C5 - monitoring and controlling chemical reactions/
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
1
New cards
Rate Of Reaction
A measure of how fast the reaction happens
\
Can be observed by measuring how quickly the reactants are used up or how quickly the products are formed.
\
Depends on temperature, concentration (or pressure for gases) and the size of particles (for solids) and surface area
\
Can be observed by measuring how quickly the reactants are used up or how quickly the products are formed.
\
Depends on temperature, concentration (or pressure for gases) and the size of particles (for solids) and surface area
2
New cards
Rate Of Reaction Equation
amount of reactant used / time
amount of product formed / time
amount of product formed / time
3
New cards
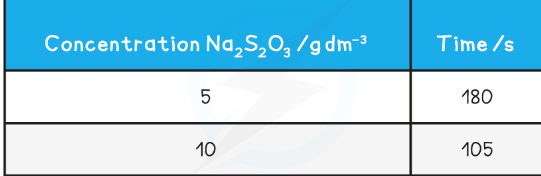
Disappearing cross practical
To investigate the effect of changing concentration on the rate of reaction by measuring the formation of a precipitate
\
Same person should record time taken for cross to disappear as measurement is open to bias, it is based on human perception
\
==**Method:**==
Measure 50 cm3 of sodium thiosulfate solution into a flask
Measure 5 cm3 of dilute HCl into a measuring cylinder
Draw a cross on a piece of paper and put it underneath the flask
Add the acid into the flask and immediately start the stopwatch
Solid sulfur is formed which precipitates in solution, cloudy
\
==Na2S2O3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + S + SO2 + H2O==
\
Look at cross and stop timing when cross is no longer be seen
\
Repeat using different concentrations of sodium thiosulfate solution (mix different volumes of sodium thiosulfate solution with water to dilute it)
\
As there are more reactant particles in a given volume collisions occur more frequently, increasing the rate of reaction
\
Same person should record time taken for cross to disappear as measurement is open to bias, it is based on human perception
\
==**Method:**==
Measure 50 cm3 of sodium thiosulfate solution into a flask
Measure 5 cm3 of dilute HCl into a measuring cylinder
Draw a cross on a piece of paper and put it underneath the flask
Add the acid into the flask and immediately start the stopwatch
Solid sulfur is formed which precipitates in solution, cloudy
\
==Na2S2O3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + S + SO2 + H2O==
\
Look at cross and stop timing when cross is no longer be seen
\
Repeat using different concentrations of sodium thiosulfate solution (mix different volumes of sodium thiosulfate solution with water to dilute it)
\
As there are more reactant particles in a given volume collisions occur more frequently, increasing the rate of reaction
4
New cards
Measuring gas volume
To investigate the effect of changing concentration on the rate of reaction by measuring the volume of gas given off
\
Magnesium and sulfuric acid will react immediately so the flask must be connected to the gas syringe straight after adding the magnesium to avoid gas escaping
\
==**Method**==
Measure 50 cm3 of 1.0 mol/dm3 sulfuric acid solution into a flask
Add magnesium ribbon to flask and connect it to gas collection equipment
Start stopwatch and record the volume of gas every 10 seconds
When reaction is complete, repeat using 1.5 mol/dm3 sulfuric acid
\
be careful you use the right size of gas syringe because if the experiment is to vigorous you can blow the plunger out the end of the syringe.
\
time on the x-axis and concentration and volume of gas on the y-axis. With an increase in the concentration of a solution, the rate of reaction will increase so the volume of gas increases
\
==**Conclusion:**==
As there are more reactant particles in a given volume collisions occur more frequently, increasing the rate of reaction
\
Magnesium and sulfuric acid will react immediately so the flask must be connected to the gas syringe straight after adding the magnesium to avoid gas escaping
\
==**Method**==
Measure 50 cm3 of 1.0 mol/dm3 sulfuric acid solution into a flask
Add magnesium ribbon to flask and connect it to gas collection equipment
Start stopwatch and record the volume of gas every 10 seconds
When reaction is complete, repeat using 1.5 mol/dm3 sulfuric acid
\
be careful you use the right size of gas syringe because if the experiment is to vigorous you can blow the plunger out the end of the syringe.
\
time on the x-axis and concentration and volume of gas on the y-axis. With an increase in the concentration of a solution, the rate of reaction will increase so the volume of gas increases
\
==**Conclusion:**==
As there are more reactant particles in a given volume collisions occur more frequently, increasing the rate of reaction
5
New cards
The volume of gas given off
\
6
New cards
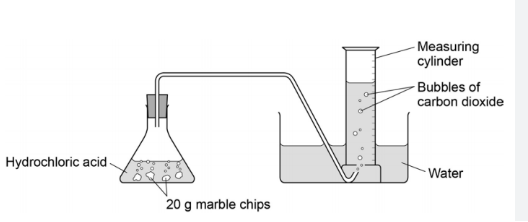
Reaction of hydrochloric acid and marble chips
You can use this experiment to show how surface area affects the rate of reaction.
\
Set up the apparatus set up in the image
\
Measure the volume of gas produced using a gas syringe. Take readings at regular time intervals and record your results in a table.
\
You can plot a graph of your results - time goes on the x axis and volume goes on the y axis
\
Repeat the experiment with the same volume, concentration of acid and mass of marble chips, but with the marble more crushed up.
\
Then repeat with the same mass of powdered chalk.
\
Set up the apparatus set up in the image
\
Measure the volume of gas produced using a gas syringe. Take readings at regular time intervals and record your results in a table.
\
You can plot a graph of your results - time goes on the x axis and volume goes on the y axis
\
Repeat the experiment with the same volume, concentration of acid and mass of marble chips, but with the marble more crushed up.
\
Then repeat with the same mass of powdered chalk.
7
New cards
What happens to the rate of reaction of the solid is in finer particles? Reaction of hydrochloric acid and marble chips
Using finer particles means that the marble has a larger surface area.
\
Lines 1 to 3 on the graph show the finer the particles are (and the greater the surface area of the solid reactants) , the faster the reaction goes.
\
Line 4 shows the reaction if a greater mass of small marble chips is added . The extra surface area gives a faster reaction and there is also more gas evolved overall.
\
Lines 1 to 3 on the graph show the finer the particles are (and the greater the surface area of the solid reactants) , the faster the reaction goes.
\
Line 4 shows the reaction if a greater mass of small marble chips is added . The extra surface area gives a faster reaction and there is also more gas evolved overall.
8
New cards
What happens during the reaction of Magnesium and dilute hydrochloric acid?
This reaction is good for measuring the effects of changing the concentration on reaction rate.
\
This reaction gives off hydrogen gas, so you can measure lots of mass as the gas is formed using a mass balance.
\
This reaction gives off hydrogen gas, so you can measure lots of mass as the gas is formed using a mass balance.
9
New cards
How can you tell a rate of reaction is faster on a graph?
The quicker they are the steeper the gradient.
You can work out the gradient by the equation of:
Change in Y/Change in X
You can work out the gradient by the equation of:
Change in Y/Change in X
10
New cards
What is the collision theory?
Reaction rates are explained by this, the rate of a chemical reaction depends on this;
\
The collision frequency of reacting particles (how often they collide), reactions happen if particles collide so if you increase the number of collisions, the reactions happen more quickly (the rate increases)
\
The more successful collisions, the faster the reaction
\
The energy transferred during a collision. Particles have to collide with enough energy for the collision to be successful.
\
The collision frequency of reacting particles (how often they collide), reactions happen if particles collide so if you increase the number of collisions, the reactions happen more quickly (the rate increases)
\
The more successful collisions, the faster the reaction
\
The energy transferred during a collision. Particles have to collide with enough energy for the collision to be successful.
11
New cards
What happens to the rate of reaction if you increase temperature?
When the temperature is increased the particles move faster, if they move faster they’re going to have more collisions.Reactions only happen if particles collide with enough energy.
\
Therefore, at higher temperatures there will be more successful collisions as more particles collide with each other with more energy so increasing the temperature also increases the rate of reaction.
\
Therefore, at higher temperatures there will be more successful collisions as more particles collide with each other with more energy so increasing the temperature also increases the rate of reaction.
12
New cards
What happens if we increase the concentration or pressure (gas) in the rate of reaction?
If a solution is made more concentrated, there are more particles of a reactant in the same volume . This makes collisions more likely as there is more of them, so the reaction rate increases.
\
In a gas, increasing the pressure means that the particles are more crowded. This means that the frequency of collisions between particles will increase - so the rate of reaction will also increase.
\
In a gas, increasing the pressure means that the particles are more crowded. This means that the frequency of collisions between particles will increase - so the rate of reaction will also increase.
13
New cards
What happens if we increase the smaller solid particles (or surface area) in the rate of reaction?
If one reactant is a solid, breaking it into smaller pieces will increase the surface area to volume ratio (more of the solid will be exposed, compared to the overall volume)
\
The particles around it will have more area to work on, so the frequency of collisions will increase.
\
This means that the rate of reaction is faster for solids with a larger surface area to volume ratio (smaller solid particles)
\
The particles around it will have more area to work on, so the frequency of collisions will increase.
\
This means that the rate of reaction is faster for solids with a larger surface area to volume ratio (smaller solid particles)
14
New cards
What is a catalyst?
a substance which increases the rate of reaction, without being chemically changed or used up in the reaction.
\
You only need a small amount to catalyse large amounts of reactants.
\
Catalysts work by decreasing the activation energy needed for a reaction to occur. They do this by providing an alternative reaction pathway that has lower activation energy.
\
You only need a small amount to catalyse large amounts of reactants.
\
Catalysts work by decreasing the activation energy needed for a reaction to occur. They do this by providing an alternative reaction pathway that has lower activation energy.
15
New cards
How can you identify catalysts in chemical reactions?
16
New cards
What are enzymes?
Enzymes control cell reactions and are biological catalysts. This means they catalyse (speed up) the chemical reactions in living cells. Reactions catalysed by enzymes include respiration, photosynthesis and protein synthesis.
17
New cards
What is a reversible reaction?
the products react with each other to produce the original reactants. A reaction that can go both ways.
18
New cards
How will reversible reactions reach equillibrium?
As the reactants react, their concentrations fall - so the forward reaction will slow down. But as more products are made their concentration rise, the backward reaction will speed up.
\
After a while the forward reaction will be at the same speed as the backward one - this is equilibrium. This means both reactions are happening but there is no overall effect - dynamic equilibrium.
\
Dynamic equilibrium means the concentration of the reactants and products have reached a balance and won’t change.
\
Equilibrium can only take place if the reversible reaction takes place in a “closed system”. This mean none of the reactants or products can escape.
\
After a while the forward reaction will be at the same speed as the backward one - this is equilibrium. This means both reactions are happening but there is no overall effect - dynamic equilibrium.
\
Dynamic equilibrium means the concentration of the reactants and products have reached a balance and won’t change.
\
Equilibrium can only take place if the reversible reaction takes place in a “closed system”. This mean none of the reactants or products can escape.
19
New cards
How does temperature change the position of equilibrium in a reversible reaction?
Exothermic in one direction, endothermic in the other
\
If you decrease the temp, the equilibrium will move in the exothermic direction to produce more heat.
\
If you increase the temperature, the equilibrium will move in the endothermic direction to absorb the extra heat.
\
If you decrease the temp, the equilibrium will move in the exothermic direction to produce more heat.
\
If you increase the temperature, the equilibrium will move in the endothermic direction to absorb the extra heat.
20
New cards
How does pressure (gases) change the position of equilibrium?
If you increase the pressure, the equilibrium will move towards the side that has fewer moles of gas to reduce pressure.
\
If you decrease the pressure, it will move towards the side that has more moles of gas to increase pressure.
\
If you decrease the pressure, it will move towards the side that has more moles of gas to increase pressure.
21
New cards
How does concentration change the position of equilibrium?
If you increase the concentration of the reactants, the equilibrium will move to the right to use up the reactants (making more products)
\
If you increase the concentration of the products, it will move to the left to use up products (making more reactants)
\
Decreasing the concentrations will have the opposite effect
\
If you increase the concentration of the products, it will move to the left to use up products (making more reactants)
\
Decreasing the concentrations will have the opposite effect