Chemistry and Physics: Endothermic, Quantum, and Spectral Concepts
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Is the melting of ice endothermic or exothermic?
Endothermic, as heat goes from the surroundings into the ice cube to melt it.
Is the equation H2O → 1/2 O2 + H2 endothermic or exothermic?
since it requires heat to breakdown water, it's endothermic
How much heat is require to raise temp of 7.35g H2o from 21.0C → 98.0C?
2370J
Calculate the specific heat capacity of metal.
- 150g metal heated to 100 degrees celcius
- 50g water, 22C & 28.8C
1. Do Q for water first
2. Q lead = -Q water
3. Solve for C
Specific heat capacity of metal is -0.133J/gC
If a 182g sample of Au is added to 22.1g H2O, the initial water temp is 25C, and the final is 27,5C, and the CAu is 0.128J/gc, what's the initial temperature of Au?
1. negative Qwater + QAu = 0
2. Do Q equation for each & solve for Ti
Initial temp is 37.4
125mL of 0.250M CsOH was mixed with 50mL of 0.625M HF. the temperature went from 21.5C → 24.4C. assume density of all solutions is 1.00g/mL, and the specific heat capacity is 4.2J/gC.
Calculate the change in heat per mol CsOH
-67 KJ/mol
CaO + 3C → CaC2 + CO, ΔH = 464.8 KJ/mol
If 10g CaO reacts with excess C, how much heat is absorbed?
82.9KJ absorbed when 10g CaO reacts
1/2 N2 + O2 → NO2, what is ΔH if the mini reactions are:
a. 1/2N2 + 1/2O2 → NO | ΔH = 90.25 KJ/mol
b. NO + 1/2O2 → NO2 | ΔH = -57.07 KJ/mol
ΔH = 33.18 KJ mol
3C + 4H2 → C3H8, what is ΔH if mini reactions:
a. C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O | ΔH = -2219.1 KJ/Mol
b. C + O2 → CO2 | ΔH = -393.5 KJ/mol
c. H2 + 1/2O2 → H2O | ΔH = -285.8 KJ/mol
ΔH = -104.5 KJ/mol
which would have higher frequency, gamma rays or microwaves?
gamma rays because gamma rays have more energy, so the frequency is higher
which has a higher wavelength? gamma rays of microwaves?
microwaves, because lower energy = higher wavelength
which color of light has the higest energy, blue or yellow?
ROYGBIV, closer to V = more energy
blue would have highest energy
electro magnetic specrum formla
speed of light (3 10&8 m/s) = wavelength frequency
energy = plancks contsant * frequency
calculate the wavelength of light emitted from the n = 4 to n = 2 energy state
486 nm
exothermic
heat from system -> surroundings
endothermic
heat from surroundings -> system
1 calorie
4.184 joules
ΔH°f
forming 1 mole from standard state, measured in KJ/mol
standard state
most common
ie. H -> H2 gas
N -> N2
electromagnetic spectrum formula, poroportionality
c=λ*v
since c = constant, wavelength & frequency are inversely proportoinal
v = frequency
λ = wavelength
photoelectric effect energy formula
photons collide w electrons, electrons increase
E = plancks * frequency
directly proportional to eachother bc E has no limit
how do waves interact with atoms?
light shines on atoms
white light -> prism -> continous spectrum
or white light -> atom -> line spectrum
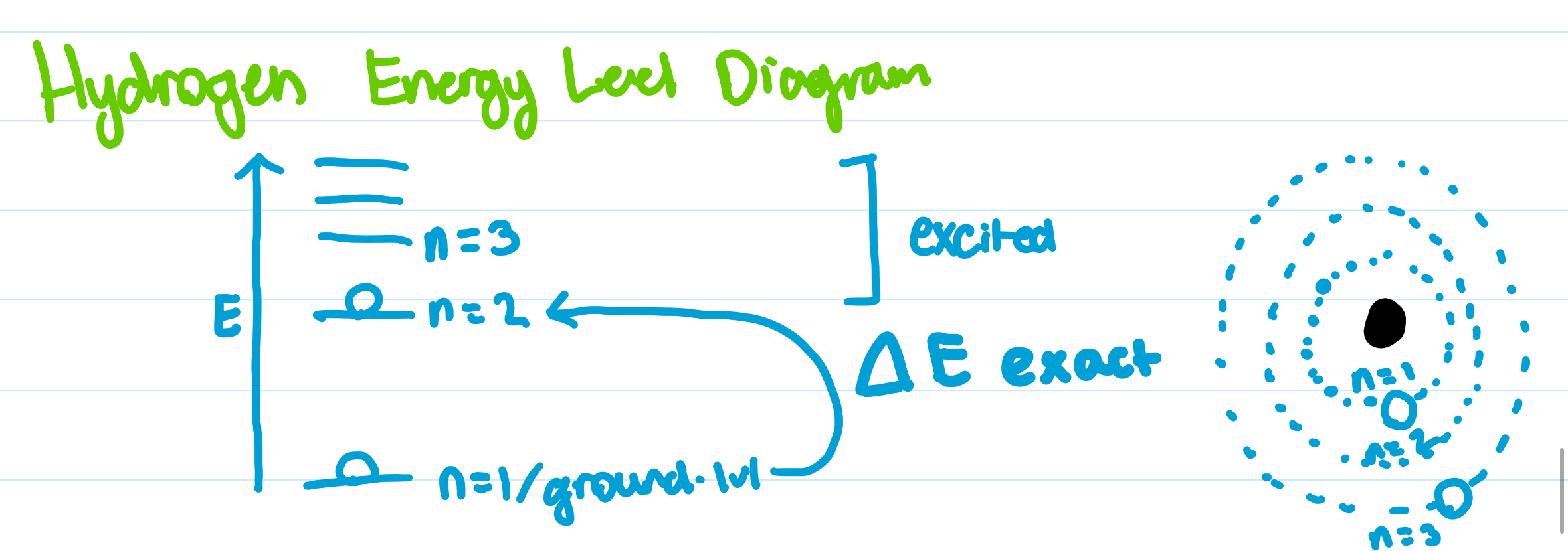
balmer series
starts at n = 2, for hydrogen atoms
visible spectrum
ROYGBIV
R = Long wavelength, short frequency
V = short wavelength, high frequency
energy level diagram
PUT PHOTO HERE
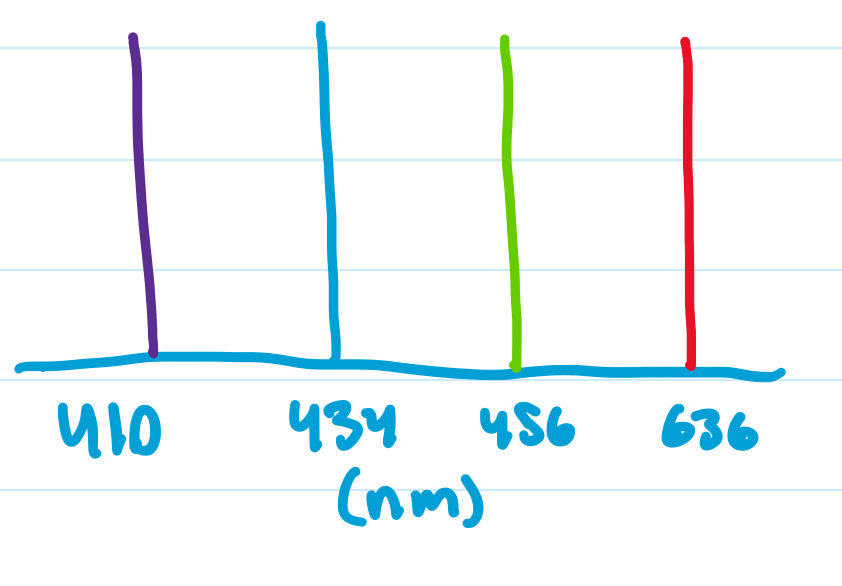
which e transition has the longest wavelength?
n = 4 -> n = 3
n = 2 -> n = 1
n = 4 -> n=3 would have the longest wavelength because ΔE is smallest, so small frequency, big wavelength
where is the electron?
- in energy level (n-shell -> ℓ-subshell -> mℓ-orbital)
- in orbital (mℓ)
- for hydrogen atom bc hydrogen has only 1 electron, and if there was multiple electrons they would repel eachother
heisenburg uncertainty principle
can't measure position/momentum/energy @ same time
schrodinger
- treated eletrons as wavelength
- wave equations predicted probaility of finding electron in orbital
schrodingers variables
1. n
2. ℓ
3. mℓ
n
- principle quantum #
- possible values: n = 1,2,3...
- show energy lvl/shell
- ctrls size of orbital (distance of electron away from nucleus)
ℓ
- angular momentum #
- possible values: 0,1,2,3 (n - 1 is max)
- shows subshell/grp of orbitals
ℓ subshells
0 -> s
1 -> p
2 -> d
3 -> f
4 -> g
mℓ
- magnetic quantum #
- poss values: mℓ = 0, ±1, ±2, ±ℓ
- each mℓ value -> unique orbital w/ subshell
ie. if ℓ = 2, mℓ can be -2, -1, 0, +1, +2
angular nodes, how to calculate orbitals?
if ℓ = 1, there is a p-subshell of p-orbitals
ie. ℓ = 2, d = 5 orbitals, bc mℓ is -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, (5 values)
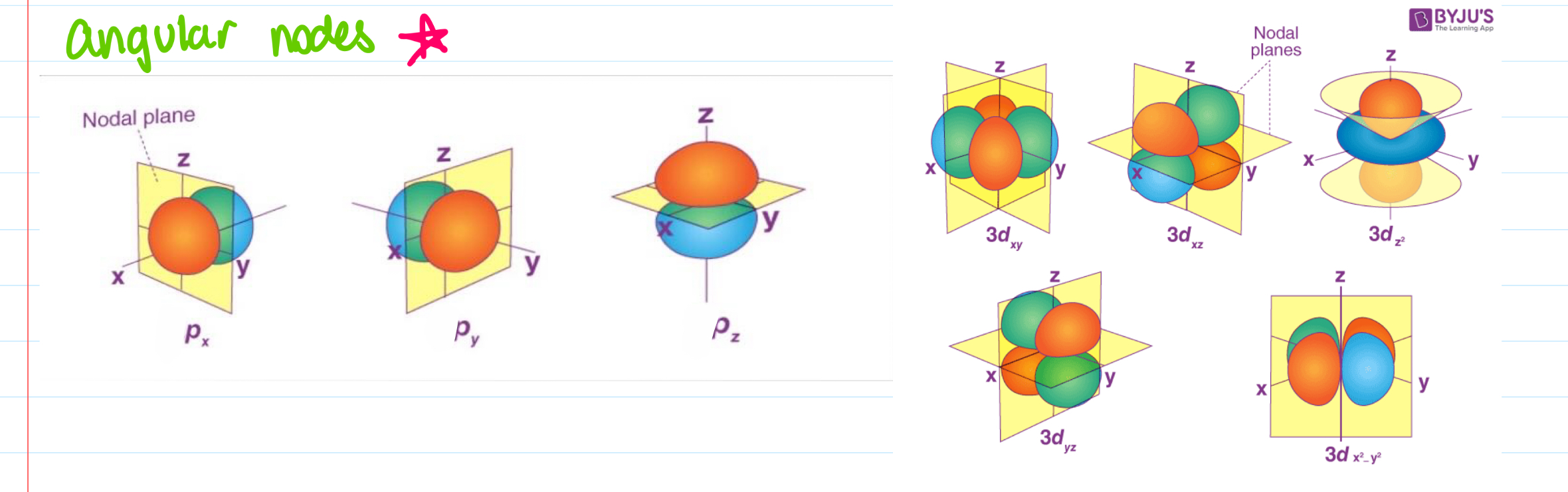
if the electron is in n=3, what subshell could it be in?
ℓ = 0 (s), 1 (p), 2 (d) subshell orbitals
# orbitals total
n²
is n = 3, ℓ = 0, mℓ = -1 a possible set of quantum numbers?
no, because since ℓ = 0, mℓ can only be +ℓ (like 1)