CMS II: Ortho - Shoulder
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
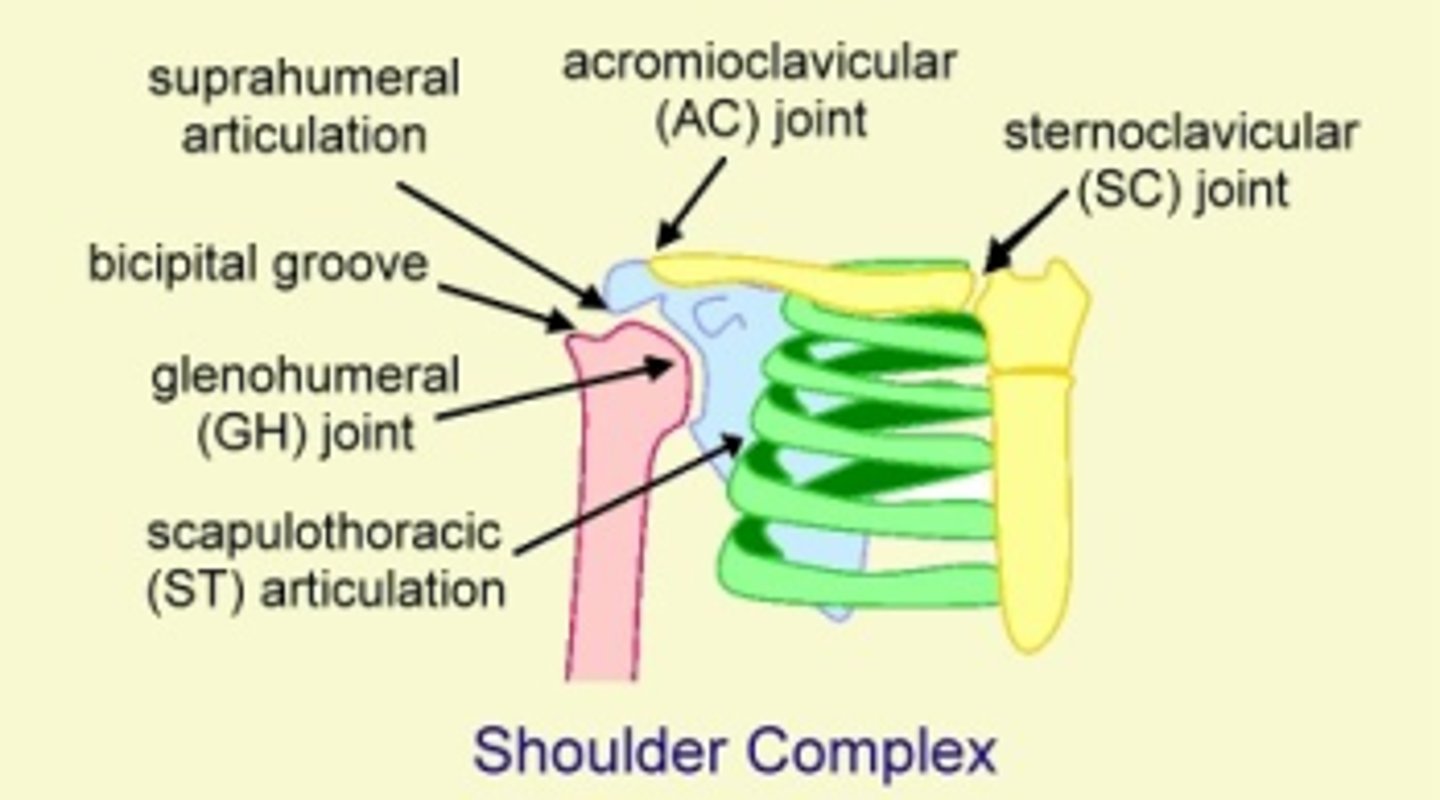
What are the THREE joints of the shoulder?
Glenohumeral
Acromioclavicular
Sternoclavicular
Where does the short head of the biceps bind to in the shoulder?
coracoid process of the scapula
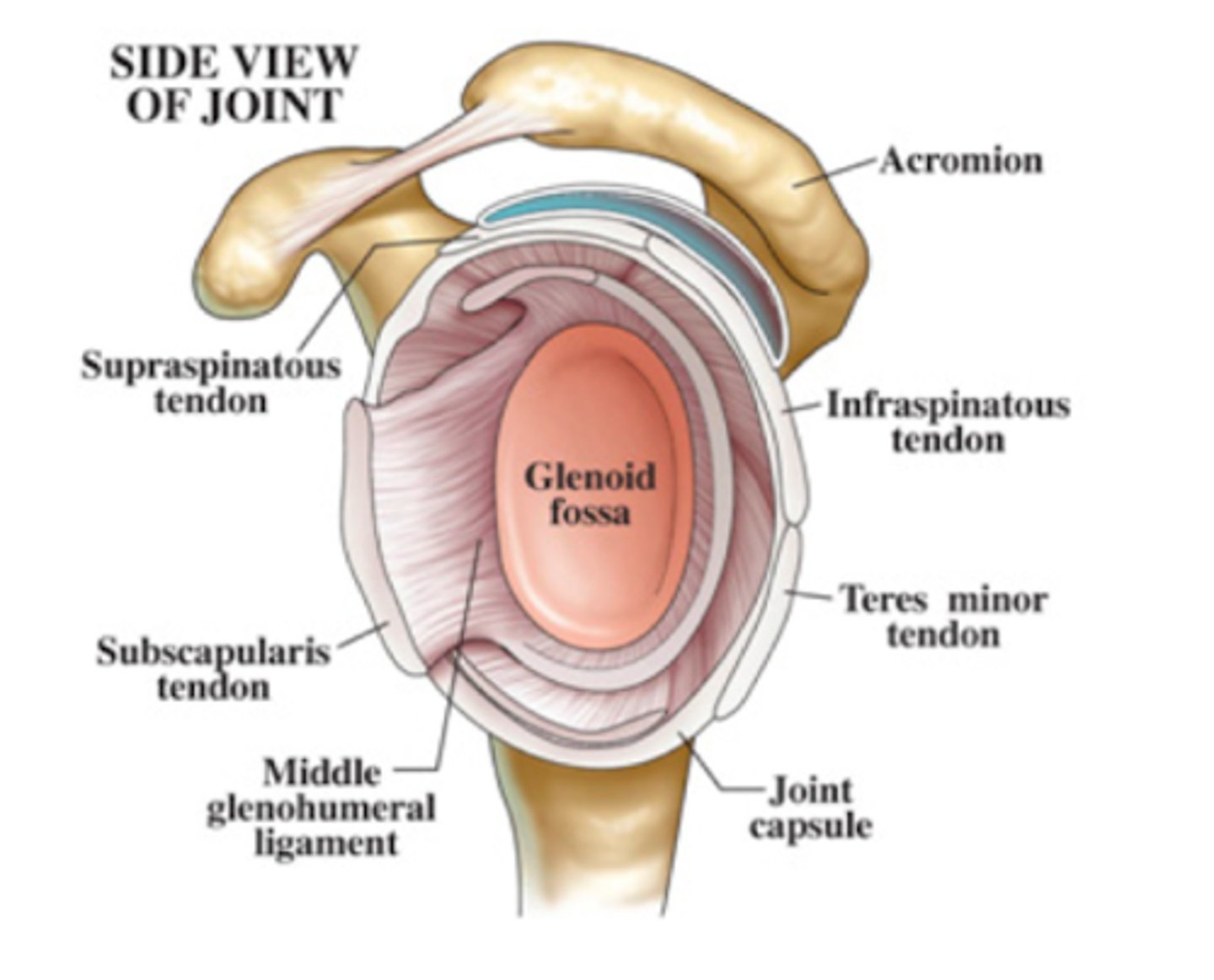
What does SITS stand for?
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres minor
Subscapularis
*4 muscles that compose the rotator cuff
The tendon of the long head of biceps runs ______ to the humeral head and is held in place by what ligament?
anterior; held by the transverse humeral ligament
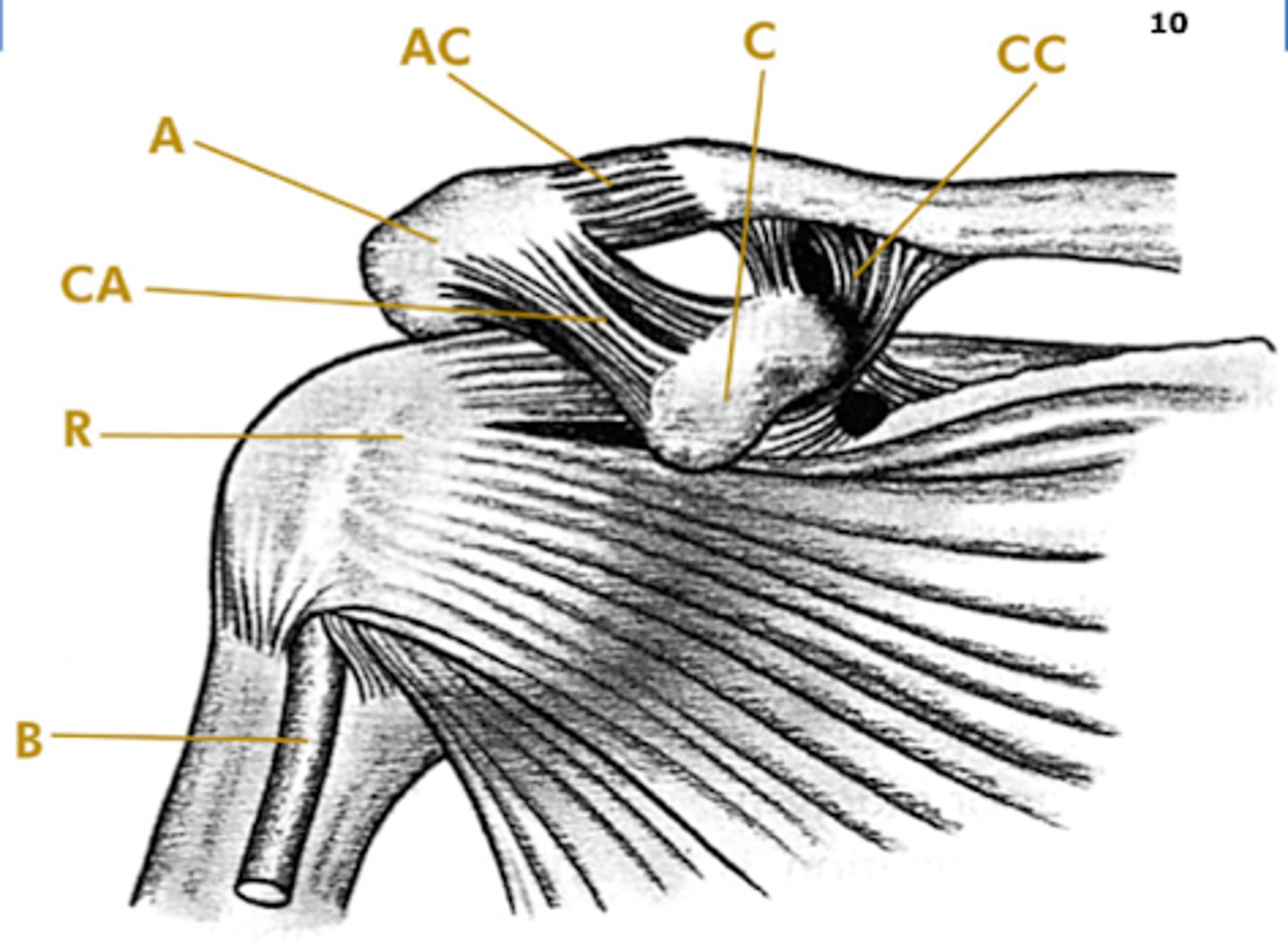
REVIEW: Bones and Ligaments of the Shoulder.
B → Long head biceps
CC → coracoclavicular ligaments
A → acromion
C → coracoid process
CA → coracoacromial ligament
AC → acromioclavicular joint capsule
What degrees of ADDUCTION does the shoulder have?
45
What degrees of ABDUCTION does the shoulder have?
180
What FOUR muscles participate in shoulder ABDUCTION?
Supraspinatus (0-30)
Deltoid (30-100)
Trapezius + levator scapulae (100-180)
What degrees of FLEXION does the shoulder have?
180
What degrees of EXTENSION does the shoulder have?
45
What degrees of INTERNAL ROTATION does the shoulder have?
75
What degrees of EXTERNAL ROTATION does the shoulder have?
80
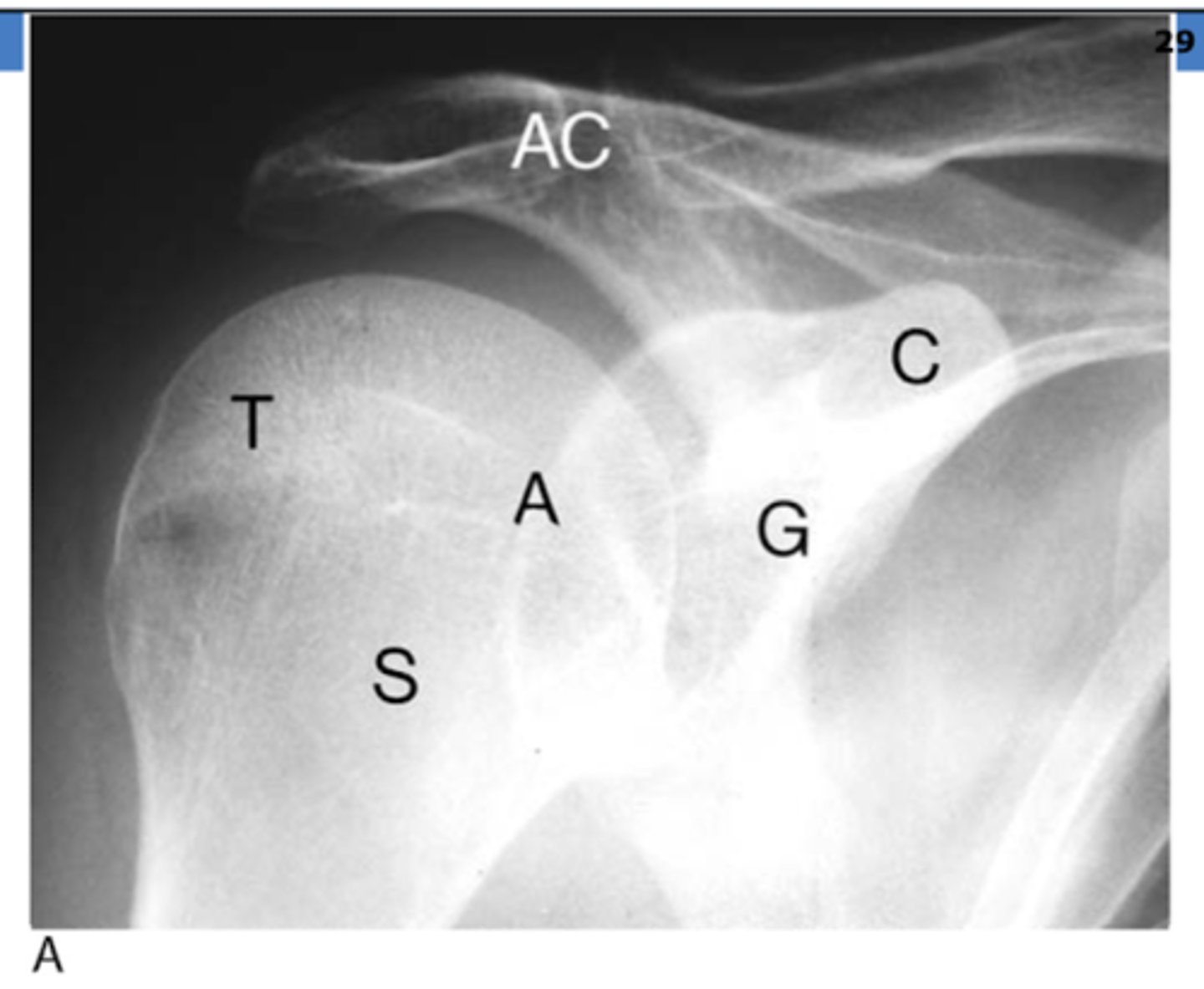
REVIEW: Shoulder XR (AP view)
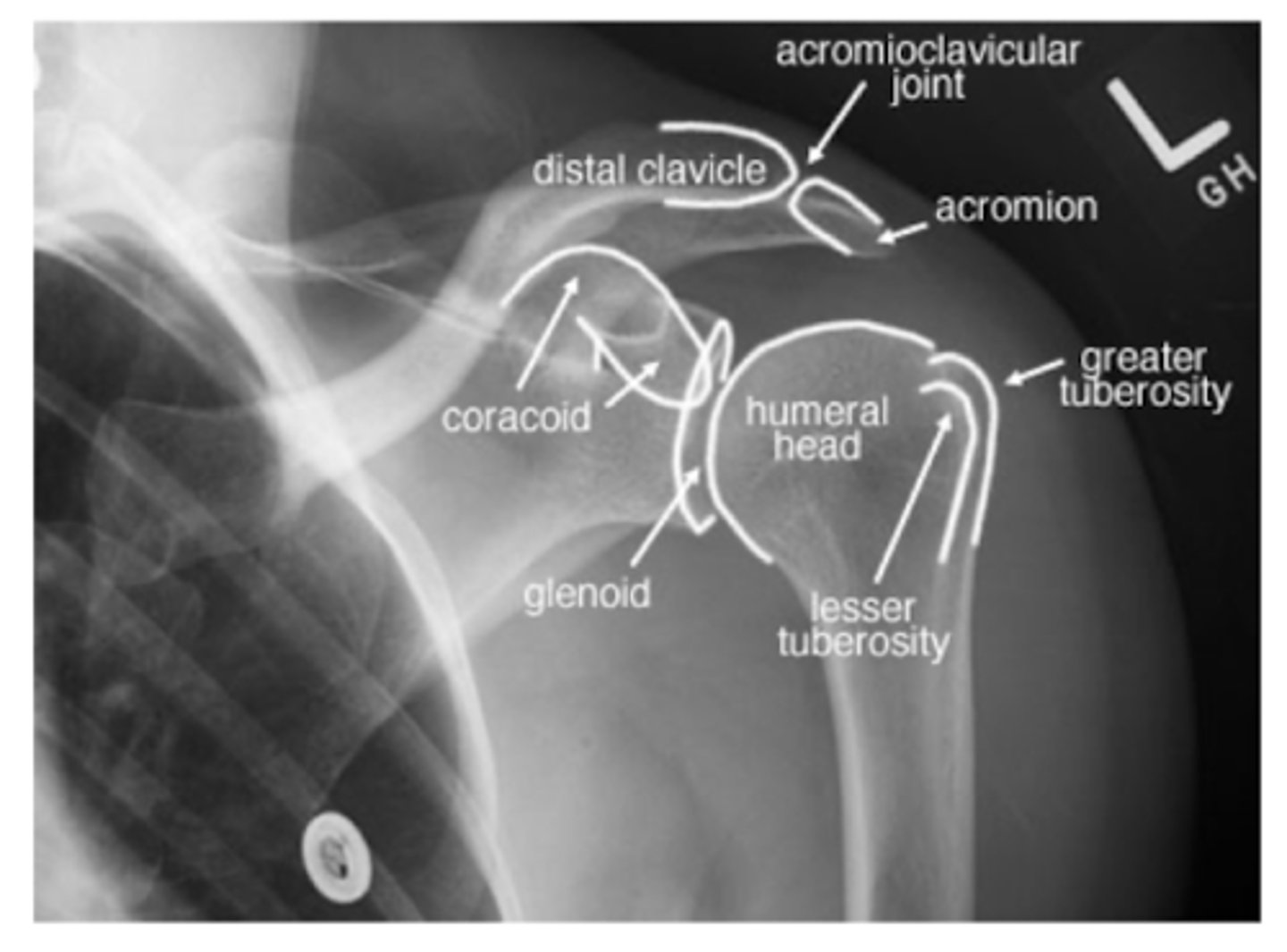
REVIEW: Shoulder XR (AP view - II)
T → greater tuberosity
S → surgical neck of humerus
A → anatomical neck of humerus
G → glenoid fossa
C → coracoid process
AC → acromion process
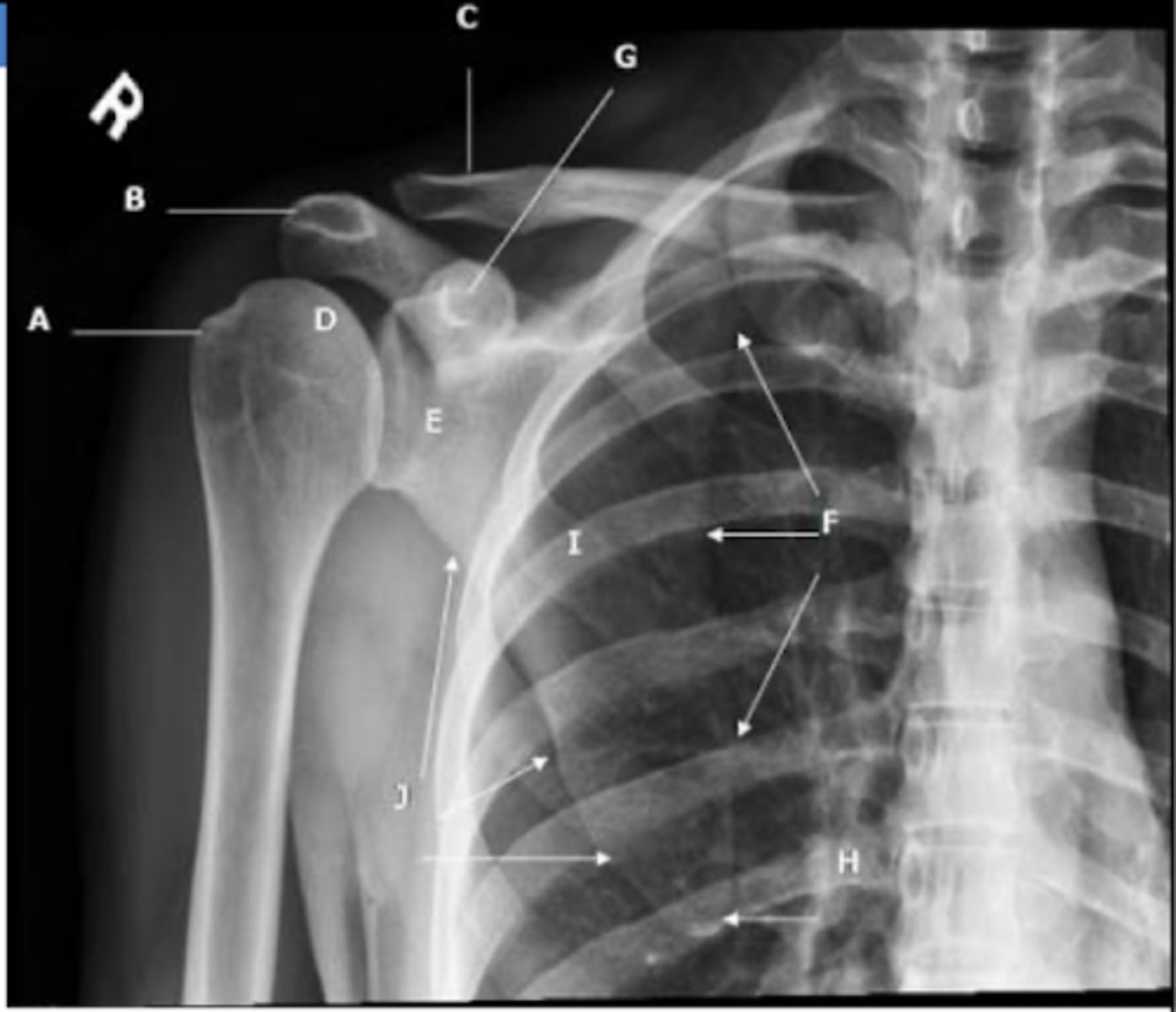
REVIEW: Shoulder XR (AP view - III)
A → greater tubercle
B → acromion
C → clavicle
D → humeral head
E → glenoid process
F → medial/vertebral border of the scapula
G → coracoid process
H → inferior angle of scapula
J → axillary/lateral border of scapula
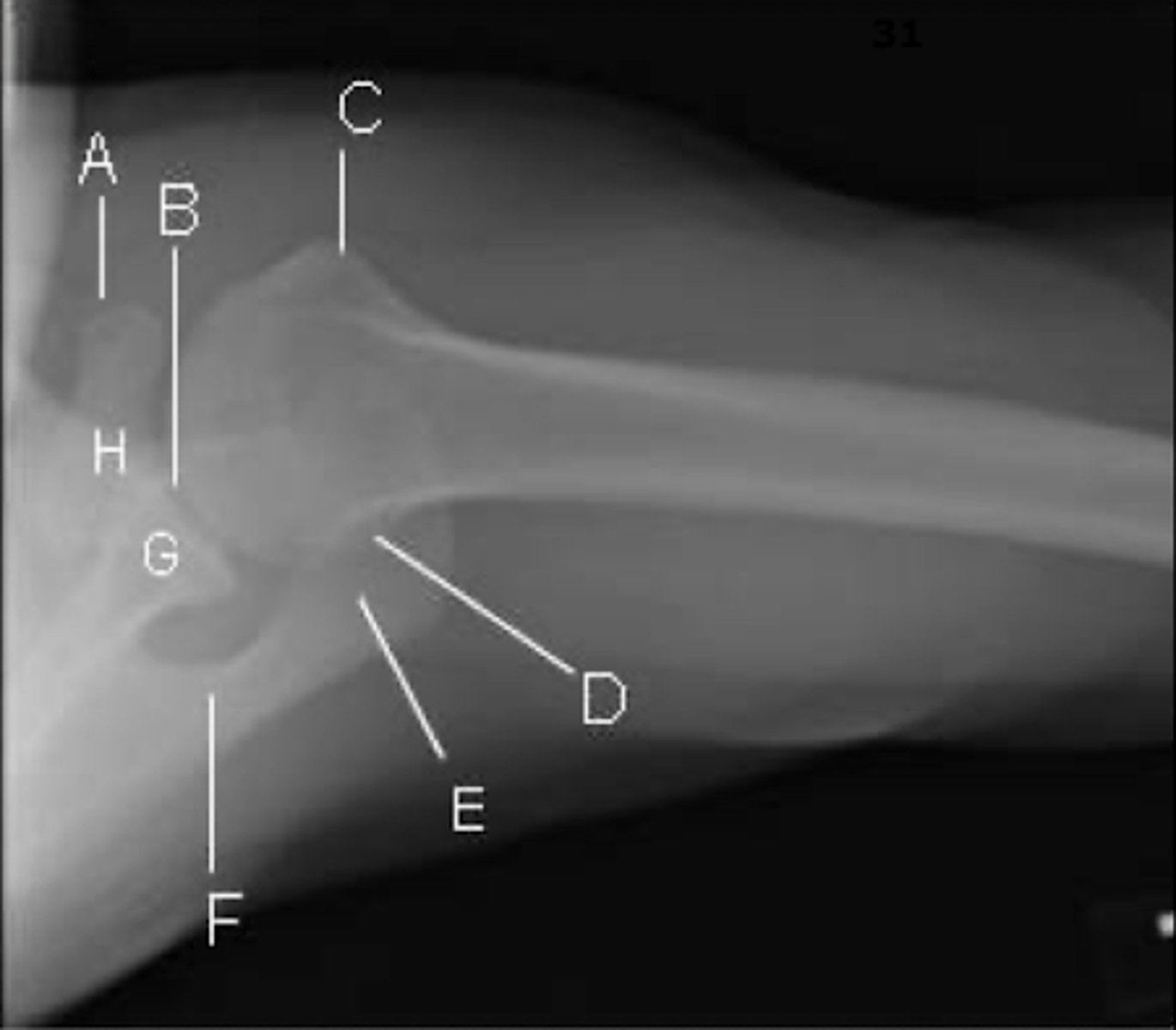
REVIEW: Shoulder XR (Axillary view)
A → coracoid process
B → glenohumeral joint
C → less tubercle
- externally rotated so will look more anterior
D → posterolateral humeral head
E → acromion
F → spine of the scapula
G → glenoid process
H → base of the coracoid
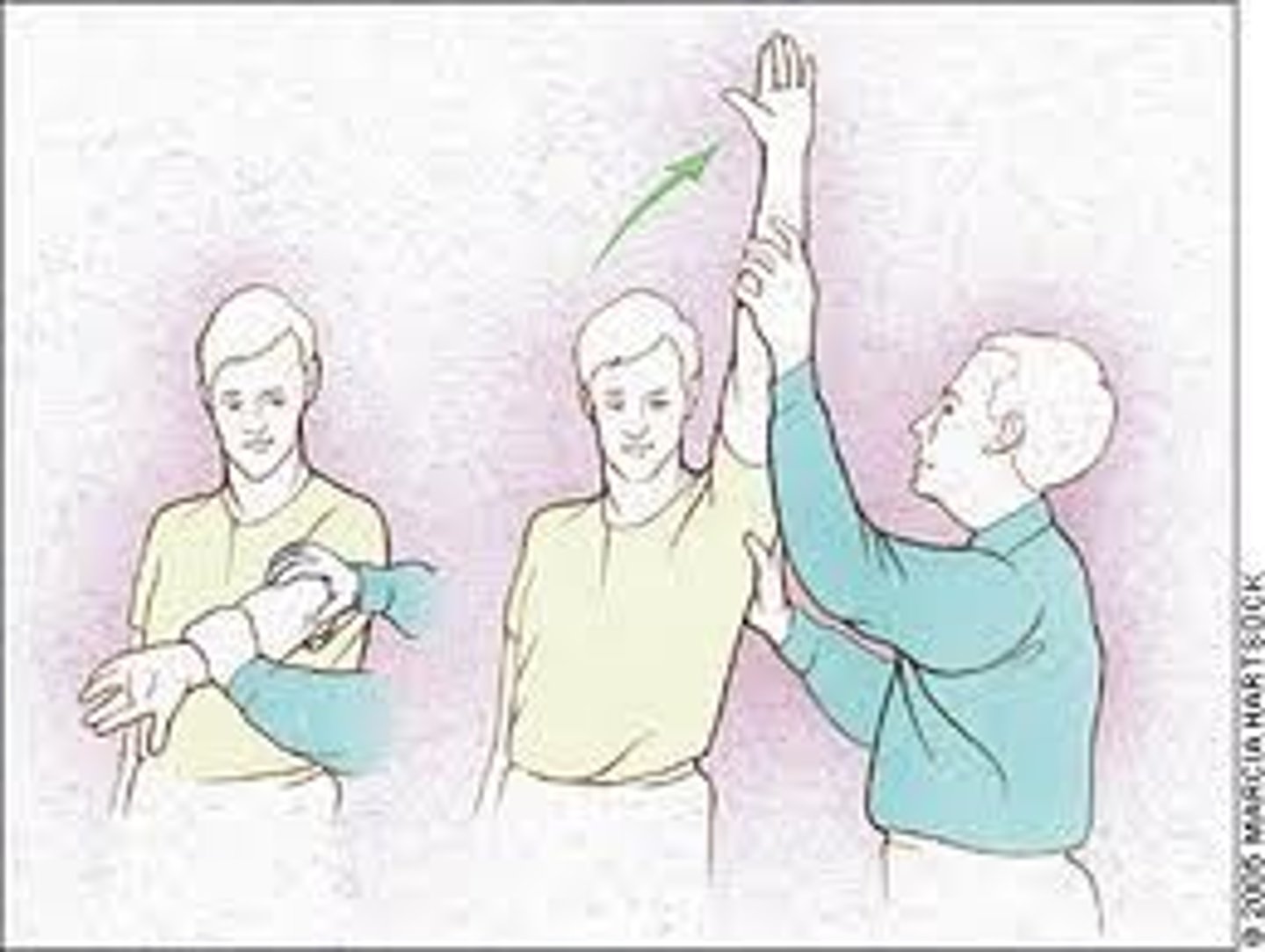
What special test can evaluate for impingement of structures passing under the coracoacromial ligament?
Neer's
What TWO special tests can be used to reinforce a (+) Neer's?
Hawkins
Kennedy impingement
What term can be used to describe arthritis of the shoulder due to destruction of joint cartilage?
glenohumeral arthritis
Where is GH arthritis most common?
posterior aspect of the shoulder
T/F. RA will typically present with multiple joint involvement - often bilaterally.
TRUE
Which shoulder XR view is more reliable?
axillary view
What SIX findings on diagnostic studies suggests an RTC deficiency?
Flattening of the humeral head
Joint space narrowing (<7mm)
Cartilage destruction
Erosion
Osteopenia
Superior migration of the humeral head
**rotator cuff syndrome
What can be used in the treatment of shoulder arthritis?
NSAIDs
Heat and/or ice
Stretching exercises
Glucosamine and/or chondroitin sulfate
Steroid injections
- can be detrimental for RTC deficiency (limited use)
If advanced → TSA or reverse TSA
What are TWO rotator cuff syndromes?
Shoulder impingement
Rotator cuff tear
What causes shoulder impingement (RTC tendinitis)?
occurs when the supraspinatus tendon is pulled under the coracoacromial arch
What are the FOUR components of the coracoacromial arch?
Coracoid process
Coracoacromial ligament
Acromion
AC joint capsule
Inflammation of the subacromial bursa and RTC tendons is most commonly seen in what population?
middle age patients
What FOUR symptoms can present with shoulder impingement?
Anterior + lateral shoulder pain
Worse with overhead activity + lowering arm
Night pain + difficulty sleeping on affected side
What THREE special tests if (+) suggest shoulder impingement?
Neer's
Hawkin's
Empty can test
What special test if (+) suggest supraspinatus tendon weakness/tear/irritation?
Empty can test
** (+) → pain
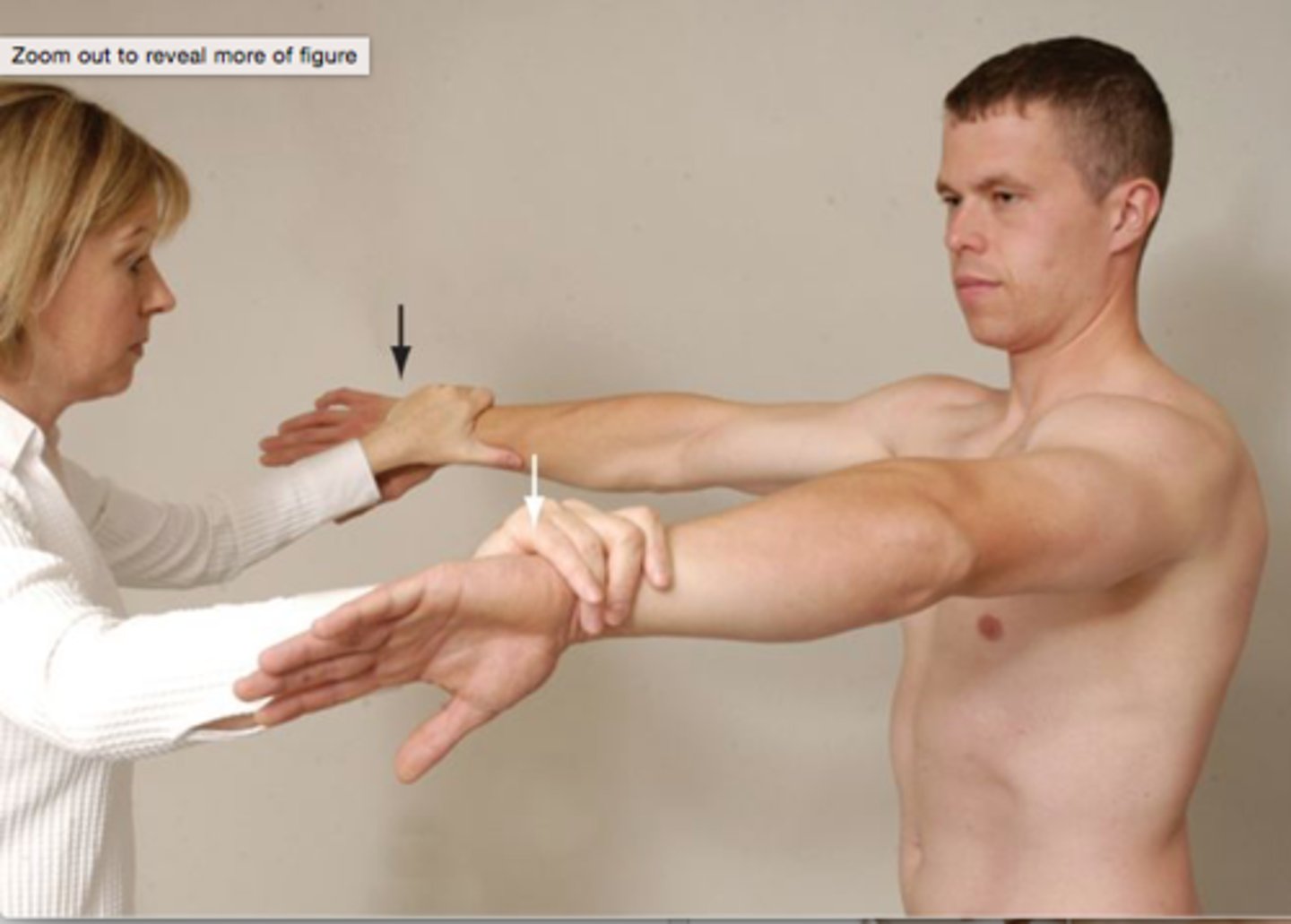
Shoulder impingement commonly presents with what type of arthritis?
RA
What can be used in the treatment of shoulder impingement?
NSAIDs
Rest
Stretching/Strengthening exercises
Subacromial steroid injections
What does atrophy of muscles on the top and posterior aspect of the shoulder suggest?
RTC tear
What population most commonly presents with full-thickness RTC tears?
>60 year olds
What THREE symptoms can present with a RTC tear?
Shoulder pain
- worse at night
"Catching" or "Grating" during overhead use
Decrease in ROM
- Abduction and lateral weakness
If the back of the shoulder appears SUNKEN, what does it suggest?
weakness of the infraspinatus muscles
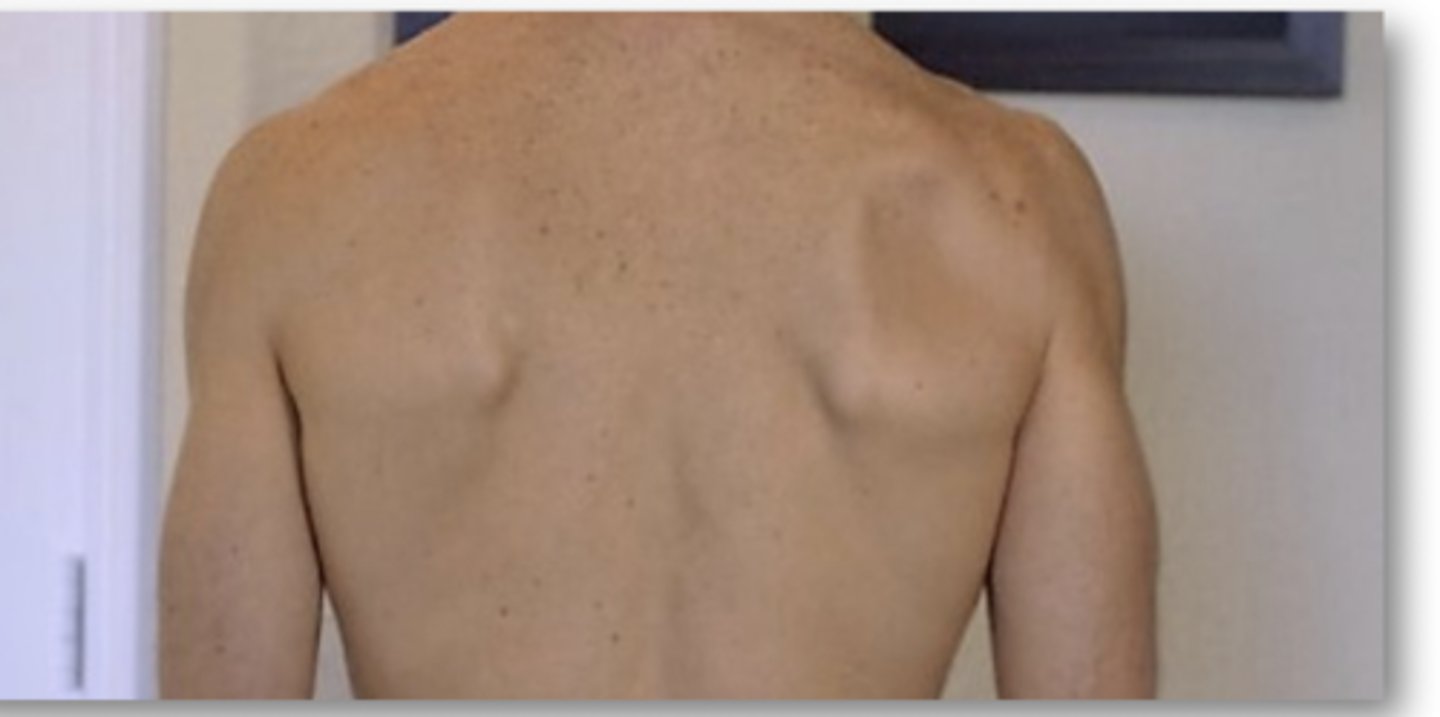
What FIVE special tests if (+) can suggest RTC tear?
Neer's
Hawkin's
IR Lag sign
ER Lag sign
Drop arm test
- unable to hold arm up
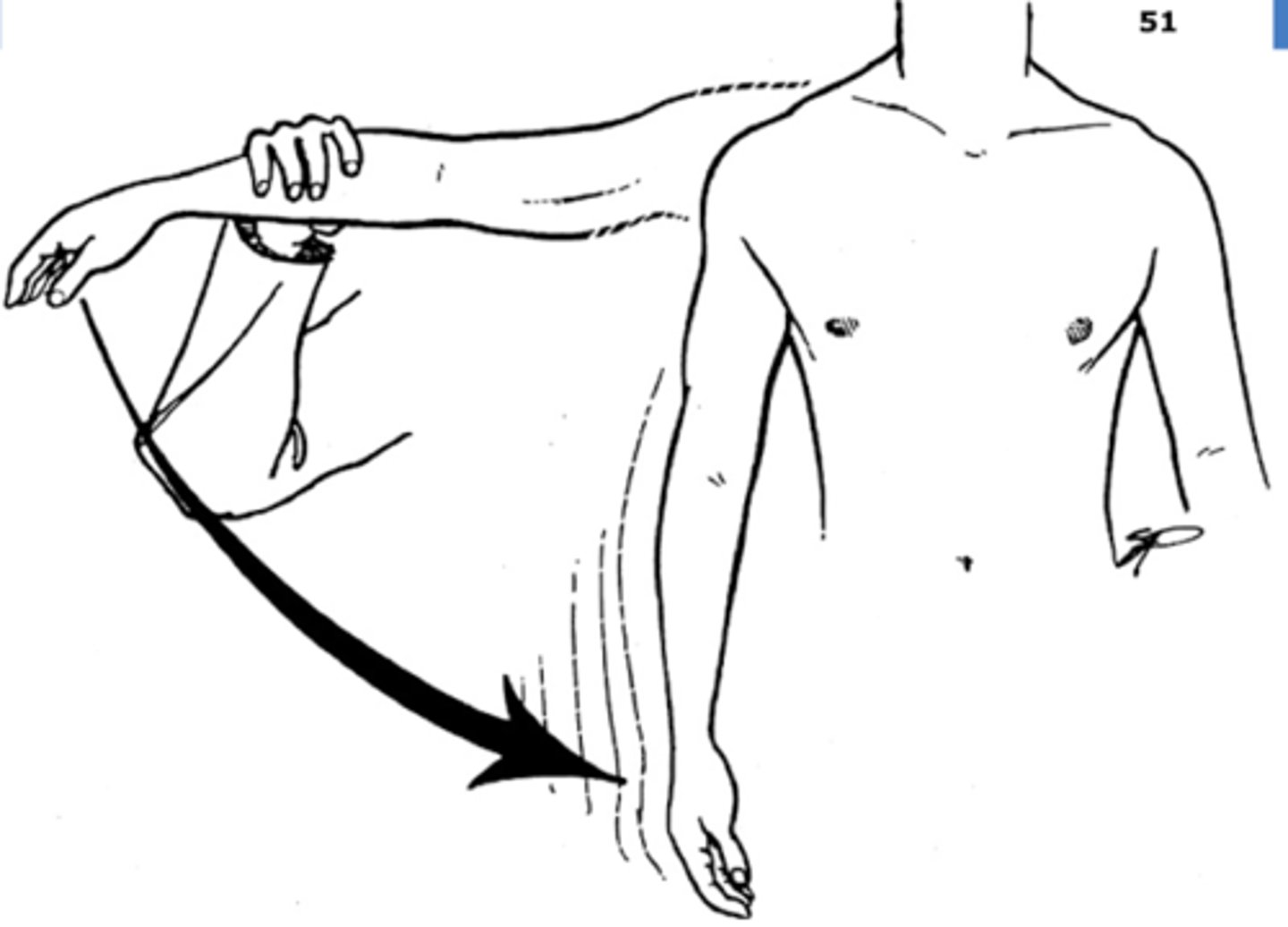
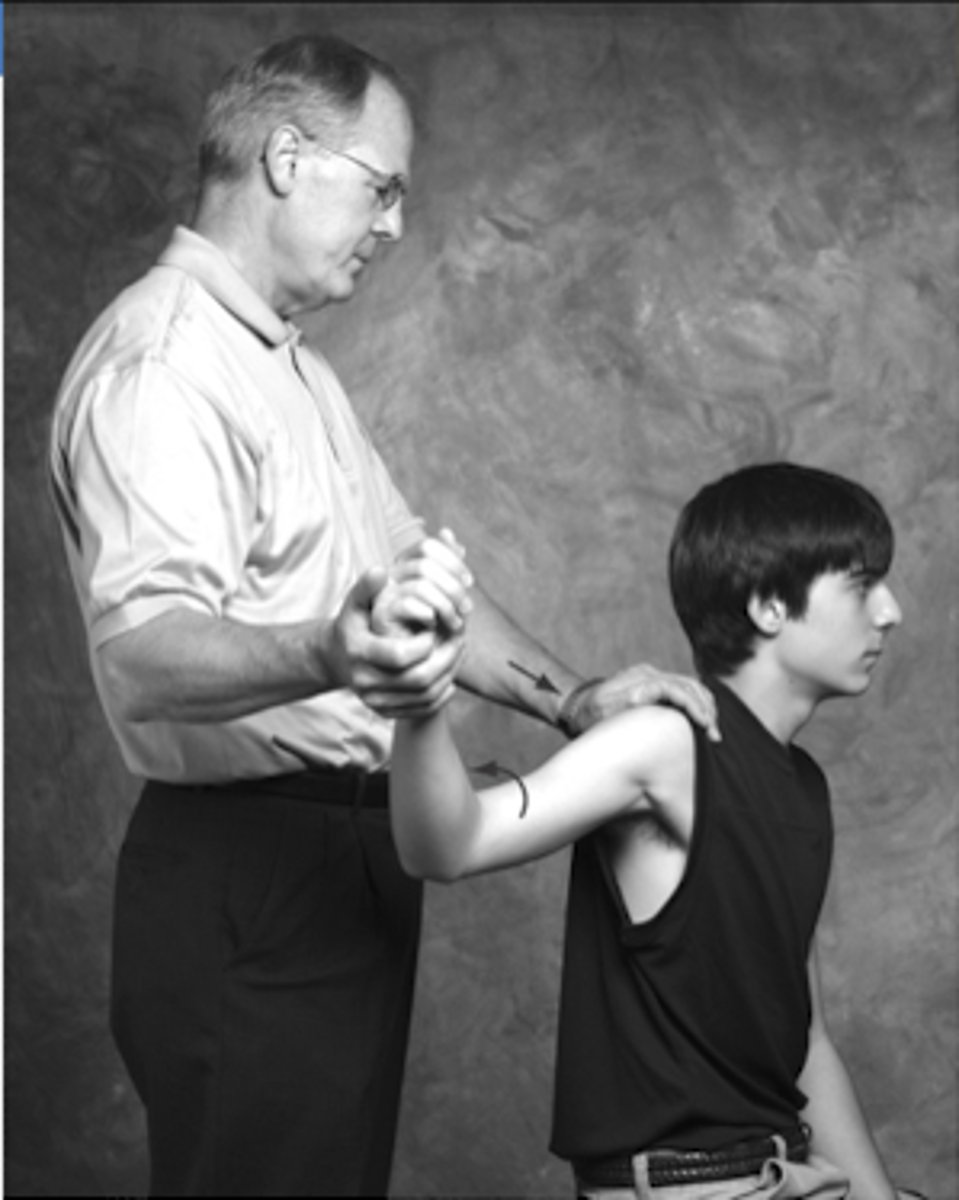
What special test can be used to evaluate the integrity of the external rotators?
external rotator lag
**infraspinatus + TM
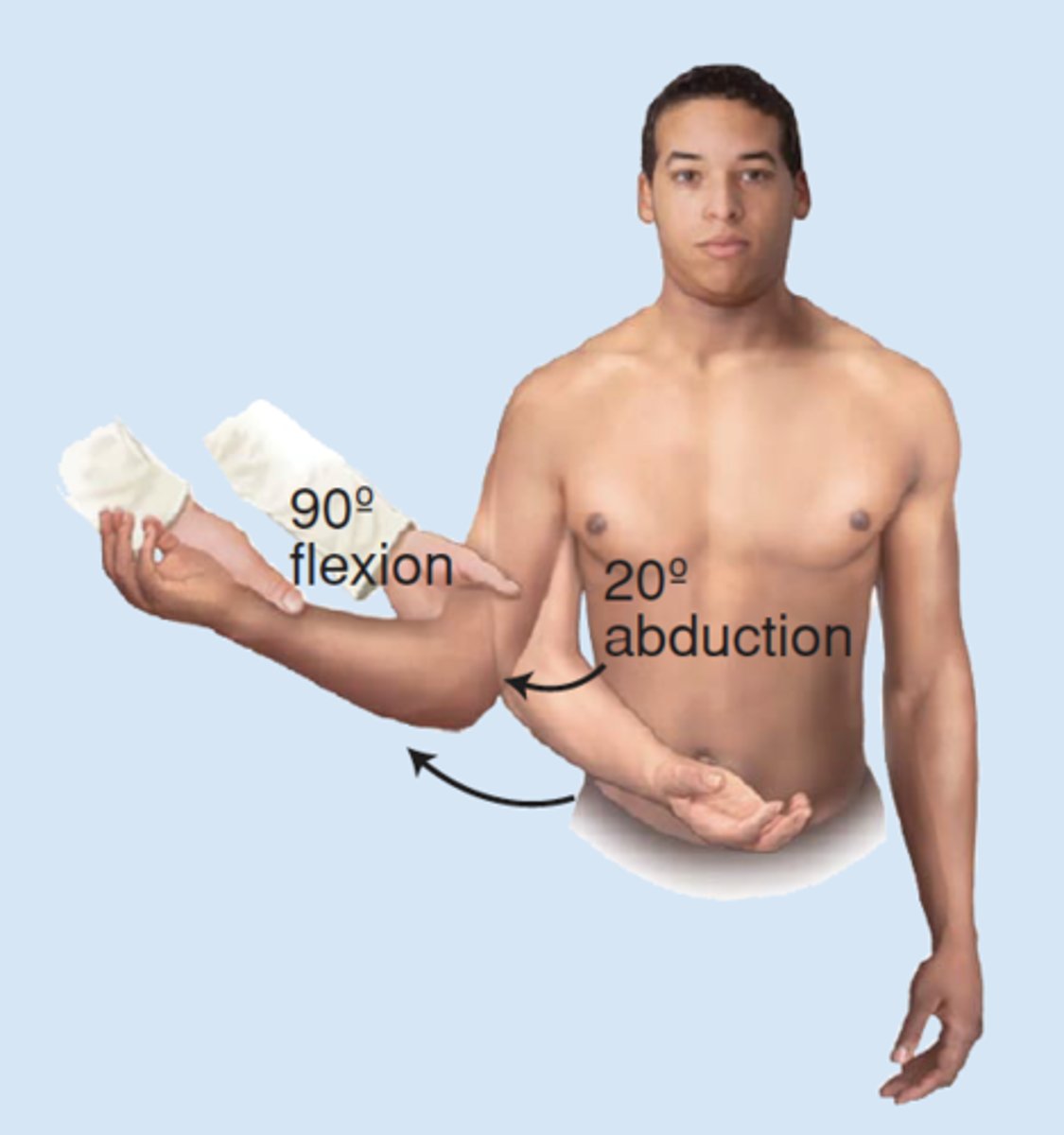
What special test can be used to evaluate the integrity of the internal rotator?
internal rotator lag (lift off test)
**supraspinatus
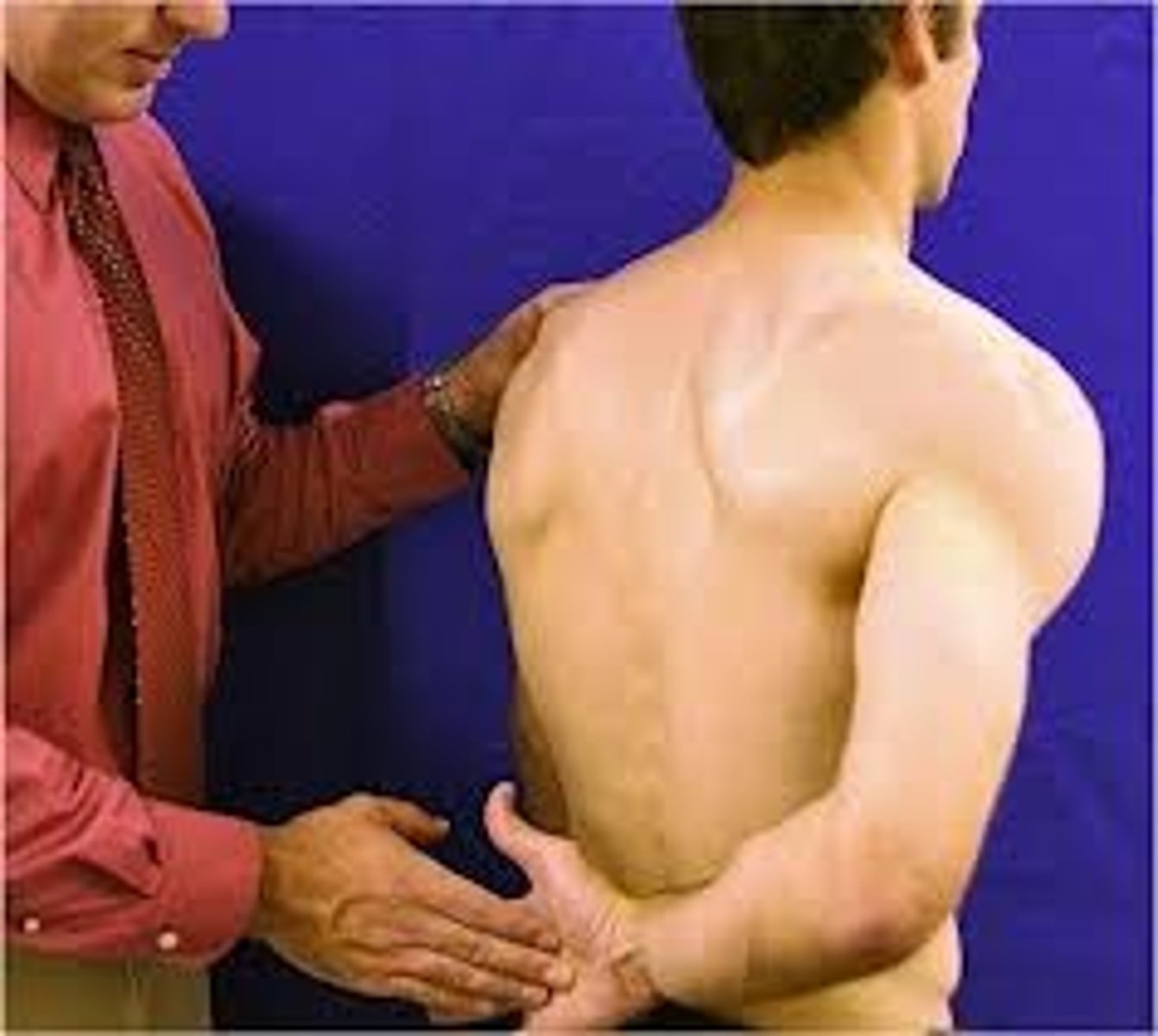
What muscle does the drop arm test evaluate?
supraspinatus
What diagnostic imaging study can CONFIRM the presence of a RTC tear?
MRI
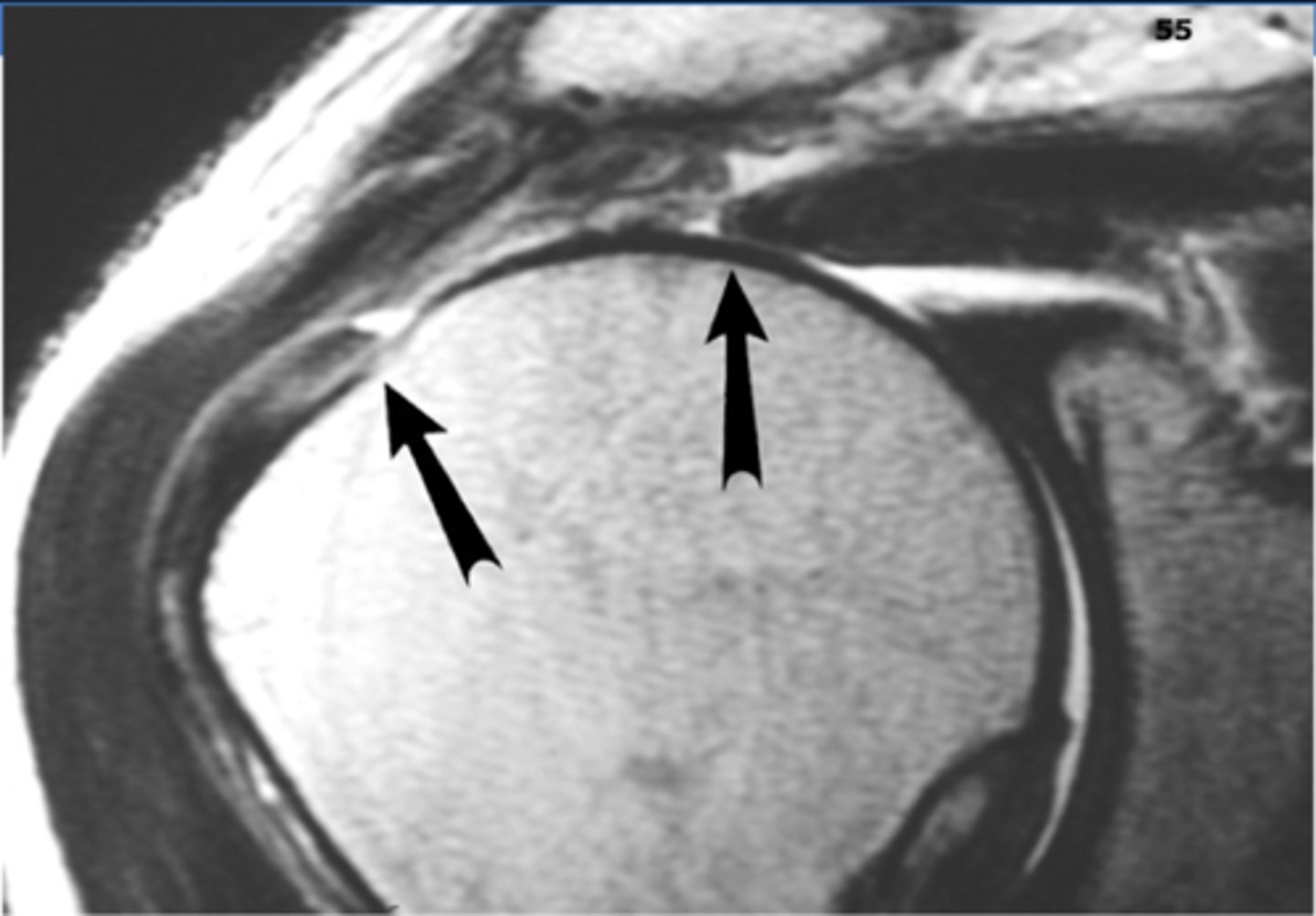
What is recommended in the treatment of a RTC tear?
NSAIDs
PT
Steroid injections (limited)
Surgery if fail rehab or traumatic
What shoulder tendon is most typically affected by calcific tendonitis?
supraspinatus
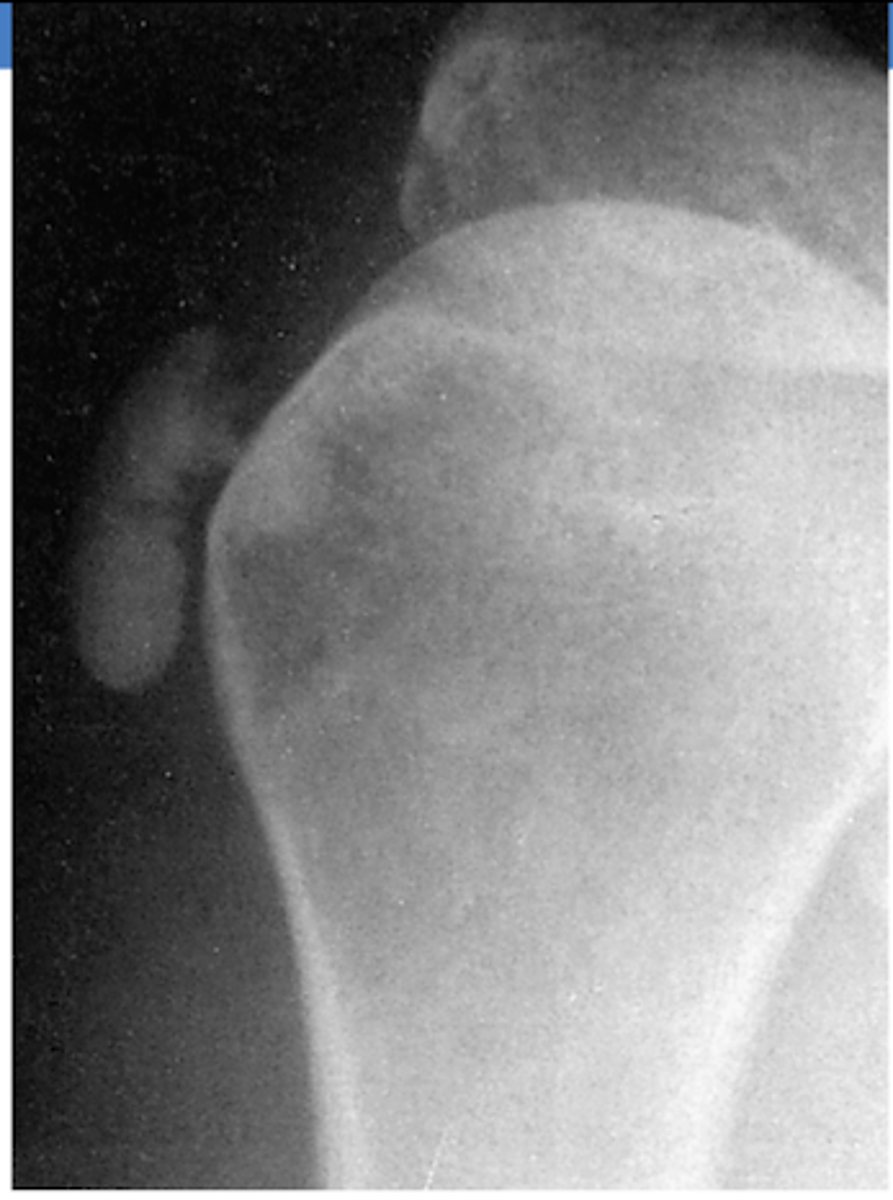
What is the most common symptom of bicipital tendonitis?
pain in the anterolateral aspect of the shoulder
**common in young athletes
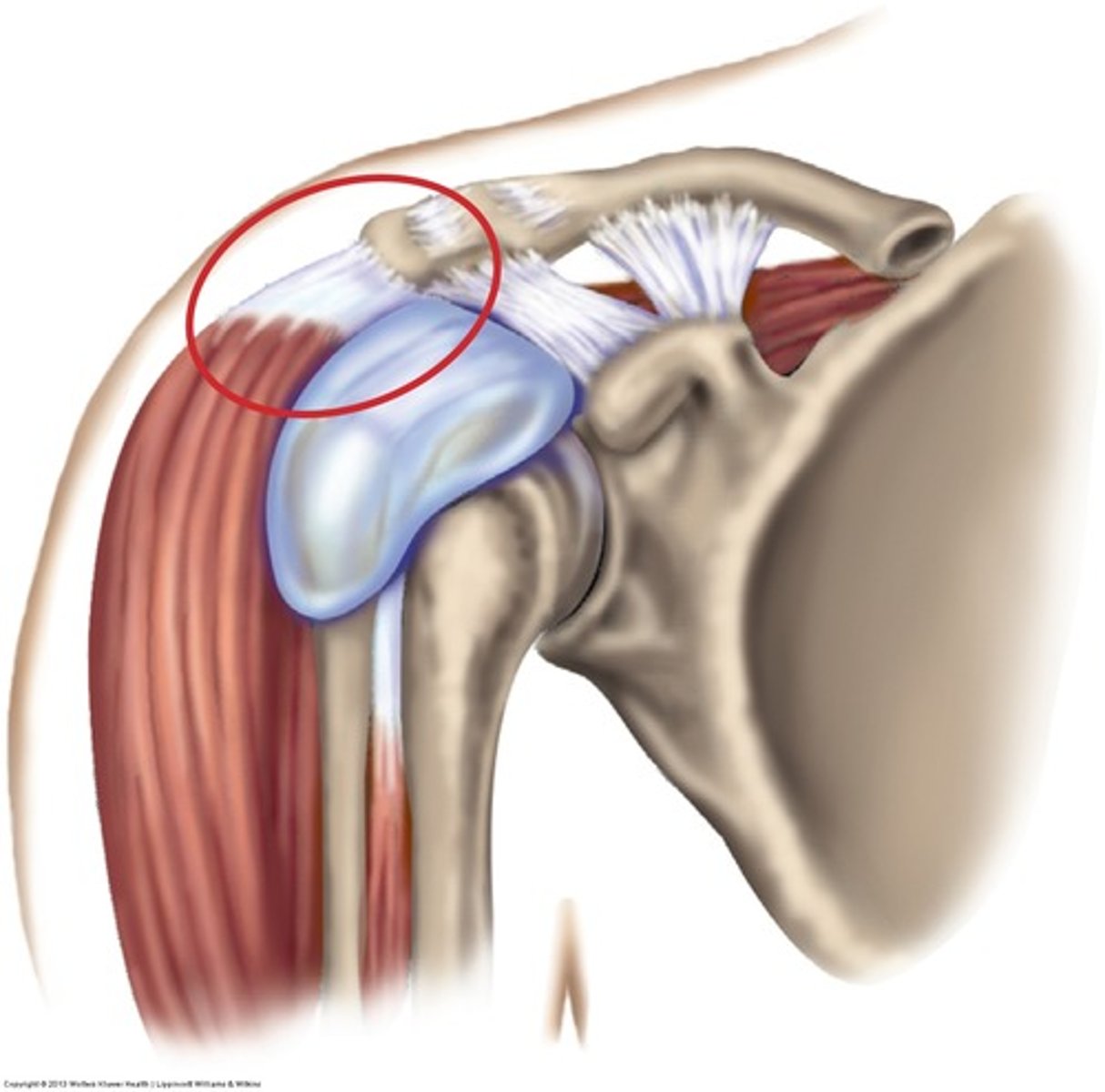
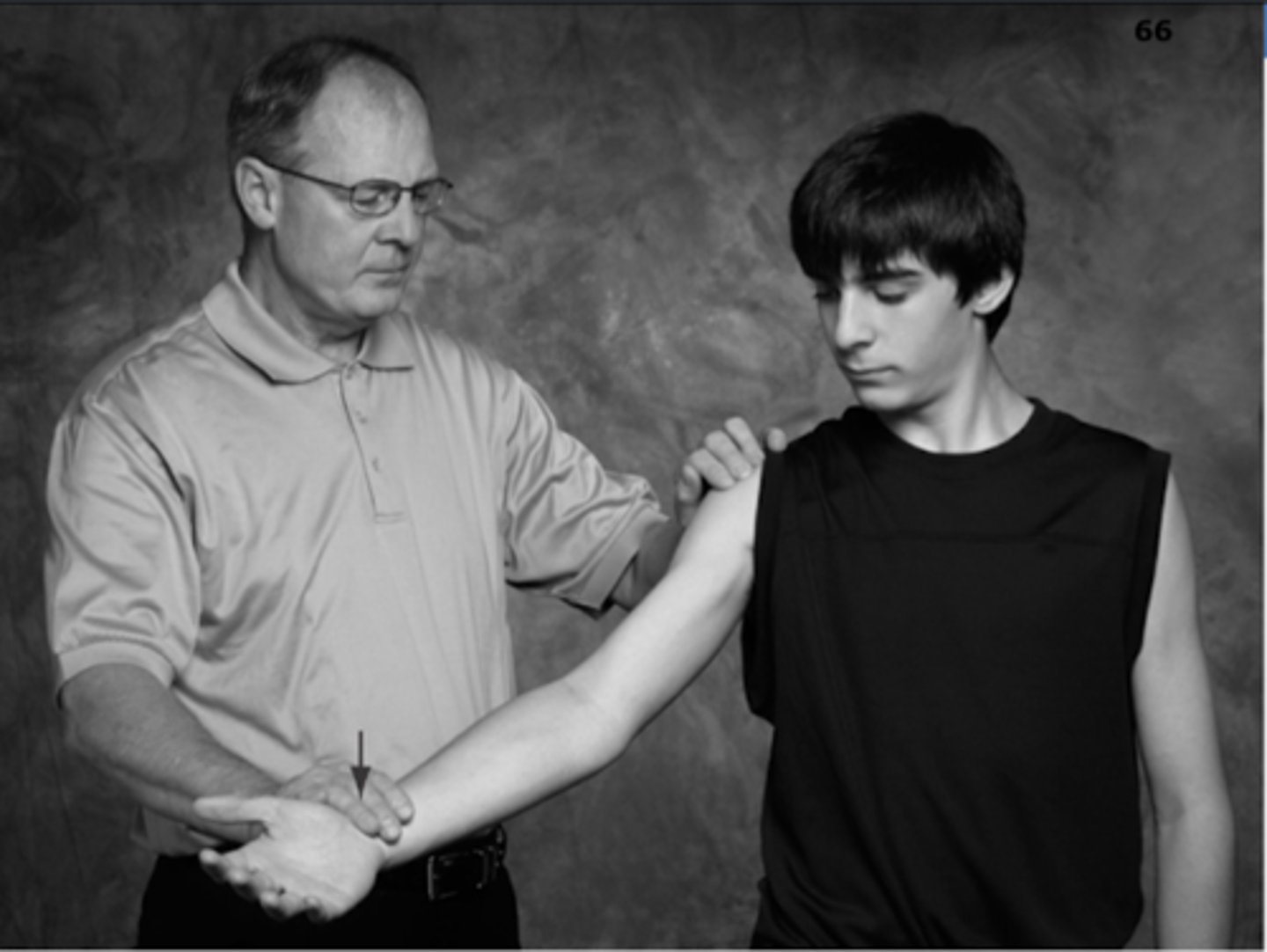
What special test if (+) suggests bicipital tendonitis?
Speed's test
- elevation against resistance
(+) = pain
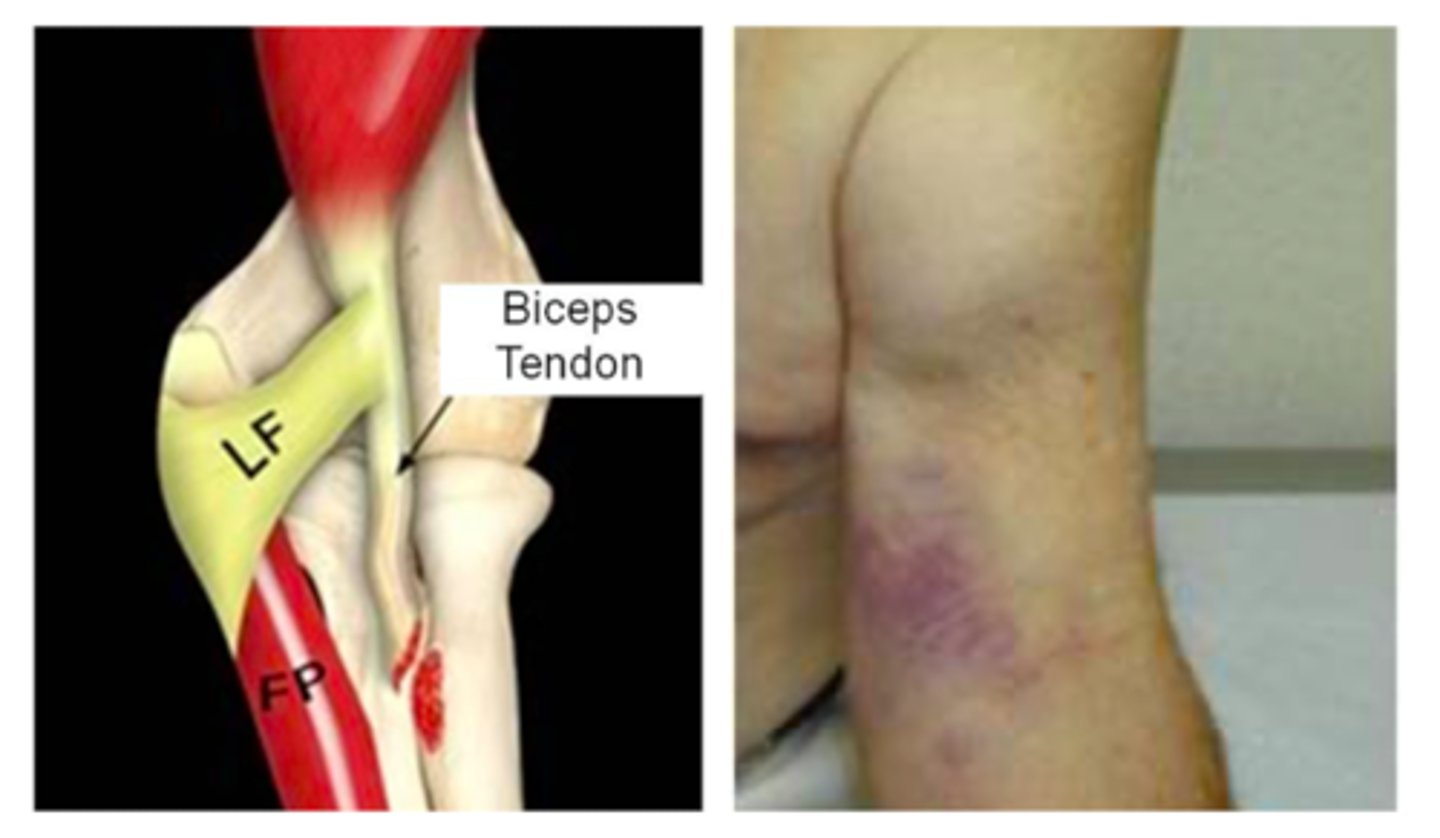
If a young patient with a Hx of heavy lifting presents with a large mass in the shoulder with bruising and a (+) Popeye sign, what is the most likely diagnosis?
biceps rupture
- will feel a pop/snap following by pain
What biceps tendon is most commonly ruptured?
long head (96%)
What FOUR special tests can be used to evaluate the biceps tendons?
Speed's
Yergason's
Ludington's
Lippman's
What TWO procedures are involved treatment of PROXIMAL biceps tendon rupture?
tenodesis
subacromial decompression
What occurs in a tenodesis?
consists of cutting the normal attachment of the biceps tendon on the shoulder socket and reattaching the tendon to the arm bone (humerus)
What is involved treatment of DISTAL biceps tendon rupture in young/athletic patients?
anatomical reattachment
Where on the shoulder does dislocation most commonly occur?
glenohumeral joint
What type of dislocations are most commonly seen in the shoulder?
anterior and multidirectional
If an individual dislocates their shoulder following ABDUCTION + ER, what type of dislocation is present?
anterior
**inferior + medial
If an individual dislocates their shoulder following ADDUCTION + IR, what type of dislocation is present?
posterior
**superior + lateral
What nerve most commonly injured with a shoulder dislocation?
axillary nerve injury
What TWO special tests if (+) suggest a shoulder dislocation?
Apprehension test
Sulcus sign
What special test evaluates the INFERIOR instability of the GH joint?
Sulcus sign
What special test evaluates the MULTIDIRECTIONAL instability of the GH joint?
Rowe's test
What TWO special tests evaluate the anterior/posterior capsular mechanism?
Anterior drawer test
Posterior drawer test
What TWO special tests evaluate for anterior/posterior labrum/capsule instability?
Anterior apprehension test
Posterior apprehension test
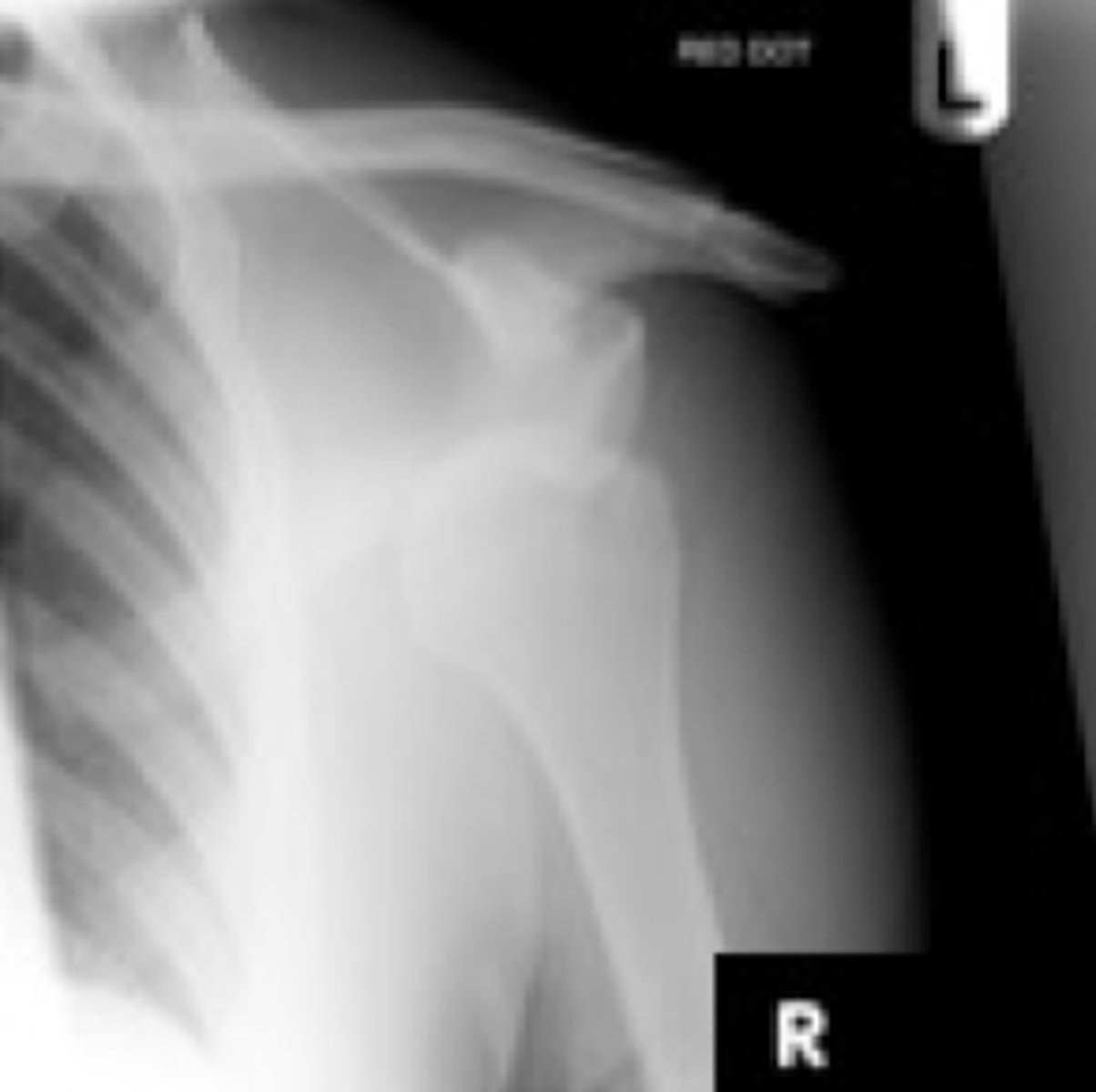
What is a Hill-Sachs lesion?
compression fracture of posterior humeral head due to ANTERIOR dislocation
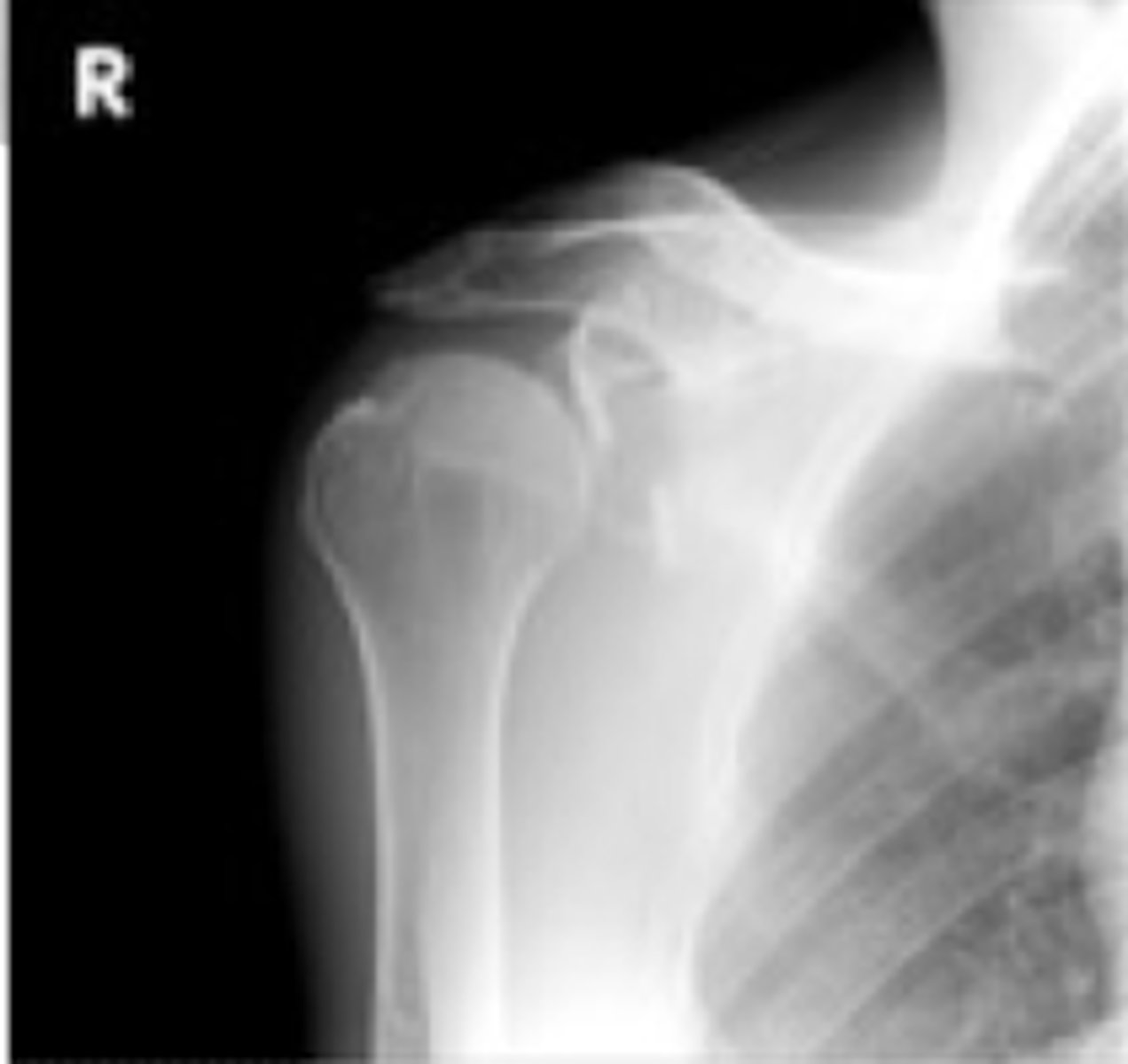
What is a Bankart lesion?
glenoid labrum tear in the anterior joint that occurs due to an ANTERIOR dislocation most commonly
In order to evaluate for a POSTERIOR shoulder dislocation, what XR view must be obtained?
axillary
- if unable → trans-scapular lateral view
What TWO S/S suggest an axillary nerve injury?
deltoid weakness
C5 numbness
What TWO XR findings on AP view suggests a POSTERIOR shoulder dislocation?
light bulb sign (IR of humerus)
rim sign (>6mm joint widening)
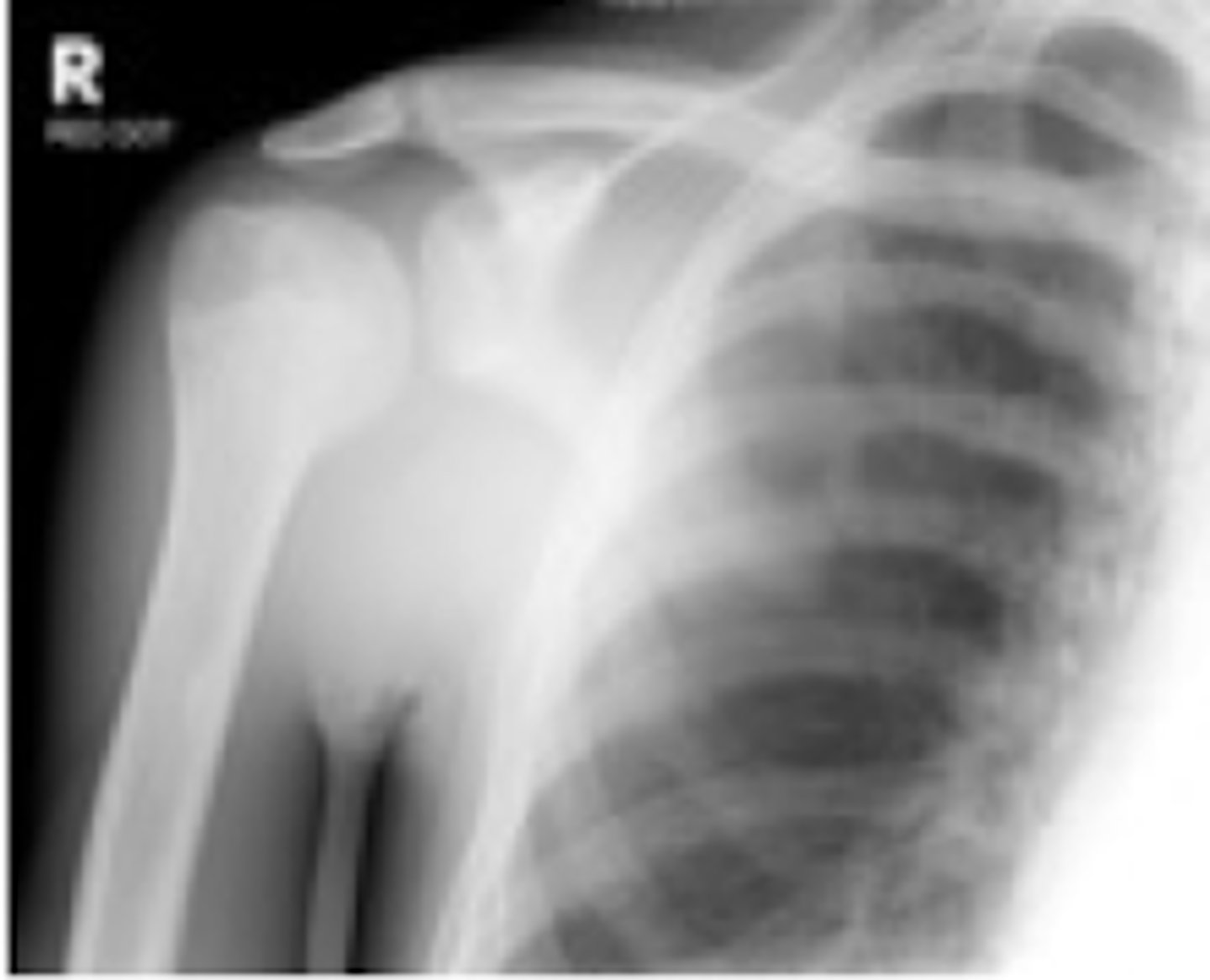
What XR findings on axillary view suggests a POSTERIOR shoulder dislocation?
humeral head will move towards the acromion and away from the ribs
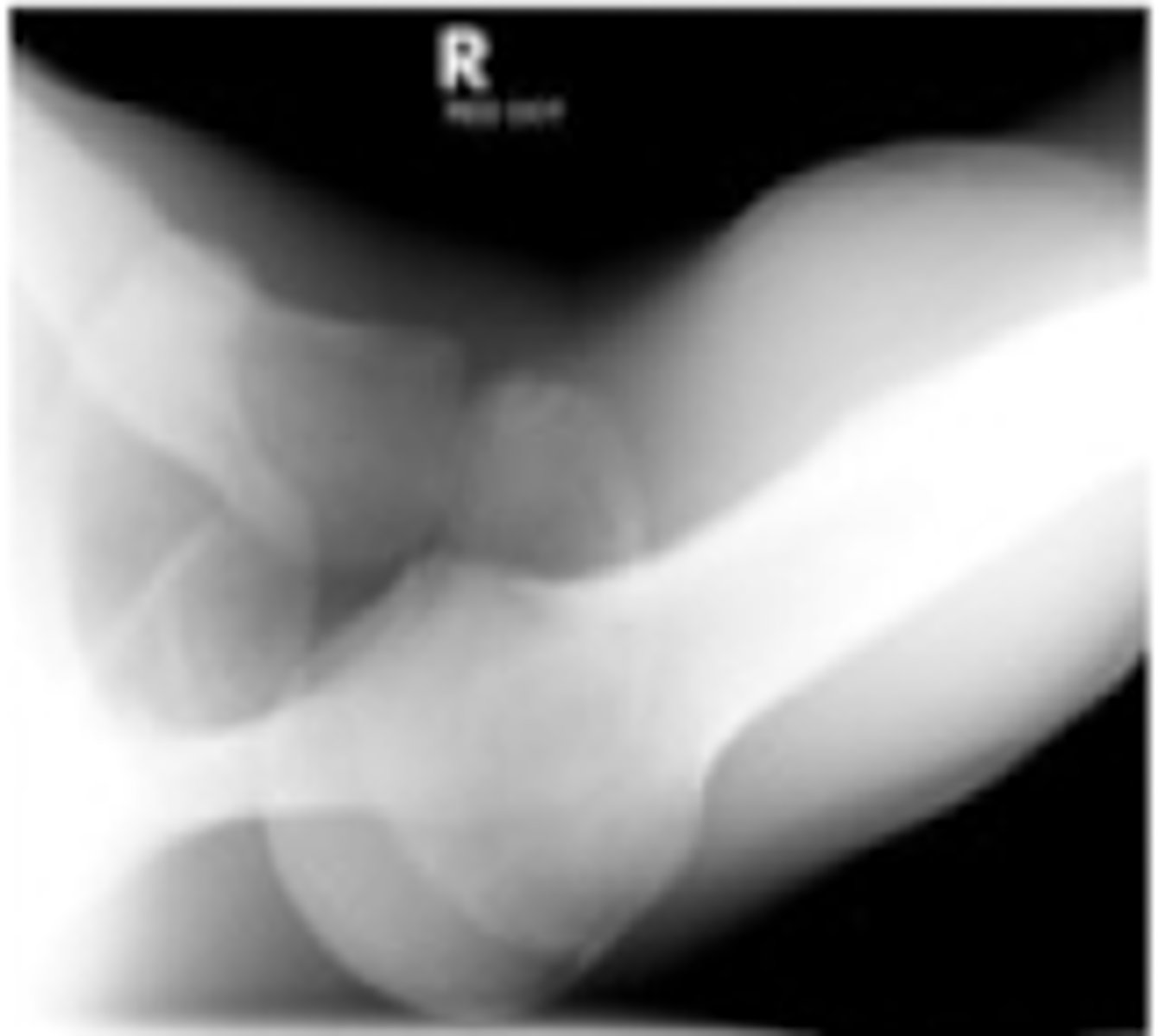
What is the treatment for a shoulder dislocation?
reduction (either Stimson or longitudinal)
PT (after 1-3 weeks of neutral arm position)
A patient with an ANTERIOR dislocation should be immobilized when?
when it is their 1st dislocation
What is the most common method for surgically stabilizing a shoulder prone to ANTERIOR dislocation?
Bankart repair
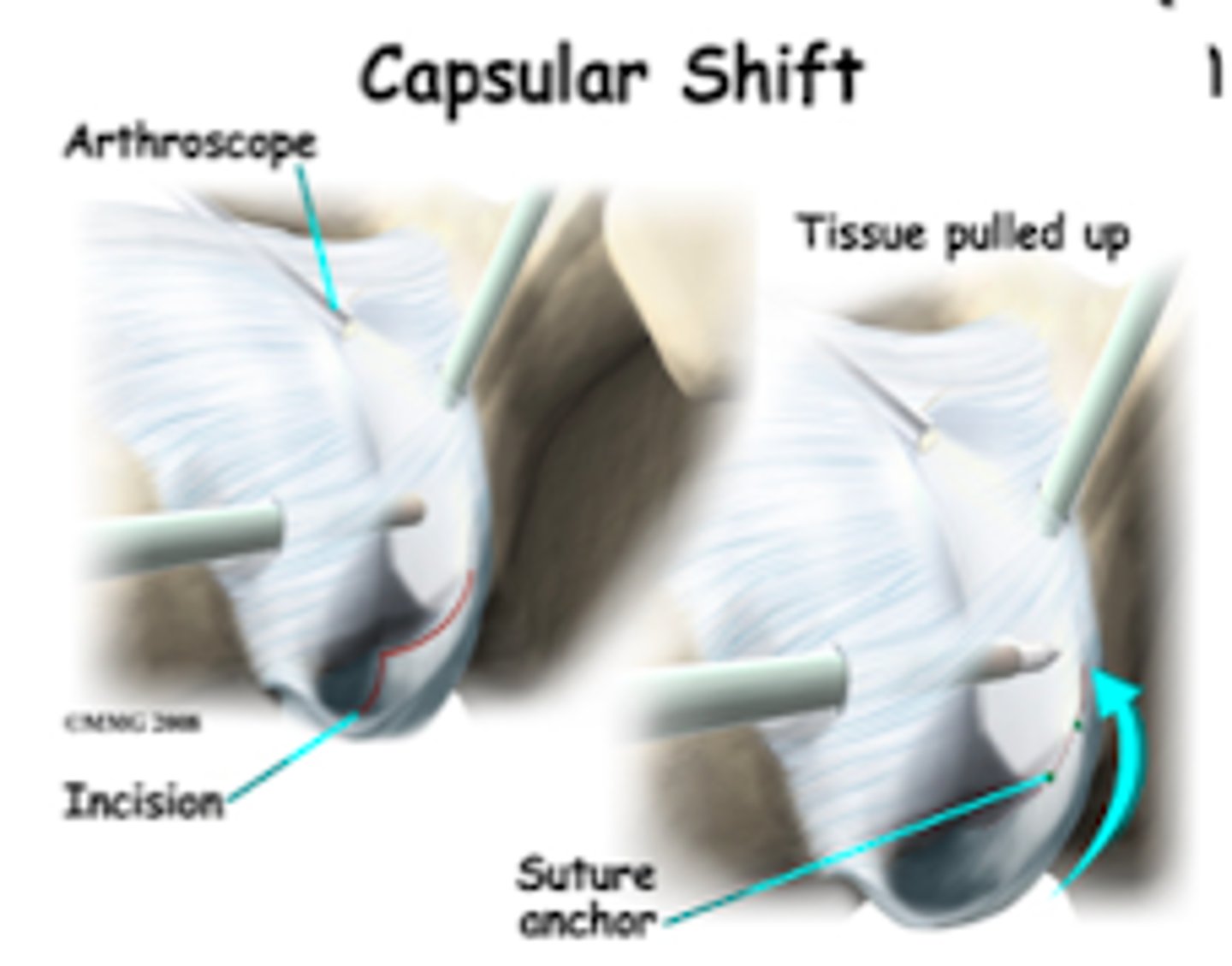
What surgical approach tightens the joint capsule to increase stability?
capsular shift
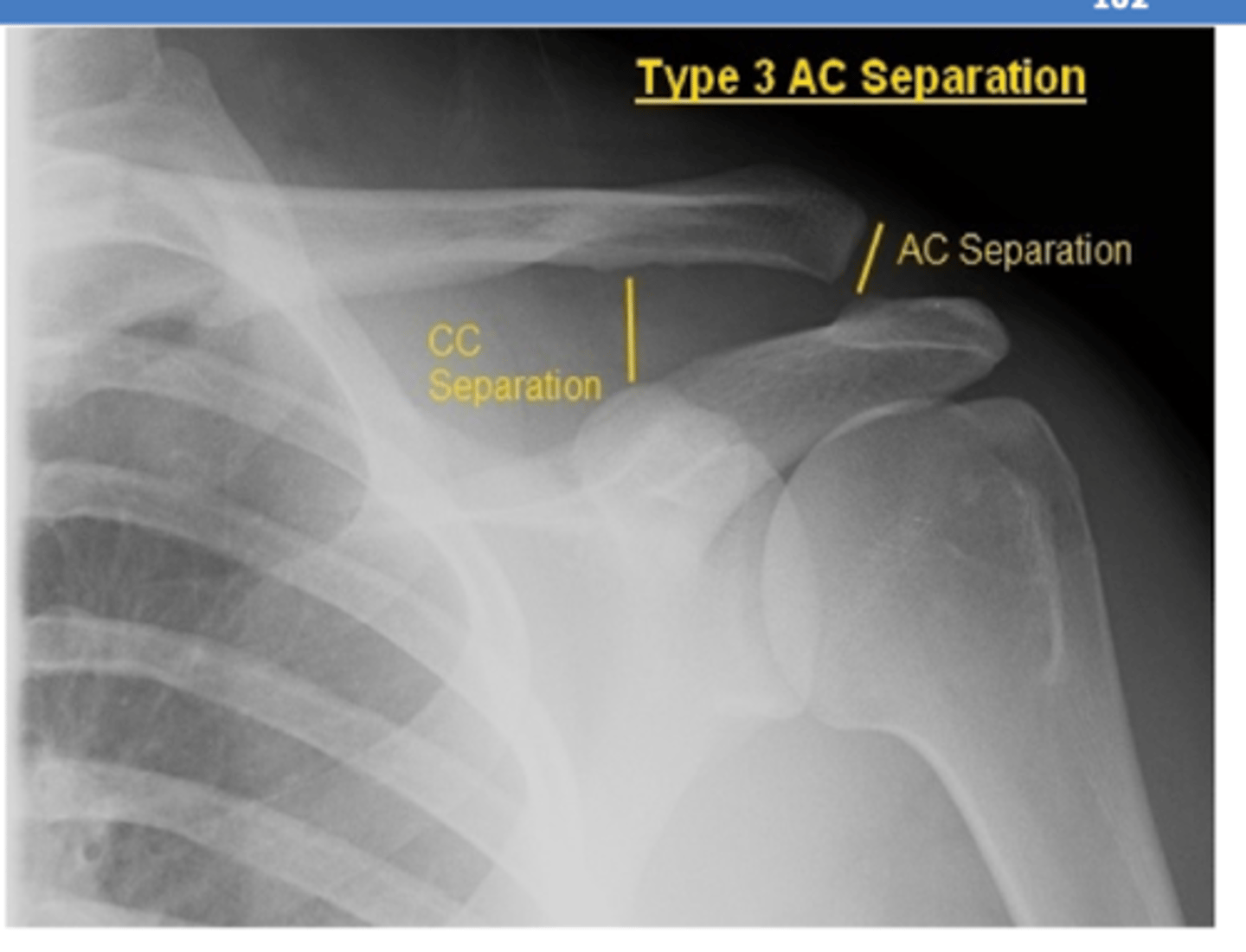
If a patient presents with pain over their AC joint and distal clavicle following fall onto tip of shoulder, what diagnosis is most likely?
AC separation
- will have pain with movement in ALL direction
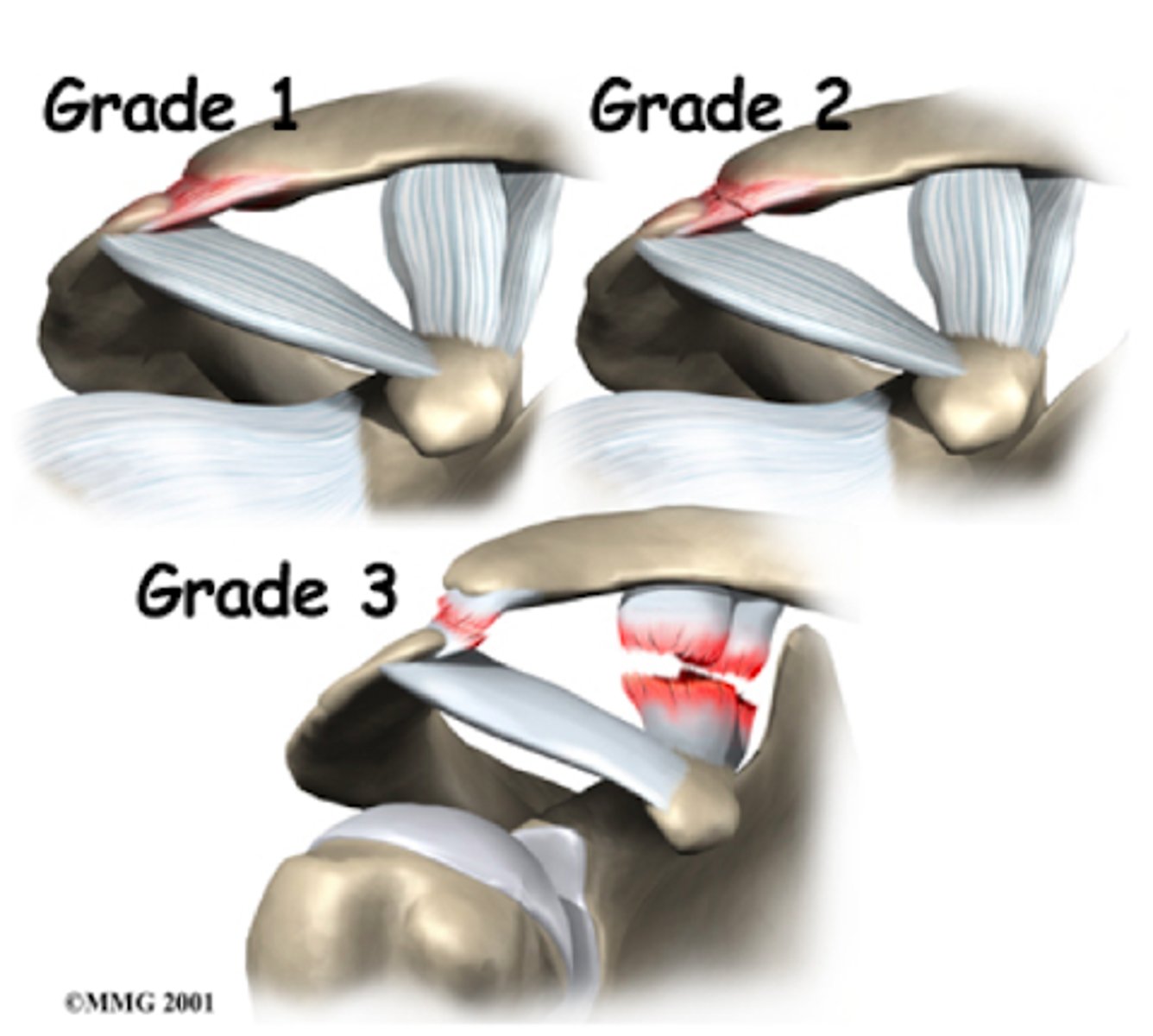
What are THREE most common types of AC separation?
I → partial disruption of AC ligaments; CC ligaments intact
- no separation
II → AC ligaments are torn; CC ligaments intact
- partial separation of clavicle from acromion
III → AC + CC ligaments are torn
- complete separation
**IV-VI = not common
REVIEW: AC joint separation XR.
What TWO special tests can be used to evaluate for AC joint pathologies?
Crossover/Adduction test
O'Brien's test
What is the treatment for Type 1-3* AC separation?
Wear sling
Ice
Analgesics
Activity as tolerated
What is the treatment for Type 4-6 AC separation?
surgical repair
**3 might also need surgical repair
What is the most common risk factor for a frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis)?
DM
If DM patient presents with loss of shoulder ER with painful motion, what diagnosis should be considered?
adhesive capsulitis
What is the treatment for adhesive capsulitis?
NSAIDs
Moist heat
PT/Home exercise program
- with stretching
Intra-articular steroid injection
If refractory → surgery
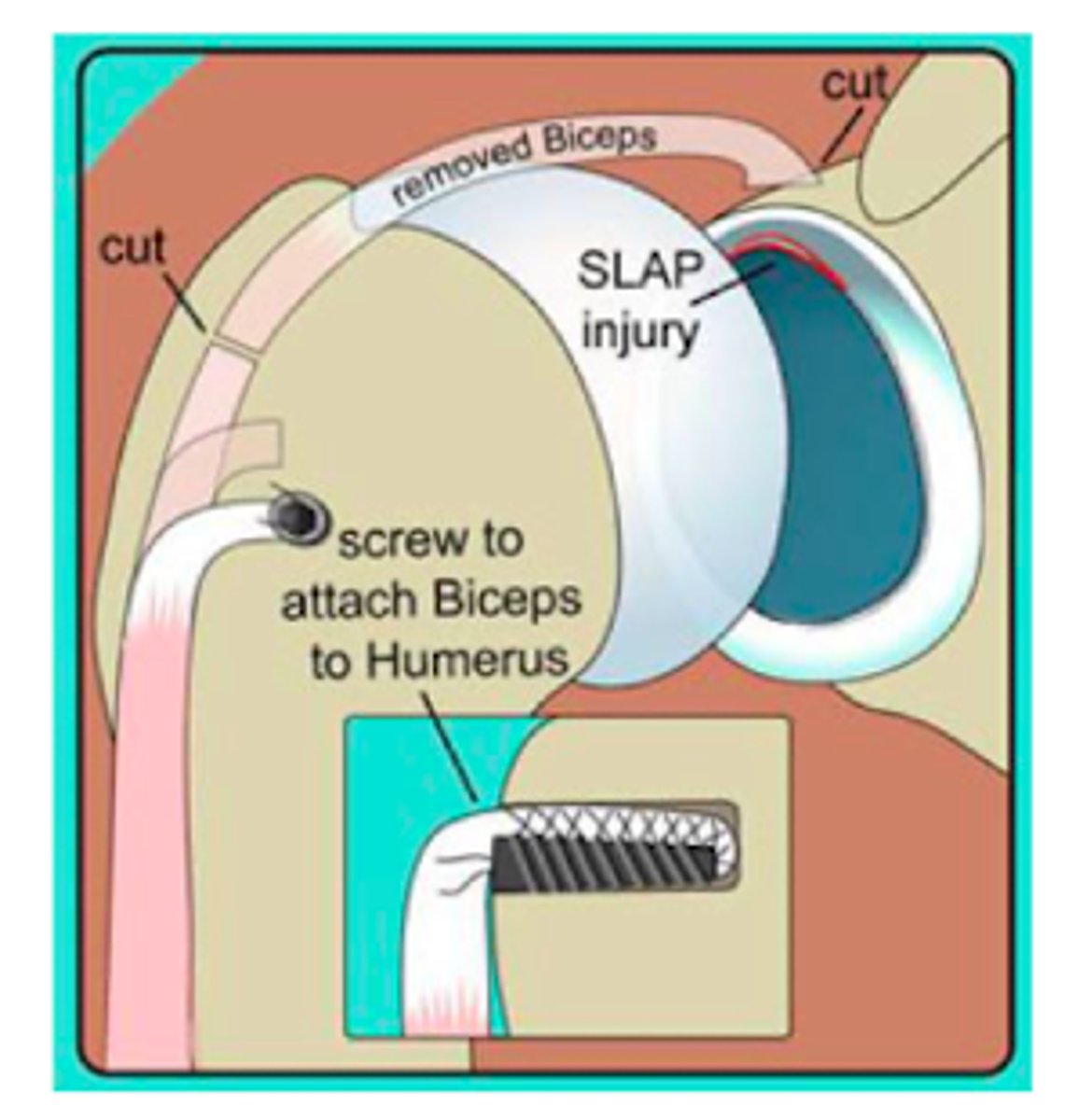
What is a SLAP injury?
superior labrum anterior-to-posterior lesions/tears
T/F. SLAP is often a diagnosis of exclusion.
TRUE - can be confirmed at the time of surgery
What THREE special tests can evaluate for shoulder labral tears?
O'brien
Clunk
Anterior slide
What is the GOLD STANDARD for diagnosing SLAP?
MRA (arthrogram)
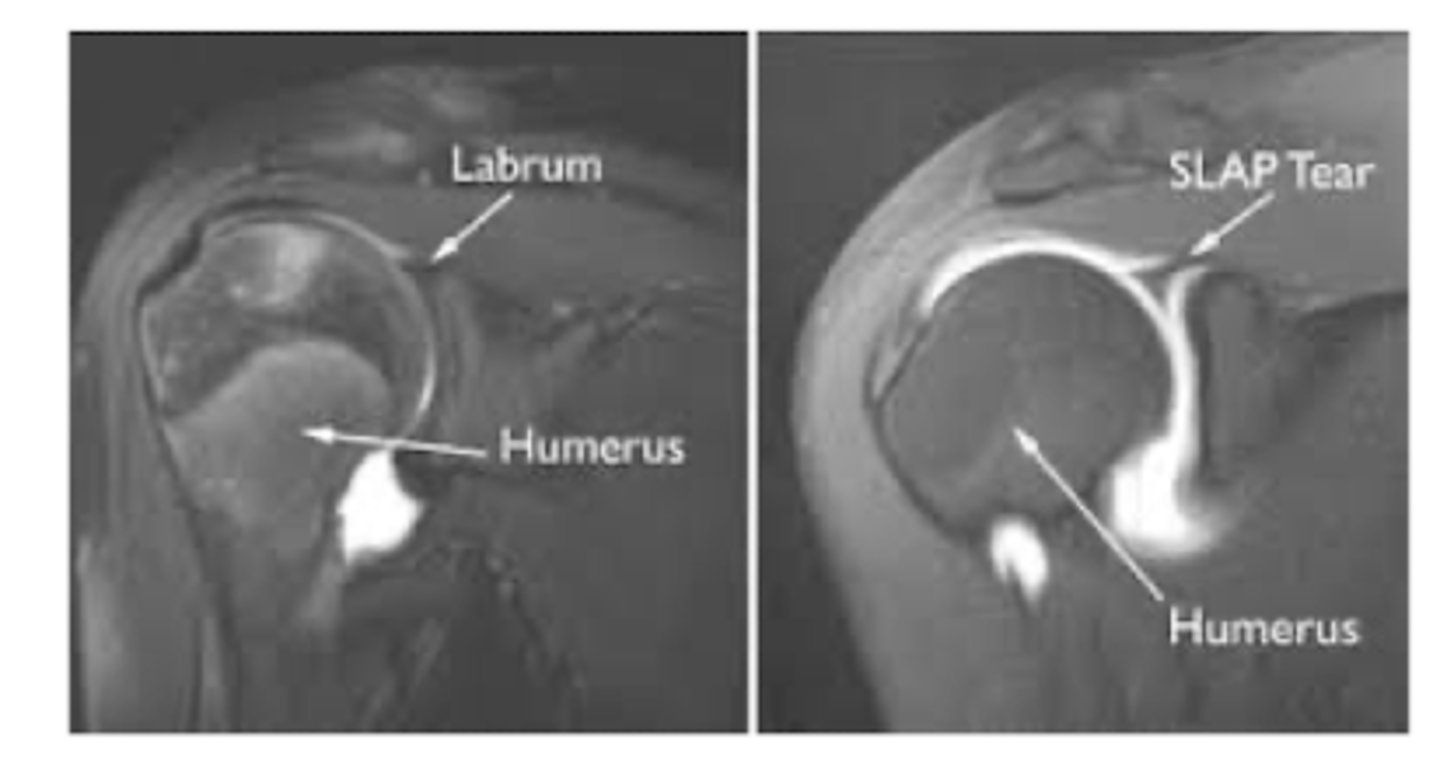
What is the treatment for SLAP?
NSAIDs
PT
Surgery
An elderly individual who falls on an outstretched hand m/c present with what type of fracture?
shoulder
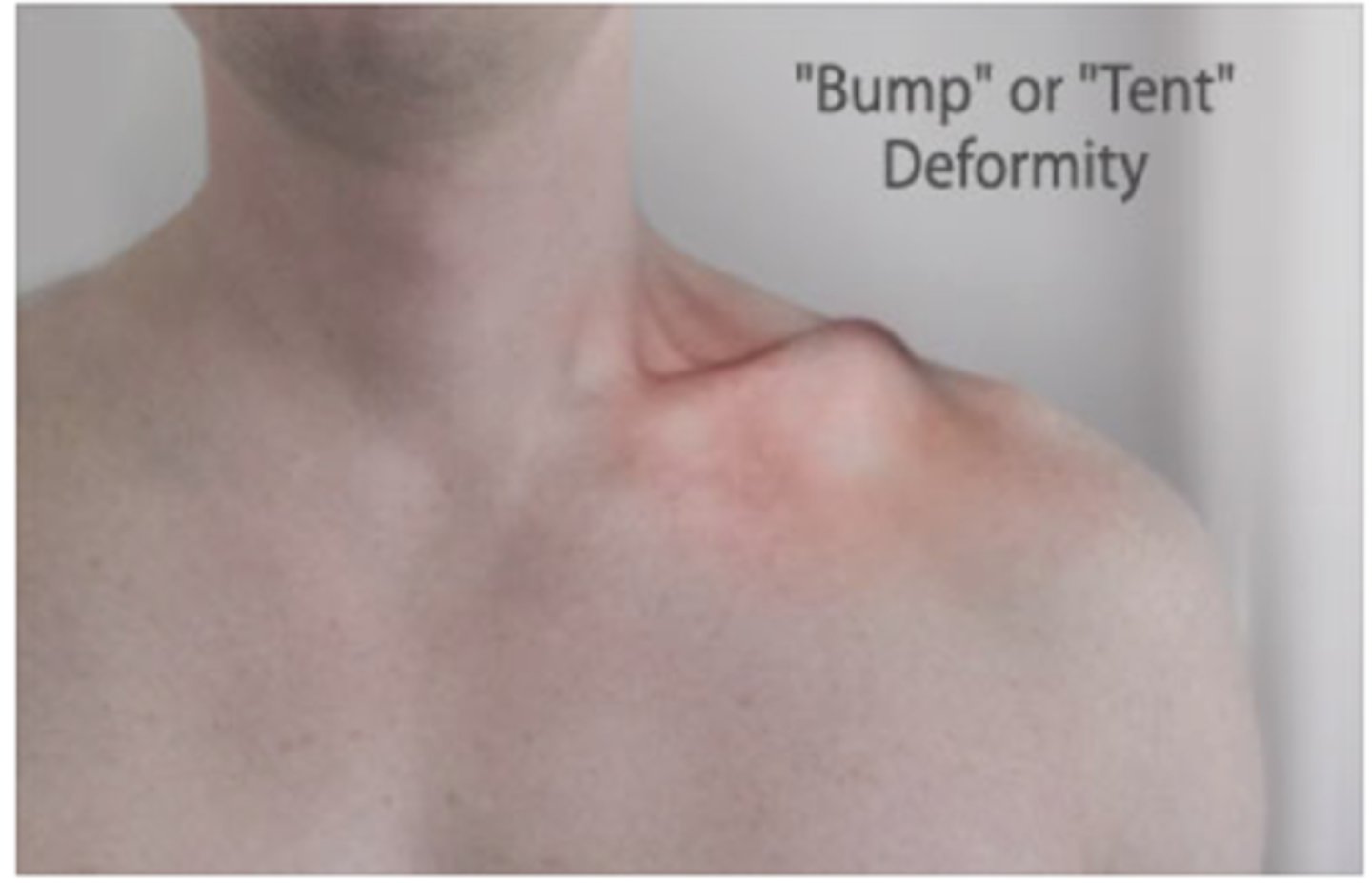
Where is a clavicle fracture most common?
middle 1/3
What on PE can suggest a clavicle fracture?
bump or tent deformity
shoulder droop
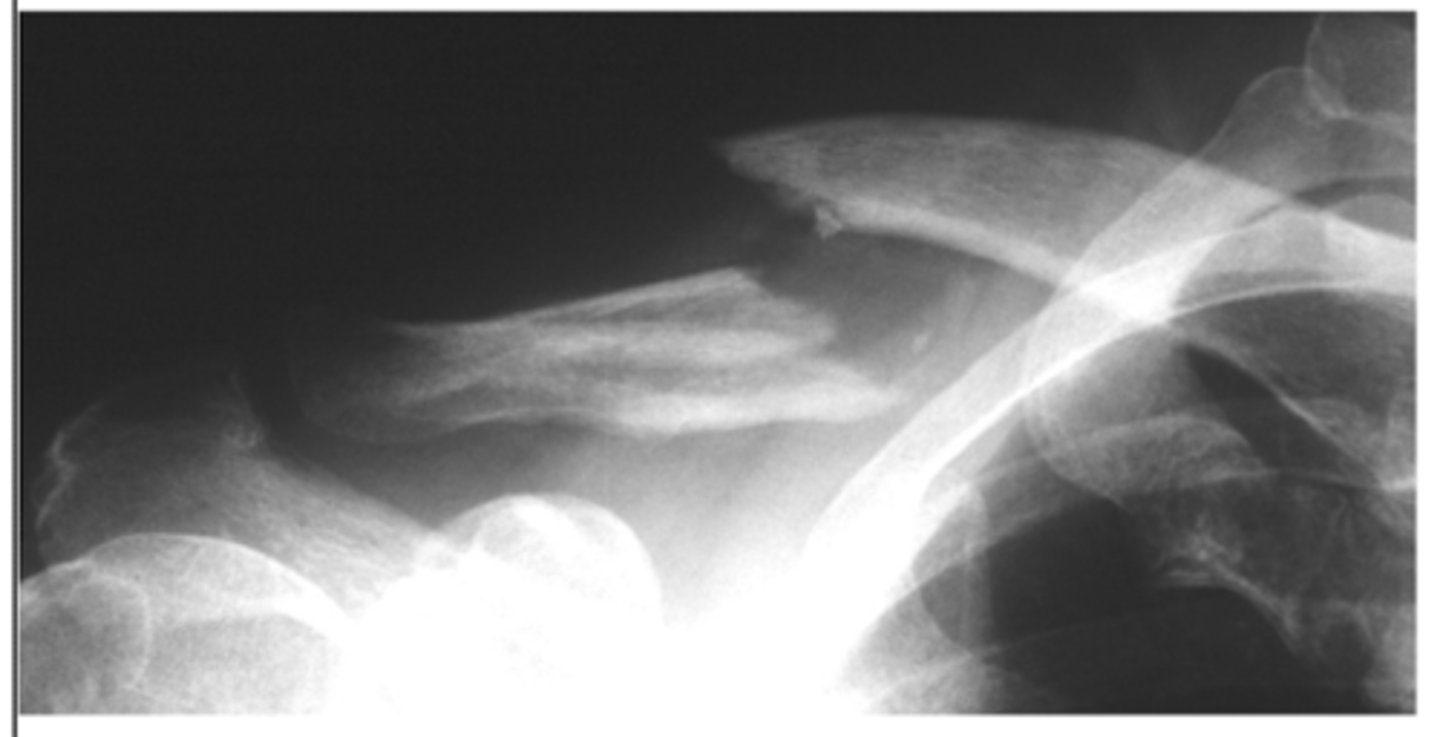
What TWO XR views can confirm a clavicle fracture?
AP view
10 degrees cephalic tilt
What is the most common treatment for a clavicle fracture?
non-surgical
- immobilization
- NSAIDs
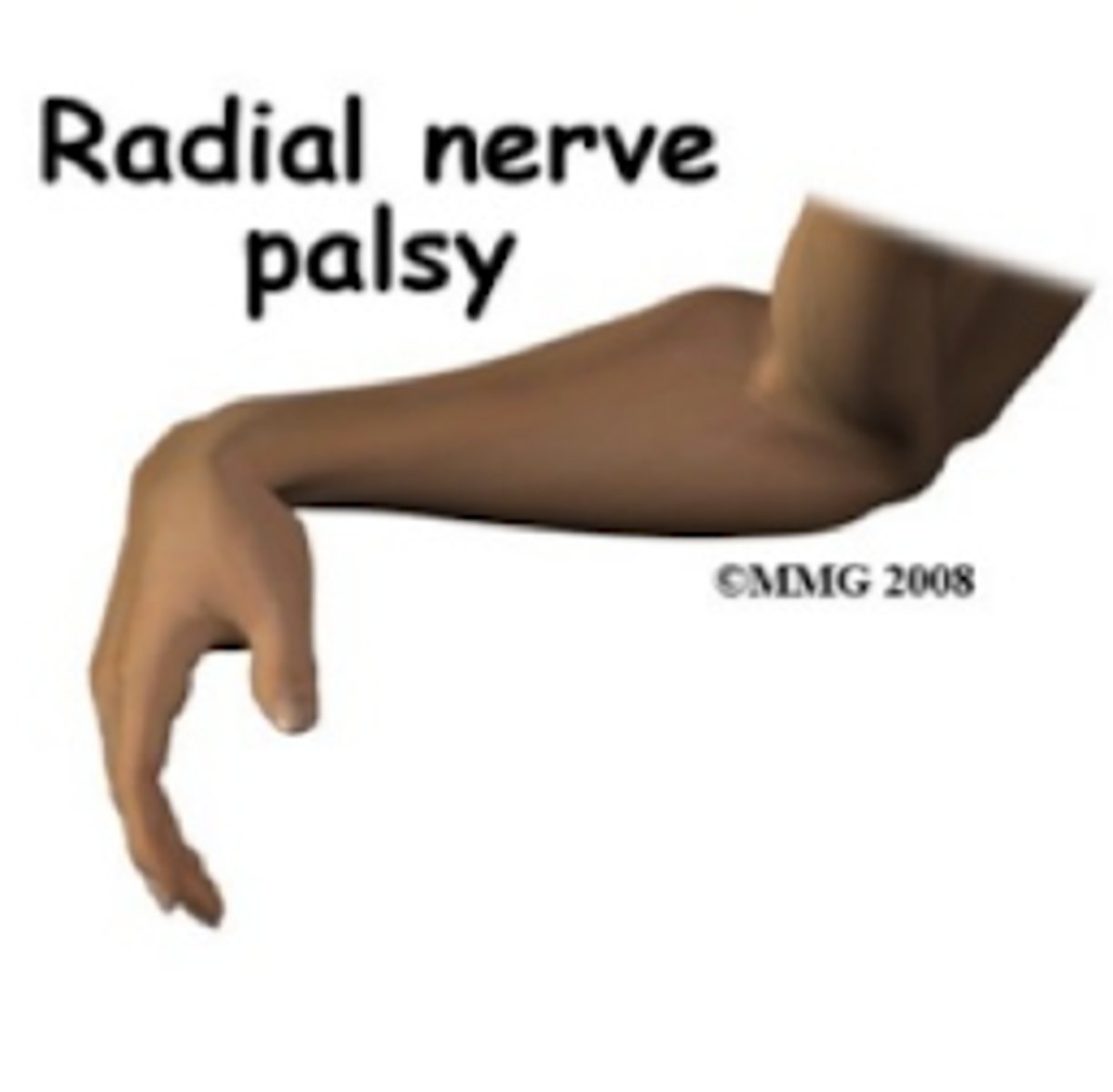
What nerve is most commonly injured with a humeral shaft fracture? What S/S suggest injury?
radial
- will be unable to extend wrist/fingers
- lose sensation on the dorsum of the hand
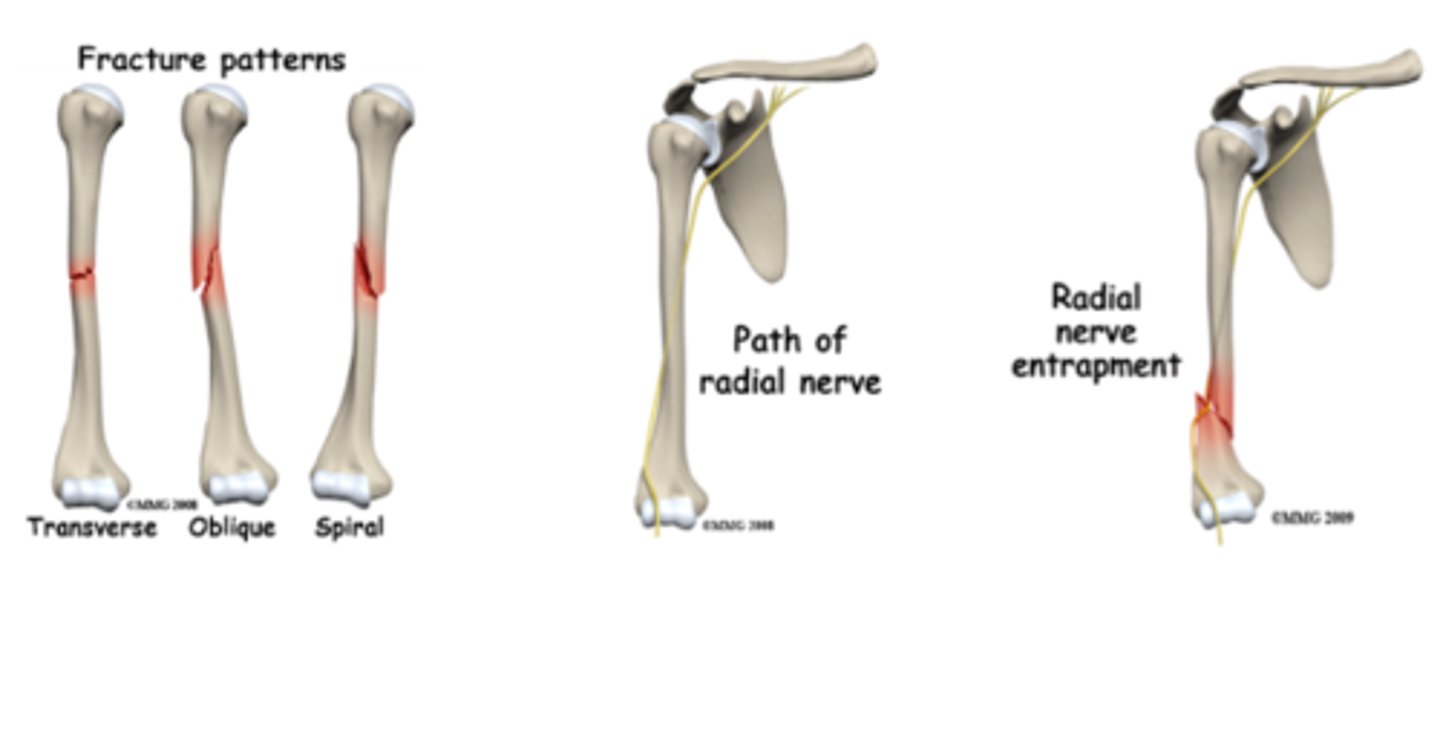
Wrist drop is most often seen in what type of nerve injury?
radial (Saturday night/Crutch palsy)
T/F. Most humeral shaft fractures are treated non-surgically.
TRUE
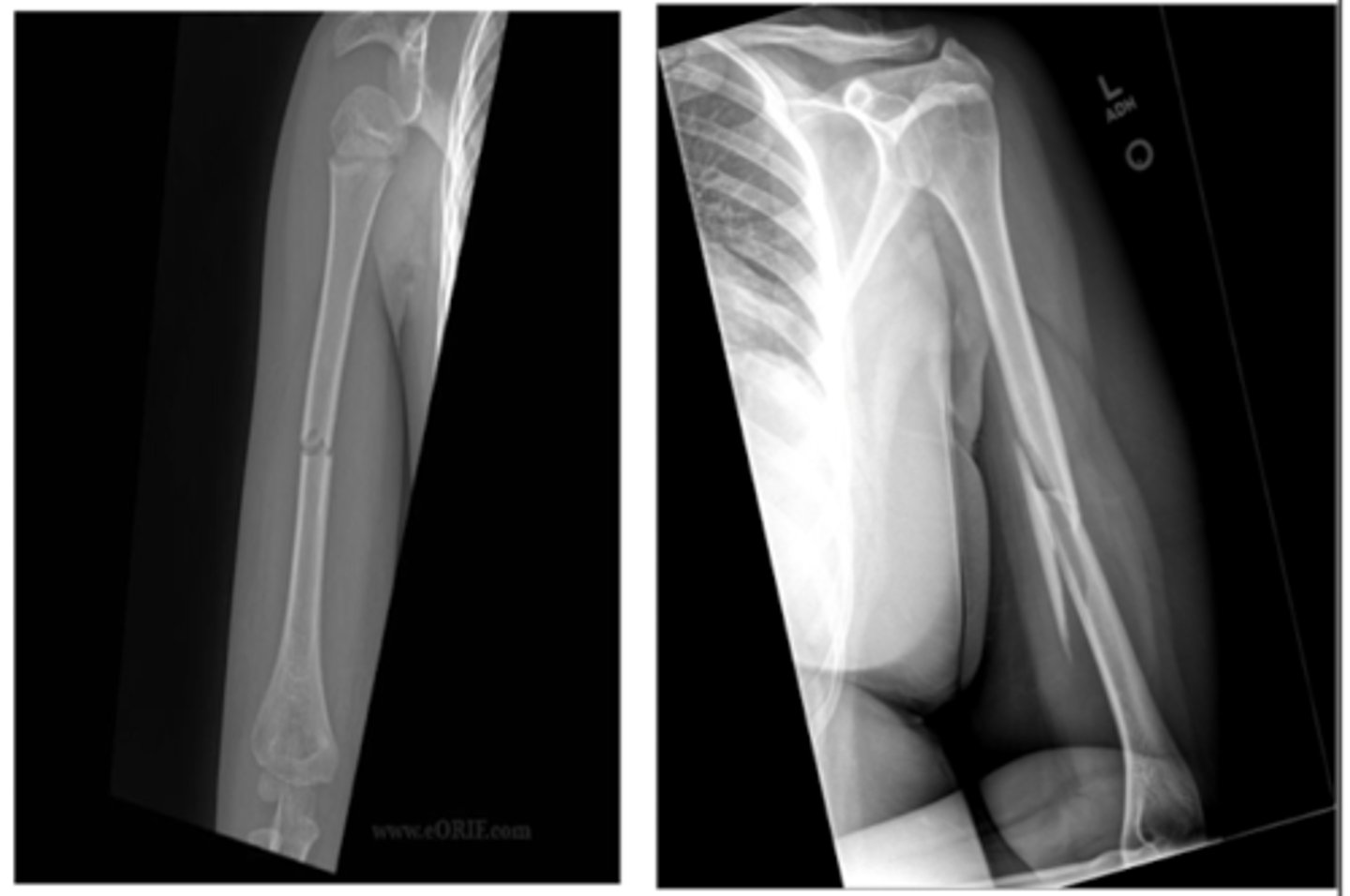
If needed, what are THREE surgical options for a humeral shaft fracture?
IM rod
ORIF
External fixation
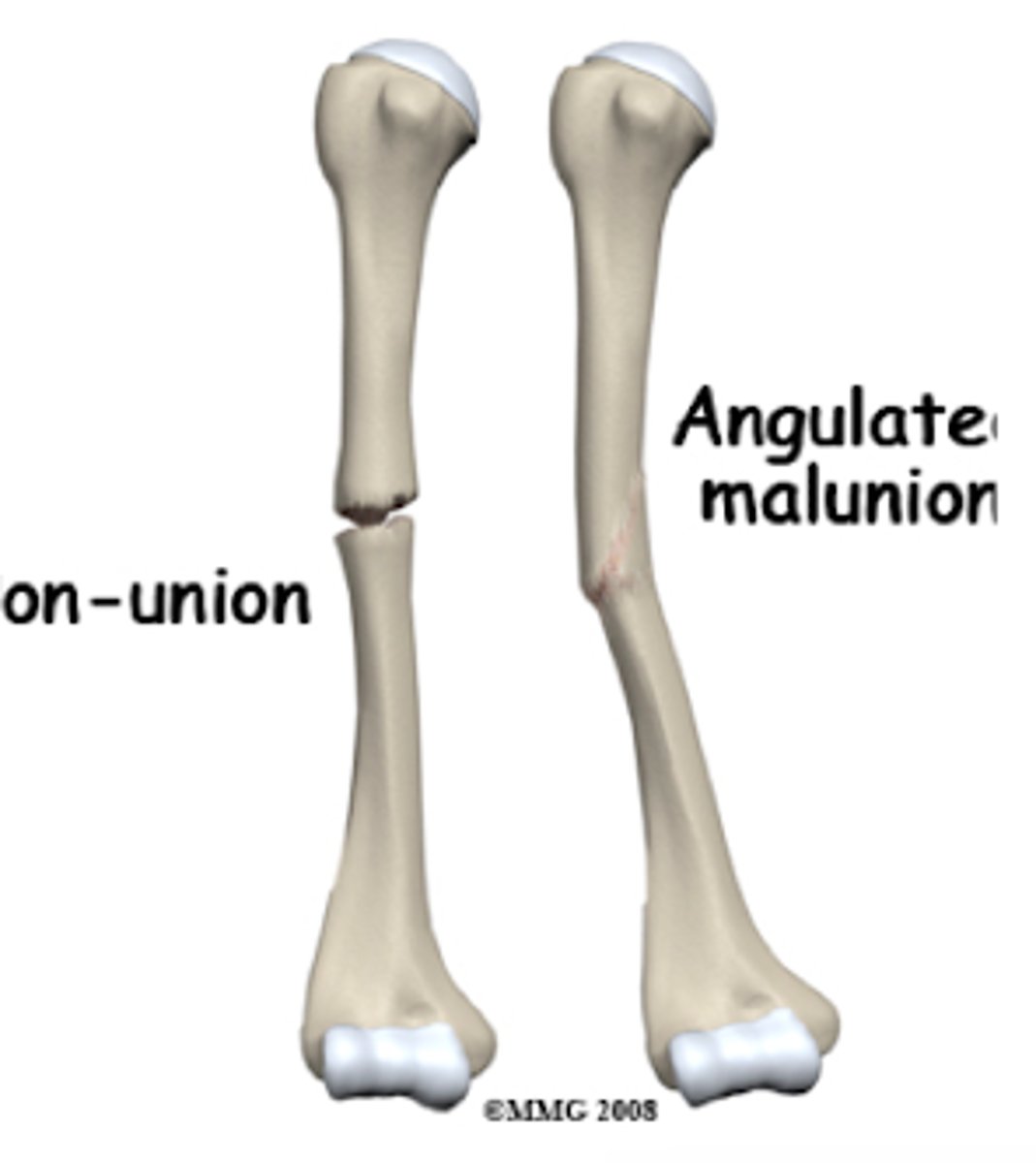
What is a common complication of a humeral shaft fracture?
malunion
What is the most common proximal humeral fracture ?
2-part Fx at the surgical neck
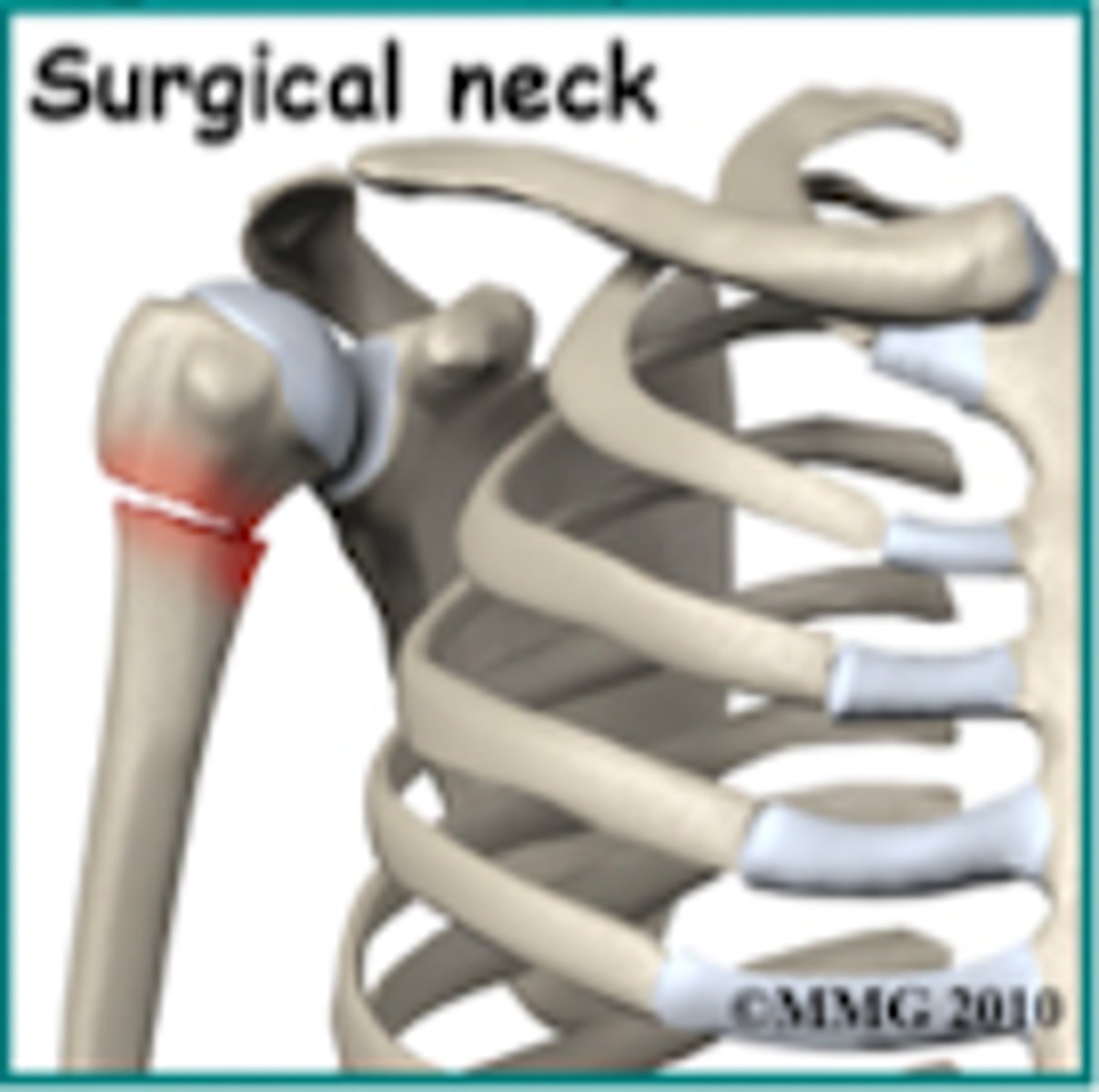
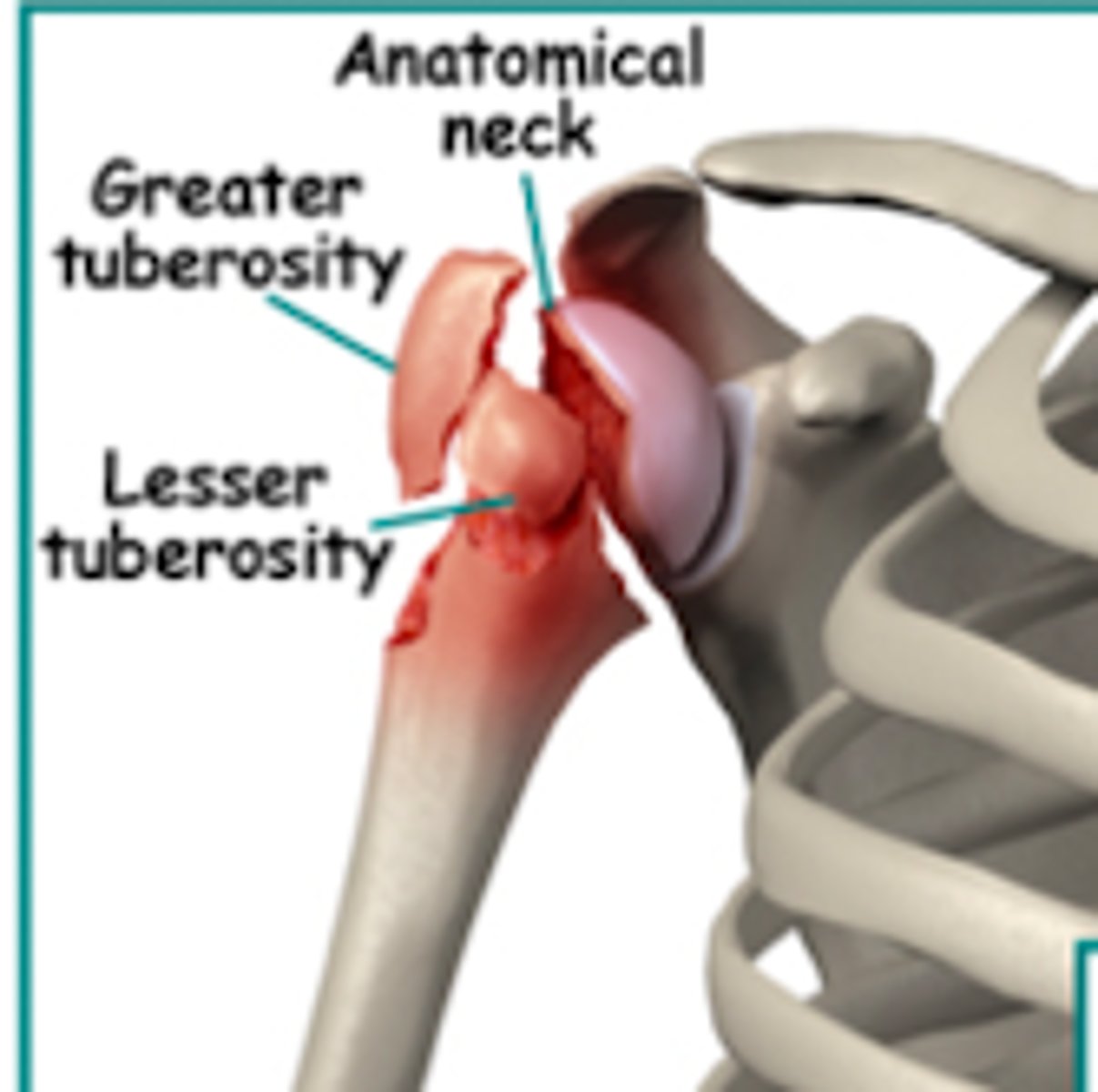
What is involved in a 3-part proximal humeral fracture?
Humeral head
Shaft
One of the tuberosities
When is surgery indicated for a proximal humeral fracture?
>1cm displacement or >45 angulation
What nerve is most commonly injured in a proximal humeral fracture?
axillary