HOA - AMACE
1/378
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
379 Terms
ROCK CAVE
Earliest form of dwelling developed by man (NATURAL CAVE, ARTIFICAL CAVE, CAVE, ABOVE THE GROUND)
MONOLITH
isolated single upright stone
also known as "MENHIR"
MENHIR
memorial of victory
prototype of Egyptian Pyramid
MEGALITHIC
several number of stones
DOLMEN
2 or more upright stones supporting a horizontal slab
CROMLECH
3 or more upright stones
WILTSHIRE, SALISBURY PLAIN
stonehenge location
3,000
STONE CIRCLE
TUMULI
earthen mounds use for burials of several to couple hundred
of ordinary persons. Prototypes of pyramids in Egypt also of the " beehive huts".
CARYATIDS
drapped female figure without hands & carrying nothing.
CANEPHORAE
same as caryatids but this time w/ basket on her head.
ATLAS
male figure in kneeling position supporting the world at his
shoulders.
TELAMON
male figure in standing position in place of a column.
ANTACOLUMN
pier or pilaster formed by a thickening at the end of the wall.
ORDER
it includes the column ( capital , shaft , base ) with an entablature, which is following
a certain rule with regards to systems of designing.'
DORIC ORDER
the simplest , earliest and the most perfect among the orders , made up
of wood.
IONIC ORDER
the most sophisticated, less heavy than the Doric order.
CORINTHIAN ORDER
the slenderest, elegant, and the most elaborated order.
COMPOSITE ORDER
roman elaboration of the Corinthian order.
TUSCAN ORDER
the simplified version of the Roman Doric order and has no shaft flutes.
SUPERCOLUMNATION
the placing of one order after another or above another.
INTERCOLUMNATION
the clear space between two adjacent columns usually measured
at the lower parts of the shafts.
ARCADE
a line of counterthrusting arches raised on columns of piers.
ENTASIS
a swelling or curving along the outline of a column shaft . It was designed to counter-act
the " Optical illusion " which gives a shaft bounded by straight line appearance of curving inwards
AVENUE OF SPHINX
Part of an Egyptian temple; where mystical monster were placed

TEMPLE OF KHONS
Ramses III, Egyptian, Karnak, Egypt

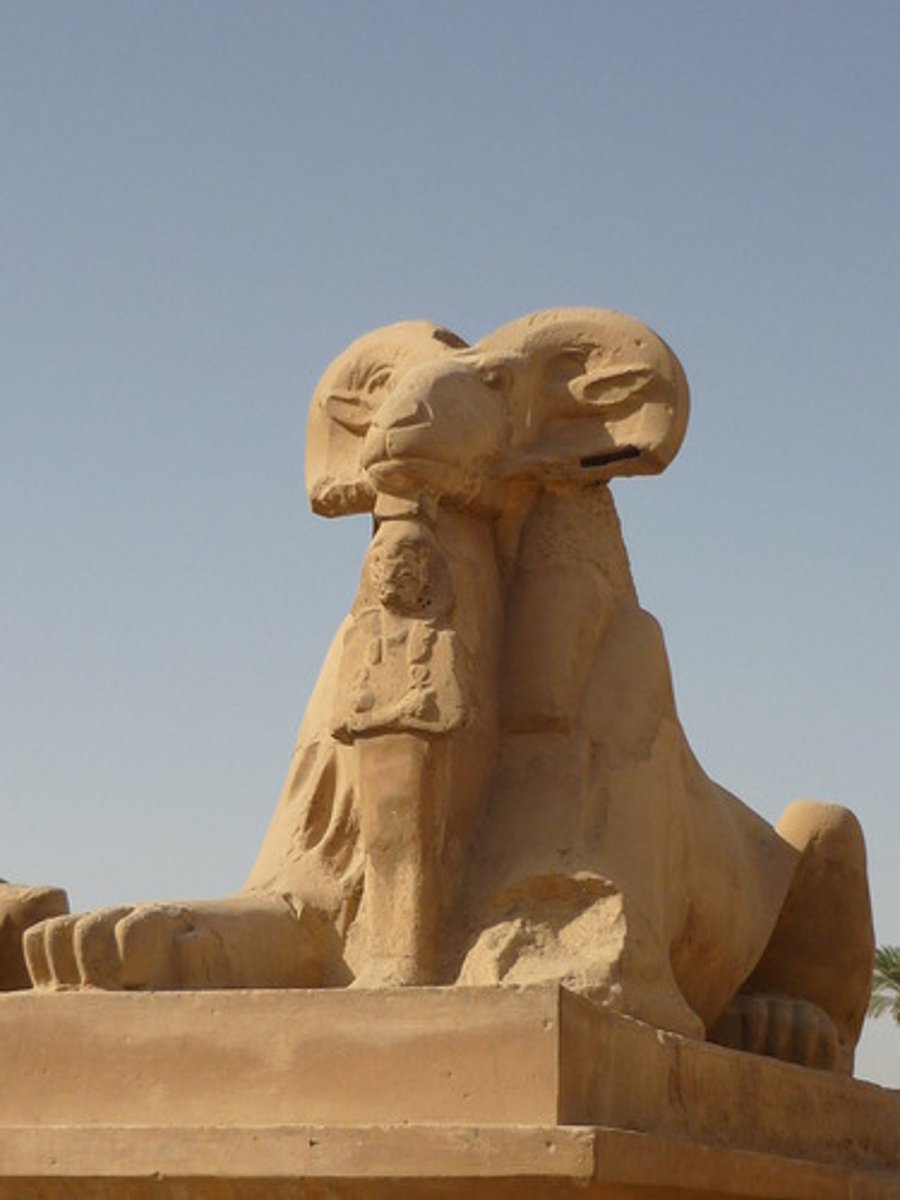
CRIOSPHINX
Ram headed sphinx

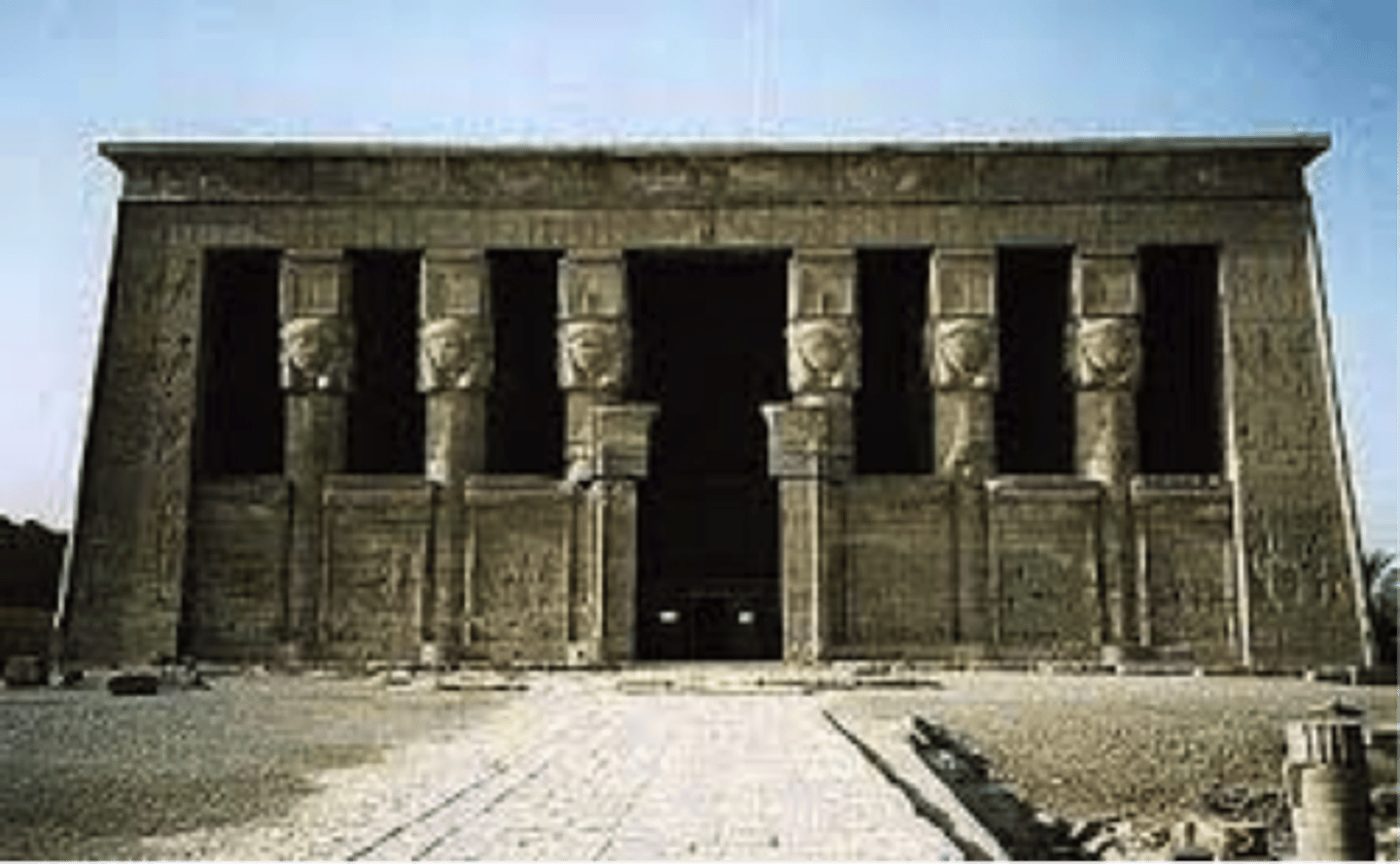
TEMPLE OF HATHOR
Dedicated to female goddess Hathor. Inside is a carving of a person holding up a large object. Daniken's theory is that it's an Egyptian "lightbulb".

ANDROSPHINX
A human-headed sphinx
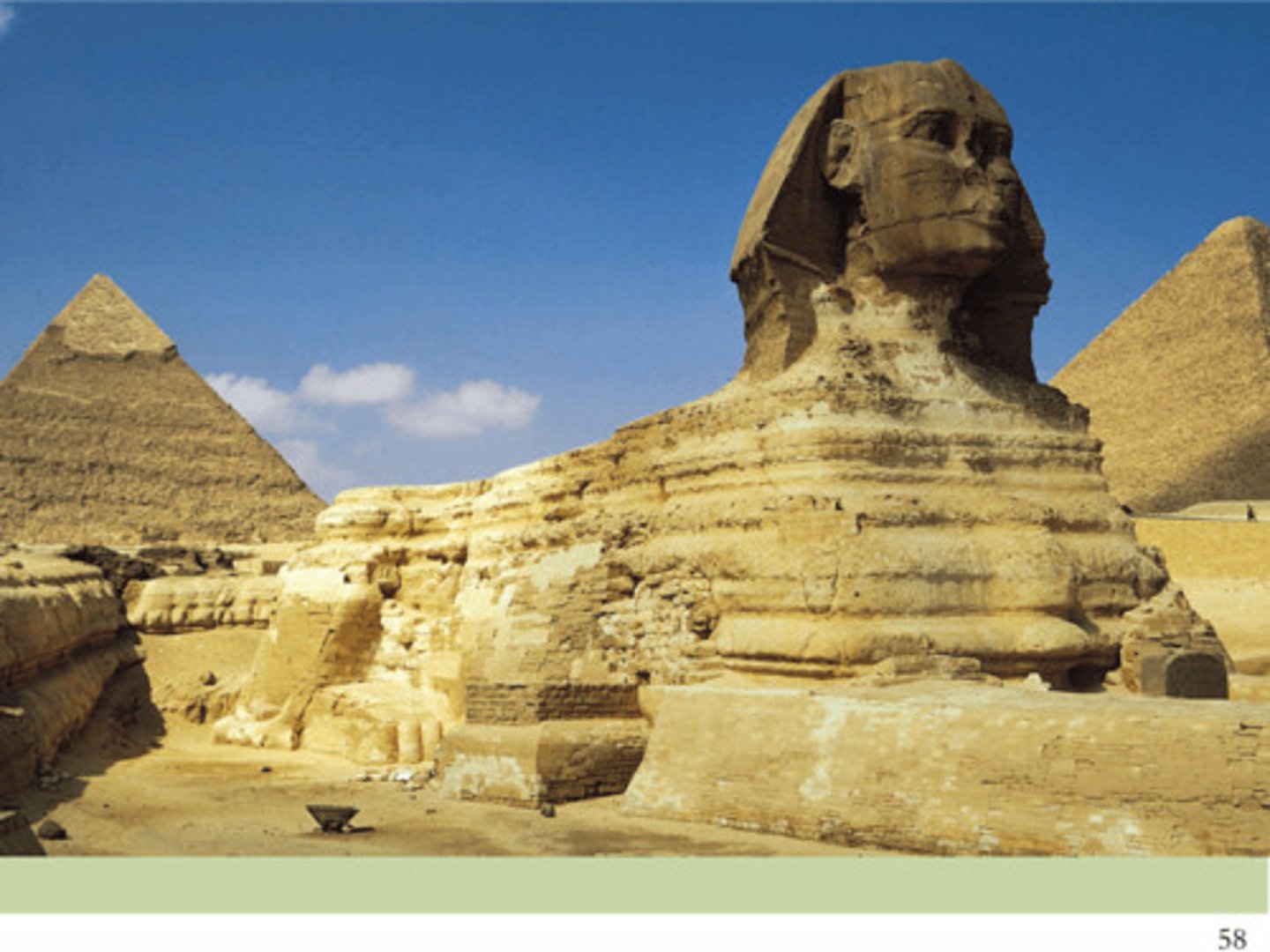

TEMPLE OF QUEEN HATSHEPSUT
Senmut, Egyptian, Deir-el-Bahari, Egypt
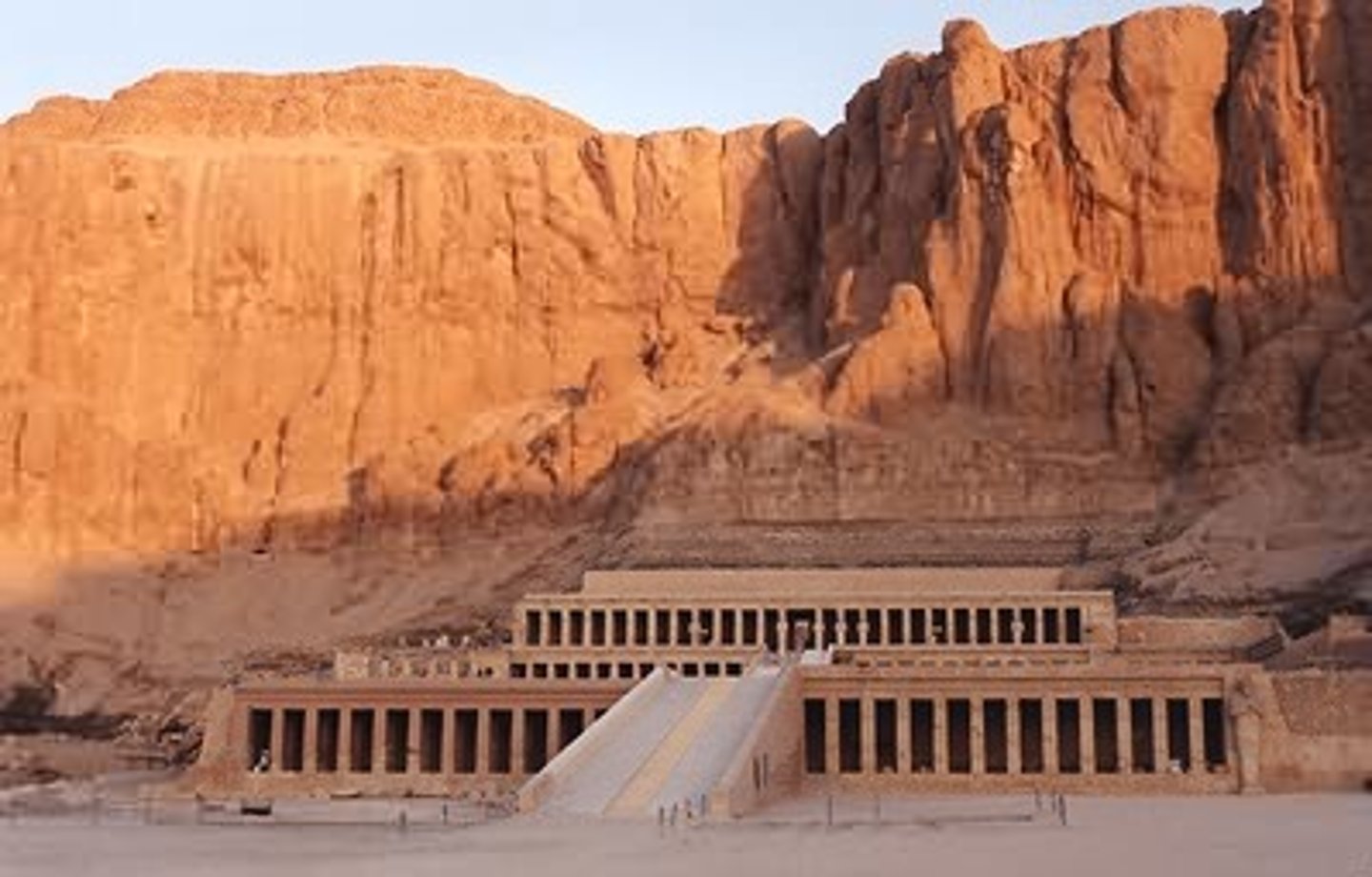

PYLON AT EDFU
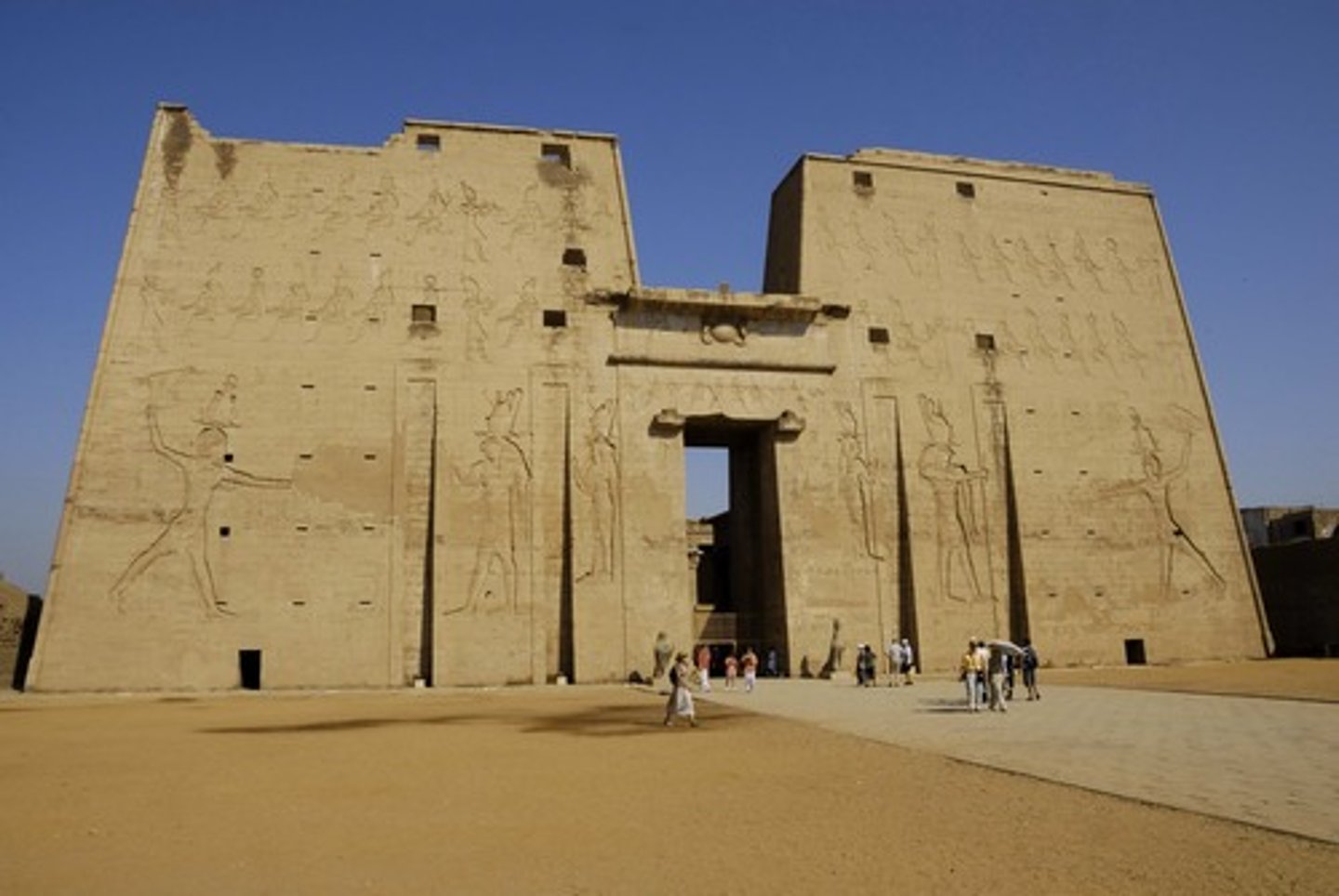

TEMPLE OF AMON
found at Karnak, it is the largest and most famous of the many temples built and dedicated to the gods
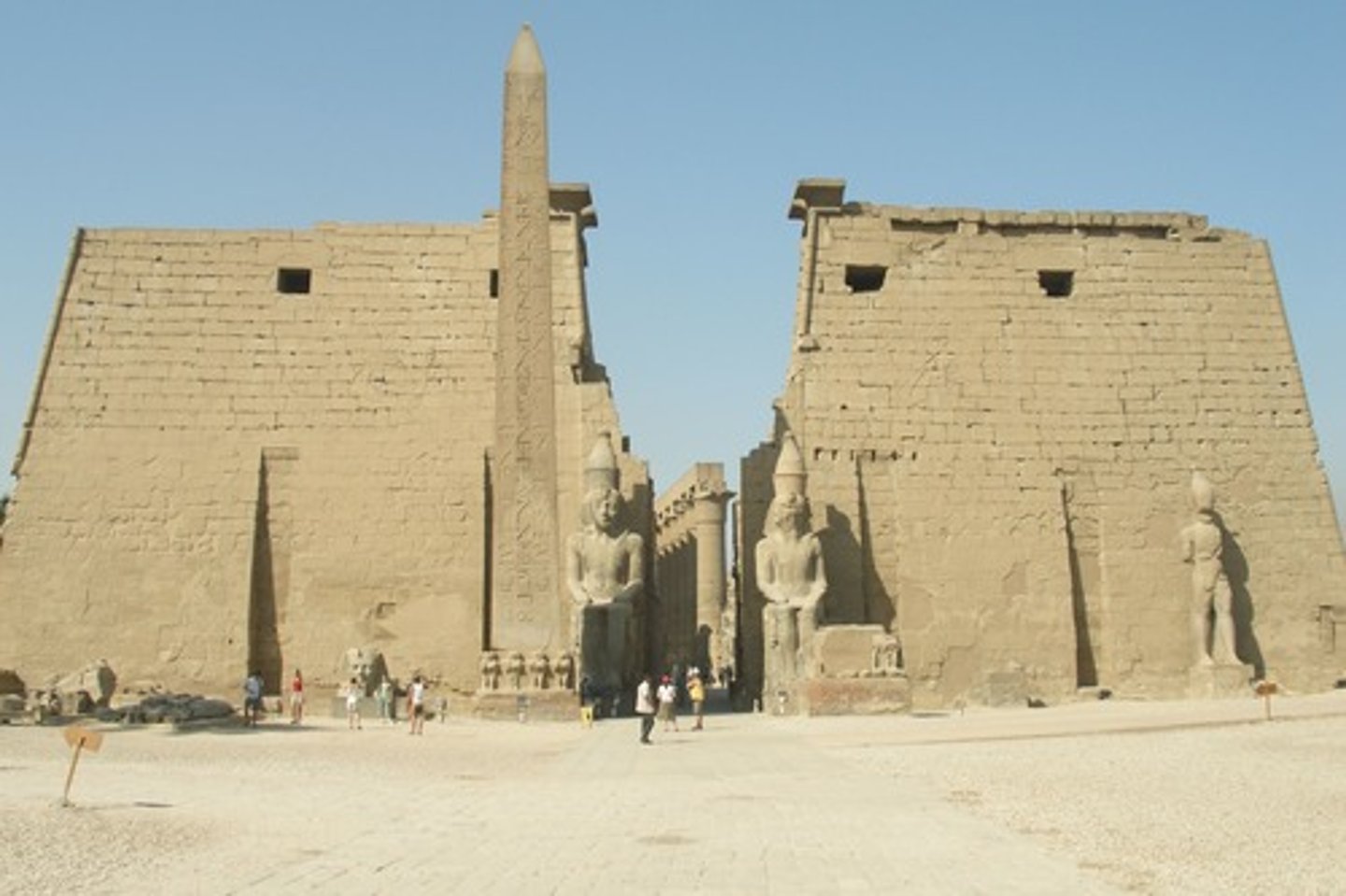

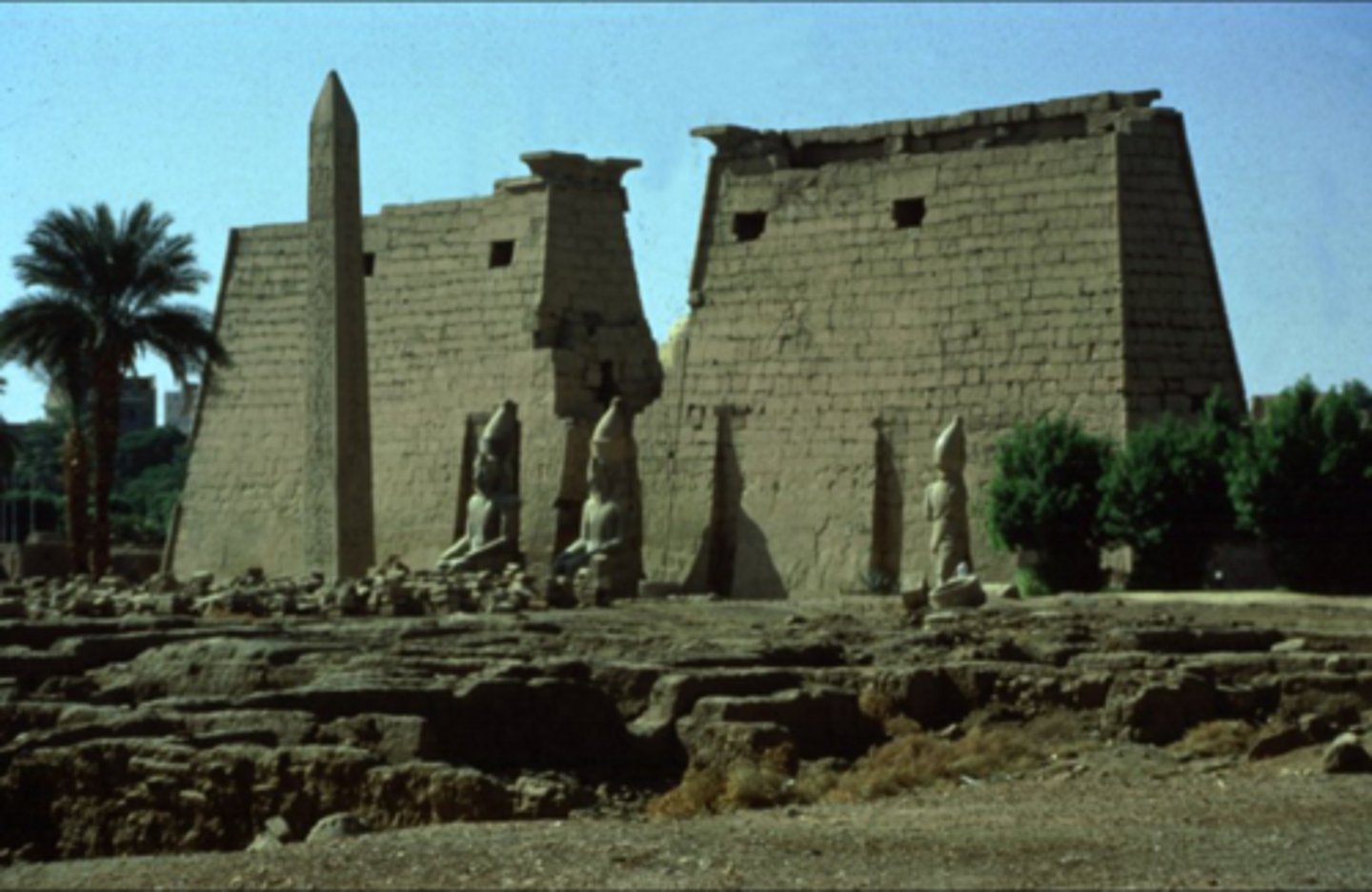
TEMPLE OF LUXOR
Mostly built by menophis III, dedicated to the Theban Triad of Amin, Mut and Khons
EGYPT
" The Land of Pharaoh ", & "desert Land ". The " Nile River" is their means
of communication , highway , & lifeline . Egypt's greatest wealth was its fertile "soil".
SOFT STONE
limestone , sandstone , alabaster .
HARD STONE
granite , quartzite , basalt , porphyry
AMUN-RA
the head god- he was the most powerful god in the New Kingdom.
RAH
Egyptian sun god
ATUM
creator god
OSIRIS
God of the underworld
ISIS
Wife of Osiris
HORUS
God of the sky
SET
god of evil
THOT
ibis headed god of wisdom
ANUBIS
God of the dead
PTAH
god of craftsmen
SERAPIS
bull god
MENTUHETEP II
developed the 3rd type of tomb "Rock-cut Tomb".
SENUSRETS
erected the earliest known "Obelisk" at Heliopolis.
AMENEMHAT I
founded "Great Temple of Ammon Kharnak" Grandest of all temples
THOTMES I
began the additions to the Temple of AMMON, Kharnak.
HATSHEPSUT
First female pharaoh
THOTMES IV
the one responsible for the cleaning away of sand from the "Sphinx"
AMENOPHIS III
erected the "Colossi of Memnon", one of the wonders of the world.
RAMESES I
The beginner of the great hypostyle hall at karnak and the founder of the 19th dynasty.
RAMESES II
finished the construction of the "Hypostyle Hall", & erection of the
"Rock Temple @ ABU- SIMBEL ", and the "Remission",Thebes.
PTOLEMY II
built the Pharaohs or the "Light House"
PTOLEMY III
founded the "Greatest Serapeum" at Alexandria.
BATTERWALL
inclination from base to top of the façade.
SERDAB
inner chamber containing the statues of the deceased member of the family
SARCOPHAGUS
a large stone coffin
STEP PYRAMID
type of pyramid with sides that rise in giant steps
PYRAMID OF ZOSER
famous six-tiered mastaba
BENT PYRAMID
3rd pyramid, built by Seneferu, first attempt at classic shape but made too steep and had to be sloped
SLOPE PYRAMID
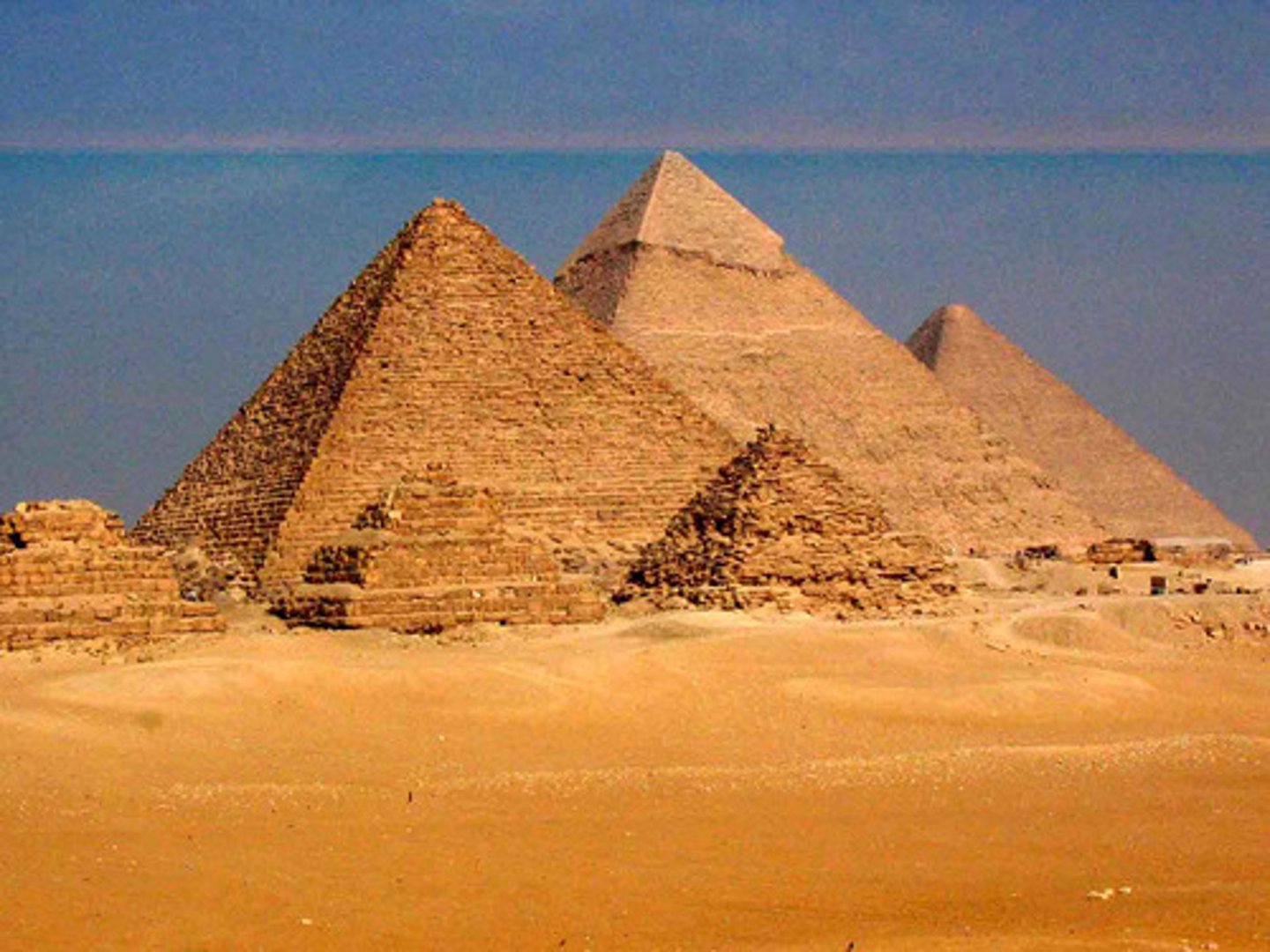

ROCK CUT TOMB
a burial chamber that is cut into an existing, naturally-occurring rock formation, usually along the side of a hill
ENTRANCE PYLON
massive sloping towers fronted by an obelisks known as gateways
in Egypt .
HYPAETHRAL COURT
[Egypt] Part of the temple that is open to the sky
HYPOSTYLE HALL
a hall with a roof supported by columns
GREAT TEMPLE OF ABU-SIMBEL
The four-seated colossal statues of Rameses II is carved in the pylon of the ___.
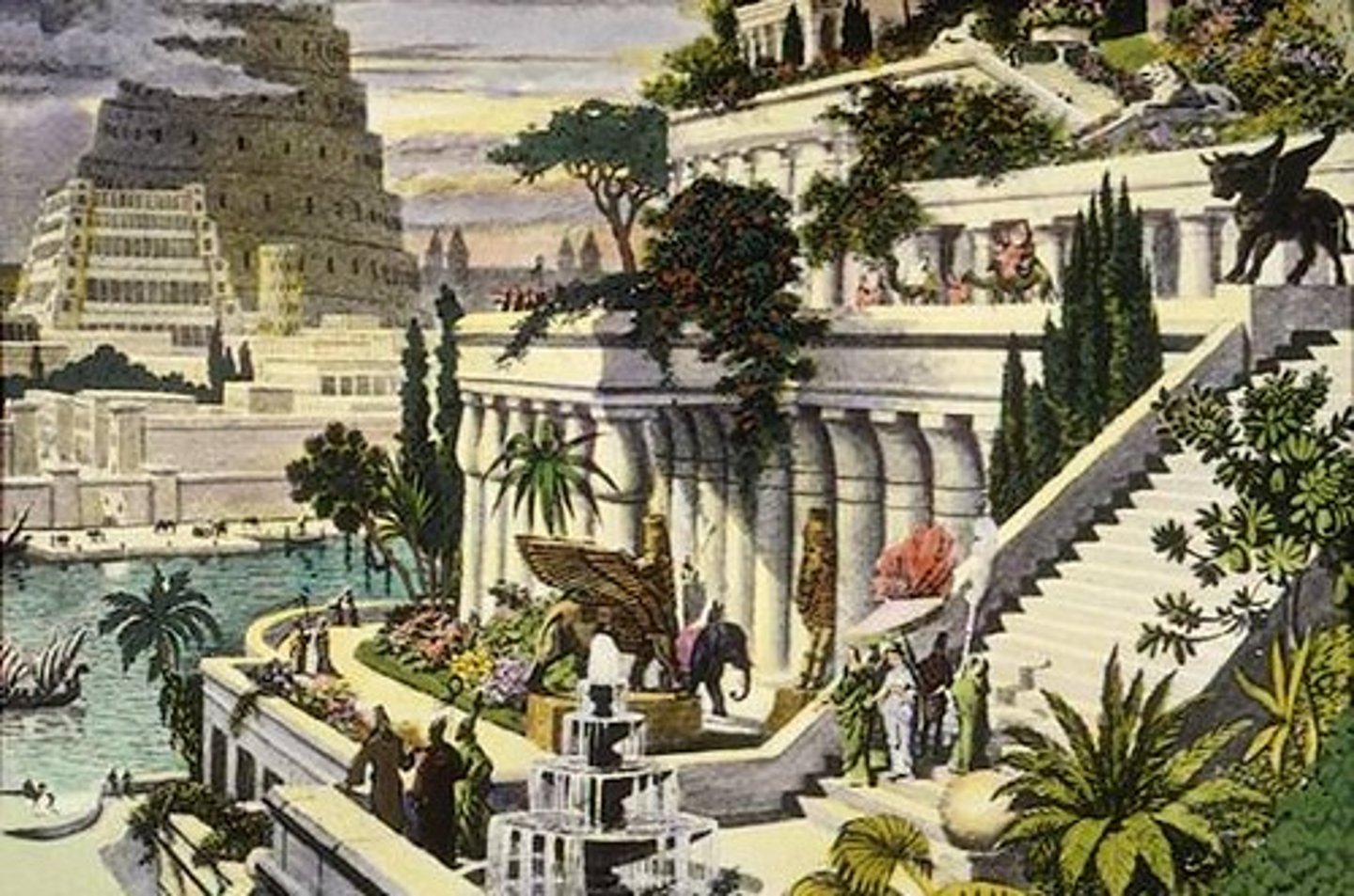
TOWER OF BABEL
A tall building proposed by the Hamites in order to "make a name for themselves."

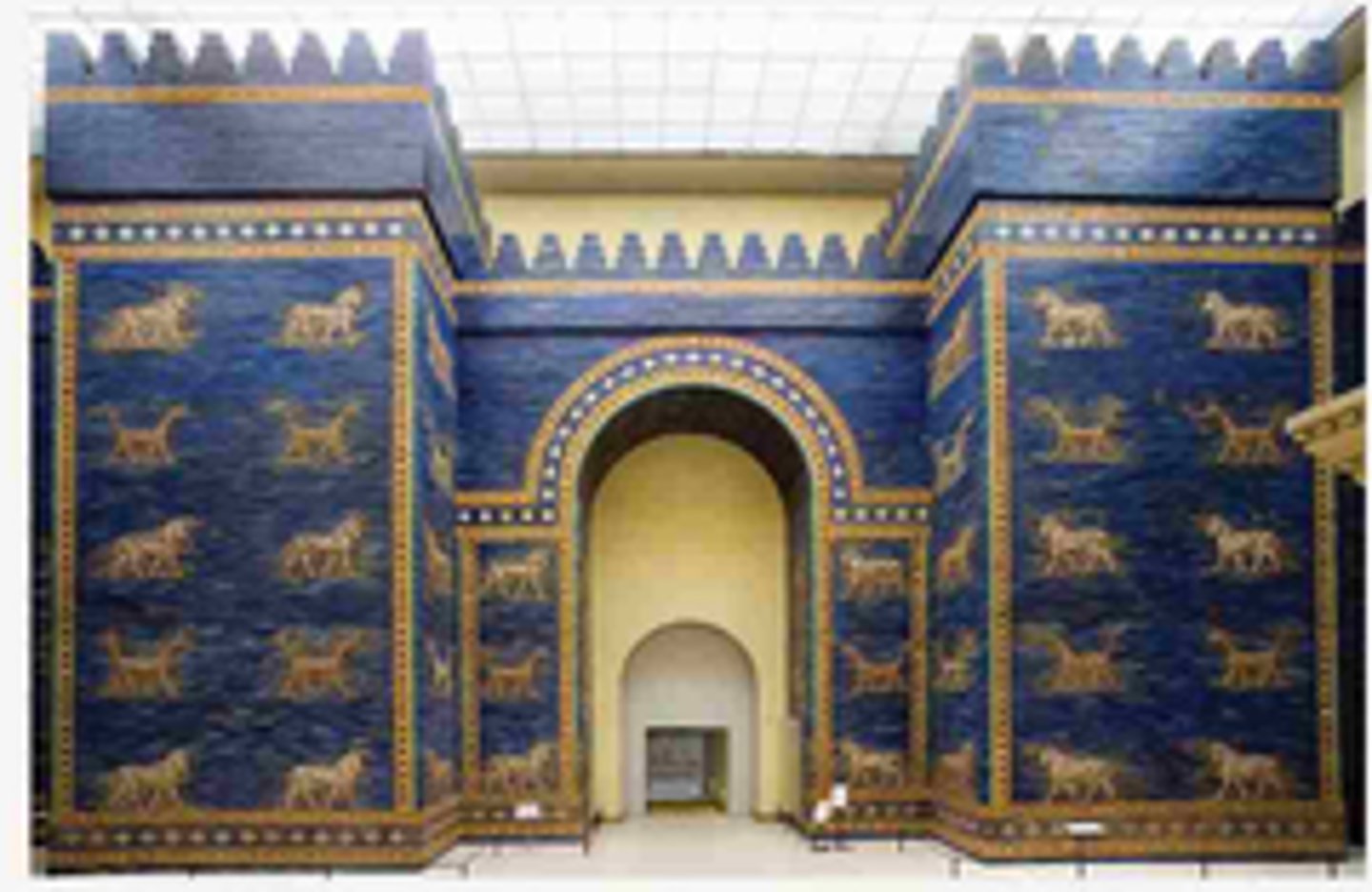
ISHTAR GATE
The entrance gate into Babylon. It was built by Nebuchadnezzar.

HANGING GARDENS
terraced gardens built by Nebuchadnezzar

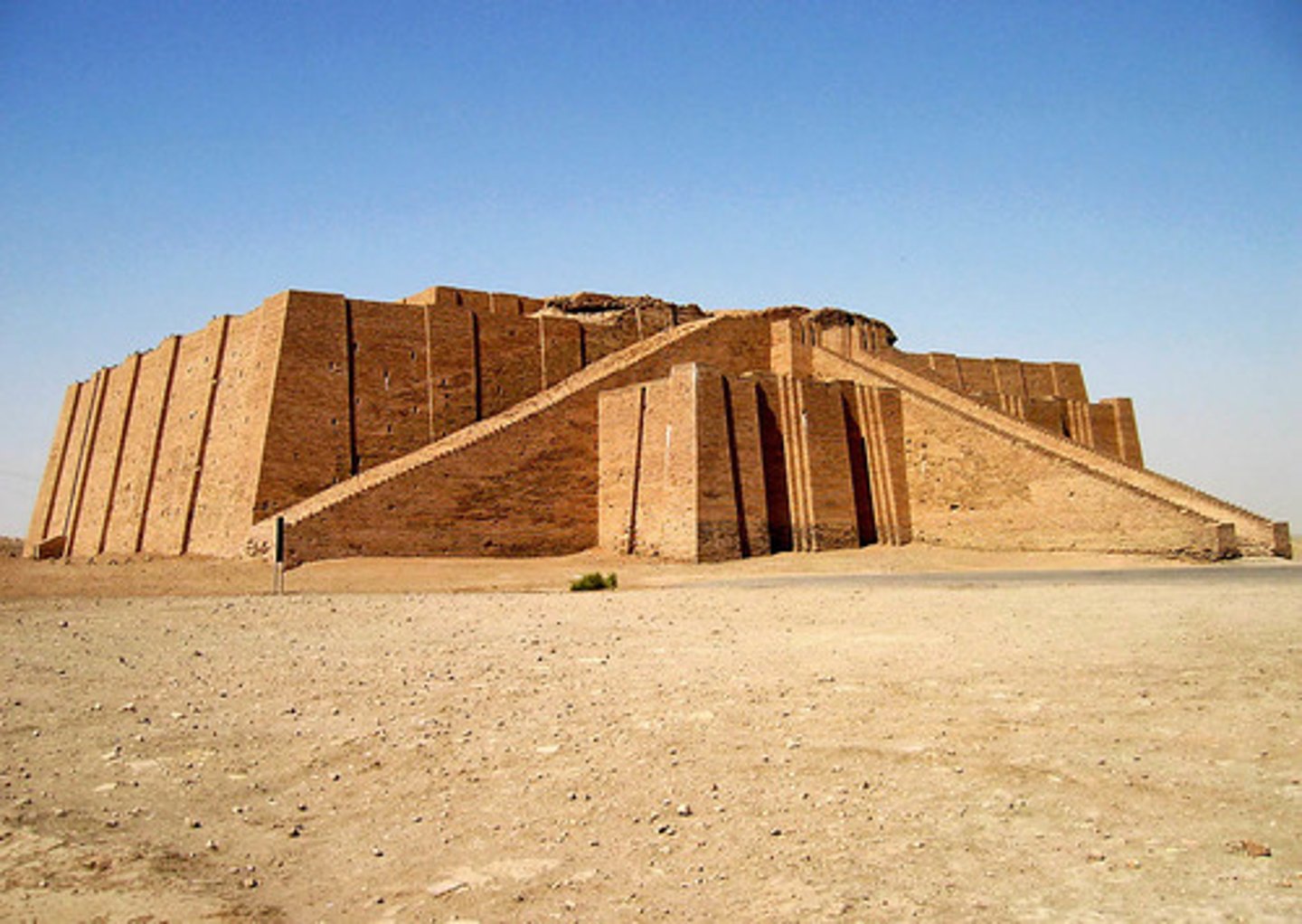
ZIGGURAT
chief bldg. structure , square or rectangle in plan
w/ steeply battered sides & an open flatform on top containing the "Fire Altar ".

WINGED BULL
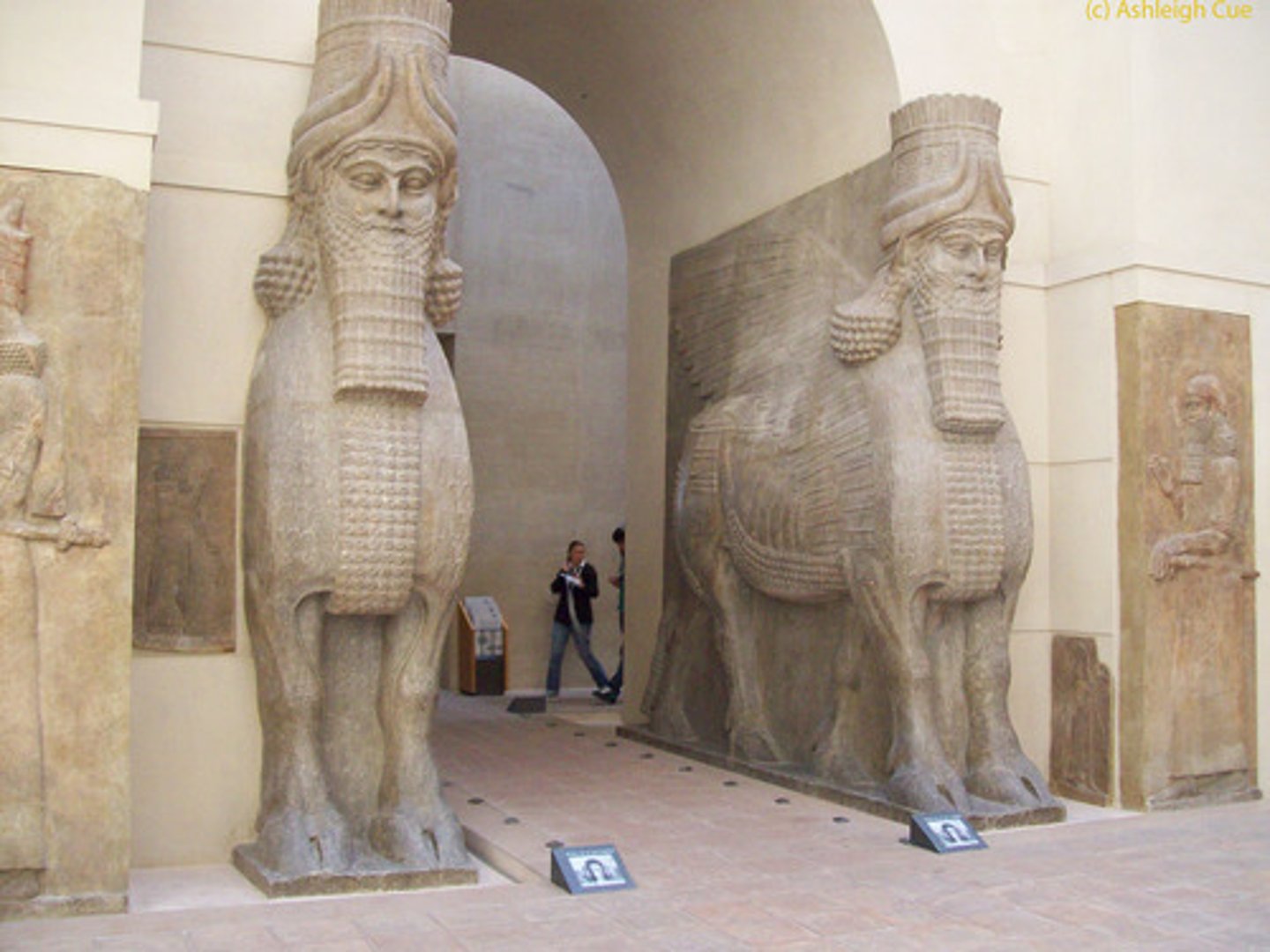

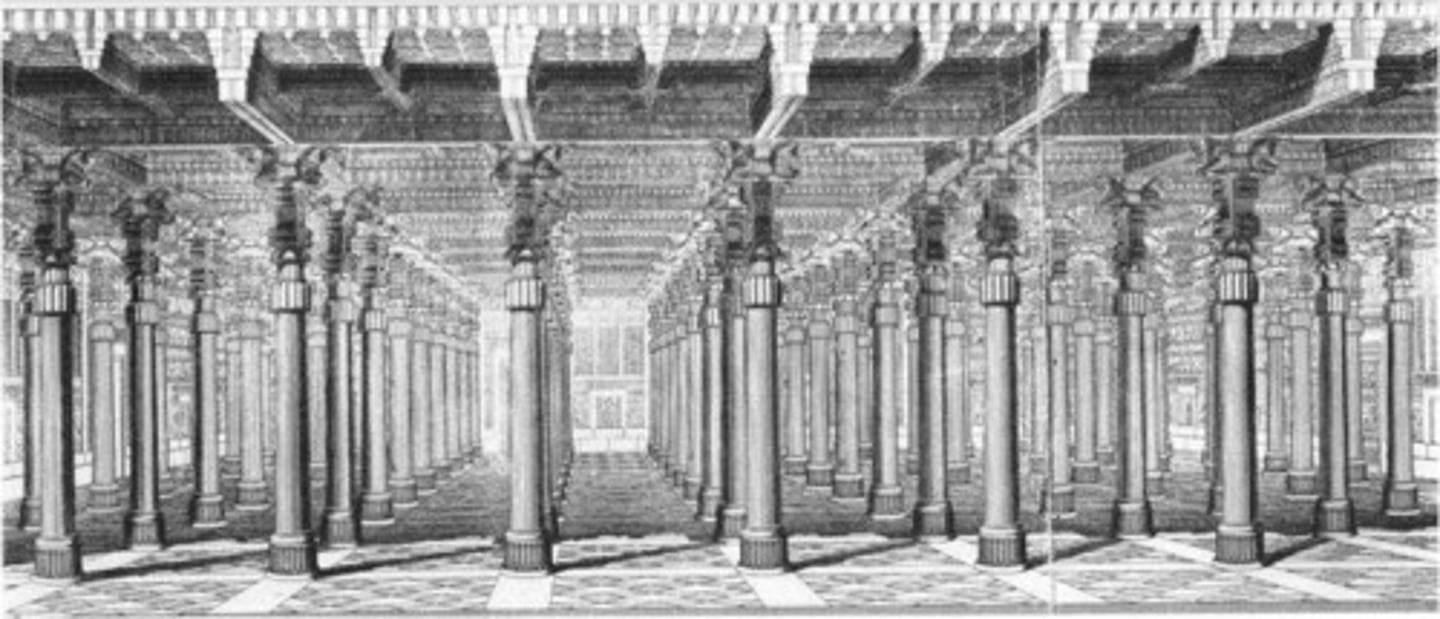
HALL OF HUNDRED COLUMNS
King Xerxes throne hall in Persepolis. it was the largest roofed area at 250 feet squared

MASSIVENESS, MONUMENTALITY, GRANDEUR
MESOPOTAMIAN ARCH CHARACTERISTICS
PERSIAN ARCHITECTURE
Columnar and Trabeated with flat timber roof sometimes domed.
ASSYRIAN AND BABYLONIAN ARCHITECTURE
Arcuated type of construction ; Arch , vault and
flat strips, buttresses w/ glazed tile adornment.
ARCHAIC ZIGGURAT
usually have one flat top rectangular mound carrying the upper temple. e.g White Temple at Warka
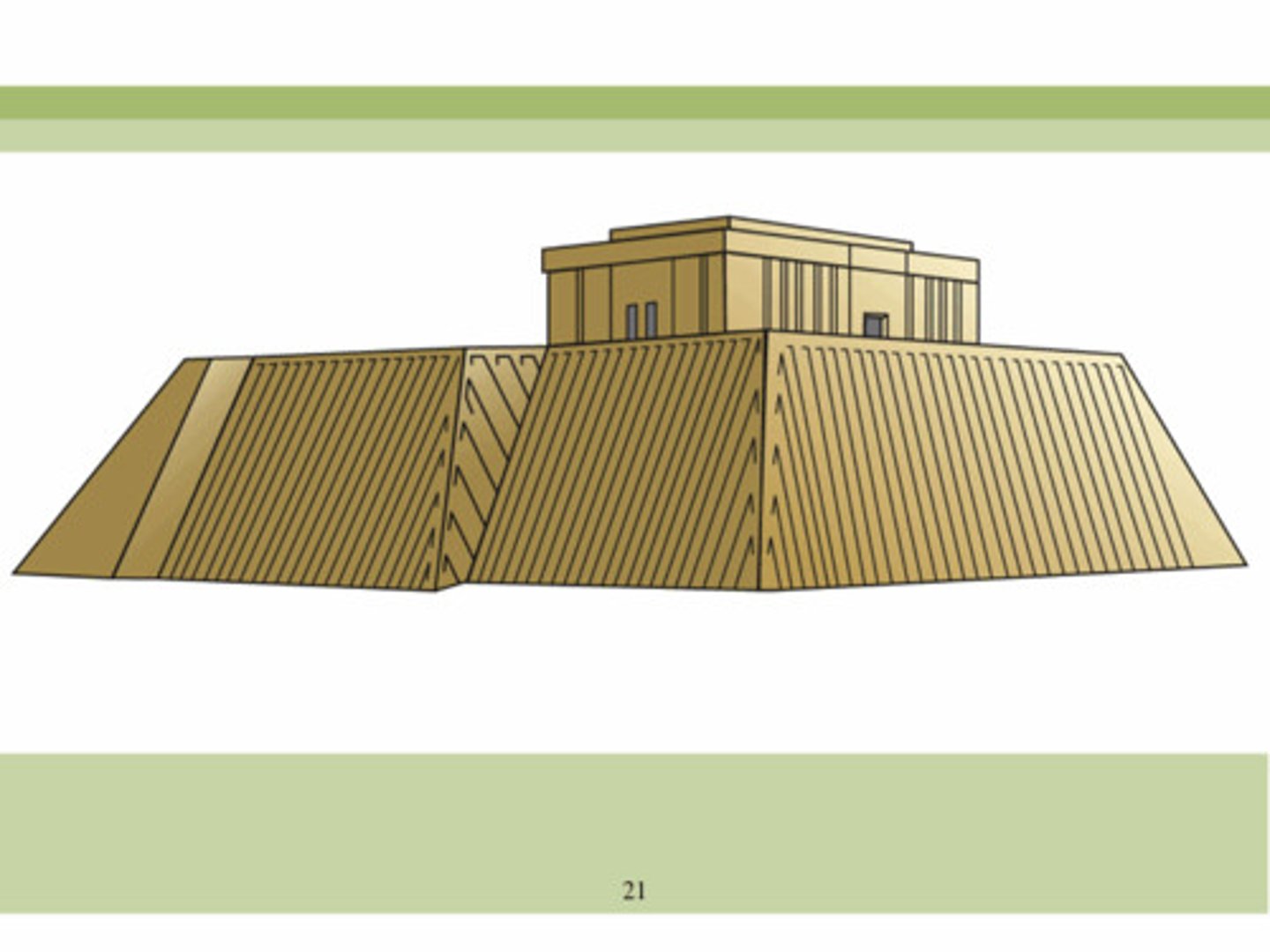
PALACE OF SARGON
entrance portals flanked with status of headed
winged bulls & lions. It contains 700 rooms.
SERAGLIO
The palace proper in Assyrian palaces.
HAREM
usually designed w/ a private family apartments or women's quarter.
KHAN
service chambers
GREEK EARLY PERIOD
Aegeans , Minoans & Myceneans were
the only people in Greece.
HELLENIC PERIOD
essentially columnar & trabeated in Acropolis which was Crowned by
" Parthenon". By the 16th Cent. parthenon was converted into a Christian church.
AEGEAN ARCHITECTURE
a). Low pitch or flat roof on multi - storey structure .
b). Stairway was developed for vertical circulation .
c). Houses termed as " Megaron " & palaces were principal bldg. types
MEGARON
Areas:
1). Enclosed porch
2). Living apartment or megaron proper
3). " Thalamus " or sleeping room
CYCLOPEAN WALL
a masonry made-up of huge stone blocks laid mortar

POLYGONAL WALL
a masonry w/c is constructed w/ stones having polygonal faces.
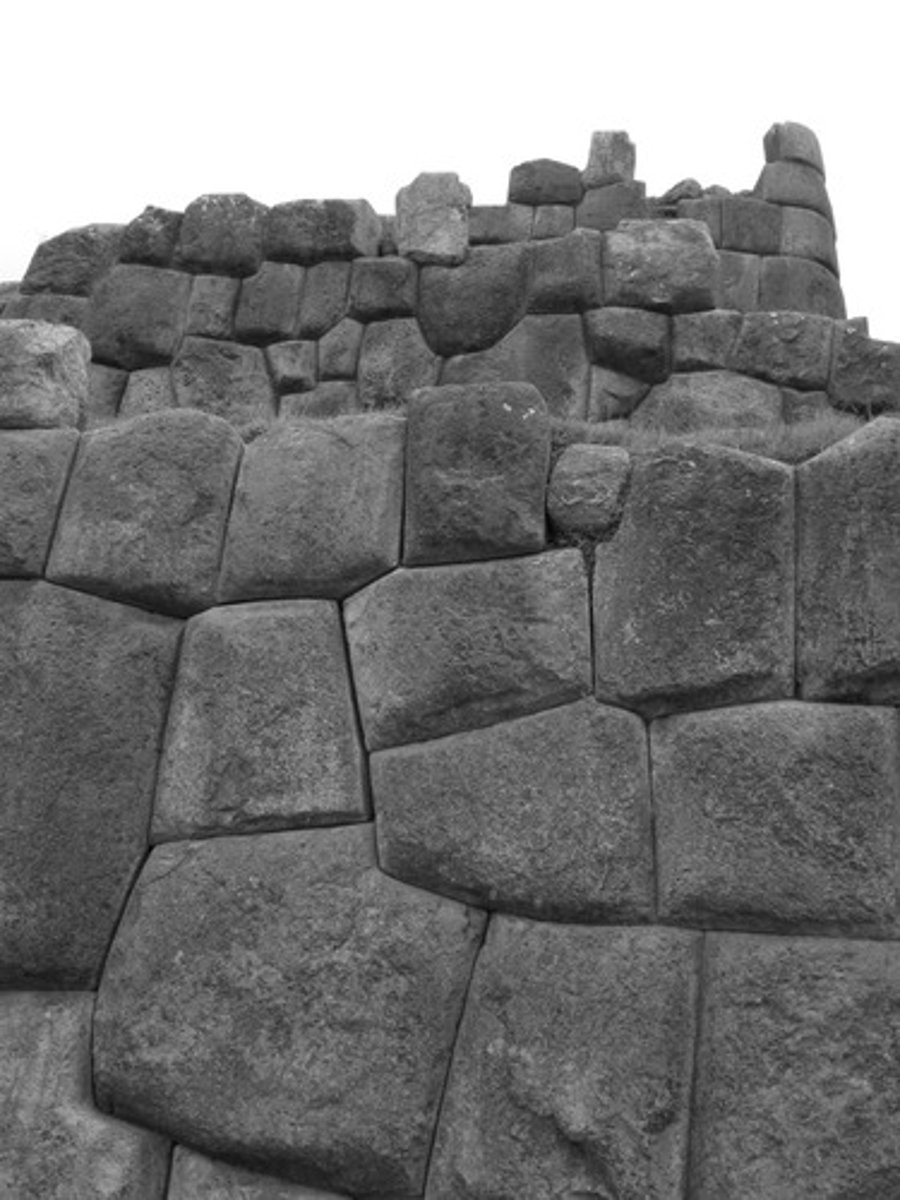

RECTANGULAR WALL
block of stone cut into rectangular shapes.
INCLINED BLOCKS
Stones with inclined blocks
GREEK ARCHITECTURE
a). Simplicity & Harmony
b). Purity of Lines
c). Perfection of Proportions
d). Refinement of Details
SUN / EAST
This " Hellenic Period " chief bldg. type were temples w/c were built towards the ___
PROPYLAEA
entry gate at the west end of the Acropolis
LACUNARIA
Coffers, sunken panels in the ceiling.
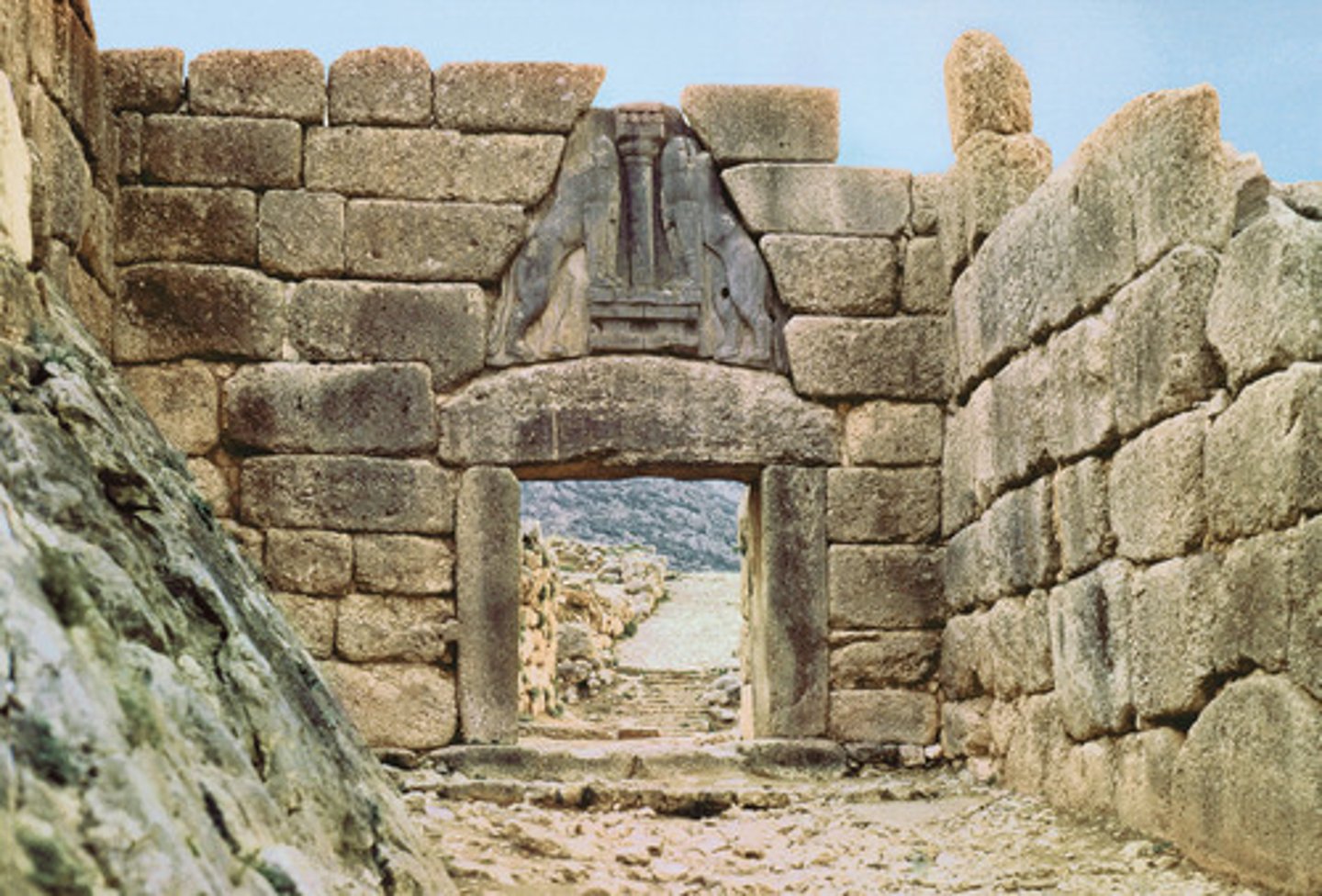
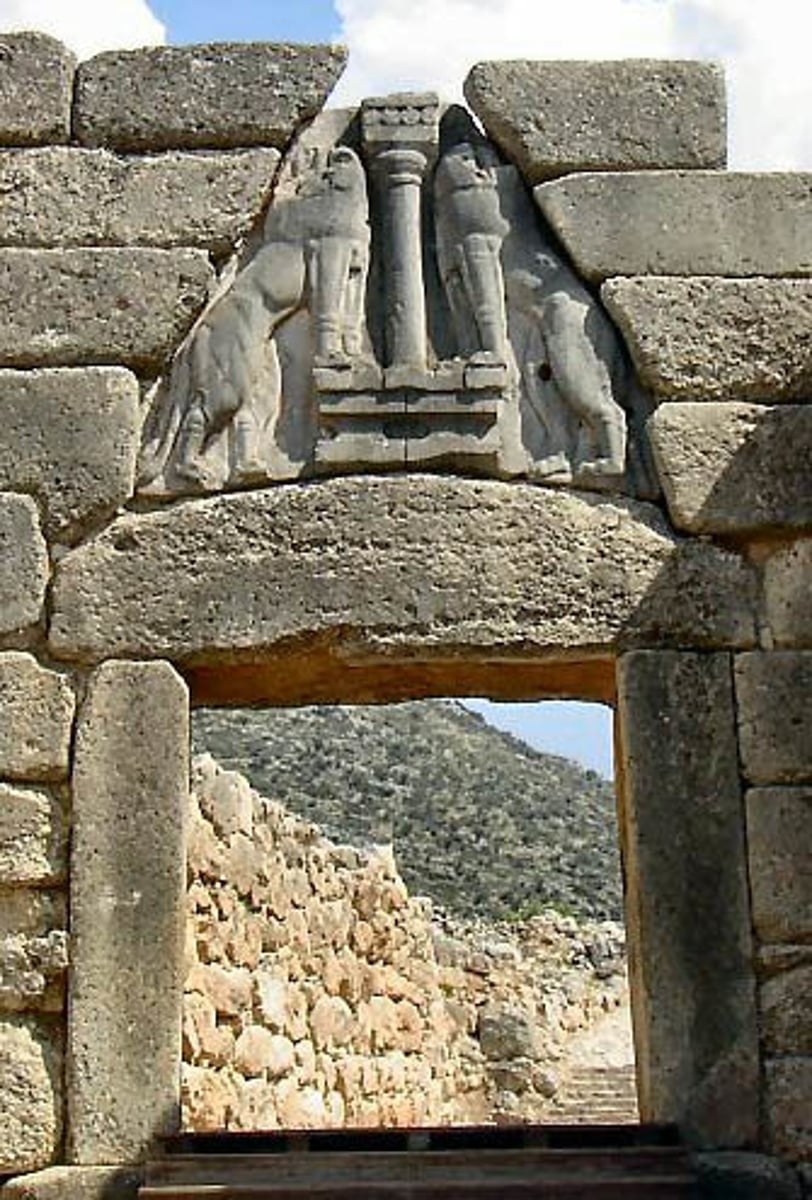
GATE OF LIONS

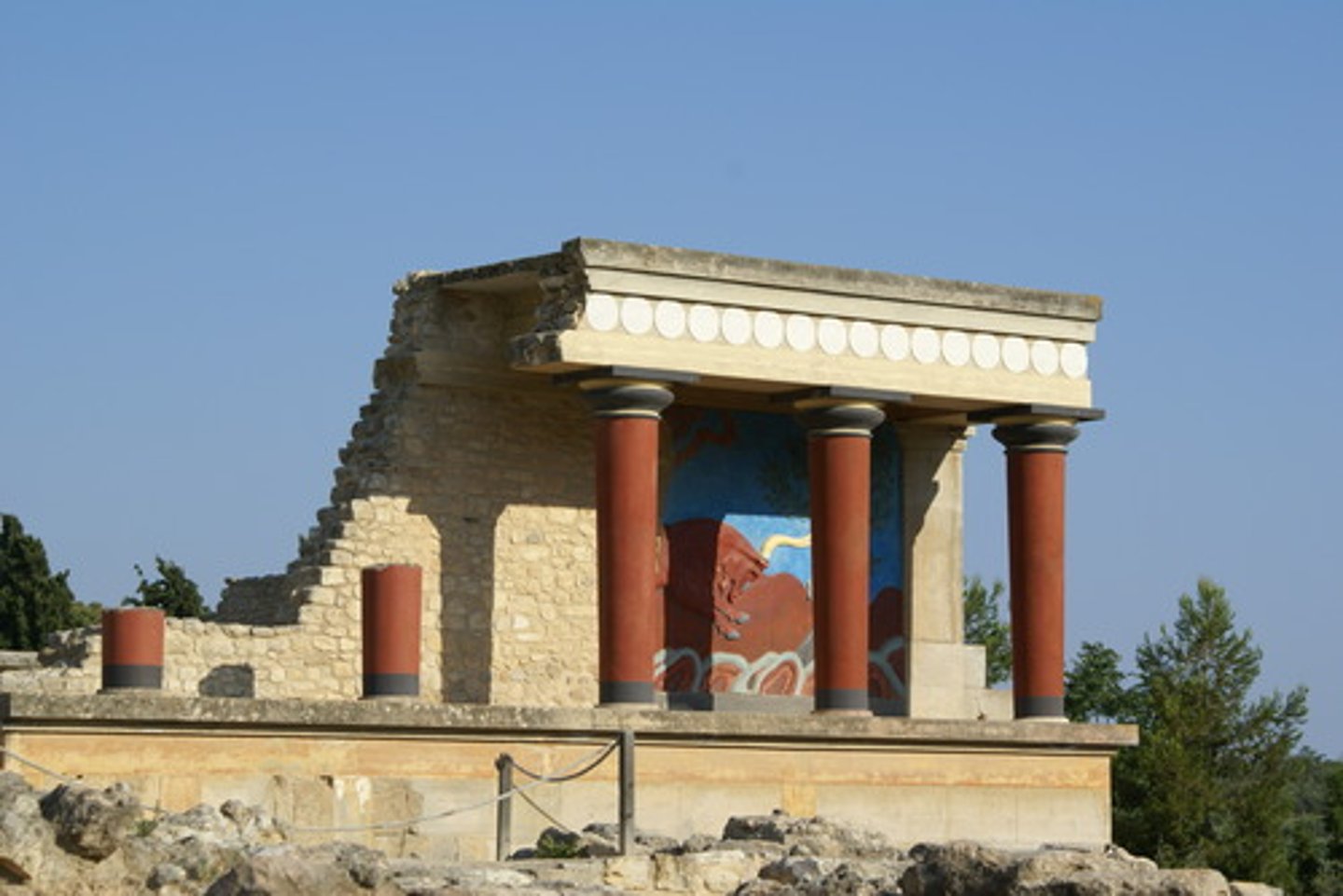
PALACE OF KING MINOS
An example of Aegean Architecture; great palace led by the king of the Minoan civilization that had huge technological and architectural advances including running water

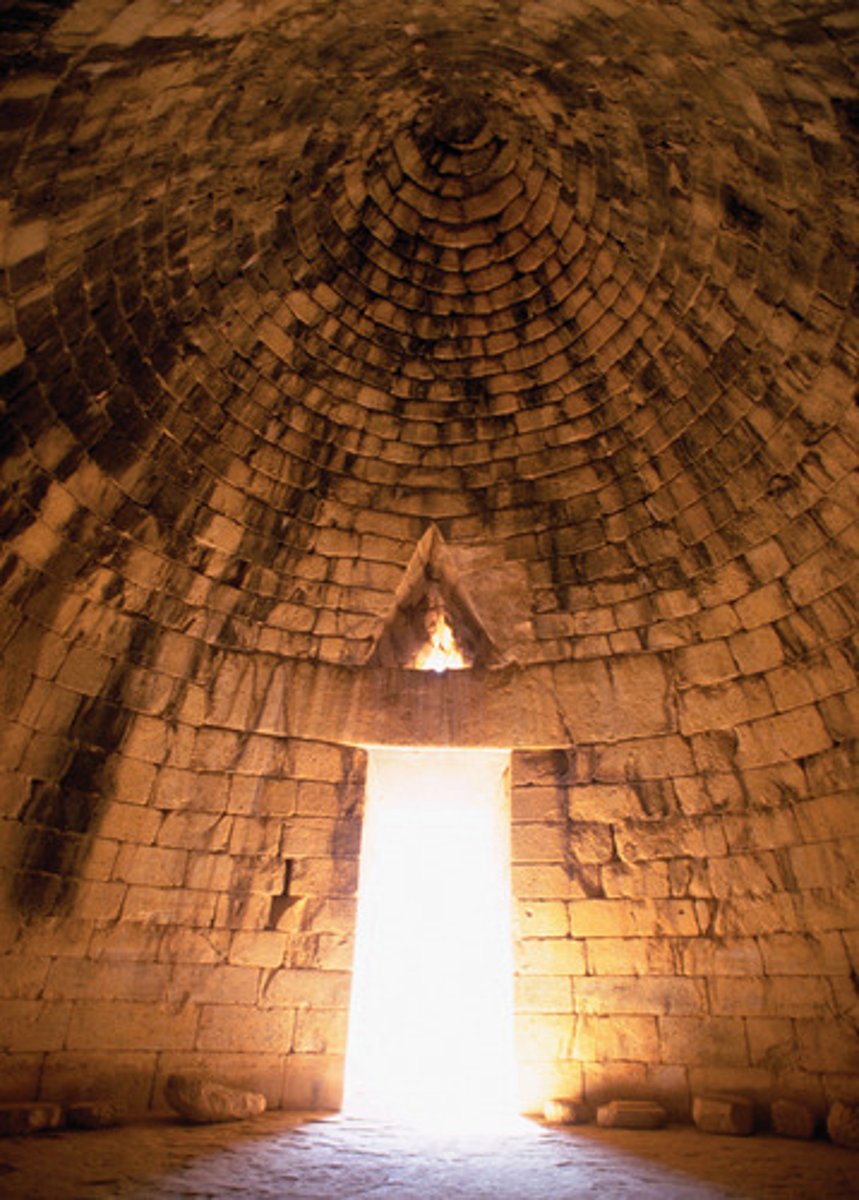
TREASURY OF ATREUS
The finest of Greek Tombs, also known as the 'tomb of Agamemnon'.
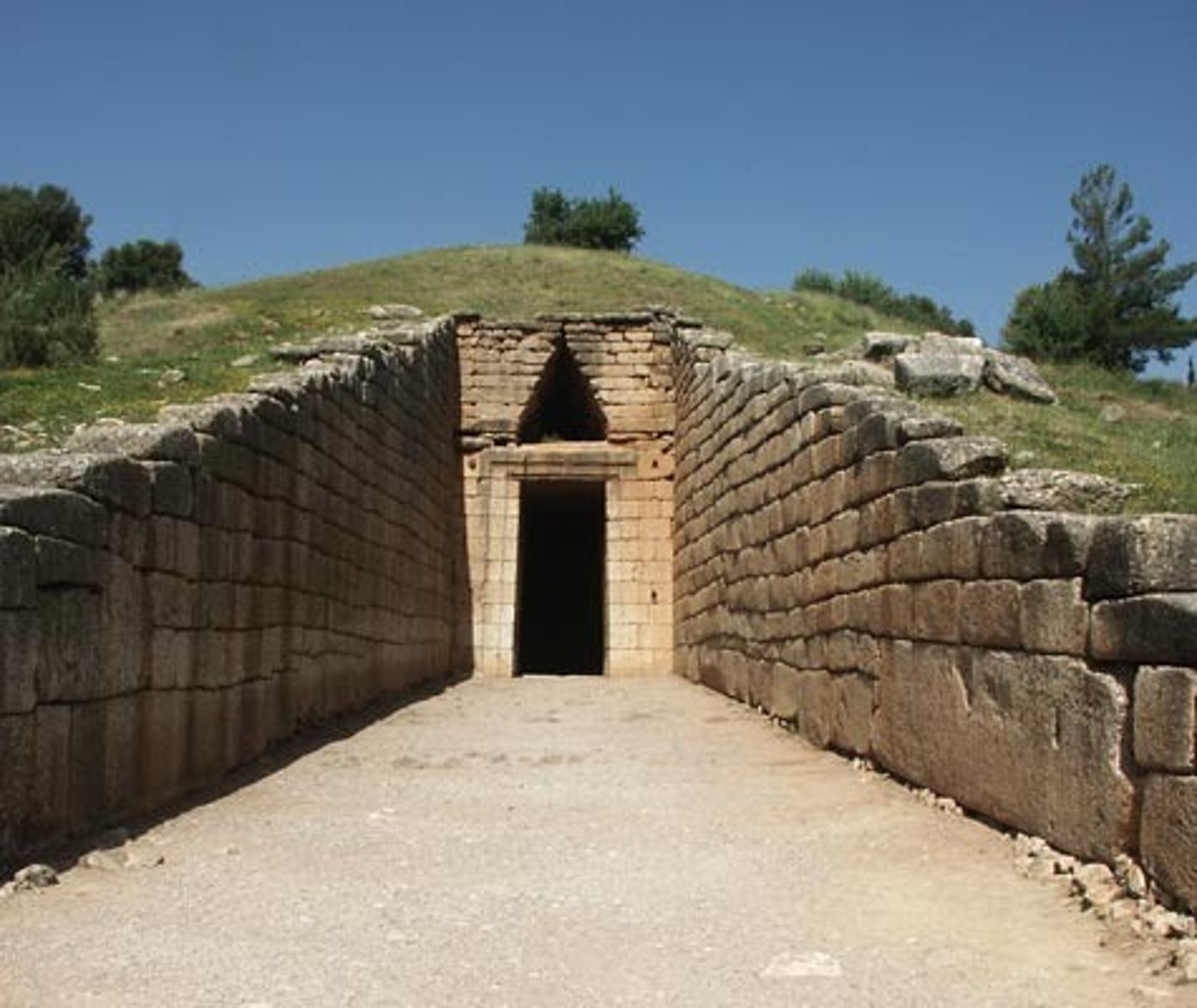

THOLOS
A temple with a circular plan. Also, the burial chamber of a tholos tomb.
