Ch 8 - Systems Development
Participants in systems development:
- Development team:
- Determines objectives of the information system
- Delivers system that meets objectives
- Project:
- Planned collection of activities that archives a goal
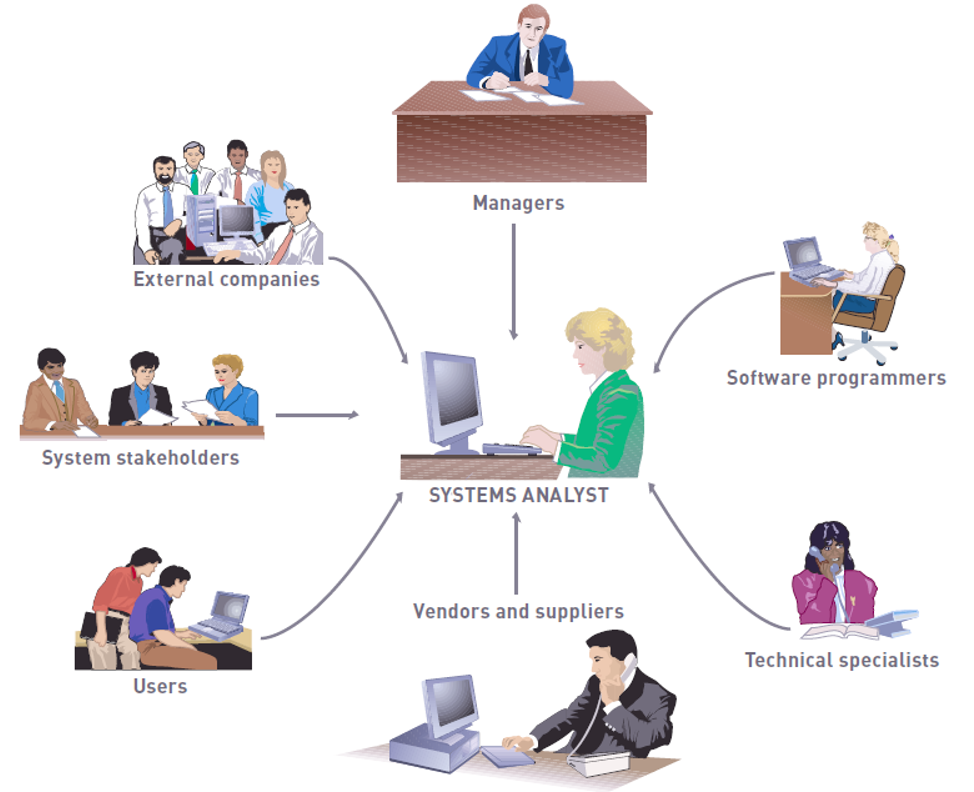
- Stakeholders:
- People who benefit from a project
- Users:
- People who interact regularly with the system
- system analyst:
- Professional who specialises in analysing and designing business systems
- programmer:
- Responsible for modifying or developing programs to satisfy user requirements
\n
Individual systems developer: person who performs all of the systems development roles
Individual users: acquire applications for both personal and professional use
End-user systems development: describes any systems development project in which business managers and assume the primary effort
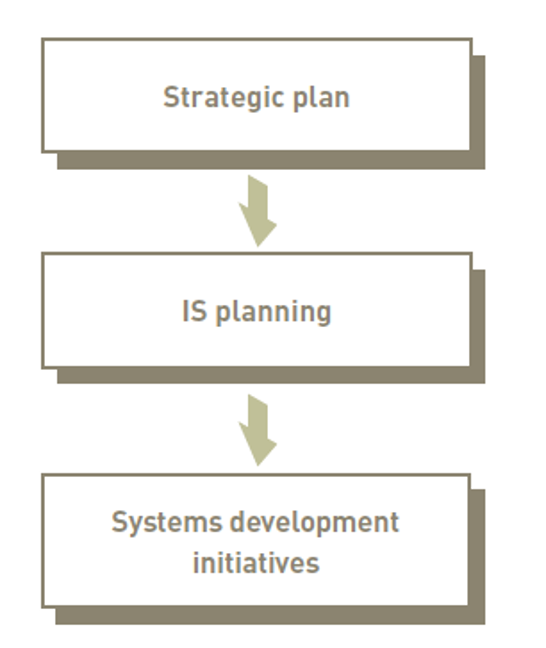
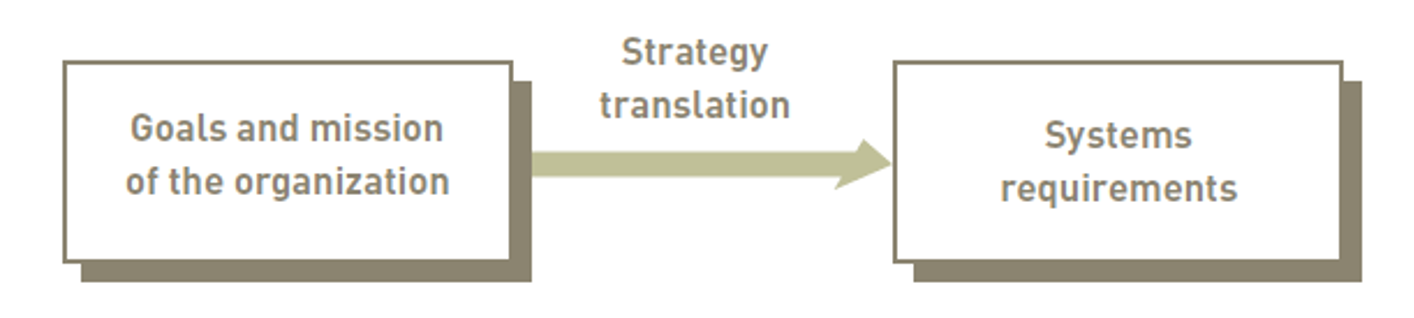
Information systems planning and aligning corporate and IS goals:
- Information systems planning: translating strategic and organisational goals info systems development initiatives
- Aligning goals and IS goals: critical for successful systems development effort
%%System Development Life Cycles%%:
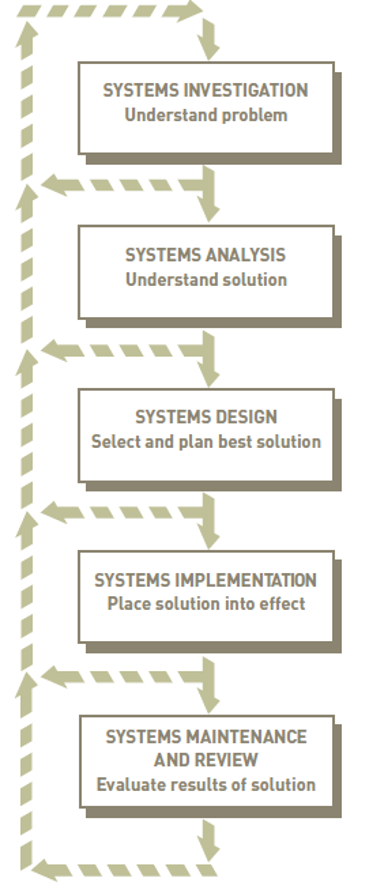
- Traditional systems development life cycle:
- Systems investigation: identifies problems and identities and considers them in a light of business goals
- Systems analysis: studies existing systems and work processes to identify strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities for improvement
- Systems design: defines how the information system will do what it must to obtain the problem’s solution
- Systems implementation: creates or acquires various system components details in systems design, assembles them, and places new or modified system info operation
- Systems maintenance and review: ensures the system operates as intended
- Modifies the system so it continues to meet changing business needs
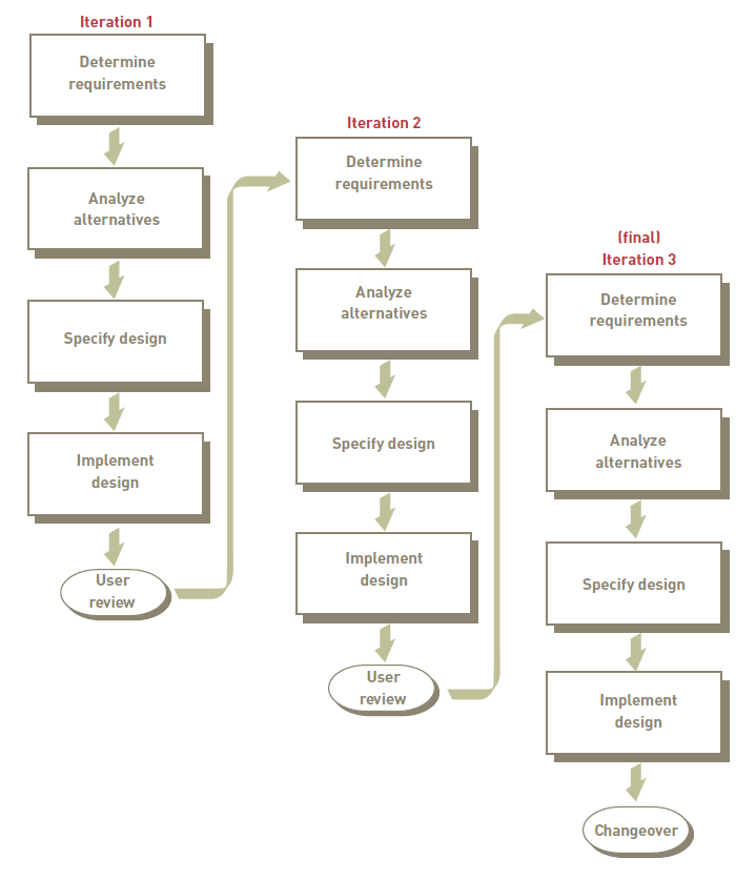
Prototyping:
- An iterative approach
- Requirements and alternative solutions to the problem are identified and analysed
- New solutions are designed, and a portion of the system is implemented
- Rapid application development (RAD): employs tools, techniques, and methodologies designed to speed application development
- Other approaches to rapid development:
- Agile development
- Extreme programming (XP)
Outsourcing and on-demand computing: Reasons for using outsourcing and on-demand computing approaches
- Reduce costs
- Obtain state-of-the-art technology
- Eliminate staffing and personnel problems
- Increases technological flexibility
Degree of Change: Continuous improvement projects vs. reengineering
- Continuous improvement projects have a high degree of success
- Reengineering projects have a high risk high benefit
Managing change: essential to recognise and deal with existing or potential problems
Project Management Tools:
- Project schedule: detailed description of what is to be done
- Project milestone: critical date for completion of a major part of the project
- Project deadline: date the entire project is set to be completed and operational
Critical path: activities that, if delayed, would delay the entire project
\n
- Object-oriented systems development: Combines logic of systems development life cycle with power of object-oriented modelling and programming
- OOSD: identifies potential problems and opportunities
- Defines what kind of system users require
- Designing the program
- Programming or modifying modules
- Evaluation by users
- Periodic review and modification
Feasibility analysis: Assesses:
- Technical feasibility
- Economic feasibility
- Legal feasibility
- Operational feasibility
- Schedule feasibility
- Object-oriented approach is used through all phases of system development
Investigation process: Initiated by a systems request form
Systems analysis: The examination of existing systems
- The systems investigation report summarises results of systems investigation
Data modelling: accomplished through the use of entity-relationship (ER) diagram
Activity modelling:
- Accomplished through the use of data-flow diagrams
- DFDs: describe the activities that fulfils a business relationship or accomplish a business task
Requirements analysis: determines user, stakeholder, and organisational needs
System Design:
- Logical design: describes functional requirements of a system
- Physical design: specifies the characteristics of the system components necessary to put the logical design into action
- Purpose of systems design: To prepare the detailed design needs for a new system or modifications to an existing system
- Environmental design: Involves systems development efforts that slash power consumption and take less physical space
- Request for proposal (RFP): document that specifies required resources such as hardware and software in detail
- Purpose of systems implementation: To install a system and make everything, including users, ready for its operation
- IS vendor: Company that offers hardware, software, telecommunications systems, databases, IS personnel, or other computer-related resources
- Software: Can be purchased from external vendors or developed in house
- Systems operation: The use of a new or modified system \n \n \n