CHEM2311 Lecture 6: Functional Groups & Intermolecular Forces
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering oxygen and nitrogen-containing functional groups, intermolecular forces (dipole moments, dipole-dipole, hydrogen bonding, London dispersion forces), and their impact on physical properties like boiling point and solubility, based on CHEM2311 Lecture 6 notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
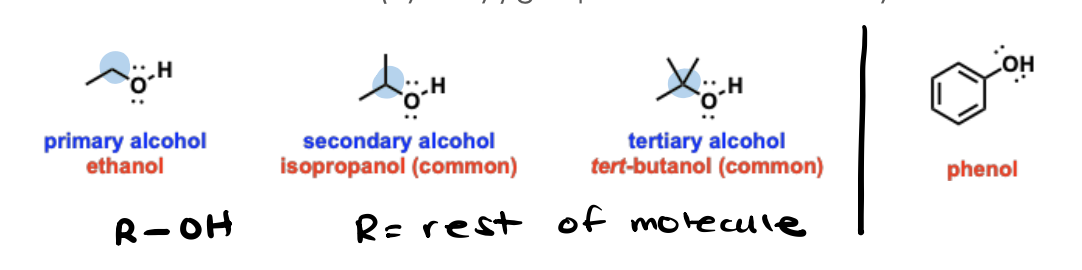
Alcohols
Oxygen-containing functional groups that contain an "OH" (hydroxyl) group connected to an alkyl chain.
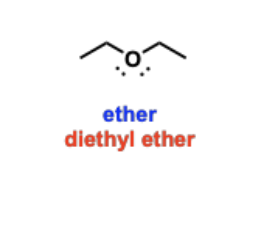
Ethers
Oxygen-containing functional groups that have an oxygen connected to two alkyl chains.
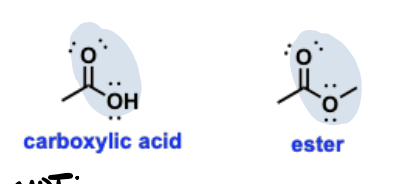
Carbonyl
A functional group containing a carbon-oxygen double bond (C=O).
Aldehydes
Oxygen-containing functional groups that contain a carbonyl (C=O) bonded to at least one alkyl group and one hydrogen atom.
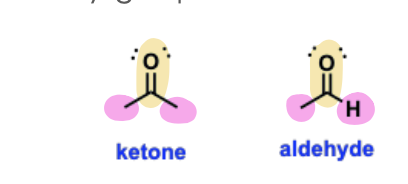
Ketones
Oxygen-containing functional groups that contain a carbonyl (C=O) bonded to two alkyl groups.
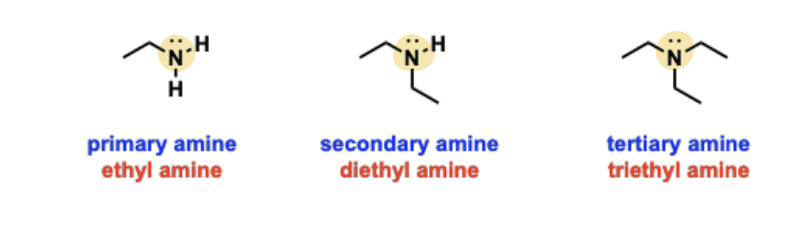
Amines
Nitrogen-containing functional groups that contain an "NHR" (amino) group connected to an alkyl chain, classified by the number of bonds nitrogen makes to an alkyl group (1°, 2°, or 3°).
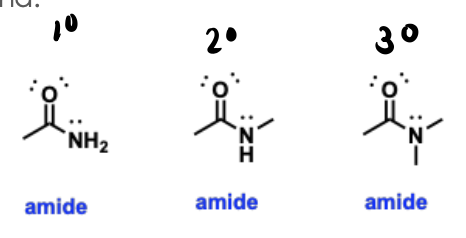
Amides
Nitrogen-containing functional groups that are like the nitrogen version of carboxylic acids and esters, containing a carbonyl group bonded to a nitrogen atom.
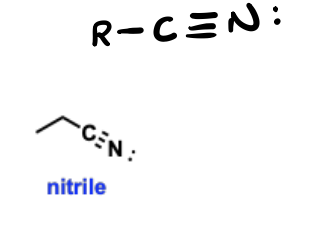
Nitriles
Nitrogen-containing functional groups that contain a carbon-nitrogen triple bond (C≡N).
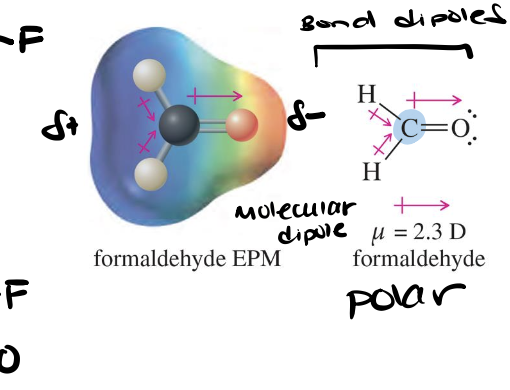
Dipole moment (μ)
A measure of charge separation within a bond or molecule, represented as a vector with direction and magnitude (μ = f x d, units Debey D).
Bond dipoles
The charge separation within a specific bond due to differences in electronegativity between the bonded atoms.
Molecular dipole
The vector sum of all bond dipole moments and lone pair electrons in a molecule, reflecting the overall polarity of the molecule.
Intermolecular Forces (IMFs)
Attractive and repulsive forces between two or more molecules (not intramolecular bonds), whose strength impacts physical properties like boiling point and solubility.
Dipole-Dipole interactions
Intermolecular forces that occur between two polar molecules.
Hydrogen bonding
The strongest type of intermolecular force, requiring one molecule to have a very polar bond to a hydrogen atom (H-F, H-O, or H-N) and another molecule to have a lone pair on a highly electronegative atom (F, O, or N).
London Dispersion Forces (LDFs)
Weak, temporary attractive forces that arise from temporary dipoles induced in non-polar molecules by neighboring molecules. Present in all substances, but primarily significant for non-polar ones.
Boiling Point and IMFs
A substance's boiling point increases as the strength of its intermolecular forces increases.
Branching (in alkanes) and LDFs
Increased branching in alkanes leads to a smaller surface area, fewer contact points between molecules, weaker London Dispersion Forces, and thus a lower boiling point.
Polarizability
The extent to which an atom's or molecule's electron cloud can be displaced or distorted by a positive charge. Large atoms with less tightly held electrons are typically more polarizable.
Polarizability and LDFs
Higher polarizability generally leads to stronger London Dispersion Forces.
Solubility
The extent to which a solute dissolves into a solvent, governed by the general rule 'like dissolves like' (polar dissolves polar, nonpolar dissolves nonpolar).
Hydrophilic
Describes a substance that is soluble in water.
Hydrophobic
Describes a substance with low or no solubility in water.