Radiologic Equipment and Maintenance Overview
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
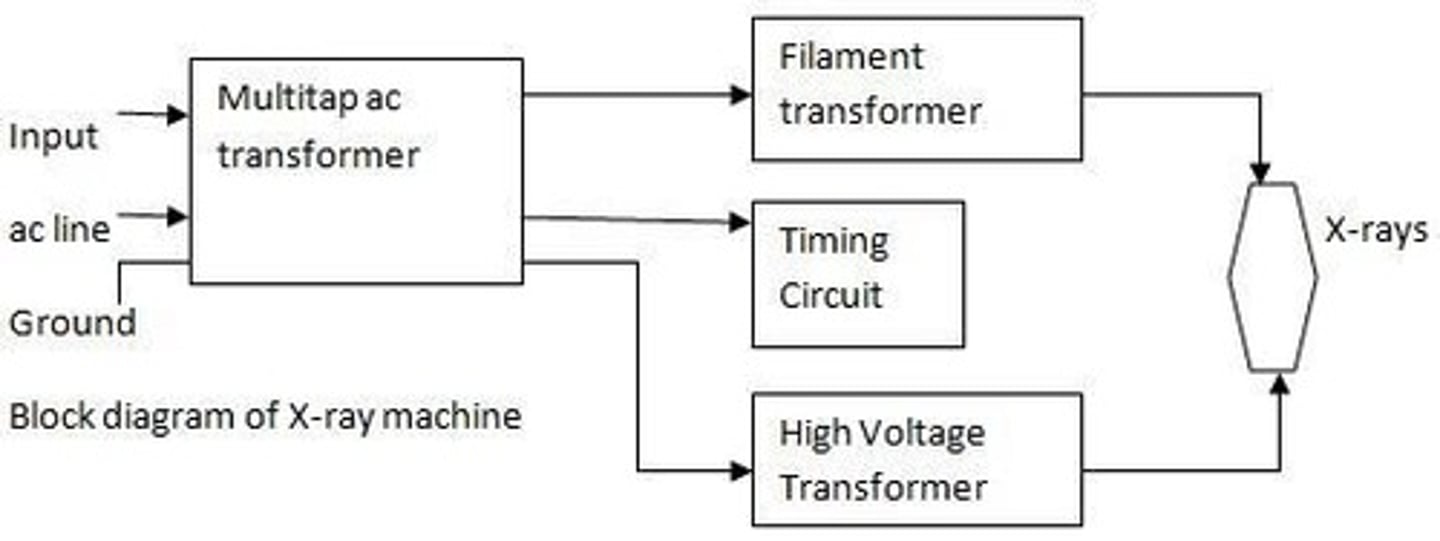
X-ray Machine
Converts electric energy into electromagnetic energy.
Electrostatics
Study of stationary electric charges.
Electrodynamics
Study of electric charges in motion.
Electrification
Process of electrifying through contact, friction, induction.
Electric Charge
Fundamental unit is the coulomb (C).
Coulomb (C)
1C equals 6.3×10^18 electron charges.
mAs
Measure of electric charge in amperes per second.
Electrostatic Force
Like charges repel; unlike charges attract.
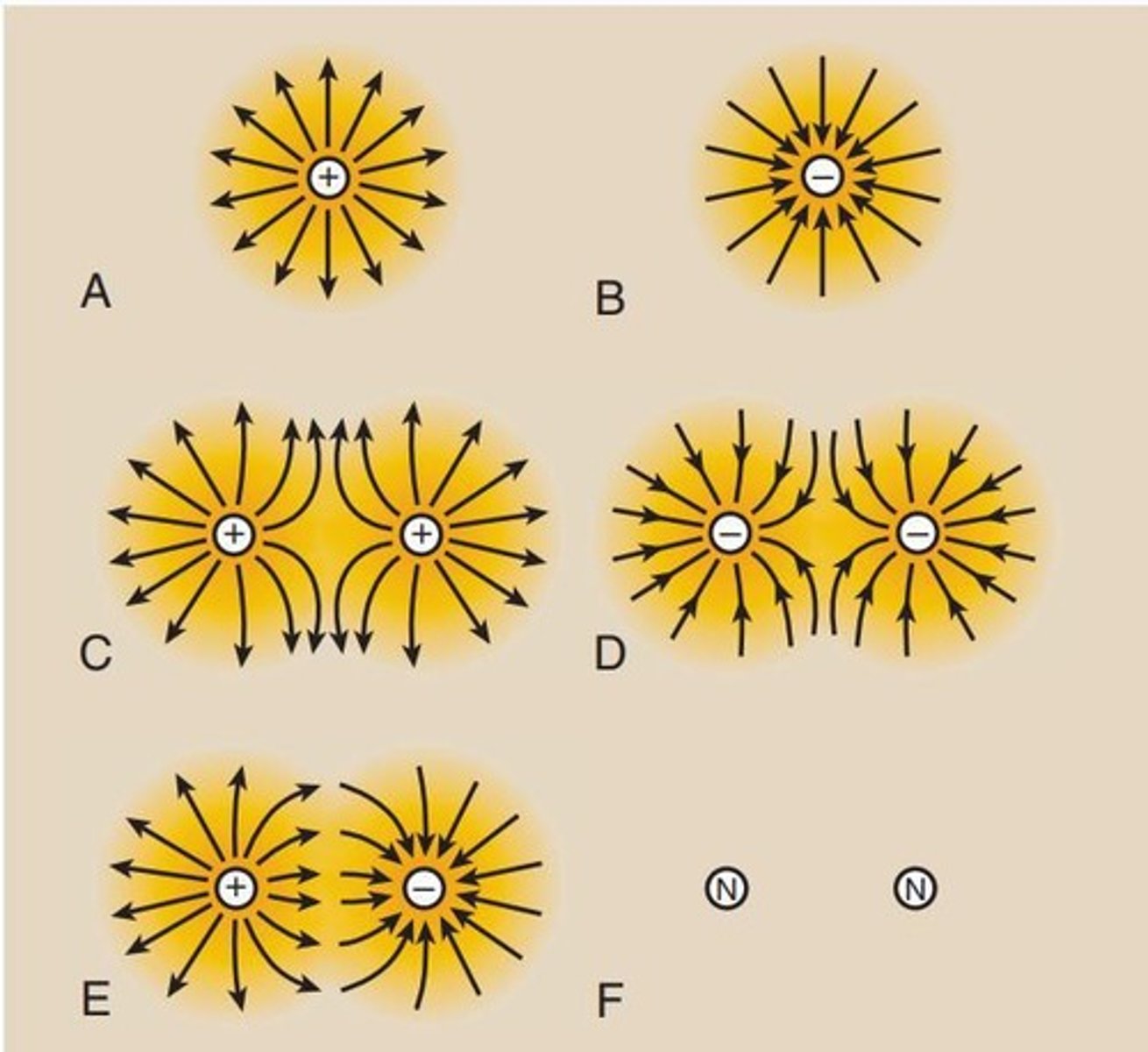
Electric Charge Distribution
Charge is concentrated on sharp surface curvatures.
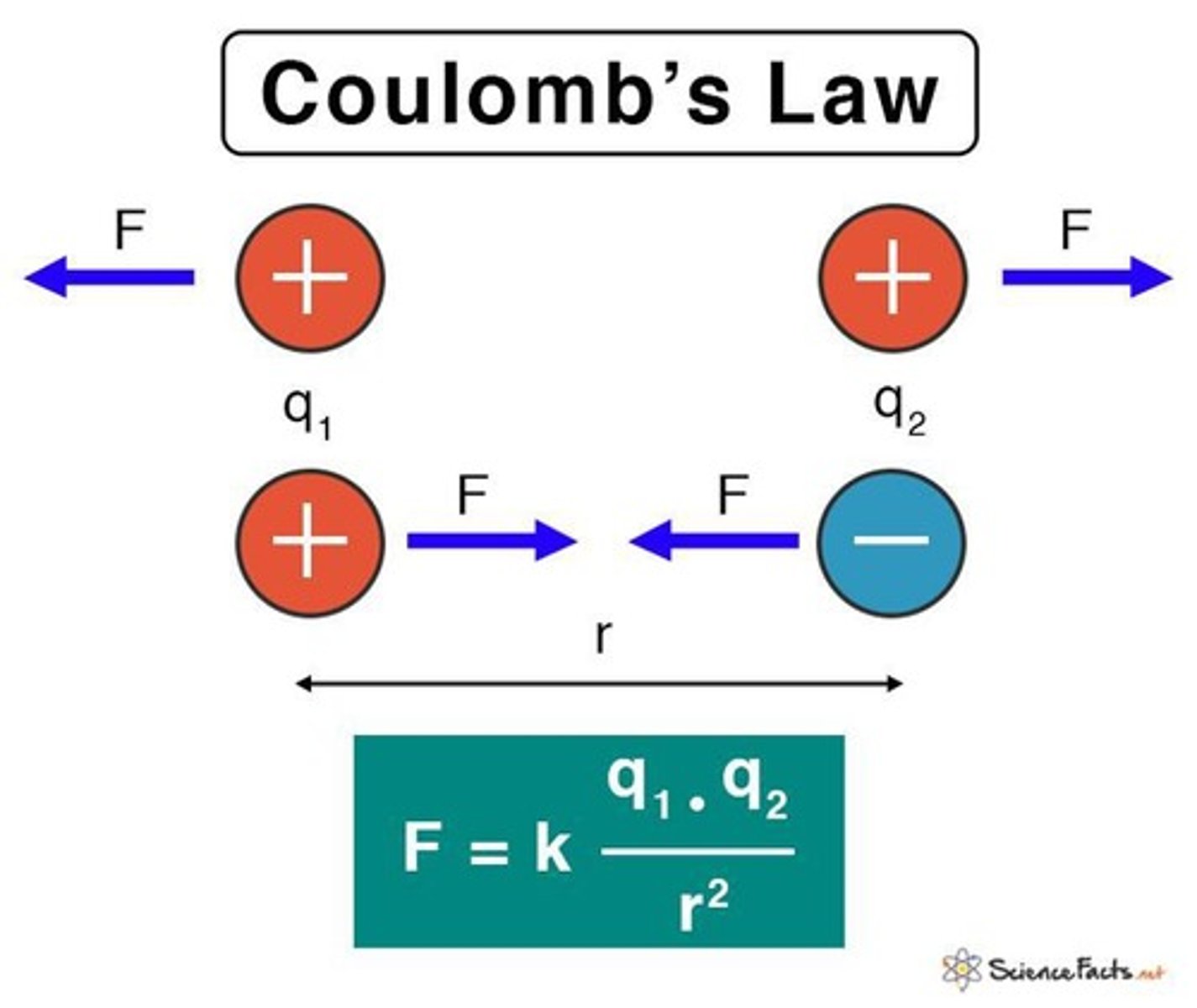
Coulomb's Law
Force proportional to product of charges, inversely distance squared.
Electric Potential
Potential energy per unit charge, measured in volts.
Volt (V)
1 Volt equals 1 Joule per Coulomb.
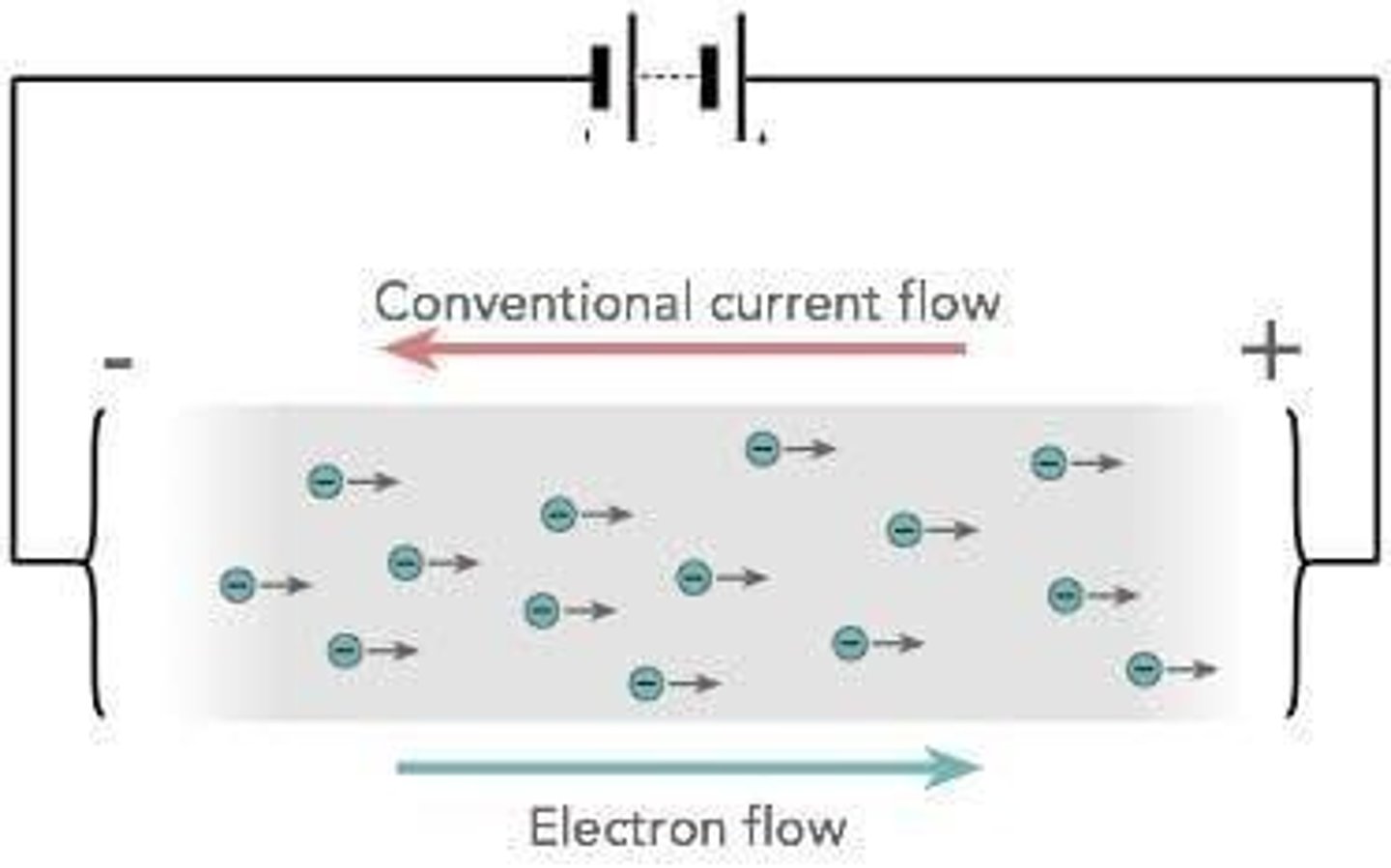
Electric Current
Flow of electric charge, opposite to electron flow.
Conductor
Material allowing easy electron flow, e.g., copper.
Insulator
Material that does not allow electron flow, e.g., rubber.
Semiconductor
Material behaving as insulator or conductor under conditions.
Superconductor
Material with no resistance below critical temperature.
Electric Circuit
Closed path for controlled electric current.
Electric Resistance
Opposition to electric current flow.
Electric Potential Energy
Energy stored due to position of electric charges.
Electric Field
Region around charged objects affecting other charges.
Electrostatic Repulsion
Similar charges push away from each other.
Electric Charge Magnitude
Protons and electrons have equal but opposite charges.
Electric Potential
Measured in volts; energy per unit charge.
Volt (V)
Unit of electric potential; 1 J/C.
Potential Energy
Energy stored due to position; measured in joules.
Electric Current
Flow of electric charge; opposite to electron flow.
Conductor
Material allowing easy electron flow; e.g., copper.
Insulator
Material preventing electron flow; e.g., rubber.
Semiconductor
Material acting as conductor or insulator under conditions.
Ohm's Law
V = I × R; relationship of voltage, current, resistance.
Series Circuit
Circuit elements connected in a single path.
Parallel Circuit
Circuit elements connected across common points.
Electric Power
Rate of doing work; P = V × I.
Watt (W)
Unit of power; 1 A at 1 V.
Magnetism
Property of matter related to magnetic fields.
Magnetic Field
Area around a magnet where magnetic forces act.
Magnetic Moment
Dipole created by spinning charged particles.
Magnetic Domain
Region with aligned atomic magnetic dipoles.
Magnetic Permeability
Material's ability to conduct magnetic field lines.
Natural Magnet
Magnet occurring in nature; e.g., Earth.
Permanent Magnet
Magnet made from ferromagnetic material in strong field.
Electromagnet
Magnet created by electric current in wire.
Resistance (Ω)
Opposition to current flow in a conductor.
Current (A)
Flow rate of electric charge; measured in amperes.
Electric Current
Flow of electric charge through a conductor.
Magnetic Field
Region around a magnet where magnetic forces act.
North Pole
One of the two ends of a magnet.
South Pole
The opposite end of a magnet from the North Pole.
Magnetism Reduction
Decreased magnetism from hitting or heating a magnet.
Magnetic Repulsion
Same poles of magnets push each other away.
Magnetic Attraction
Opposite poles of magnets pull each other together.
Magnetic Force Formula
Force is proportional to pole strength over distance squared.
Tesla (T)
SI unit for measuring magnetic field strength.
Gauss (G)
Old unit for measuring magnetic field strength.
1 Tesla
Equal to 10,000 Gauss.
Earth's Magnetic Field
Approximately 50 micro Tesla at core.
MRI System Strength
Can reach up to 3 Tesla.
Luigi Galvani
Observed frog leg twitching with metal contact.
Alessandro Volta
Invented the first battery using zinc-copper plates.
Hans Christian Oersted
Showed current through wire produces magnetism.
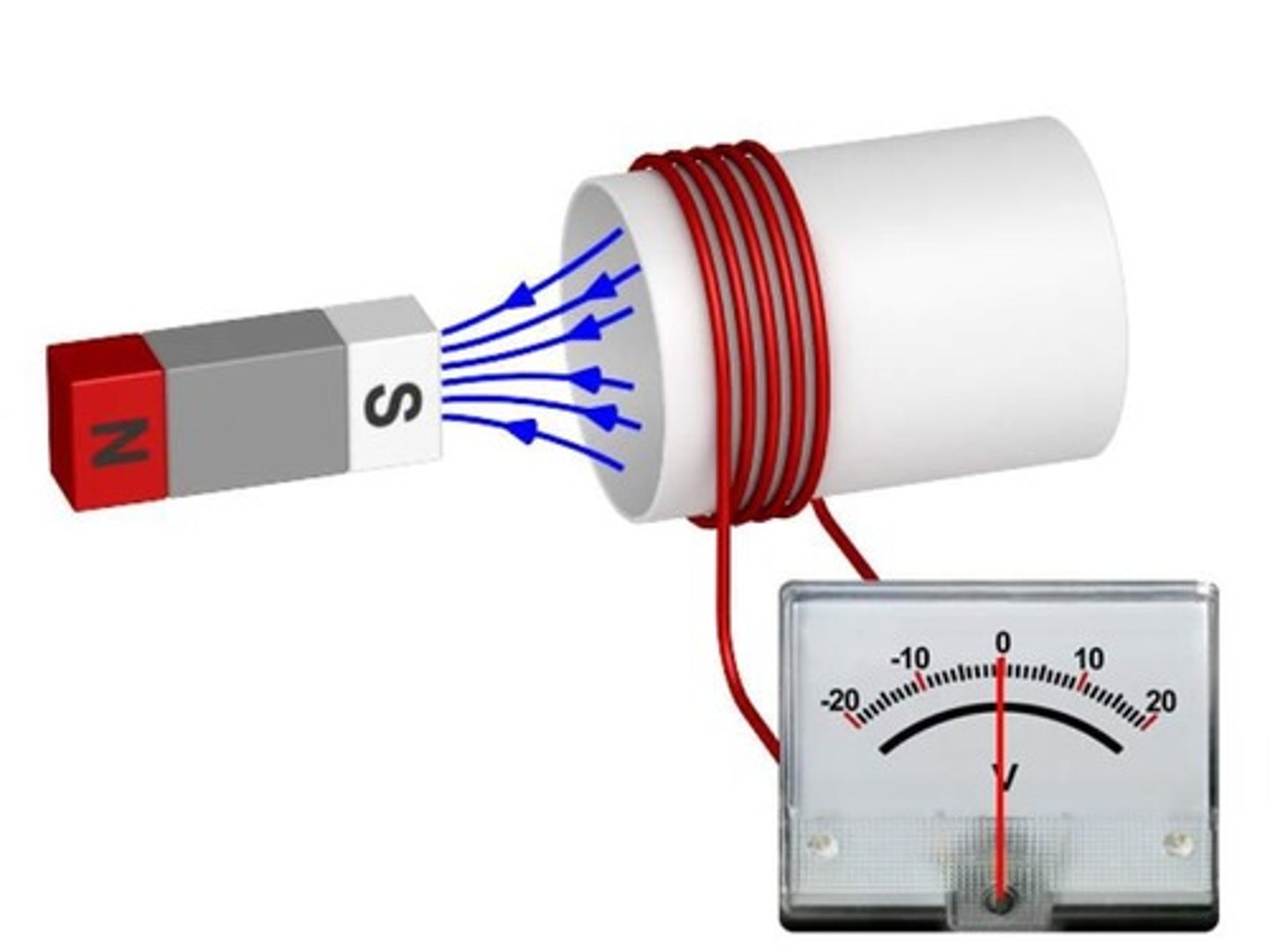
Michael Faraday
Demonstrated moving magnetic fields generate electric current.
Heinrich Lenz
Established electricity and magnetism produce each other.
Electromagnetic Induction
Current induced by changing magnetic field in circuit.
Electric Motor
Converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Electric Generator
Converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Induction Motor
Type of motor used in x-ray tubes.
Transformer Function
Transforms electric potential and current intensity.
Transformer Law
Voltage change proportional to turns ratio of coils.
Step-Up Transformer
Increases voltage; turns ratio greater than one.
Step-Down Transformer
Decreases voltage; turns ratio less than one.
Closed-Core Transformer
Laminated iron layers reduce energy losses.
Shell-Type Transformer
More efficient; confines magnetic field lines better.
Autotransformer
Single winding acts as both primary and secondary.
Operating Console
Controls x-ray tube current and voltage settings.
Line Compensator
Adjusts voltage to 220 V for x-ray system.
Radiation Quality
Penetrability of x-ray beam, expressed in kVp.
Radiation Quantity
Number of x-rays or beam intensity, in mG.
Autotransformer
Supplies precise voltage to x-ray circuits.
Exposure Timers
Terminate exposure after approximately 6 seconds.
Synchronous Timers
Runs at 60 rpm, uses electric motor.
Electronic Timers
Accurate to 1 ms, controlled by microprocessor.
mAs Timers
Monitors product of mA and exposure time.