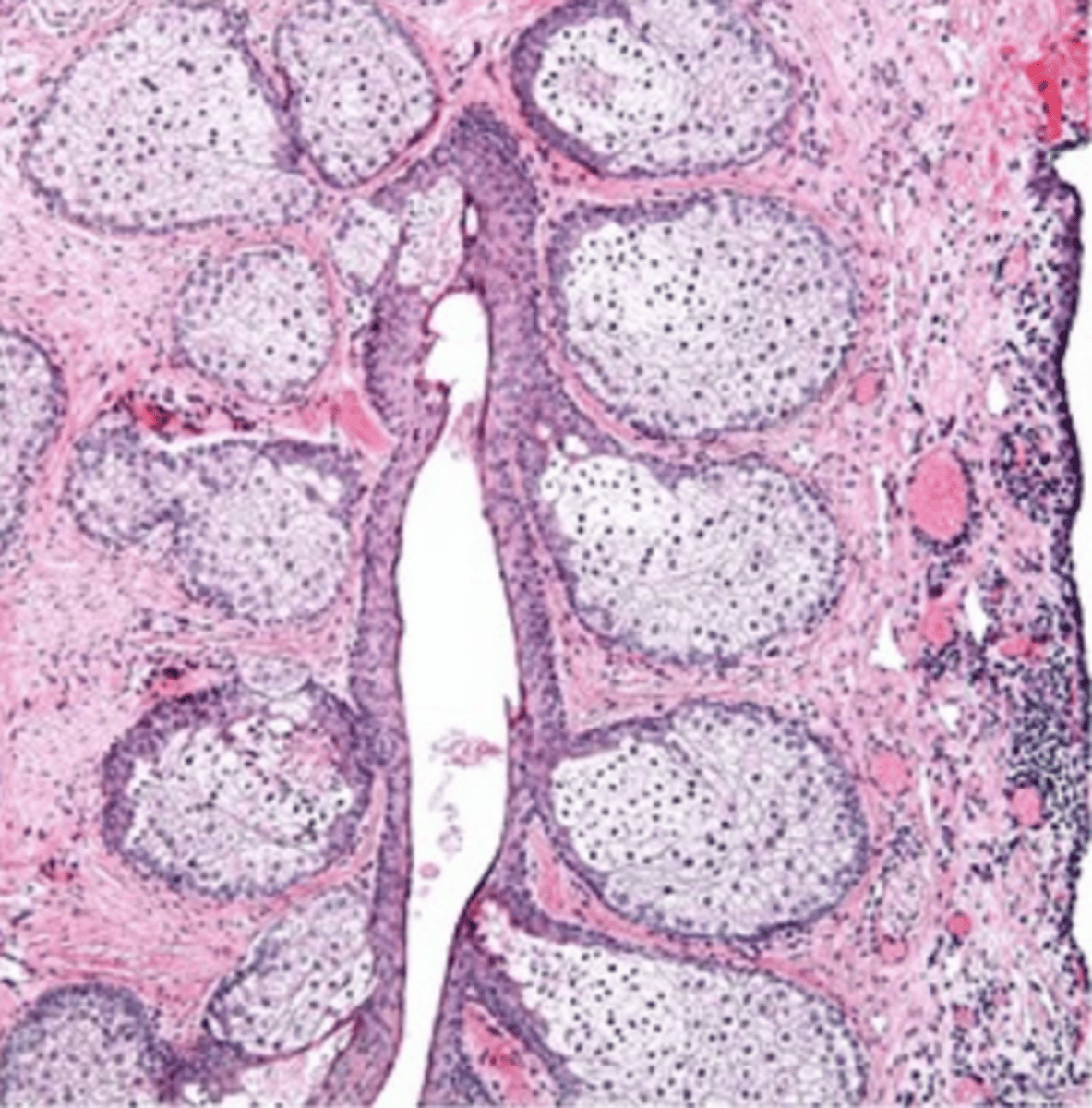
eyelid surface
(just posterior to eyelashes but in front of the mucocutaneous junction)
What do the ducts of meibomian (tarsal) glands open into?
holocrine
What is the mode of secretion of meibomian (tarsal) glands?
meibomian gland
type of eyelid gland
glands of Zeis
eyelid specialized sebaceous glands that are specifically associated with the eyelashes
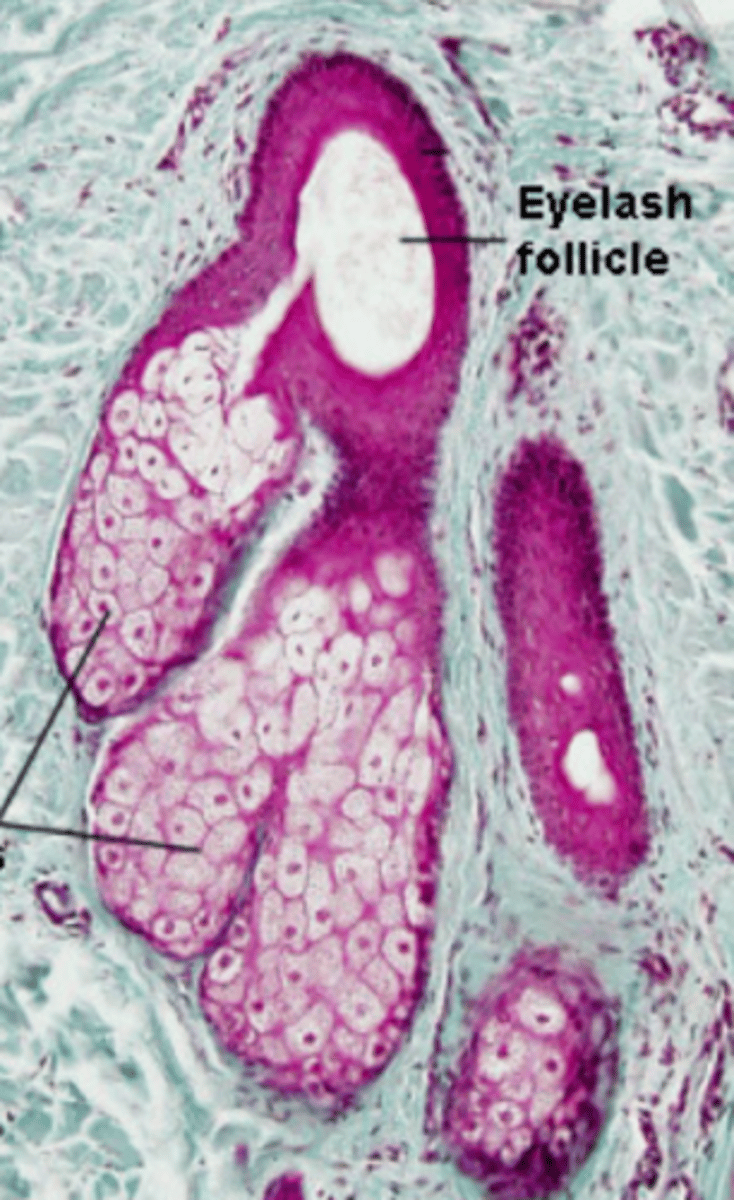
true (specifically eyelashes)
True or false: Glands of Zeis are associated with hair follicles.
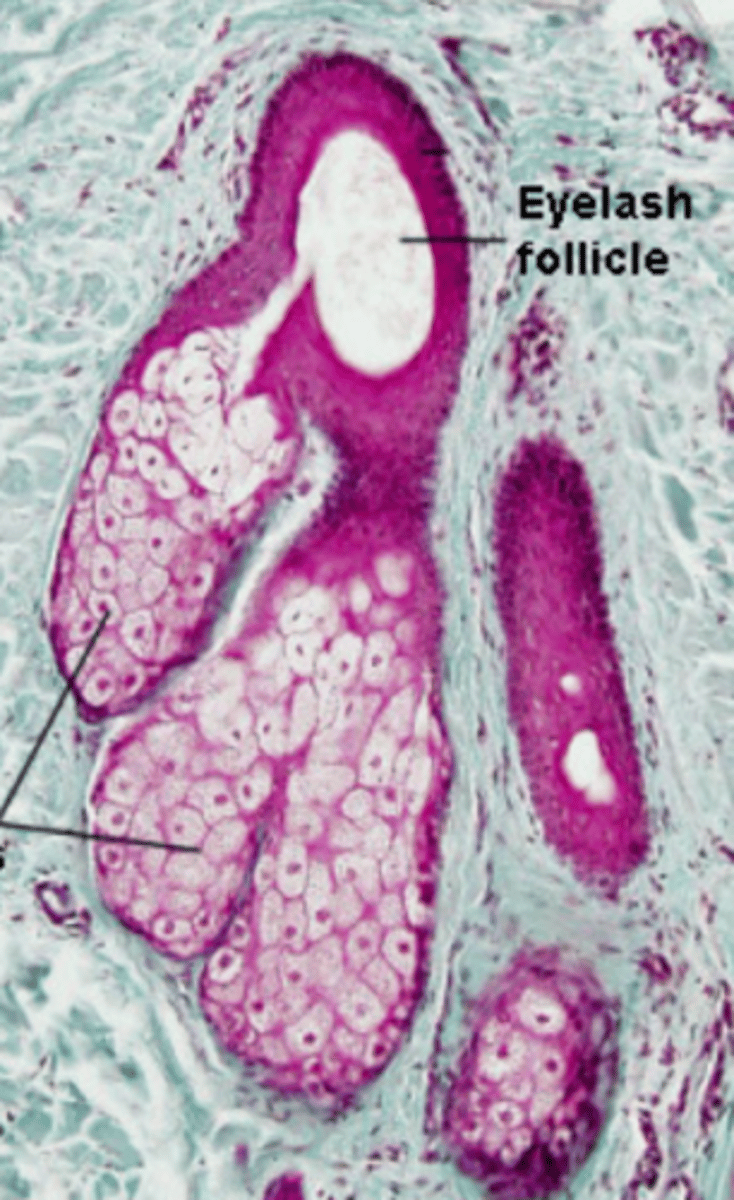
sebum-like material (to keep eyelashes waterproof)
What is the main secretory product of glands of Zeis?
pale, central nucleus, near eyelash follicles
How do glands of Zeis appear?
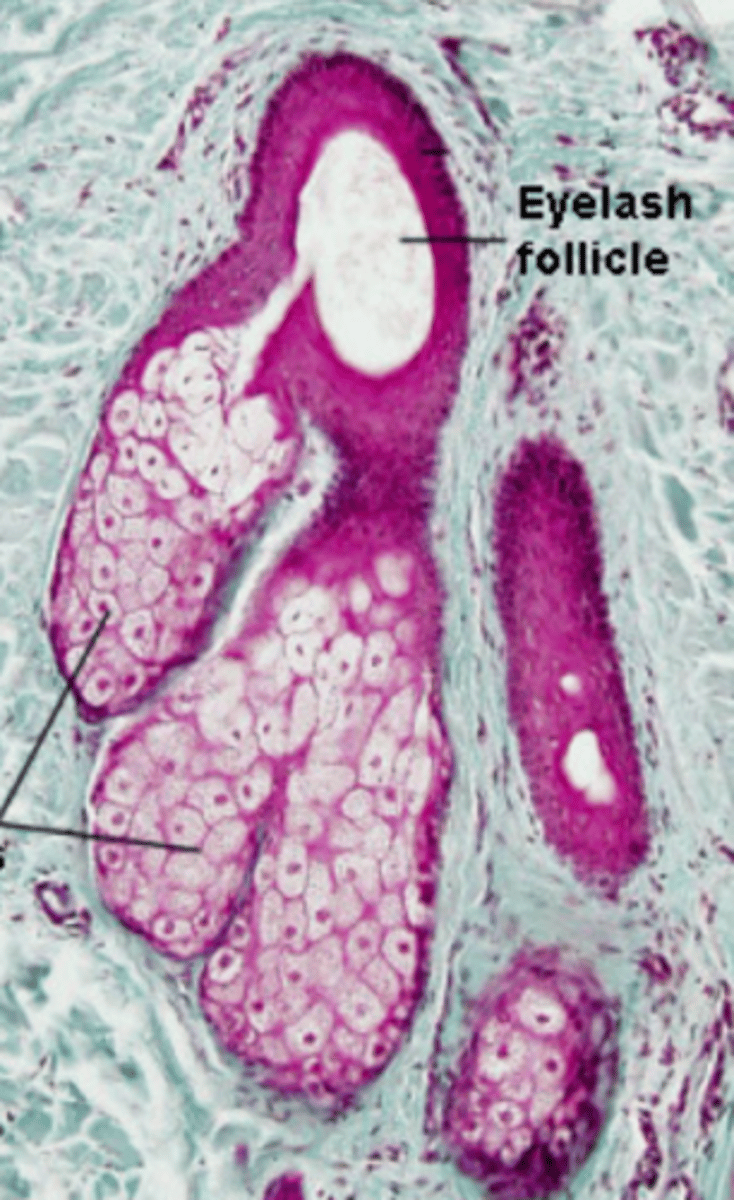
eyelash follicles
What do the ducts of glands of Zeis glands open into?
holocrine
What is the mode of secretion of glands of Zeis?
gland of Zeis
type of eyelid gland
meibomian, Zeis
What sebaceous glands are found in the eye?
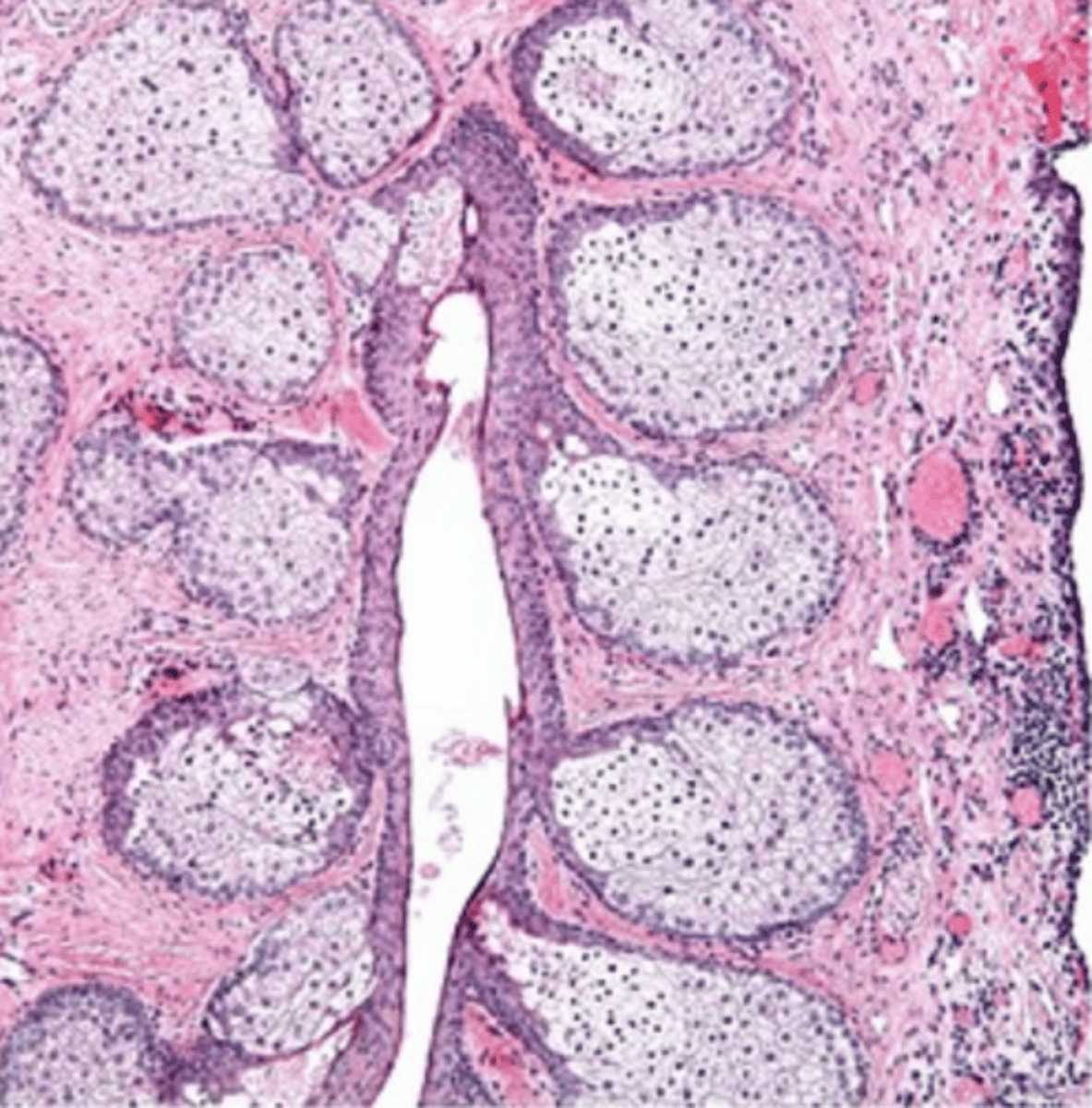
major lacrimal gland
one of the main eyelid glands that is located in the superolateral portion of the orbit just behind the bony margin of the orbit
has the classic glandular structure and consists of lobules of secretory profiles separated by CT septa
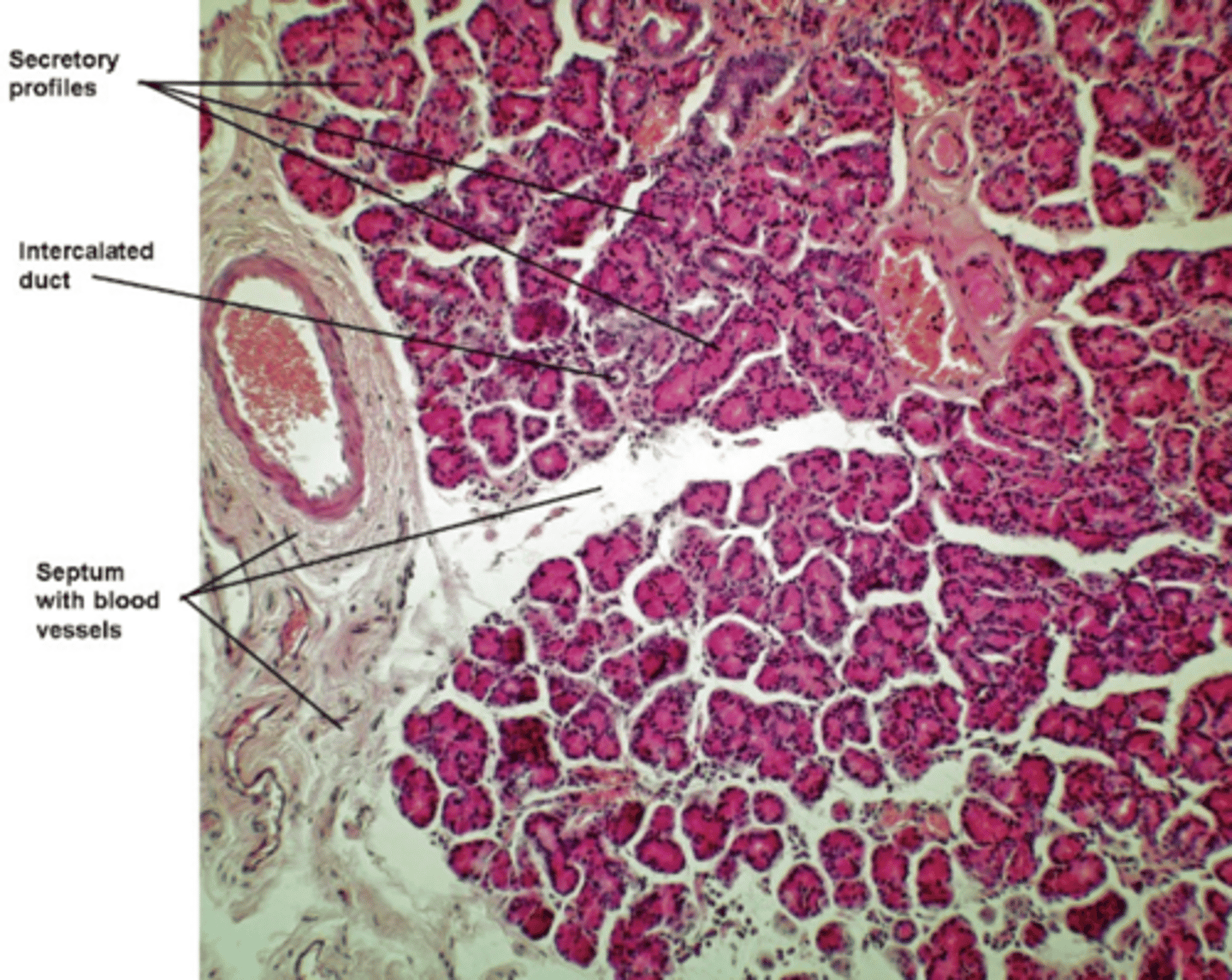
superior conjunctival fornix
What do the ducts of major lacrimal glands open into?
glands of Krause and Wolfring
two accessory lacrimal glands
upper and lower conjunctival fornix
Where are glands of Krause located?
inner surface of each eyelid
(above tarsal plate in upper lid, below tarsal plate in lower lid)
Where are glands of Wolfring located?
merocrine
ALL of the lacrimal glands (major, Krause, Wolfring) have what mode of secretion?
aqueous layer of tear film
What is the main secretory product of all of the lacrimal glands?
major, Wolfring, Krause
What different types of lacrimal glands are there?
eccrine, apocrine
two varieties of sweat (or sudoriferous) glands associated with the skin
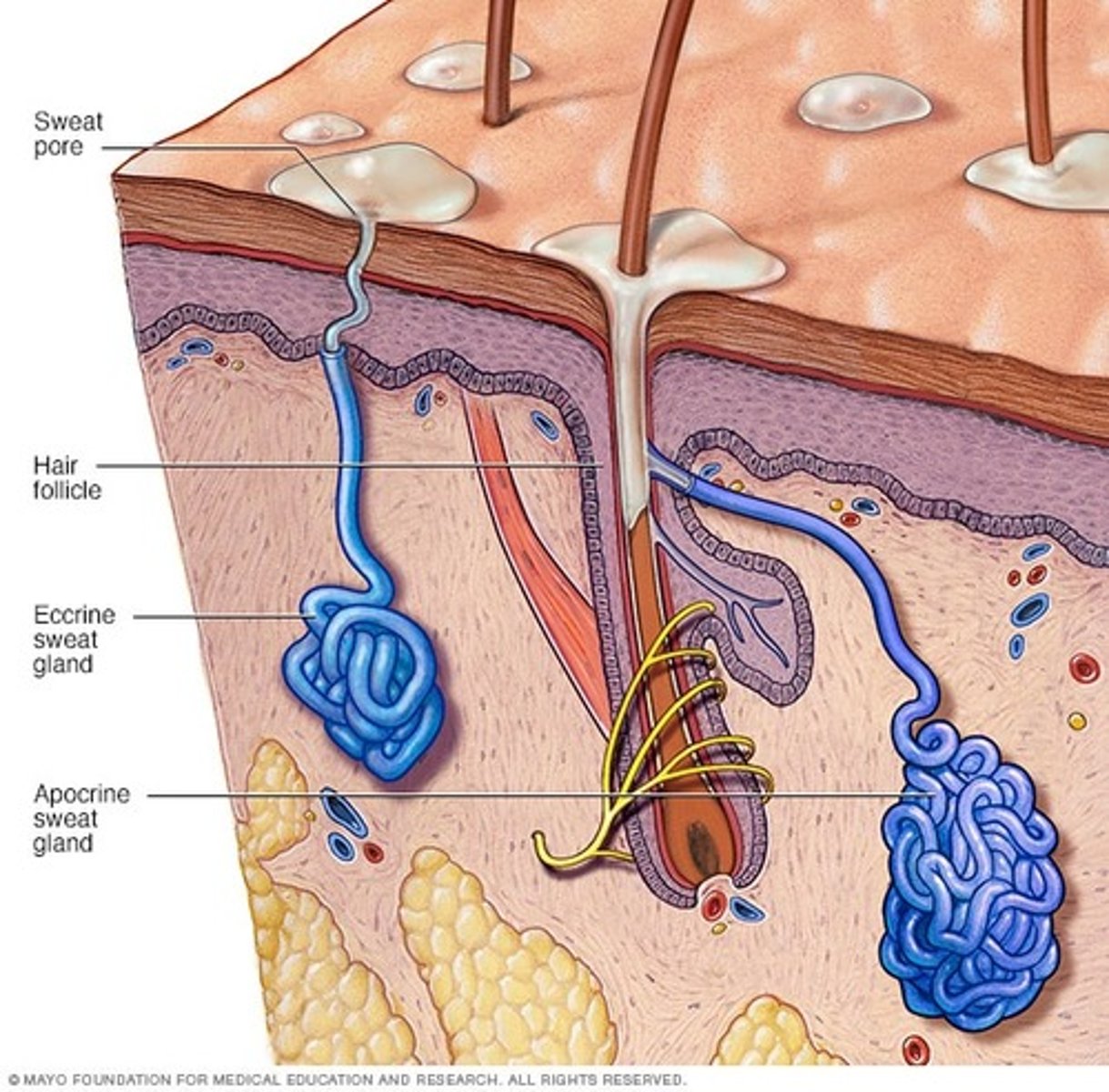
eccrine (sweat glands)
sweat glands that secrete "typical" sweat, have ducts that open directly on the surface of the skin, and are found in almost all regions of the skin
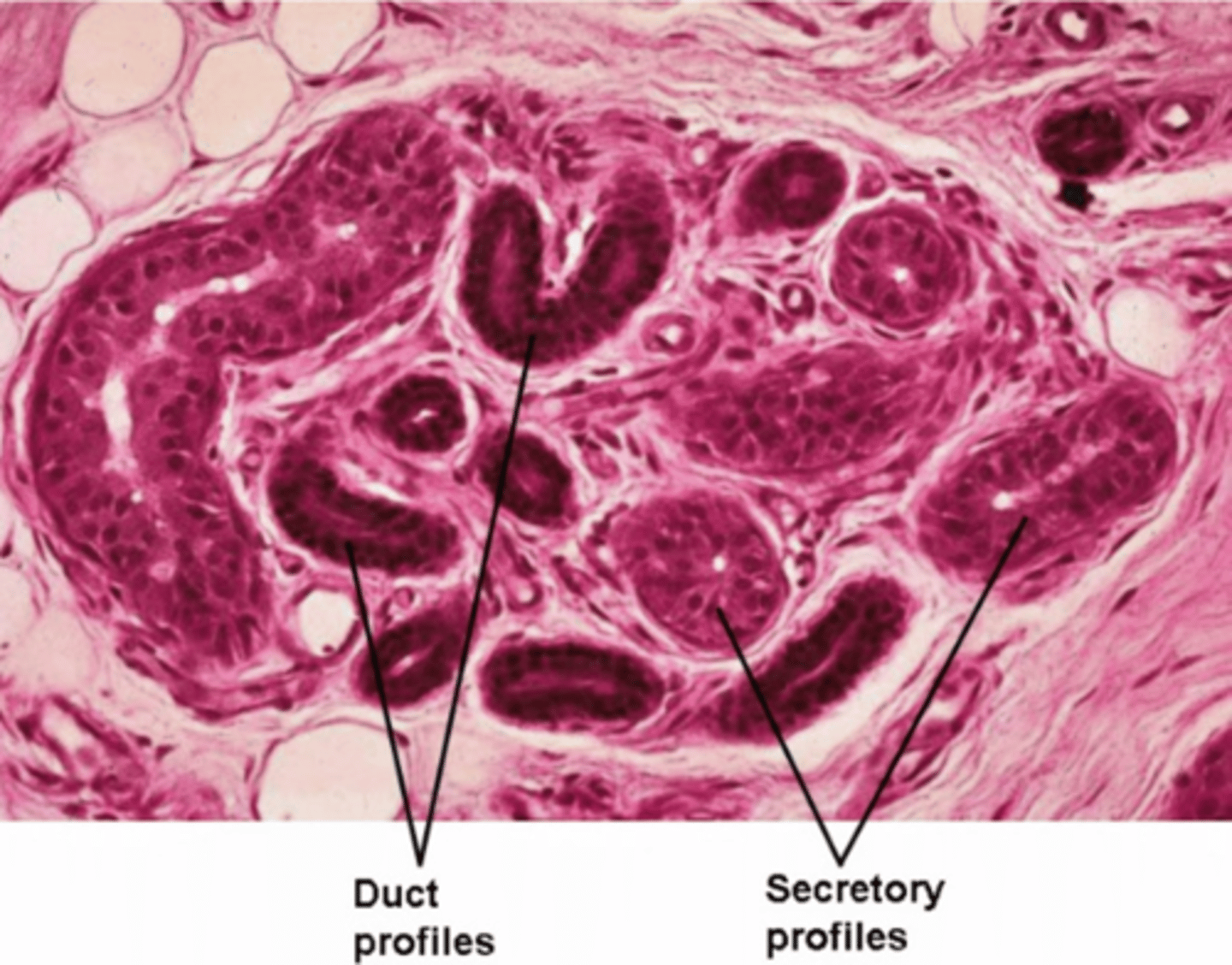
haphazard coils, pale cells, lumen not always visible, duct portion stains darker
How do eccrine sweat glands appear?
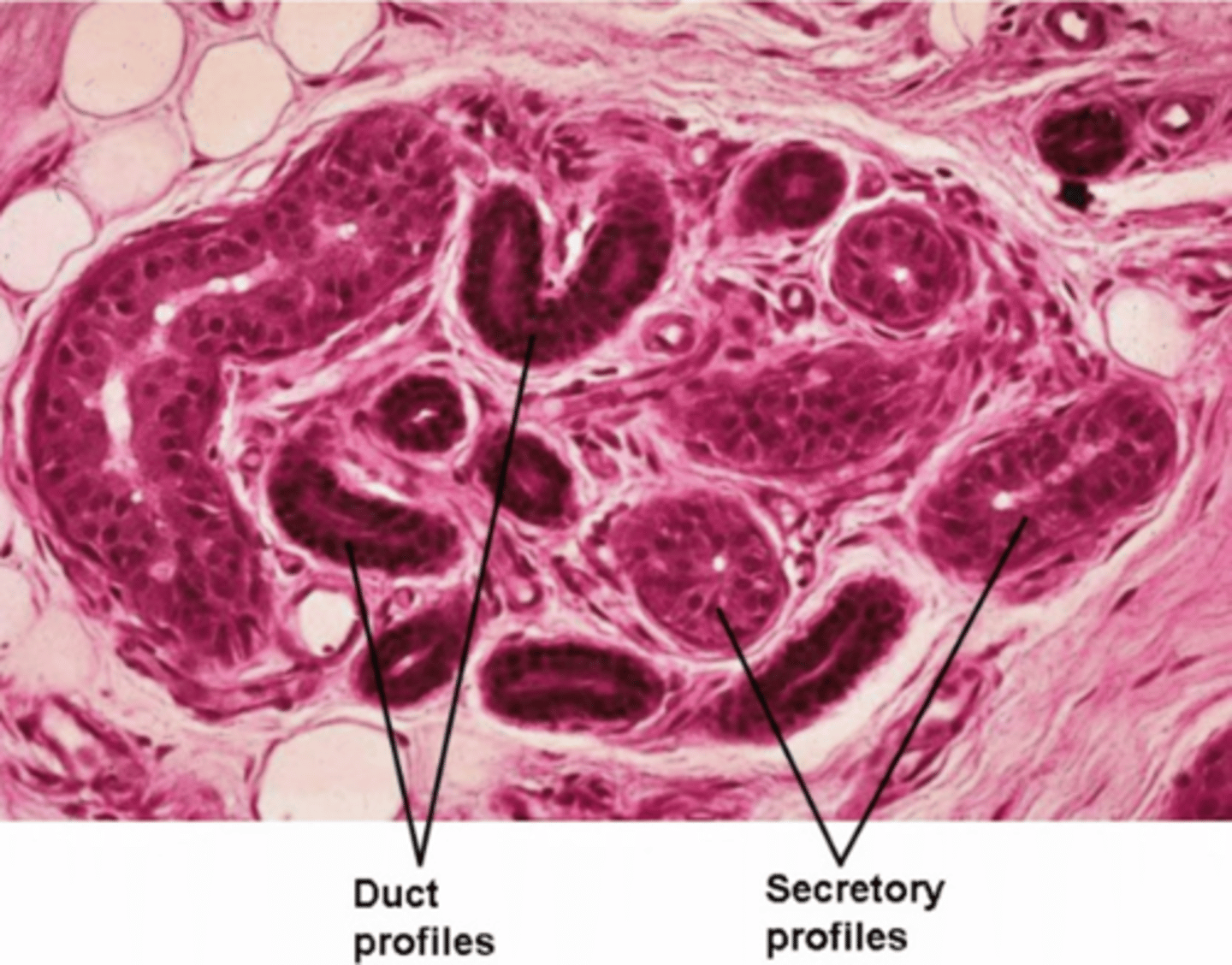
secretory region is simple cuboidal/columnar, duct portion is stratified cuboidal
What is the classification of epithelium found in eccrine sweat glands?
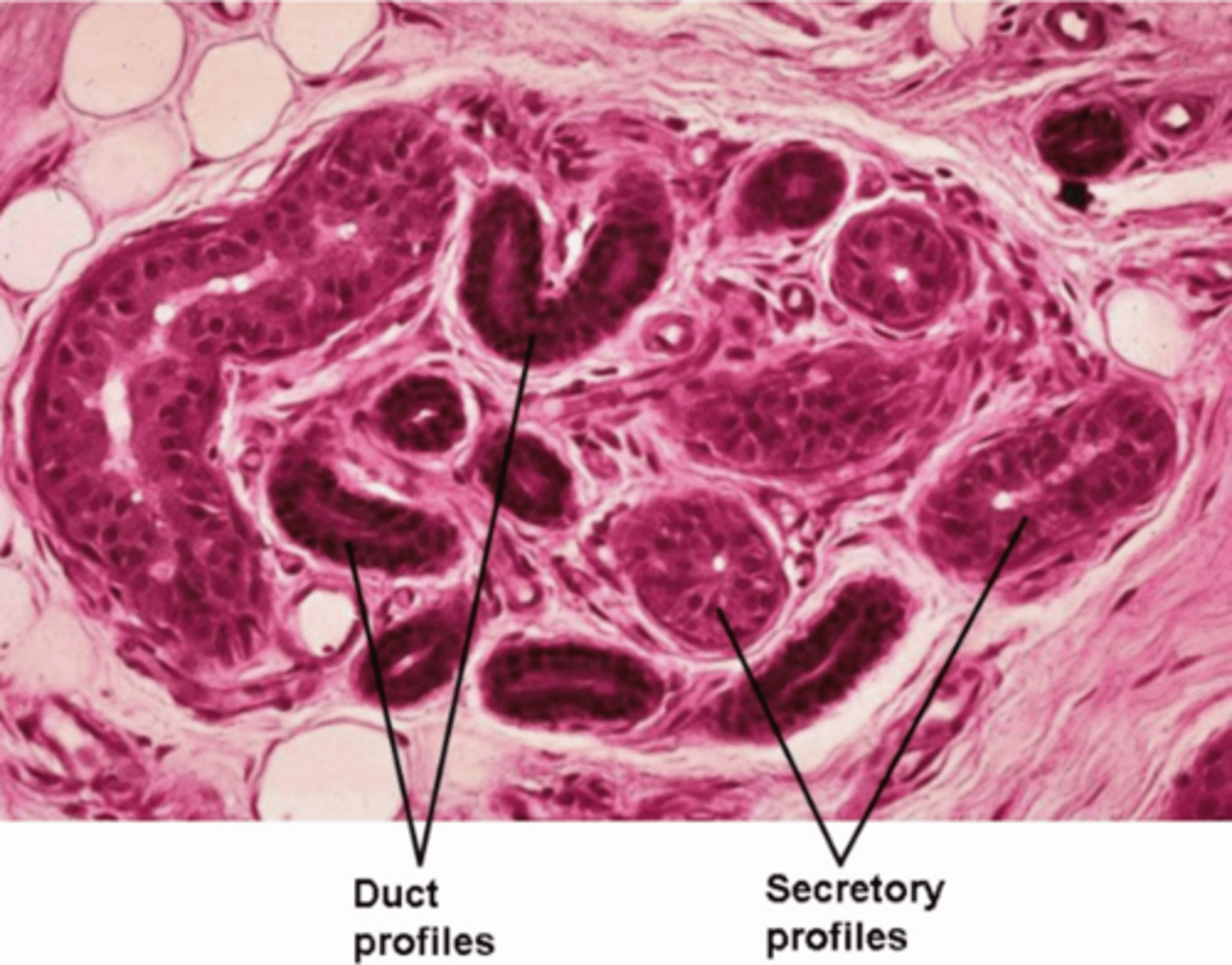
merocrine
What mode of secretion do eccrine sweat glands use?
eccrine sweat gland
type of eyelid gland
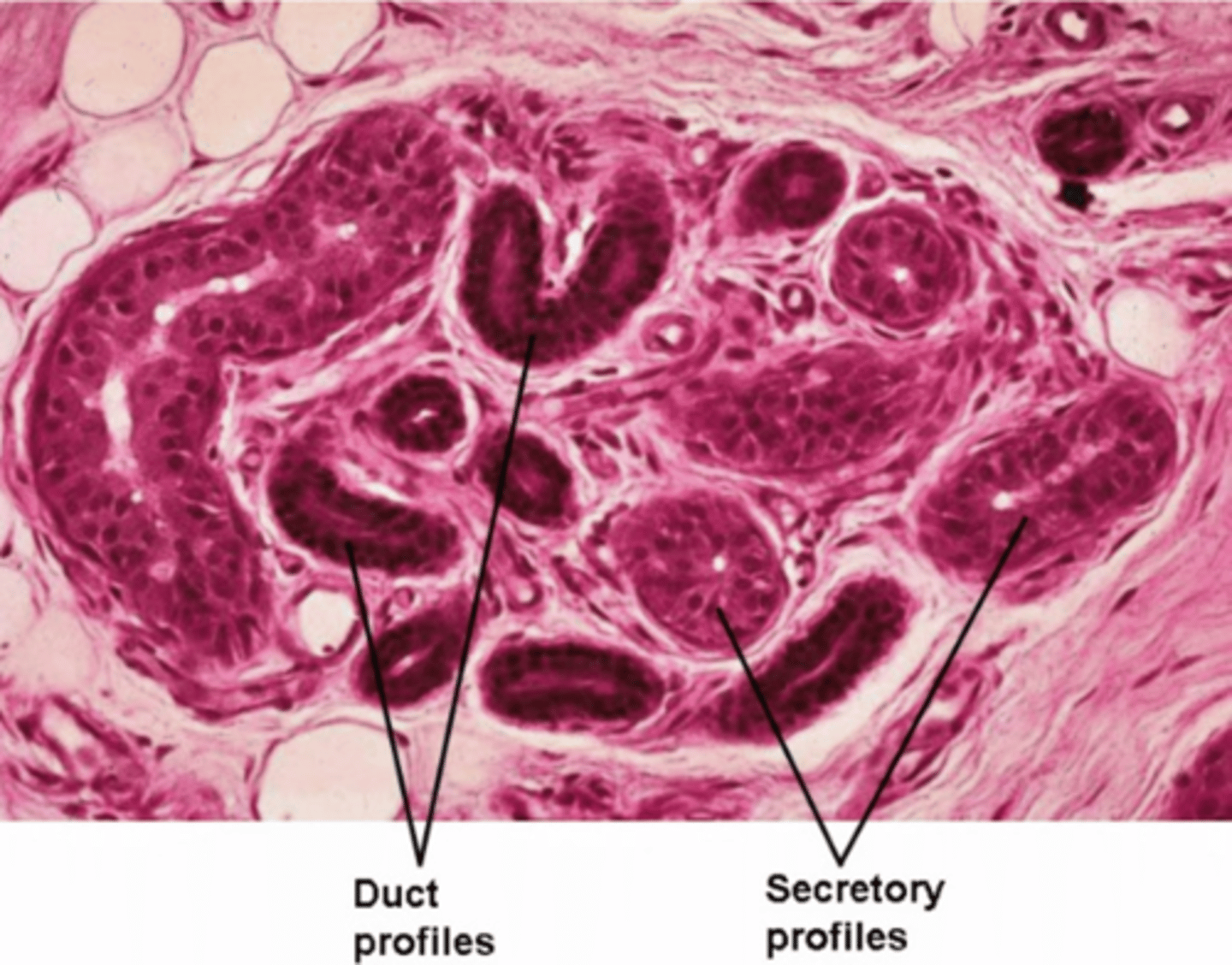
temperature control, excretion of nitrogenous compounds
Typical sweat secreted by sudoriferous glands is hypotonic and has a relatively low concentration of protein. So what is its purpose?
apocrine
sweat glands that secrete sweat that is more lipid in nature, have ducts that open into hair follicles, and are found only in a few restricted regions
eccrine opens onto skin surface and is found all over, apocrine opens into hair follicles and is only found in specific places
What is the general difference between eccrine and apocrine sweat glands?
apocrine
Which type of sweat glands secrete sweat with more LIPIDS: eccrine or apocrine?
glands of Moll
apocrine sweat glands associated specifically with the eyelashes
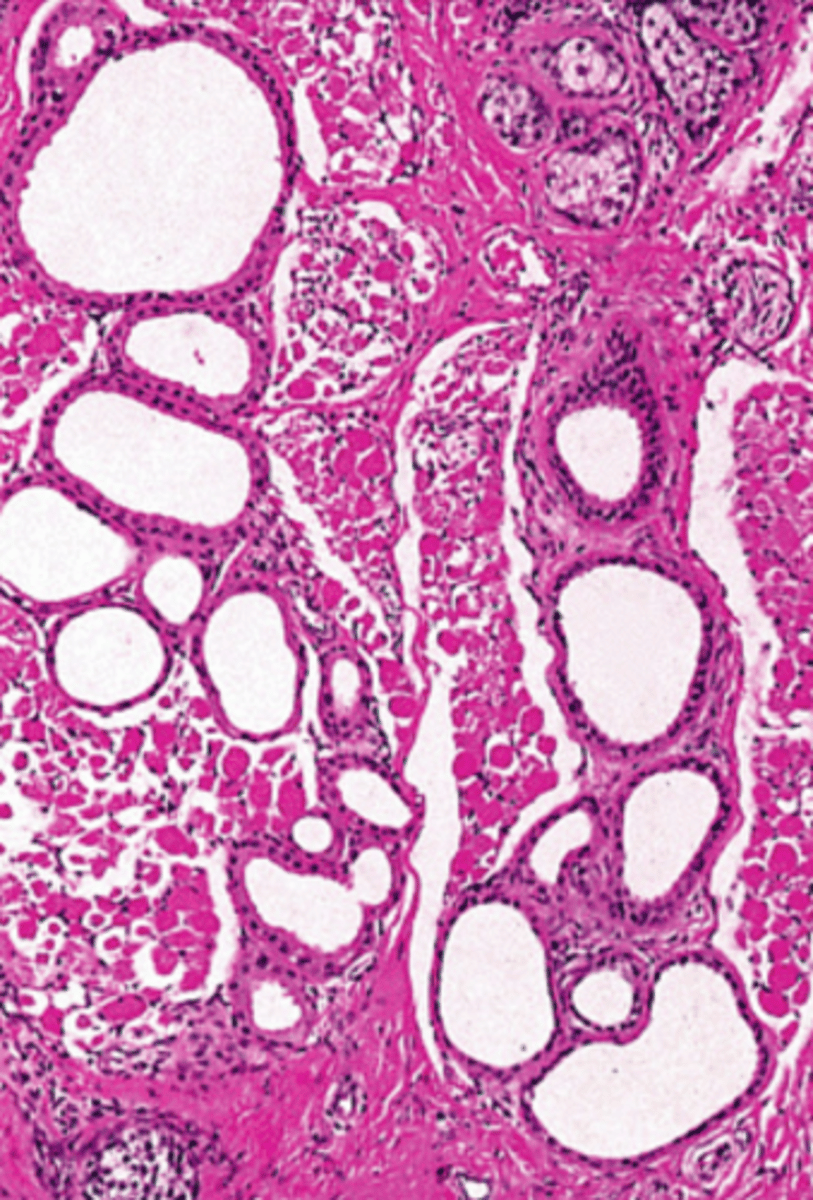
apocrine
Are glands of Moll eccrine or apocrine sweat glands?
Moll secretes sweat, Zeis secretes sebum-like material for waterproofing eyelashes
What is the difference between glands of Moll and glands of Zeis in regards to what they secrete if they're both associated with eyelashes?
simple cuboidal
What is the classification of epithelium found in the secretory part of apocrine sweat glands? (i.e. glands of Moll)
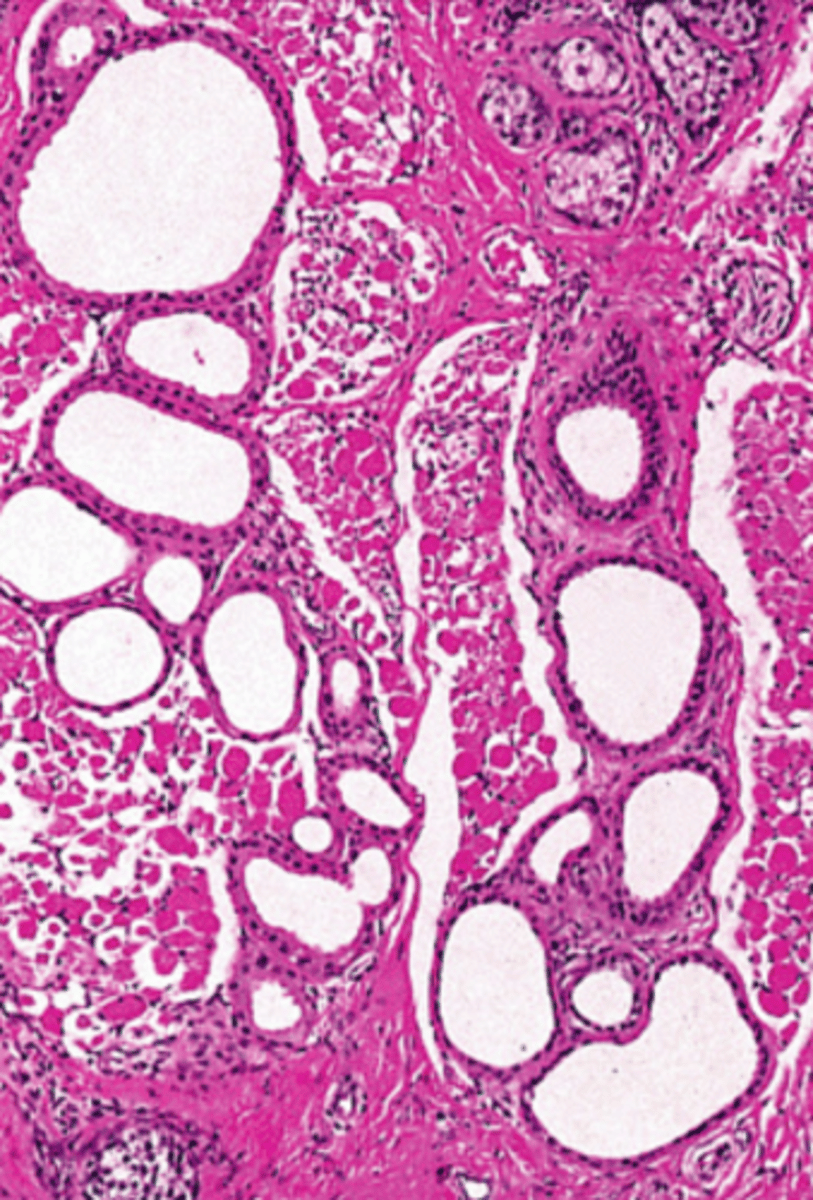
apocrine sweat gland/gland of Moll
type of eyelid gland
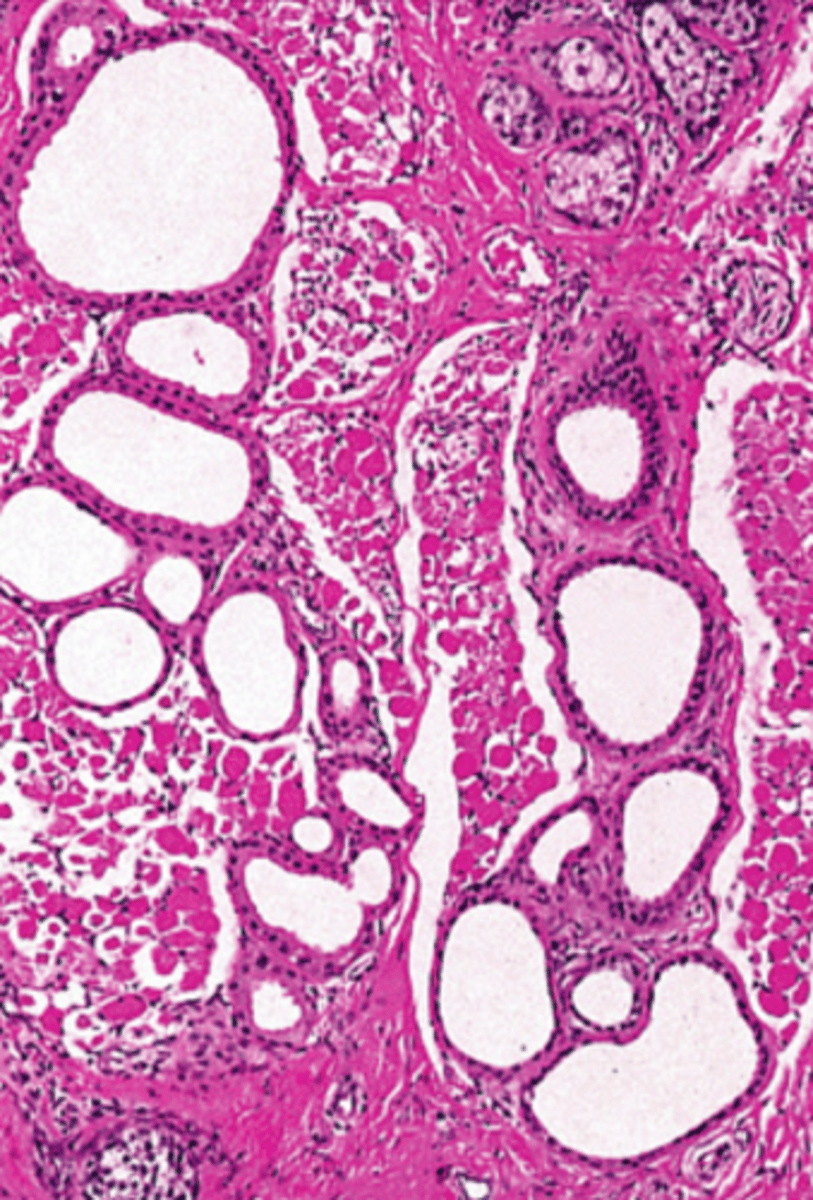
eccrine stains dark around small lumen, apocrine stains pink around large lumen
difference between eccrine and apocrine sweat glands in regards to how they stain and surround their respective lumen
apocrine
Which glands secrete an atypical sweat that has a lipid moiety NOT found in typical sweat: eccrine or apocrine (Moll)?
protein part of sweat is merocrine, lipid part is apocrine
What mode of secretion do apocrine sweat glands use?
individual empty looking columnar cells with basal nucleus
Basic identification: What do goblet cells look like?
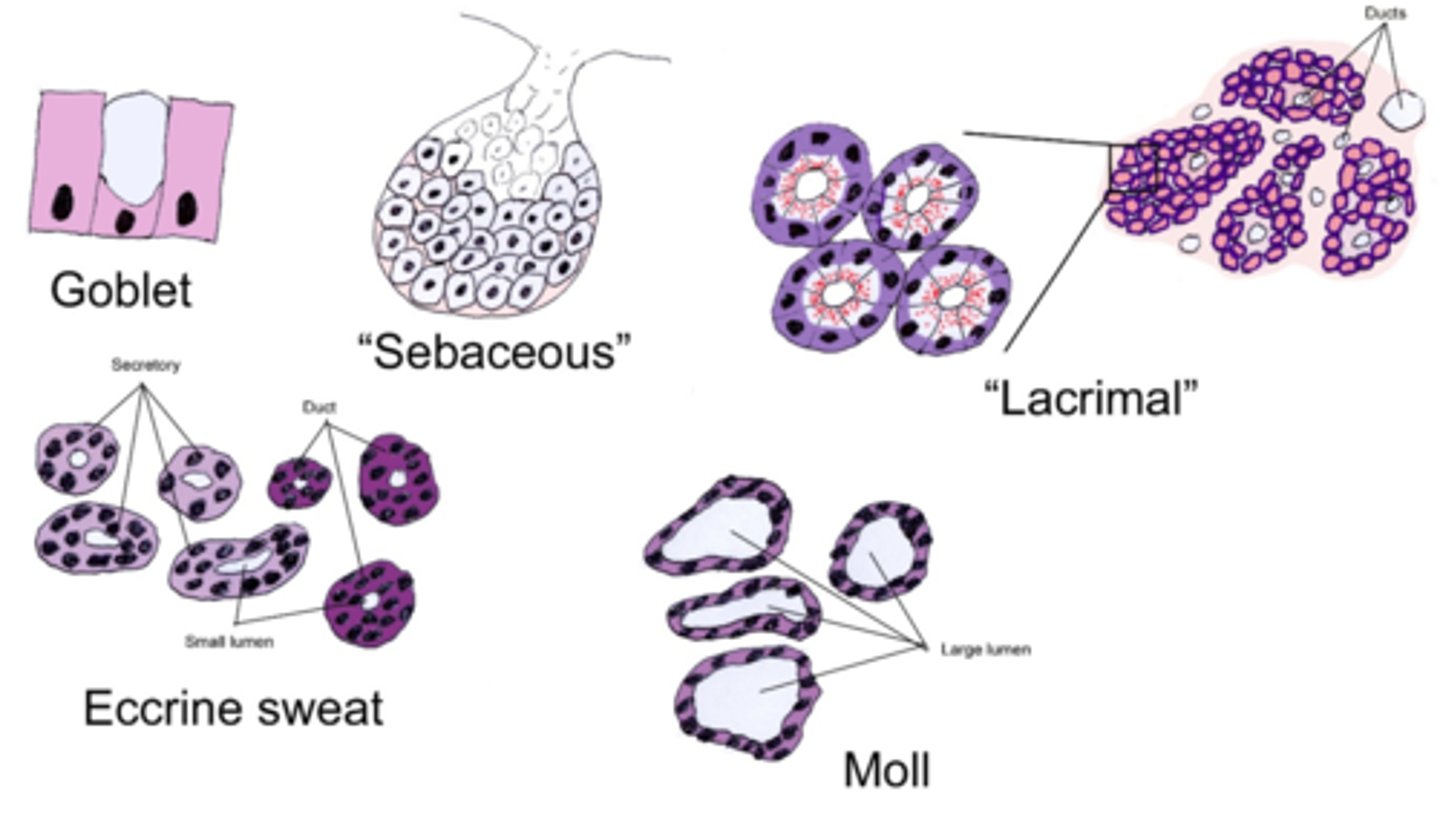
rounded bag of empty looking cells with a central nucleus
Basic identification: What do sebaceous glands look like?
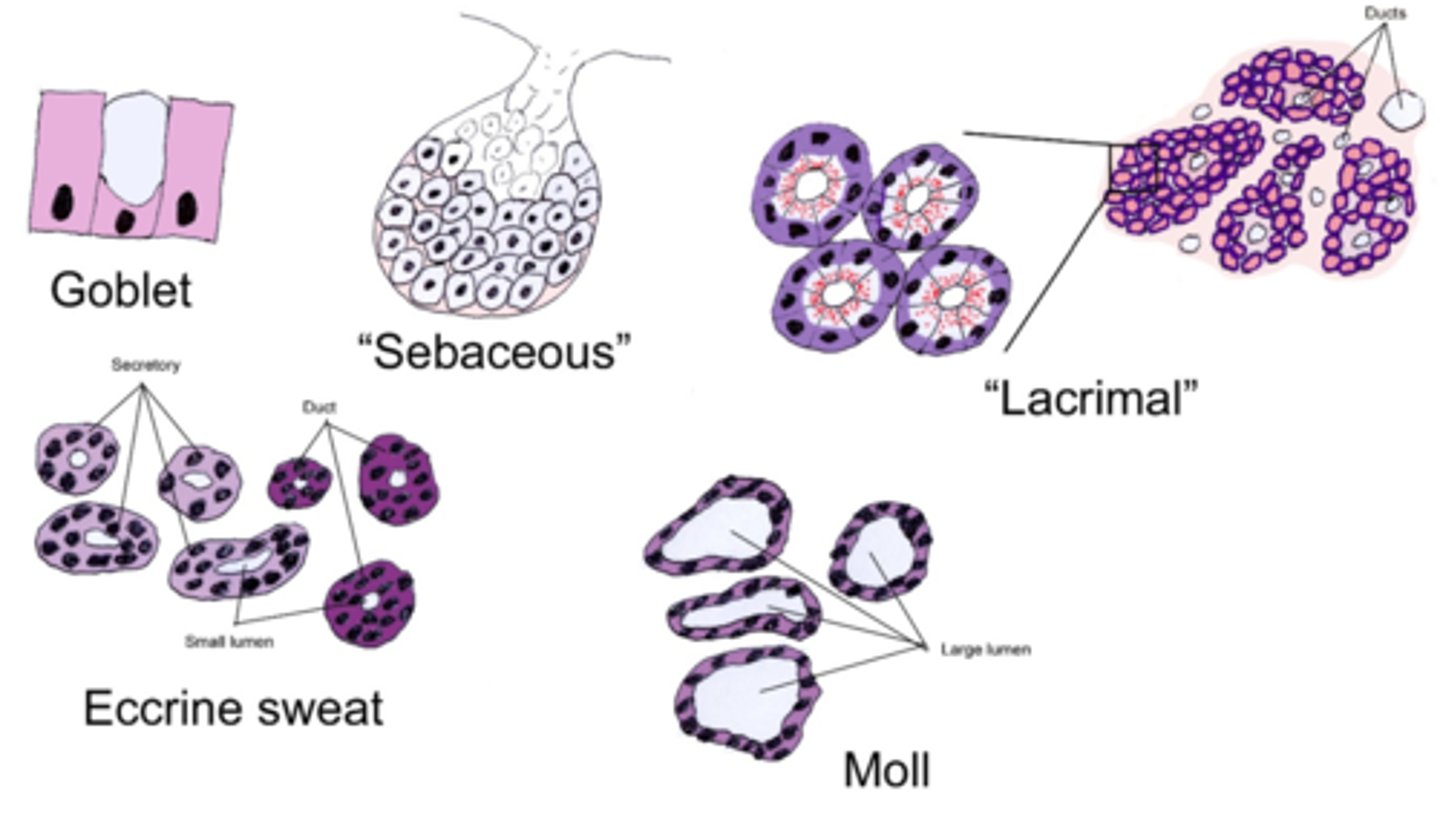
pink apical, purple basal, pie shaped groups of cells closely packed into lobules
Basic identification: What do lacrimal glands look like?
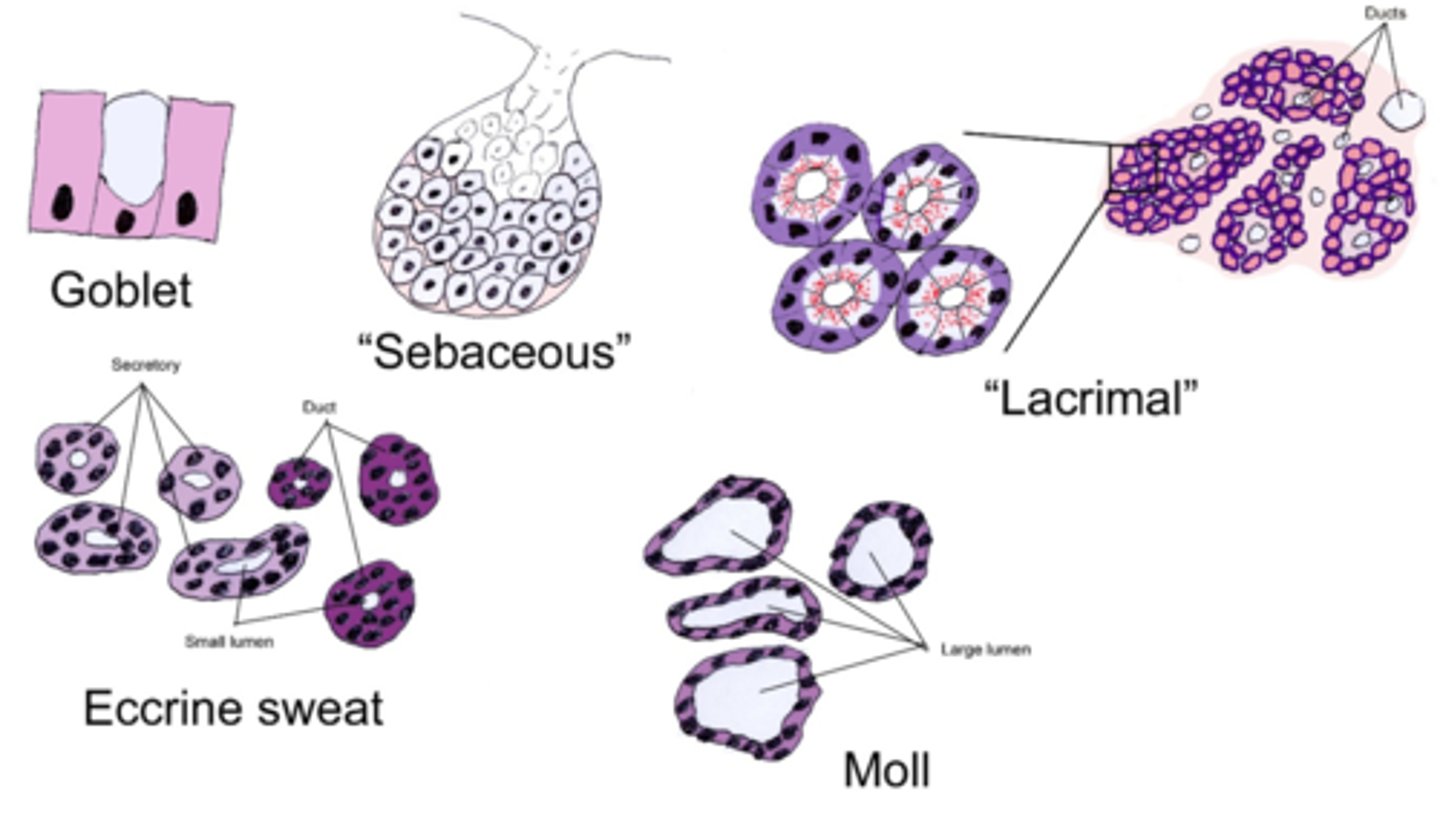
roundish groups of cells with a hole in the middle
(eccrine has a small lumen with some dark and some light profiles, apocrine/Moll has a large lumen associated with an eyelash follicle)
Basic identification: What do sweat glands in general look like?
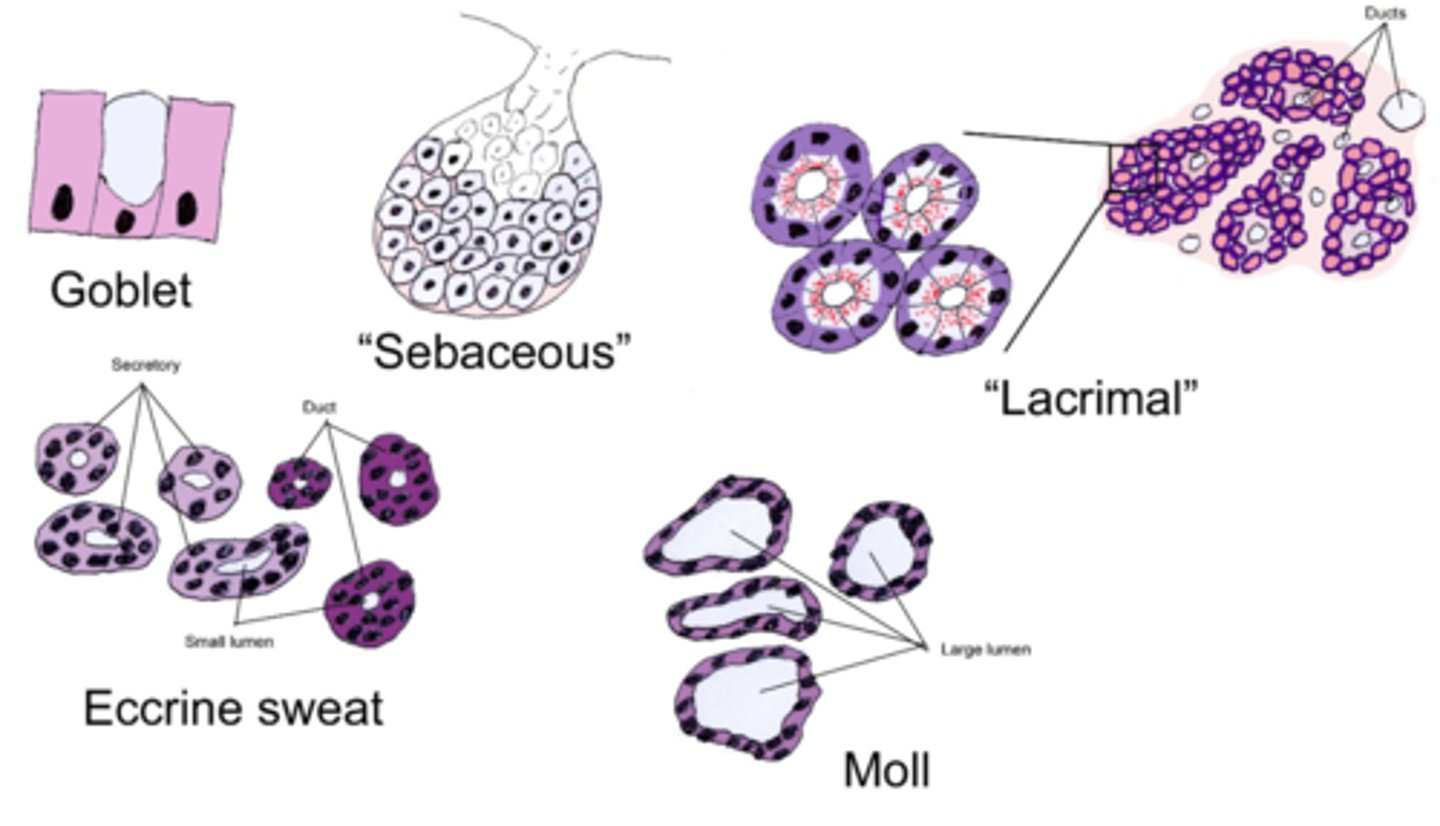
goblet cell
Epithelium flow chart:
Empty looking individual tall cells in some sort of columnar epithelium - if yes, than what type of gland?
sebaceous
Epithelium flow chart:
-- Empty looking individual tall cells in some sort of columnar epithelium - no
-- Rounded "bag" of empty looking cells with central nuclei - if yes, then what family of glands?
meibomian/tarsal gland
Epithelium flow chart:
-- Empty looking individual tall cells in some sort of columnar epithelium - no
-- Rounded "bag" of empty looking cells with central nuclei - yes
-- What if it has many "bags" and the duct opens on the eyelid margin?
gland of Zeis
Epithelium flow chart:
-- Empty looking individual tall cells in some sort of columnar epithelium - no
-- Rounded "bag" of empty looking cells with central nuclei - yes
-- What if it is associated with an eyelash follicle?
regular sebaceous gland
Epithelium flow chart:
-- Empty looking individual tall cells in some sort of columnar epithelium - no
-- Rounded "bag" of empty looking cells with central nuclei - yes
-- What if it is associated with any hair follicle other than an eyelash?
sweat
Epithelium flow chart:
-- Empty looking individual tall cells in some sort of columnar epithelium - no
-- Rounded "bag" of empty looking cells with central nuclei - no
-- Loosely arranged roundish groups of cells with a hole in the middle - if yes, then what family?
main lacrimal gland
Epithelium flow chart:
-- Empty looking individual tall cells in some sort of columnar epithelium - no
-- Rounded "bag" of empty looking cells with central nuclei - no
-- 2 toned (apical pink, basal purple) pie-shaped groups of cells closely packed into lobules - yes
-- What if it has multiple lobules? (NOT in eyelid)
Krause gland
Epithelium flow chart:
-- Empty looking individual tall cells in some sort of columnar epithelium - no
-- Rounded "bag" of empty looking cells with central nuclei - no
-- 2 toned (apical pink, basal purple) pie-shaped groups of cells closely packed into lobules - yes
-- What if it has 1 lobule in the superior conjunctival fornix?