BIO 201 - Nervous System: Central Nervous System (CNS)
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
4 anatomic and functional regions of the brain
cerebrum, diencephalon, cerebellum, & brainstem
Ventricles
a system of fluid filled cavities (spaces) that are filed with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) which is derived from the plasma and serves to protect the brain by allowing it to float in the insulating fluid of the CSF
Meninges
a set of 3 membranes; dura mater (superficial), arachnoid mater, pia mater (deep)
Fissures
deeper grooves/furrows formed by the meningeal layer of the dura mater and are embedded
Sulci
shallow grooves in the brain
Gyri
folds in the brain
Flow of CSF (step 1)
Left and right lateral ventricles (fluid-filled spaces found in each cerebellar hemisphere)
Flow of CSF (step 2)
Interventricular foramen (an opening/pathway between the lateral ventricles and third ventricle)
Flow of CSF (step 3)
Third ventricle (found below the corpus callosum (white matter) and in between the thalami.
Flow of CSF (step 4)
Cerebral aqueduct (passes through the midbrain of the brainstem)
Flow of CSF (step 5)
Fourth ventricle (located between the pons of the brainstem and cerebellum)
Flow of CSF (step 6)
Out of the apertures and central canal
Flow of CSF (step 7)
To the subarachnoid space that surrounds the brain and spinal cord.
Flow of CSF (step 8)
Reabsorbed by arachnoid granulations into the dural venous sinuses, such as the superior sagittal sinus
Cerebrum includes:
frontal lobe, parietal lobe, insula, temporal lobe, occipital lobe, corpus callosum, basal nuclei, central sulcus, lateral sulcus, parieto-occipital sulcus, transverse fissure, longitudinal fissure, precentral gyrus, postcentral gyrus
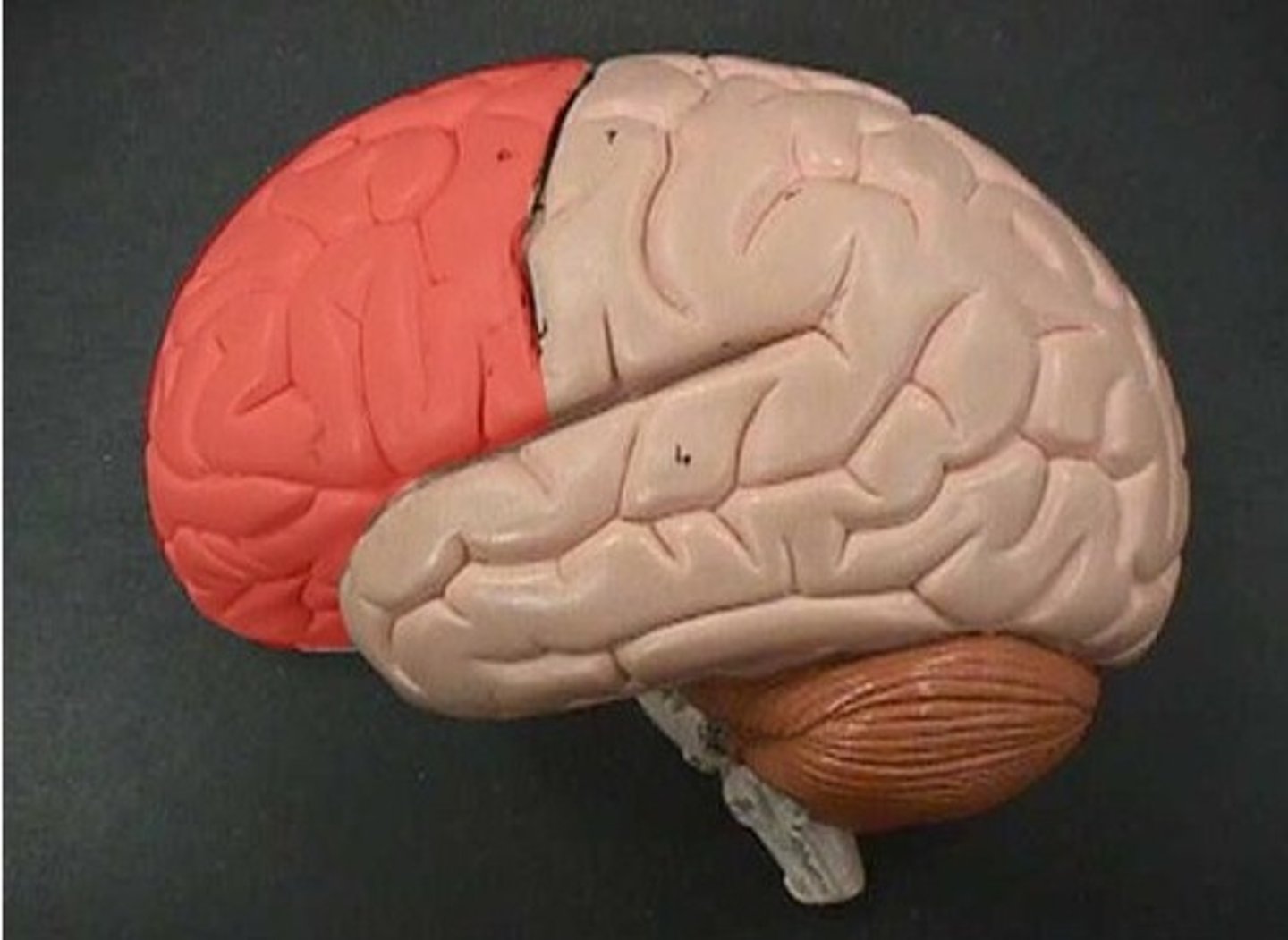
Frontal lobe (def)
responsible for emotion, mood, memory, social judgement, and aggression
Frontal lobe
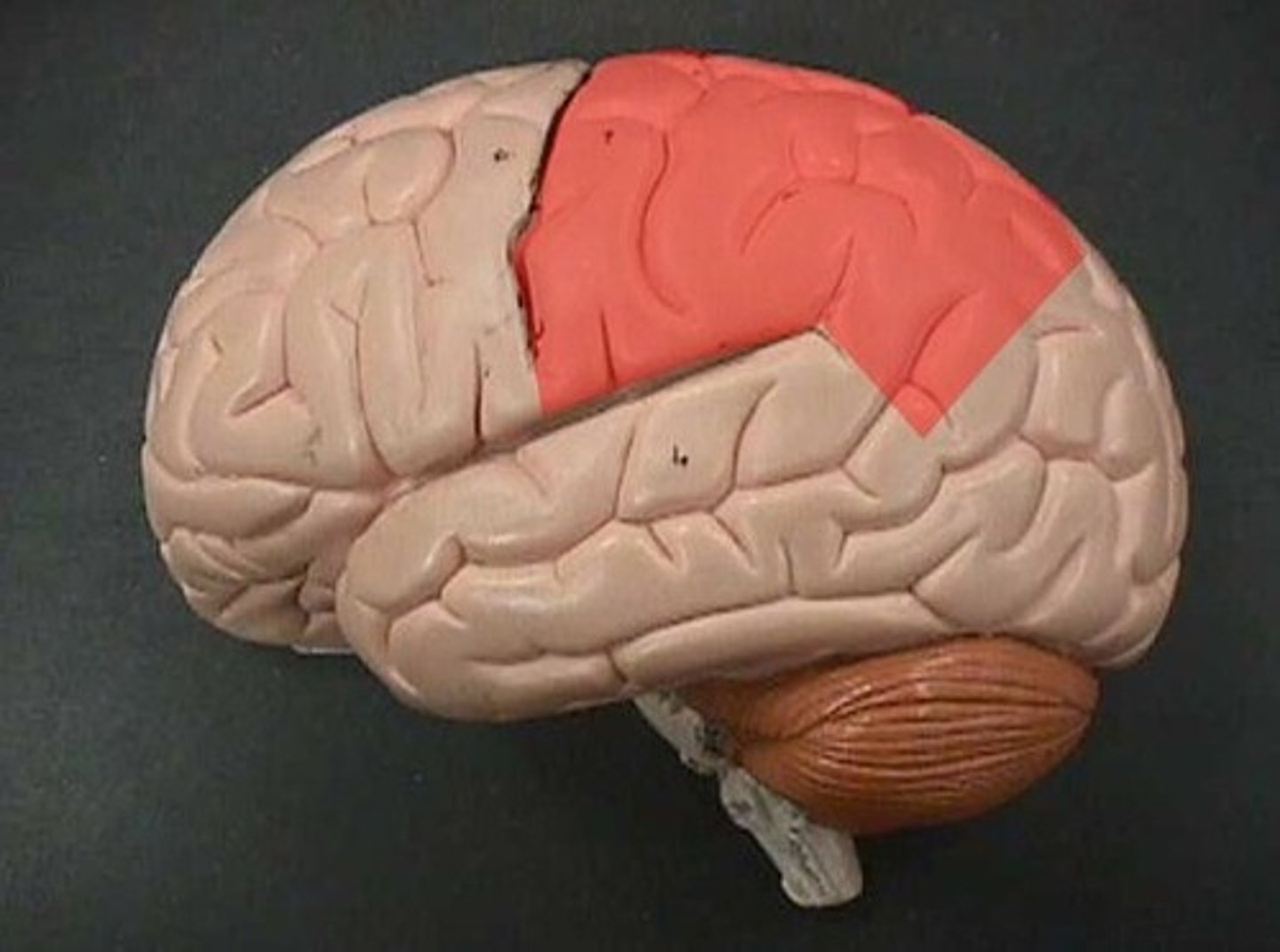
Parietal lobe (def)
responsible for sensory reception and integration of taste and some visual information
Parietal lobe
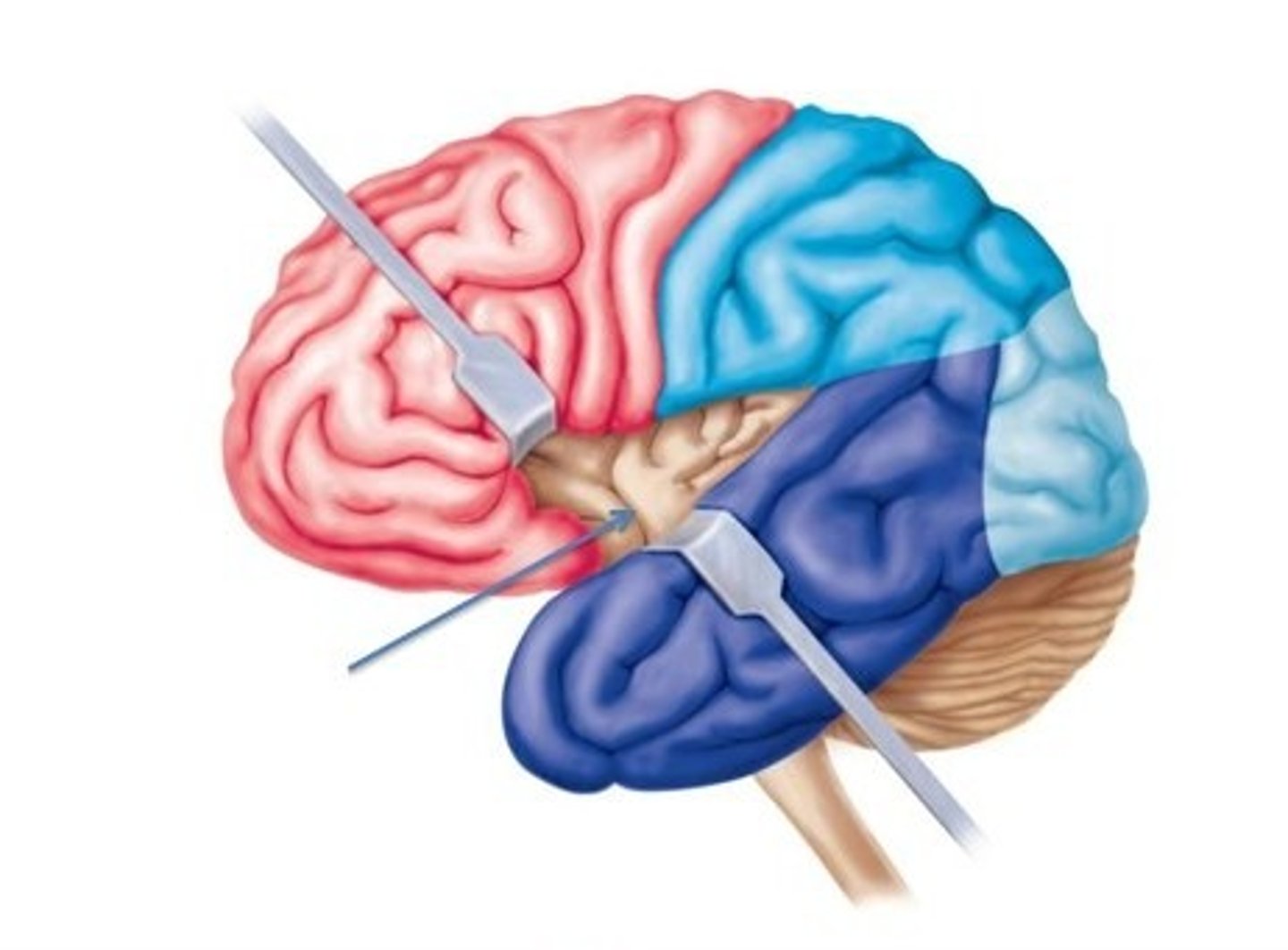
Insula (def)
apparently plays a role in understanding spoken language. Located deep into the lateral sulcus
Insula
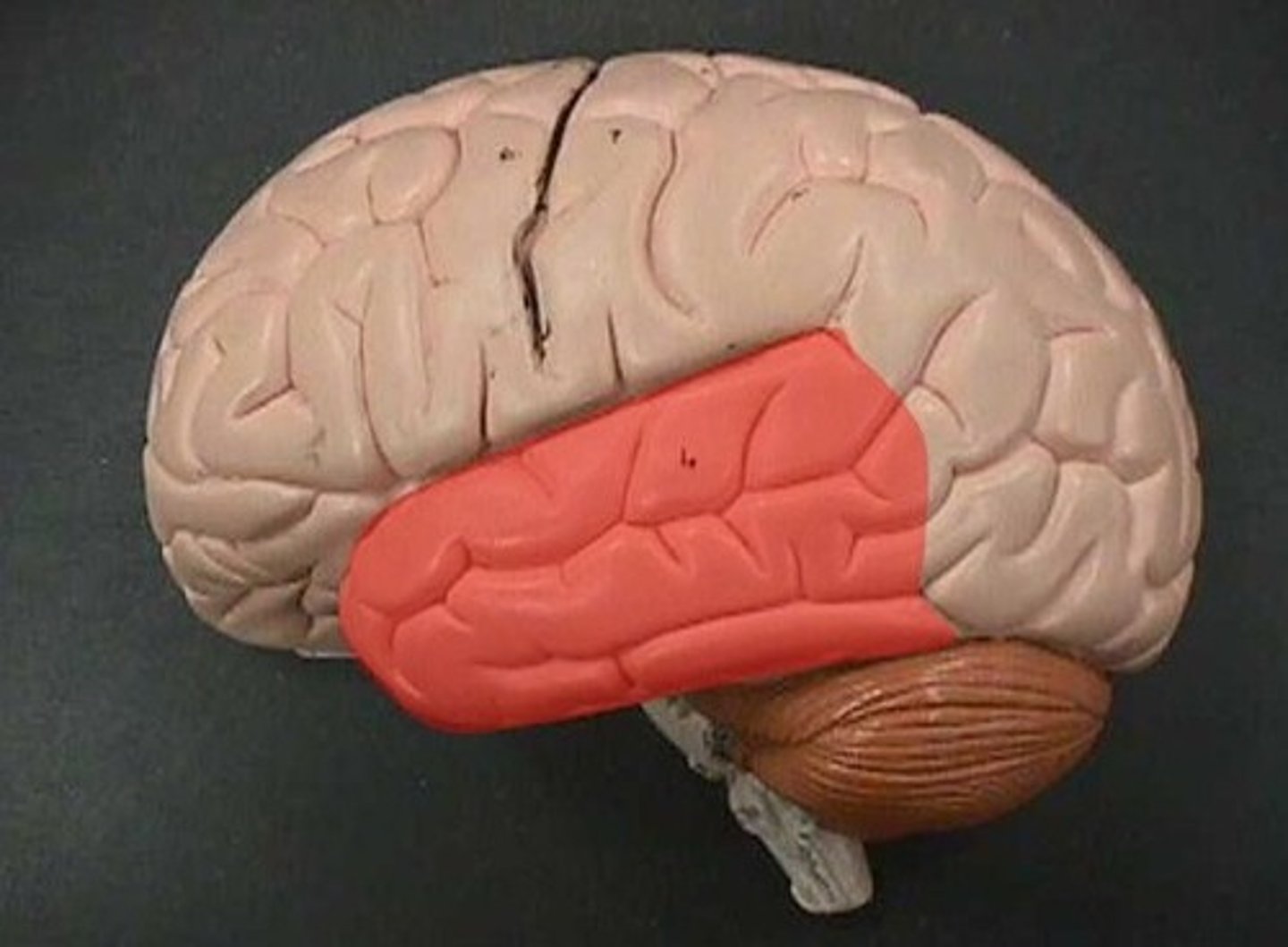
Temporal lobe (def)
responsible for hearing, smell, learning, memory, visual recognition, and emotional behavior
Temporal lobe
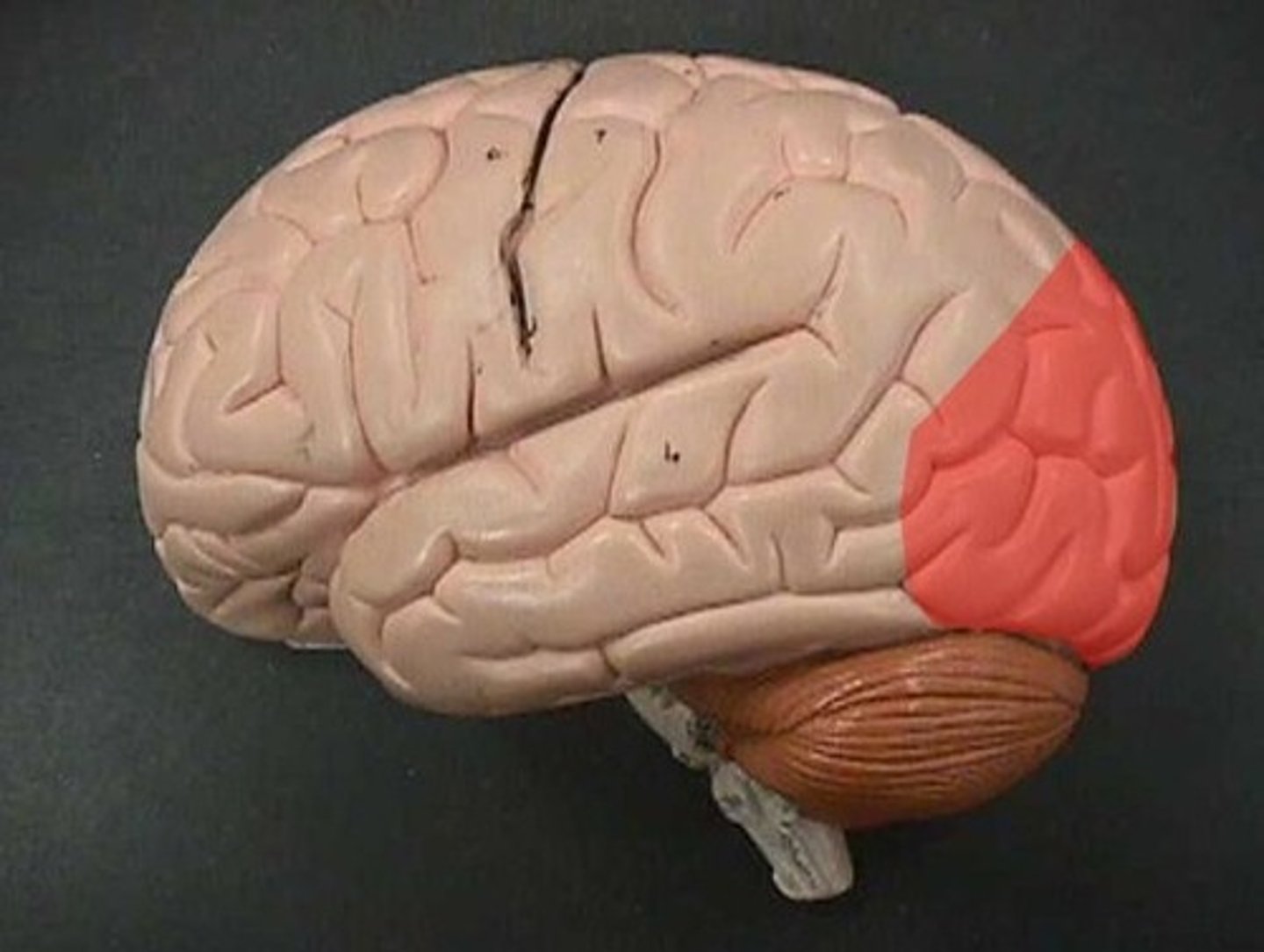
Occipital lobe (def)
the principal visual center of the brain
Occipital lobe
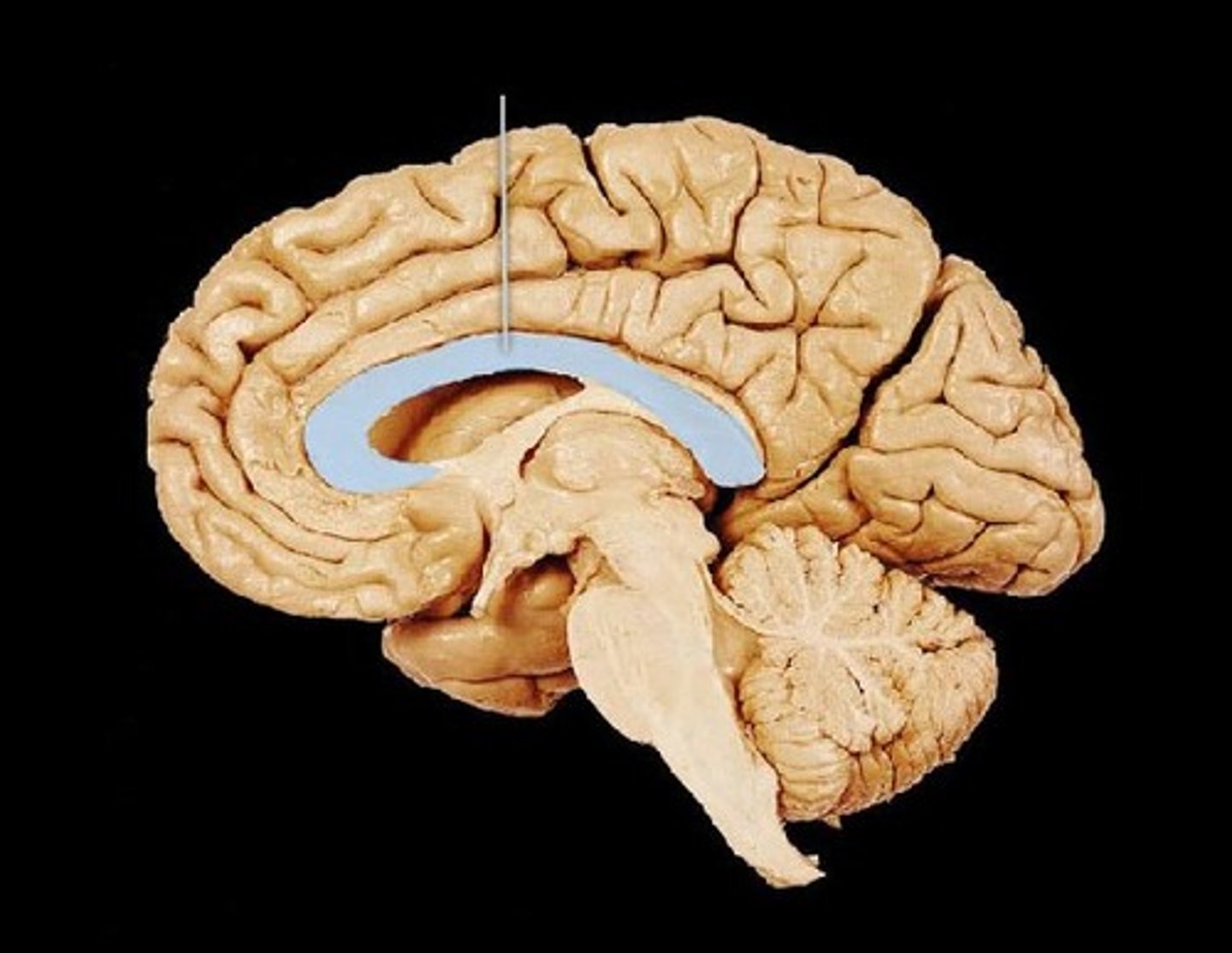
Corpus callosum (def)
nerve axons/tracts that connect the cerebral hemispheres to each other
Corpus callosum
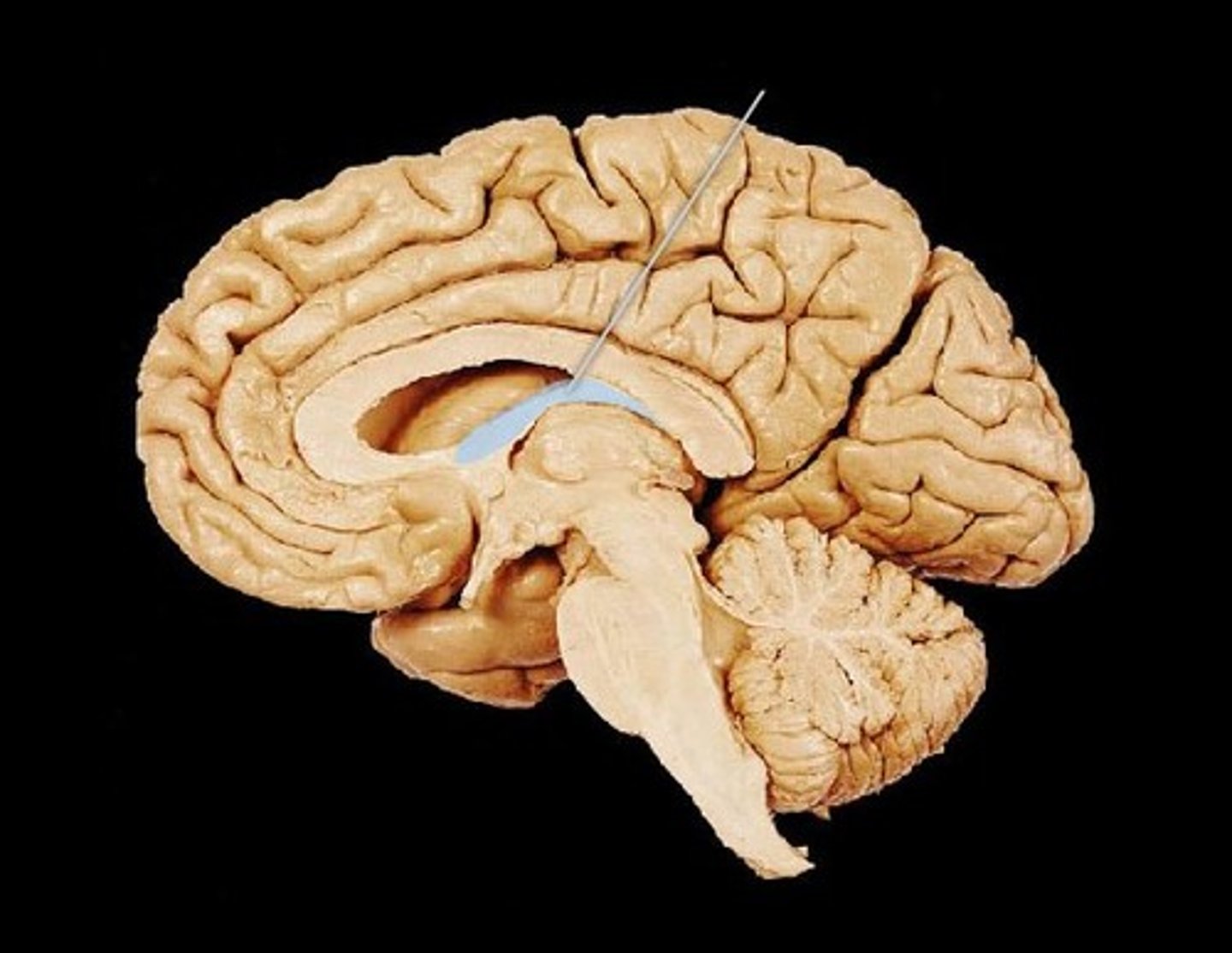
Fornix
Basal nuclei (def)
involved in motor control. Contains the putamen, globus pallidus, and caudate nucleus.
Basal nuclei
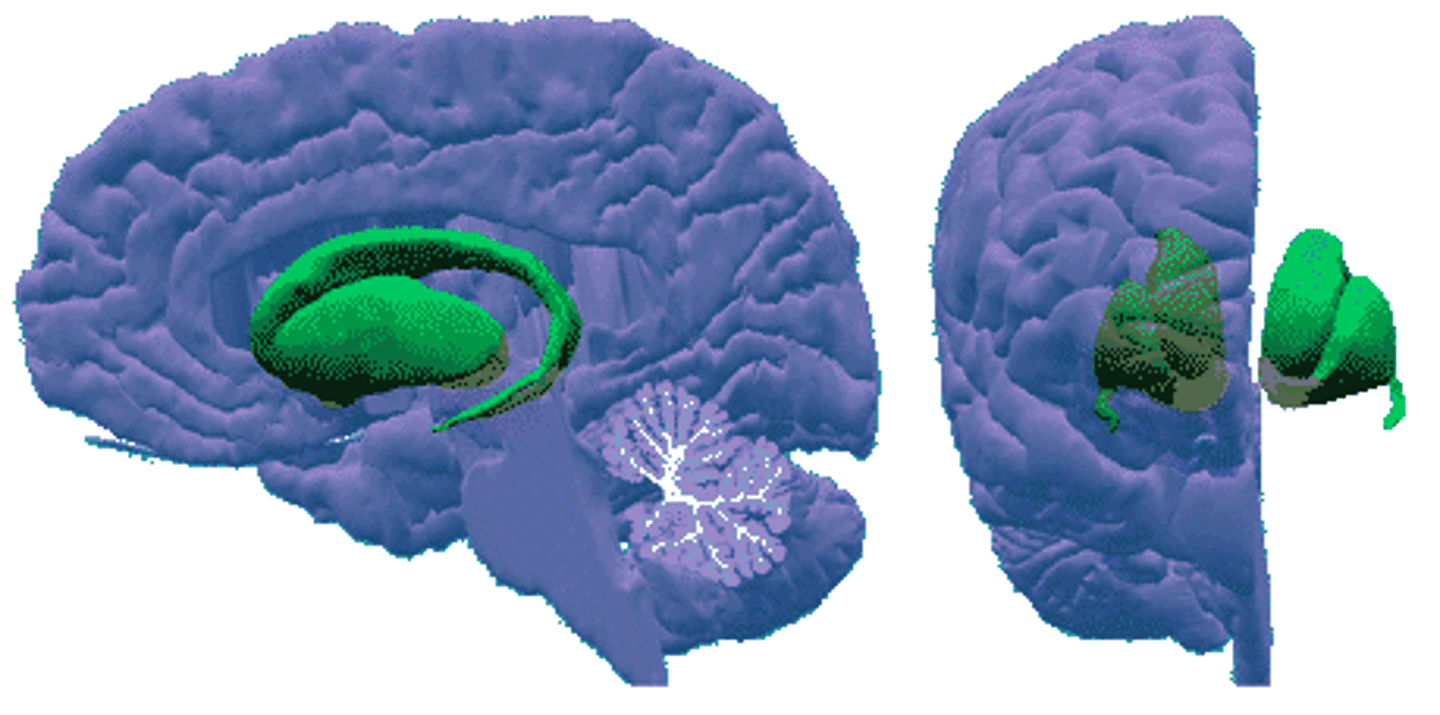
Caudate nucleus
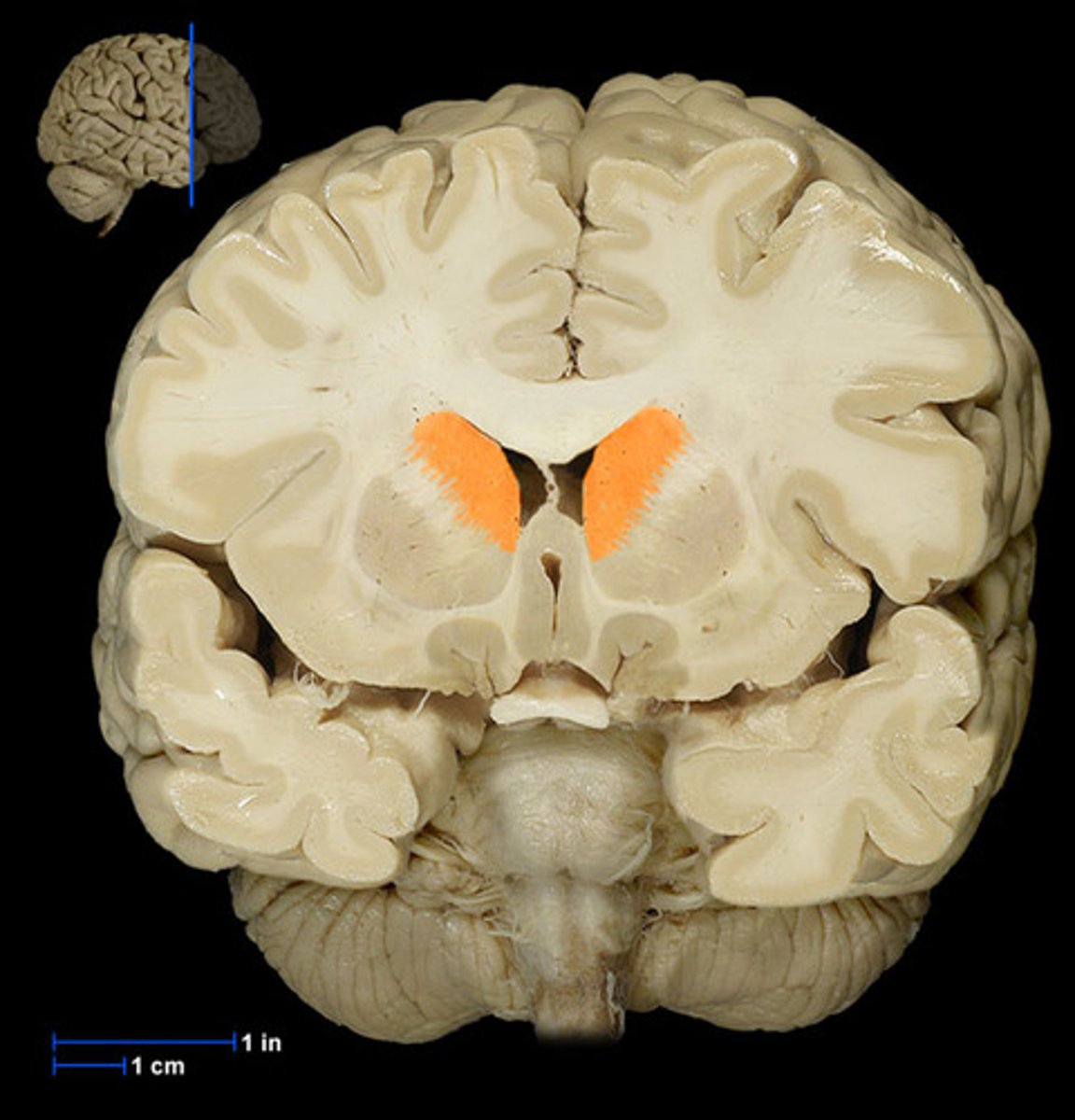
Putamen
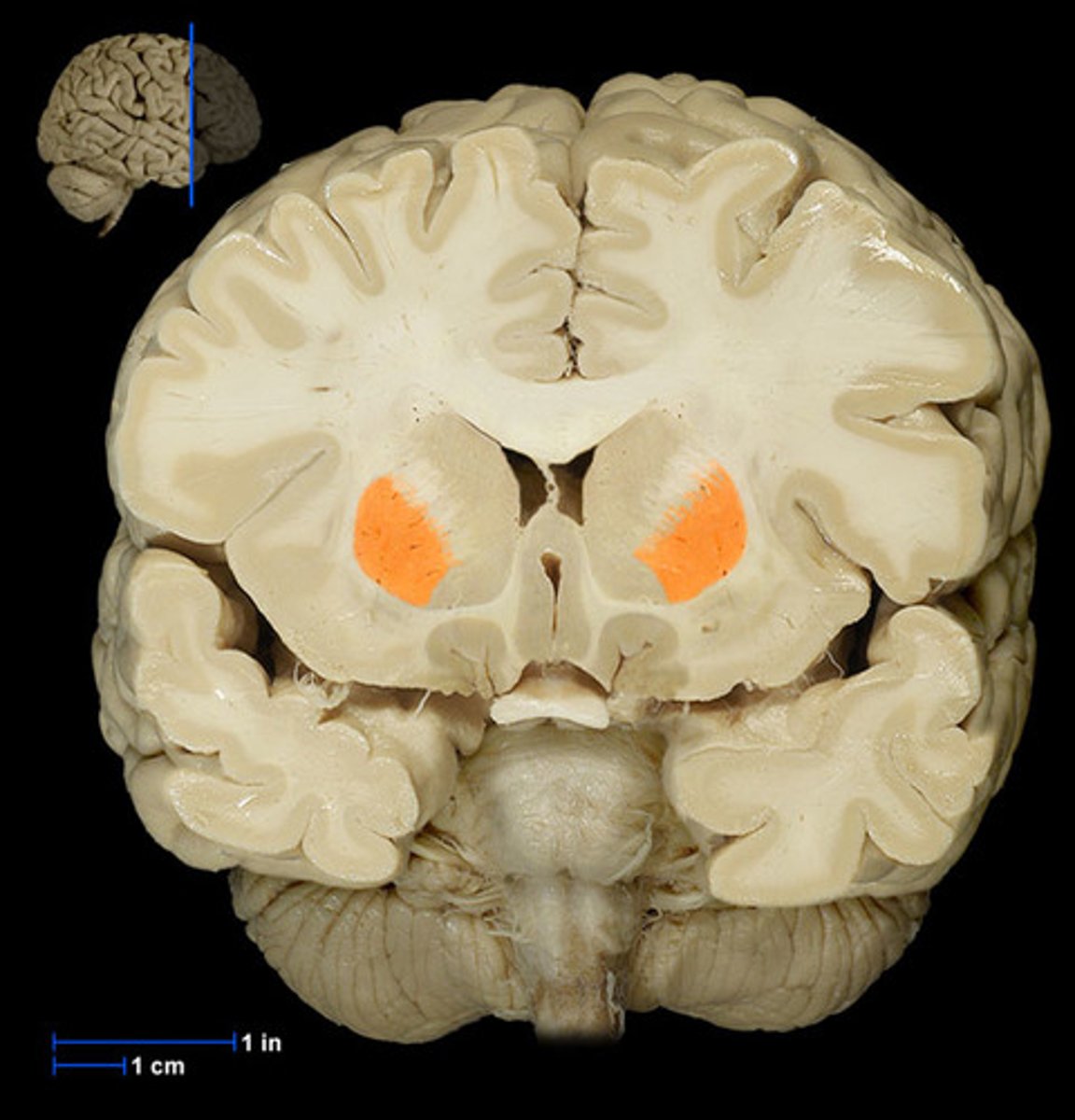
Globus pallidus
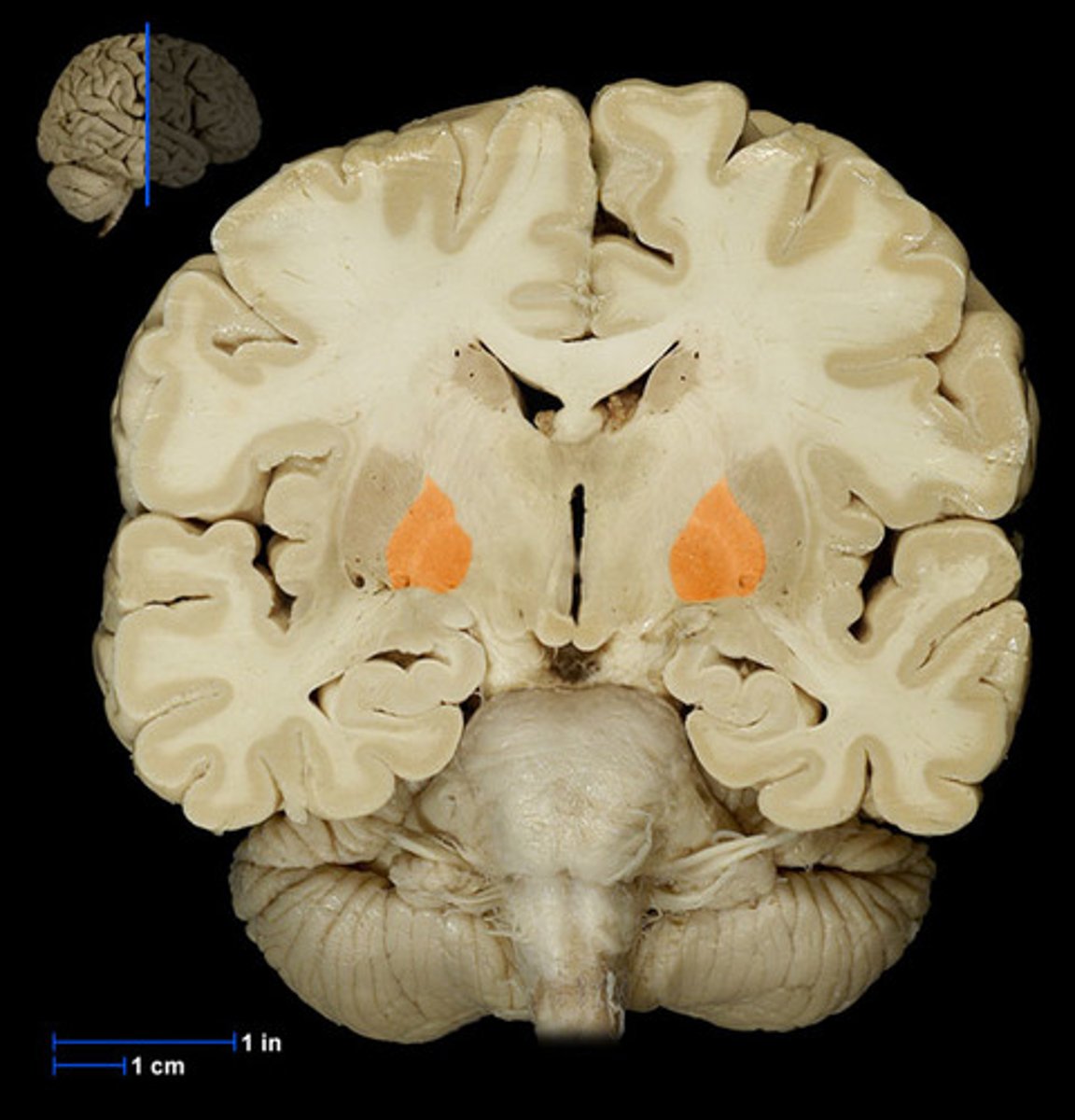
Central sulcus (def)
shallow groove found between the frontal and parietal lobes
Central sulcus
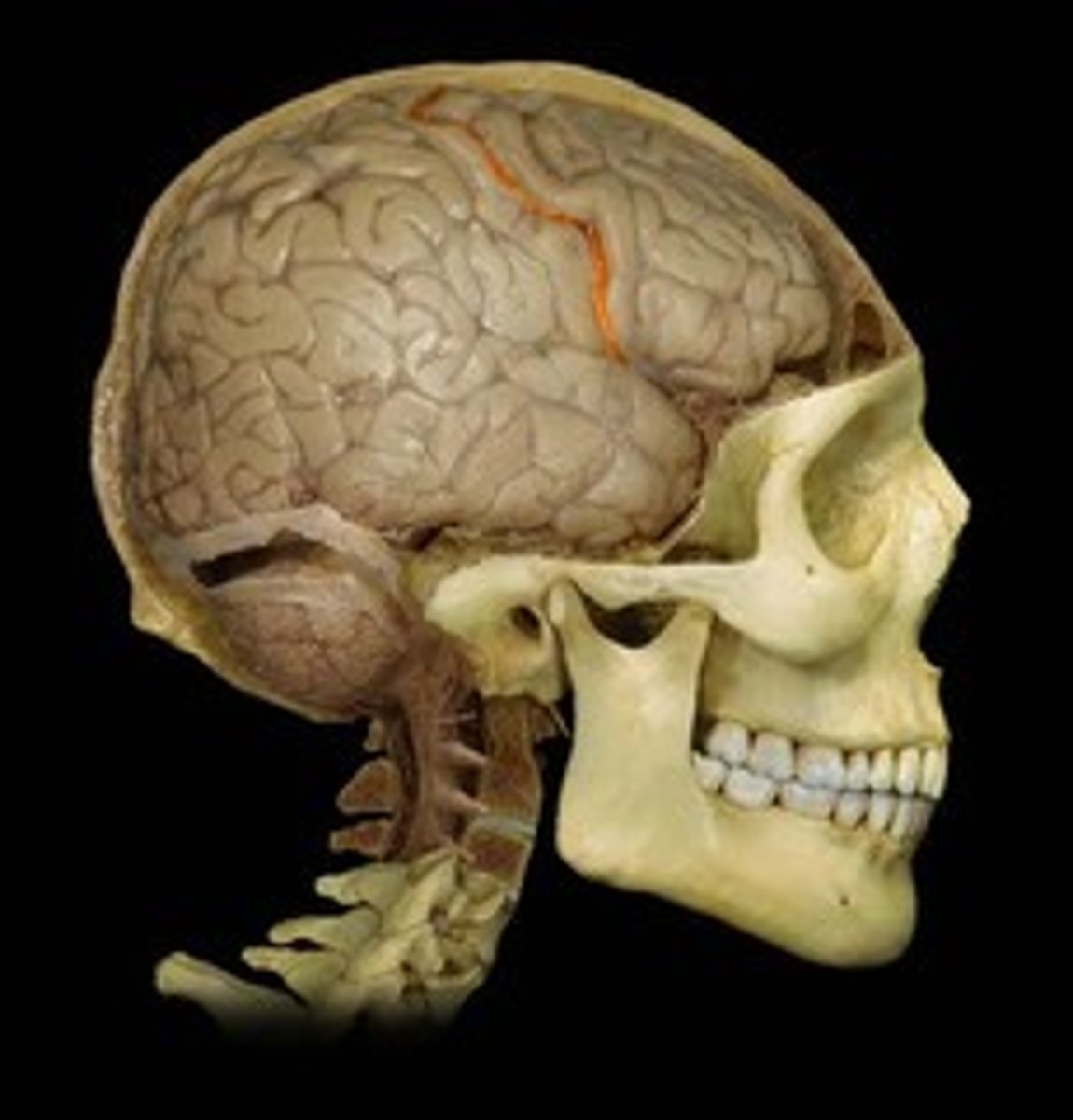
Lateral sulcus (def)
shallow groove found between the frontal and temporal lobes
Lateral sulcus
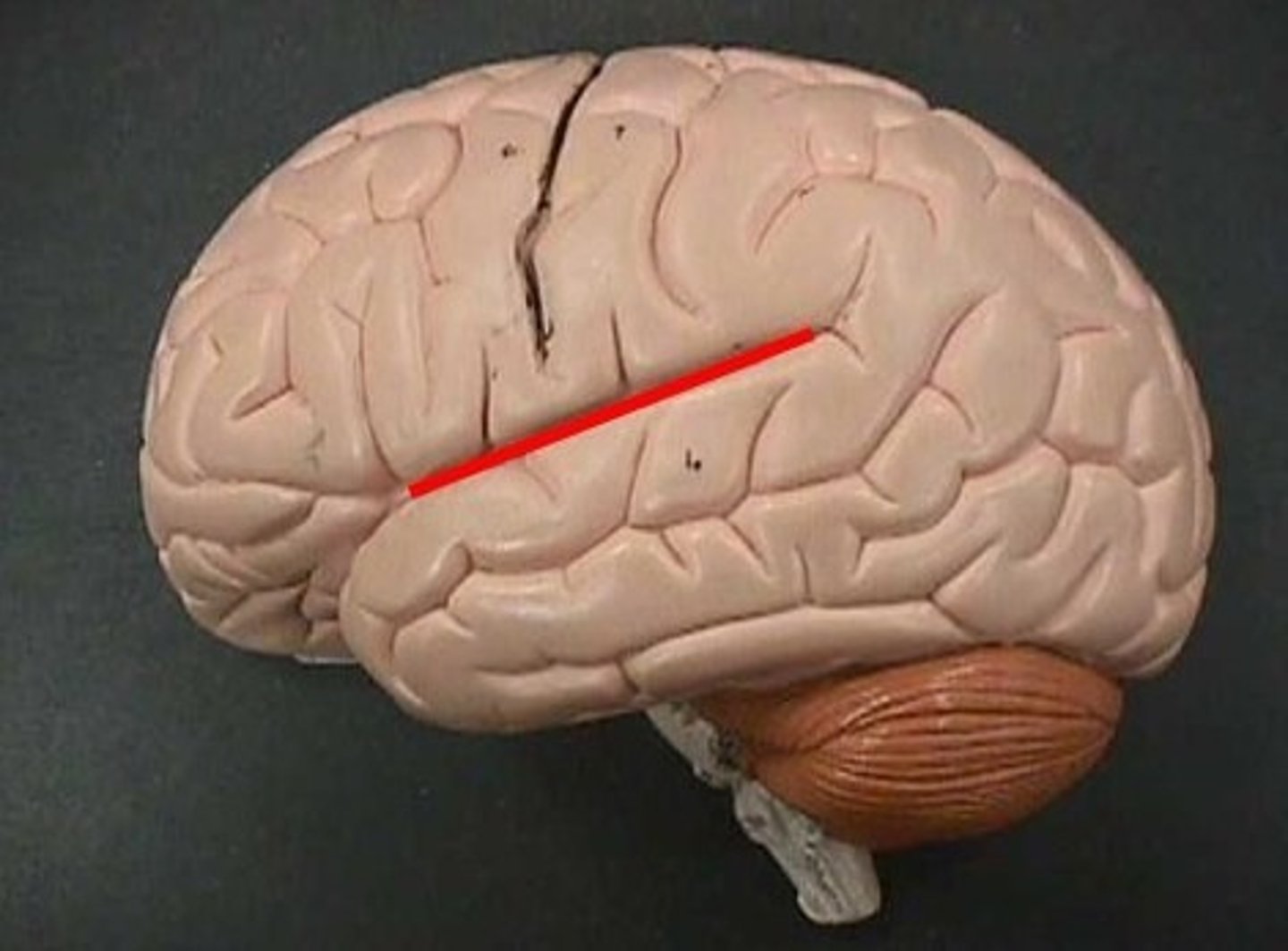
Parieto-occipital sulcus (def)
shallow groove found between the parietal and occipital lobes
Parieto-occipital sulcus
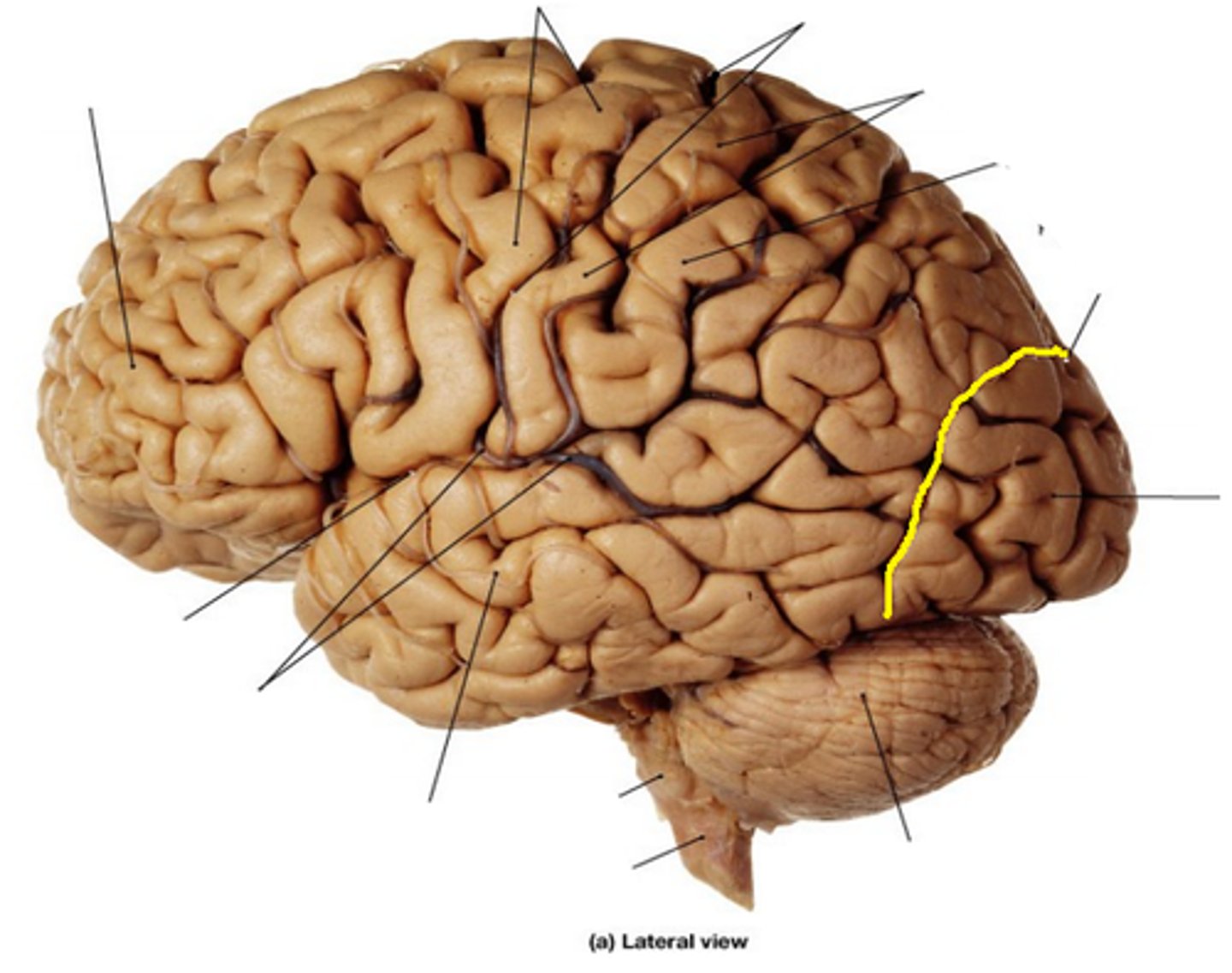
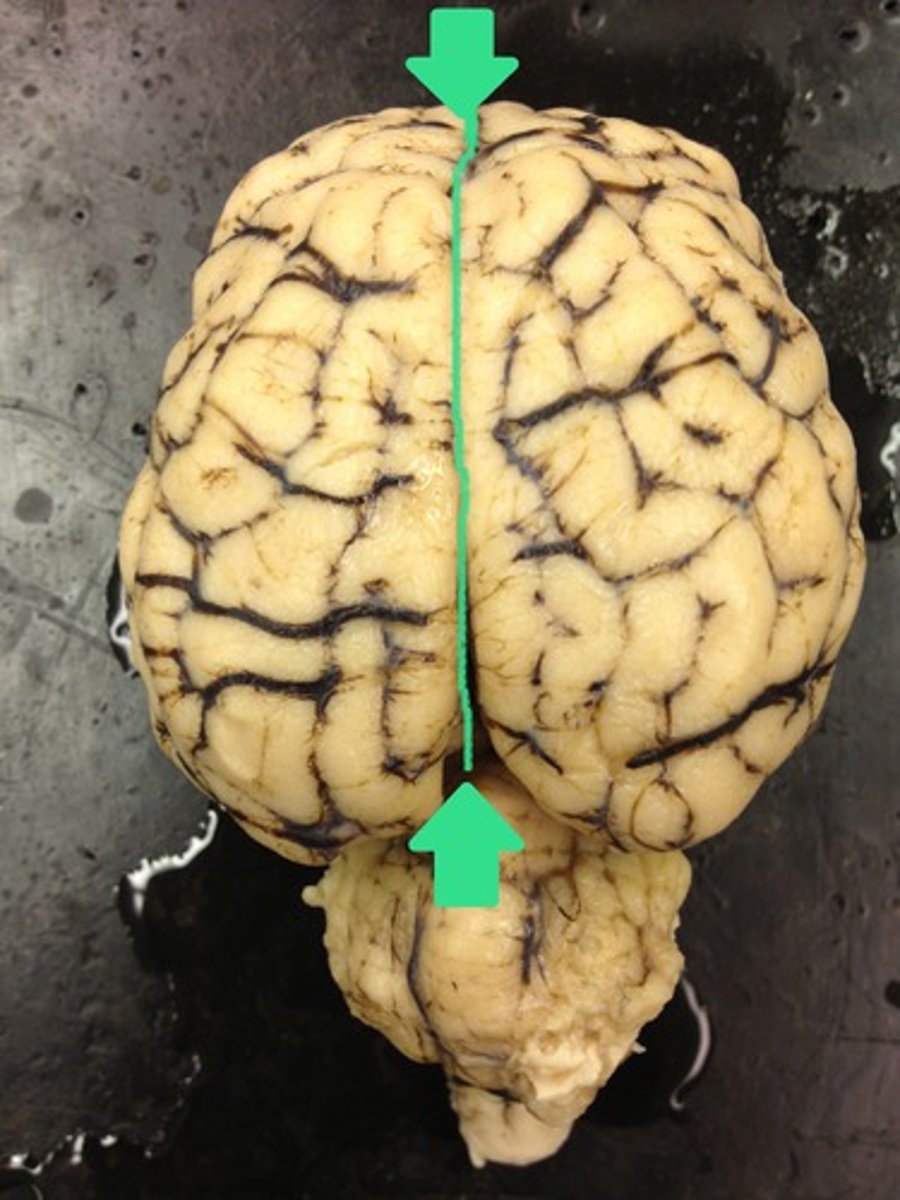
Transverse fissure (def)
deep groove found between the cerebellum and cerebrum
Transverse fissure
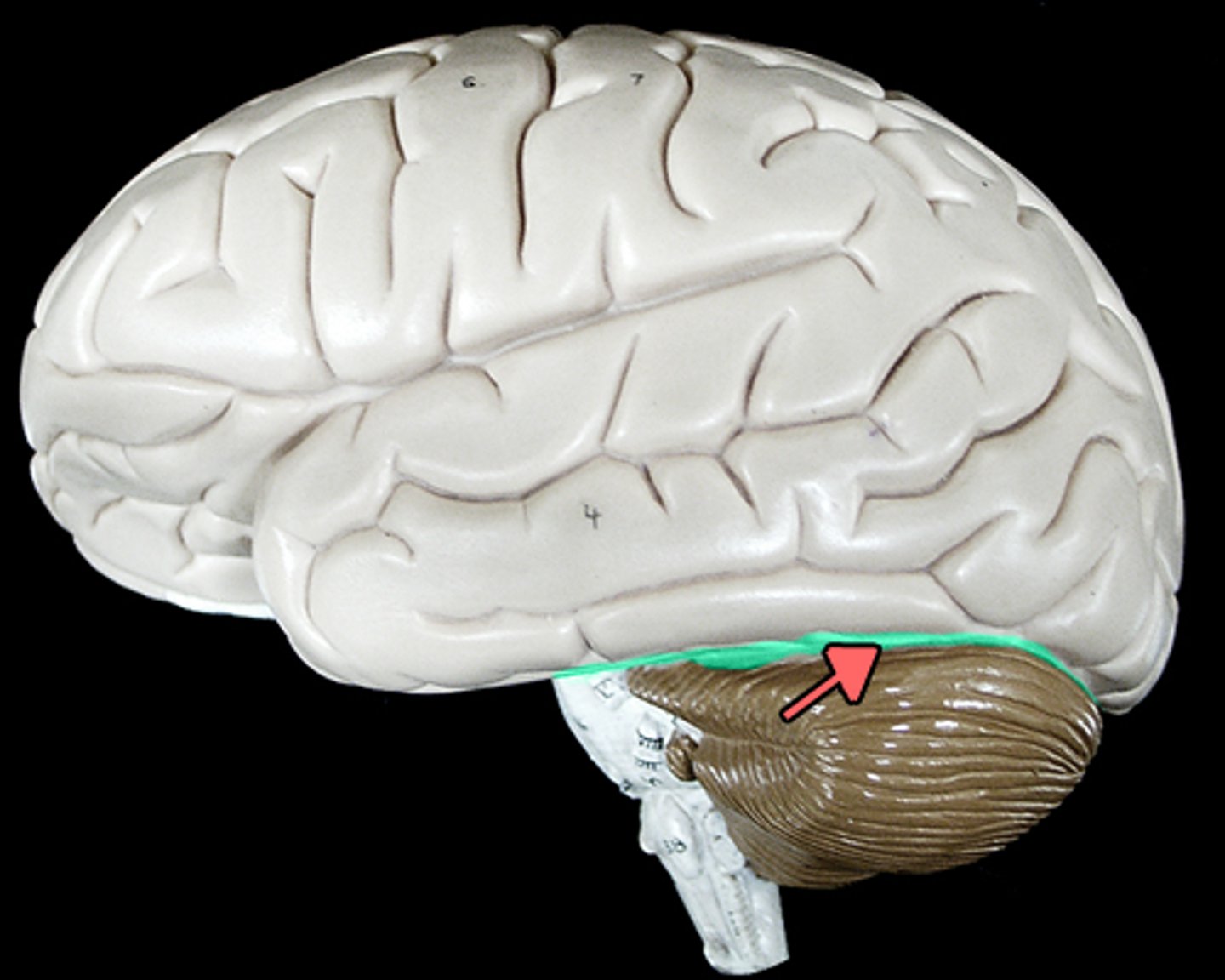
Longitudinal fissure (def)
deep groove found between each cerebral hemisphere
Longitudinal fissure
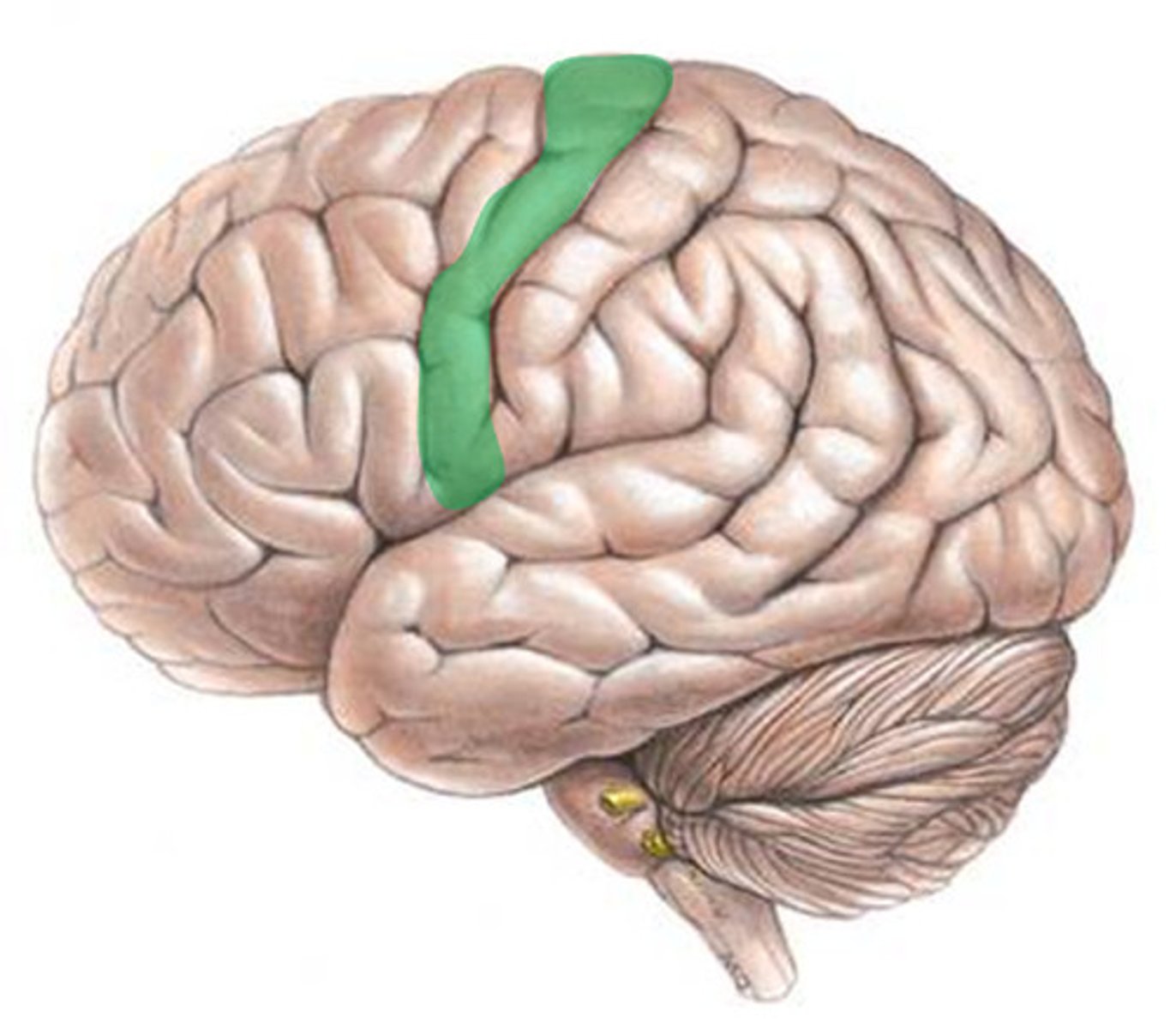
Precentral gyrus (def)
the immediate fold anterior to the central sulcus and located in the frontal lobe
Precentral gyrus
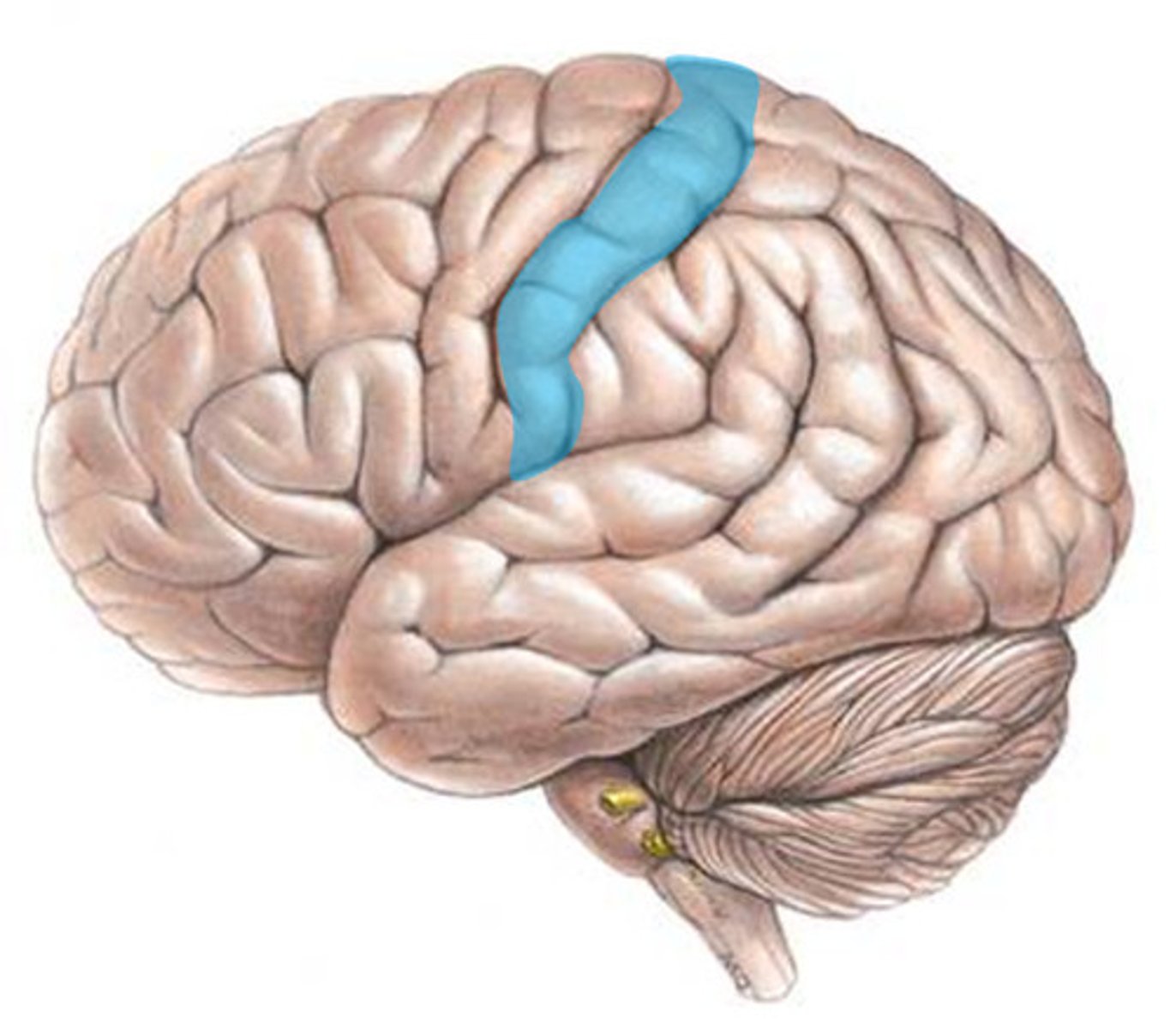
Postcentral gyrus (def)
the immediate fold posterior to the central sulcus and located in the parietal lobe
Postcentral gyrus
Gray matter
located superficially in the cerebrum and cerebellum; mainly composed of neuron cell bodies, dendrites and synapses; butterfly-shaped core
White matter
lies deep to the gray matter and is mainly composed of bundles of axon/tracts
Diencephalon
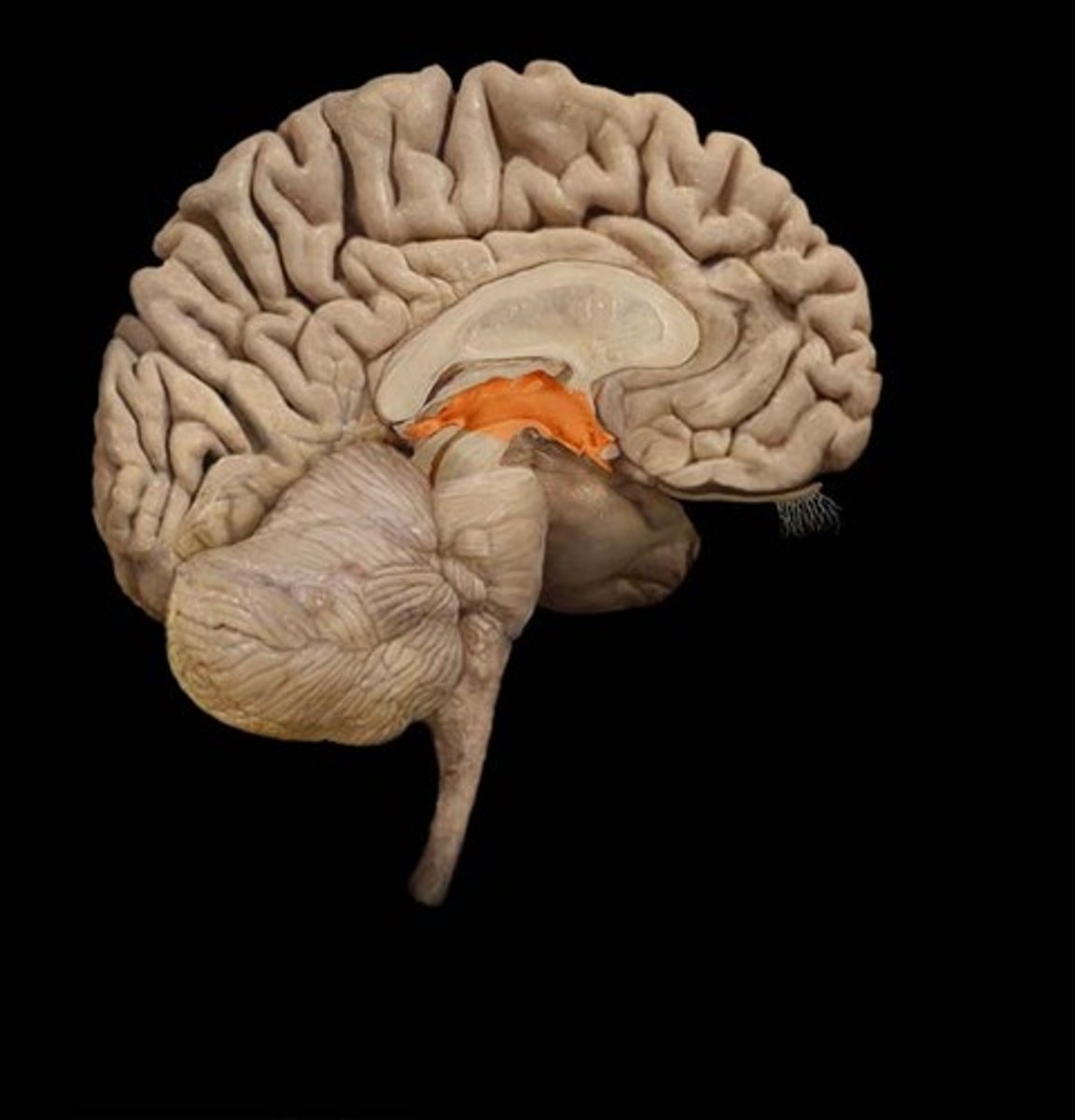
Thalamus (def)
gateway to the cerebral cortex, filters information and relay only a small portion of it to the cerebral cortex
Thalamus
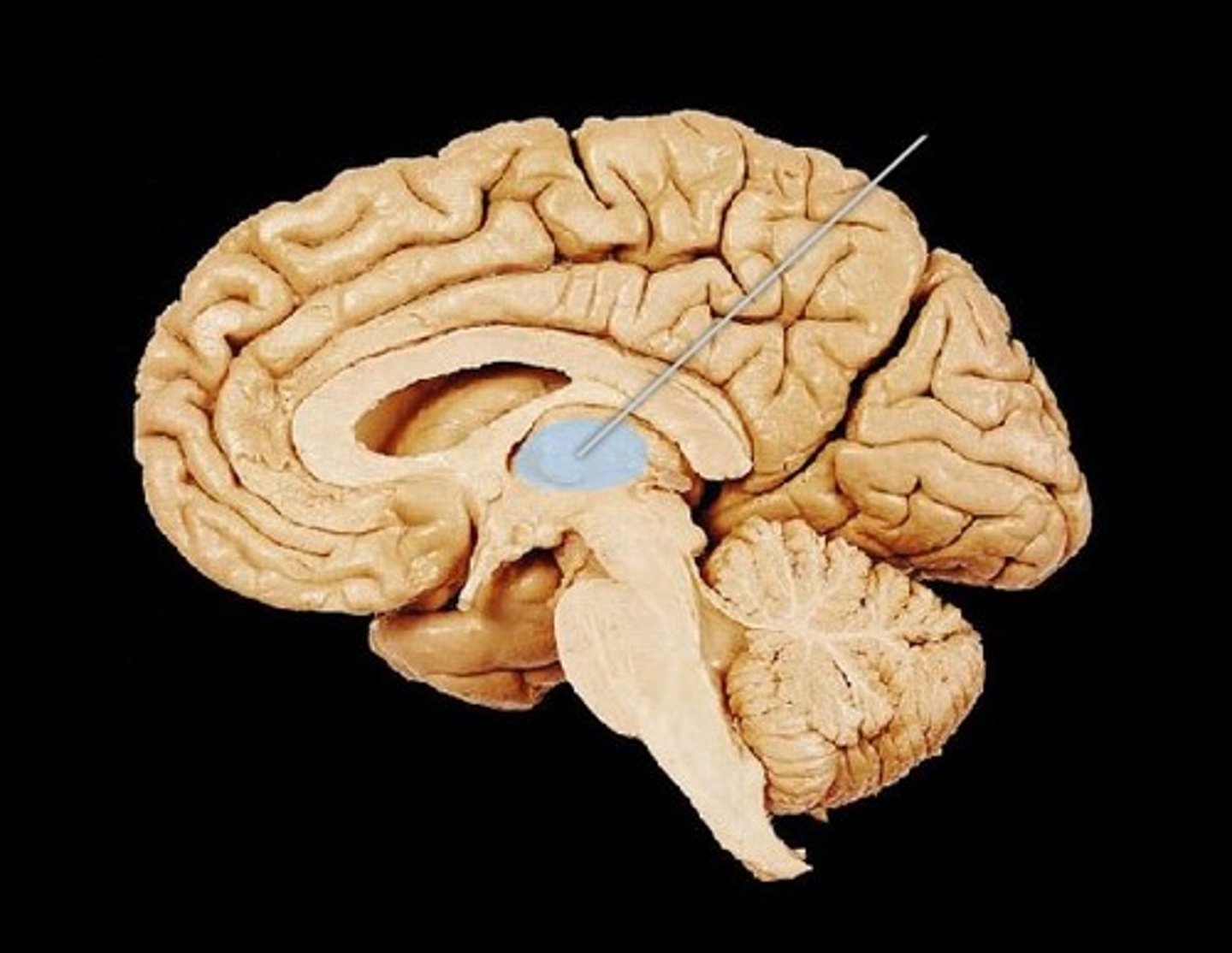
Hypothalamus (def)
major control center of the autonomic nervous system and CEO of the endocrine system. It is located anteriorly and inferiorly from the thalamus and by the hypophyseal fossa of the sphenoid bone. It is connected to the infundibulum which is connected to pituitary gland
Hypothalamus
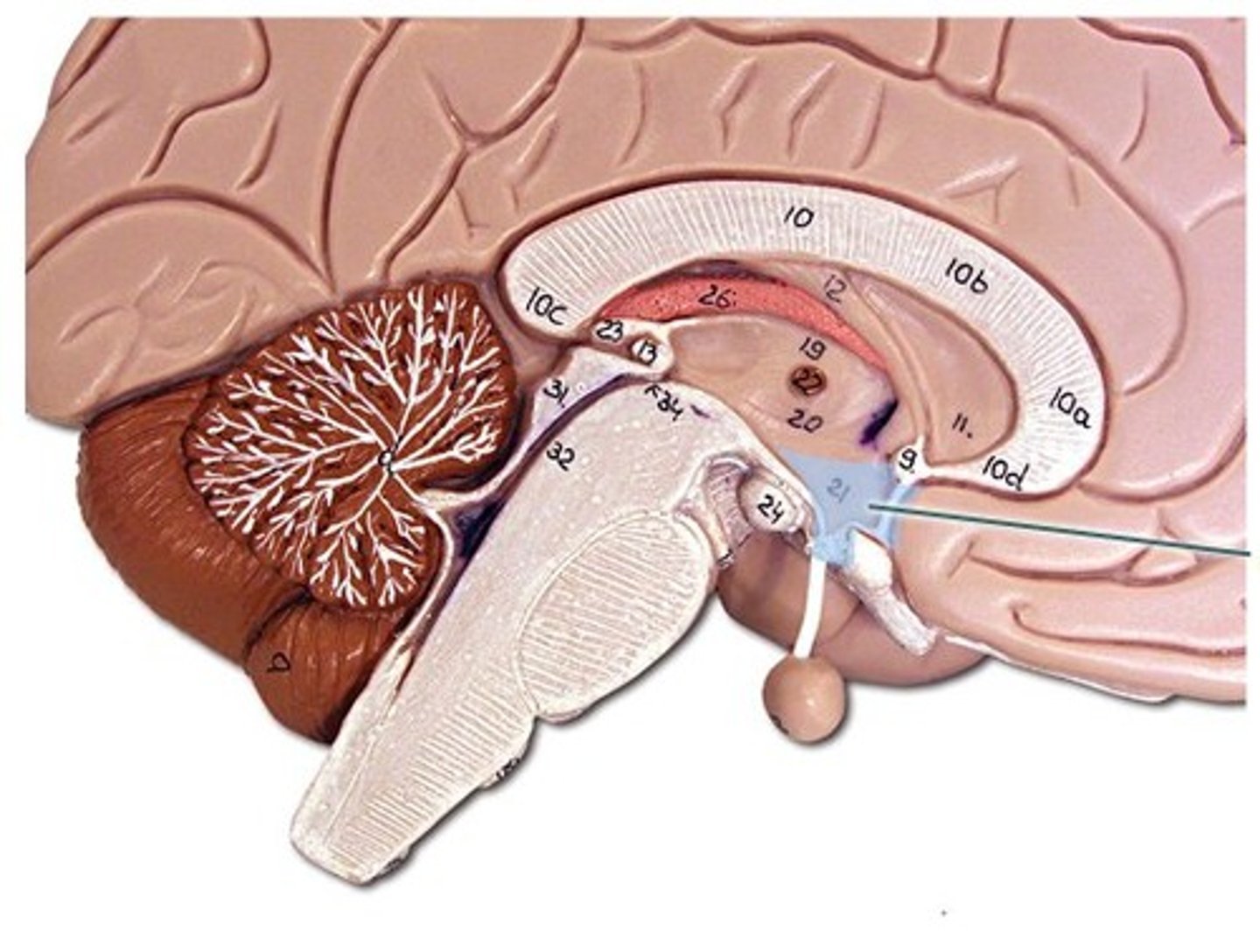
Epithalamus (def)
associated with the pineal gland, who is responsible for releasing the hormone melatonin which has a role in sleep. It is located posteriorly and superiorly from the thalamus
Epithalamus
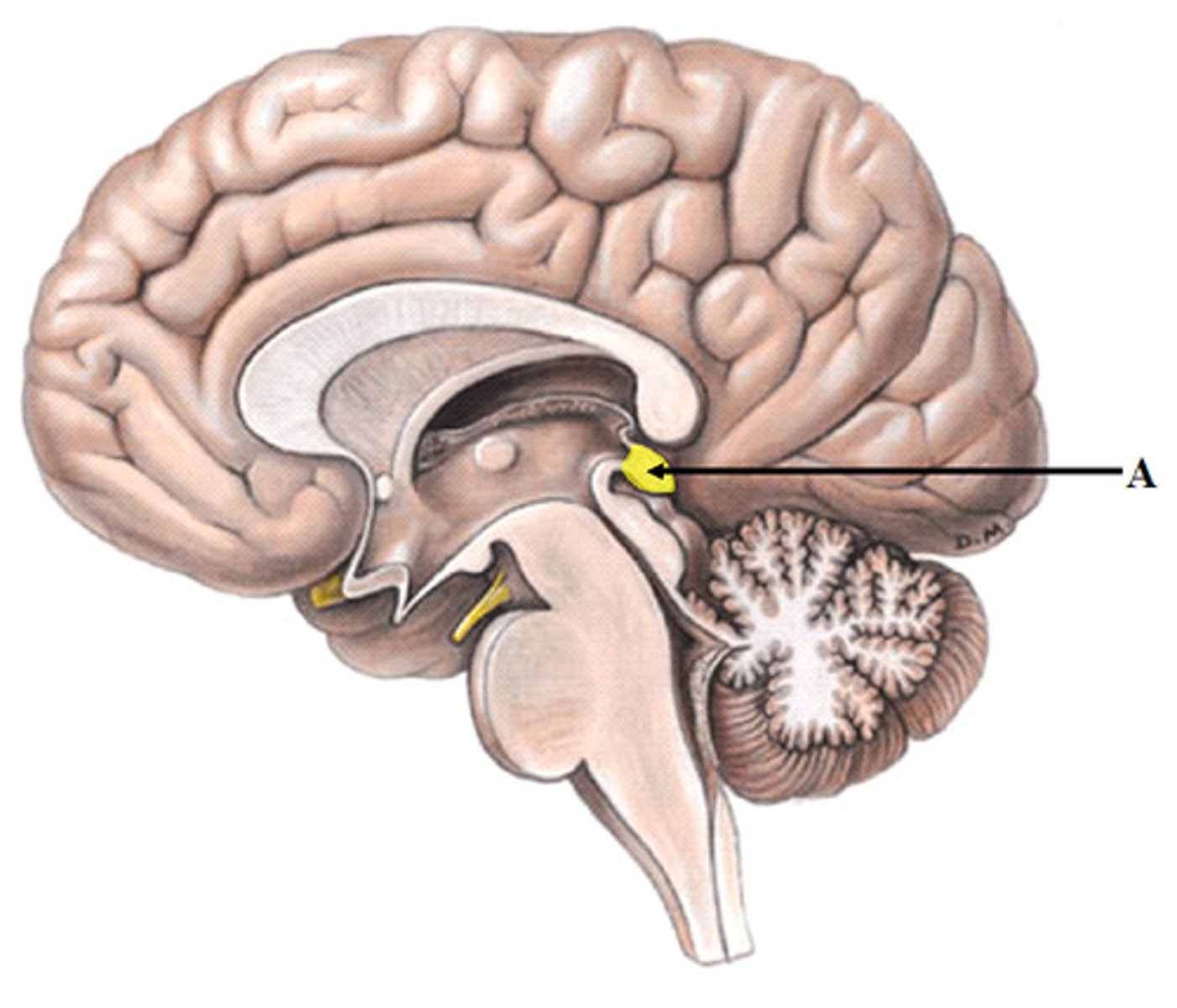
Cerebral cortex (def)
central control point for muscle coordination
Cerebral cortex

Arbor vitae (def)
white matter of the cerebellum. Translates to the "tree of life"
Arbor vitae
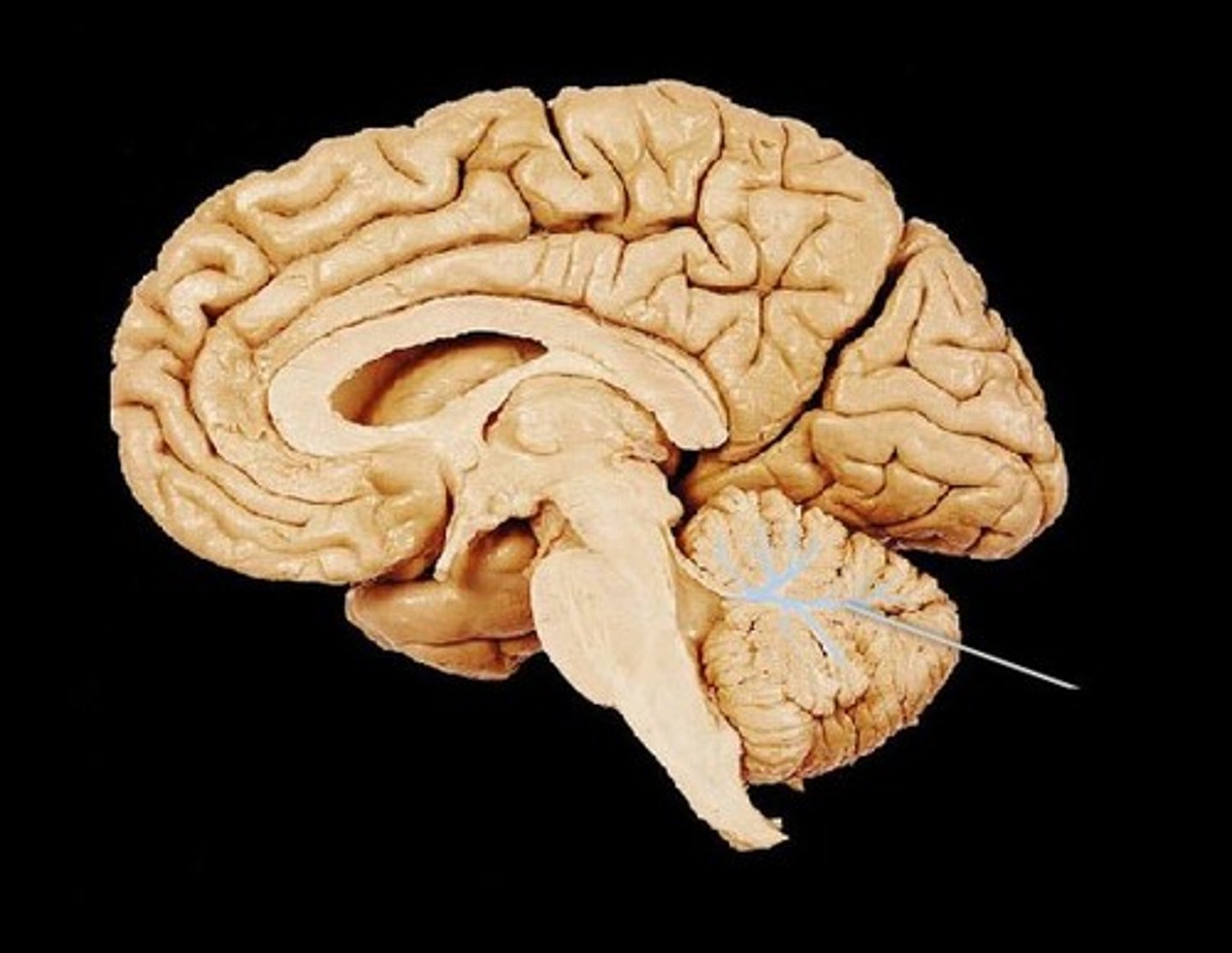
Folia (def)
folds found within the cerebellum. This is the equivalent of gyrus in the cerebrum
Folia
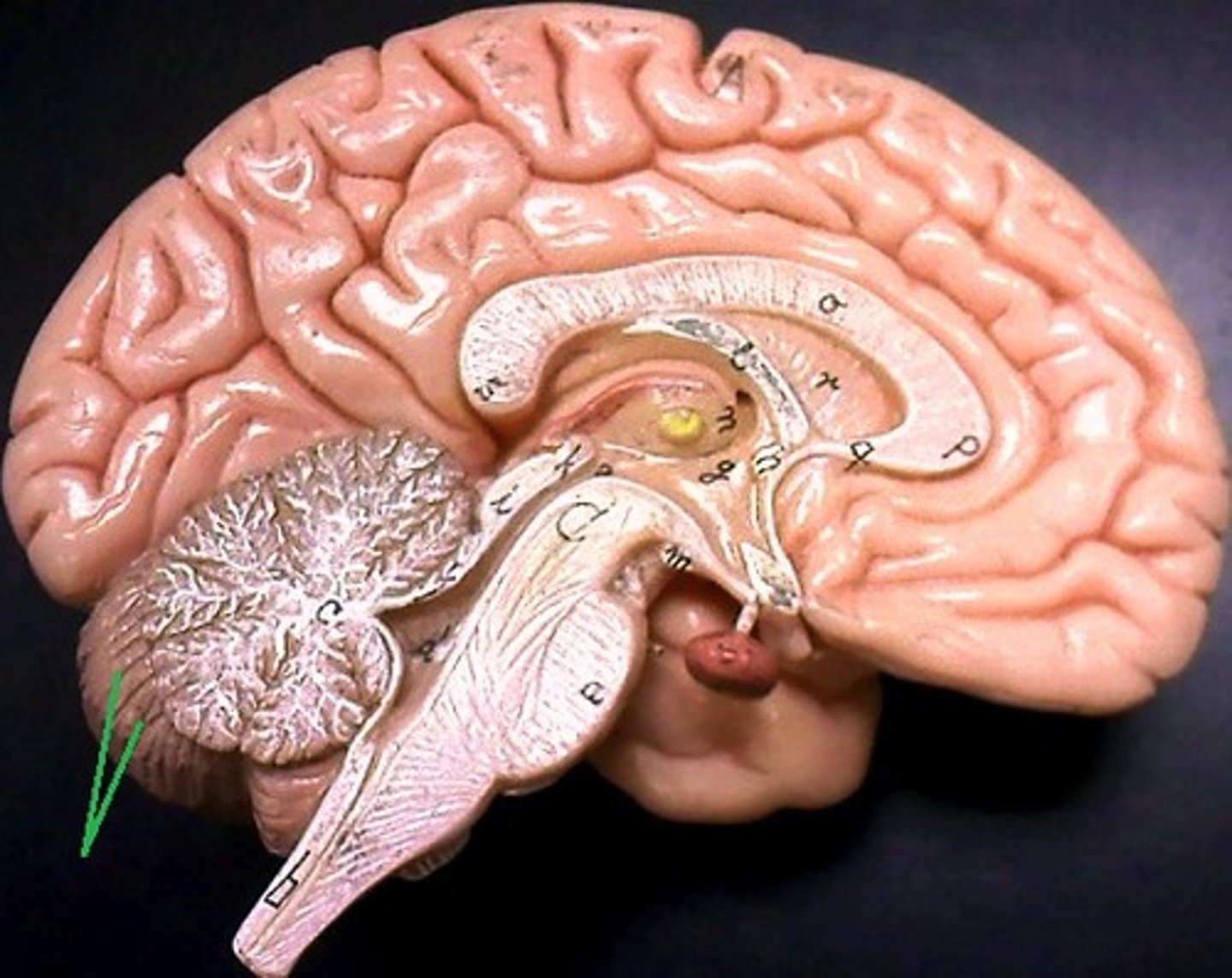
Midbrain (def)
associated with controlling our awareness to pain, collaborates in fine motor control
Midbrain
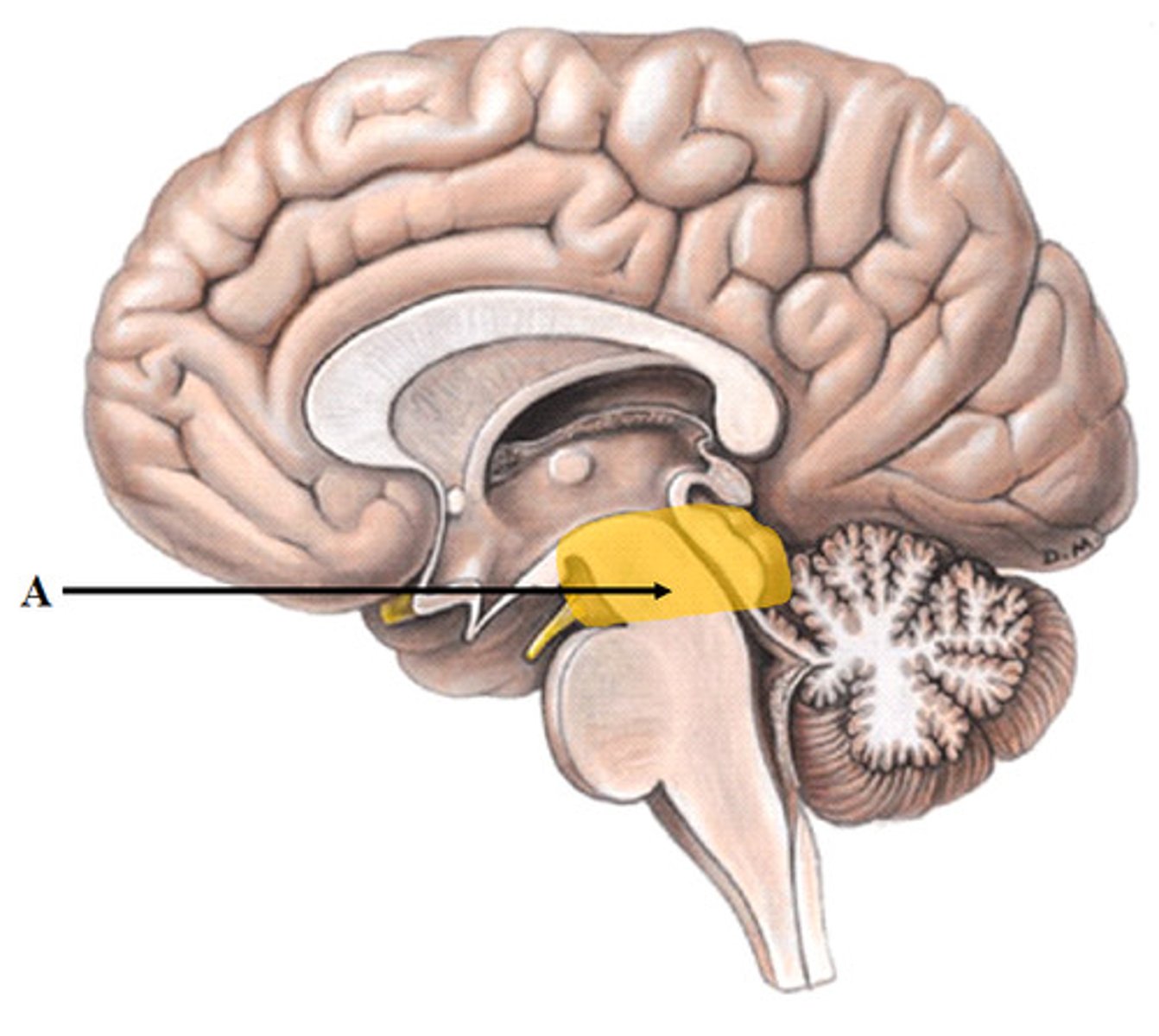
Pons (def)
responsible for relaying signals for sleep, hearing, equilibrium, taste, eye movements, swallowing, bladder control, and posture
Pons
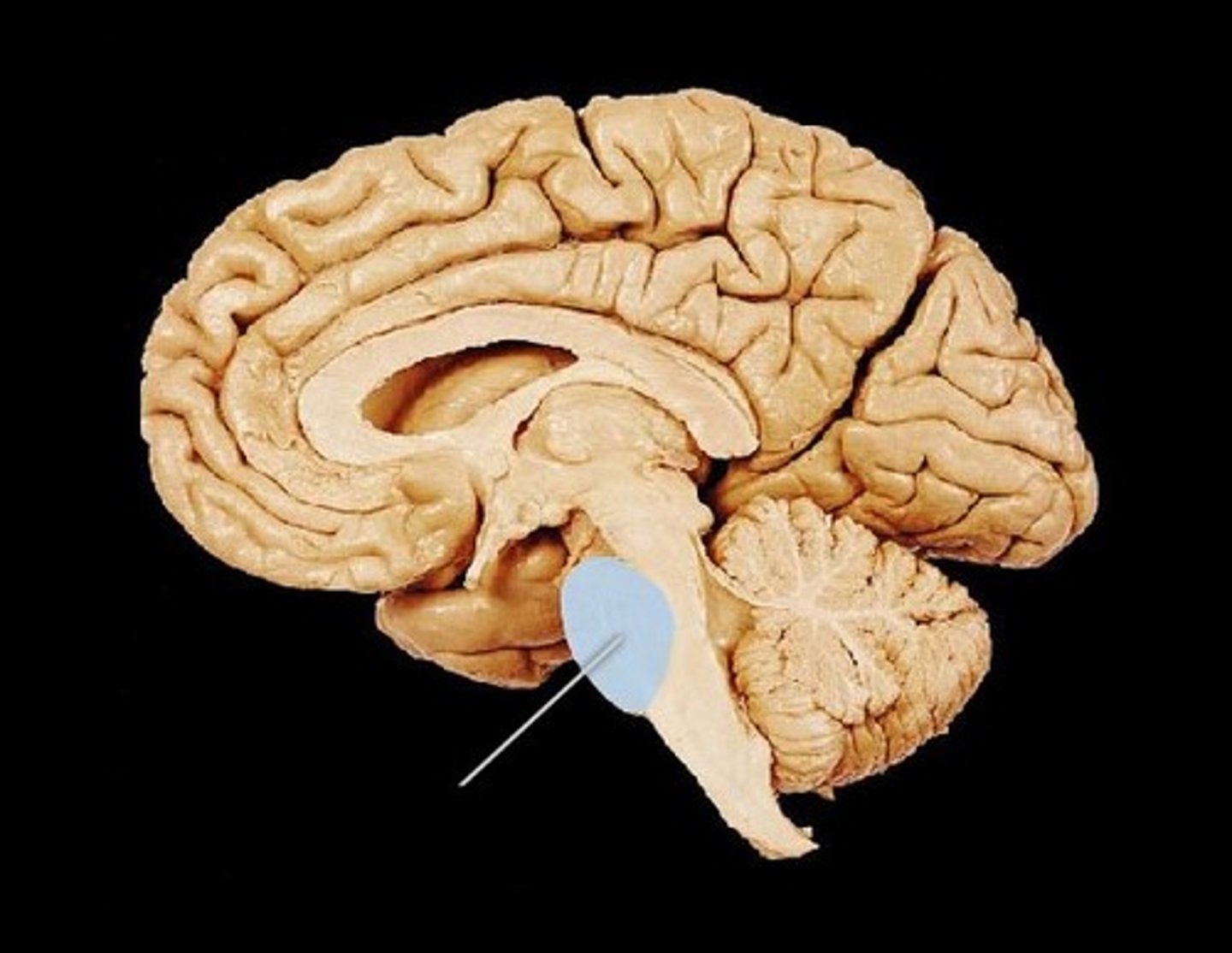
Medulla oblongata (def)
cardiac, respiratory, and vasomotor center. Once it passes through the foramen magnum of the occipital bone, it will change to the spinal cord
Medulla oblongata
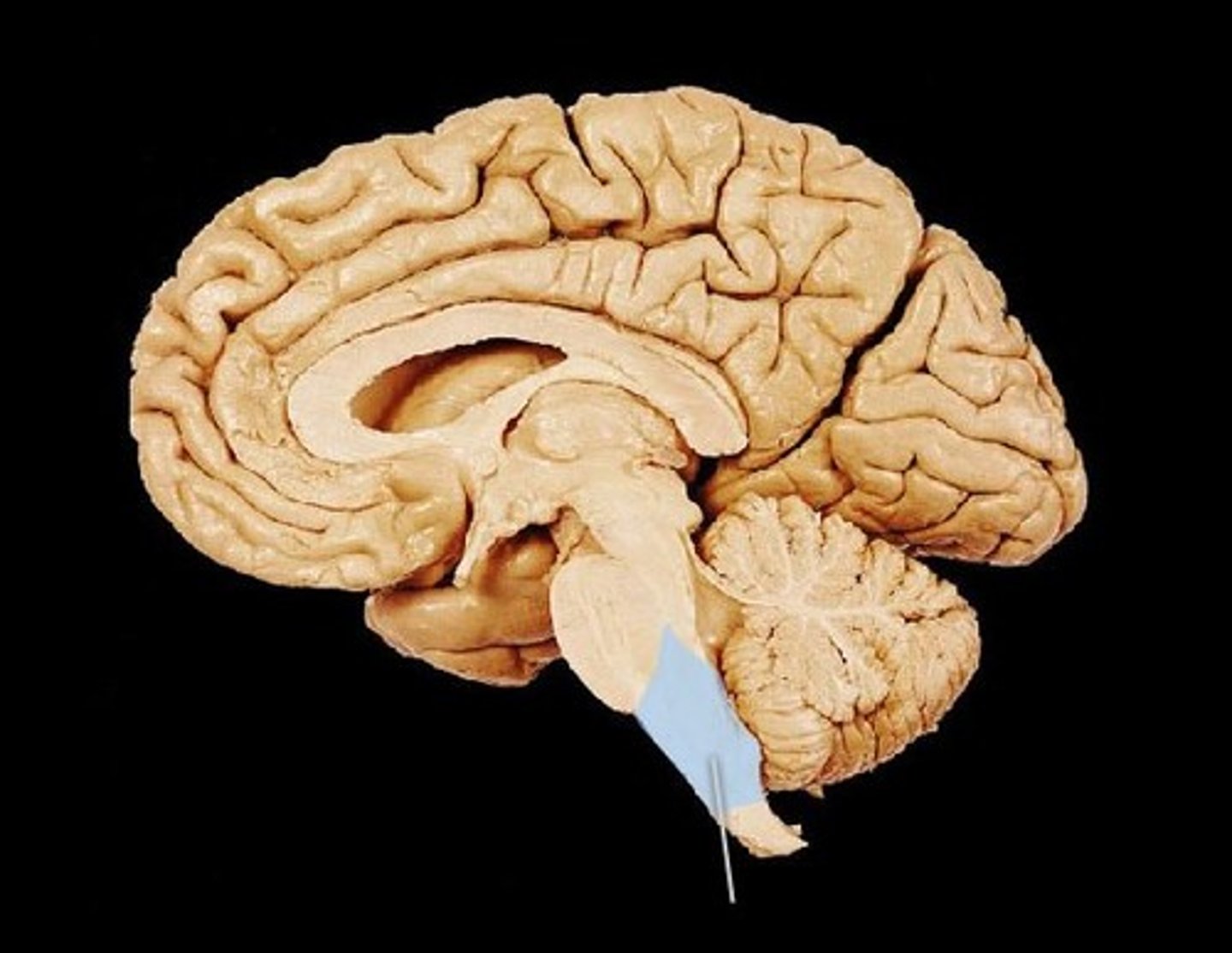
Conus medullaris (def)
bundle of nerve roots that resemble a horse's tail fill the rest of the vertebral column from L2 to S4
Conus medullaris
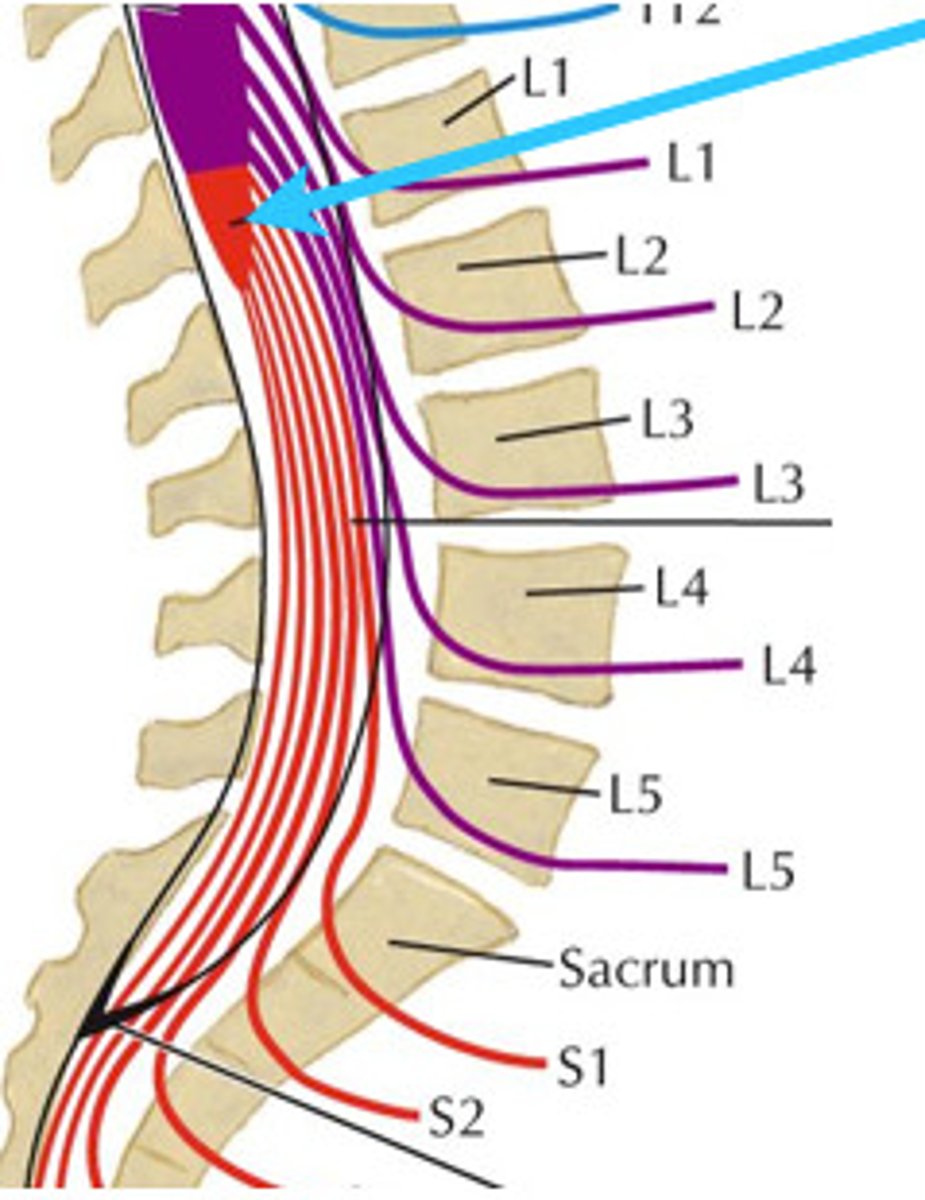
Cauda equina (def)
innervates the pelvic organs and lower extremity
Cauda equina
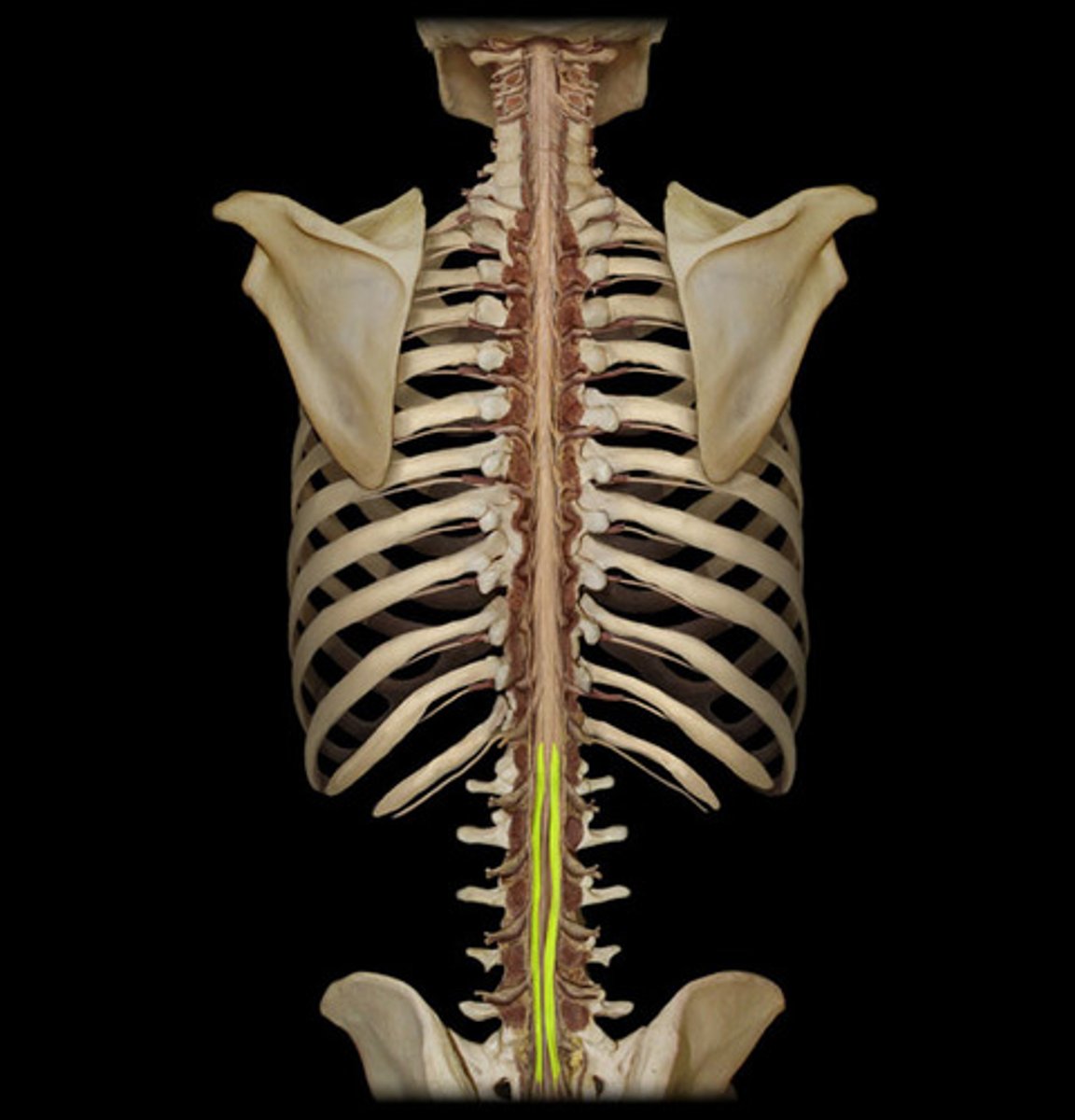
Epidural space
space between the dura and spinal column; because in the spinal cord, the dura mater is not adherent to the vertebrae the way it is in the skull; filled with loose connective tissue, adipose tissue, and blood vessles
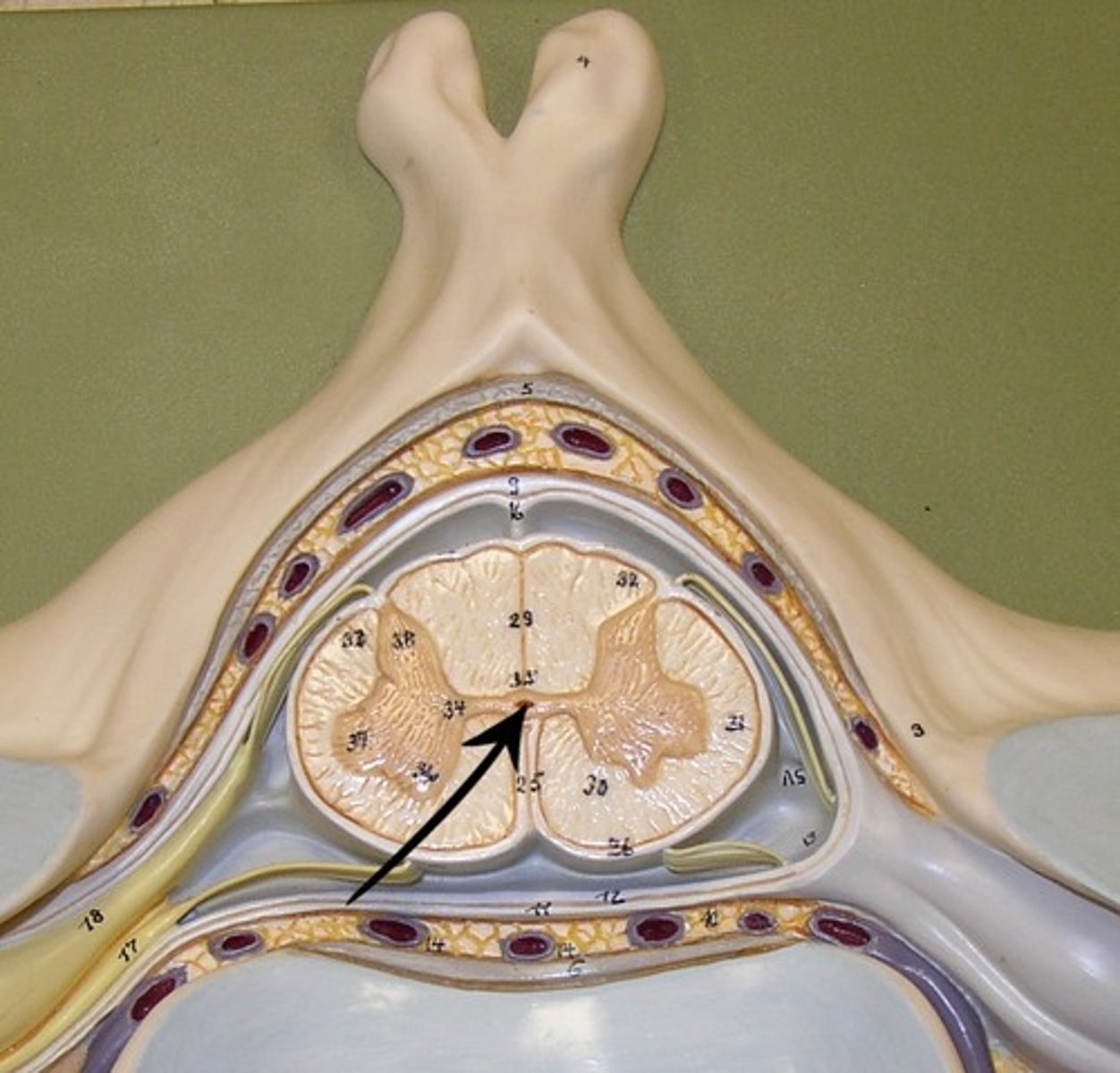
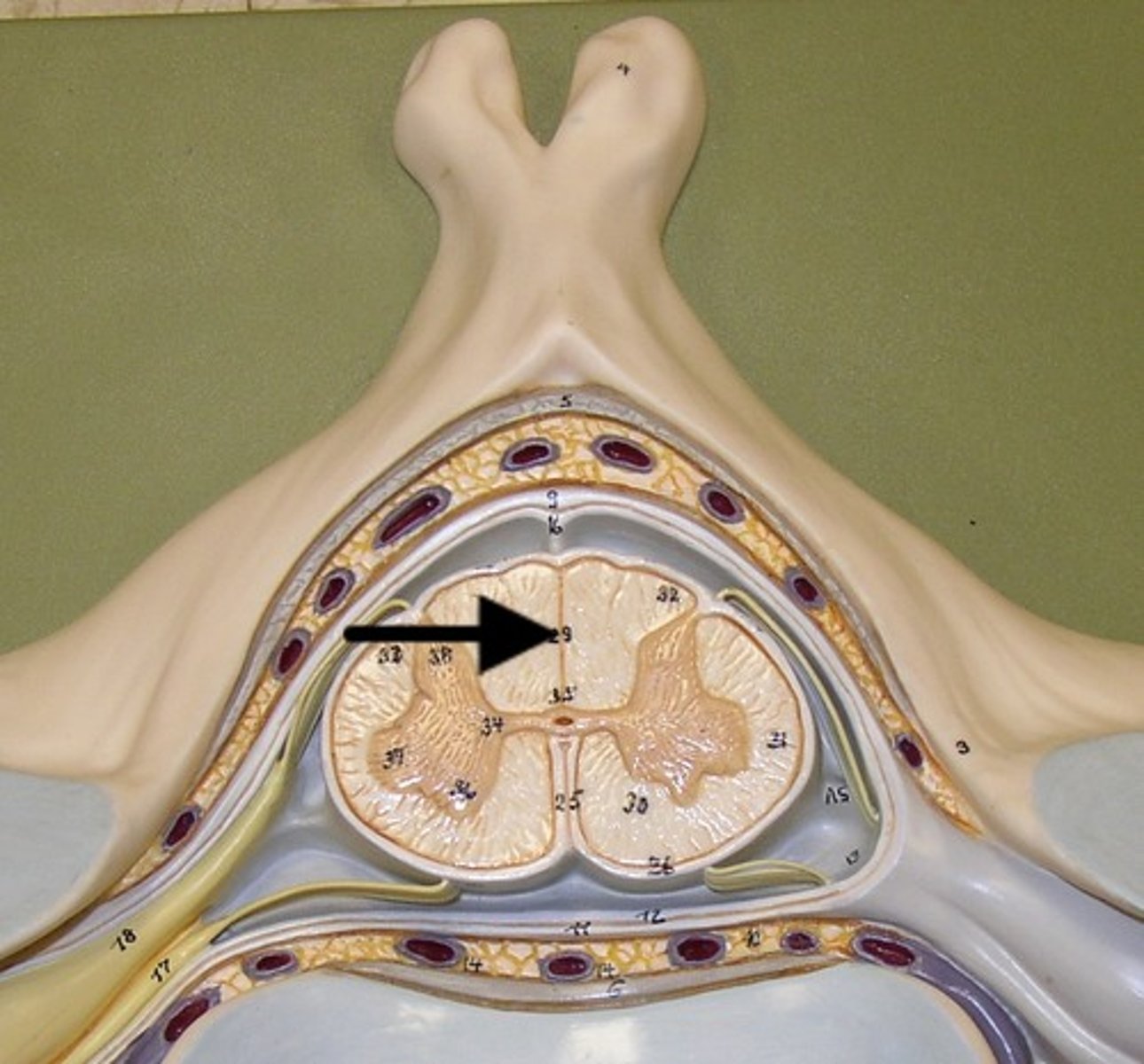
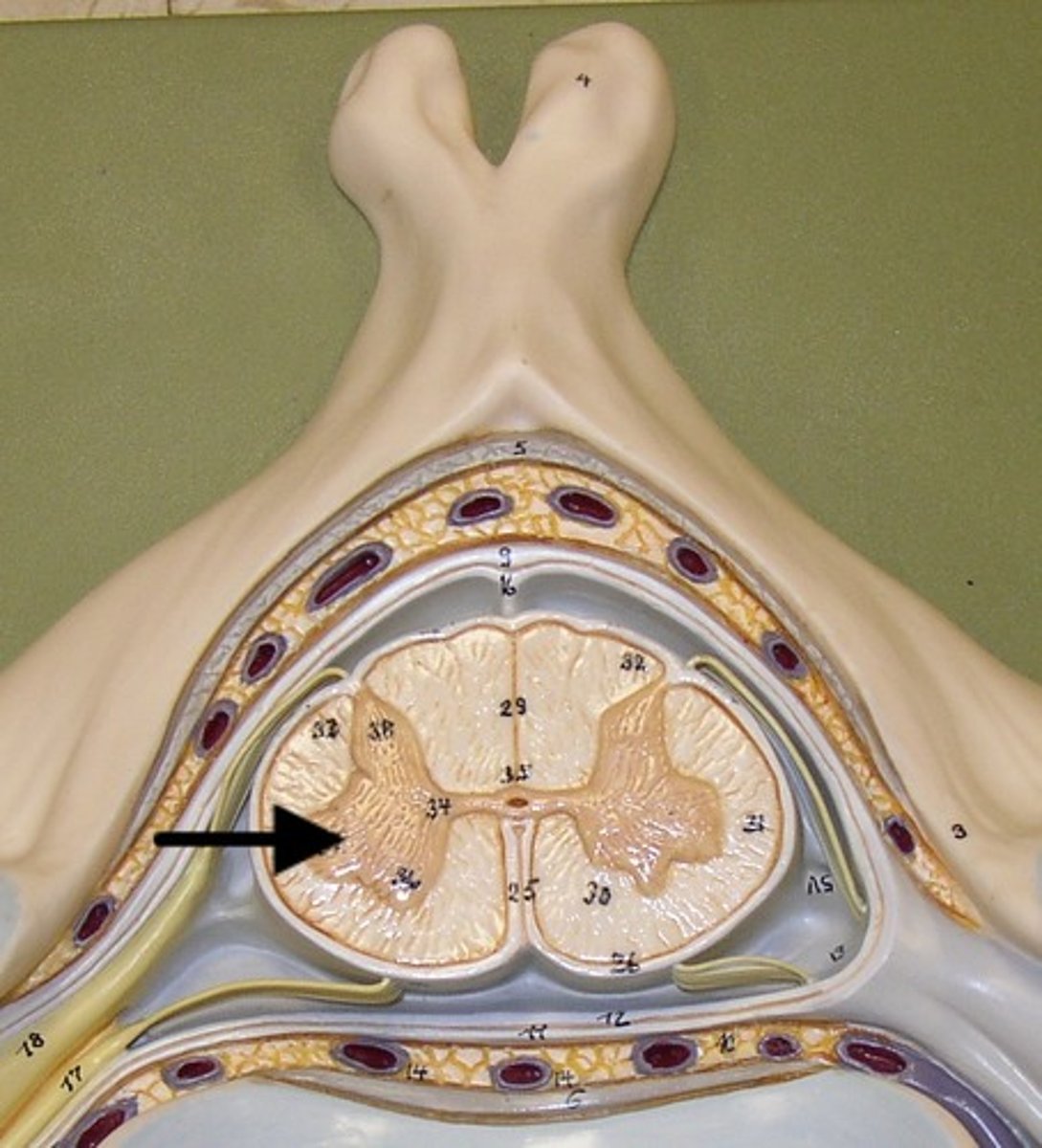
Anterior median fissure (def)
a deep groove in the spinal cord
Anterior median fissure
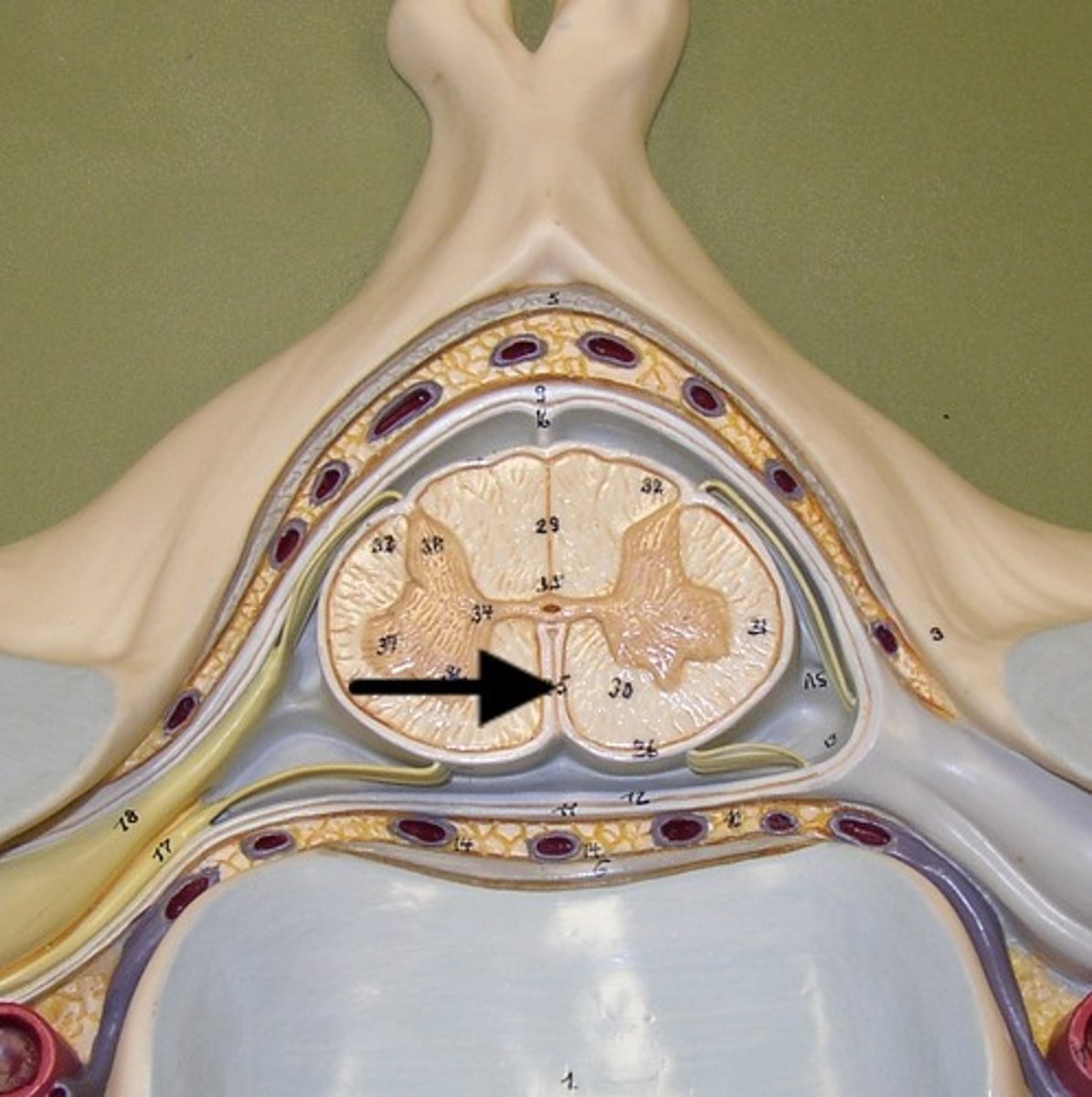
Posterior median sulcus (def)
shallow groove in the spinal cord
Posterior median sulcus
Lower motor neurons
the anterior (ventral) portion, aka anterior horn, is the cell bodies of the motor neurons of the spinal cord
Ventral nerve roots (def)
where the axons of the nerves of the lower motor neurons exit
Dorsal root ganglia (posterior root ganglion) (def)
house the cell bodies of the sensory neurons and are housed just outside the cord
Dorsal root ganglia (posterior root ganglion)
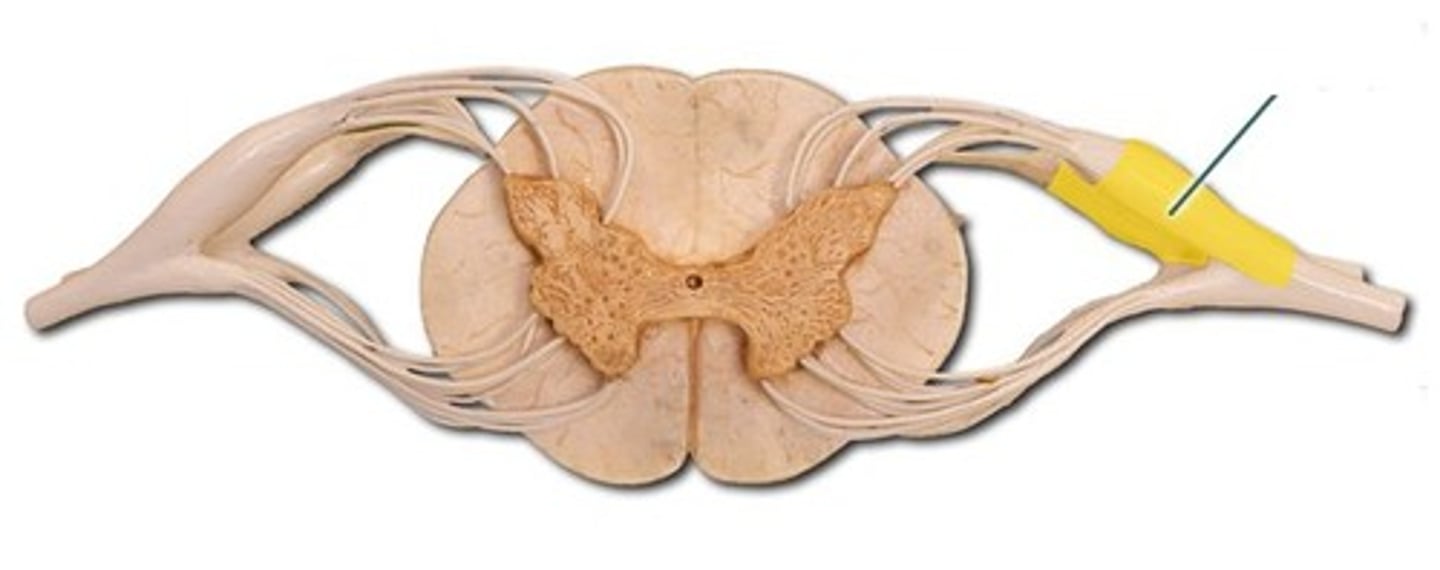
Lateral horn (def)
in the thoracic & lumbar regions; present and contains cell bodies of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system
Lateral horn
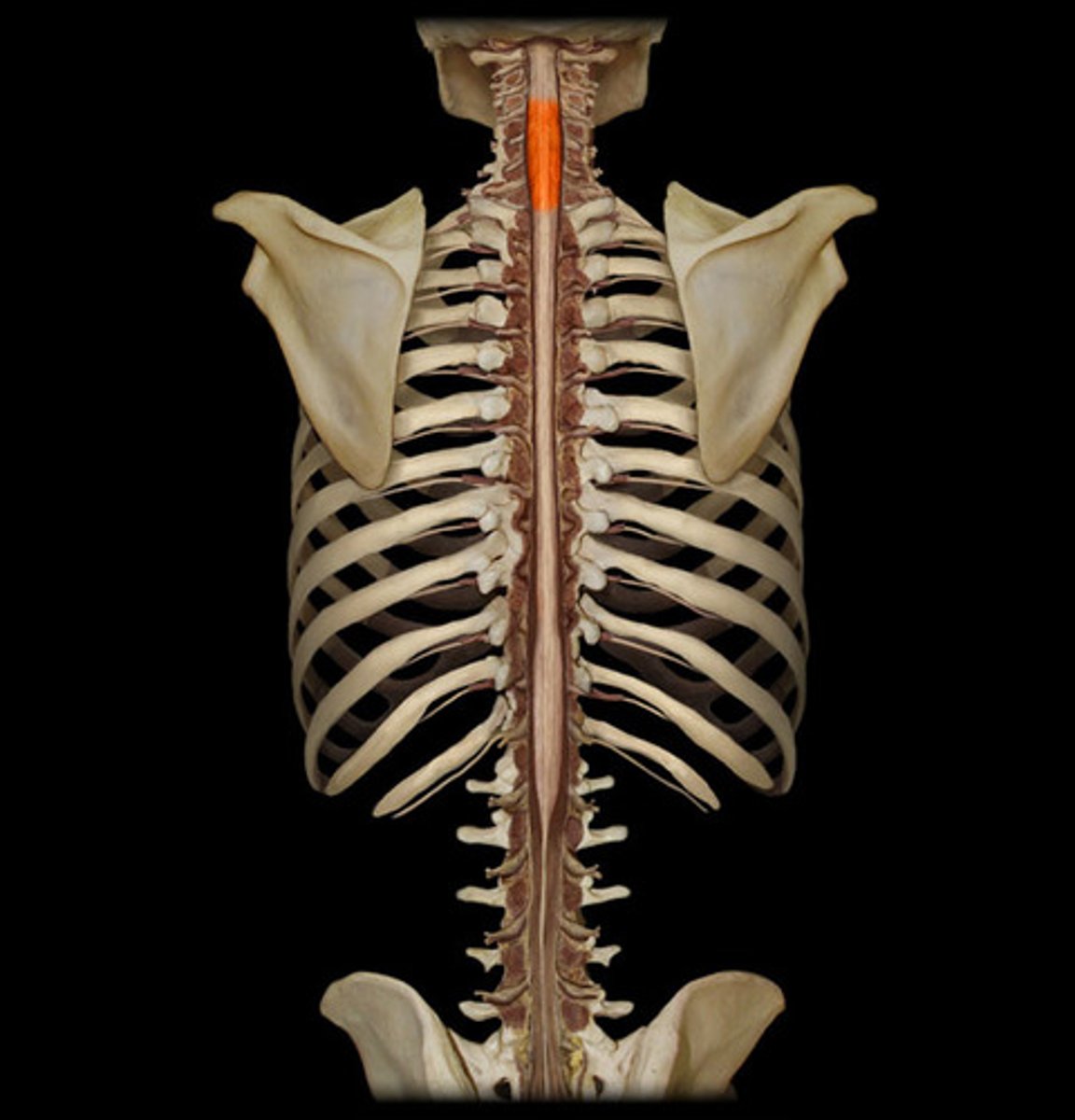
Cervical enlargement (def)
gives rise to the nerves of the upper limbs
Cervical enlargement
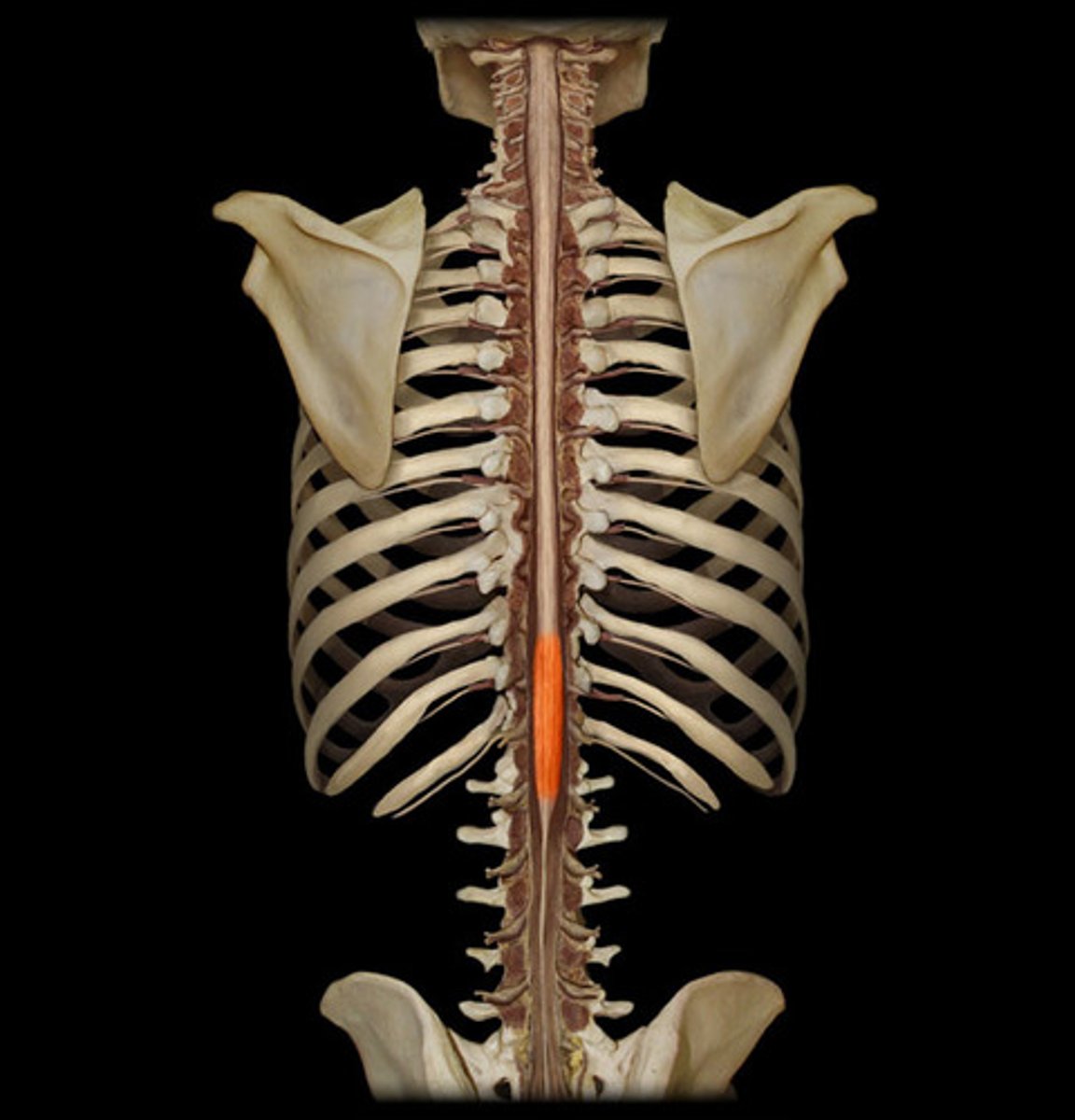
Lumbar enlargement (def)
gives rise to the lumbar and pelvic nerves
Lumbar enlargement
Ascending fibers
groups of axons that carry information up the cord
Descending fibers
groups of axons that carry information down the cord
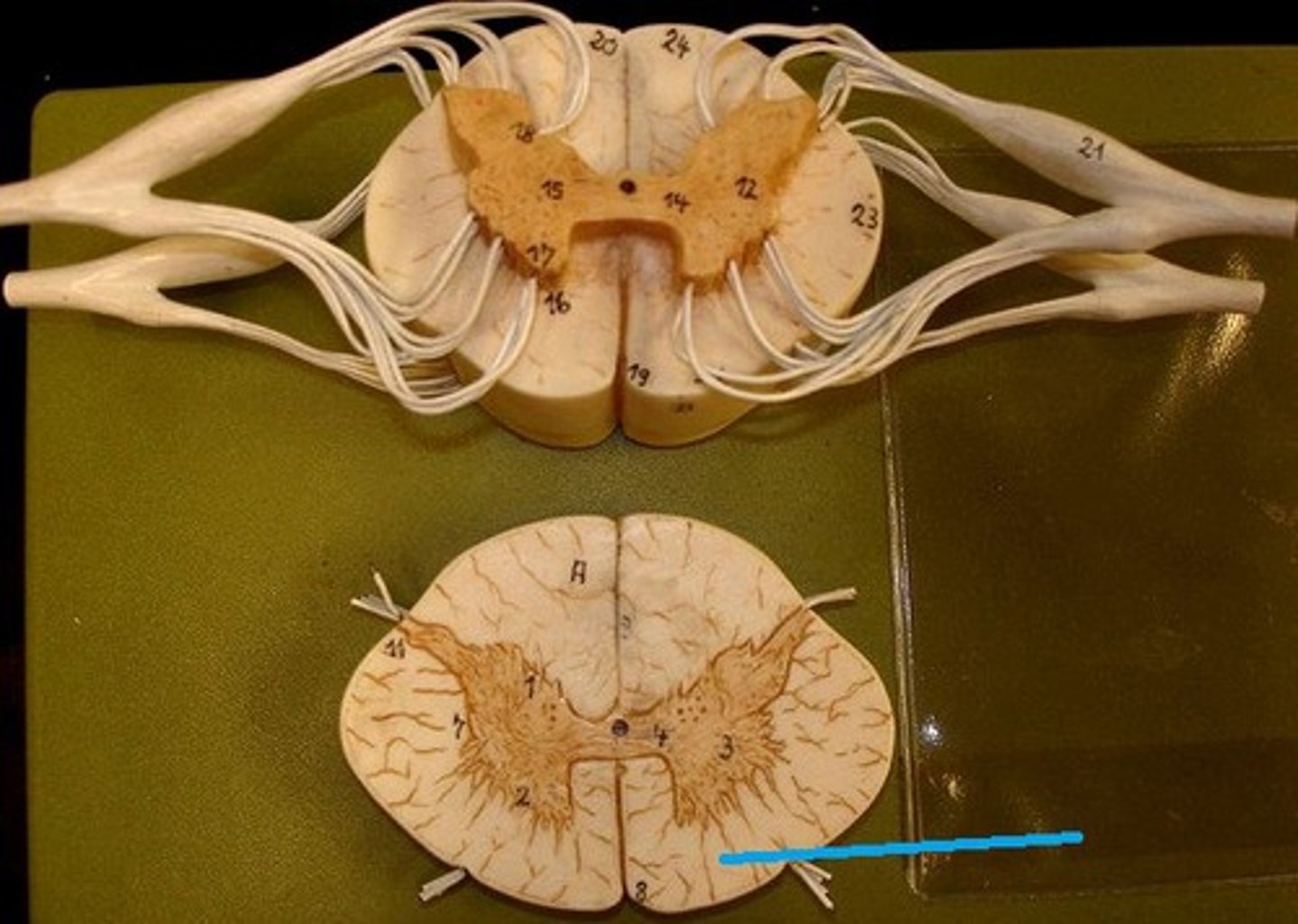
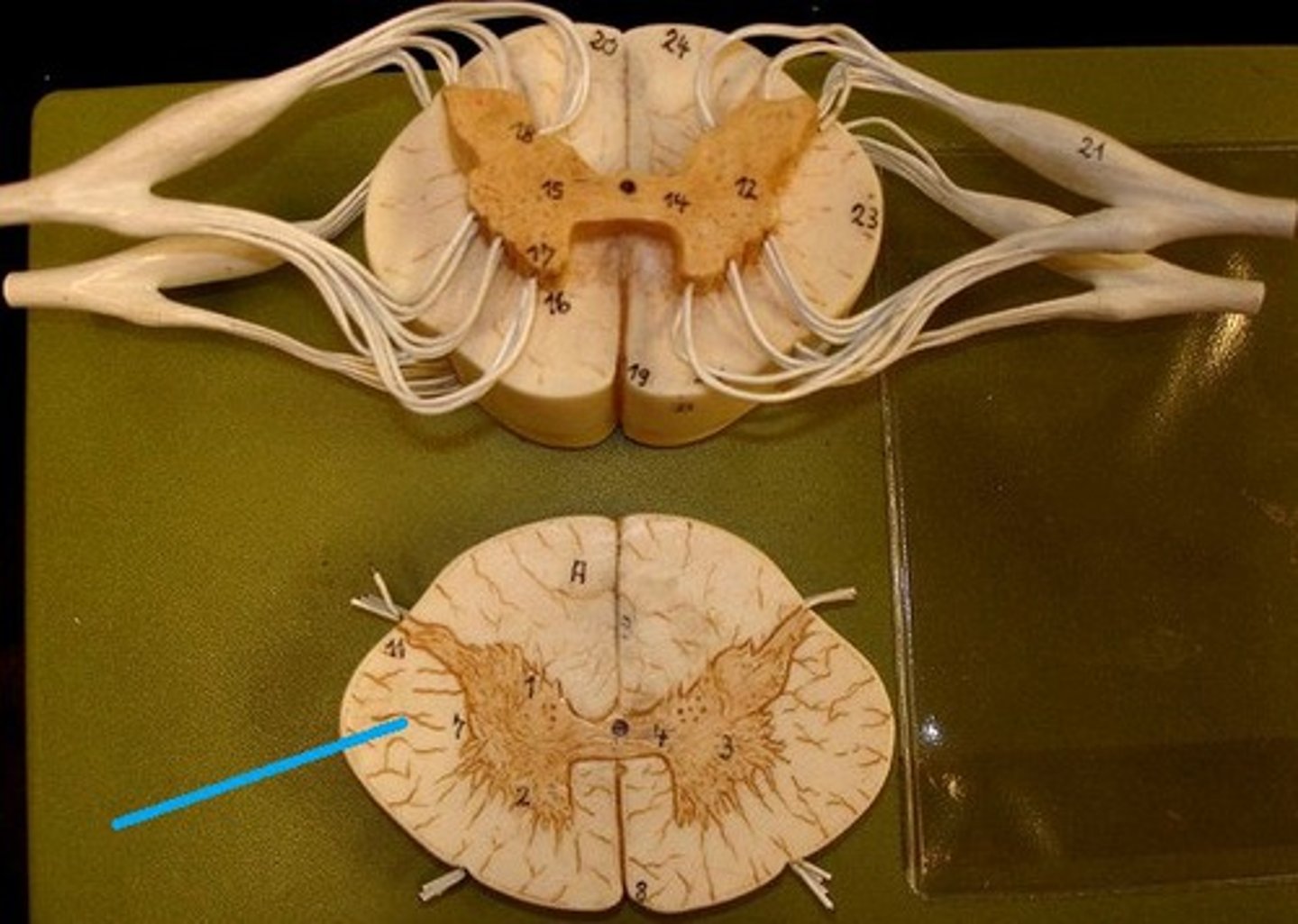
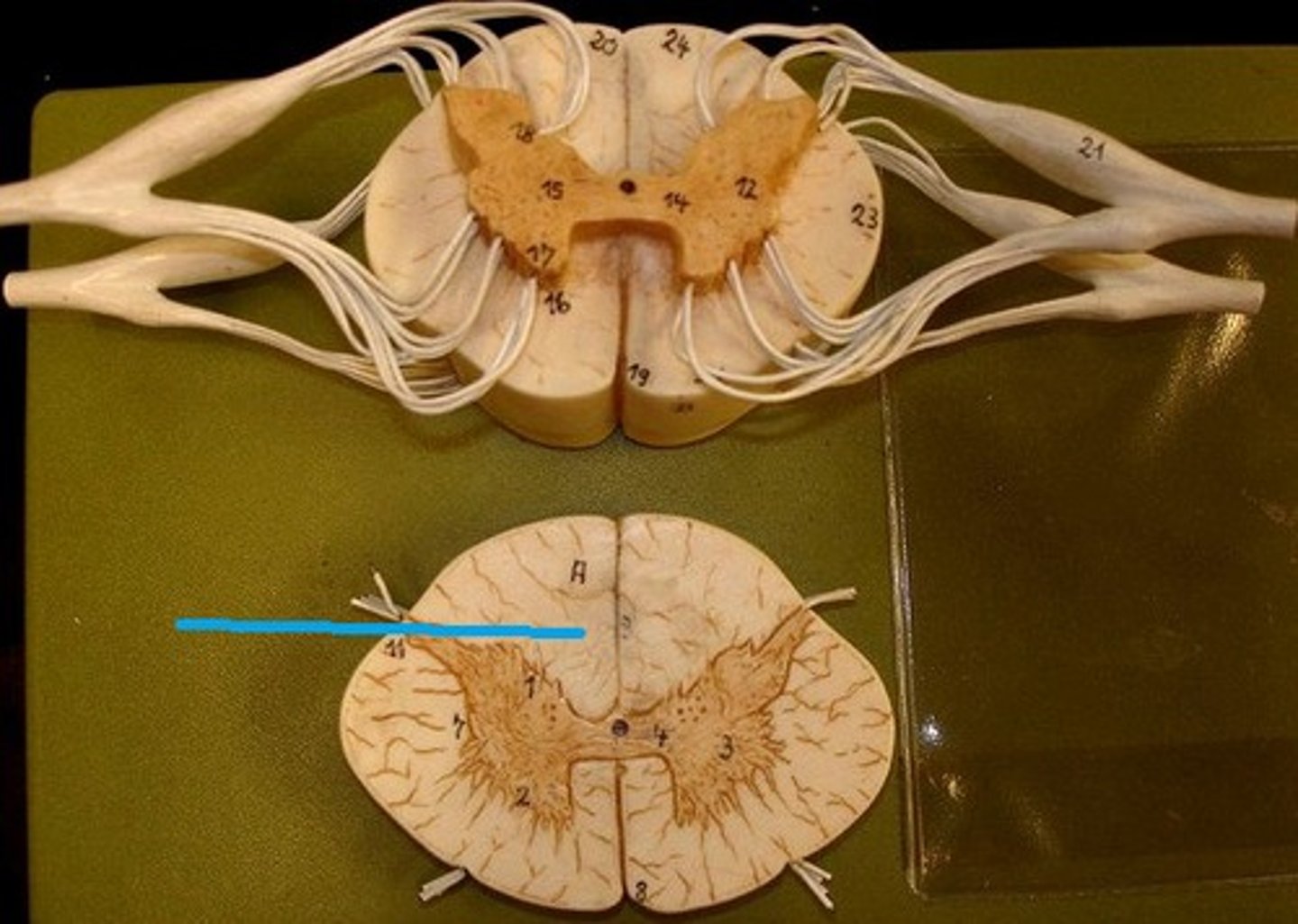
Funiculi (or column)
anterior, posterior, and lateral funiculi; divided up into tracts which contain axons that have the same functional role and are defined primarily by the structures they connect
Anterior funiculi
Lateral funiculi
Posterior funiculi
Denticulate ligaments
surrounding fibers which anchors the spinal cord and limits its side-to-side movements; extensions of the pia matter that extends to the dura mater
Central canal