Chapter 19- Ammonia
- Reactions going either way (forwards and backwards) are called reversible reactions. A double-headed arrow is used to represent reversible reactions.
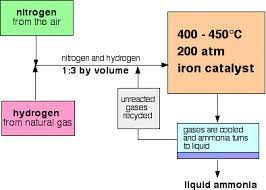
- The Haber process (the process of manufacturing ammonia) is a reversible reaction.
- Hydrogen and nitrogen are the raw materials. Nitrogen is extracted from the air by fractional distillation and hydrogen is obtained by the cracking of hydrocarbons.
- Since nitrogen is unreactive, a high temperature of 450 degrees celsius is required for the haber process.’
Iron is used as a catalyst to speed up the reaction.
CONDITIONS FOR THE HABER PROCESS
- To ensure maximum yield of ammonia:
- a lower temperature is used (although it reduces the rate of reaction)
- high pressure is used (although it increases the cost for the process)
- iron is used a catalyst (it speeds up the reaction but doesn’t affect the amount of yield. )
DISPLACEMENT OF AMMONIUM SALTS
When an ammonium salt is heated with an alkali, ammonia gas is produced.