Final Exam - Temporal Vision
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Spatial vision
changes in luminance across space
Temporal vision
changes in luminance across time. Closely related to motion perception.
hertz (cycles/second)
what is the unit for temporal frequency?
Magno retinocortical pathway
pathway that codes both temporal and motion information. Knowledge of this pathway is used in the diagnosis and management of certain diseases in the visual system.
Temporal acuity
the smallest time interval that can be resolved as a flickering light. Useful in assessing the magnocellular pathway. Measured by determining the critical flicker frequency.
Critical flicker frequency (CFF)
temporal acuity is psychophysically measured by determining this value. The frequency at which a flickering is detected as flickering 50% of the time and as fused the other 50% of the time.
Temporal sinusoids
stimulus whose luminance varies sinusoidally over time. The temporal equivalent of spatial sine wave gratings.
Depth of modulation
the temporal analogous of spatial contrast. Describes the detectability of a flickering stimulus. Ie) higher modulation, just like higher contrast, is easier to detect as flickering

Flicker
the perception that can be elicited by the temporal modulation of a stimulus.
higher
Higher or lower modulation the more flicker. Ie) fluorescent bulbs
lower
Higher or lower modulation the less flicker. Ie) incandescent bulbs
Temporal frequency
describes the rate of a flickering stimulus. Given in hertz.
60 Hz
Temporal frequency of north American households is
integrity of the retina
temporal acuity is useful for assessing the _____ before cataract surgery
myopes, central depressant use, and stimulant drugs
temporal acuities are decrease in these three cases
larger stimulus size
outside of the fovea temporal CFF increases with...
minimal
temporal CFF increases with ______ contrast
smaller targets
In the fovea, temporal CFF increases with...
wavelengths
temporal CFF is equal for all..
Ferry-Porter law
high frequency CFF is directly proportional to the log of the stimulus luminance (retinal illumination). Occurs due to increasing levels of light adaptation and speeding up of retinal processes.
Granit-Harper law
high frequency CFF is directly proportional to the log of the stimulus area. Due to the fact that the peripheral retina is better in detecting flicker than the central retina. Stimulus is more likely to appear as flickering if it is large.
Temporal contrast sensitivity function
a complete description of temporal vision obtained by measuring threshold of modulation over a large number of temporal frequencies.
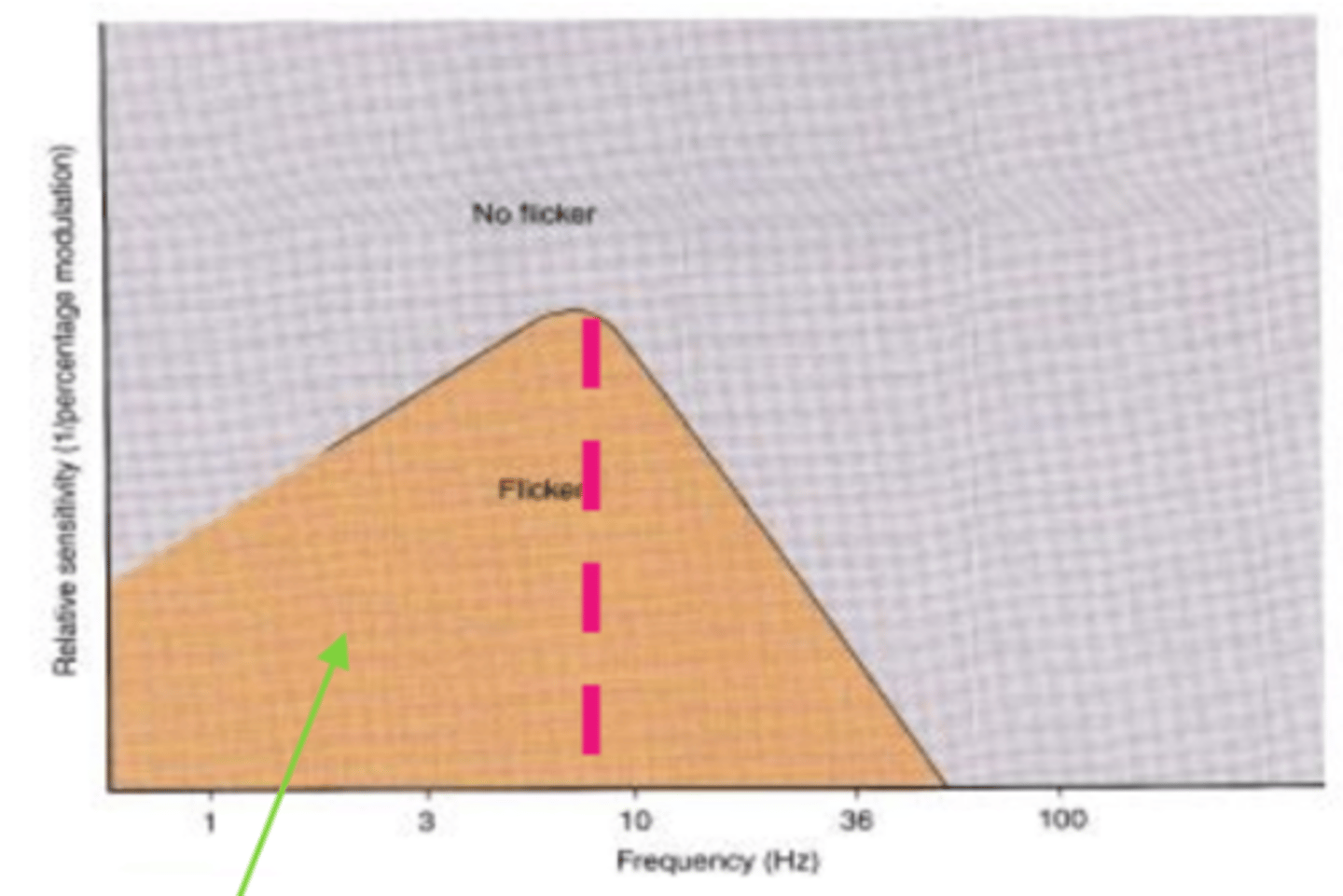
flicker
Area below the curve of the temporal CSF is seen as
steady
Area above the curve of the temporal CSF is seen as
Lateral inhibitory process
process of the retina where sensitivity to low temporal frequencies is reduced. Ie) minute hand on a clock, watching the sun set, etc.
Purkinje tree
branch like pattern seen by patients due to lateral inhibitory processes of the retina.
Troxler phenomenon
phenomenon describing the disappearance of low temporal frequency, nonmoving stimuli in the periphery occurring due to neural adaptation.

Microsaccades
prevent the disappearance of peripheral stimulus. Lack of eye movements may make the stimulus fade and disappear.
neural constraints in coding
High frequency cutoff of the temporal CSF is due to
lateral inhibition
Low frequency cutoff of the temporal CSF is due to _____ of the peripheral retina.
Broca-Sulzer effect
suprathreshold flashes between 50-100 ms appear brighter than stimuli of shorter or longer durations.
Bruke-Bartley effect
flickering light of about 10 Hz appears brighter than a steady light of the same luminance.
Talbot-plateau law
light stimulus that is flickering at a frequency greater than the CFF appears equally bright as a non flickering stimulus of the same luminance.
Successive contrast
exposure to one stimulus affects the perception of a later stimulus if they are given in rapid succession.
Masking
the use of one stimulus to reduce the visibility of another stimulus. Provides information regarding both the spatial and temporal processing of visual information.
Simultaneous masking
masking where the mask and the target appear at the same time
amblyopia
Simultaneous masking is more pronounced in patients with _______. This is observed where VA measurements are worse for the standard eye chart versus an isolated optotype due to the experience of the crowding phenomenon.
Forward masking
masking where the mask is presented before the target
Paracontrast masking
form of forward masking where the mask appears first and the target appears second with both being close to each other in space.
Backward masking
masking where the mask is presented after the target. Occurs when the mask is substantially brighter than the targets.
Metacontrast masking
form of backward masking where the target appears first and the mask appears second with both being close to each other in space. Contributed by lateral inhibition within the retina and stimulation of the faster magnocellular pathway
Glaucoma
RP
ARMD
Temporal vision is affected in these three conditions
FDF (flicker defined form) perimetry
clinical machine measuring temporal vision. Dots on form a border in counterphase pattern and the patient is asked to detect the border which becomes more visible as the dots' contrast increases. Useful in detecting early stages of glaucoma. Ie) Heidelberg edge perimeter