Chemistry Ch 3 & 21
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
Democritus’ beliefs
believed matter was made up of small particles called “atomos” = “indivisible”
Aristotle’s beliefs
disagreed with Democritus
believed matter was continuous
4 categories of matter: Earth, Air, Fire, Water
Law of Conservation of Matter
Mass of the reactants = Mass of the products
Law of Definite Proportions
whenever a compound is made, it has the same ratios of each element
Law of Multiple Properties
2 elements can combine in different ratios to form different compounds
Dalton’s atomic theory
All matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms
Atoms of a given element are identical of size, mass, and other properties
Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed
Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole number ratios to form chemical compounds
In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged
What has changed from Dalton’s atomic theory to modern atomic theory? What hasn’t changed?
Changes
- atoms are divisible into subatomic particles
- a given element can have atoms with different masses
Unchanged
- atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged in chemical reactions
- atoms cannot be created or destroyed
What was Democritus the first to propose?
Matter is not infinitely divisible
T/F: Philosophers thousands of years ago tested their ideas using the scientific method.
False
How does a cathode ray work?
electric charge is applied —> current passes through cathode ray tubes —> surface of tube opposite of cathode glows
a ray of radiation (cathode ray) travels from the cathode to the anode
Observations of Thomson’s cathode ray experiment
cathode rays (electrons) were deflected by a magnetic field in the same manner as a wire carrying electric current, which was known to have a negative charge
tldr the rays were deflected away from a negatively charged object
Conclusions of Thomson’s cathode ray experiment
charge to mass ratio of cathode rays = 1.76 × 10^11 C/kg
this ratio is always the same regardless of the metal or gas used
discovery of the electron
electrons are present in all elements
atom is divisible
e^- is a fundamental particle
charge:mass ratio is very large
Milikan’s oil drop experiment
measured the charge of an electron
scientists later found electron mass
Plum pudding model: who and what
JJ Thomson
atom has a spherical shape
plum = protons, pudding = electrons
In what experiment was the nucleus discovered?
Rutherford’s gold foil experiment
Rutherford’s gold foil experiment
studied how positively charged alpha particles interacted with solid matter
bombarded a thin piece of gold foil with alpha particles
Discoveries and conclusions of Rutherford’s gold foil experiment
some particles deflected back towards the source, but most went through
therefore the plum pudding model was incorrect
led to the conclusion that the atom is composed of a dense, positively charged nucleus surrounded by negative electrons
Nuclear strong force
holds nuclear particles together
Who discovered the neutron?
Chadwick
Isotopes: Hyphen notation
X-A (X = chemical symbol, A = mass number)
Isotopes: Nuclear symbol notation
A X (Z = atomic number)
Z
Nuclide
general term for any nucleus of an isotope
Hydrogen isotopes
Protium (H-1), Deuterium (H-2), Tritium (H-3)
What is the mass in amu of C-12?
12 amu
How to calculate average atomic mass?
weighted average, abundances in decimals
(mass1)(abundance1) + (mass2)(abundance2)
Nucleons
neutrons and protons
Mass defect
difference in mass between the nucleus and its component nucleons
Nuclear binding energy
the energy released when a nucleus is formed from nucleons
the amt of energy needed to break 1 mol of nuclei into individual nucleons
measure of the stability of a nucleus (strong force)
T/F: The atom is spherical
True
T/F: In the Rutherford nuclear-atom model, heavy subatomic particles reside in the nucleus
True
Band of stability
the stable nuclei cluster over a range of neutron-proton ratios
*outside this band, all nuclei are radioactive and all atoms undergo reactions (decay) to become stable; band ends at Pb-208 (all elements atomic numbers >82 radioactive)
Stable nuclei n-p ratio
1:1, in higher atomic numbers it gets closer to 1.5:1
Magic numbers
numbers of electrons that complete shells
Transmutation
change in the identity of a nucleus as a result of a change in the number of its protons
What ratio does the type of radioactive decay depend on?
n:p
Alpha decay
an alpha particle is emitted from the nucleus
restricted to only very heavy particles w more than 82 protons
4/2 He
Alpha particle
2 protons and 2 neutrons; Helium-4
Mole
SI unit for the amount of substance
- amt of substance that contains as many particles as there are atoms in exactly 12g of C-12
Avogadro’s Number
6.022 × 10^(23)
number of particles in 1 mole of a pure substance
Molar mass
numerically equal to the atomic mass
mass of one mole of a pure substance
g/mol or kg/mol
Mole to gram conversion
multiply by molar mass
Gram to mole conversion
divide by molar mass
Mole to number of atoms conversion
multiply by Avogadro’s number
Number of atoms to moles conversion
divide by Avogadro’s number
Grams to number of atoms conversion
divide by molar mass and multiply by Avogadro’s number
Number of atoms to grams conversion
multiply by molar mass and divide by Avogadro’s number
Einstein’s equation relates which quantities?
Energy, mass, speed of light
The mass of the nucleus is always _____ the sum of the masses of the individual protons and neutrons that make up the nucleus
less than
Beta Decay
radioisotope as too many neutrons relative to its number of protons
decreases the n:p ratio by converting a neutron into a proton and electron
atomic number +1, mass unchanged
Beta particle
an electron emitted from the nucleus
0/-1 B
Positron
a particle that has the same mass as an electron but as a positive charge, and emitted from the nucleus
0/+1 B
Positron emission
a proton is converted into a neutron by emitting a positron
this decreases the number of protons
atomic number -1, mass unchanged
Electron capture
decreases the number of protons in unstable nuclei below the band of stability
an inner orbital electron is captured by the nucleus of its own atom
to increase the number of neutrons, an inner orbital electron combines with a proton to form an neutron
atomic number -1, mass unchanged
Gamma ray decay
high-energy electromagnetic waves emitted from a nucleus as it changes from an excited state to a ground energy state
Alpha particle stopped by:
a few sheets of paper
Beta particle stopped by:
a few cm of lead
Gamma ray stopped by:
several cm of lead
Parent nuclide
unstable nucleus
Daughter nuclide
stable nucleus
When does decay stop?
When the atom becomes stable
Half-LIfe
the time required for half the atoms of a radioactive nuclide to decay
More stable nuclides decay ____ and have _____ half-lives
slowly, longer
Half-Life equation
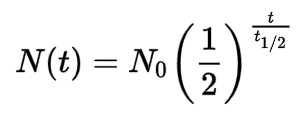
Artificial Transmutation
made by artificial radioactive nuclides (not found on Earth)
How are artificial radioactive nuclides made?
bombardment of stable nucleus with a neutron or alpha, beta, or gamma radation
Transuranium elements
elements atomic numbers 93 and above
- all were produced in a lab by induced transmutation
Stability of transuranium elements
UNSTABLE!!
What determines whether an atom spontaneously decays and the type of radiation it emits?
its n:p ratio
What type of radiation has the greatest penetrating power?
Gamma radiation
Alpha particles are ____ charged
positively
Beta particles are attracted to a ______ charged plate, meaning they are _____ charged
postitively, negatively
Which kind of radiation is most difficult to shield a person from?
Gamma ray
Radiation exposure
nuclear radiation can transfer the energy from nuclear decay to the electrons of atoms or molecules and cause ionization
Rem
unit that measures exposure to human tissue
R/Roentgen
unit that measures nuclear exposure
Film badges
use exposure of film to measure the approximate radiation exposure of people working with radiation
Geiger-Müller counters
instruments that detect radiation by counting electric pulses carried by gas ionized by radiation
Scintillation counters
instruments that convert scintillating light to an electric signal for detecting radiation
Radioactive dating
the approximate age of an object is determined based on the amount of certain radioactive nuclides present
age is estimated by measuring either the accumulation of a daughter nuclide or the disappearance of the parent nuclide
ex. C-14 dating
Radioactive nuclides in medicine
used to destroy certain types of cancer cells
radioactive tracers = radioactive atoms that are incorporated into substances so that movement of the substances can be followed by radiation detectors
Radioactive nuclides in agriculture
used to determine the effectiveness of the fertilizer
radiolabeled pesticides as an alternative
also used to prolong shelf life
Which disease is radiation therapy used to treat?
Cancer
What unit accounts for the type of living tissue that absorbs a dose of radiation?
Rem
Nuclear fission
a very heavy nucleus splits into more stable nuclei of intermediate mass
- releases a lot of energy, less energy per nucleon however
- can be spontaneous or induced
Chain reaction
a reaction in which the material that starts the reaction is also one of the products and can start another reaction
Critical mass
minimum amount of a nuclide that provides the number of neutrons needed to sustain a chain reaction
Subcritical mass
not massive enough to sustain a chain reaction
Supercritical mass
chain reaction rapidly escalates
Nuclear reactors
use controlled fission chain reactions to produce energy and radioactive nuclides
Shielding
outer covering; absorbs excess radiation + gamma rays; usually thick concrete
Fuel
uranium fuel rods, usually U-235
Coolant
liquid water under high pressure; absorbs excess energy
Control rods
absorb excess neutrons to contain chain reaction
Moderator
controls the speed of the neutrons (slows them down)
Problems in nuclear reactors
produce highly radioactive waste
not a lot of U-235 to use as fuel
Which type of nuclear change releases more energy per amu?
fusion
Nuclear Fusion
low mass nuclei combine to form a heavier more stable nucleus
What could nuclear fusion be used for?
generating energy
Advantages of fusion
releases more energy per gram of fuel than fission
lightweight isotopes used as fuel are abundant
products generally not radioactive
Limitations of fusion
requires extremely high energies to initiate and sustain a reaction
confinement of extreme temperature reaction (hard to confine)