Pitt Anatomy Lab Quiz 3 - cell types
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
simple columnar
single layer of column shaped cells with round nucleus, contains goblet cells
simple columnar - function
secretion of mucous, absorption
simple columnar - location
lines digestive tract and portions of the uterus and uterine tubes
simple cuboidal
single layer of cubed shaped cells, large and round with central nuclei
simple cuboidal - function
absorption, secretion, active transport
simple cuboidal - location
thyroid, ovaries, kidney duct
pseudostratified
single layer of cells with differing nuclei, nuclei located at different heights, all cells touch base membrane, not all touch apical surface, contain cilia
pseudostratified - function
goblet cells release mucous that coats passage ways
pseudostratified - location
respiratory tract, male urethra
simple squamous
single layer thick, flat or oval with a central nucleus
simple squamous - function
diffusion, secretion, filtration
simple squamous - location
capillaries, endothelium, alveoli
stratified squamous
multiple layers of cells with nuclei throughout
stratified squamous - function
protection against abrasion
stratified squamous - location
esophagus, anus, mouth, vagina, epidermis of skin
stratified cuboidal
many layers of cube cells
stratified cuboidal - function
protection, secretion
stratified cuboidal - location
sweat glands, ovary follicles, mammary glands
transitional
tissue changes shape, relaxed = cuboidal, stretched = squamous
transitional - function
allows stretching as it fills
transitional - location
bladder, urethra, ureters
stratified columnar
apical layer is composed of columnar cells, basal is cuboidal
stratified columnar - function
protection, secretion
stratified columnar - location
large ducts and some glands
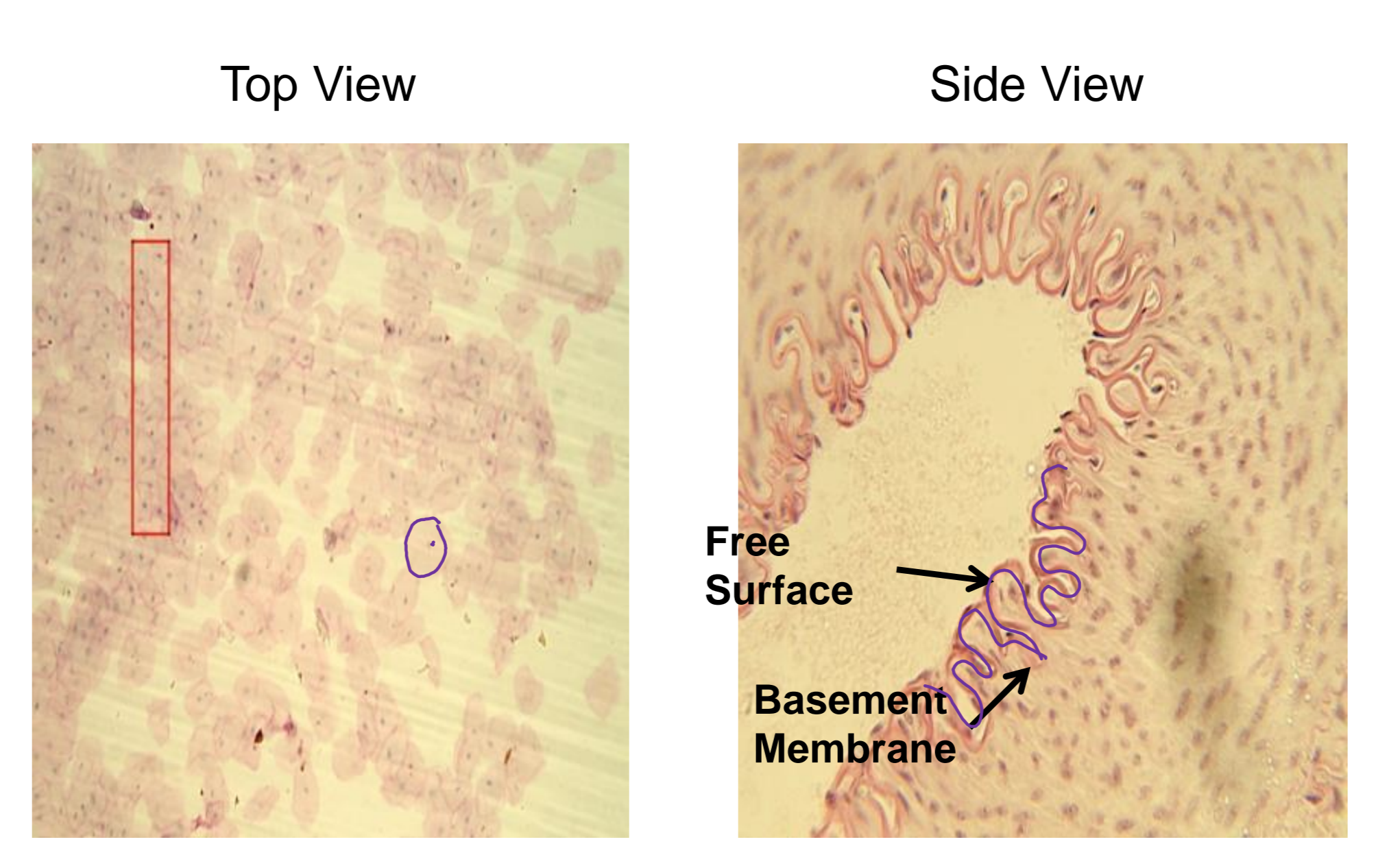
what tissue is depicted in the image
simple squamous
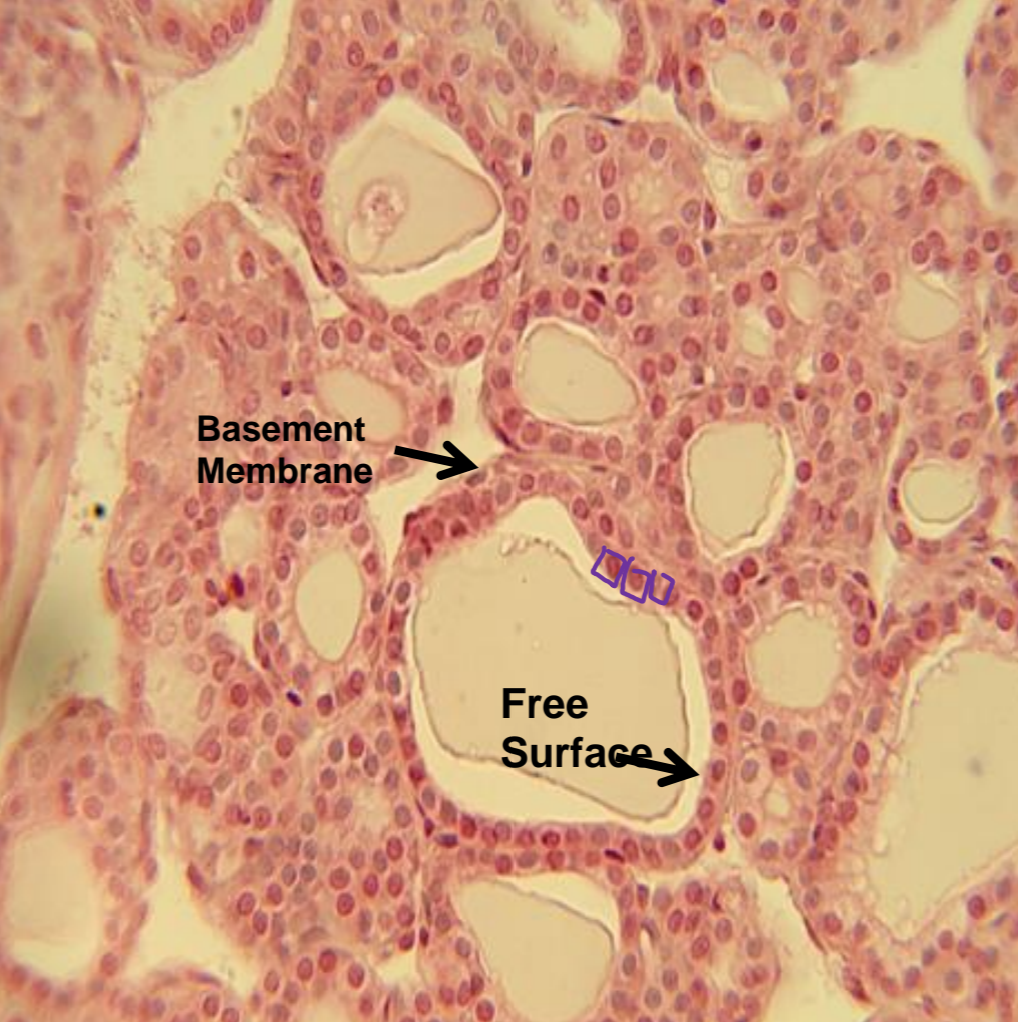
what tissue is depicted in the image
simple cuboidal
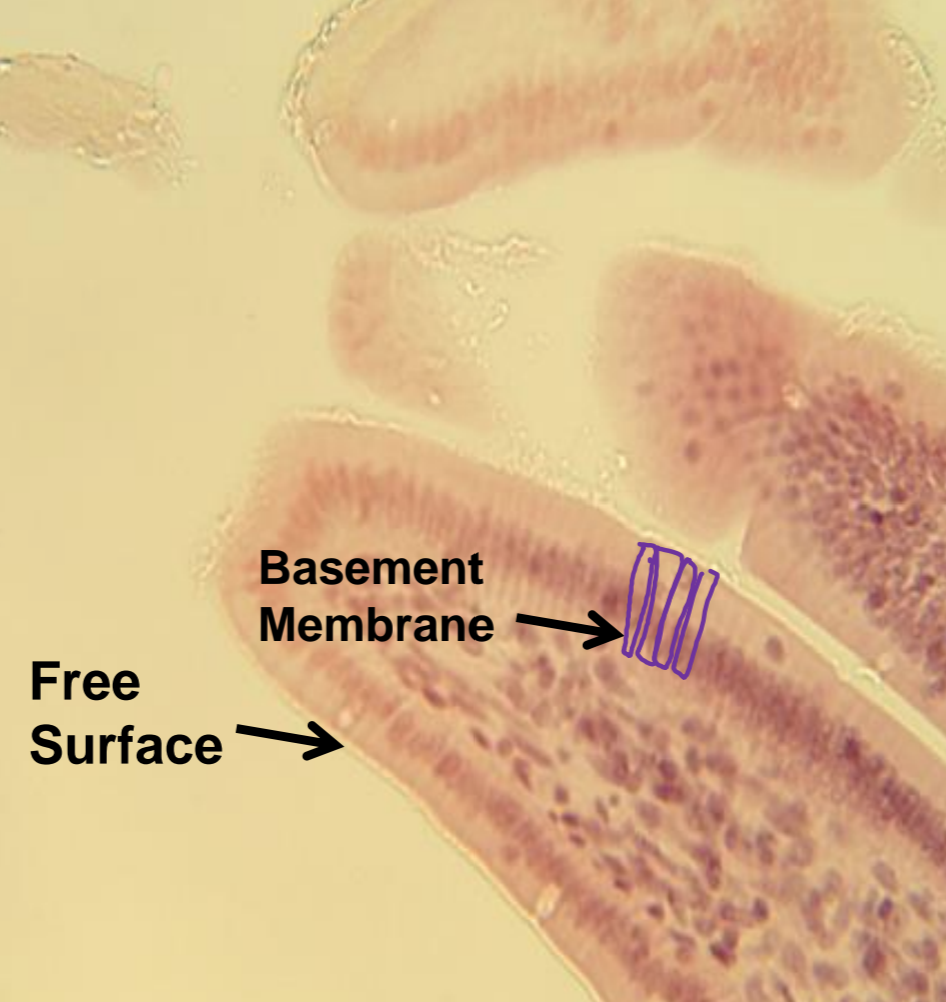
what tissue is depicted in the image
simple columnar
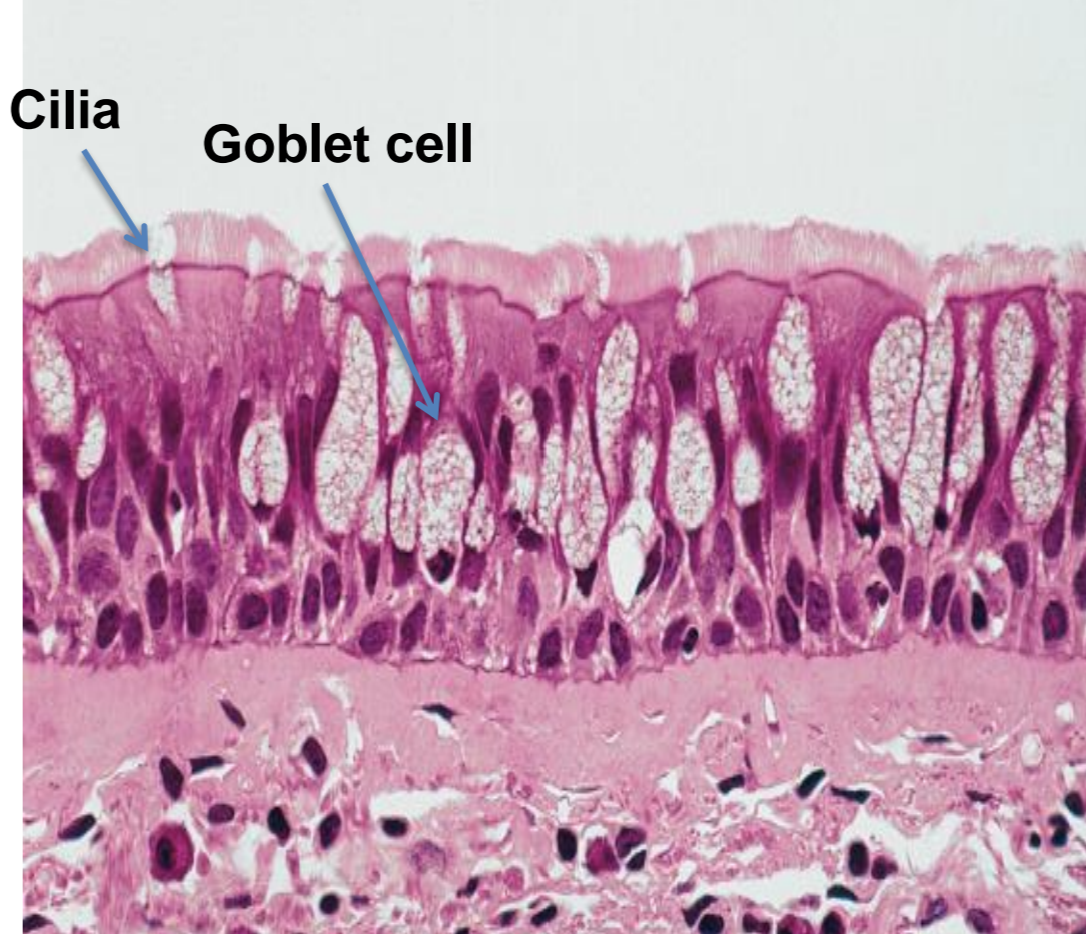
what tissue is depicted in the image
pseudostratified
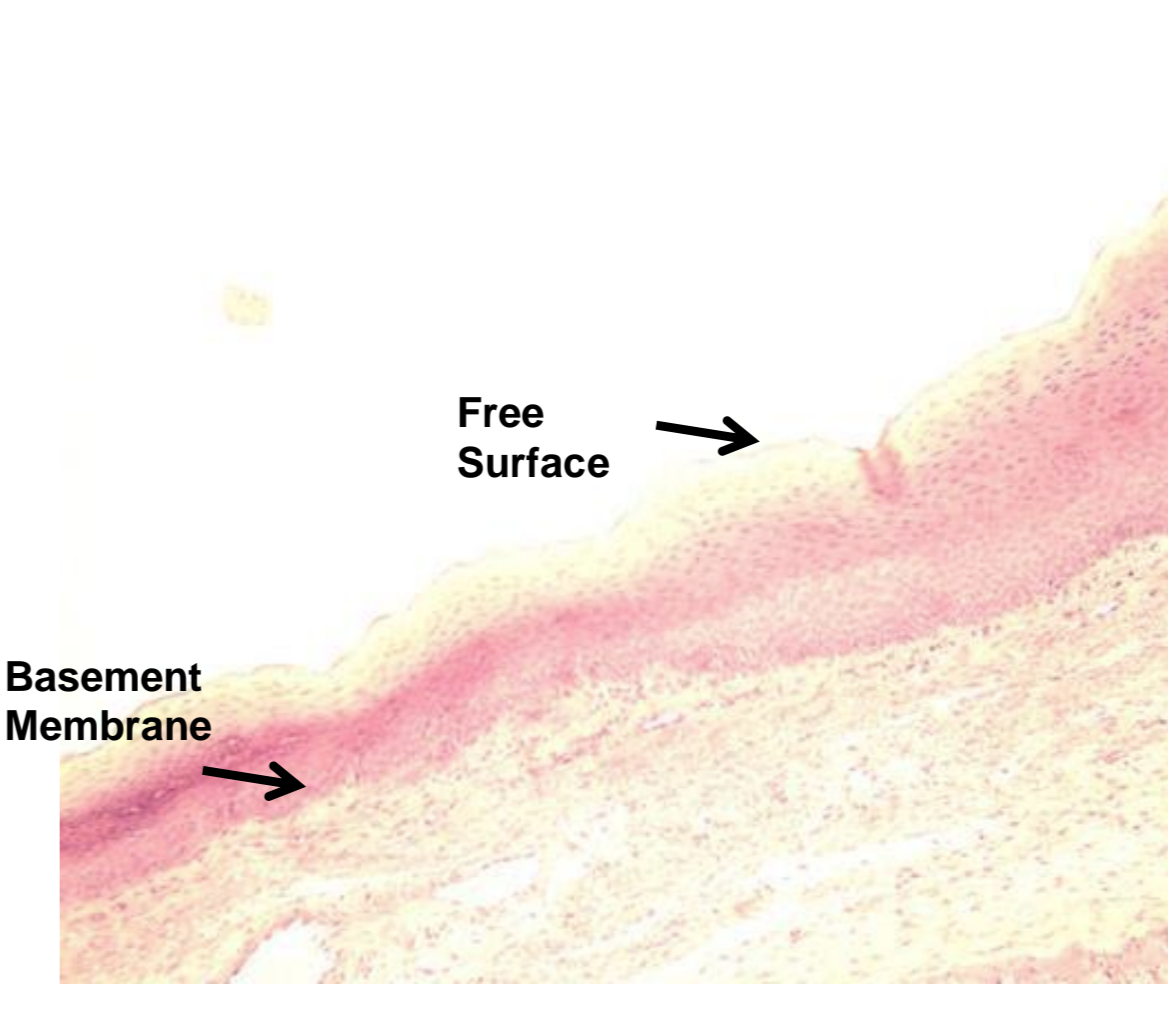
what tissue is depicted in the image
stratified squamous
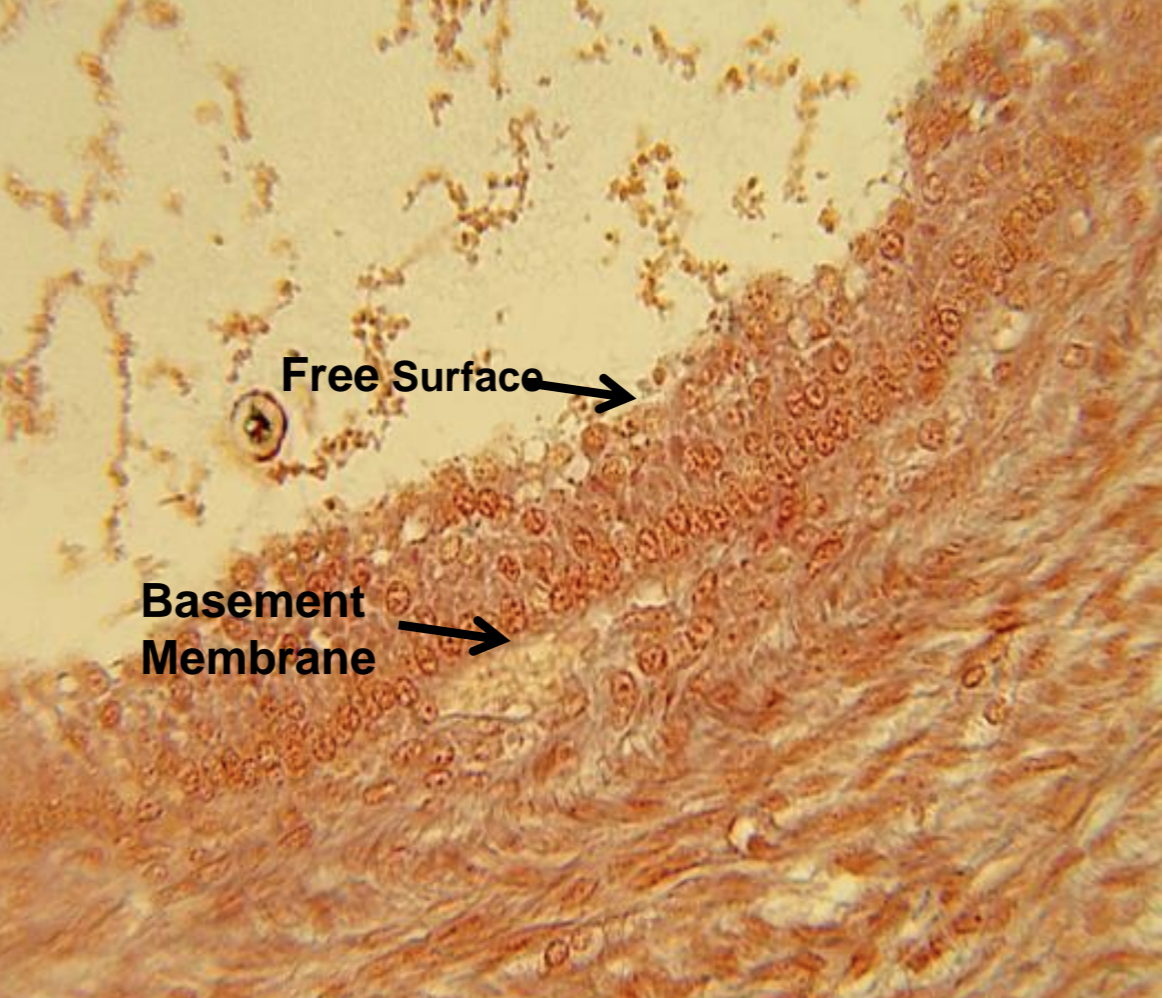
what tissue is depicted in the image
stratified cuboidal
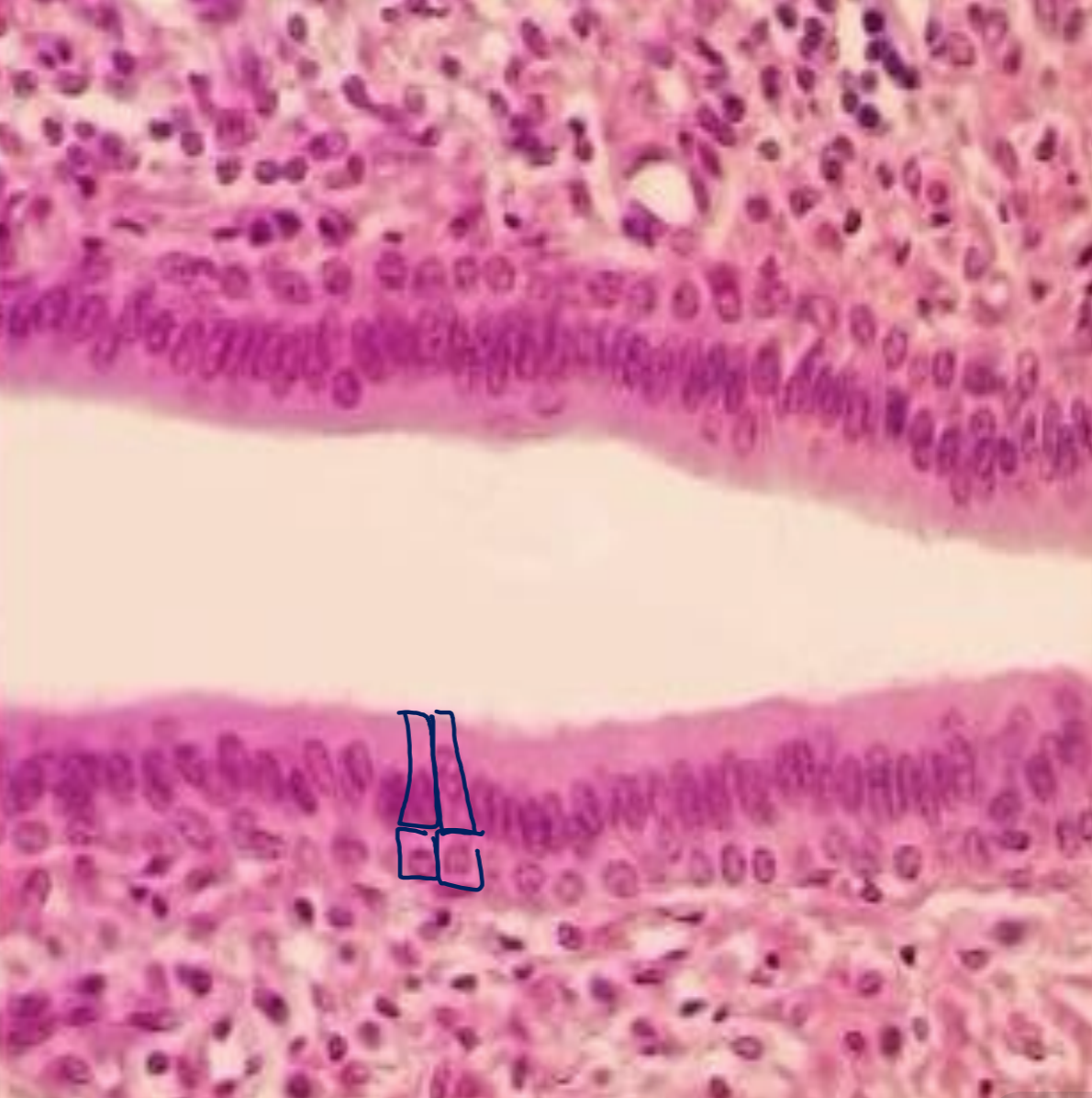
what tissue is depicted in the image
stratified columnar
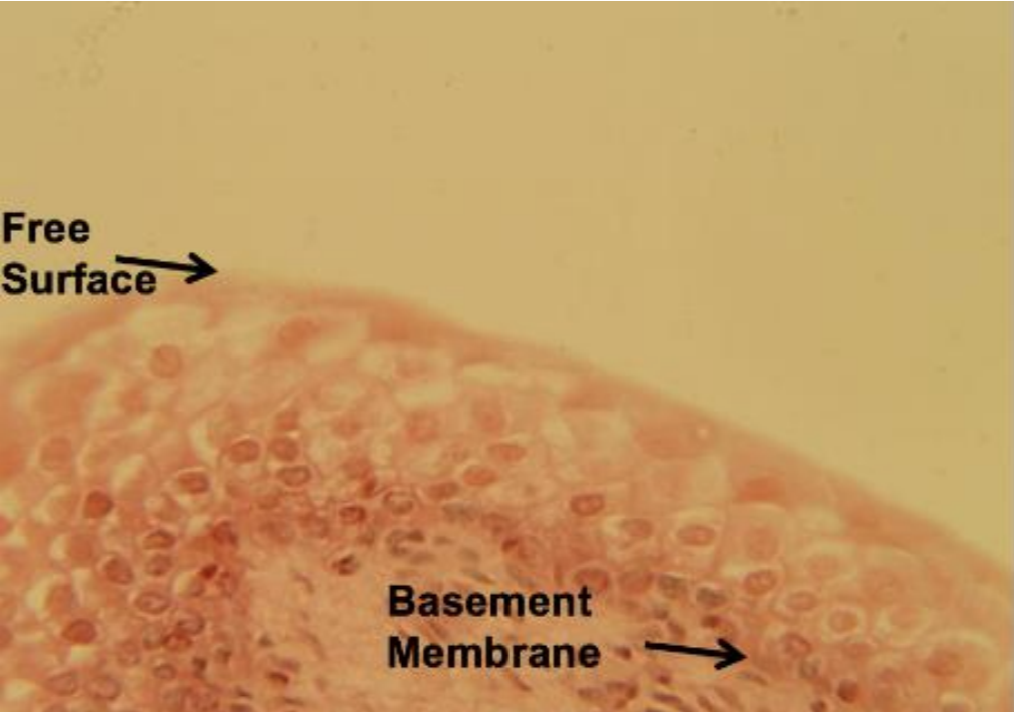
what tissue is depicted in the image
transitional
what are the parts of the extracellular matrix (areolar) aka protein fibers
collagen, reticular fibers, elastin fibers
collagen
rope-like and strong but inflexible
reticular fibers
tiny collagen fibers that act like web between cells
elastin fibers
can be stretched and returned to its original shape
areolar (ECM)
matrix contains all three fibers collagen, elastic, reticular held loosely together
areolar (ECM) - function
anchors skin to underlying tissues, anchors tissues together, surrounds capillaries and tissue, around organs
areolar (ECM) - location
everywhere in body
adipose
fat cells, a drop of fat is put in each cell and this pushes the nucleus to the edge of the cell, nucleus is highly vascular
adipose - function
cushioning, insulation, energy storage
adipose - location
center of femur, under skin, around kidney, eye balls
dense regular
unidirectional, nuclei are aligned parallel, densely packed fibers
dense regular - function
attaches muscles to bones (tendons), attaches bones to bones (ligaments)
dense regular - location
tendons, ligaments, aponeuroses
dense irregular
random assignment, multiple directions
dense irregular - function
strong in all directions
dense irregular - location
dermis of skin, capsules around organs and joints
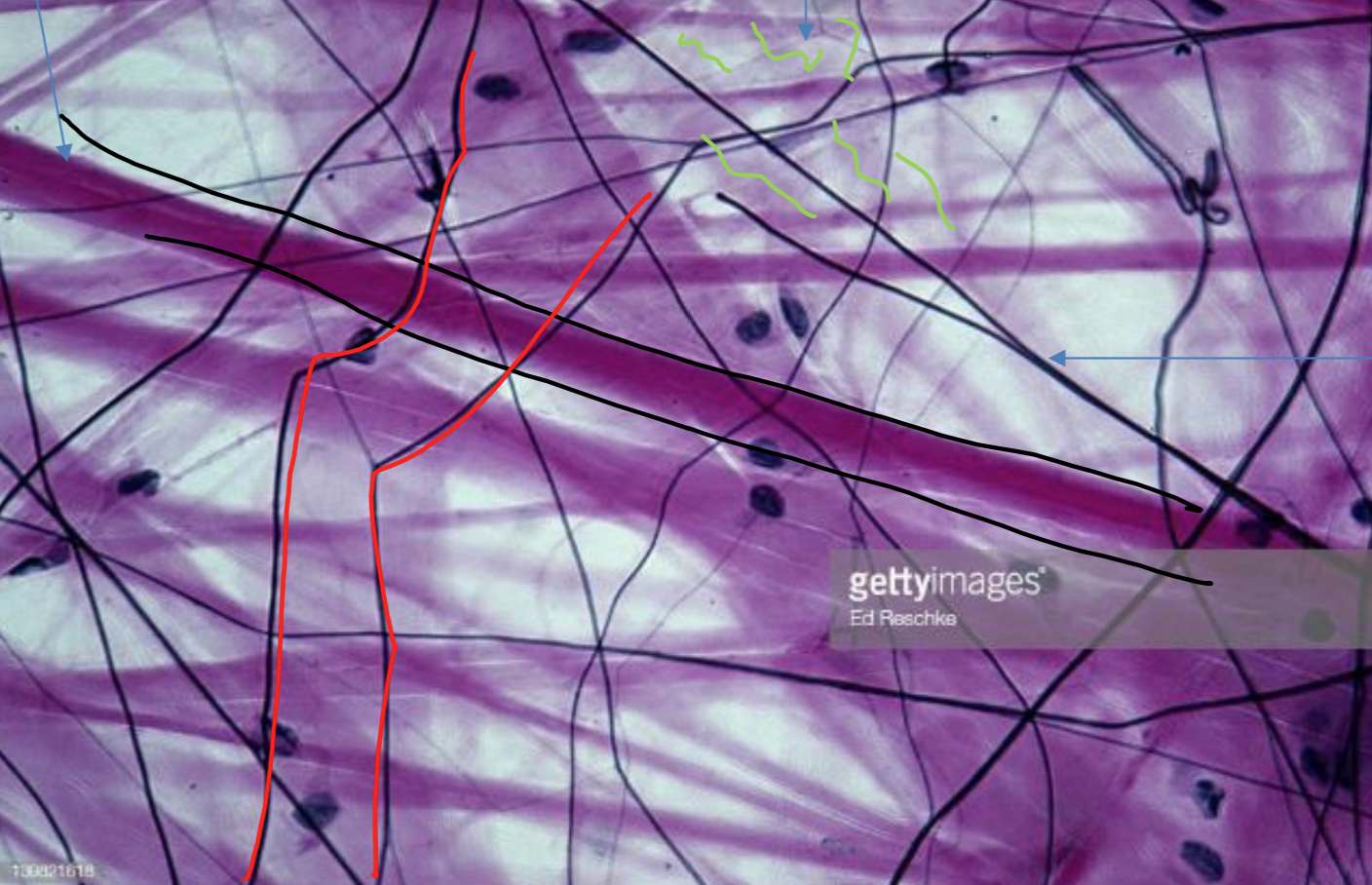
what tissue is depicted in the image
areolar (ECM)
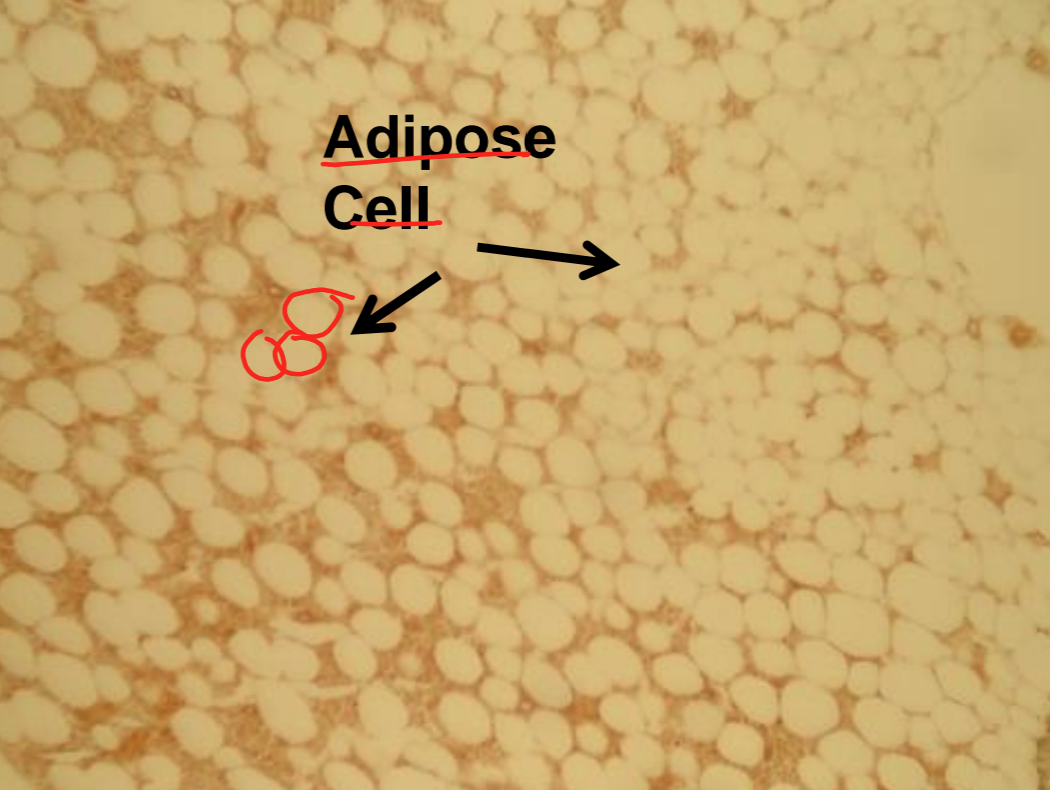
what tissue is depicted in the image
adipose
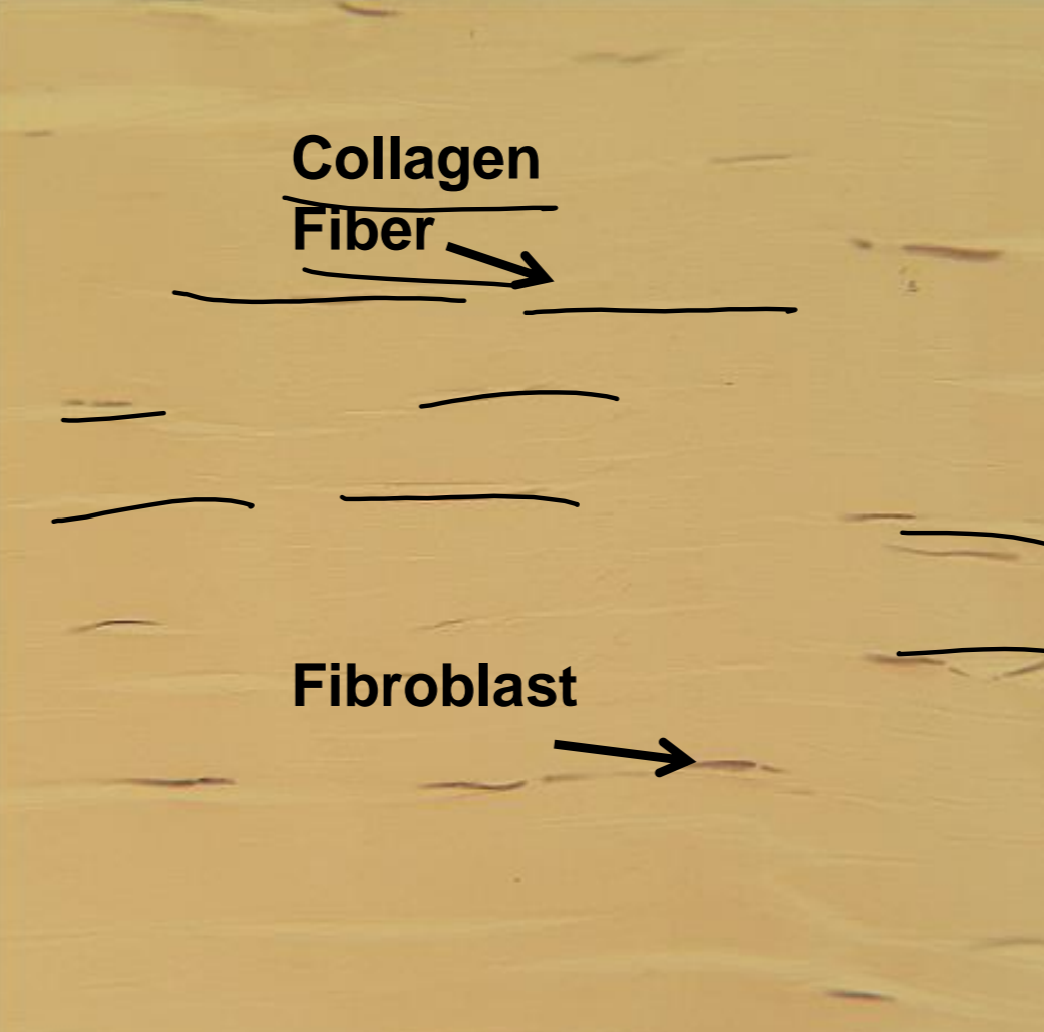
what tissue is depicted in the image
dense regular
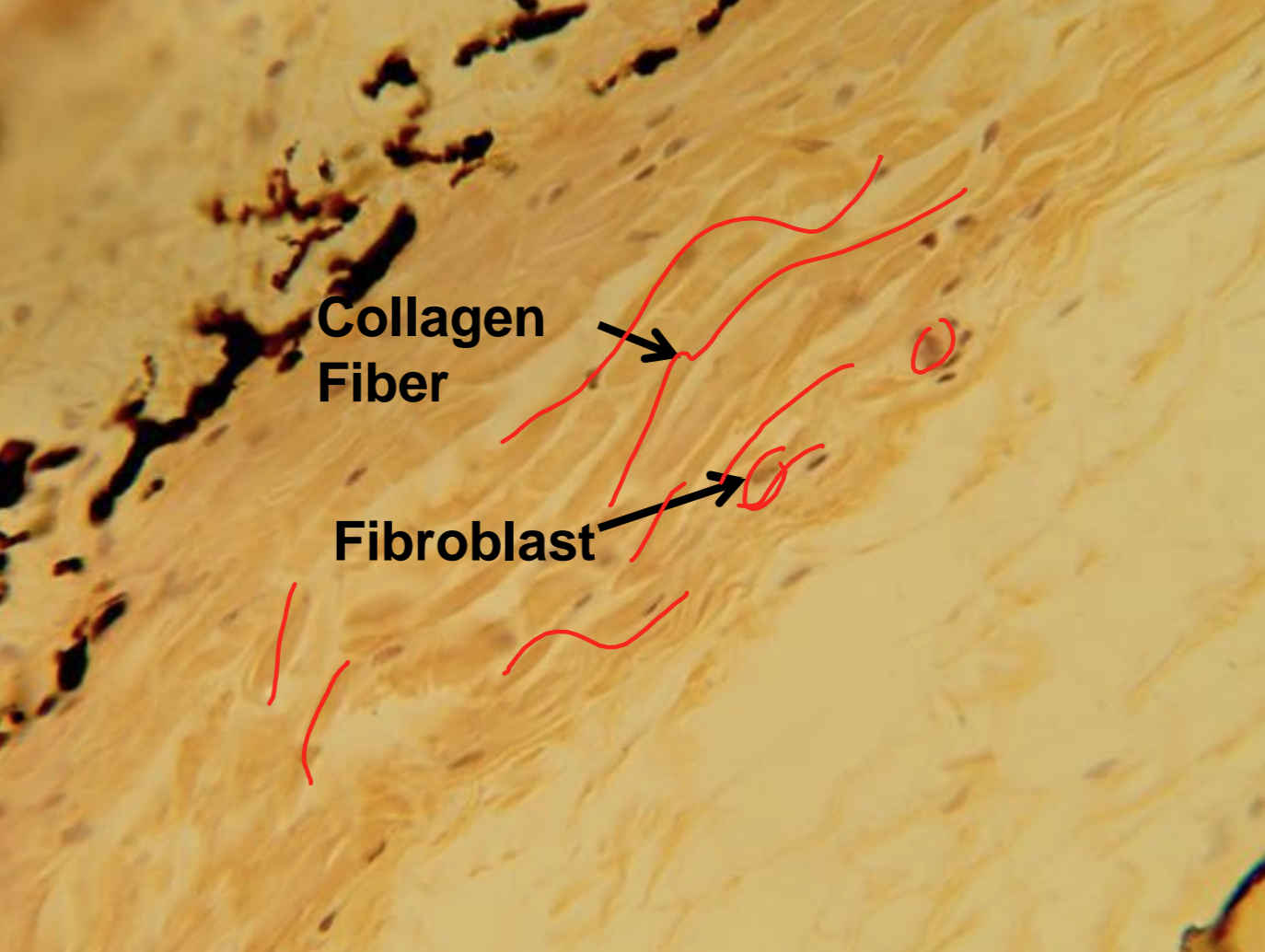
what tissue is depicted in the image
dense irregular
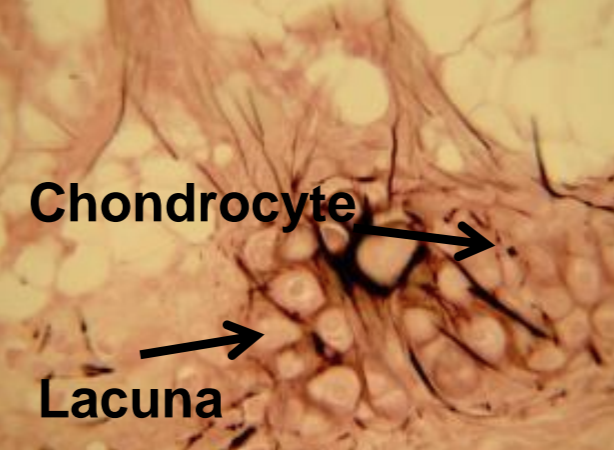
what tissue is depicted in the image
elastic
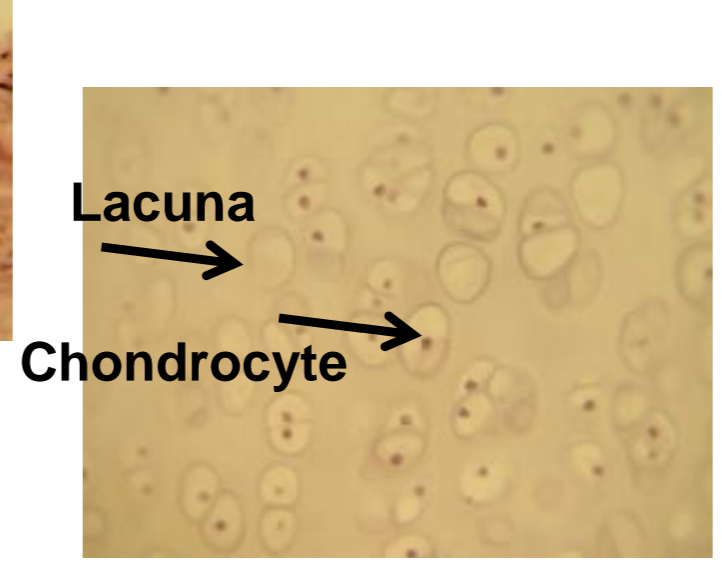
what tissue is depicted in the image
hyaline
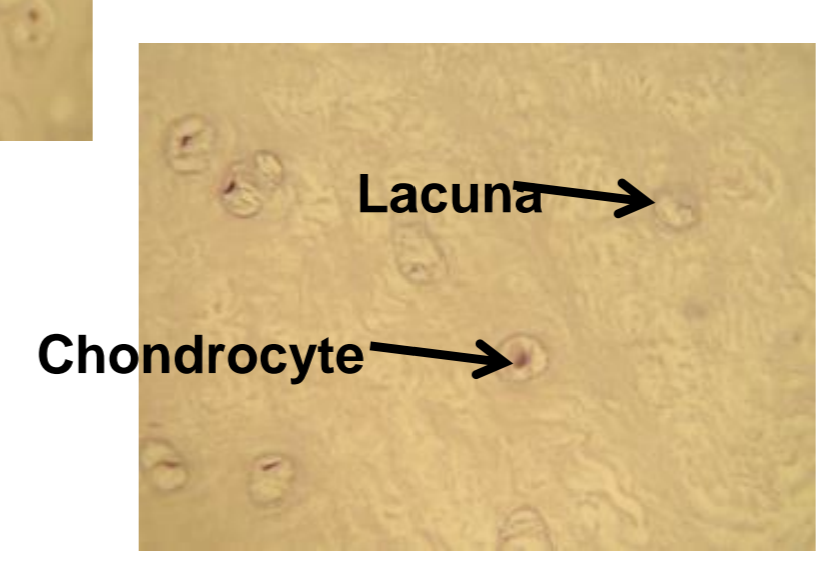
what tissue is depicted in the image
fibrocartilage
hyaline cartilage
articular surfaces and joints, has lacuna and chondrocyte
elastic cartilage
larynx, nose, ear, very flexible, has lacuna and chondrocyte
fibrocartilage
absorbs shock, intervertebral disks, has lacuna and chondrocyte
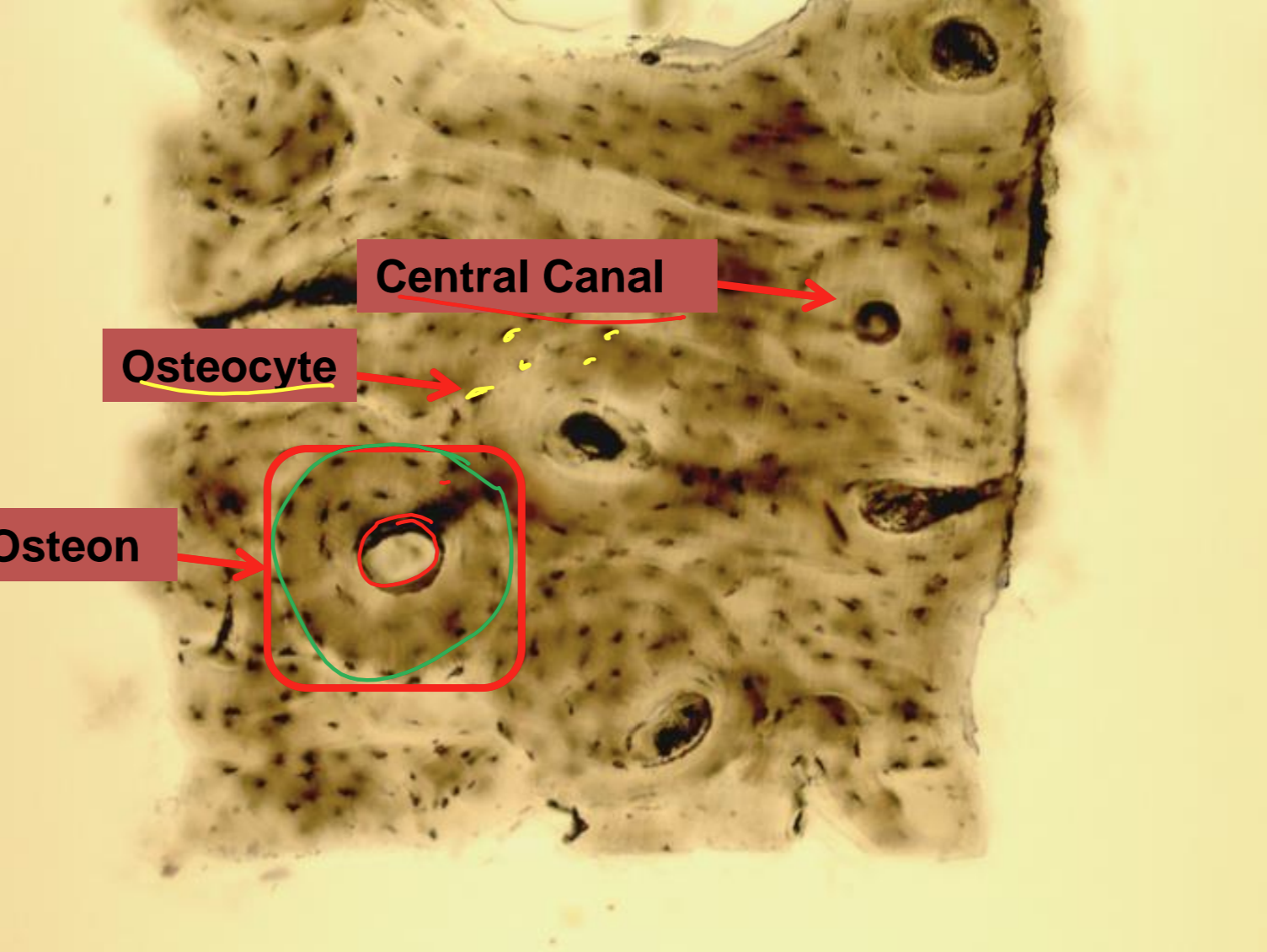
what tissue is depicted in the image
bone
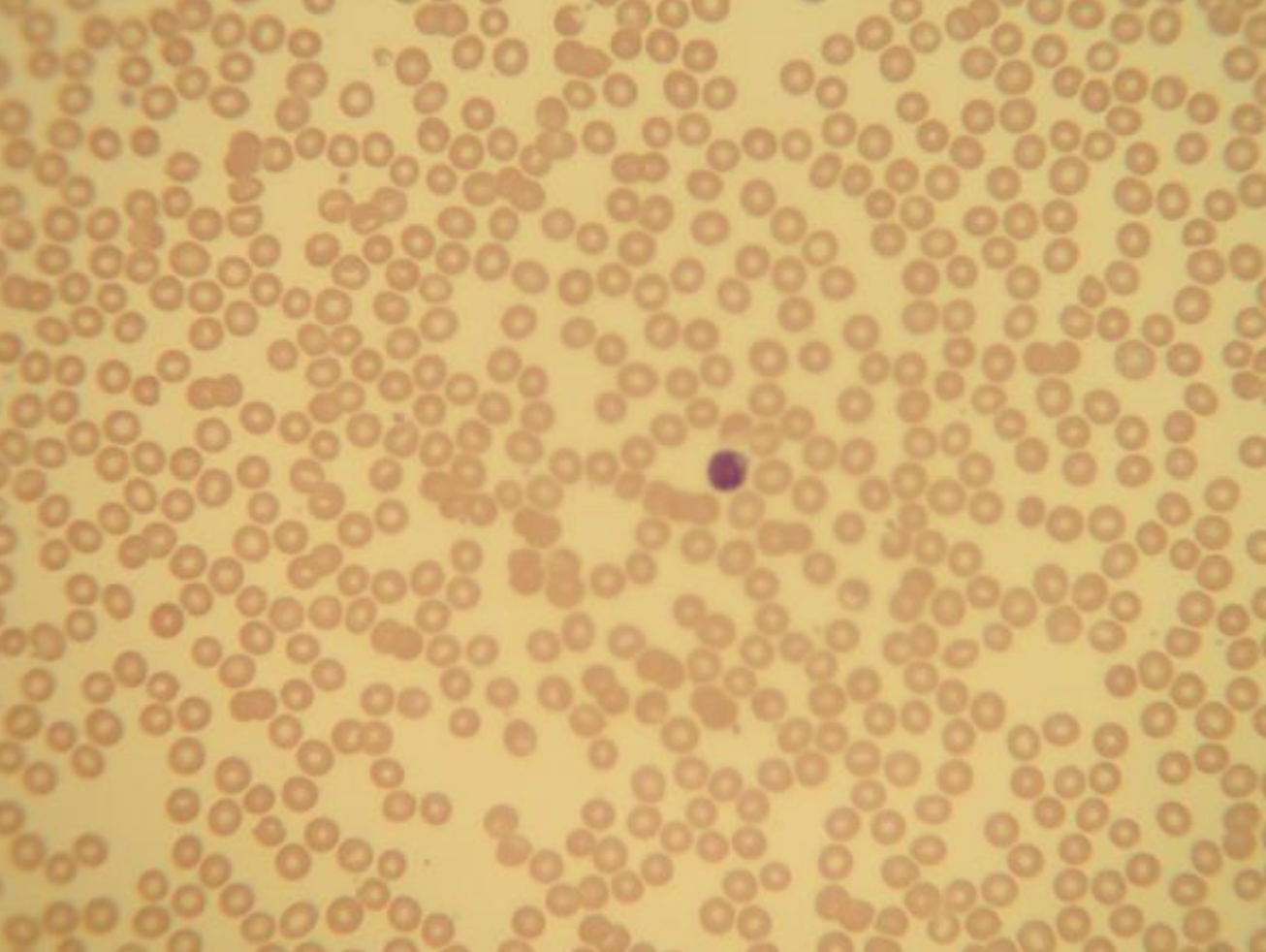
what tissue is depicted in the image
blood
bone
consists of mineralized ECM, lacunae is holes in the matrix where osteocytes reside
blood cells
suspended in fluid matrix, classified as connective tissue because it derives from mesenchyme
nervous tissue - function
specialized to carry electrical signals called action potentials
nervous tissue
dendrites, cell body, axon
nervous tissue - location
brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves
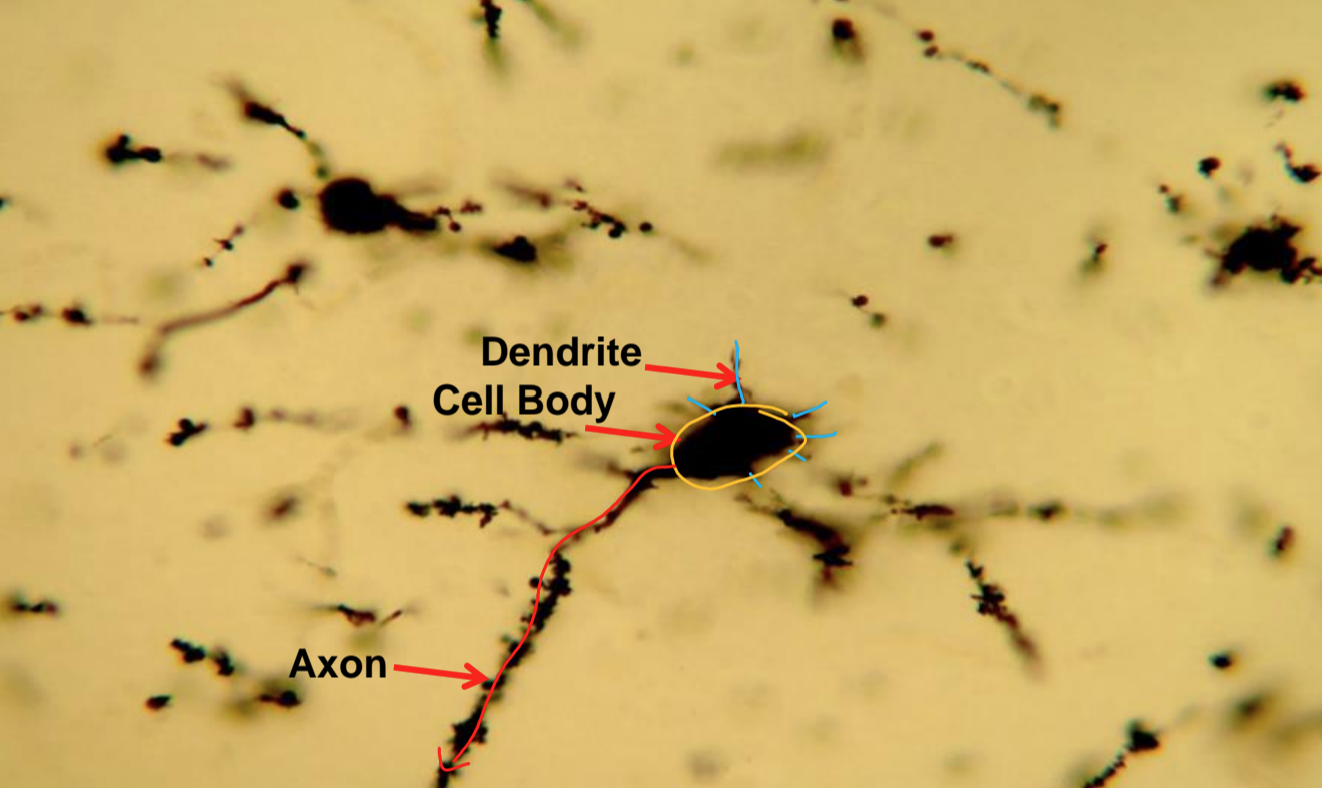
what tissue is depicted in the image
nervous tissue
skeletal muscle tissue
striated, voluntary, multinucleated
cardiac muscle tissue
striated, involuntary, uninucleated
smooth muscle tissue
nonstriated, involuntary, uninucleated
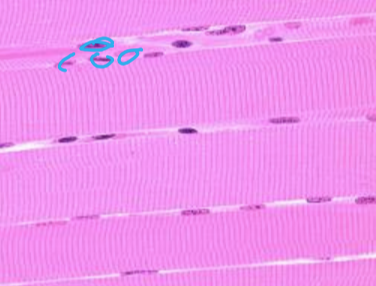
what tissue is depicted in the image
skeletal muscle tissue
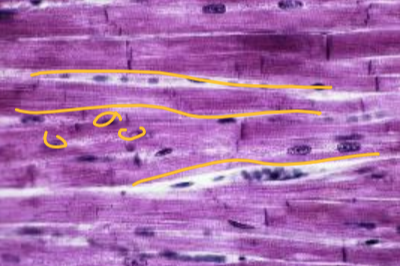
what tissue is depicted in the image
cardiac muscle tissue
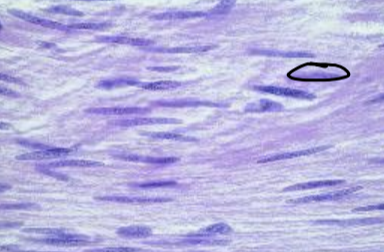
what tissue is depicted in the image
smooth muscle tissue