Earth Sciences (Rocks and Volcanoes 2)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Magma’s composition
proportion of silica
Viscosity
resistance to flow (runny to sticky)
More silica in magma
more strong silicon-oxygen bonds (even before
crystallization begins) = more resistance
to flow (higher viscosity)
Importance of dissolved gases in magma
With more of this, the more explosiveness there will be
Mafic/Basaltic Magma’s silica content and viscosity
50% silica content & least viscosity (thin/runny)
Mafic/Basaltic Magma’s gas content and explosiveness
0.5 - 2% gas, least explosivity
Mafic/Basaltic Magma’s temperature
1100 - 1200 celcius
Andesitic/intermediate Magma’s silica content and viscosity
60% silica content & inermediate viscosity
Andesitic/intermediate Magma’s gas content and explosiveness
3-4% gas and intermediate explosivity
Andesitic/intermediate Magma’s temperature
900-1000 celcius
Rhyolitic/Felsic Magma’s silica content and viscosity
70% silica content and greatest viscosity
Rhyolitic/Felsic Magma’s gas content and explosivity
4-6% gas content, greatest explosivitiy
Rhyolitic/Felsic Magma’s temperature
700 - 800 celcius
Pyroclastic materials
Ejected fragments from eruptions that range in size from dust to pieces several tonnes in weight
Welded Tuff
Hot ash falls and glassy shards fuse to form it

Scoria
bubbly mafic pieces

Pumice
bubbly felsic pieces, very low density (may float)

Pyroclastic Flow
consist of hot gases infused with hot ash and
larger rock fragmentsRush down side of volcano at speeds up to 200 km/hr
• 100º - 800ºC
• Often the main cause of death
during volcanic activity
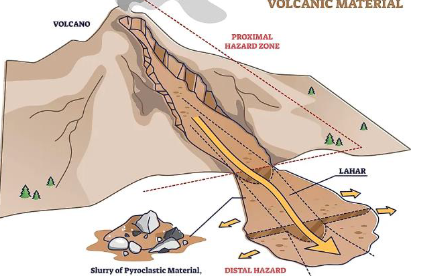
Lahar
a volcanic mudflow that's a mixture of water,
ash, rock fragments, and other materials that flow down a
volcano's slopes.
These flows can travel at speeds of 70-
80 km/hr.
Shield volcanoes
Broad, slightly domed-shaped, formed at divergent boundaries
• Composed primarily of mafic lava
• Generally cover large areas, flows can travel
up to 150km
• Mauna Loa on Hawaii is a good example
Stratovolcanoes (composite volcanoes)
• Explosions cause pyroclastic debris, formed at convergent boundaries
• Most are located adjacent to the Pacific Ocean (Ring of
Fire)
• Large, symmetrical volcano (hundreds of metres high &
several kilometres wide at base)
• Composed of interbedded lava flows and layers of ash, like mount fuji