Physmod_ Electrophysiologic-Examination-and-Evaluation
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
________ & ________ as practiced by PT encompass both the professional and technical components of the observation, recording, analysis, and interpretation of bioelectric muscle and nerve potentials, detected by means of surface or needle electrodes, for the purpose of evaluating the integrity of the neuromuscular system.
Electrophysiologic examinations and evaluations
Electrophysiologic Evaluations include
Clinical electromyography [EMG]
Motor and sensory nerve conduction studies
[NCV]Electrodiagnostic procedures
Other evoked potential procedures
Biofeedback
Monitoring and transforming physiologic data into understandable feedback
A training technique that enables an individual to gain some element of voluntary control over muscular or autonomic nervous system functions using a device that produces auditory or visual stimuli
An adjunct tool and not a treatment in itself
Evoked Potentials
________
Tests peripheral motor & sensory neurons on both orthodromic & antidromic responses
Estimates the rate of movement of the induced impulse along the course of the nerve
Nerve Conduction Velocity
Nerve Conduction Velocity
__________
Provides information on the sensory nerve axon and its pathway from the distal cutaneous receptors to the dorsal root ganglia
________
Assessment of motor nerve fibers from their origins in the anterior horn cells to the neuromuscular junction of the muscle that the nerve innervates
Sensory Nerve Action Potential
Compound Muscle Action Potential (CMAP)
NCV
Help clinician answer the following questions
Involvement of peripheral nerves?
Sensory? Motor? Both?
Location? How many?
Magnitude? Partial or Complete?
Increasing/Decreasing impairment?
Localized/Systemic disorder?
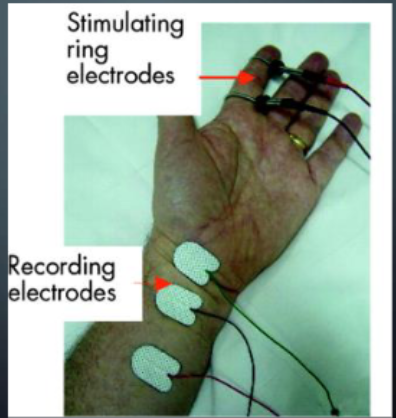
NCV Stimulating Electrodes
__ small electrodes applied to the nerve fixed on the skin about _cm apart
____ electrodes
Uses _____ monophasic PC
_____ is distal to the anode, closest to the most proximal recording electrode
2 small electrodes applied to the nerve fixed on the skin about 2cm apart
Handheld electrodes
Uses rectangular monophasic PC
Cathode is distal to the anode, closest to the most proximal recording electrode
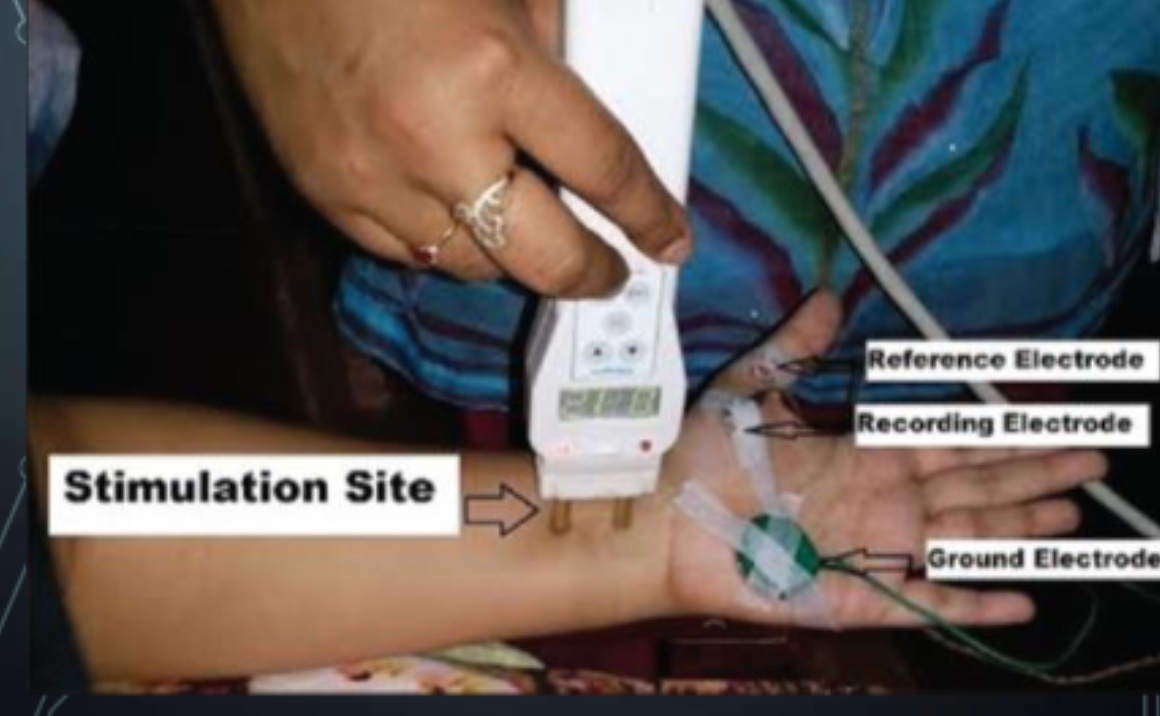
NCV Stimulating : Other Electrodes
________: placed over the stimulated muscle/nerve
________: distally placed
________: placed on other areas usually on a bony area
Active/Recording: placed over the stimulated muscle/nerve
Reference: distally placed
Ground: placed on other areas usually on a
bony area
NCV
_________
Linear distance between two points along the course of a nerve
Measured in ___
__________
Conduction time between stimulus and the start of muscle contraction or activation of the nerve
Measured in ___
NCV = Distance / Latency
Distance
mm
Latency
msec
NCV = Distance / Latency
NCV Factors to Consider
Body Temperature
temperature → __ conduction velocity / _ distal latency ( INC_/DEC?)
UE is _-_ m/s faster vs LE
More ____ segments are faster vs distal
Age
<3-5 y/o = LOWER by __% vs normal adults
>40 = ____ slowing vs middle-aged
6th & 7th decade = __ m/sec LESS than middle-aged
Body Temperature
temperature → INC conduction velocity / DEC distal latency
UE is 7-10 m/s faster vs LE
More proximal segments are faster vs distal
Age
<3-5 y/o = lower by 50% vs normal adults
>40 = gradual slowing vs middle-aged
6th & 7th decade = 10 m/sec less than middle-aged
NCV
Reduced in compression lesions like CTS, PNI, demyelinating disorders
Neuromuscular Junction Transmission
Assesses the function of the neuromuscular
junction
Repetitive Nerve Stimulation Test (RNS)
a.k.a. “Jolly Test”
Test for myasthenia gravis
Centrally Evoked Potentials
Somatosensory Evoked Potential (SSEP)
Visual Evoked Potential (VEP)
Brainstem Auditory Evoked Potential (BAEP)
___________
Aka Faradic and Galvanic Test
Assessment of lower motor neuron lesions
A motor point is stimulated.
Reaction of Degeneration Test
Reaction of Degeneration Test
Faradic Current
_____ pulse duration (<1msec)
>_-_ Hz frequency
Monophasic or _______ PC using cathode as the active electrode
Produces _______ or sustained contraction
Short pulse duration (<1msec)
>20-50 Hz frequency
Monophasic or asymmetrical biphasic PC using cathode as the active electrode
Produces smooth tetanic or sustained contraction
Reaction of Degeneration Test
Galvanic Current
Long pulse duration (> or = ___ msec)
Monophasic or _________ DC using cathode as the active electrode
Produces brisk ________
Long pulse duration (> or = 100msec)
Monophasic or Interrupted DC using cathode as the active electrode
Produces brisk muscle twitches
Reaction of Degeneration Test Interpretation
Status of Muscle Innervation → FC
Normal Peripheral Nerve →
Partial RD: degen of part of nerve fibers →
Complete RD: degen of all nerve fibers; muscle tissue retains
contractile elements →Absolute RD : degen of allnerve fibers; muscle tissue severely
atrophic, fibrotic or non-contractile →
Status of Muscle Innervation → FC
Normal Peripheral Nerve → Smooth Tetanic or sustained contraction
Partial RD → Partial or diminished tetanic contraction
Complete RD → No contraction
Absolute RD → No Contraction
Reaction of Degeneration Test Interpretation
Status of Muscle Innervation → GC
Normal Peripheral Nerve →
Partial RD: degen of part of nerve fibers →
Complete RD: degen of all nerve fibers; muscle tissue retains
contractile elements →Absolute RD : degen of allnerve fibers; muscle tissue severely
atrophic, fibrotic or non-contractile →
Status of Muscle Innervation → GC
Normal Peripheral Nerve → Brisk muscle twitches
Partial RD → Partial or diminished sluggish twitches
Complete RD → Very slow, sluggish twitches
Absolute RD → No Contraction
Reaction of Degeneration Test Use & Limitations
A quick screening test for differentiating a muscle with ____ peripheral innervation vs a muscle with peripheral _____
Not done at least ____ days after onset of the problem
May be indicated in conditions of unexplained ______
A quick screening test for differentiating a muscle with normal peripheral innervation vs a muscle with peripheral denervation
Not done at least 10 days after onset of the problem
May be indicated in conditions of unexplained
paralysis
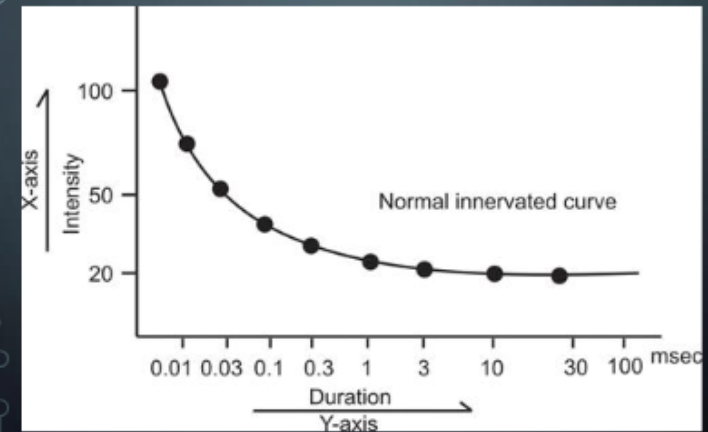
Strength Duration Curve & Chronaxie Test
Electrodiagnosis of ______ nervous system disorders
Used to assess the location, severity, and progress of peripheral ____ nerve degeneration
Obtained by joining points that graphically represent the threshold values of stimulation (intensity) along the y-axis for various duration of stimulus (pulse duration) displayed along the x-axis
Uses ____, _____ PC (sawtooth, triangular)
Strength Duration Curve & Chronaxie Test
Electrodiagnosis of peripheral nervous system disorders
Used to assess the location, severity, and progress of peripheral motor nerve degeneration
Obtained by joining points that graphically represent the threshold values of stimulation (intensity) along the y-axis for various duration of stimulus (pulse duration) displayed along the x-axis
Uses square, monophasic PC (sawtooth, triangular)
Strength Duration Curve & Chronaxie Test
_____ as stimulating electrode
May use _-_ pulse durations
Usually uses these pulse durations (in msec): 100, 30, 10, 3, 1, 0.3, 0.1, 0.03, 0.01
Longest pulse duration must be at least __ms
Cathode as stimulating electrode
May use 8-10 pulse durations
Usually uses these pulse durations (in msec): 100, 30, 10, 3, 1, 0.3, 0.1, 0.03, 0.01
Longest pulse duration must be at least 100ms
Strength Duration Curve & Chronaxie Test
________
Least amount of intensity needed to elicit visible muscle contraction for an indefinite duration
5-35volts/ 2-18mA
_______
Minimum time required to produce a muscle contraction with an intensity set at twice the rheobase
0.05 - 0.5 msec or <1 msec
Rheobase
Chronaxia
Strength Duration Curve & Chronaxie Test
Factors Affecting the SD Curve
Skin resistance
Subcutaneous tissues (eg fats)
Skin temperature
Electrode size
Electrode placement
Age
Fatigue
Strength Duration Curve & Chronaxie Test
Advantages
Quick and easy to perform
Requires minimal training
More economica
Disadvantages
Only provides qualitative data in relation to degree of denervation
Cannot locate site of lesion
Only few fibers can be assessed in large muscles
Volitional Potentials
_________
Study of muscle activity
Monitoring, detection, or assessment of skeletal muscle activity so that the information gained can be used by the patient and clinician to influence future activity of the skeletal muscle, whether for increasing or
decreasing activity
Electromyographic Biofeedback
Electromyographic Biofeedback
No _____ is delivered to the patient
Electrical activities of the neuromuscular system is detected for _____ use
Recorded upon ______ contraction of the muscle
Not a therapeutic agent, but part of the therapeutic process
No current is delivered to the patient
Electrical activities of the neuromuscular system is detected for therapeutic use
Recorded upon voluntary contraction of the muscle
Not a therapeutic agent, but part of the therapeutic process
EMG BIOFEEDBACK
wdiw
EMG BIOFEEDBACK
Facilitatory Biofeedback
____ activity (post-injury or post-operatively)
Normalize ____ functions
Improve volitional motor control following ____ dysfunction
Inhibitory Biofeedback
DEC muscle activity (spasticity in ____ dysfunctions)
DEC muscle activity (due to _____ stress)
DEC muscle activity / guarding(due to _____ pain)
Facilitatory Biofeedback
muscle activity (post-injury or post-operatively)
Normalize muscle functions
Improve volitional motor control following CNS
dysfunction
Inhibitory Biofeedback
DEC muscle activity (spasticity in CNS dysfunctions)
DEC muscle activity (due to postural stress)
DEC muscle activity / guarding(due to chronic pain)
EMG BIOFEEDBACK
_____________
Measurement of the electricity produced by
the movement in muscleInvolves the evaluation and recording of
muscle activityUsed for identifying neuromuscular diseases
and disorders of motor controlInstrument: electromyograph
CLINICAL ELECTROMYOGRAM (EMG)
EMG Biofeedback
Electrodes
_________
Sensor
Considerations:
Electrode spacing
Crosstalk
___________
Over bony surface
Used to minimize extraneous electrical activity (noise)
Recording Electrodes
Ground Electrode
EMG Biofeedback: Recording Electrodes
_____ EMG ( sEMG)
non-invasive
_____ EMG ( nEMG)
Invasive
Surface EMG ( sEMG)
non-invasive
Needle EMG ( nEMG)
Invasive
EMG Biofeedback
Signal Amplification & Filtration
To _____ the signal-to-noise ratio
To _____ the distortion of signal
Noise Sources during EMG
Inherent noise of electrical parts inside the signal detection and recording instrument
Ambient noise from the environment
Motion artefacts (electrodes-skin interface)
Inherent instability of EMG signal (random firing
of motor units)
Signal Amplification & Filtration
To maximize the signal-to-noise ratio
To minimize the distortion of signal
Noise Sources during EMG
Inherent noise of electrical parts inside the signal detection and recording instrument
Ambient noise from the environment
Motion artefacts (electrodes-skin interface)
Inherent instability of EMG signal (random firing
of motor units)
EMG Biofeedback : Signal Amplification & Filtration
Amplification & Filtering Circuity
Electrodes → 1st stage amplification → High Pass filter → Low-pass filter → 2nd stage amplification → Low Pass Filter → Analog Digital Converter
Band Pass Filtering
High-pass filter: attenuates contents ___ a cut-off frequency; Hz/_-_ Hz cut-off
Low-pass filter: attenuates contents ____ a cut-off frequency; ____ Hz cut-off
Band Pass Filtering
High-pass filter: attenuates contents below a cut-off frequency; 5 Hz/10-20 Hz cut-off
Low-pass filter: attenuates contents above a cut-off frequency; 500 Hz cut-off
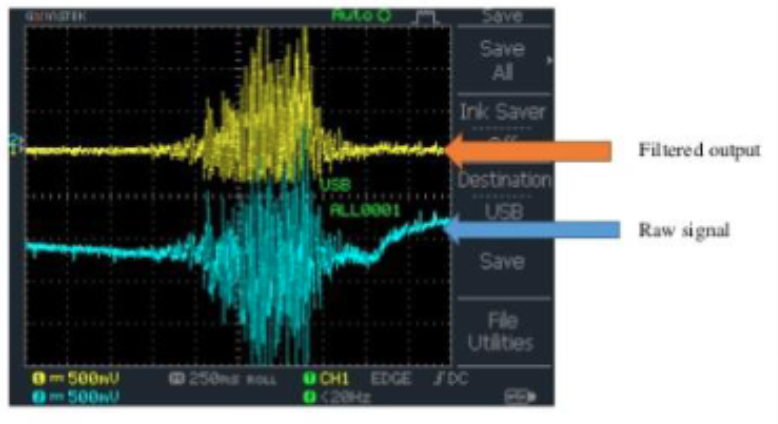

EMG Biofeedback
_________
Taking the absolute value of the signal
Also known as Full-wave Rectification
Rectification + Low-pass Filter = “Linear Envelop”
Traditional low-pass filter of rectified signal = Butterworth or Chebyshev
Signal Rectification
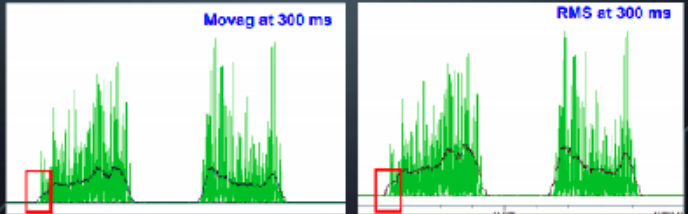
EMG Biofeedback : Signal Smoothing
__________
Certain amount of data are averaged using the sliding window technique
__________
Based on square root calculation; reflects the mean power of the signal; preferred method
Moving Average
Root Mean Square
EMG Biofeedback :Muscle Fatigue Index
__________
Used to identify weak muscles
Used to prove efficiency of strength training exercise
Muscle Fatigue Index
EMG Biofeedback : EMG AT REST
NORMAL
(+) _______ activity
______ action potentials
___ muscle action potentials ( High or none?)
ABNORMAL
(+) ________ /fasciculations
complex discharges
_ or _ insertional activity
NORMAL
(+) insertion activity
miniature endplate action potentials
no muscle action potentials
ABNORMAL
(+) fibrillations /fasciculations
complex discharges
INC or DEC insertional activity
EMG Biofeedback : EMG with Mild Contraction
NORMAL
Usually ____ or ____ muscle AP
Motor unit potentials (MUP) from ___ amplitude potentials → progressively ___-amplitude potentials
ABNORMAL
_____, amplitude either increase or decrease
Altered recruitment _____
NORMAL
Usually biphasic or triphasic muscle AP
Motor unit potentials (MUP) from small → amplitude potentials → progressively large-amplitude potentials
ABNORMAL
Polyphasic, amplitude either increase or decrease
Altered recruitment patterns
EMG Biofeedback : EMG with MAX Contraction
Normal
____ Frequency
(N) stepwise ____ interference patterns
Abnormal
____ interference pattern
____ full interference pattern
Normal
INC Frequency
(N) stepwise INC interference patterns
Abnormal
DEC interference pattern
Early full interference pattern
GENERAL GUIDELINES FOR ALL ELECTROPHYSIOLOGIC TESTING
Patient should be comfortable
Ensure correct electrode placement
Secure electrodes properly
Perform first a detailed physical examination of strength, sensation, coordination, reflexes and other neuromuscular function
Use latex gloves, goggles and gown for needle EMG
When applying electrical stimulation, check for contraindications and precautions
DONE