Exam 1 Study Guide Review
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
strength order of bonds (strongest to weakest)
ionic, covalent, hydrogen, Van der Waals
ionic bond
transfer of valence electrons between atoms; forms a salt
covalent bond
sharing of valence electrons by two atoms
molecule
consist of two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds (single, double or triple); smallest units of compounds that retains the characteristics of the said compound
nonpolar covalent bond
equal sharing of valence electrons; usually between atoms of the same element or two elements with similar electronegativities
polar covalent bond
unequal sharing of valence electrons
electronegativity
an atom’s strength of attraction/pull on the valence electrons
hydrogen bond
the non-covalent attraction between a hydrogen and an electronegative atom when the hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge
hydrogen bond example
the hydrogen (partial positive) of one H2O molecule will be attracted to the oxygen (partial negative) of another molecule
Van der Waals interaction
ever-changing regions of positive and negative charge that enable all atoms and molecules to stick to one another
the 4 properties of water
cohesive behavior, ability to moderate temperature, expansion upon freezing, universal solvent
cohesive behavior
the linking of like (water) molecules; results in surface tension
surface tension
measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquida
adhesion
the clinging of one substance (water) to another; helps to counter gravity
ability to moderate temperature
water has a high specific heat capacity (it takes a lot of energy to change the temperature of one gram of water molecules by 1 degree C
example of water’s ability to moderate temperature
an elephant sprays water on itself to cool itself through vaporization
expansion upon freezing
water is less dense as a solid than as a liquid
universal solvent
water eventually dissolves all ions by forming a hydration shell around its atoms
hydration shell
a sphere of water molecules around a dissolve ion
functional groups
components of organic molecules that are most involved in chemical reactions
kinetic energy
energy of motionth
thermal energy
kinetic energy created by the random motion of atoms and molecules
temperature
a measure, in degrees, of the average kinetic energy (thermal energy) of the atoms and molecules in a substance
carbon structure properties
length, branching, double bond position, presence of rings
isomers
compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and properties
structural isomers
different covalent arrangements of atoms
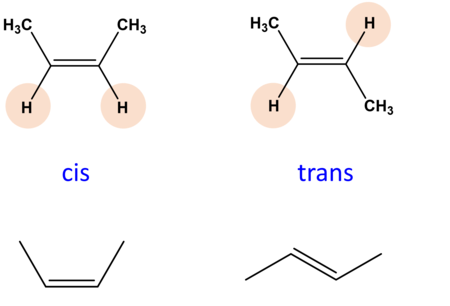
cis-trans (geometric) isomers
same covalent bonds that differ in their spatial arrangements
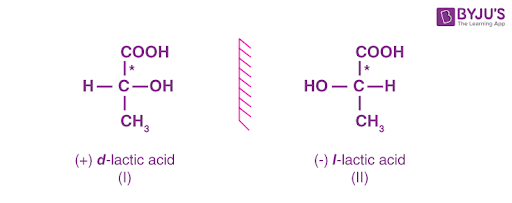
enantiomers
isomers that are mirror images of each other
essential elements in humans
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen (CHON)
trace essential elements
iron and iodine
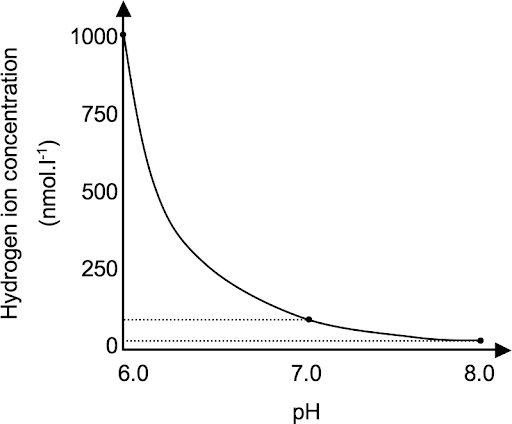
pH=-log[H+]
more H+ atoms = lower pH
Which structures are affected by sickle cell anemia?
primary and quaternary
Which structures are affected by denaturation?
secondary, tertiary and quaternary
prokaryotic cells
smaller, have a nucleoid region, are unicellular, have circular DNA, have no membrane-bound organelles, have all seven characteristics of life
eukaryotic cells
larger, have a nucleus, have membrane-bound organelles, have linear DNA, can be unicellular or multicellular, have all seven characteristics of life
What are the similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
both are cells, and both have the seven characteristics of life
Thiomargarita magnifica
prokaryote with prokaryotic ribosomes and circular DNA, but contains an enclosed nucleus and vacuole (membrane-bound organelles); exclusion of the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
advantages to compartmentalization
higher metabolism, more metabolic reactions, can undergo catabolic/anabolic reactions with many molecules, each compartment can have its own chemical/physical environment, allows division of labor amongst organelles
nucleic acids
polymers made of monomers called nucleotides; have a phosphate group, sugar (ribose), and a base group; held together by a phosphodieter bond
phosphodieter bond
between the phosphate group of one nucleic acid to the hydroxyl group of another nucleic acid
lipids
any of a large group of large biological molecules that mix poorly with water; have hydroxyl, carboxyl, and phosphate groups; held together by Ester linkages
Ester linkage/bond
between the hydroxyl of a glycerol and the carboxyl group of a fatty acid (lipids)
trans fats
unsaturated fatty acids that try to mimic the linear shape of a saturated fatty acid
amino acids
have an amino and carboxyl functional group; form peptide bonds
proteins
a biologically functional molecule consisting of one or more polypeptides folded and coiled into a specific 3-dimensional structure
8 proteins necessary for life
enzymatic
defensive
storage
transport
hormonal
receptor
contractile
structural
carbohydrates
have a carbonyl and hydroxyl group; normally ring-shaped; utilize a glycosidic linkage
glycosidic linkage
bond between hydroxyl groups (carbohydrates)
What is the difference between carbohydrates and lipids?
Carbohydrates store short-term energy and are more concentrated in plants whose seeds germinate quickly. Lipids store long-term energy because of their higher energy content, and are more concentrated in plants whose seeds undergo large stages of dormancy.
main functions of compartmentalization
environmental interactions
hereditary information transmission
genetic information storage
energy and matter transformation
example of enzymatic proteins
digestive enzymes
example of defensive proteins
antibodies
example of storage proteins
ovalbumin in eggs
example of transport proteins
hemoglobin in blood
example of hormonal proteins
insuline
example of receptor proteins
receptor-mediated endocytosis
examples of contractile proteins
actin and myosin
examples of structural proteins
keratin or collagen
examples of environmental interactions between compartments
plasma membranes and differing chemistries
examples of hereditary information transmission
turning genes into proteins
example of genetic information storage
storage of DNA in the nucleus
examples of energy and matter transformation
anabolism/catabolism, photosynthesis
What is the difference between starch and cellulose?
Starch has an alpha glycosidic linkage, which is digestible by humans. Cellulose has a beta glycosidic linkage, which is not digestible by humans.
smooth endoplasmic reticulum function
produces lipids and stores ions
rough endoplasmic reticulum function
studded with ribosomes; produces proteins
lysosome function
hydrolysis
hydrolysis
the chemical breakdown of a compound with water
golgi body function
folds proteins and makes vesicles for transport
golgi body structure
has a “receiving” side (trans face) and a “shipping” side (cis face)
Which linkages belong to which type of macromolecule?
carbohydrates: glycosidic linkages
lipids: ester linkages
proteins: peptide bonds
nucleic acids: phosphodieter linkages
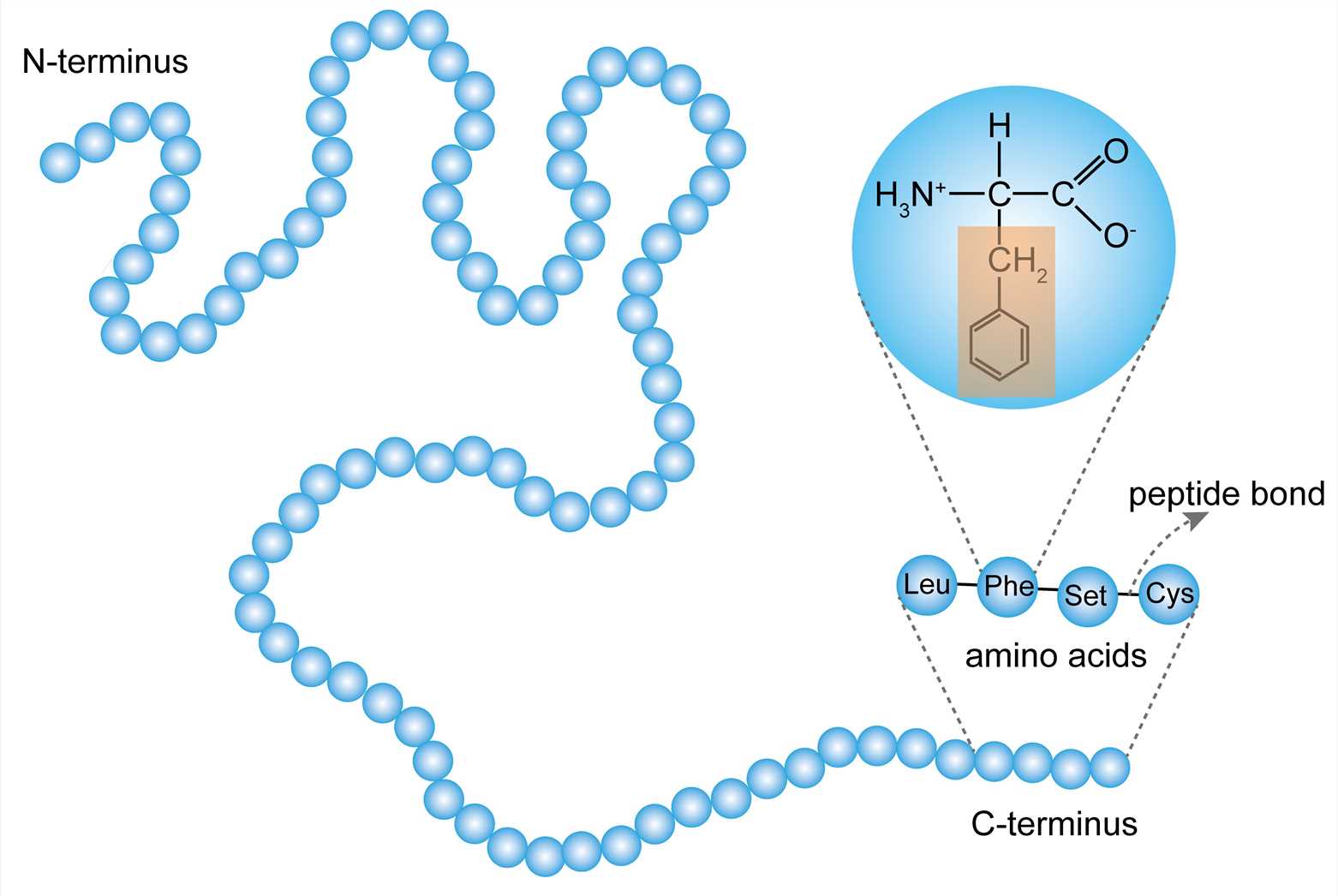
primary structure of proteins
linear sequence of amino acids
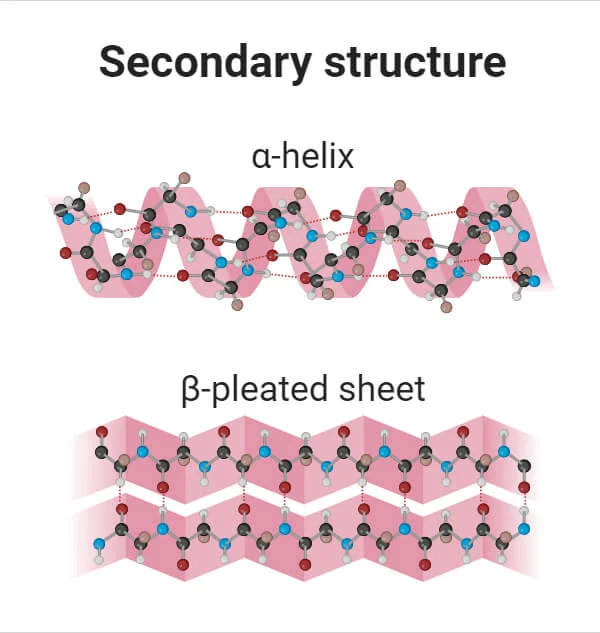
secondary structure of proteins
folding patterns of the polypeptides (alpha-helix or beta-pleated sheets)
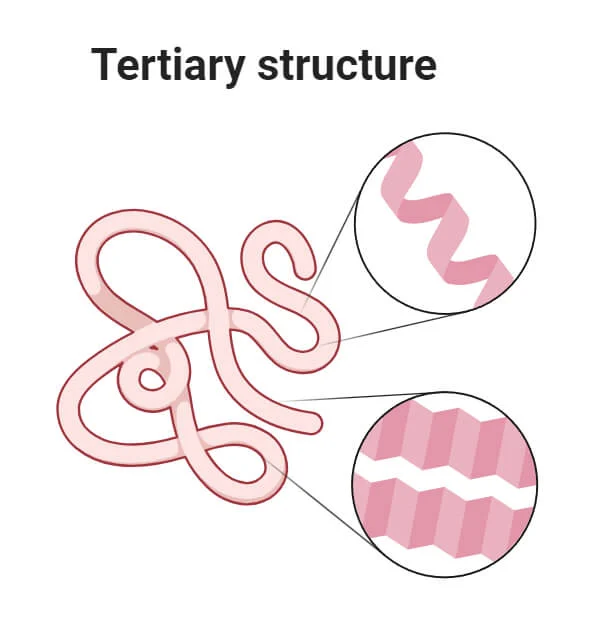
tertiary structure of proteins
3-dimensional shape of a single polypeptide chain; determined by interactions between amino acid side chains
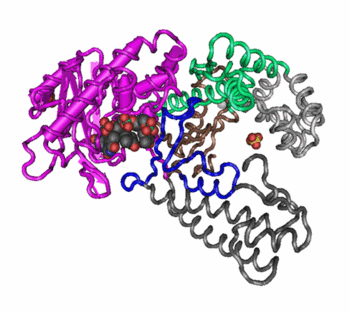
quaternary structure of proteins
arrangement of multiple polypeptide chains within a protein complex
glycosidic linkages
linkage/bond for carbohydrates
ester linkages
linkage/bond for lipids
peptide bonds
linkage/bond for proteins
phosphodieter linkages
linkage/bond for nucleic acids