Physl 210A 2nd part
1/545
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
546 Terms
Cell types of nervous system
Neurons
Glial
Astrocytes
Oligodendrocytes
Ependymal cells
Microglia
Neurons
Functional unit of the nervous system
generate action potentials
Interconnected information processors essential for all tasks of nervous system
Glial cells
Non-neuronal cells that support neurons physically and metabolically
do not generate action potentials
Provide scaffolding to have neurons line up closely with one another
Neuronal communication, transport nutrients and waste, mediate immune response, and insulation to neurons
Nerve
Bundle of axons or fibres that travel together
does not contain a complete nerve cell — only the axonal portion of many neurons
Individual fibres within this do not have any influence on one another — just follow the same pathway
Central nervous system
Integrating and command center
brain and spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system
Nerves connecting brain to peripheral structures
Afferent
Somatic sensory
Visceral sensory
Special sensory
Efferent
Somatic motor
Autonomic motor
Somatic sensory
Spatial limits of body
Visceral sensory
Information on internal organs
Special sensory
Sight, hear, equilibrium, taste, smell
Somatic motor
Skeletal muscle movement divided into
Reflexes
Rhythmic motor behaviours
Voluntary
Autonomic motor
Effects
smooth muscle
Cardiac muscle
Glands
Systems
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
Enteric
Involuntary
Ganglion
Collection of cell bodies located outside the CNS
Astrocytes
physically support neurons - scaffolding
Form blood brain barrier
Repairing
Form scar tissue → inhibits regeneration of severed axons
Turnover/recycle neurotransmitter molecules
Maintain electrolytic balance
Na+, K+, Ca2+, H+ (pH)
Oligodendrocytes
Form myelin sheaths that electrically insulate axons
have few branches
Ependymal cells
Produce cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Microglia
Ingest bacteria and debris
CNS gray matter
Consists of unmyleinated nerve cell bodies, dendrites, and axon terminals
cell bodies in organized fashion
Nuclei
Nuclei
Clusters of cell bodies in brain and spinal cord with similar functions → identified by specific names
CNS White matter
Mostly myelinated axons and very few cell bodies
myelin sheath gives colour
Tracts
Neural tissue?
Tracts
Bundle of axons that connect different regions of the CNS
same as nerves in PNS
Neural tissue
Have minimal extracellular matrix and must rely on external support for protection of trauma
outer casing of bone
3 layers of connective tissue membrane
Fluid between membranes
Protective elements of CNS
Bone
Skull → brain
Vertebrae → spinal cord
Meninges
Cerebrospinal fluid
Blood brain barrier
Meninges
3 layers of membrane that lie between bone and CNS to help stabilize neural tissue and protect from bruising against bones of skeleton
dura mater
Arachnoid mater
Pia mater
Cerebrospinal fluid
Provides physical and chemical protection
in specific spaces of the brain
Continuously secreted from brain ventricles by choroid plexus
Reabsorbed by special villi (in arachnoid membrane) into venous blood after flowing around neural tissue
Same rate as produced
Provides mechanical protection
Bathes and supports neural tissue
fluid compresses before brain hits cranium
Maintains electrolyte balance around neurons
Blood brain barrier
helps maintain a stable environment for the brain
capillaries are less porous → allow small molecules in
Protection from chemical fluctuations and harmful agents
Provides oxygen and glucose and selectively transports molecules via carrier mediated transport
Drugs must be precursors (small enough to pass)
Regular capillaries
Have passages between cells that make up walls that allow fluid with electrolytes and large molecules and white blood cells to exit from interior
Transport blood between small arteries and venues; exchange of materials between blood and interstitial fluid
Exchange nutrients, metabolic end products, cell secretions due to small wall
Branch from arterioles, smallest blood vessel in the body
Oxygen moves from blood into interstitial fluid around cells and waste products enter the blood
One endothelial cell thick
No smooth muscle or elastic tissue
Thin walled and smallest of vessels, contain large number of endocytic and exocytic vesicles — sometimes these vesicles fuse together to form continuous vesicular channels across a cell called fused vesicle channels
2 endothelial cells that came together to form a tube. Adjacent endothelial cells are joined laterally by tight junctions but leave gaps of unjoined membrane called intercellular clefts
do not function on their own — are a part of a bed and are a part of microcirculation
Dura mater
Tough outer layer part of meninges
like Saran wrap
Arachnoid mater
Spidery intermediary mesh part of meninges
loosely tied with Pia mater
Subarachnoid space
The space between arachnoid and Pia mater in the meninges
Pia mater
Delicate inner layer of the meninges
adheres to surface of brain and spinal cord
Meningitis
Infection of the meninges
Hydrocephalus
occurs when reabsorption is blocked and CSF accumulates
Treated with drainage tubes
If not— brain tissue is crushed against inner surface of skull
Creates pressure in cavities of CNS → ventricles and spinal central canal
Brain planes (visuals)
coronal or frontal plane
Front/back sections
Sagittal plane
Left/right
Horizontal or transverse plaNe
Up/down
Directions - long axis of body
Straight line in body
superior (above)
Posterior (behind)
Inferior (below)
Anterior (in front of)
Connects with axial CNS at a 120 degree angel in midbrain
Directions - long axis of CNS
Bent — cephalic flexure
dorsal
Hindbrain: back
Forebrain: top of head
Ventral
Hindbrain: front
Forebrain: towards gut
Rostal
Hindbrain: front aspect of head (top)
Forebrain: nasal region
Caudal
Hindbrain: tail region
Forebrain: posterior (back) of head
Connects with axial body at a 120 degree angel in midbrain
Brain 3 main regions
Cerebrum
Cerebellum
Brain stem
Forebrain
cerebrum
Diencephalon
Hindbrain
cerebellum
Pons
Medulla oblongata
Brain stem
midbrain
Pons
Medulla oblongata
Functions
Respiration, locomotion, cardiovascular, neurotransmitter supply
Cardiovascular, blood vessel, digestive
Sleep/wake cycle
Balance and posture
Neurotransmitter produced in brain stem are transported along axons to other parts of brain
Central Nervous System formation
During development
forms from a long tube
Lumen of the tube remains in adult brain as fluid filled space (ventricular system)
Filled with CSF
Brain formed from walls of the tube → increasing complexity
Cerebrum
Includes
corpus callosum
Cerebral cortex
Corpus callosum
Large bundle of nerves; connects right and left hemispheres
ensures communication and cooperation
Cerebral cortex
The outer layer of neural tissue of cerebrum of the brain; folded into peaks and grooves
thin outer shell of grey matter
Neurons arranged in anatomically distinct horizontal layers and functionally distinct vertical layers
Functions:
sensory perception
Motor control
Language
Cognitive functions
Sulci
Groove in the brain
Gyri
Fold/ridge in the brain
Bones of the skull
22 bones
8 cranium
14 facial
8 cranium bones that enclose the brain
Frontal bone
2 parietal bones
2 temporal bones
Occipital bone
Sphenoid bone
Ethmoid bone
Diencephalon
The region of embryonic vertebrae neural tube that gives rise to anterior forebrain structure
encloses the third ventricle cavity
Includes
Thalamus
Epithalamus
Hypothalamus
Subthalamus
Thalamus
Integrating center and relay station for sensory and motor information
projects fibres to cerebrum
Almost all sensory information
Can shape sensory information
Functions:
sensory switchboard which selects and relays sensory signal to cerebral cortex
Skeletal muscle contraction
Awareness
Epithalamus
Includes pineal gland
part of Diencephalon
Pineal gland
Melatonin secretion
Hypothalamus
Homeostasis and behavioural drives
temperature control, water balance, hunger
Fight or flight or fright
includes posterior pituitary
integration and command center for autonomic functions; temperature regulation
Posterior pituitary
Hormone secretion
Subthalamus
Movement regulation
Midbrain
AKA mesenophalon
eye movement
Auditory and visual processing
Contains the substantia nigra
Has different neuron clusters and pathways and other structures
Substantia nigra
Rich in dopamine neurons and part of basal ganglia
divided into 2 regions
Pars reticular a
Pars compacta
Basal ganglia
Group of 5 nuclei associated with motor and learning functions (paired) deep within cerebral cortex
Received input from context and provides feedback to context (thalamus) for development of motor strategies and regulation of movement
Initiate movement
Suppressing activity of muscles to inhibit movement
Forms major portion of extrapyramidal system
Looping parallel circuits regulate motor activity — circuits allow signals to travel sensorimotor cortex → basal nuclei → thalamus → context → modulate movement
Pons
Relay station between cerebrum and cerebellum
Coordination of breathing with medulla
Medulla oblongata
control of involuntary function
Autonomic centers for regulation of visceral functions
Cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive activities
Connects brain stem to spinal cord
contains major ANS reflex centers (centers for cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive activity)
Frontal section of forebrain
outer shell of gray matter composed of cell bodies
Inner layer of white mater composed of tracts of myelinated axons
6 layers of cerebral cortex
Distinct cells based on physical properties and inputs/outputs
Parallel to cortical surface
Numbered from outer to inner membrane
Corpus callosum
Limbic system
A ring of forebrain structures that surround the brain stem and are interconnected by intricate neuron pathways
learning, emotion, appetite (visceral function), sex, endocrine integration, behavioural and emotional responses
Especially for survival
Also connects to CNS
Includes
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Basal ganglia
Cingulate gyrus
Hippocampus
Amygdala
Cerebellum
Influences posture and movement indirectly by means of input to brainstem nuclei and by way of thalamus to regions of sensory motor cortex that give rise to pathways that descend to motor neurons
Receives input from sensorimotor and vestibular system (eyes, skin, muscles, joints, tendons — movement effects these receptors)
Inputs
Sensory input from spinal cord
Motor commands from cerebral cortex
Functions
Motor timing, scaling, coordination and learning
Trunk/neck, arms/hands/fingers
Balance and gait
Eye movements
Hints at cognitive processing
Frontal lobe
Personality, emotion
Motor control
Parietal lobe
Somatosensation
Occipital lobe
Vision
Temporal lobe
Hearing and memory
Spinal cord
Major pathway of information, flowing back and forth between the skin, joints, and muscles of the body
31 spinal nerves convey signal to and from spinal cord
Ascending sensory axons which transmit sensory information from body to brain
Descending axons that control movement and autonomic functions
Locomotor pattern generator (producing rhythmic movements)
Spinal reflexes
integrates autonomic reflexes (Urination, defecation); brain is able to influence these reflexes
Spinal nerve
Innervates a specific area of the skin and a specific set of muscles
one member of pair exists of right side and left side of spinal column separately
Contains afferent and efferent nerves
31 pairs that connect to spinal cord
Arise at cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, causageal region of spinal cord
Dermatome
Specific area of the skin innervated by a single spinal nerve root — supplied by a pair of spinal nerves
Myotome
Specific set of muscles innervated by a single spinal nerve root — supplied by a pair of spinal nerves
Shingles
Neurons in the dorsal root ganglia, often in 1 or 2 segments, become infected with virus related to chicken pox.
bands of sores and pains
chicken pox in children increases likelihood of this in adulthood
Dormant → mutates and activates
knowledge of dermatones used to clinically determine level of spinal cord and injury
Functions of the Spinal cord
sends sensory information from the body to the brain (dorsal root)
Spinal interneurons may route sensory information to the brain through ascending tracts
Sends motor commands from the brain to the body (ventral root)
Coordinate reflexes (acting without signals from the brain)
Also contains central pattern generators that control rhythmic movement
Can be modulated with or without information from higher brain centers
Interface between PNS and CNS
Sensory afferents enter spinal cord via dorsal root
Sensory afferents bifurcate into ascending / descending axons.
Ascending forms dorsal root columns → ascend into brainstem → sensory information to the brain
Descending branch travels causally for 2-3 spinal segments
Every mm or so for 2-3 segments (50mm humans) the ascending/descending axons send branches into the gray matter of the spinal cord which synapse in the interneurons and motor neurons
Motor neuron cell bodies are located in ventral horn
Motor efferent axons leave spinal cord and form ventral root
Cervical C1-C8
Head, neck, shoulders, arm, hand
Thoracic T1-T12
Trunk
Lumbar L1-L5
Waist, front of legs, feet
Sacral S1-S5 and Coccygeal
Buttocks, genitals, anus, back of legs, feet
Spinal cord gray matter
Neuronal cell bodies and their dendrites, short interneurons, glial cells
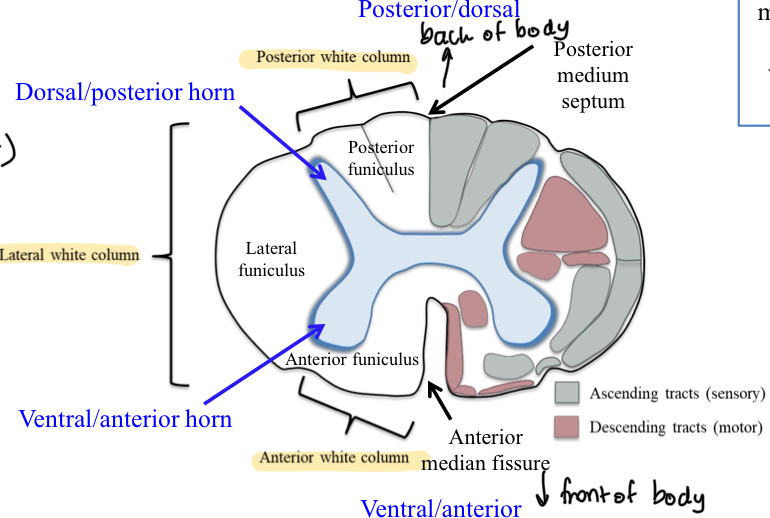
Spinal cord horn
Projection of gray matter towards outer surface of the spinal cord
dorsal/posterior — interneuron cell bodies
Ventral/anterior — motor neuron cell bodies
Lateral — autonomic neuron cell bodies
Dorsal roots
Dorsal side of the cord where axons of afferent neurons enter the spinal cord
Dorsal root ganglia
Contain the cell bodies of the afferent neurons (the swelling)
Ventral roots
The ventral side of the cord where axons of efferent neurons leave the spinal cord
Ganglia
Group of neuronal cell bodies located outside the central nervous system in the peripheral nervous system
Spinal cord white matter
Surrounds gray matter
consists of bundles of axons (with myelin) that travel up and down the spinal cord and convey sensory signals ascending to brain (cord to brain) or motor commands descending from brain (brain to cord)
Funiculi — three pairs of white matter bundles
Posterior/dorsal, lateral, anterior/ventral
Tracts/fasiciuli
Ascending/sensory
Descending/motor
Funiculi
bundles of nerve fibers (axons) in the spinal cord's white matter
Fasciculi
groups of short fibres, ascending and descending, and crossed and uncrossed, within the spinal cord
tracts —subdivisions of each column
Spinal reflex
Simple behaviour produced by central nervous system pathways that lie entirely within spinal cord
afferent sensory fibres envole reflexes → enter spinal cord and activate spinal interneurons directly or through a chain of one or more spinal interneurons
Pathways may be affected by descending pathways from brain either directly or through other spinal interneurons
Short term and long term influence over spinal cord reflex
Short term influence over spinal cord reflex
The brain rapidly adjusts spinal reflexes to suit the needs of different tasks
Long term influence over spinal cord reflex
Gradually shapes spinal reflexes during development, skill acquisition, later in life, and in response to CNS trauma and disease
Spinal cord injury
Sensation from and the motor control of functions below that level (of transection) are likely to be abnormal depending on severity
Tretaplegia/quadraplegia
the paralysis of all four limbs, the trunk, and pelvic organs, typically caused by a high-level spinal cord or brain injury
Paraplegia
the inability to voluntarily move the lower parts of the body— lower level spinal cord injury
Specializations of cerebral cortex
Sensory areas
Motor areas
Association areas
Cerebral cortex — sensory areas
Sensory input translated into perception (awareness) in cerebral cortex
all cortical areas associated with sensory
Receiving and interpreting — transduction
Includes
Gustatory cortex — taste
Primary olfactory cortex — smell
Pimraru somatic sensory cortex — parietal lobe
Visual cortex — vision
Auditory cortex — hearing
Cerebral cortex — motor areas
Plan, control, and execute voluntary movements in cerebral cortex
Cerebral cortex — association areas
Integrate information from sensory and motor areas in cerebral cortex
general visual, auditory, gustatory
Somatic senses
Receptors associated with the skin, muscles, joints, fascia, and viscera
somatosensory
Special senses
Include the senses of smell, taste, hearing, static equilibrium, dynamic equilibrium, and sight
Somatosensory system
Part of sensory system concerned with the conscious perception of touch, pressure, pain, temperature, position, movement and vibration detected by receptors in the skin, muscles, joints, fascia, and viscera
relays sensations detected in the periphery and conveys them via pathways through the spinal cord, brainstem, and thalamic relay nuclei to sensory cortex in the parietal lobe
Sensory pathways
Stimulus (interna/external) → sensory receptor that transduces stimulus into electrical graded potentials → reach threshold → action potentials travel along afferent sensory neuron to CNS → signals integrated
some stimuli pass upwards to cerebral cortex → reach conscious perception
Some acted upon without our awareness — does not reach brain
At each synapse along the way —nervous system can module and shape information
Primary sensory (first order) neuron → secondary sensory (second order) neuron → etc etc
Divided into 2 systems
Below neck — pass along sensory pathway of spinal cord (ascending pathway)
Head and neck — travel through cranial nerves
Sensory information from spinal cord → brainstem → sensory areas of cerebrum
Pathways pass through thalamus to cerebral cortex except olfactory