4.1 - Circulatory System
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
The concept of a single-celled organism is that it will directly exchange its ______ & ______ with the world.
nutrients; wastes
For multicellular organisms, they acquire extracellular fluid (ECF), which is …
fluid surrounding individual cells
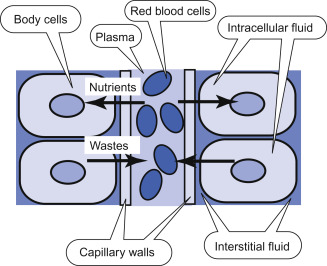
Now that there is ECF within the multicellular organisms, what does it provide for the cells?
exchange place for nutrients and wastes
So now, the cells are no longer directly exchanging their wastes/nutrients with the _____.
world (external environment)
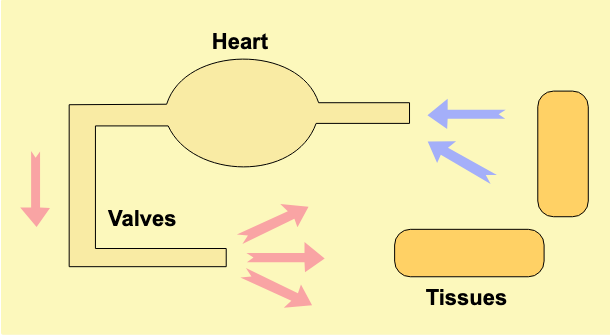
In an OPEN CIRCULATORY system, the organs/cells within body cavities are directly bathed in what? (*fluid)
hemolymph
What are two examples of organisms that use Open circulation?
arthropods, insects
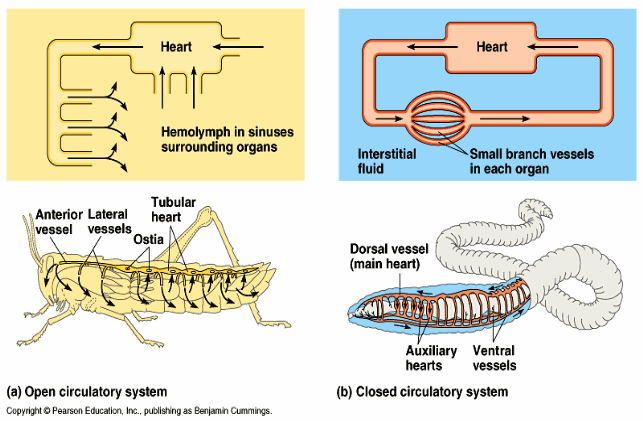
For a CLOSED CIRCULATION organism, there is now a system where…
blood is contained in vessels
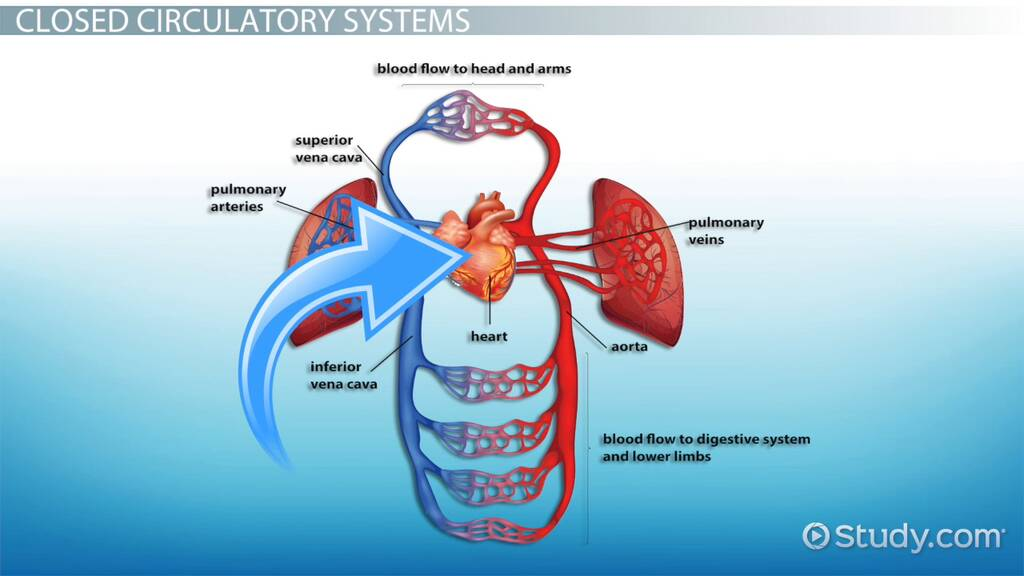
So since blood is in a confined area, it allows for messages to be shared from blood to ____.
organs
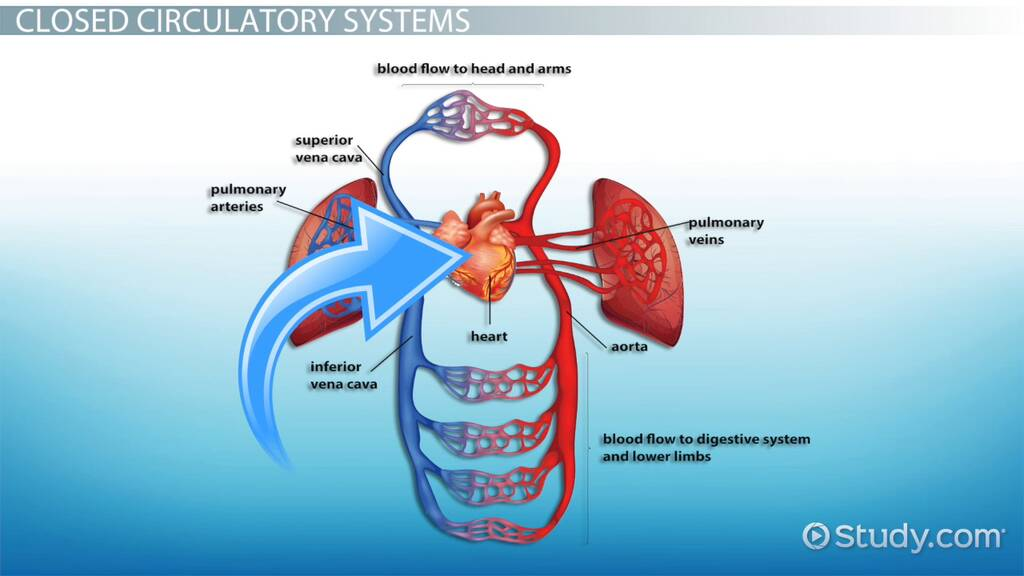
Additionally, with a closed system involving blood vessels, messages can _____ _____ distances.
travel longer
So in a Closed Circulatory Organism - the cells interact with the ECF and exchange waste, and the ECF exchanges with the ____ _____.
blood vessels
What is a lot of our body maintaining?
ECF environment (keep the cells’ baths nice)
What are some things the ECF must maintain? (3)
salinity, pH, temperature
In our Body -
We have cells in ECF which are receiving/getting ____ & _____ and getting rid of ___ & _____. (4)
O2, nutrients; CO2, wastes
When we get oxygen/nutrients and when we remove co2/wastes, what is this done by?
blood
What are 3 exchange systems that work with blood to get nutrients in & wastes out?
digestive, urinary, respiratory system
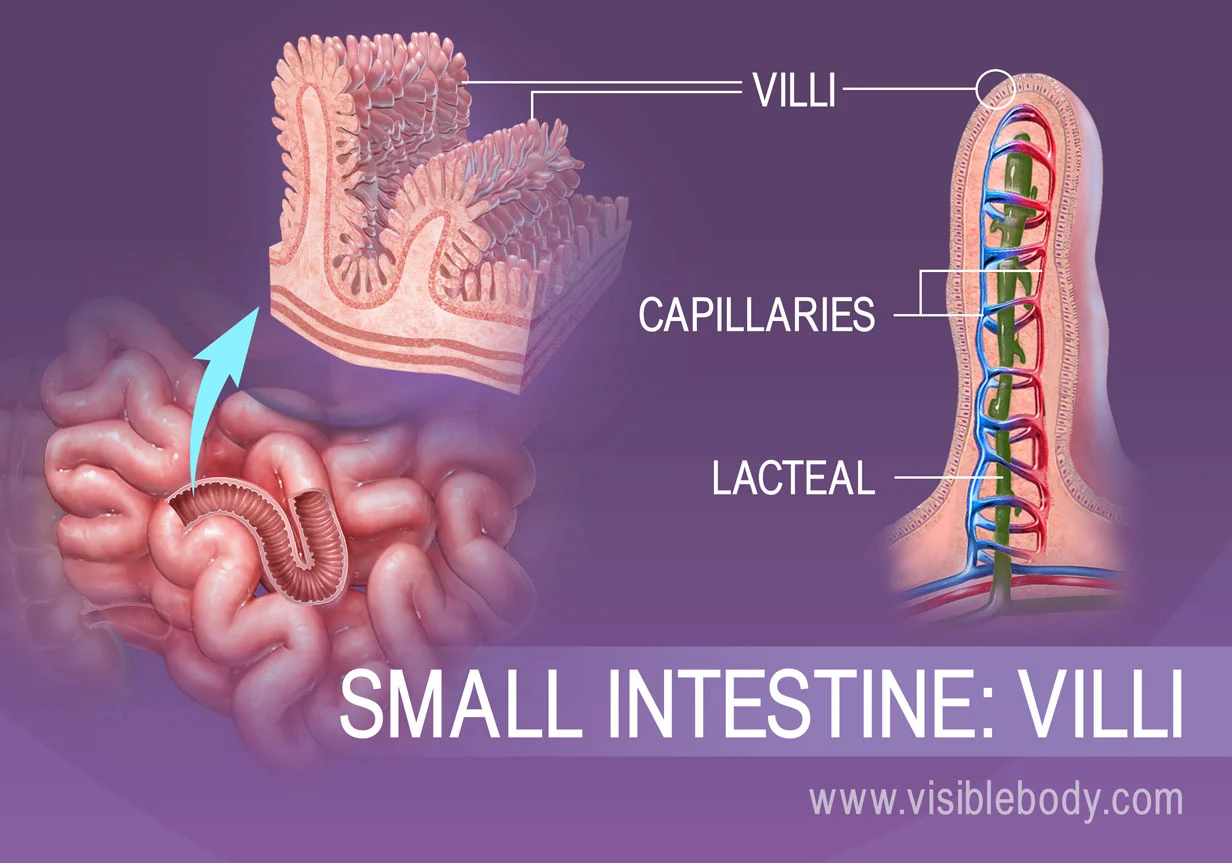
Digestive System
_______ —> _______
world; blood (eat, digest, absorb nutrients)
Urinary System
______ → ______
waste; world (waste is leaving blood)
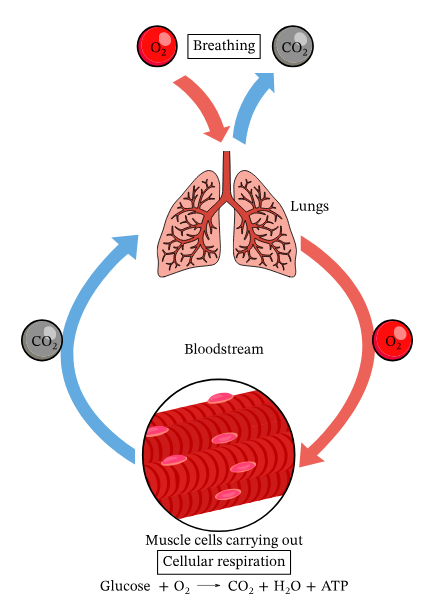
Respiratory System
O2 —→ ____ ; CO2 ——> _____
in; out
2 pumps facilitate the movement of wastes & nutrients, these pumps are apart of the ____.
heart
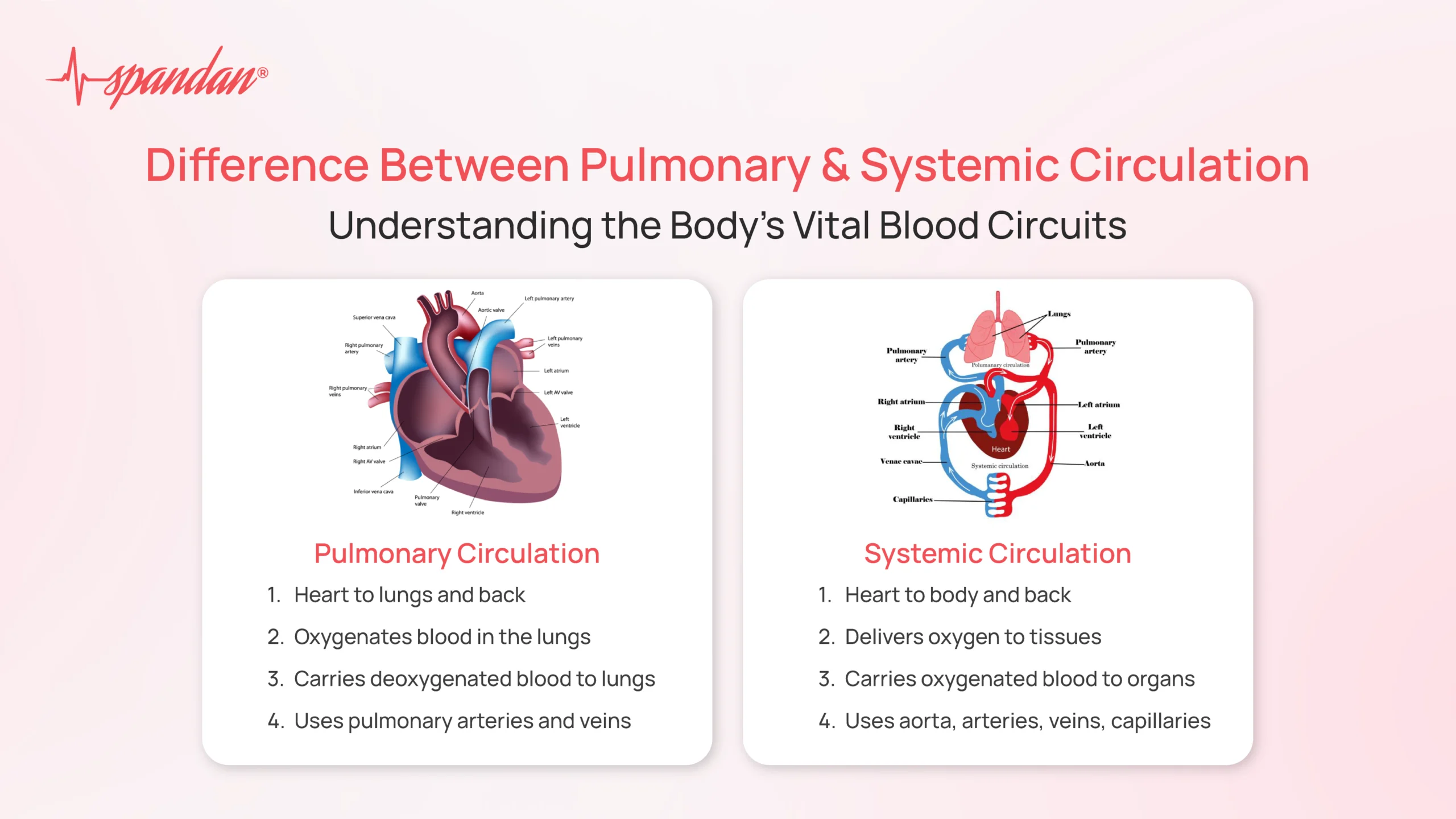
The hearts’ systemic & pulmonary pumps creates the _____/_____ of the blood.
pressure/pump
What type of tissue is blood?
connective tissue
Blood has 2 portions: ____ & ____
plasma; formed elements
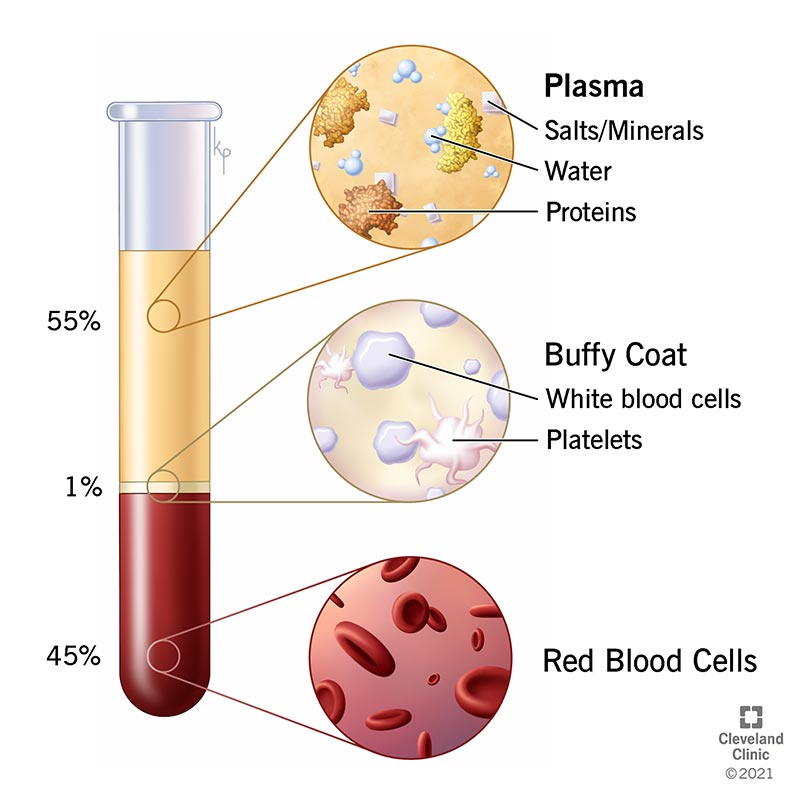
What is within Plasma? (2)
water, dissolved minerals
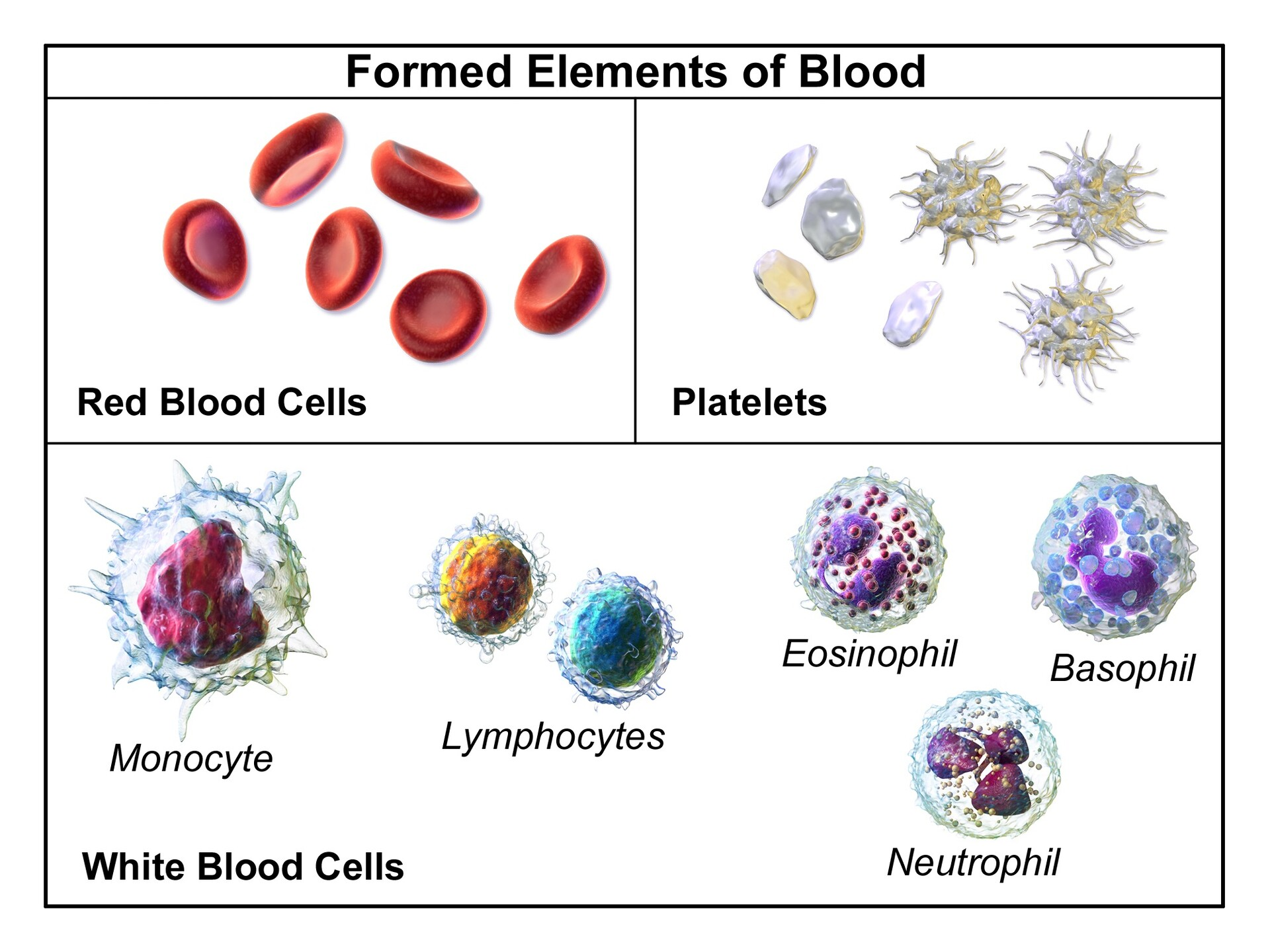
What is within the formed elements? (2)
cells, cell fragments
What are the functions of blood? (5)
O2 transport, carries messages (hormones), coagulation, heat transport, water reservoir
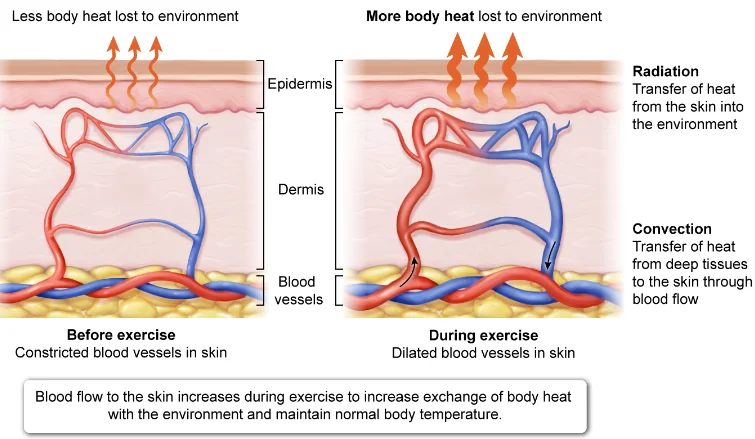
Why is it important for heat transport to be a function of blood? (regarding muscles; obvi it maintains internal temperature)
ensures that muscles doing metabolic processes don’t overheat (since muscles do generate heat)
When blood carries messages, those messges are always ____.
hormones
How is blood a water reservoir —> What can water move in and out of?
ICF ←→ ECF
What’s the exact composition (%) of water in plasma?
92%
What’s the exact composition (%) of protein in plasma?
7%
What’s the exact composition (%) of gases, electrolytes, hormones… in plasma?
1%
What are 3 things that are in the Plasmas’ Proteins
albumin, globulin, fibrinogen
What secretes albumin?
liver
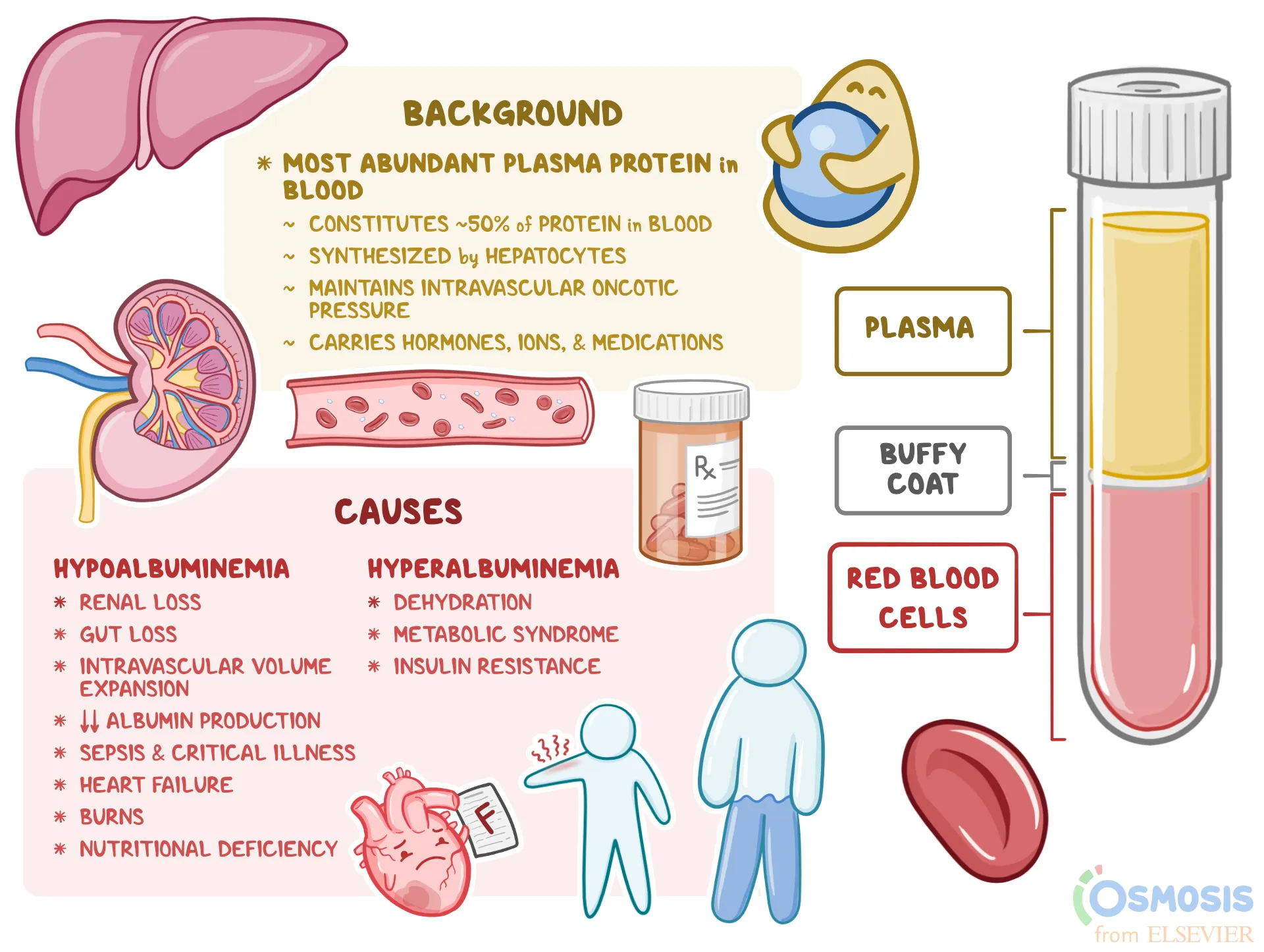
What are the functions of albumin? (2)
increases osmolarity in blood and helps with lipophillic transport (steroid can hitch a ride)
Plasma Proteins - Globulin has 3 substances it contains which are:
transferins, immunoglobulins, plasminogen
What does the suffix -”ogen” mean?
inactive
Globulins - What do transferins do?
moves iron around body
Globulins - What do immunoglobulins do?
does immune system tagging
Globulins - What’s plasminogen?
inactive version of plasma (does nothing until activated)
Plasmas’ proteins - What secretes Fibrinogen?
liver
Is fibrinogen active or inactive?
inactive
What are the 3 Formed Elements of Blood?
erythrocytes, leukocytes, thrombocytes
What are erythrocrytes (RBCs) function?
O2 transport
What are Leukocytes (WBCs) function?
immunity
What are Thrombocytes (platelets) function?
blood clotting
What is the lifespan of an Erythrocyte/Red Blood Cell?
120 days
Erythrocytes have no ____ or ____.
mitochondria; nucleus (they eject their nucleus; which is why they can’t repair if damaged)
How many erythrocytes are currently in the body?
20-30 trillion
What is the rate at which erythrocytes are made per second in bone marrow?
2 million/sec
What is the process of making RBCs in bone marrow called?
Erythropoiesis
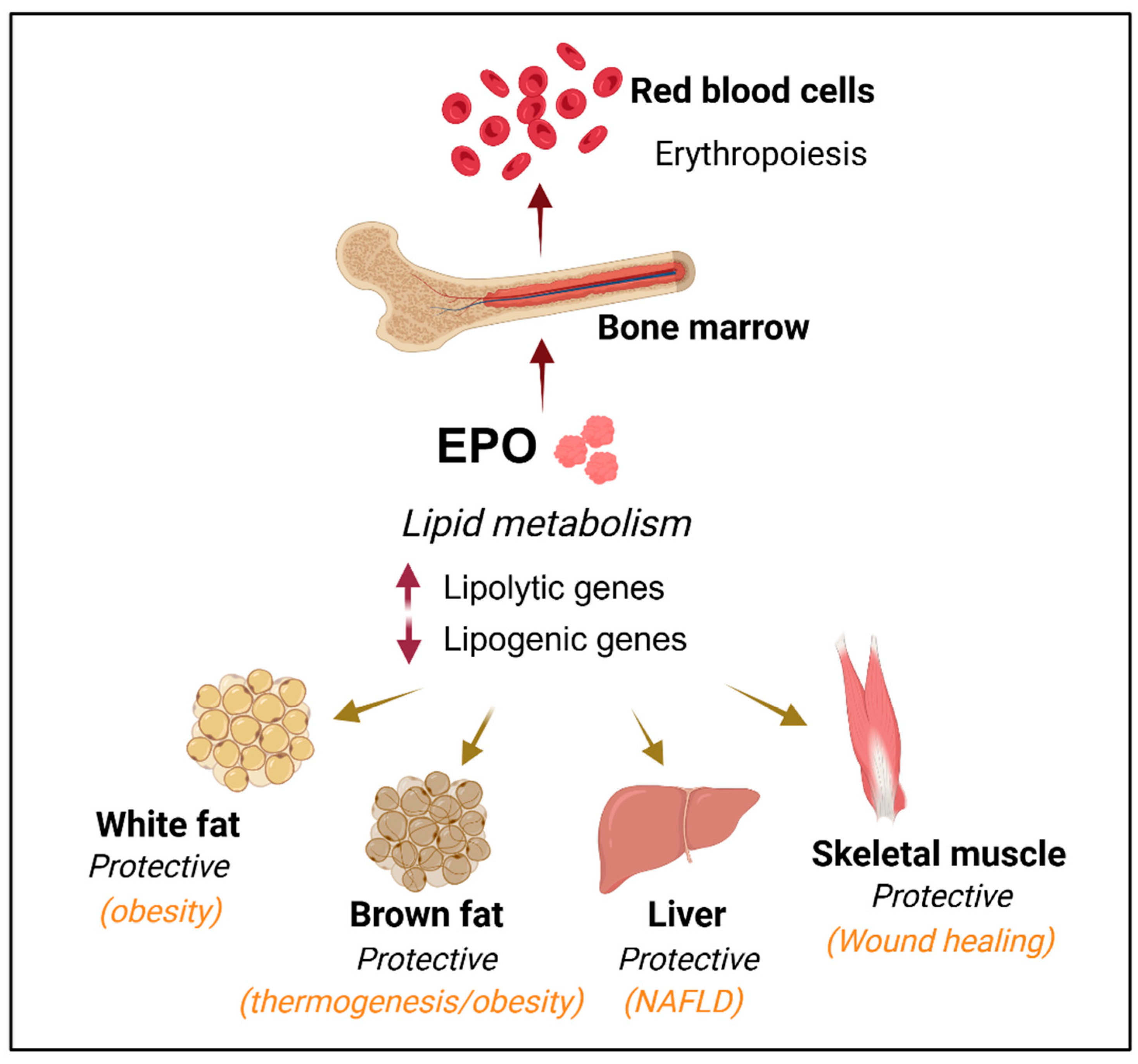
What controls Erythropoiesis? (tells it to make more or not make)
erythropoietin (EPO)
What is the width of a RBC?
8 (micrometers)
What is the thickness of a RBC?
2 (micrometers)
In RBCs there are around ___ _____ hemoglobin proteins.
250 million
What’s hemoglobin?
protein in erythrocytes that carries O2
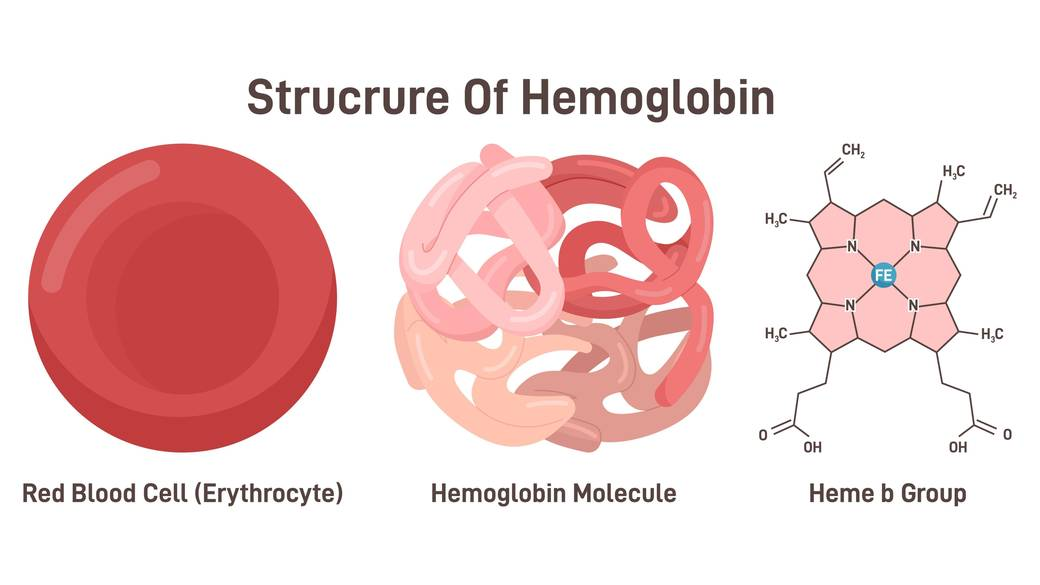
The hemoglobin is divided into 4 subunits; each subunit beings it’s own ?
polypeptide
Each subunit has a socket which is the right shape to hold ___ ____.
heme group
What’s a heme group?
pigment molecule
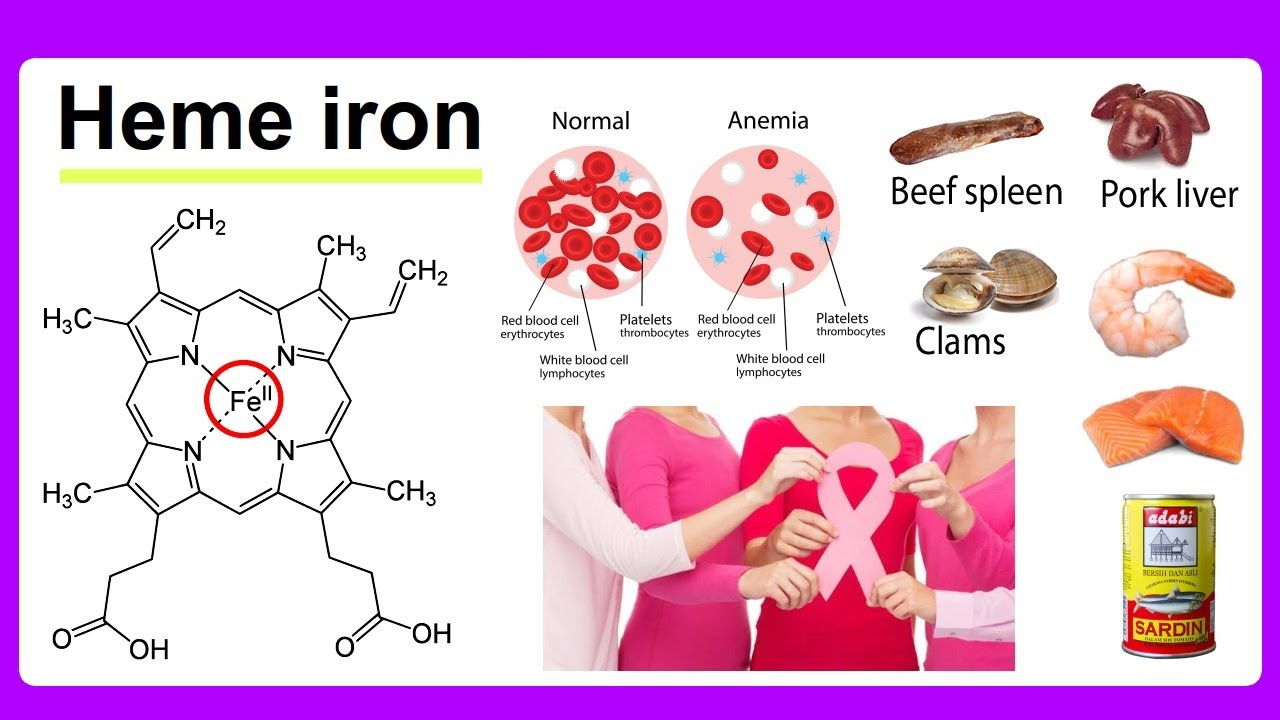
Each heme group is built around one ____ atom?
iron
Why is iron on the heme group?
it binds O2 (how the RBCs can actually carry/hold oxygen)
For every one iron it can bind ___ ____.
one O2
How many O2s can one hemoglobin hold?
4 (so all the hemoglobins together can hold LOTS of oxygen)
What happens to the RBCs that have died? (2)
get recycled by spleen and liver
Dead RBCs first get seperated into two groups:
cell components; hemoglobin
What happens to the cell components? (2)
gets recycled by spleen and liver
What happens to the hemoglobin group? (hint it gets seperated into 2 things)
seperates into protein and heme
What happens to the hemoglobin protein that got separated? (2)
recycled by spleen and liver
What happens to the seperated heme group from the hemoglobin? (divides into 2 things)
divides into iron and biliribin
What does the seperated Iron get used for?
transfernin
Where does biliribin go to?
liver
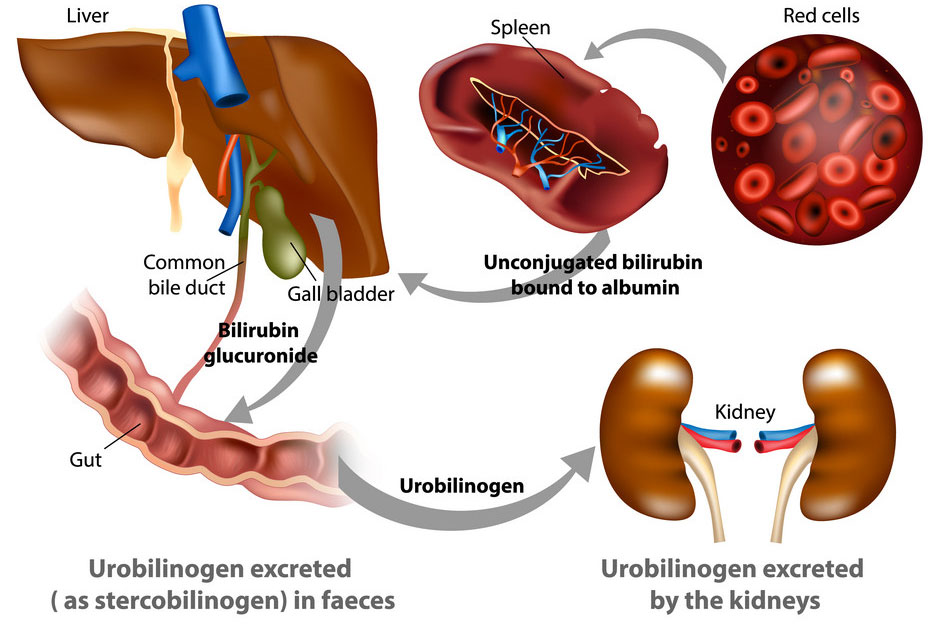
Once biliribin is in the liver what’s next?
gets processed into bile (what gives bile its yellow/greenish color)
Then the bile with the biliribin will be used for digestion and eventually _____ from body.
excreted
What are 5 types of Leukocytes/WBCs?
basophil, eosinophil, neutrophil, monocyte, lymphocyte
What do basophils do?
alerts immune system when somethings’ wrong
What does basophil secrete? (one)
histamine
What do eosinophils do? (2)
coordinates immune response & fights parasites
What do neutrophils do?
phagocytose (these are small and not long lived)
Neutrophils are made ___ and are ___ long lived.
quick; not
What’s a monocytes function?
phagocytosis
Monocytes remain in blood though until they leave blood vessels. Once out of blood, they are now ____ in tissues.
macrophages (these wander around everywhere)
What is the role of lymphocytes? (2)
coordinates immune response and memory
2 functions of lymphocytes? (hint b-cell & Tc cells)
creates antibodies, kills its own infected/cancerous cells
What is the role of lymphocytes & it’s memory capability?
remembers what it’s been exposed to (adaptive immunity)