AP Bio - Genetics
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
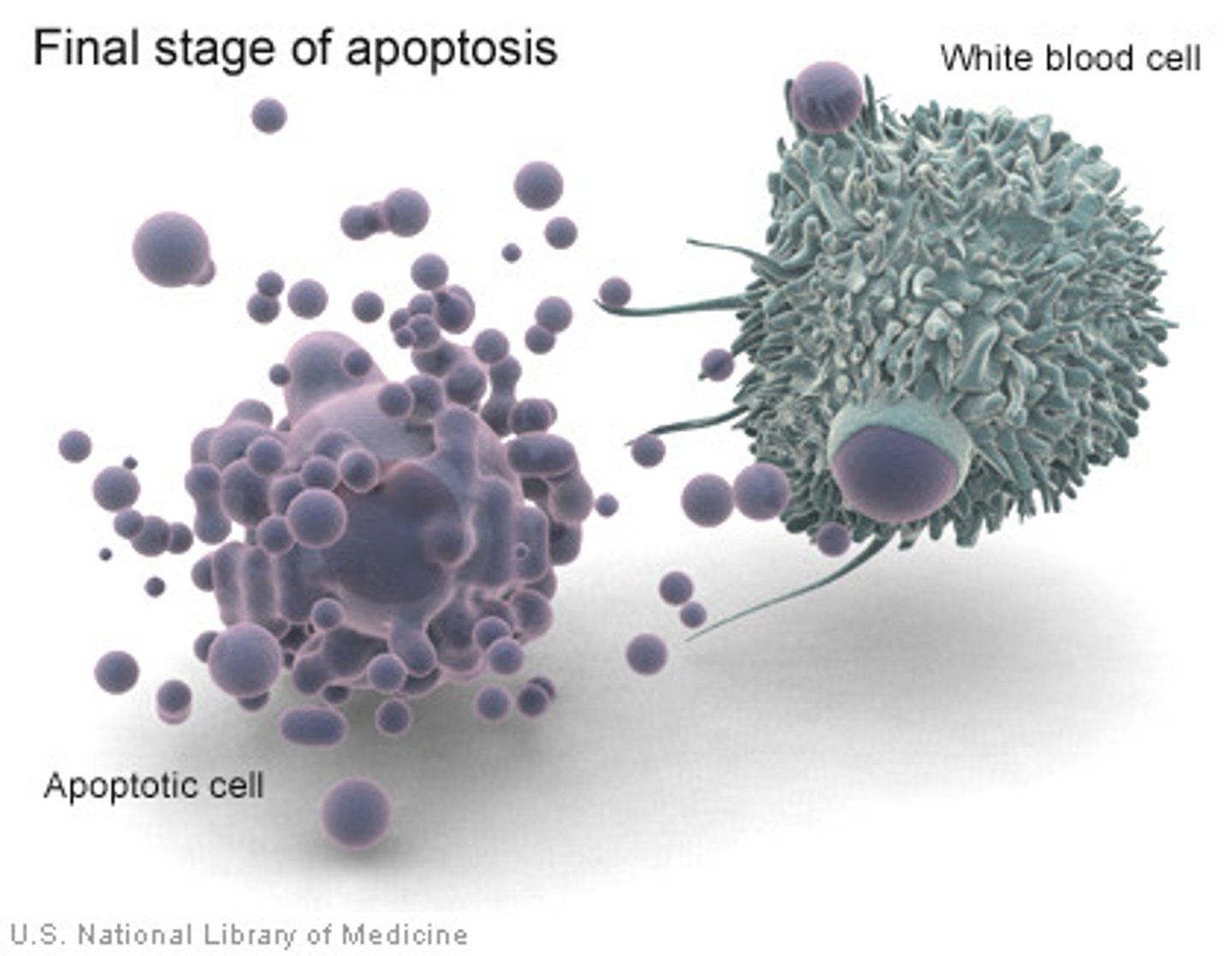
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death to remove cells that have become harmful to the organism or are no longer needed.
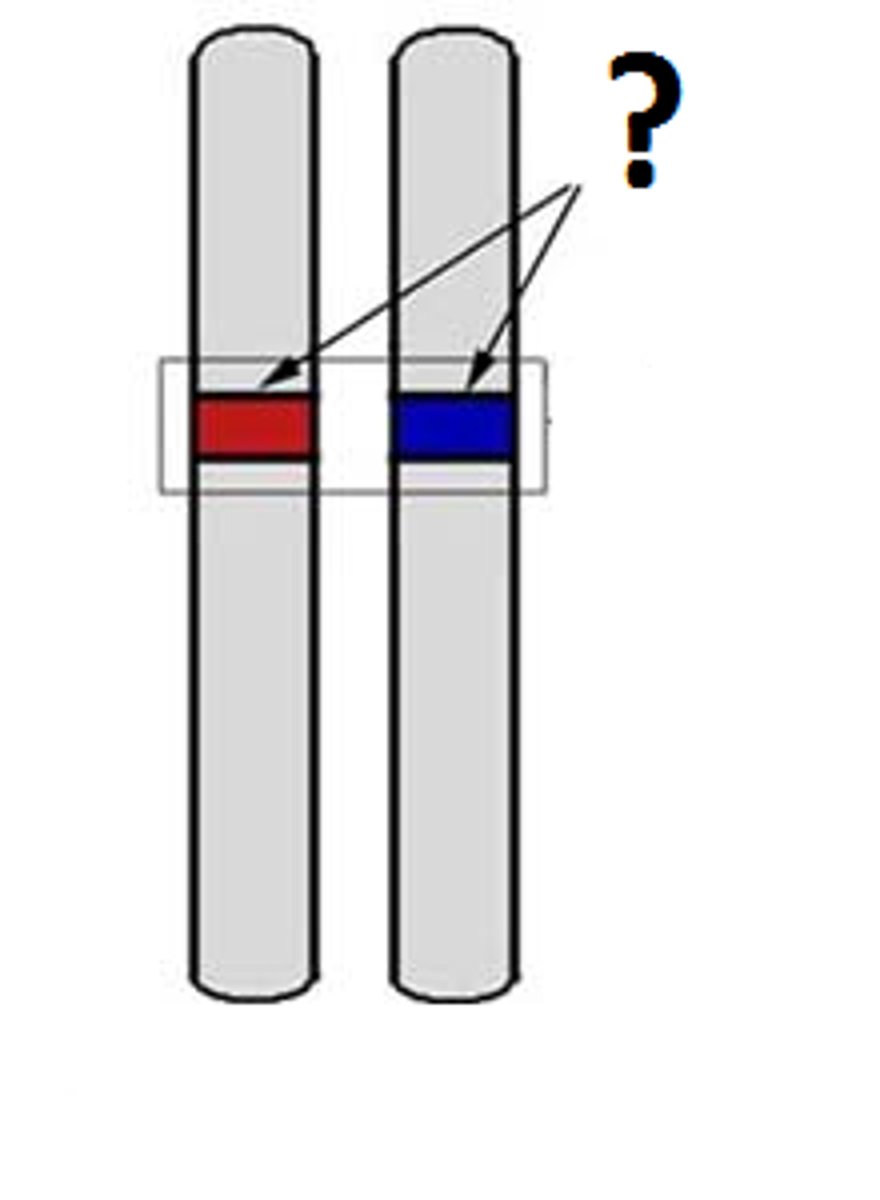
Allele
One of two or more alternative states of a gene.
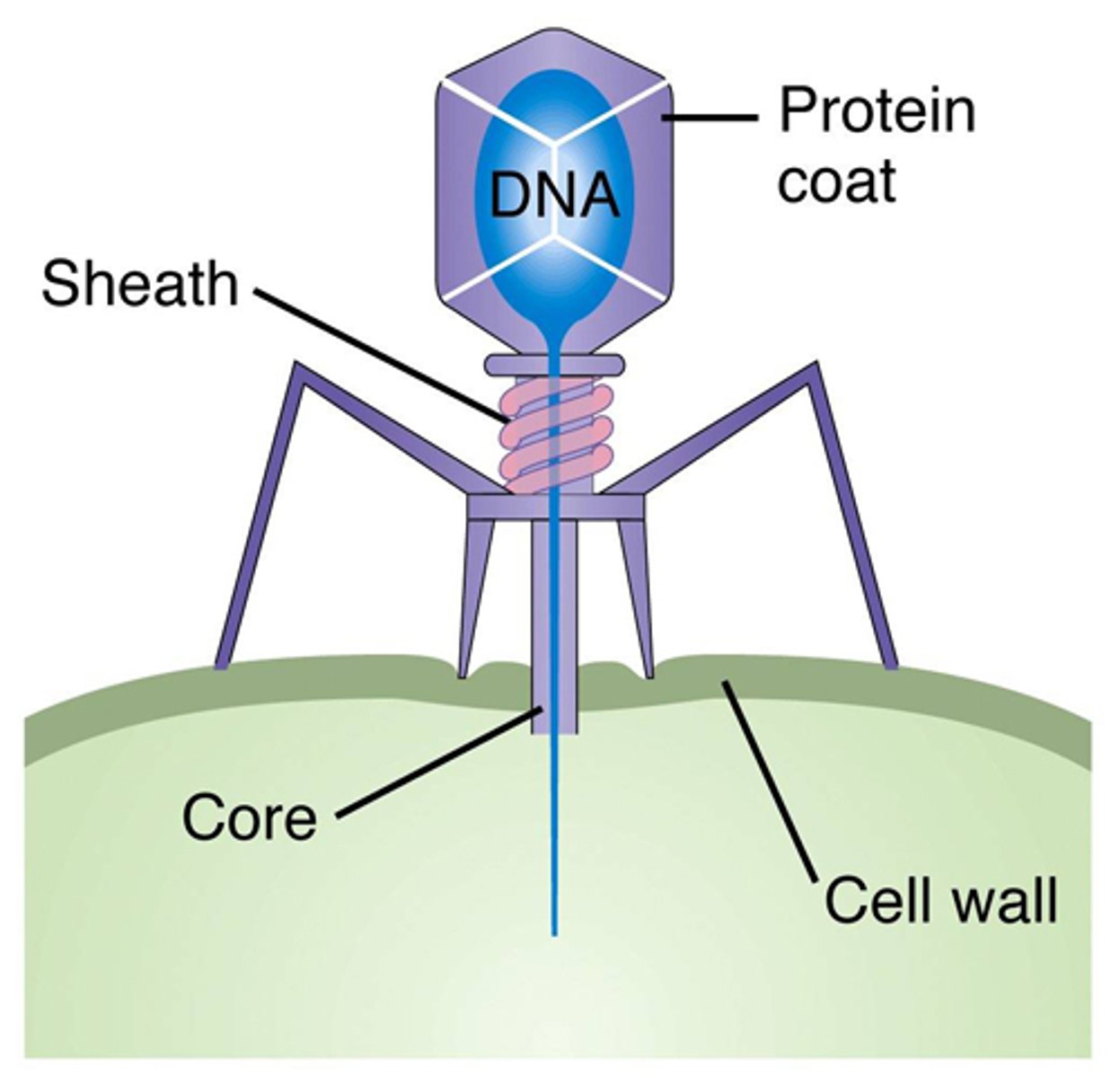
Bacteriophage
A virus that infects bacterial cells
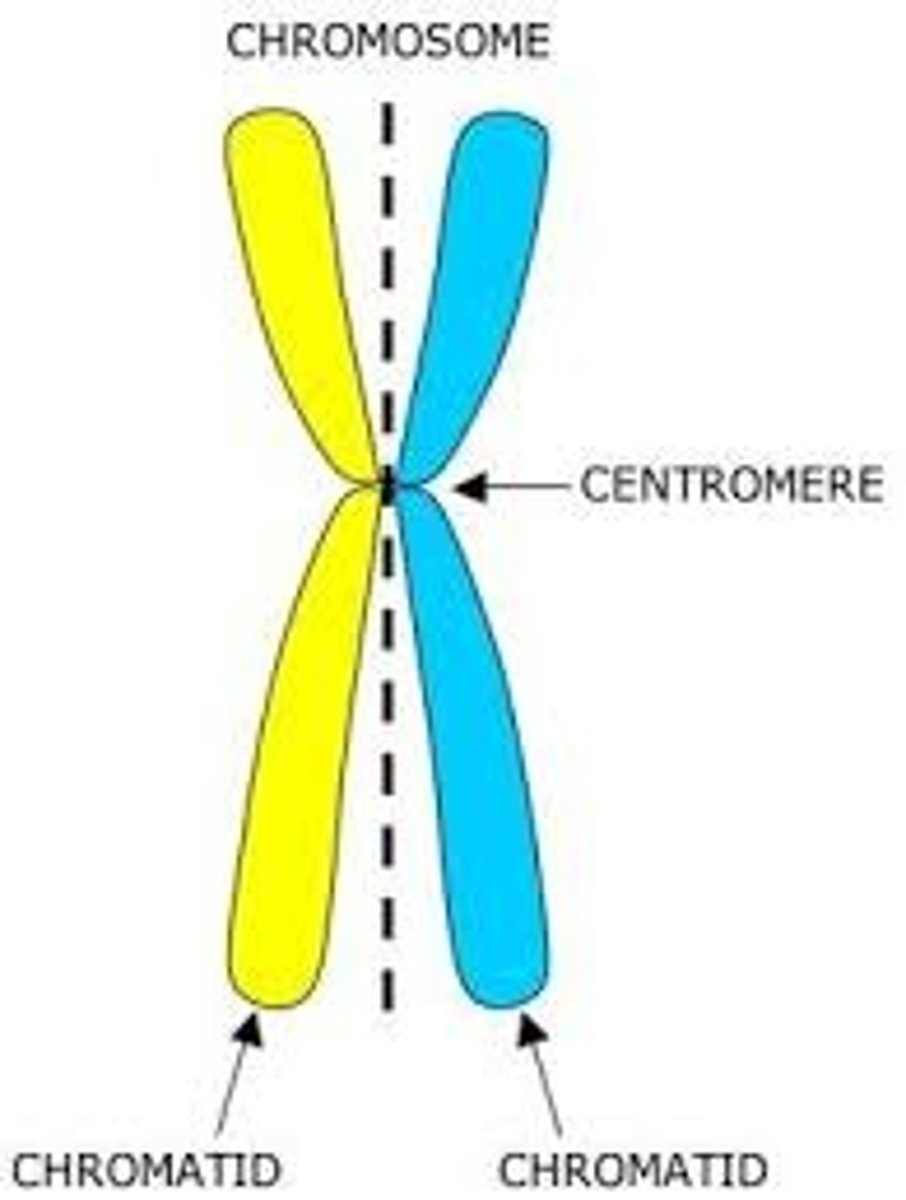
Chromatid
One of the two daughter strands of a duplicated chromosome; held together by a centromere
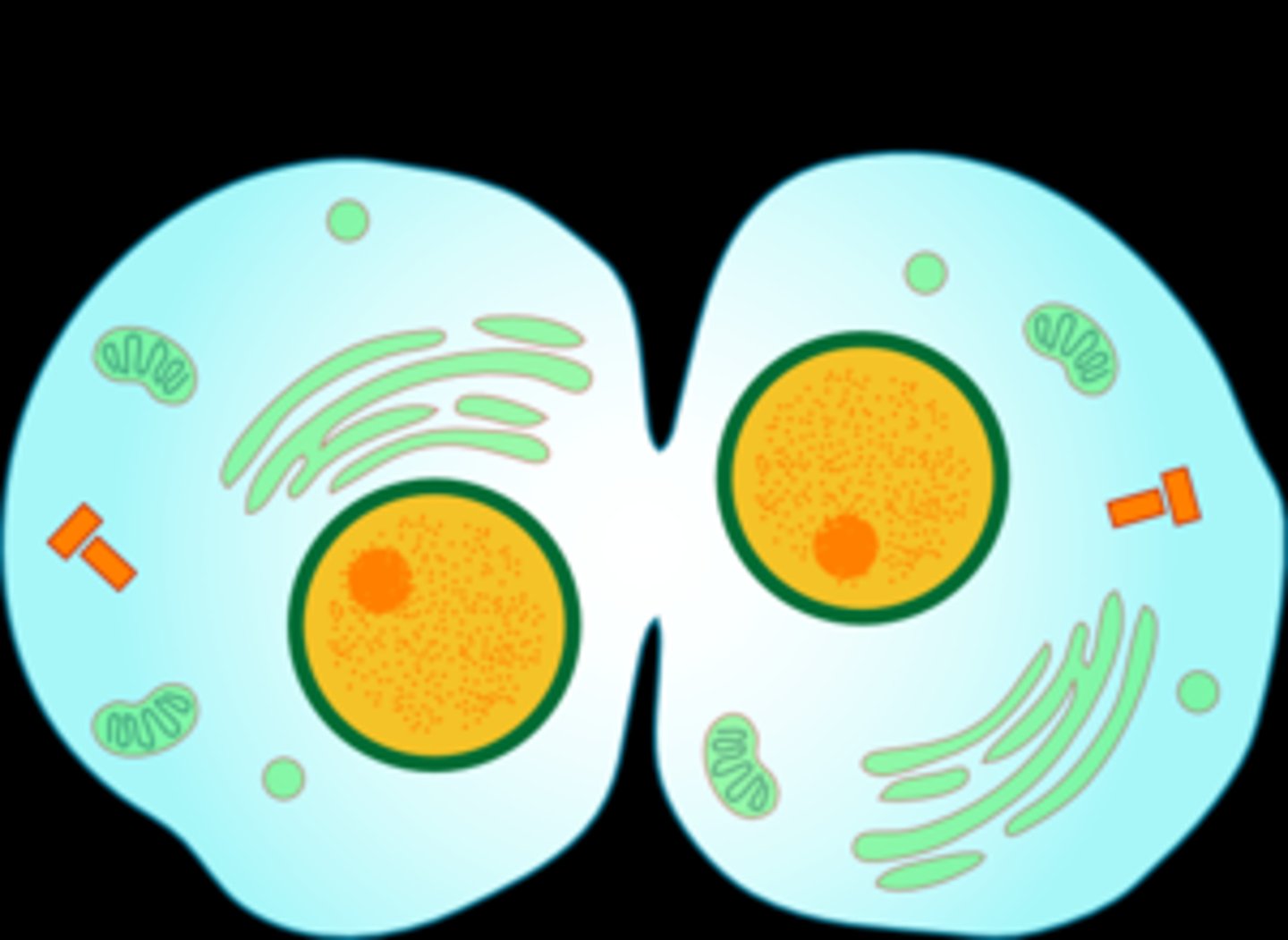
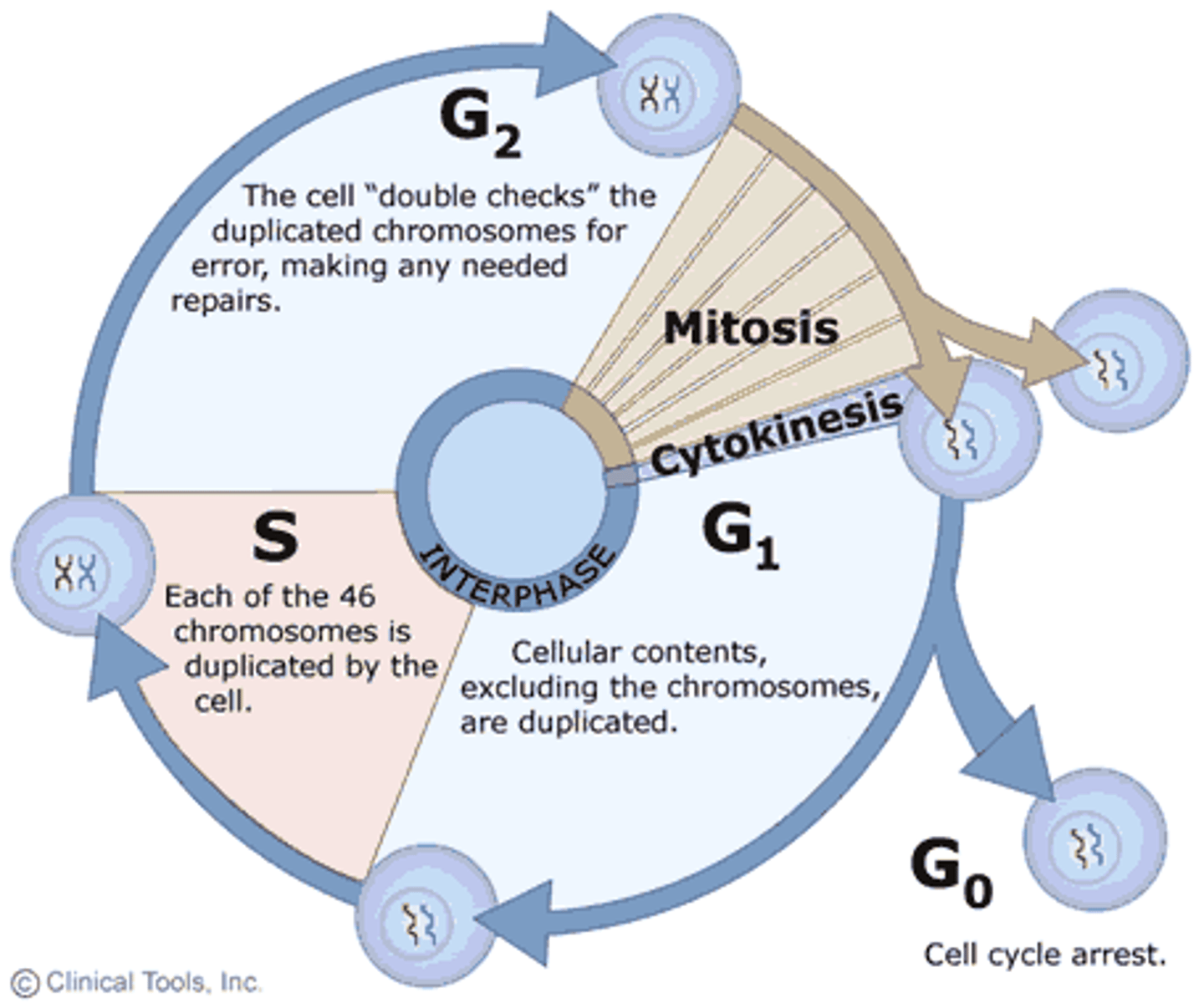
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm of a cell after nuclear division; last part of the cell cycle.
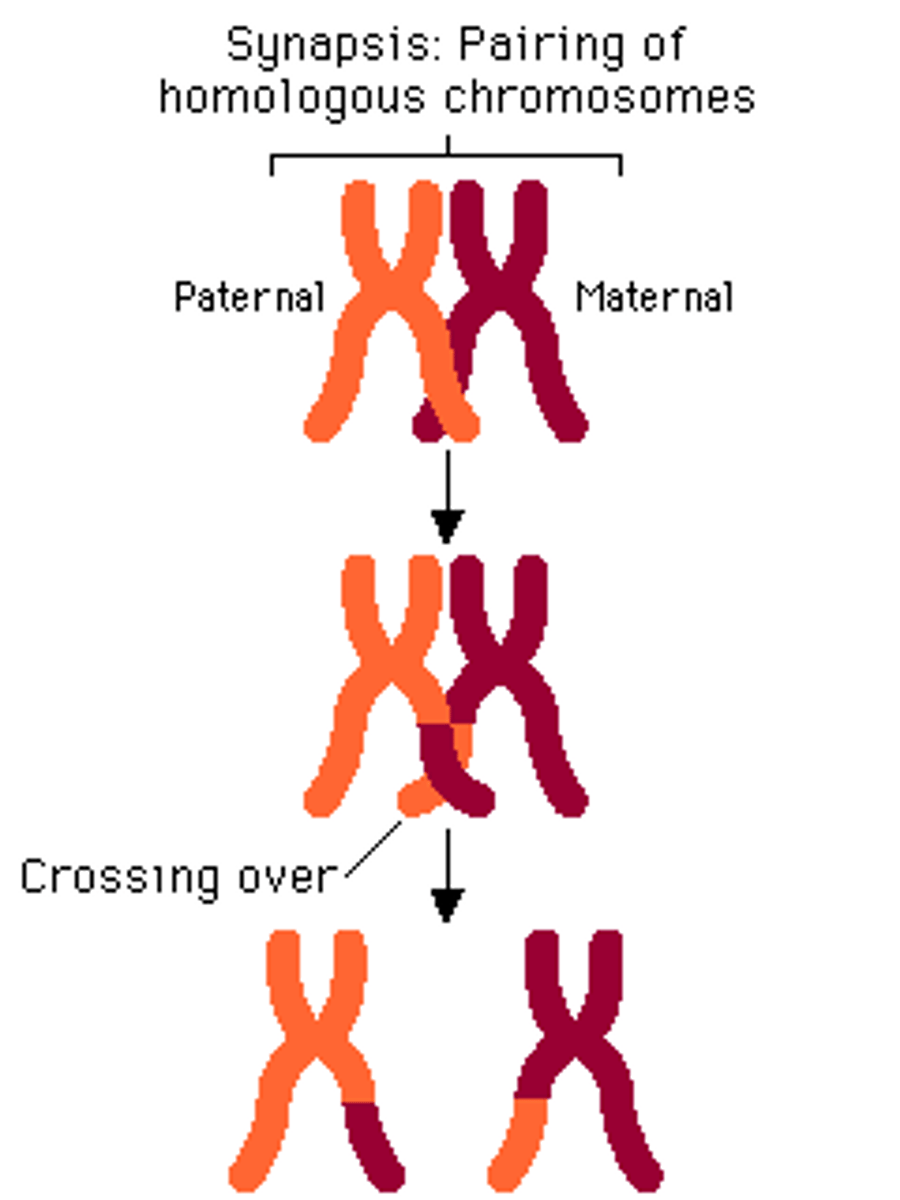
Crossing over
During meiosis I, an exchange of pieces of genetic material between homologous chromosomes; causes genetic recombination
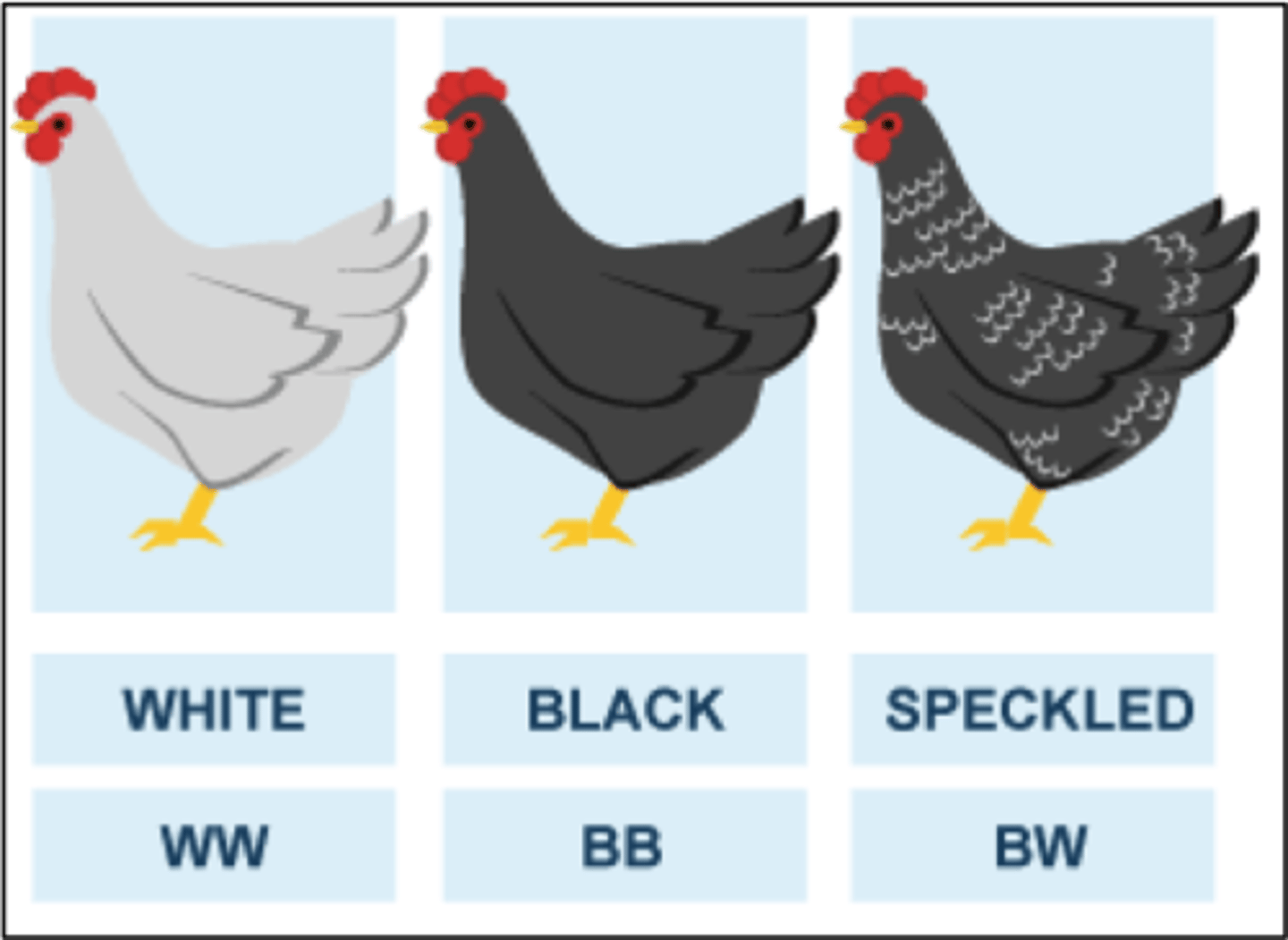
Codominance
When two or more alleles are equally represented in a heterozygote; example AB blood type.
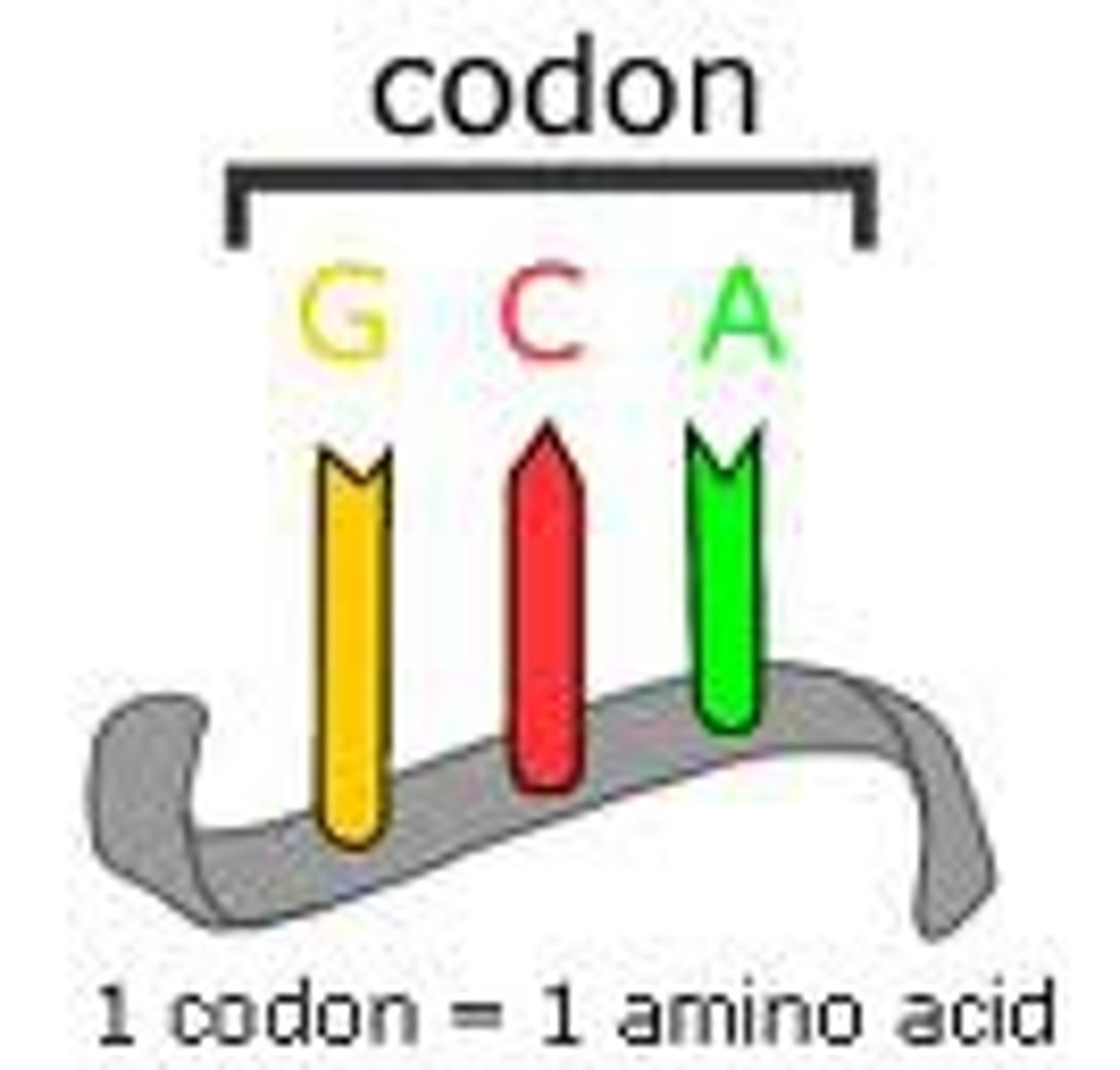
Codon
Three consecutive nucleotides that code for a specific amino acid
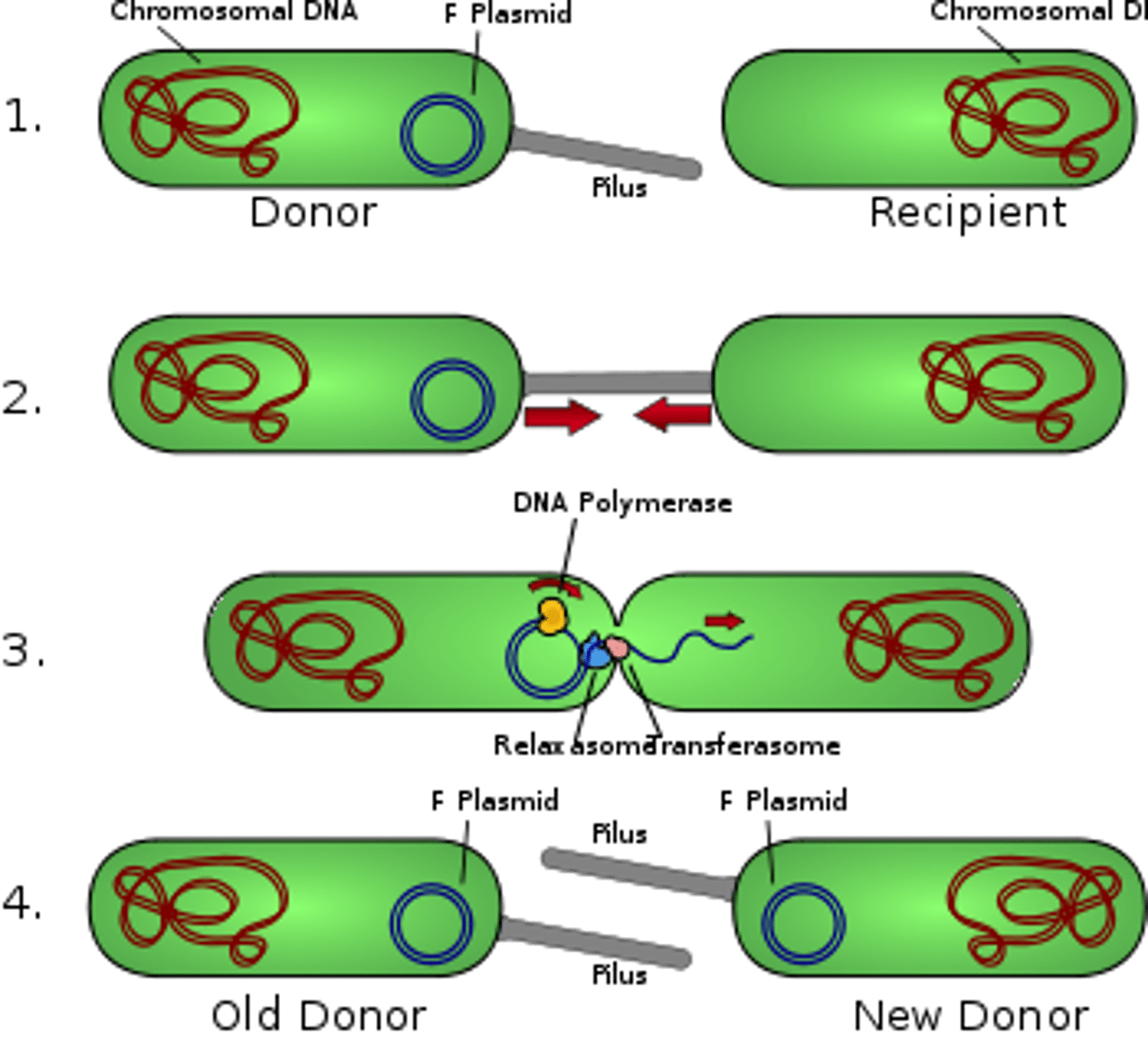
Conjugation
Transfer of DNA from one unicellular organism to another
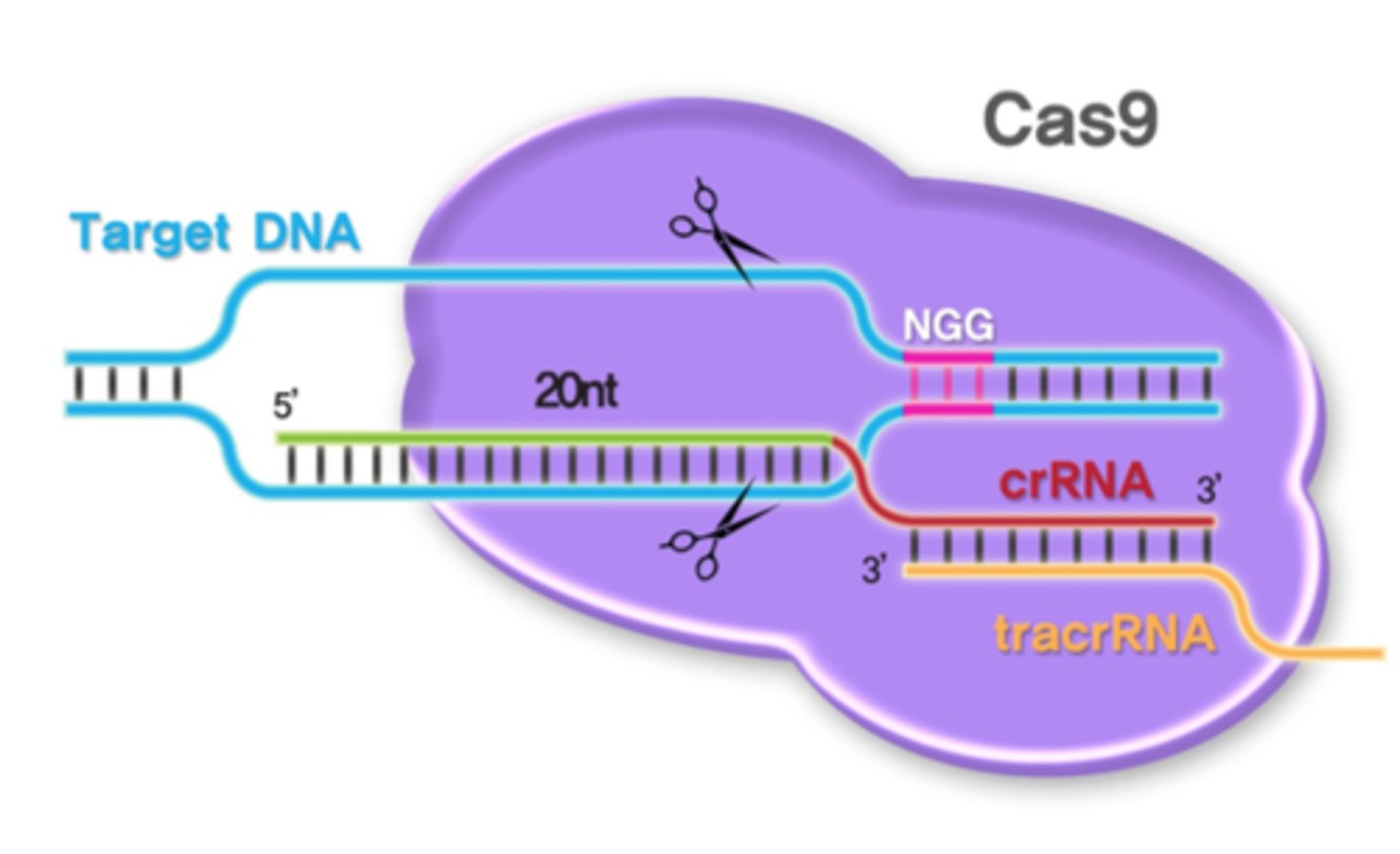
CRISPR
A segment of bacterial DNA containing repeating nucleotide sequences that can be used in genetic engineering to alter an organism's DNA
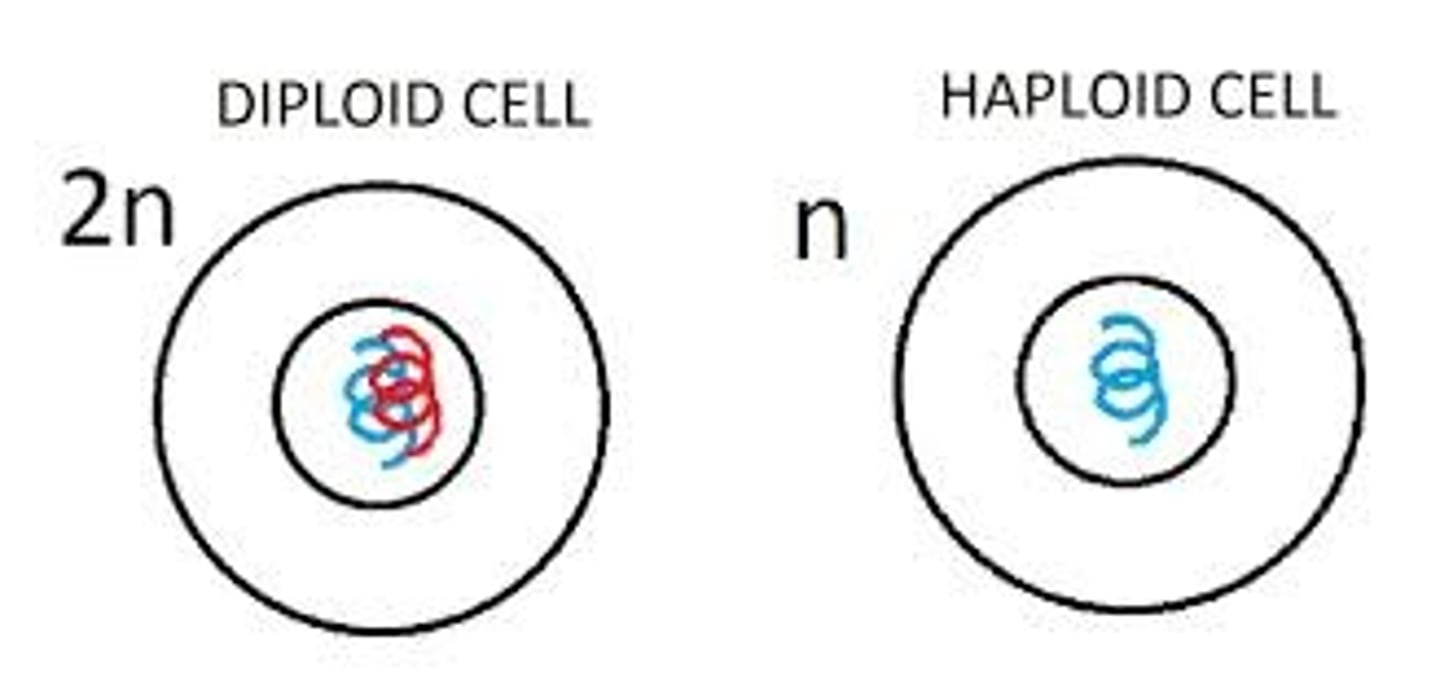
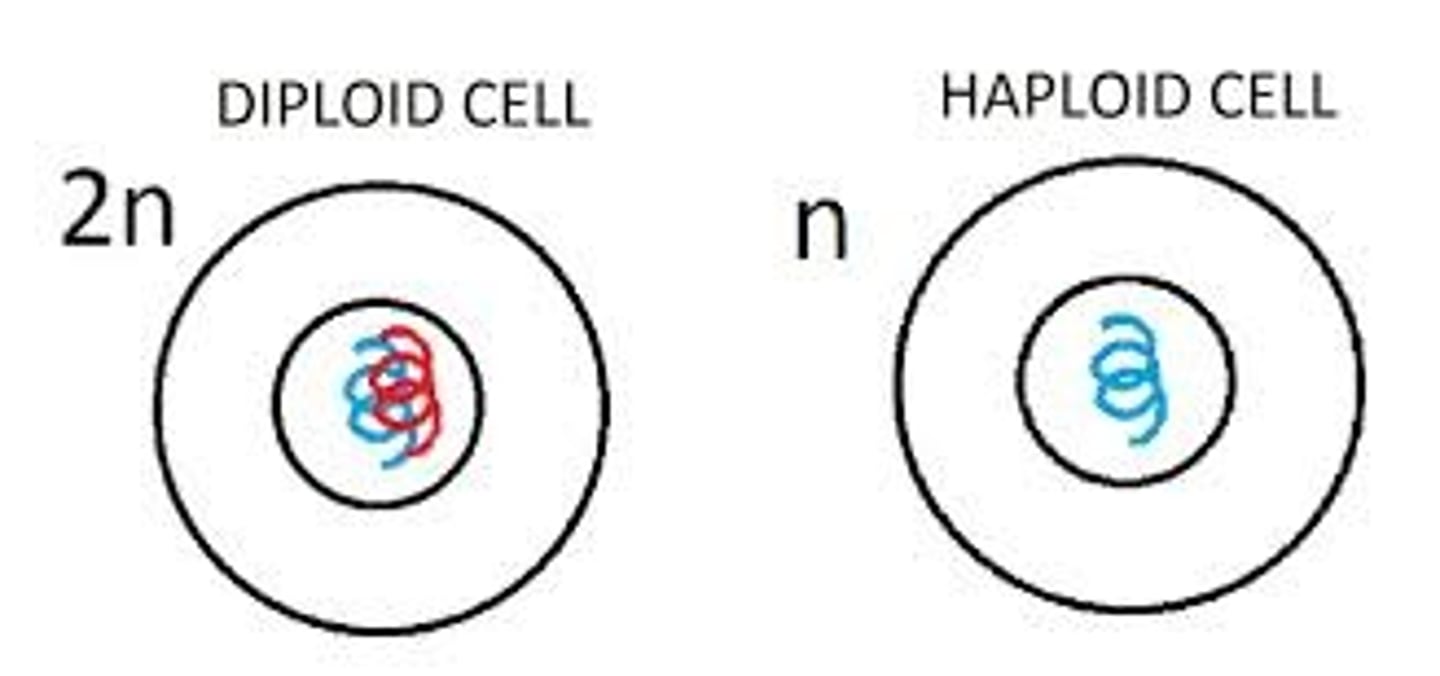
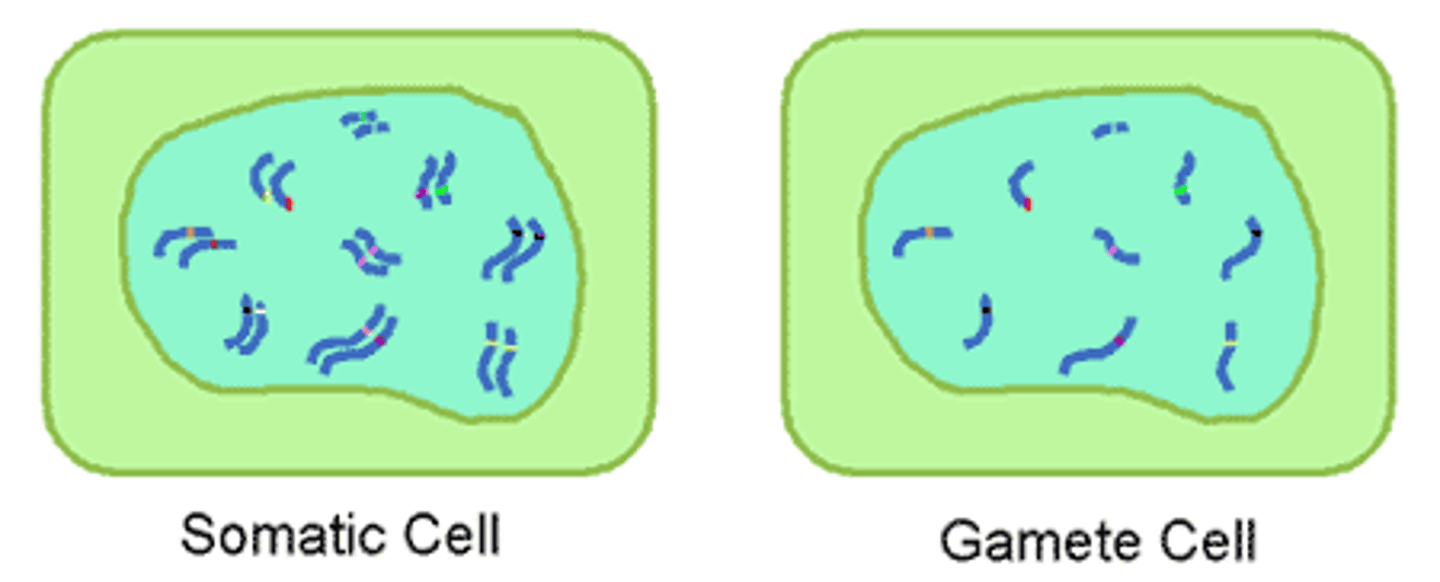
Diploid
Having two sets of chromosomes (2n); characteristic of non-gamete cells
DNA Polymerase
Enzymes that synthesize DNA; only synthesize in the 5' to 3' direction
DNA methylation
Addition of a methyl group (CH3) to the DNA strand resulting in a change in gene expression
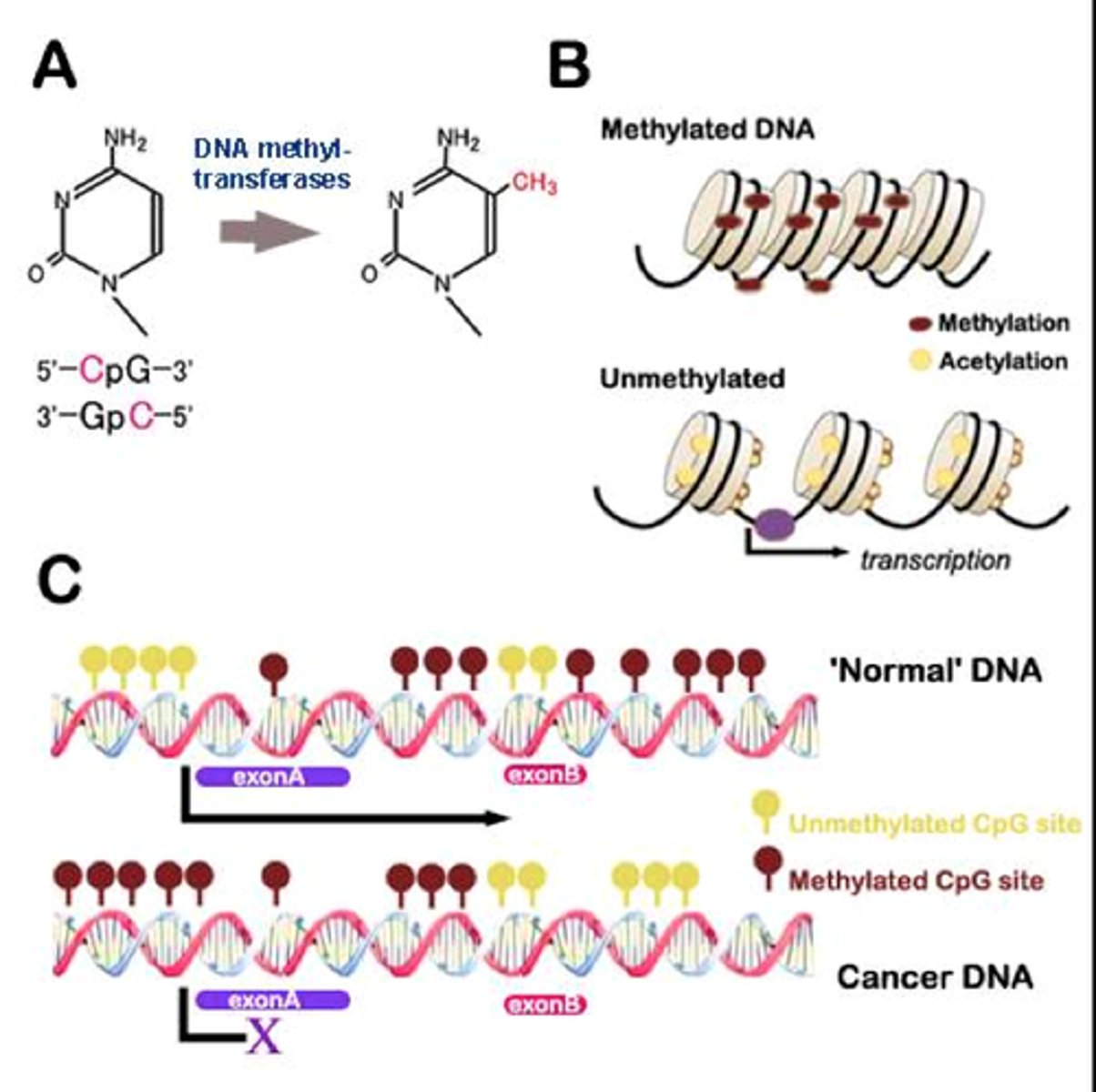
Epigenetics
The study of changes in an organism caused by gene expression rather than changes to the genetic code
Epistasis
Interaction in which one gene modifies the phenotype of another.

Frameshift Mutation
A mutation in which a nucleotide is added or deleted from DNA, creating a downstreaming effect on other codons.
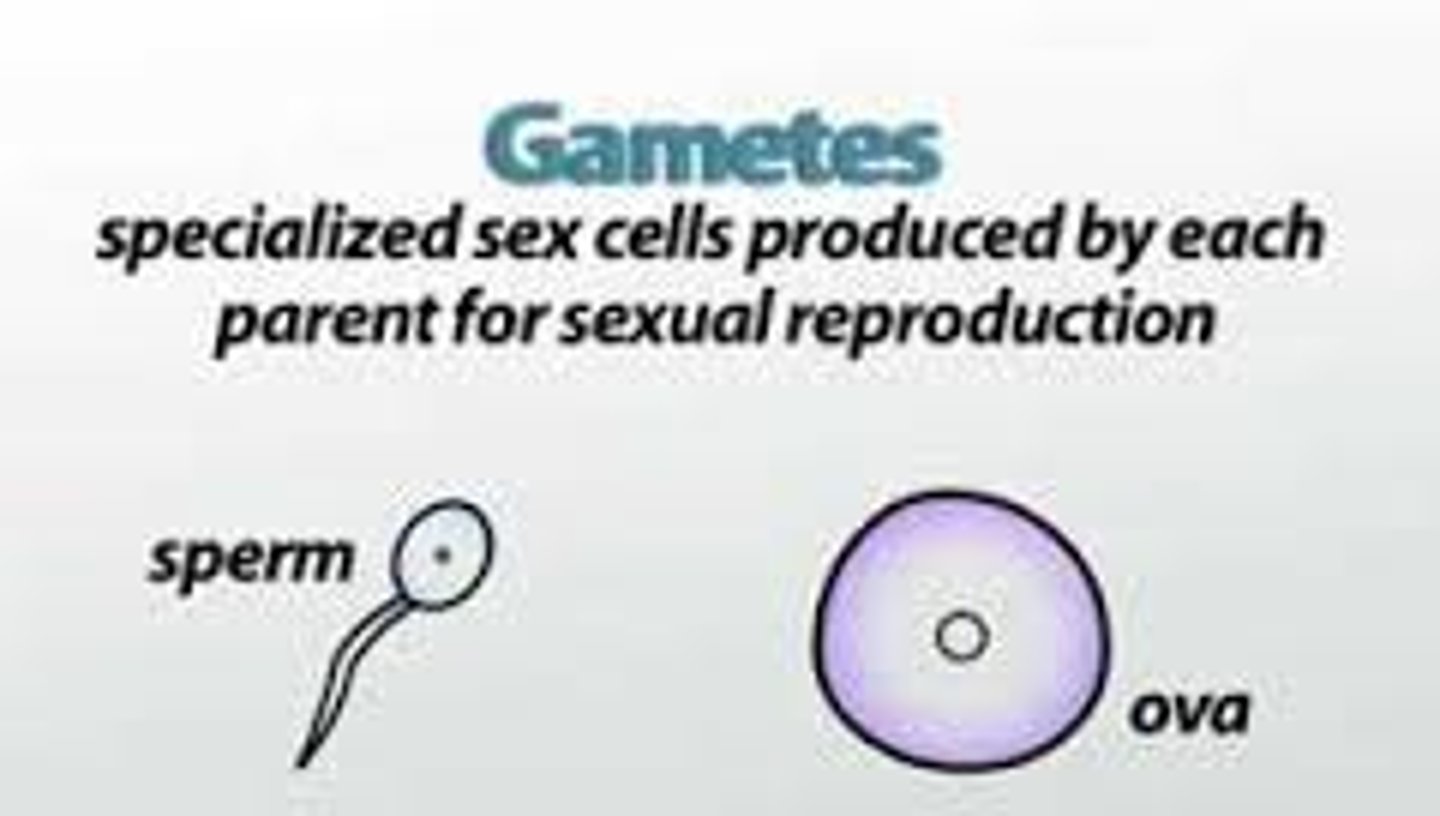
Gamete
A haploid reproductive cell (sperm/egg)
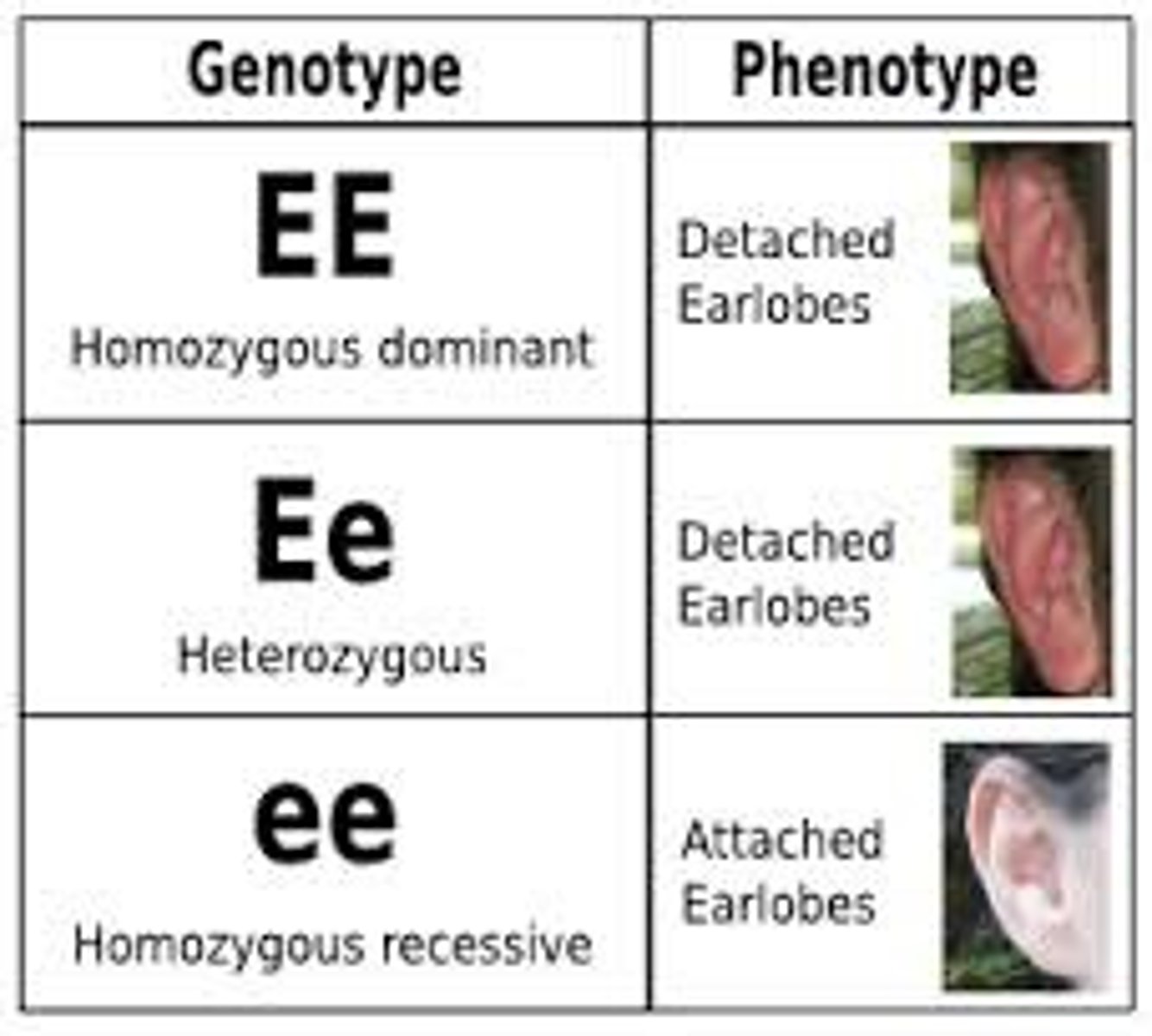
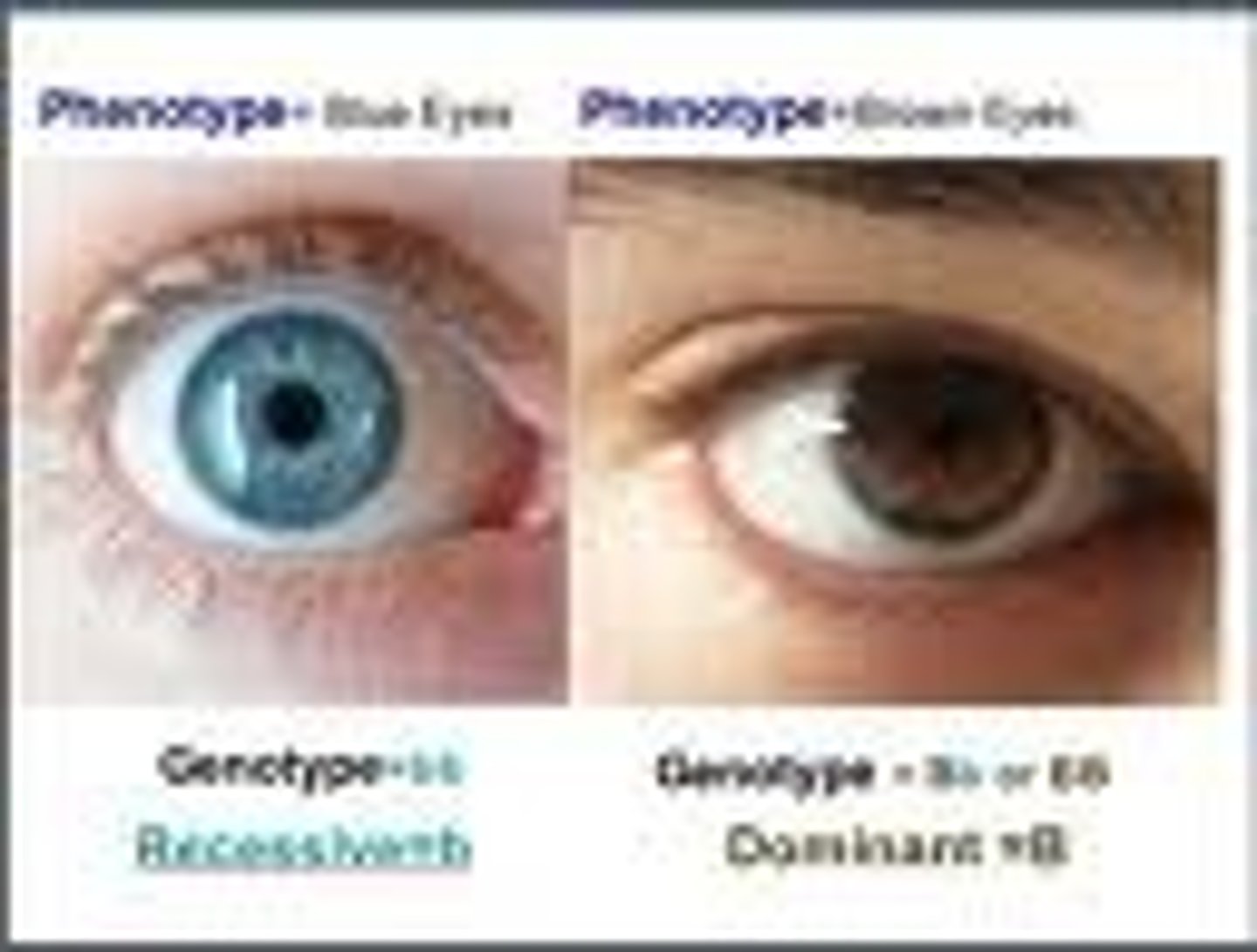
Genotype
The genetic constitution that causes a trait or set of traits
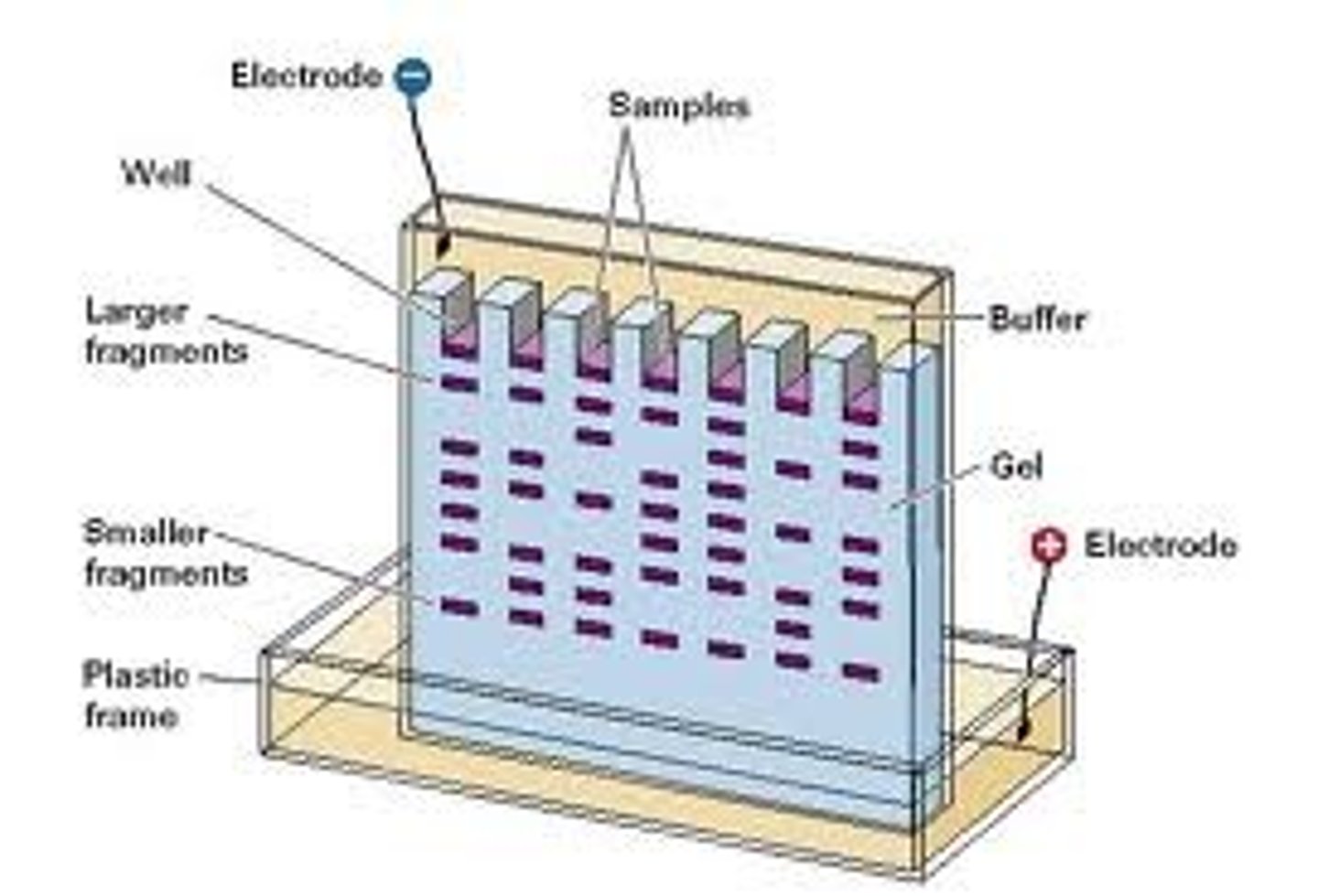
Gel Electrophoresis
A laboratory method that separates DNA, RNA, or proteins based on molecular size; used to show genetic relationships between organisms
Haploid
Having only one set of chromosomes (n); such as in sex cells
Heterozygous
Having two different alleles of the same gene (ex. Tt)

Homozygous
Having two identical alleles for a given gene (ex. TT or tt)

Homologous Chromosomes
Two of the same chromosome found in a diploid cell, one being derived from each parent
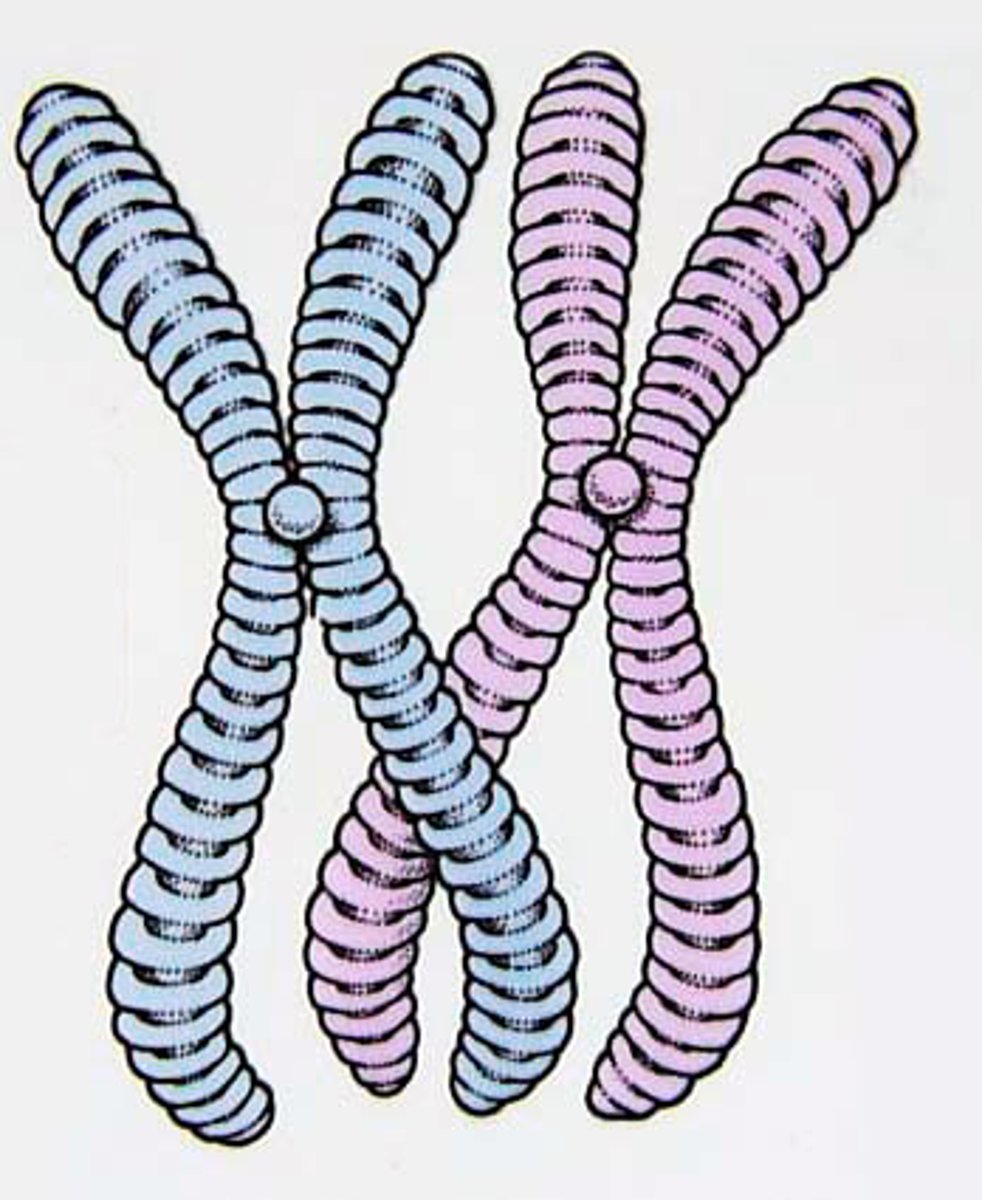
Interphase
The period between two mitotic divisions during which the cell grows and DNA replicates
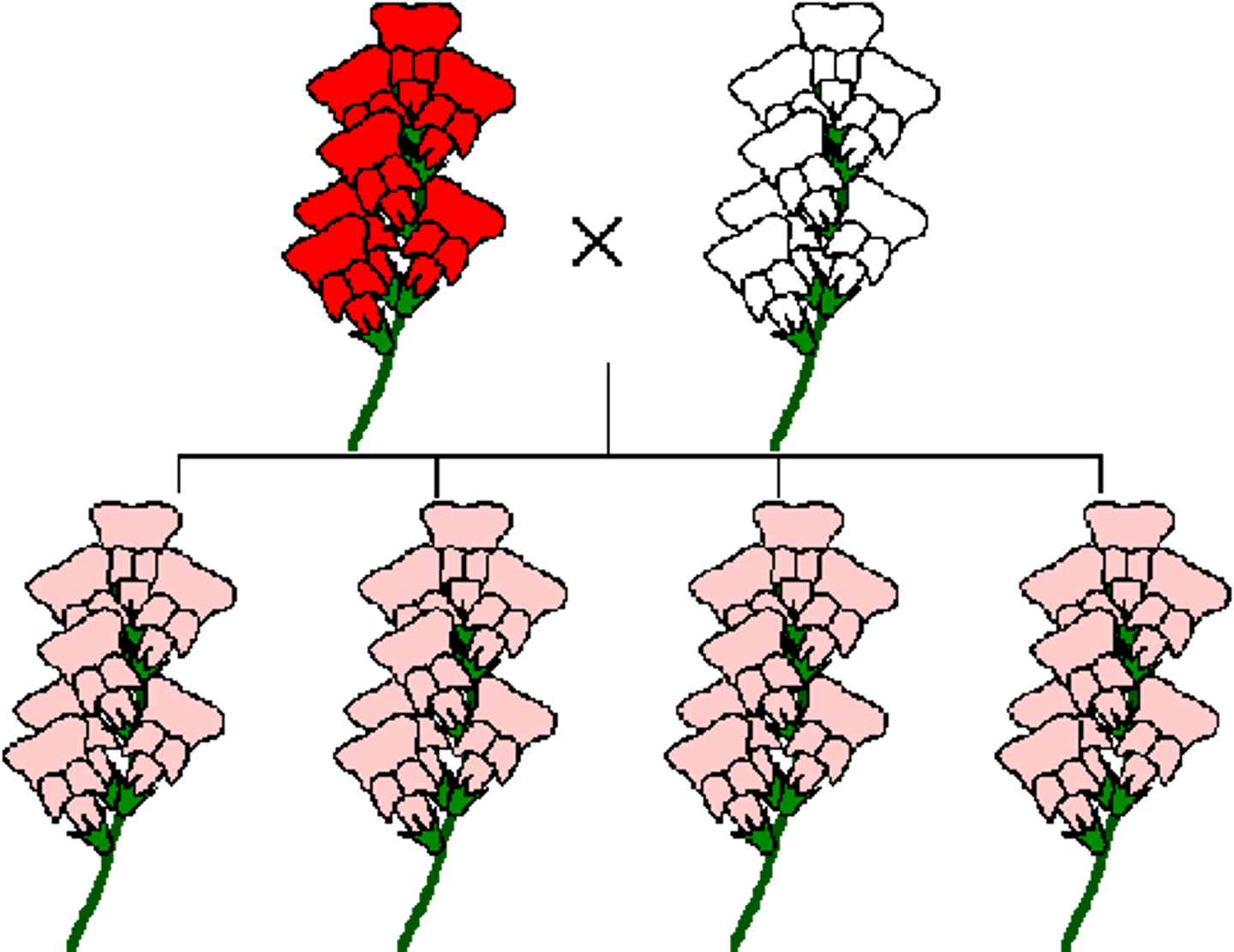
Intermediate Inheritance
When two alleles are expressed to create a phenotype that blends both traits.
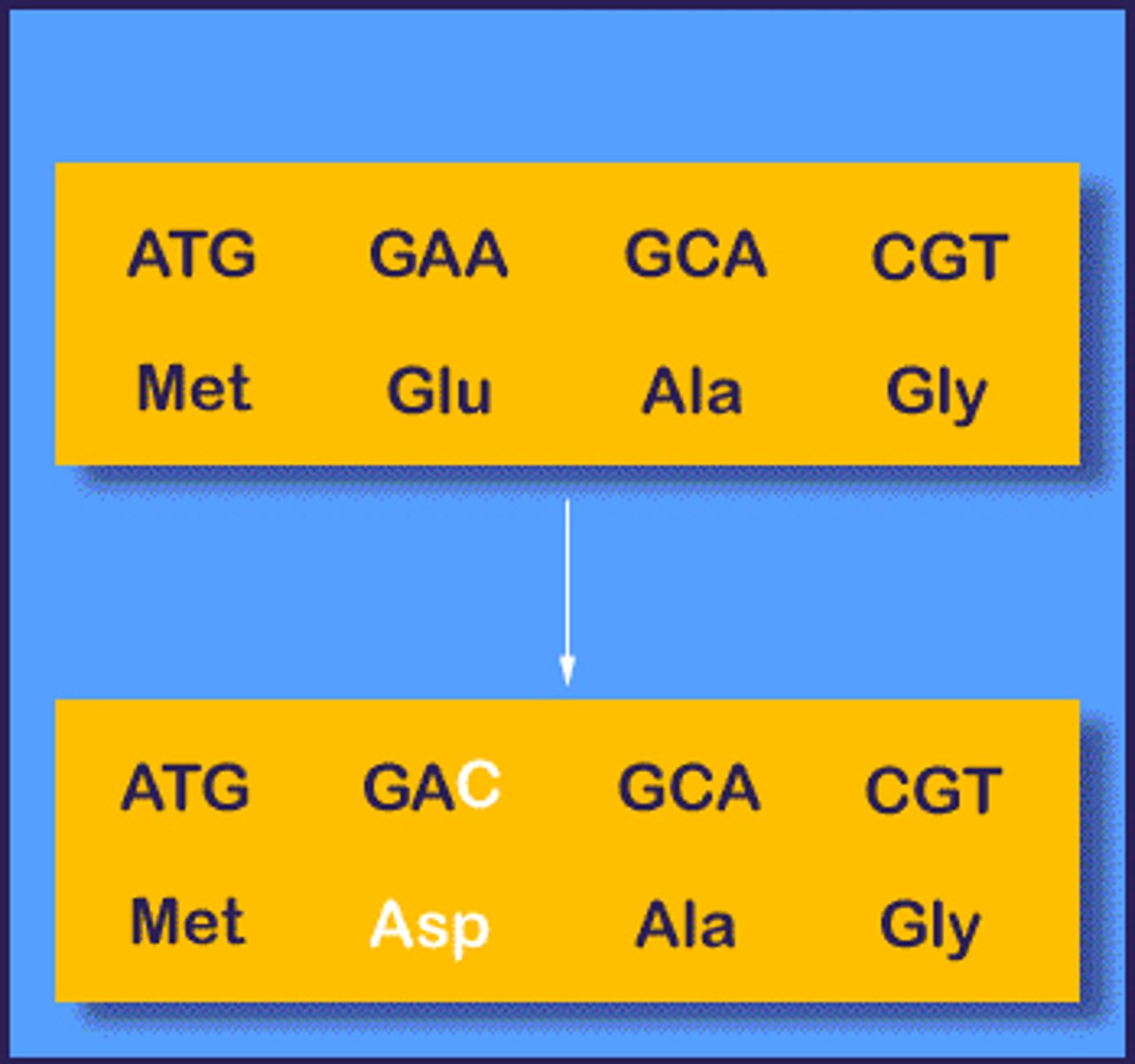
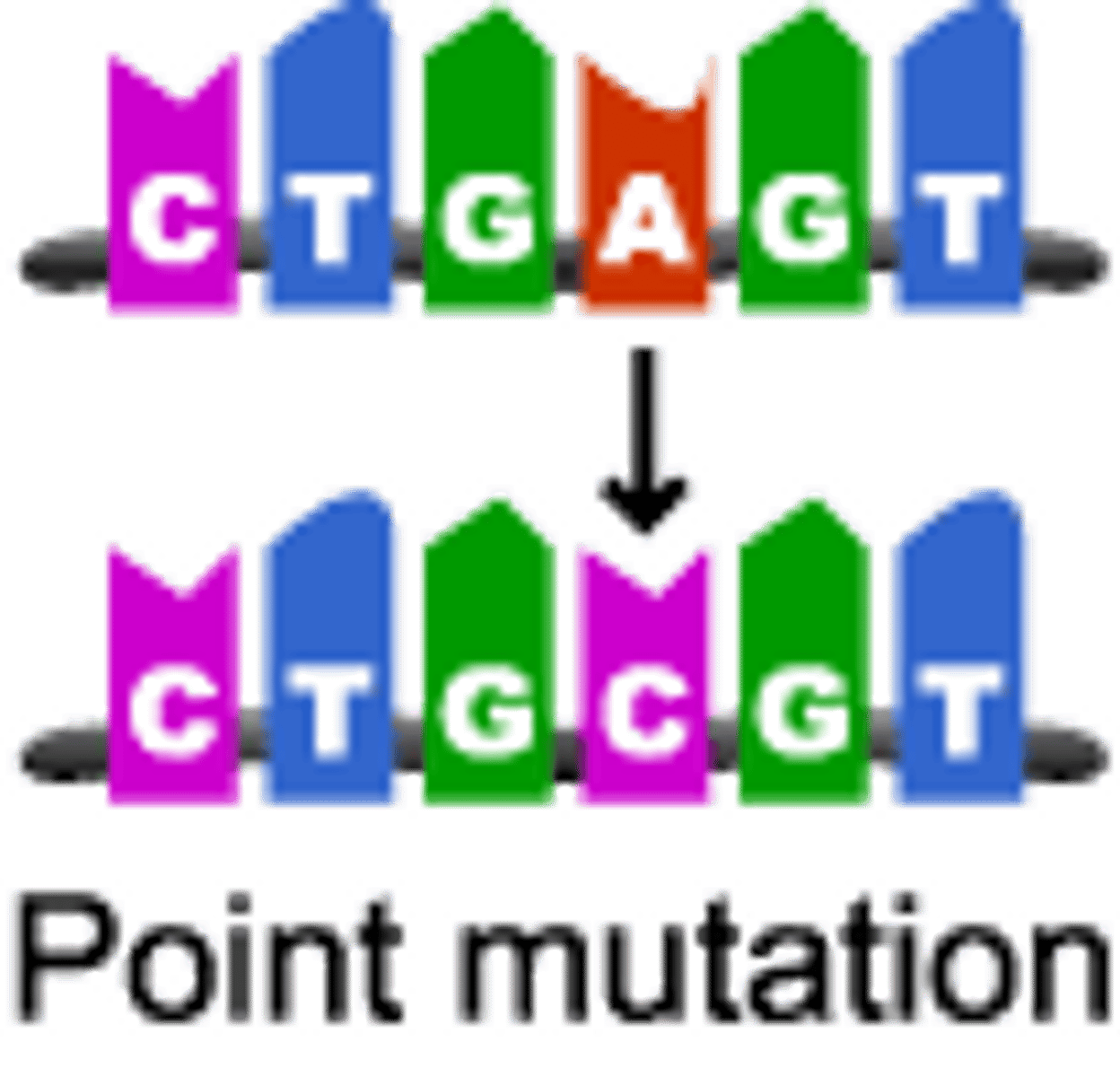
Missense Mutation
A mutation in which one base is substituted, causing a change in one amino acid
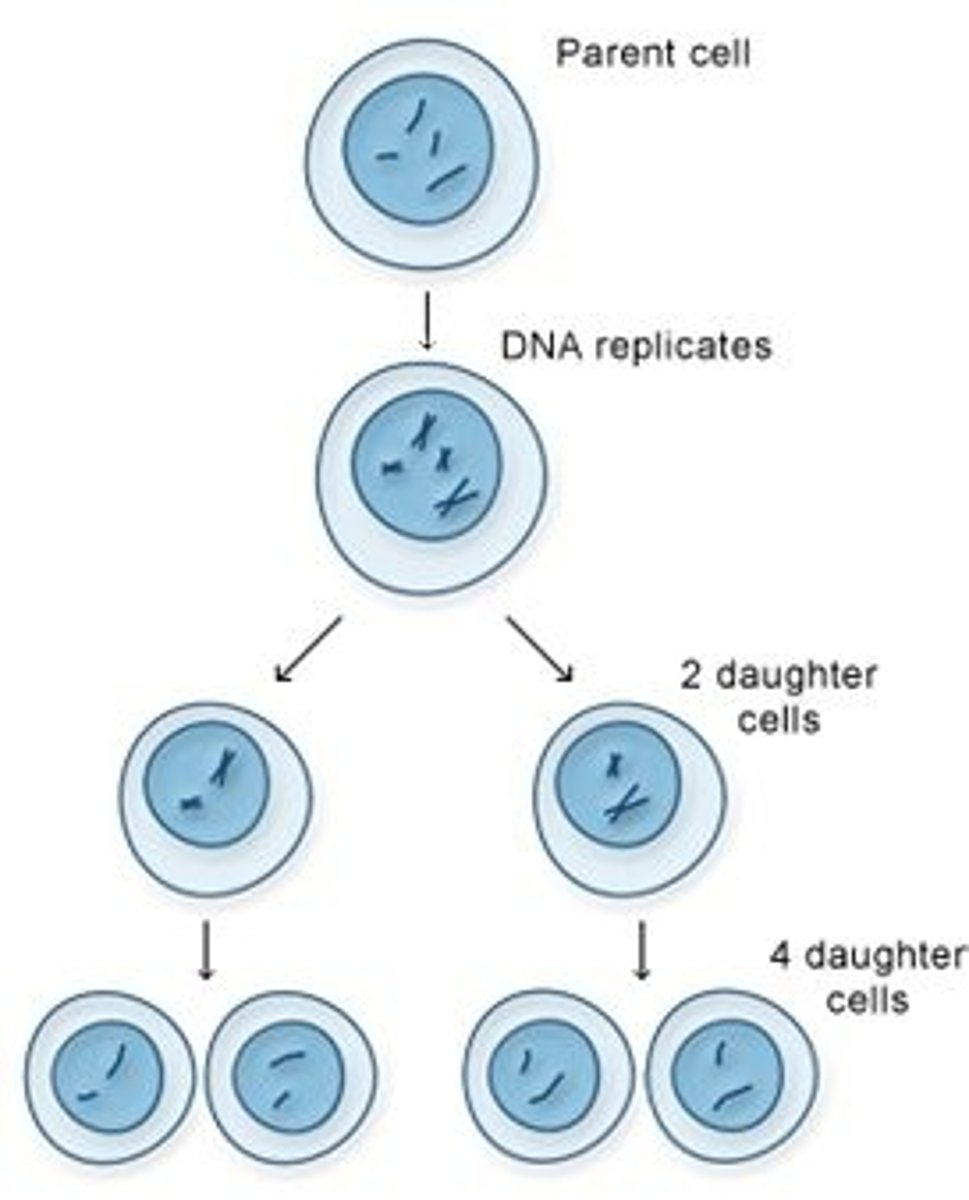
Mitosis
Division of somatic cells to create two identical daughter nuclei
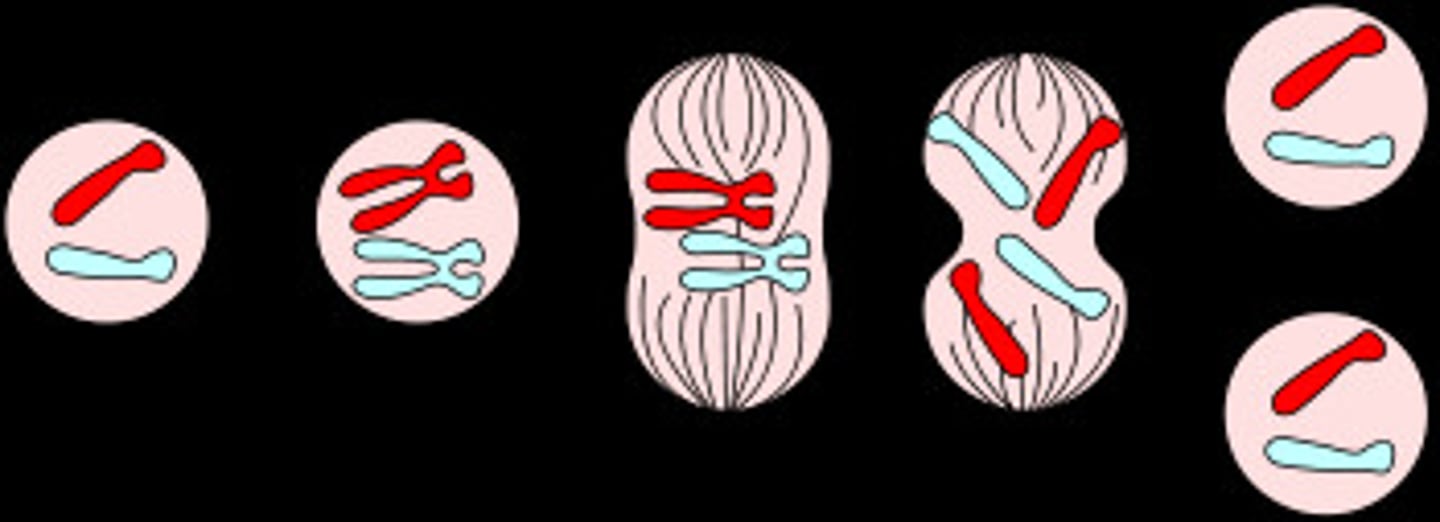
Meiosis
Division of gametes to create four unique, haploid cells
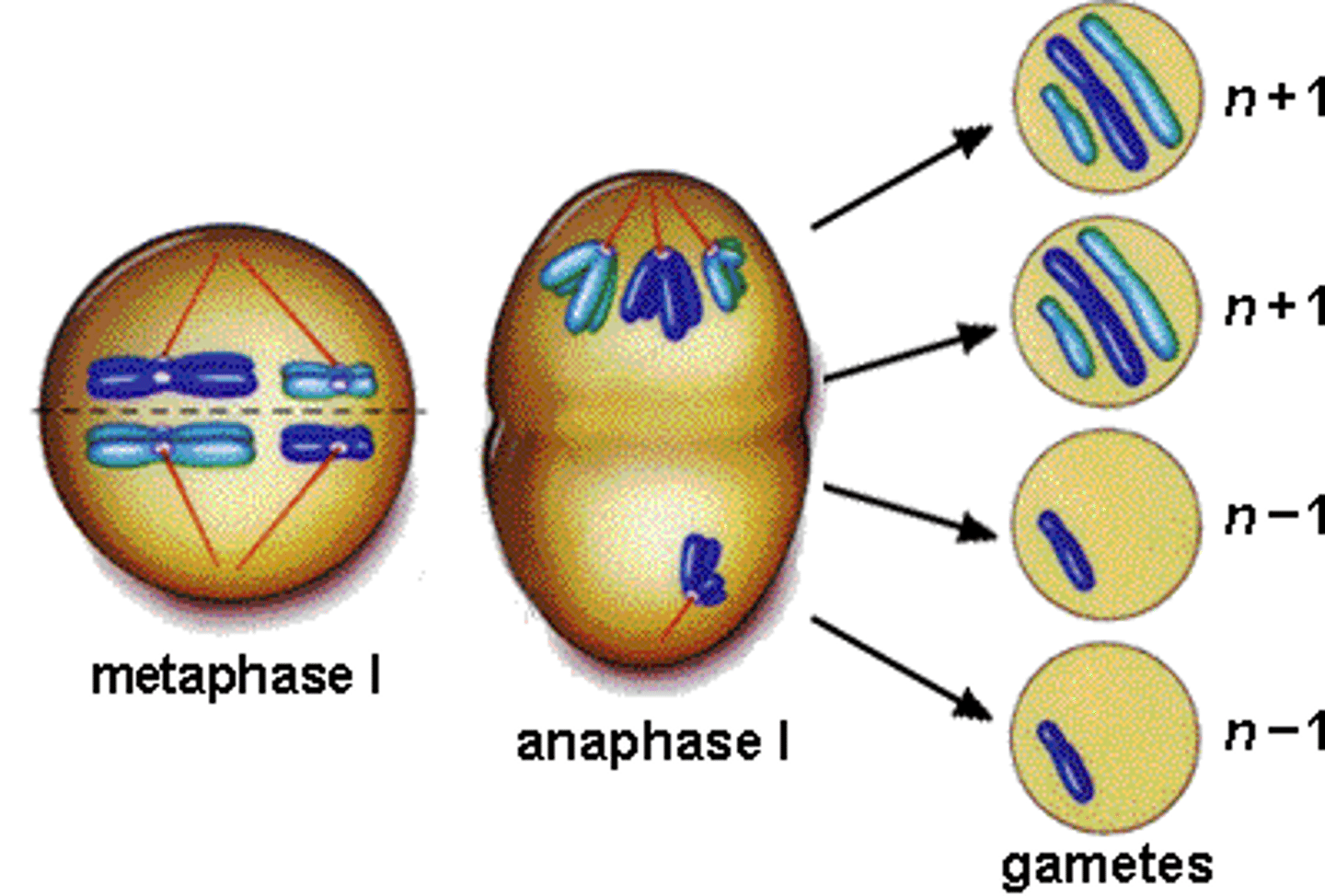
Nondisjunction
When sister chromatids fail to separate during meiosis, resulting in cells that have one too many or one too few chromosomes; can cause Down Syndrome
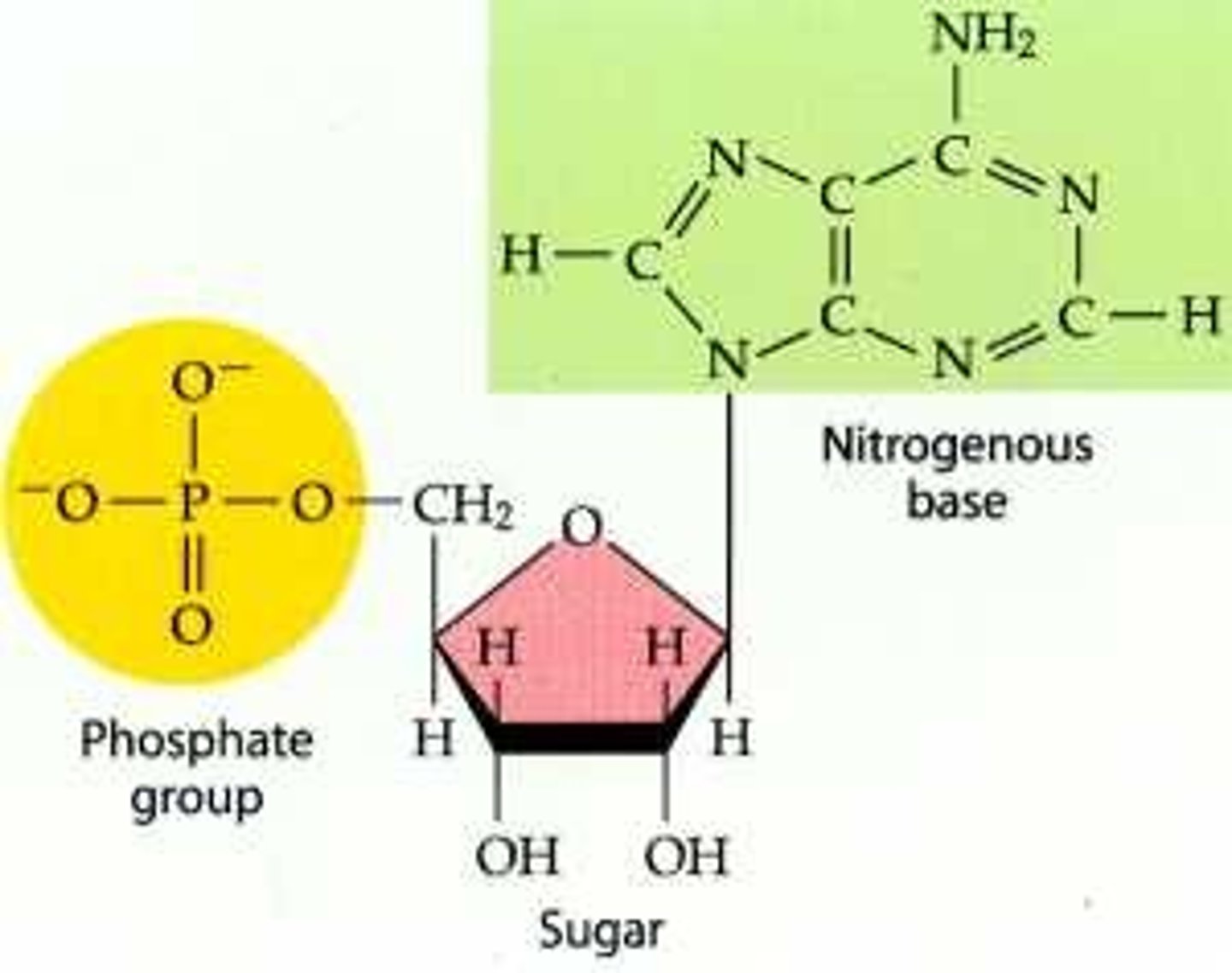
Nucleotide
The building block of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA); composed of a phosphate, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogen base (A,T,C,G, or U).
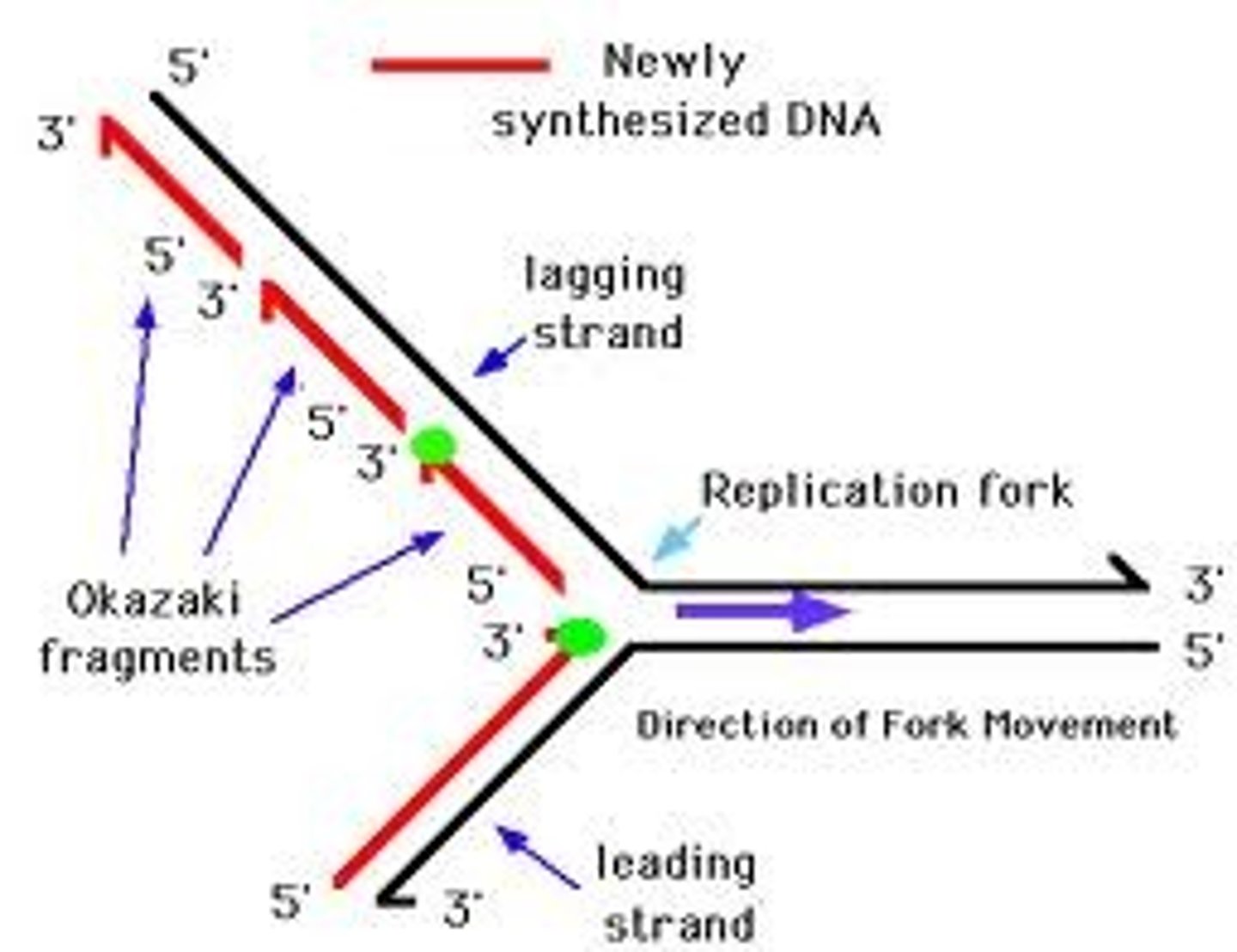
Okazaki Fragment
A short segment of DNA produced by the discontinuous replication of DNA in the 5' to 3' direction
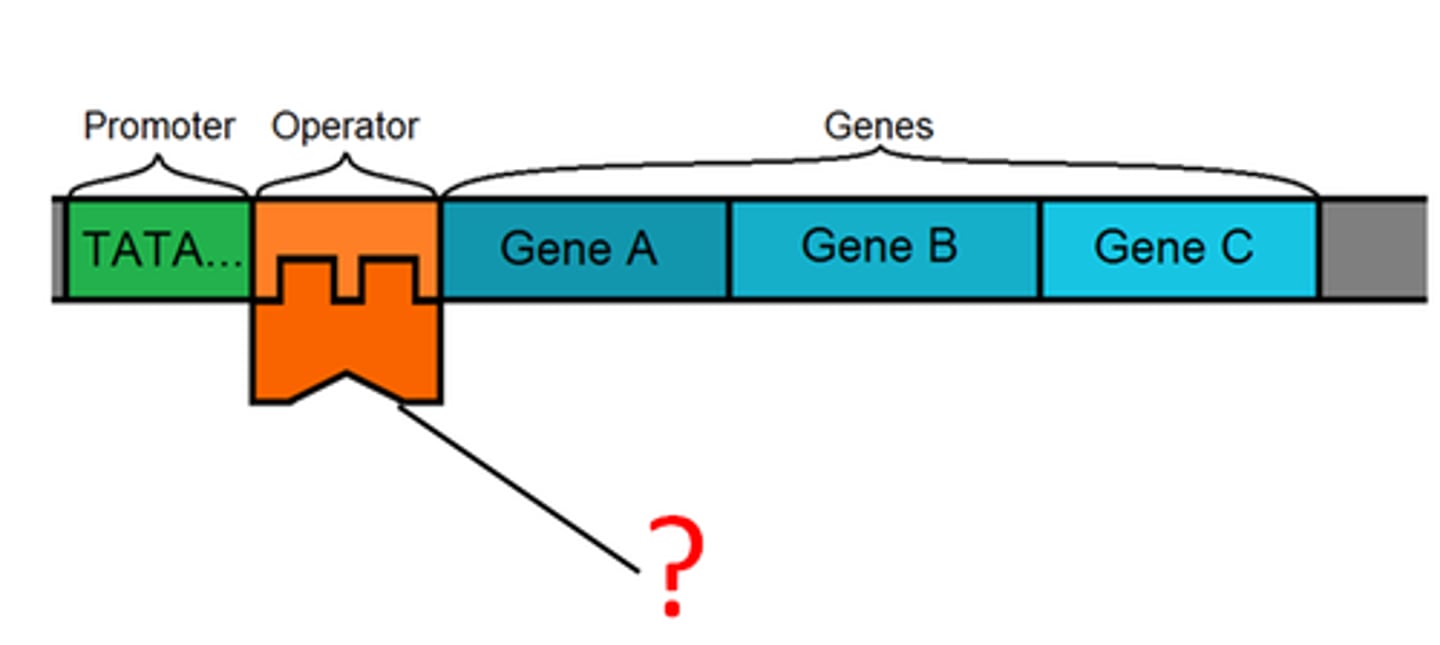
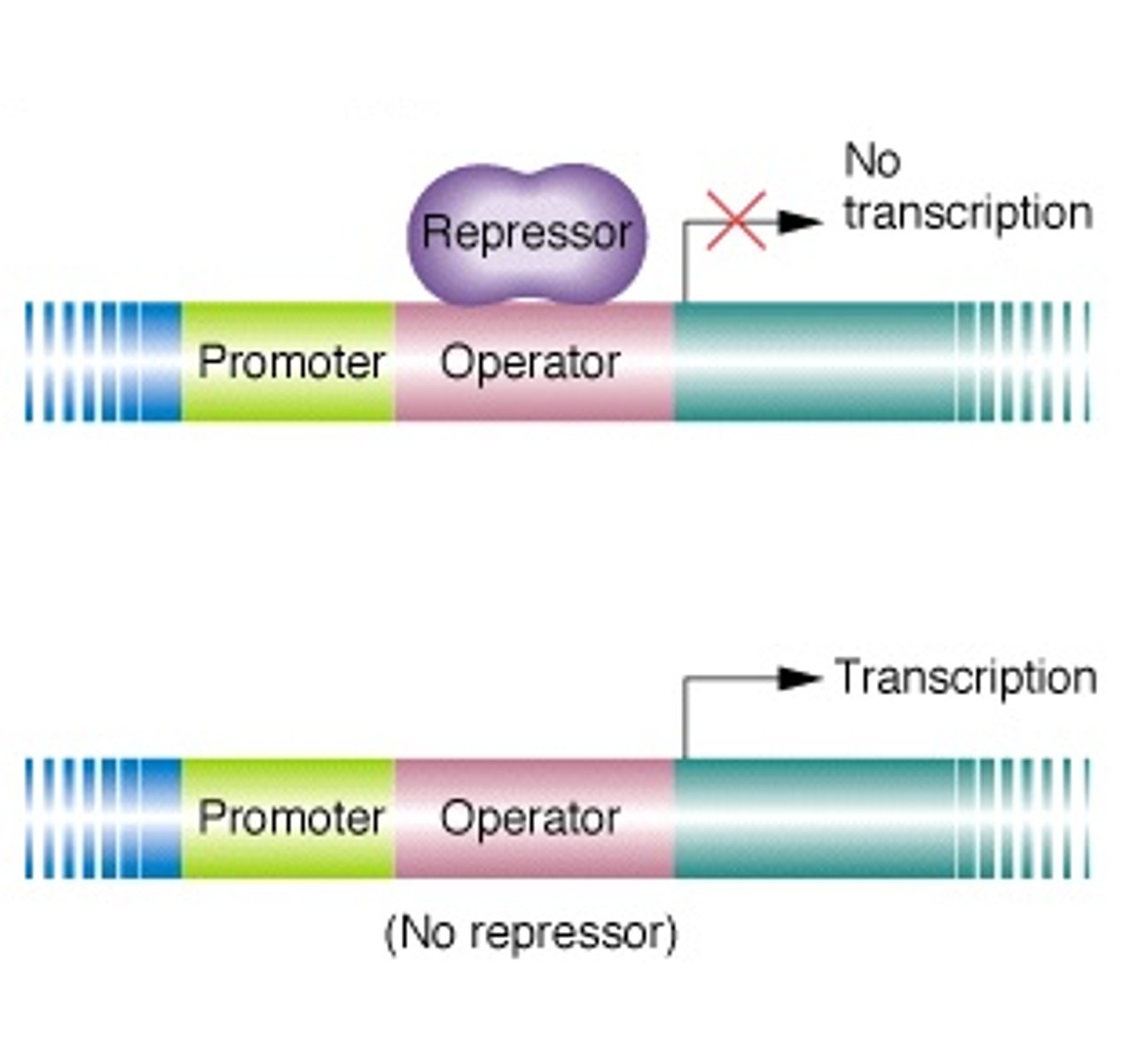
Operon
A cluster of genes transcribed together to create a single mRNA molecule
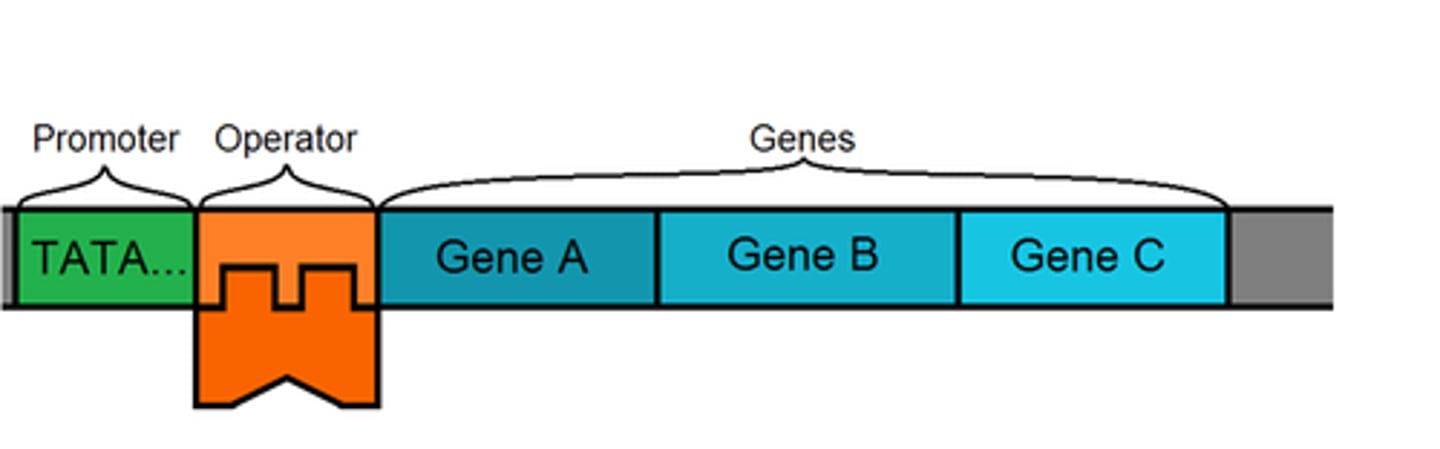
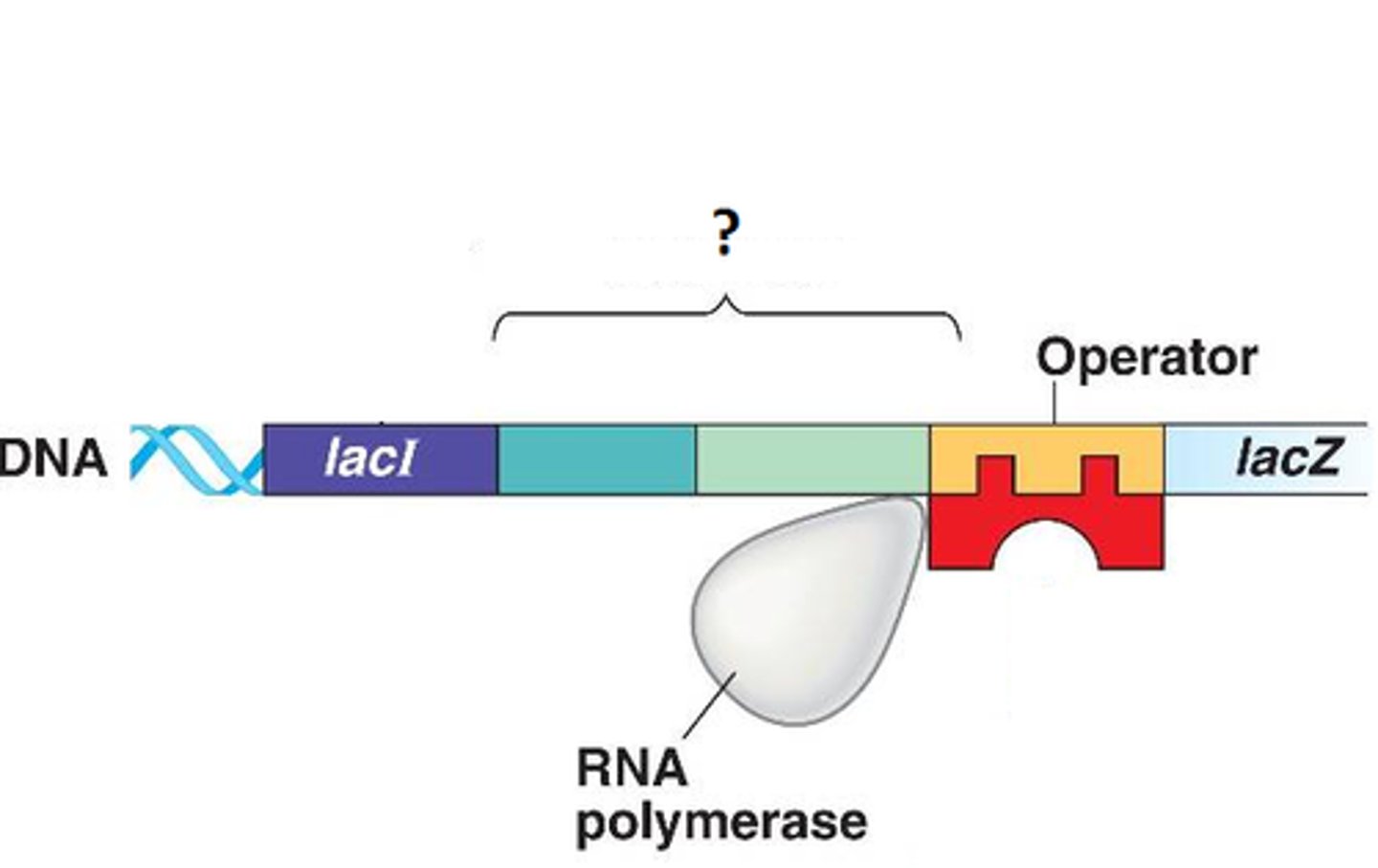
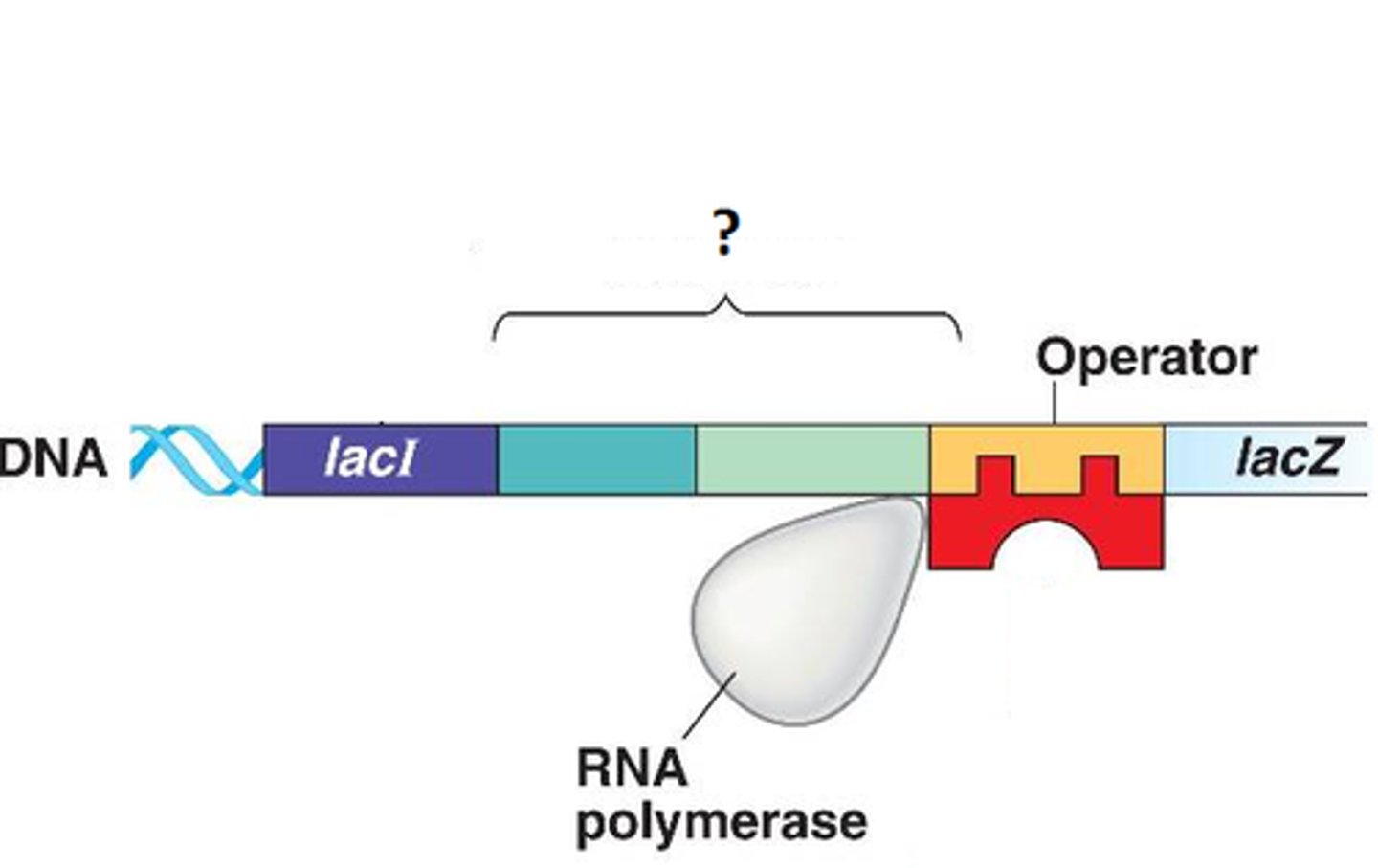
Operator
A site on DNA that a repressor can bind to to prevent transcription of mRNA
Phenotype
The physical appearance or functional expression of a trait
Pleiotropy
When one allele has more than one effect on the production of a phenotype
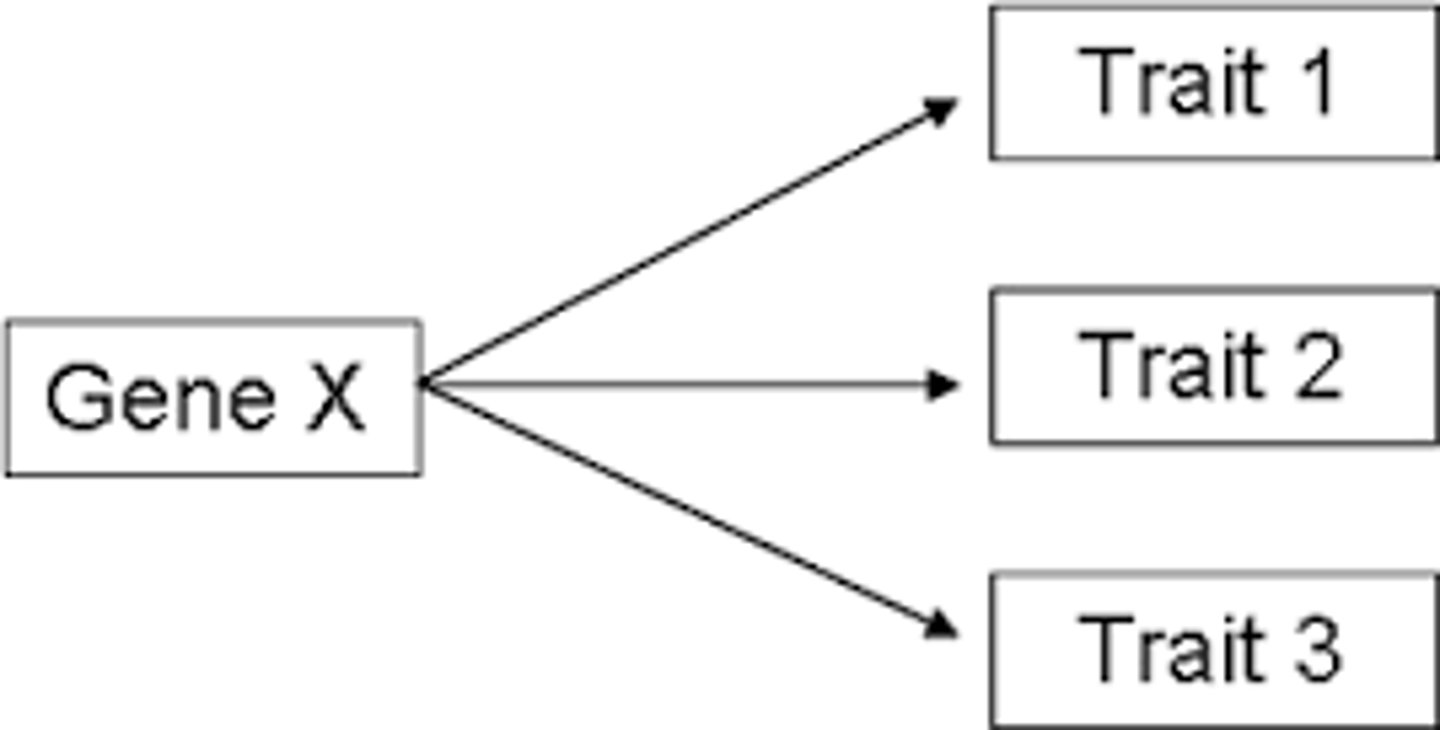
Promoter
A DNA sequence that RNA polymerase attaches to in order to begin transcription of a gene
Point Mutation
A change in one nucleotide in a DNA molecule; can be missense (changes amino acid); nonsense (codes for Stop codon), or silent (no change in amino acid)
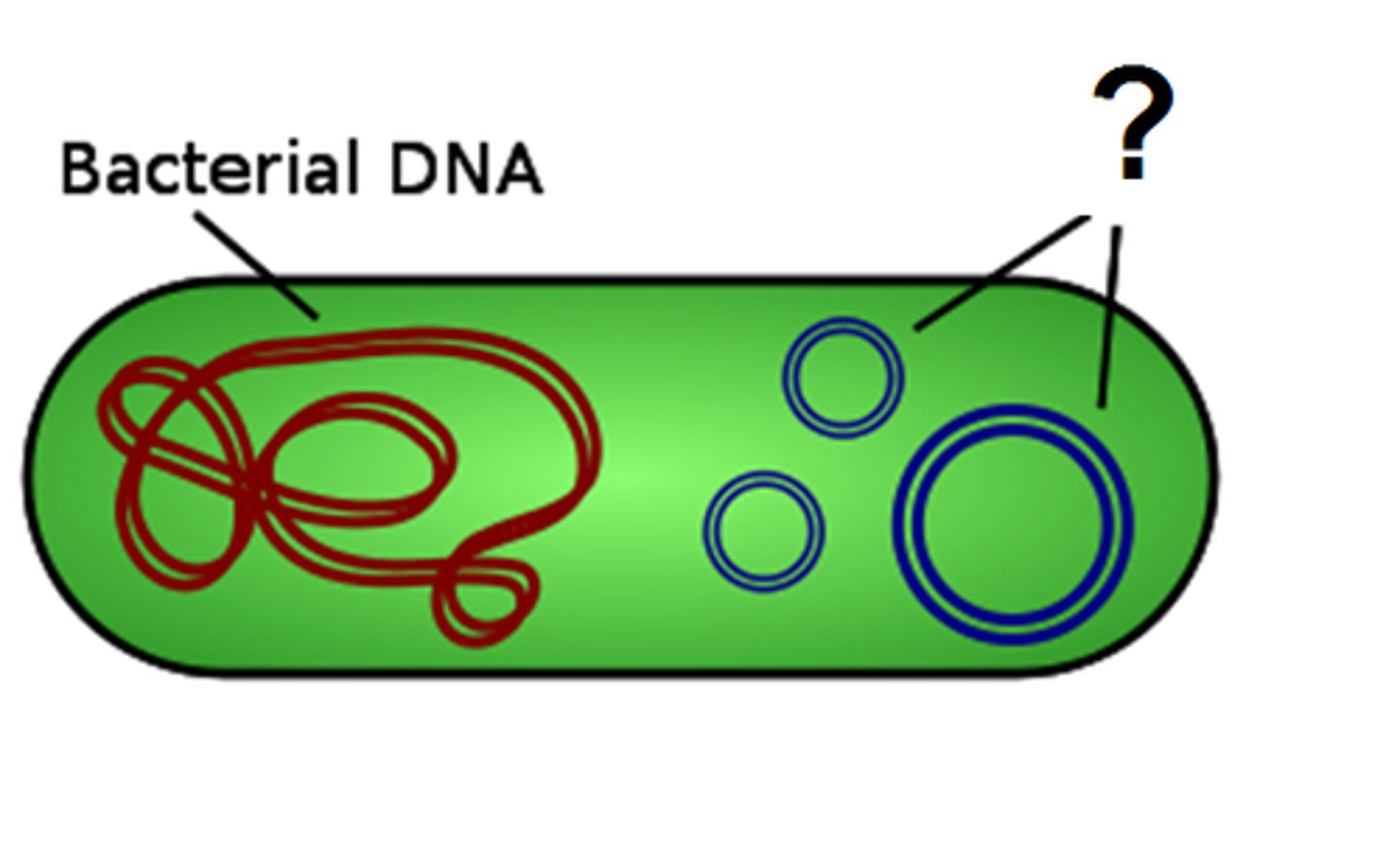
Plasmid
A small circular fragment of bacterial DNA that can self-replicate independent of chromosomal DNA
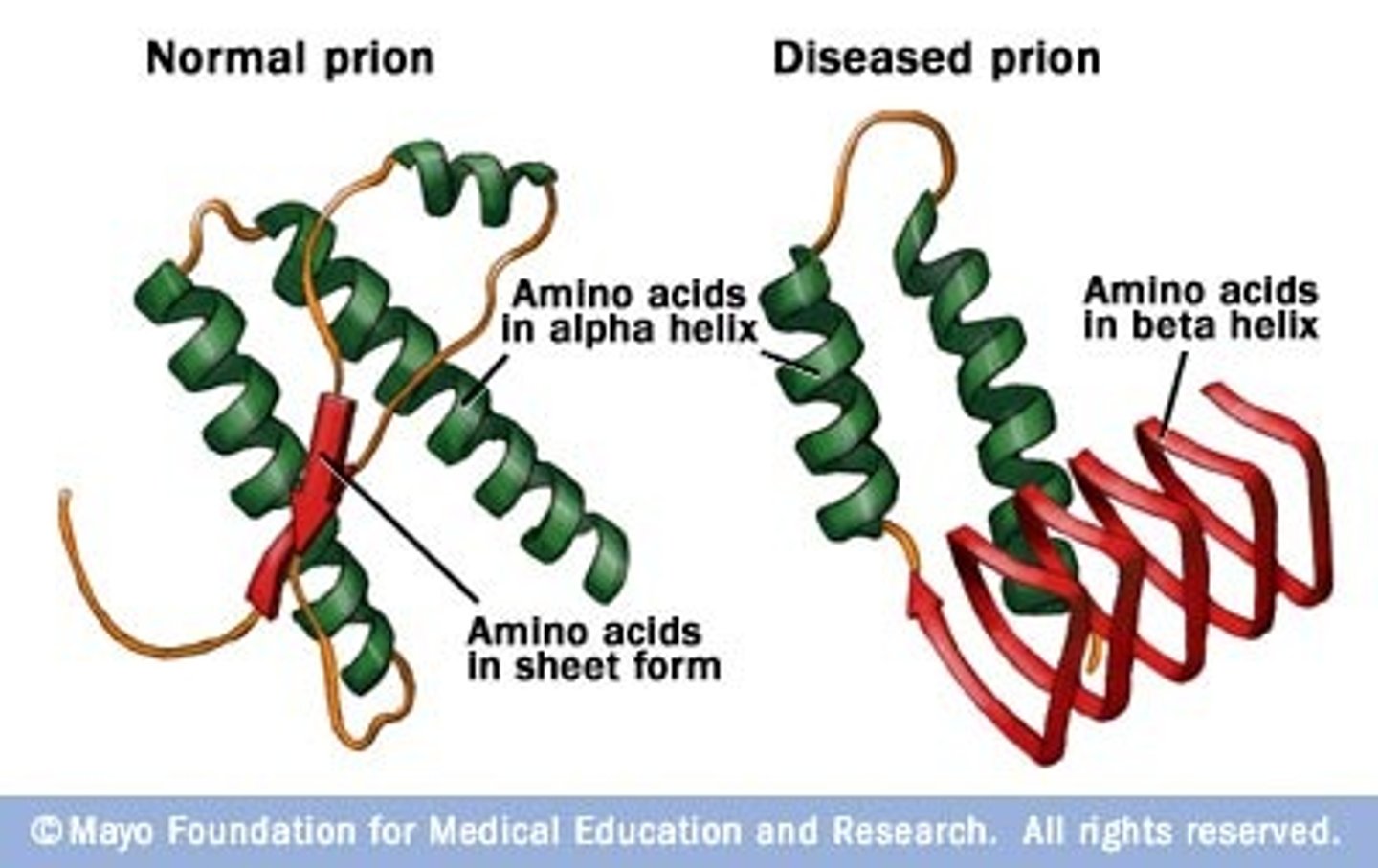
Prion
Infectious proteins that cause cell death; cause of Mad Cow disease
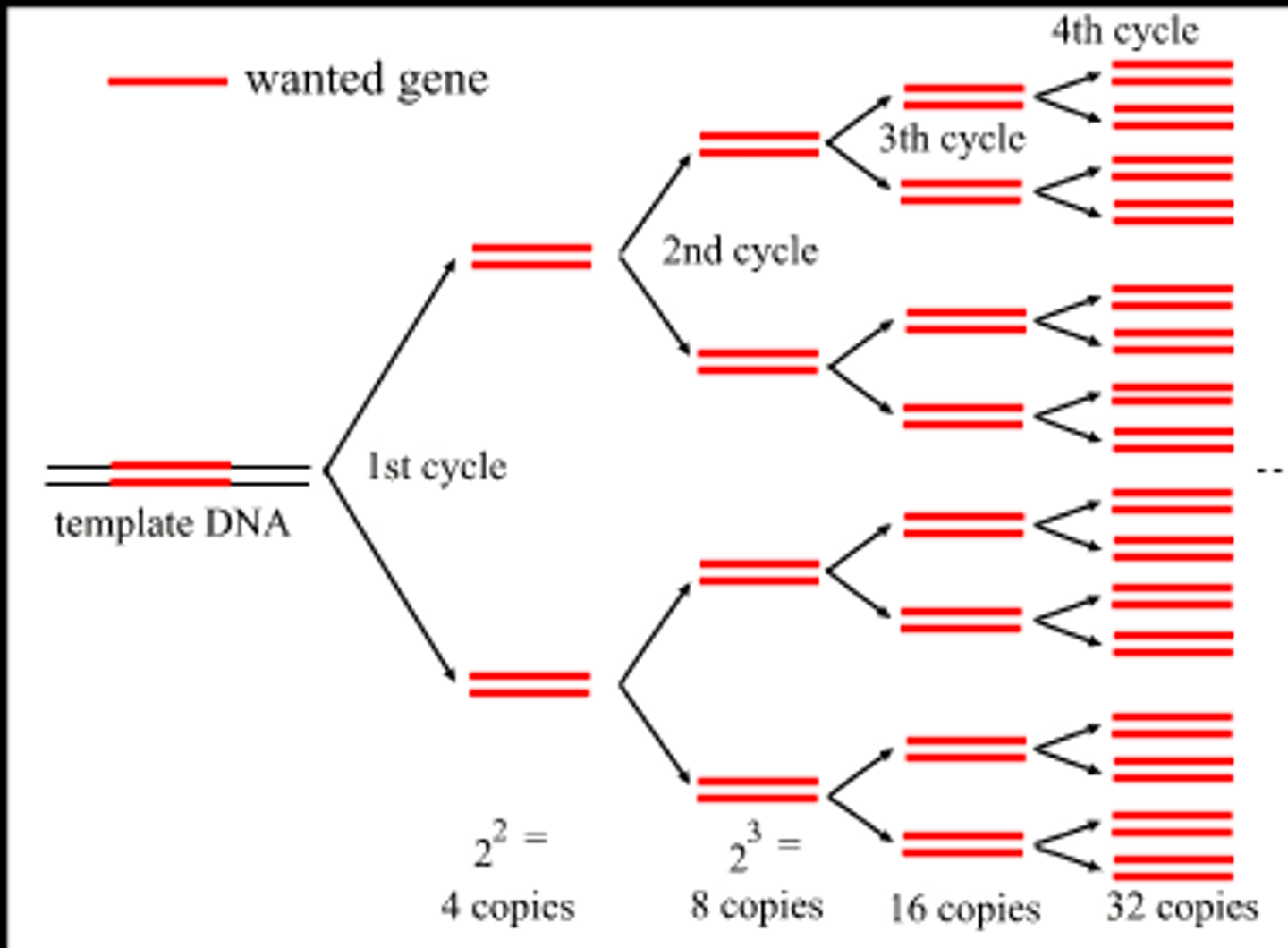
PCR
A process which uses DNA polymerase to create millions of copies of a desired DNA sequence.
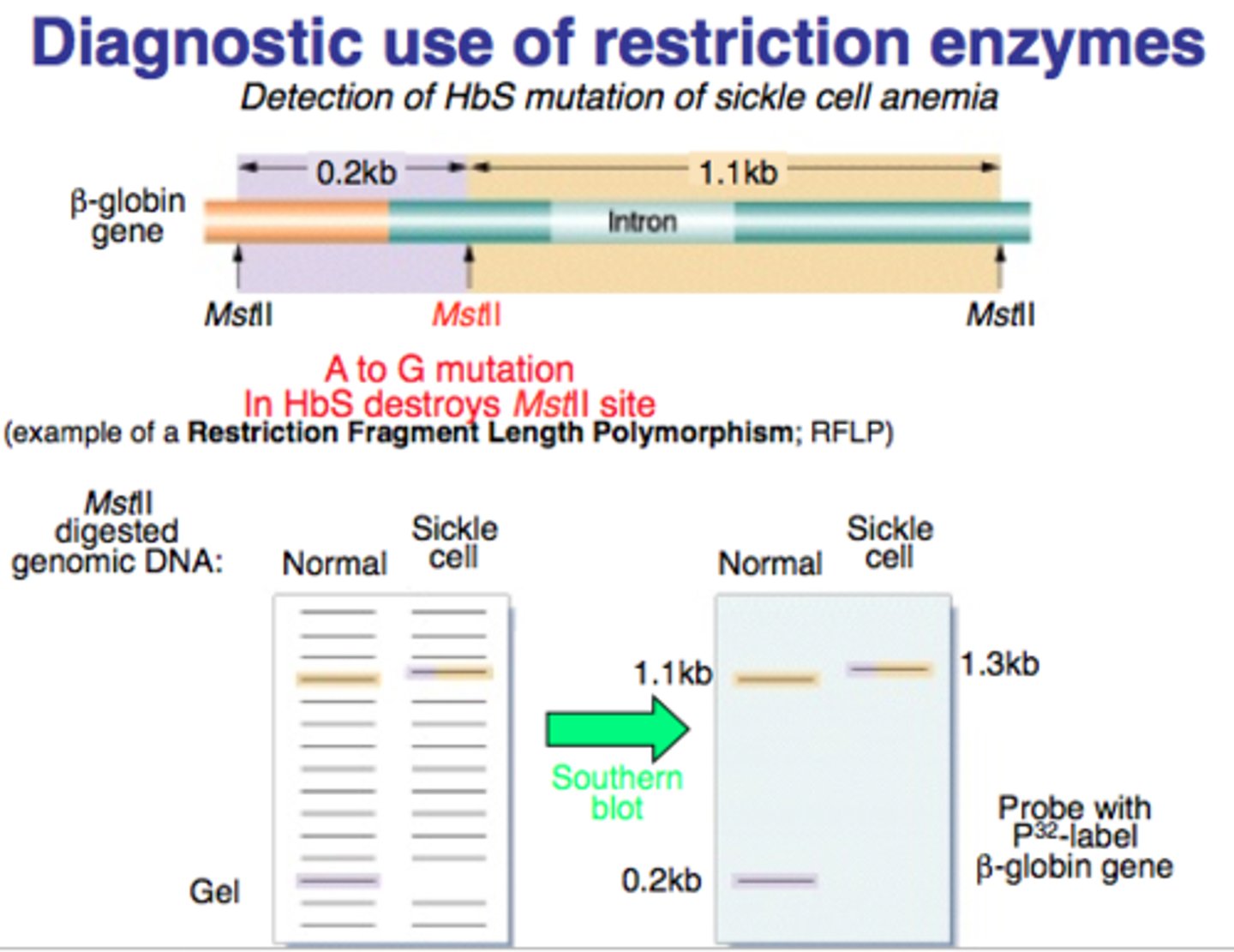
RFLP's
Fragments of DNA with varying lengths that have been cut by restriction enzymes and can be separated by size during gel electrophoresis
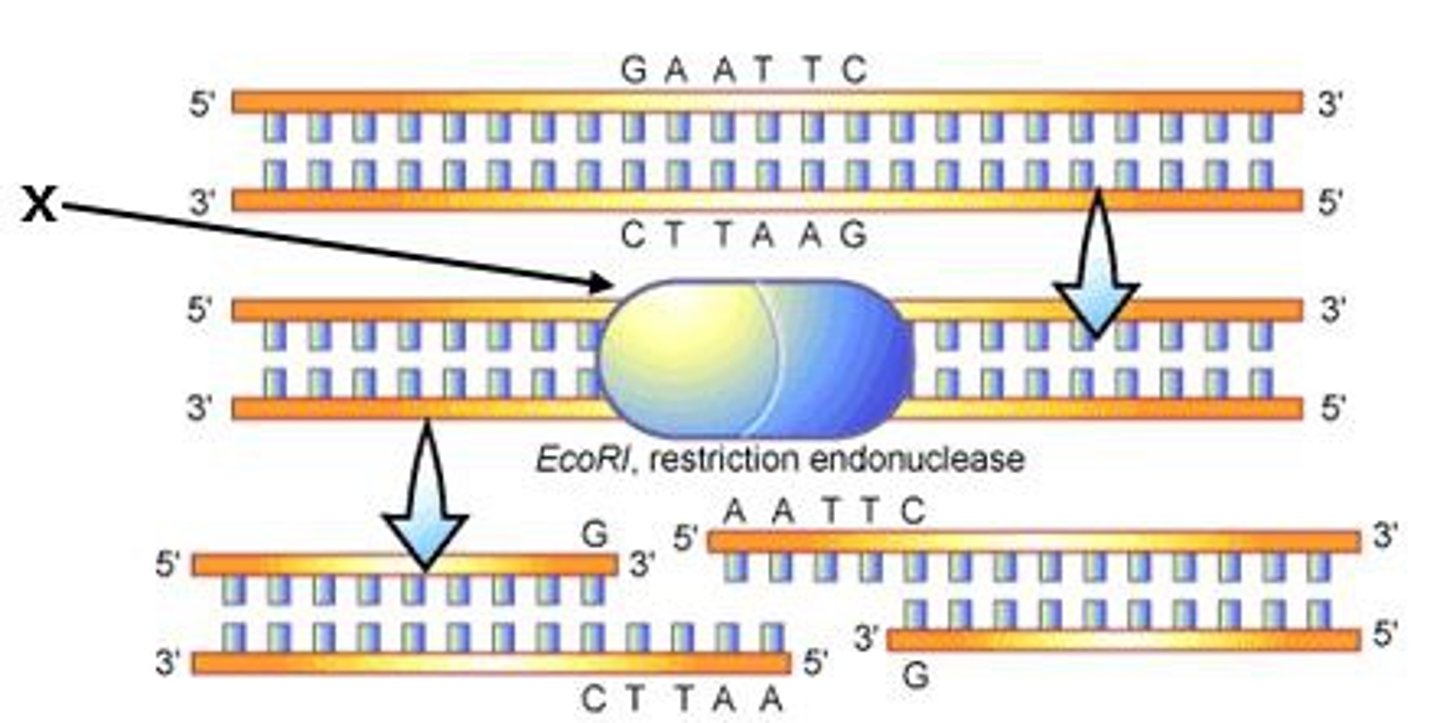
Restriction Enzymes
An enzyme that cuts DNA at a specific sequence of nucleotides
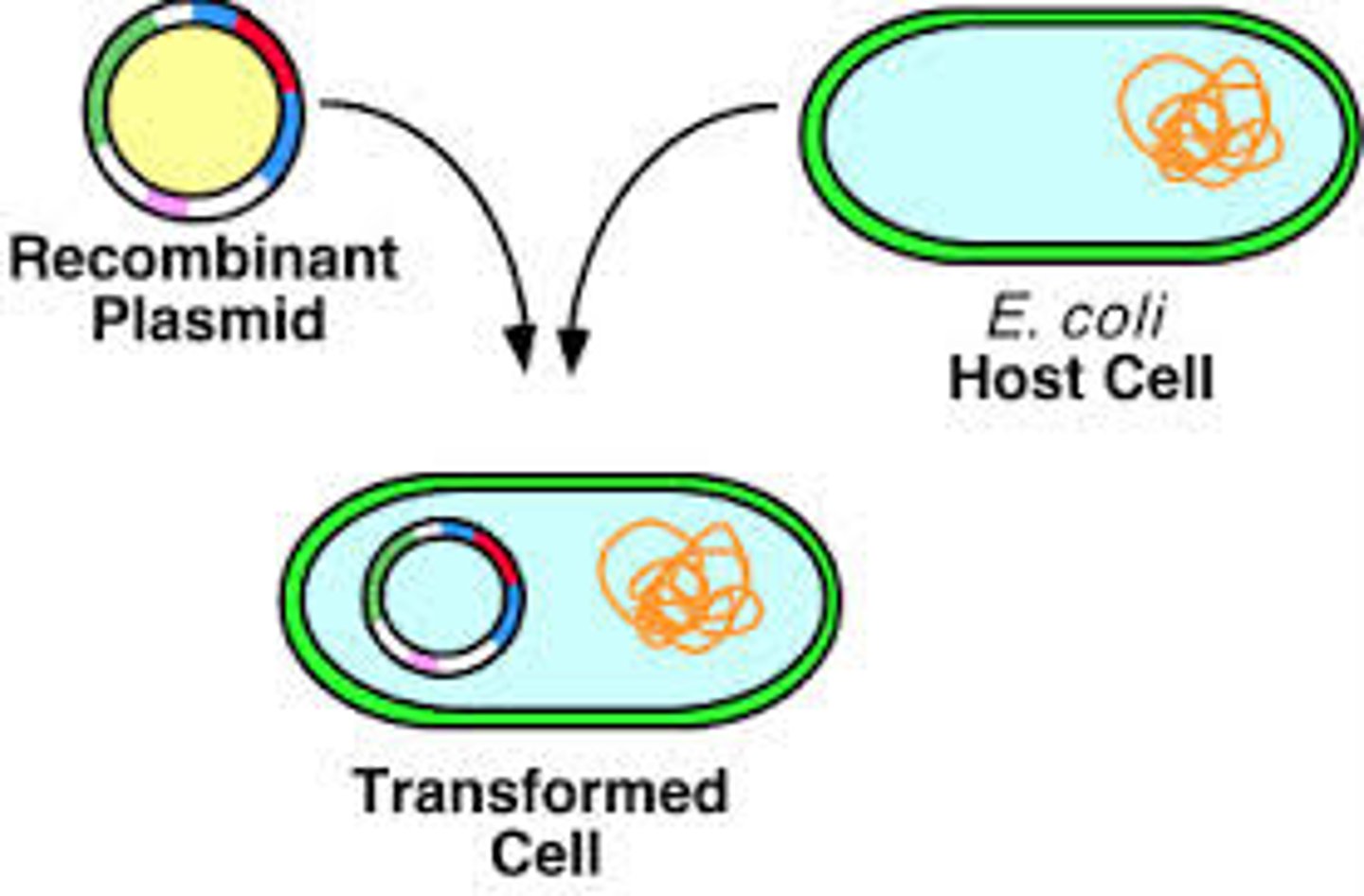
Recombinant DNA
Fragments of DNA from two different species, spliced together through genetic engineering.
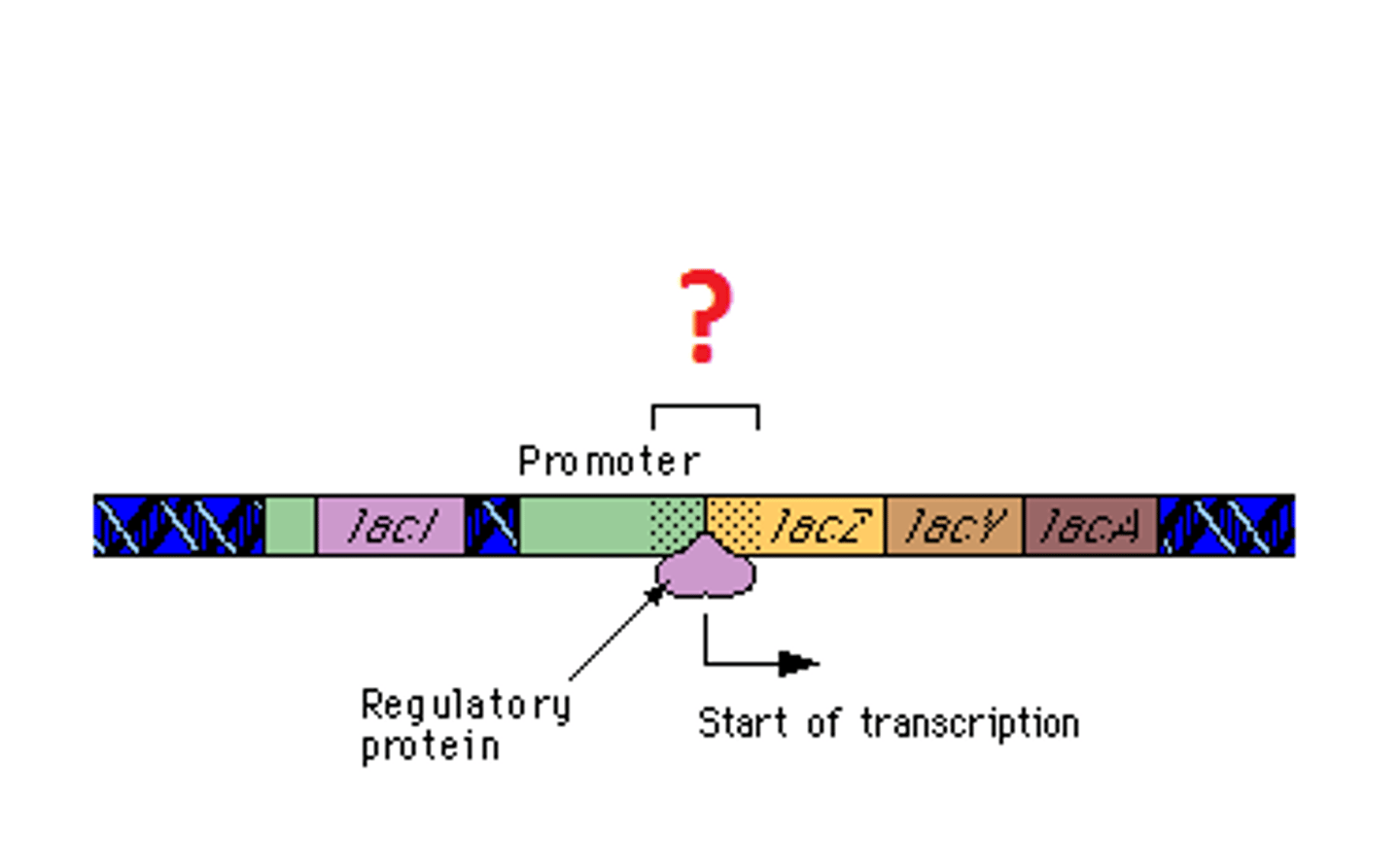
Regulator Gene
A gene that controls the expression of other genes
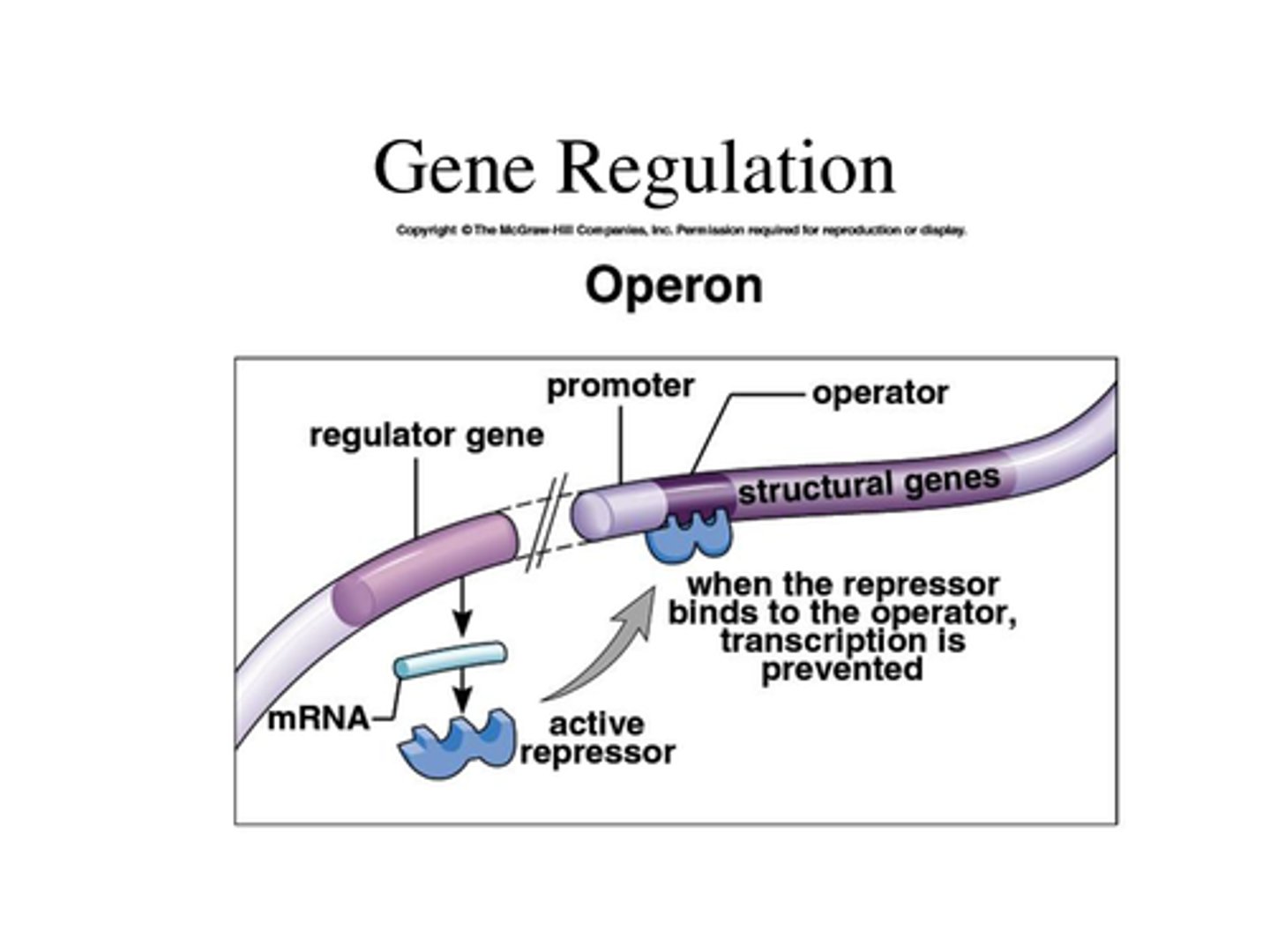
Repressor
A protein that regulates DNA transcription by preventing RNA polymerase from attaching to the operator
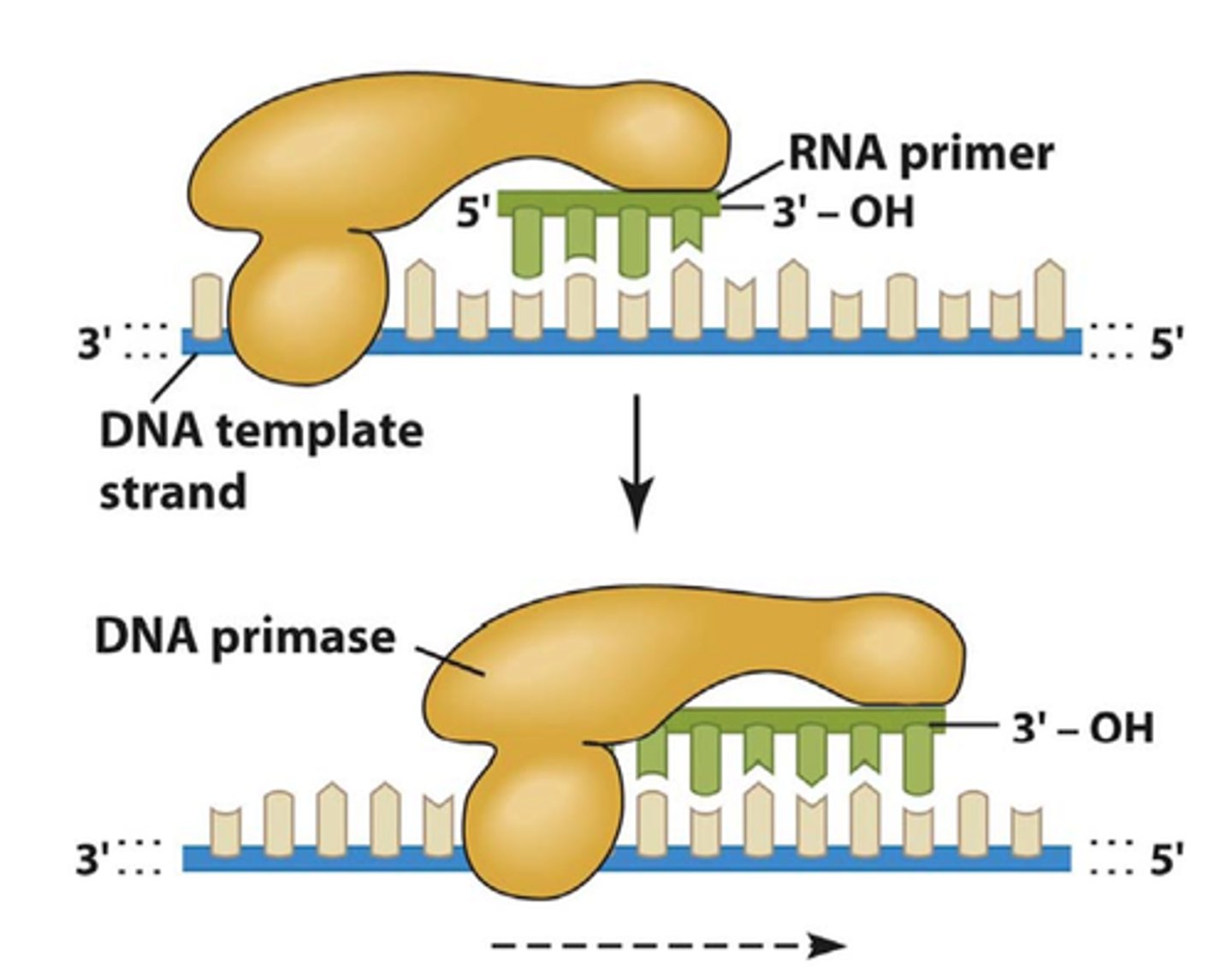
RNA Primer
A short sequence of RNA nucleotides used as the starting point for replication by DNA polymerase
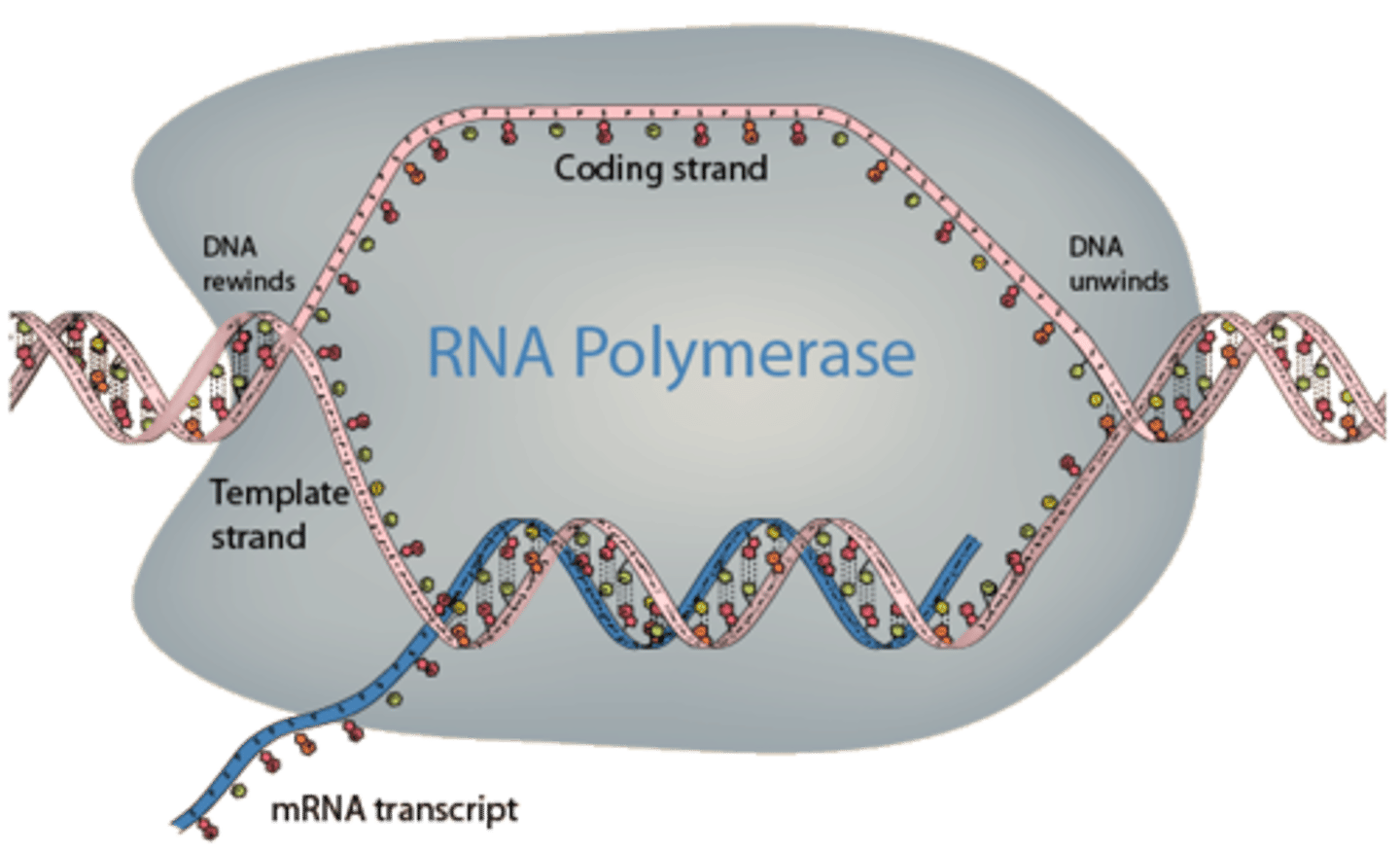
RNA Polymerase
An enzyme that synthesizes mRNA molecules based on a DNA template
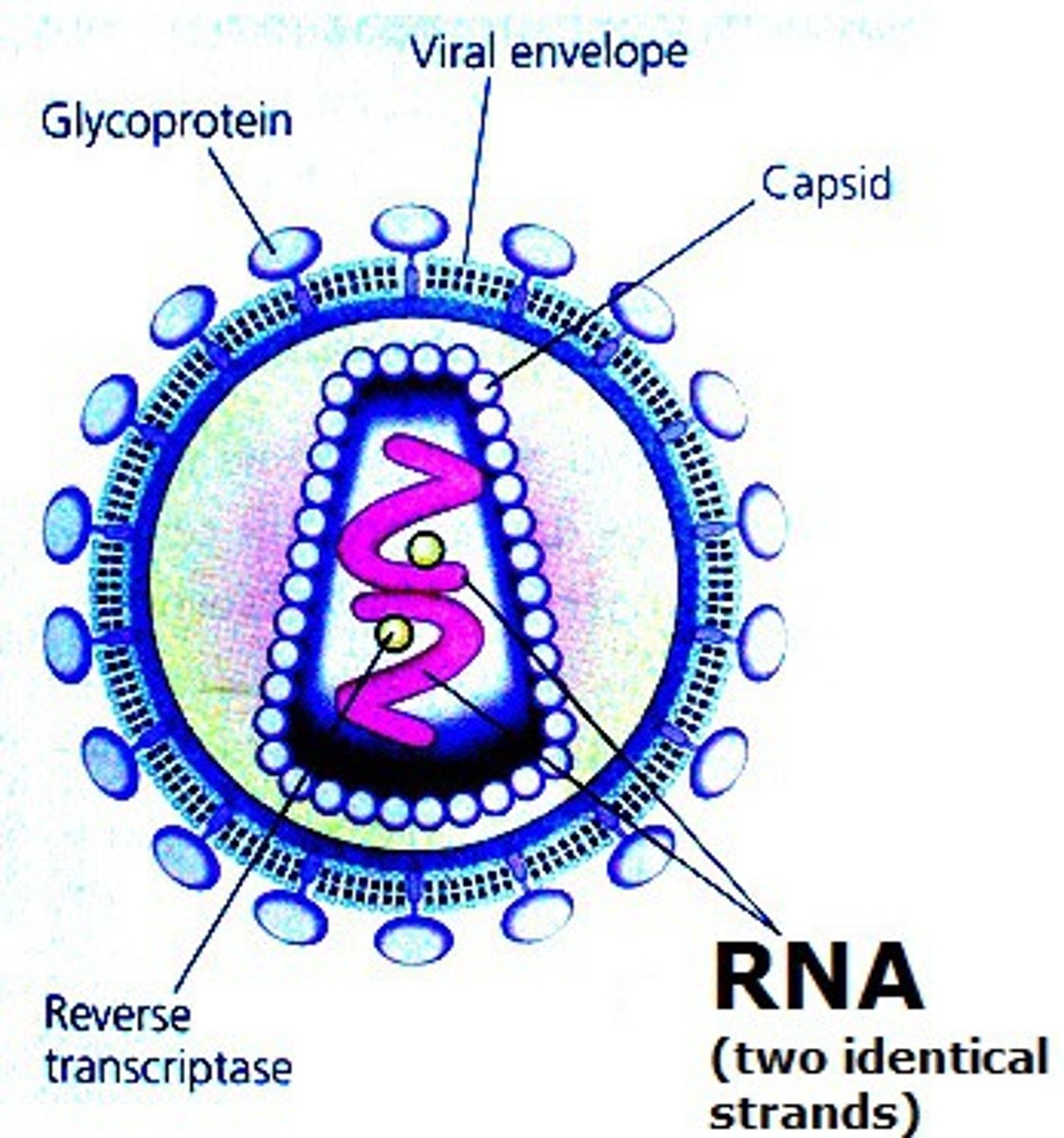
Retrovirus
A virus containing RNA instead of DNA, and an enzyme (reverse transcriptase), that uses the infected cell's machinery to build DNA
Somatic Cell
Body cells; any cell of a multicellular organism except for gametes
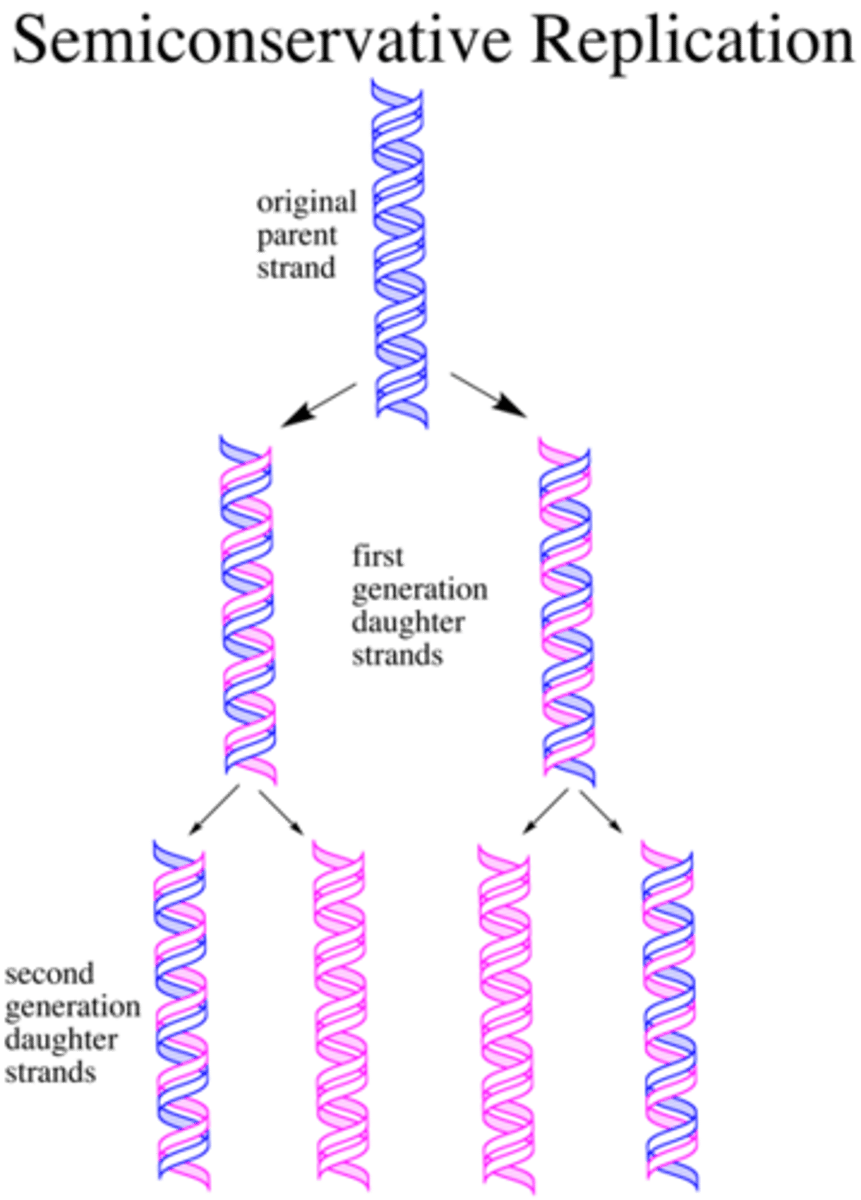
Semiconservative Replication
Each parent strand of DNA is paired with a strand of new DNA during replication.
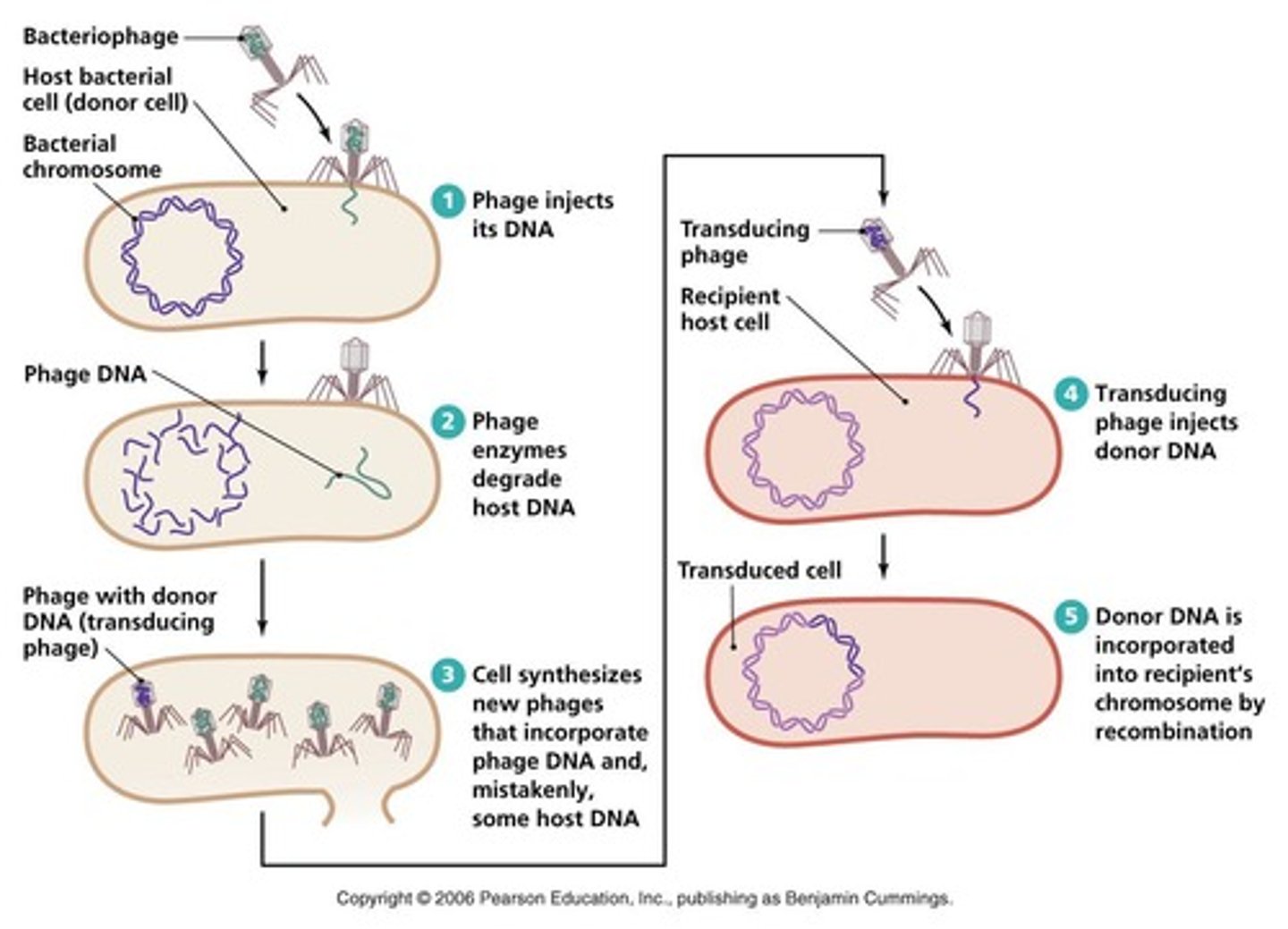
Transduction
The transfer of genetic material from one organism to another by way of a virus/vector
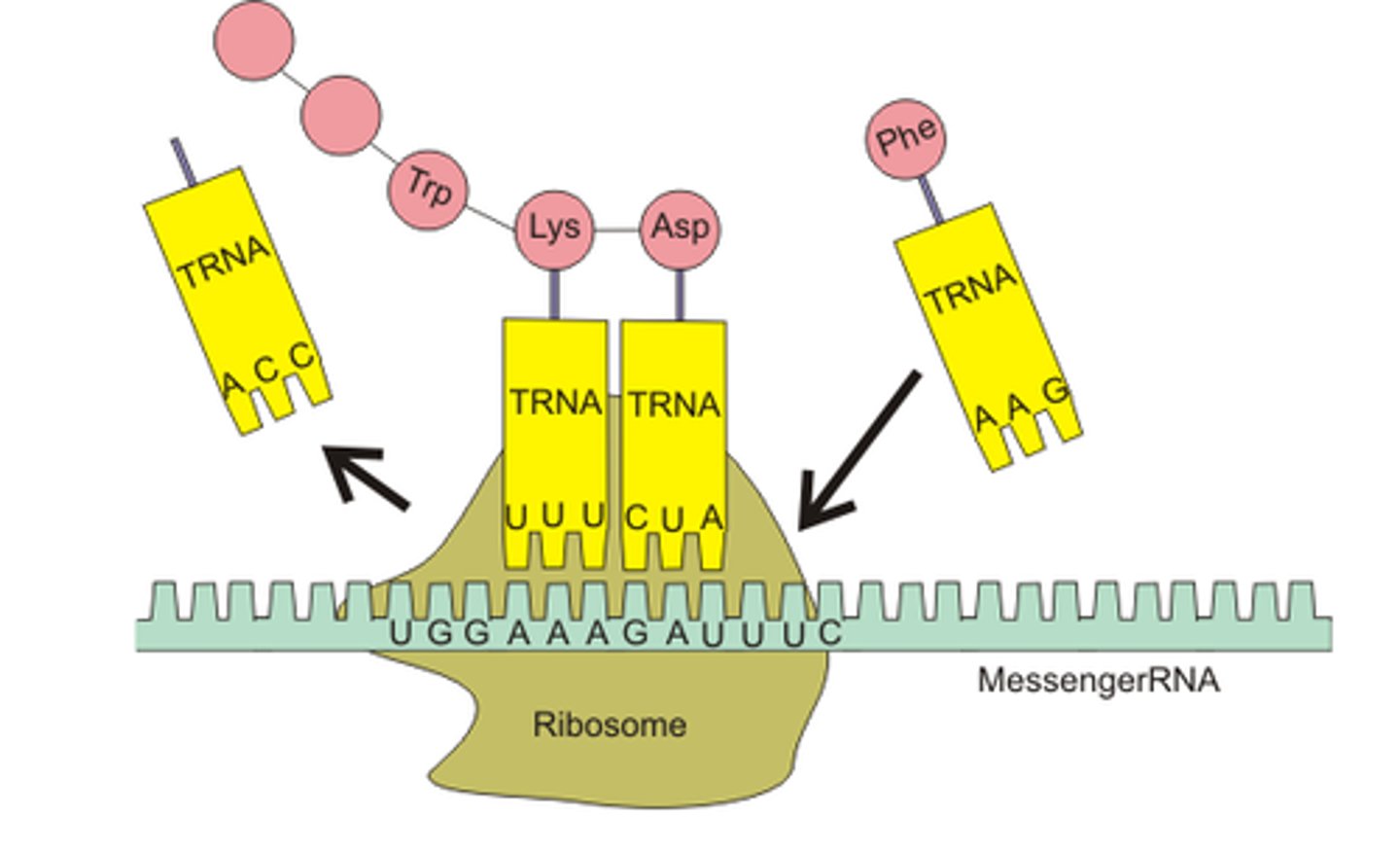
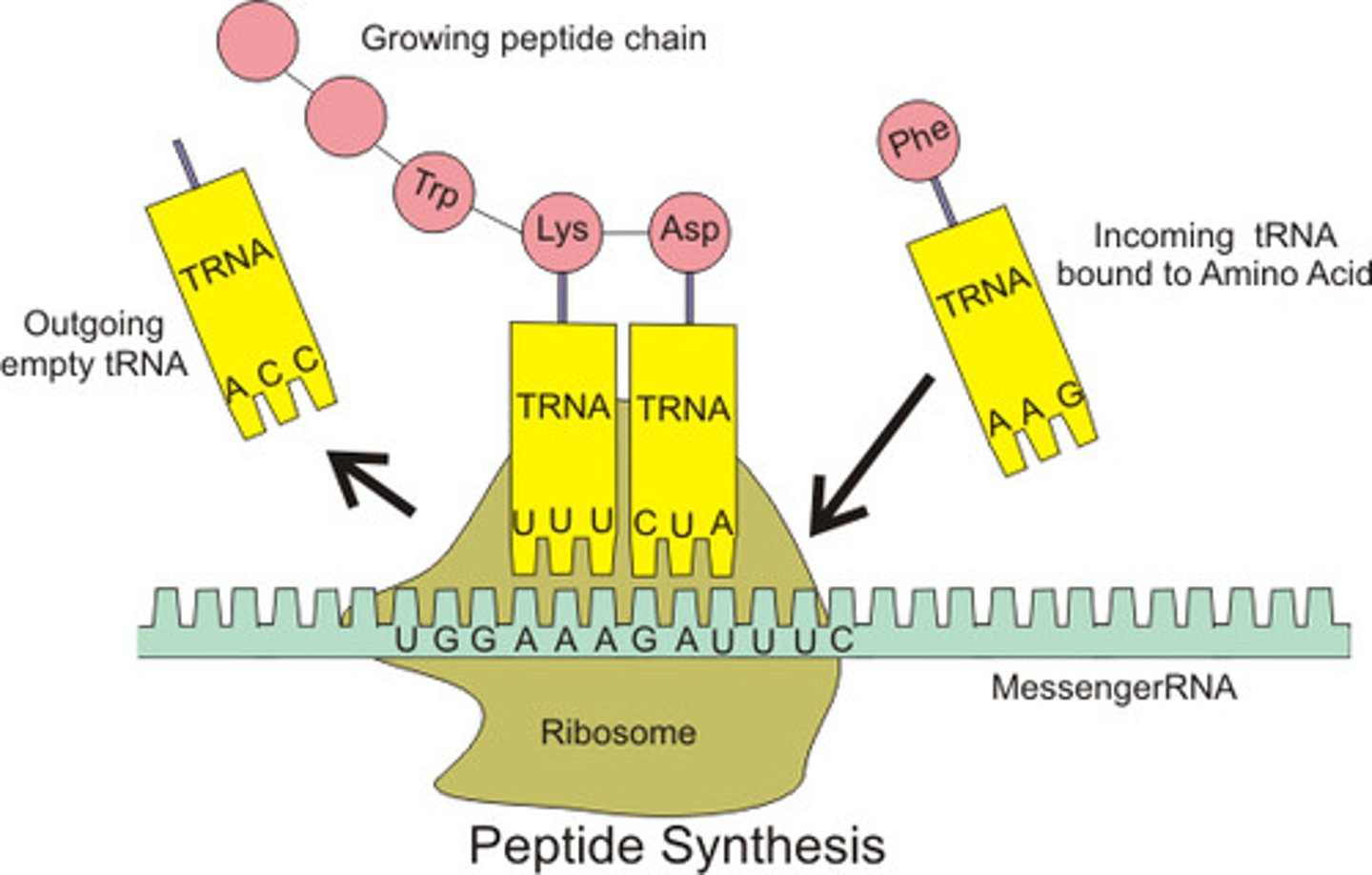
Translation
The assembly of a protein from amino acids coded for by mRNA codons
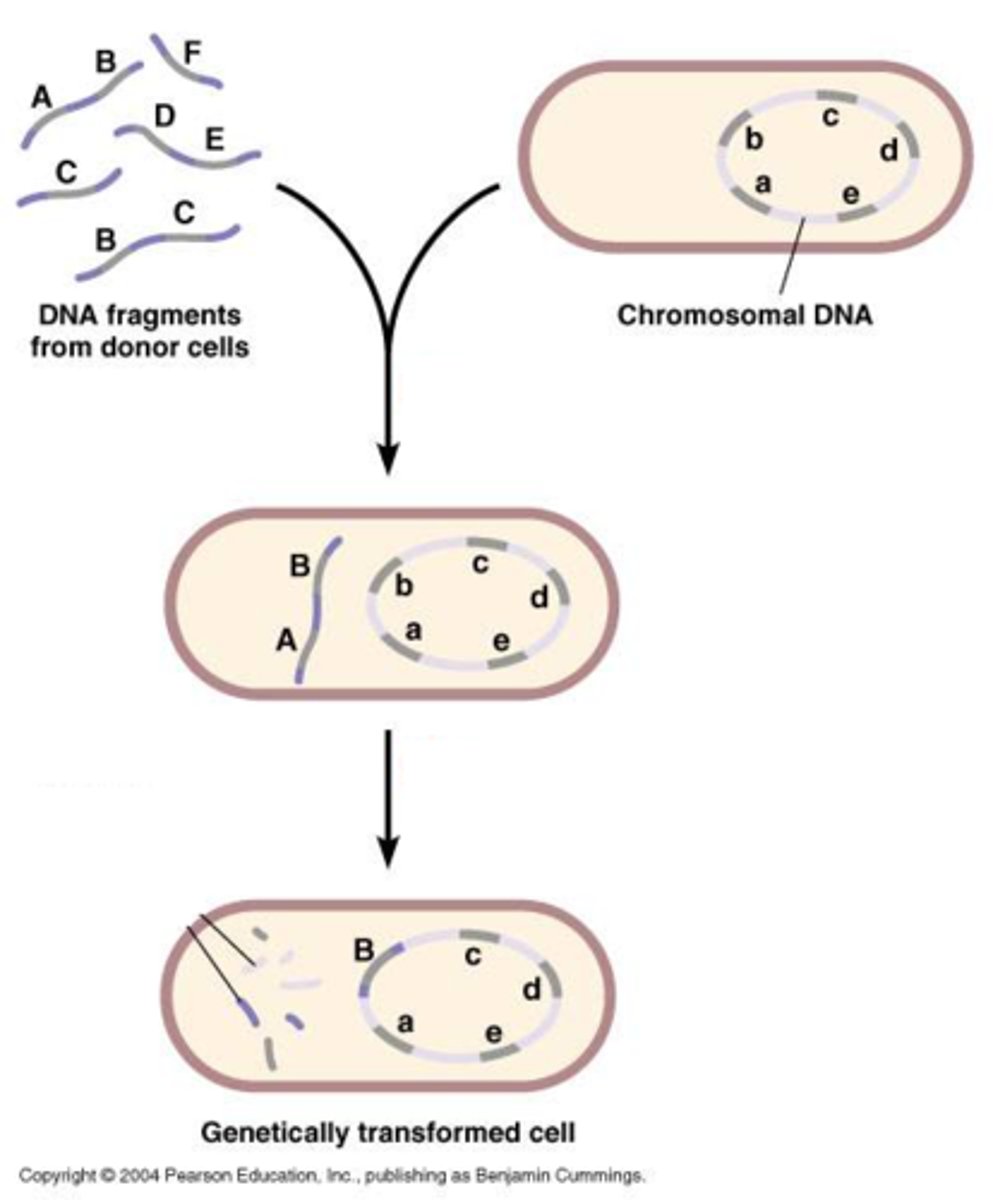
Transformation
The uptake of DNA from the environment; occurs in some bacterial species
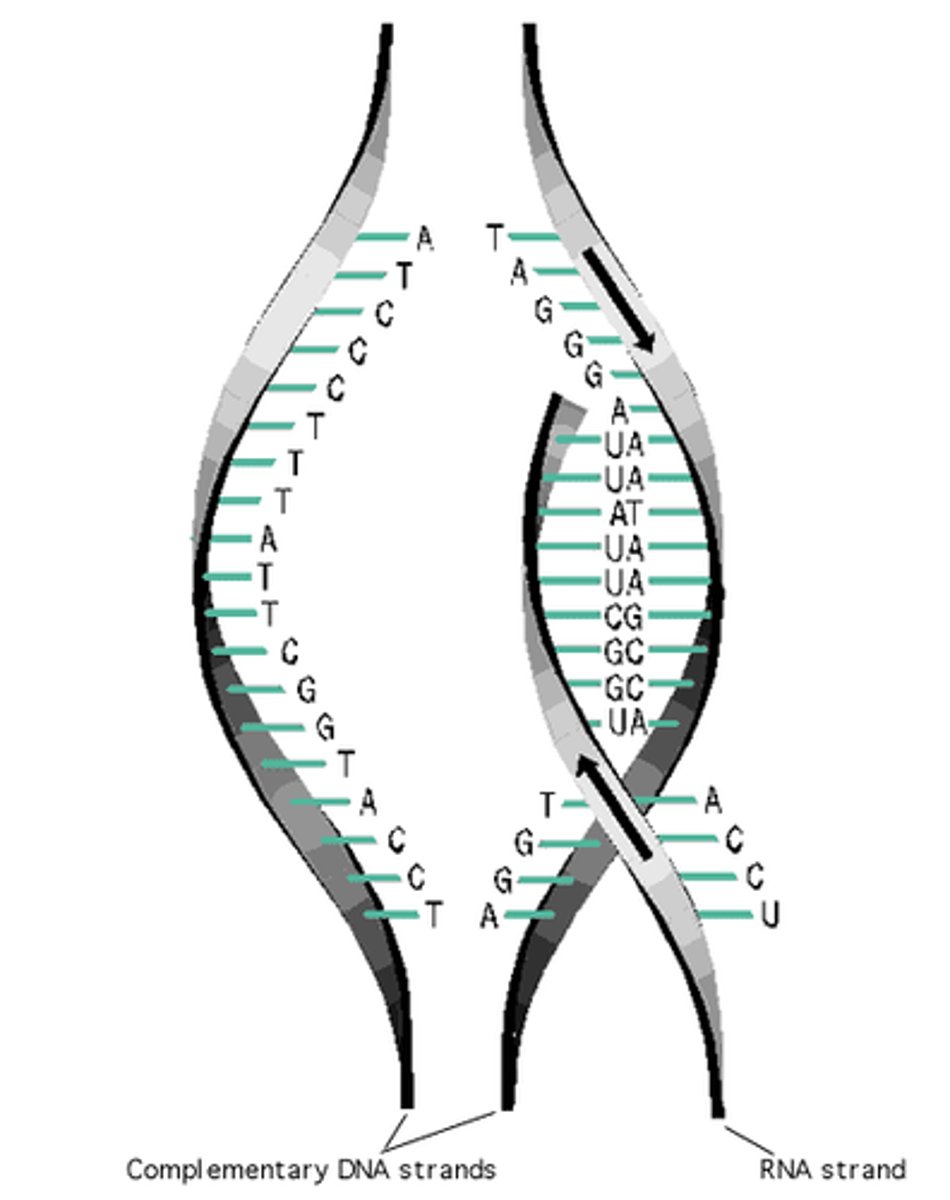
Transcription
Synthesis of an mRNA molecule based on a DNA template
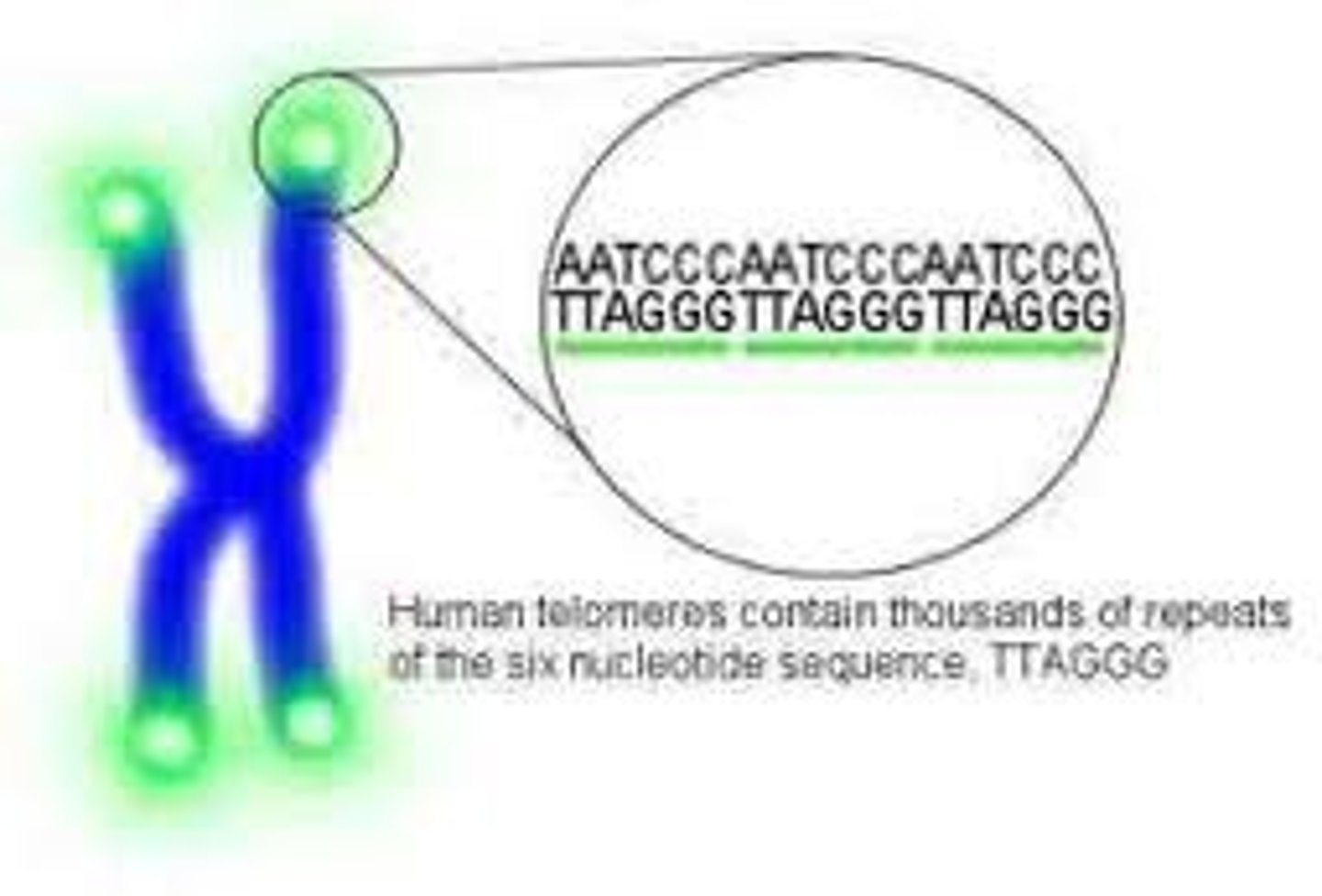
Telomere
A specialized region of DNA that caps each end of a chromosome
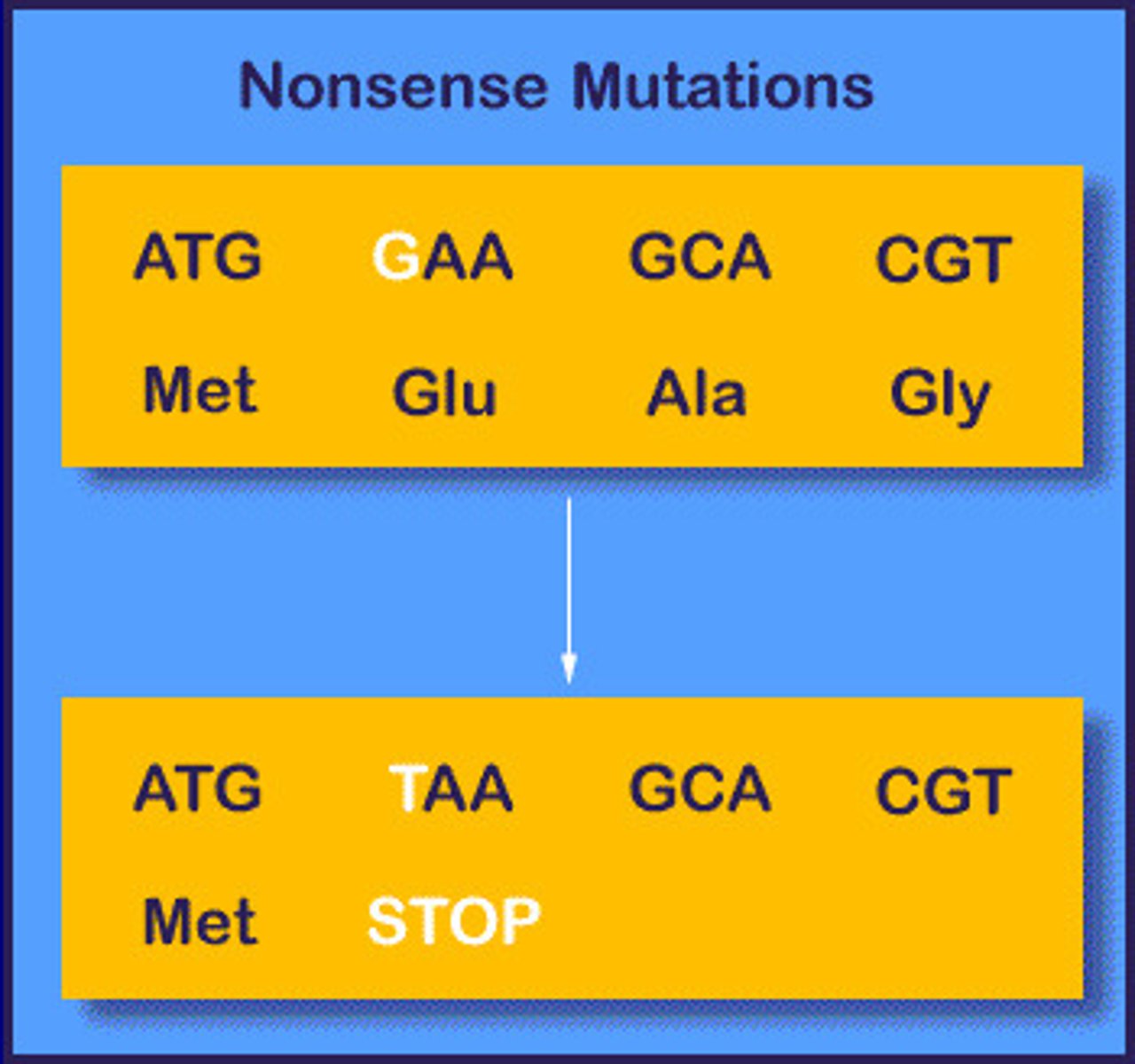
Nonsense Mutation
Point mutation where one base changes and instead of coding for an amino acid, it codes for STOP
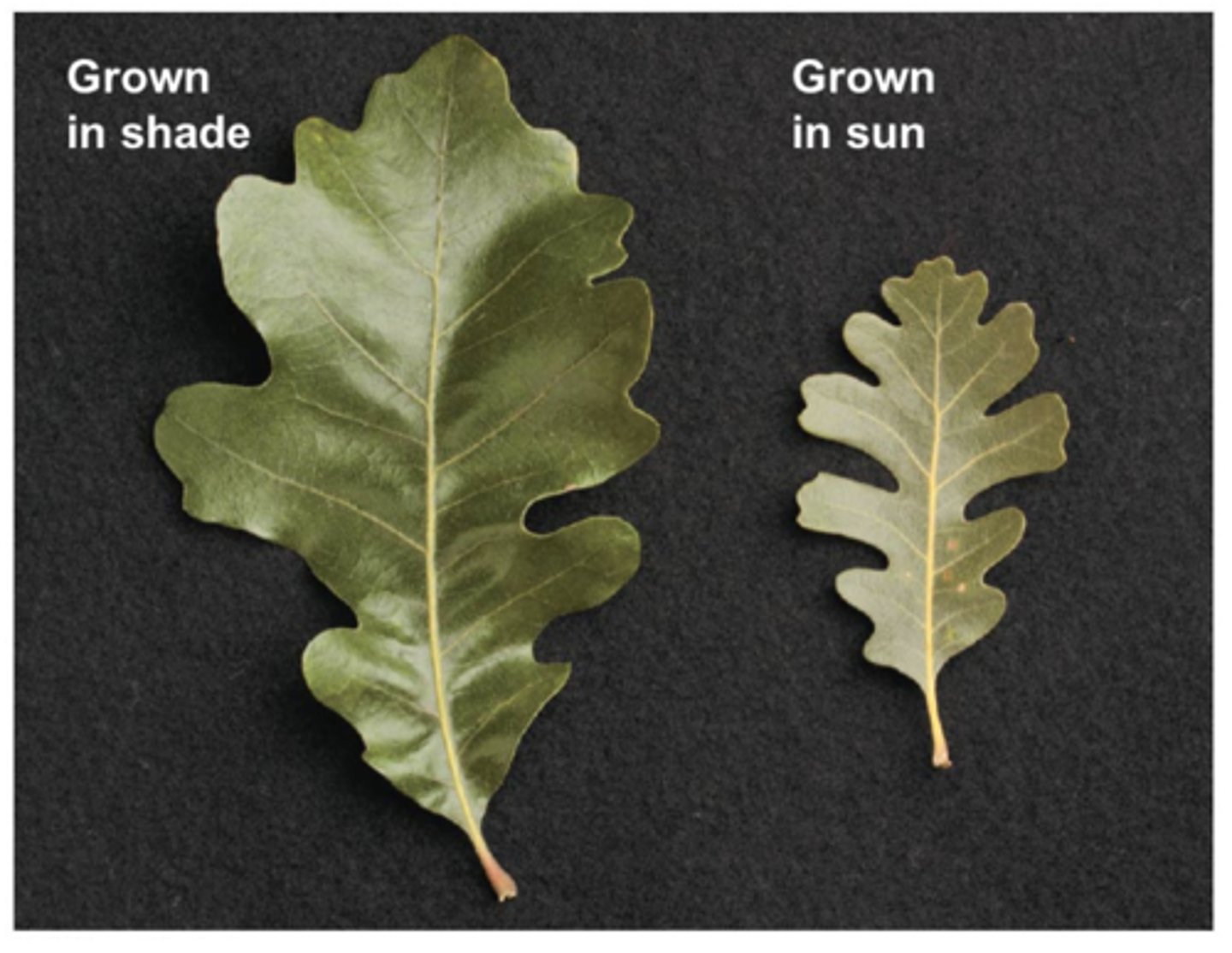
Phenotypic Plasticity
the ability of an organism to change its phenotype in response to changes in the environment.

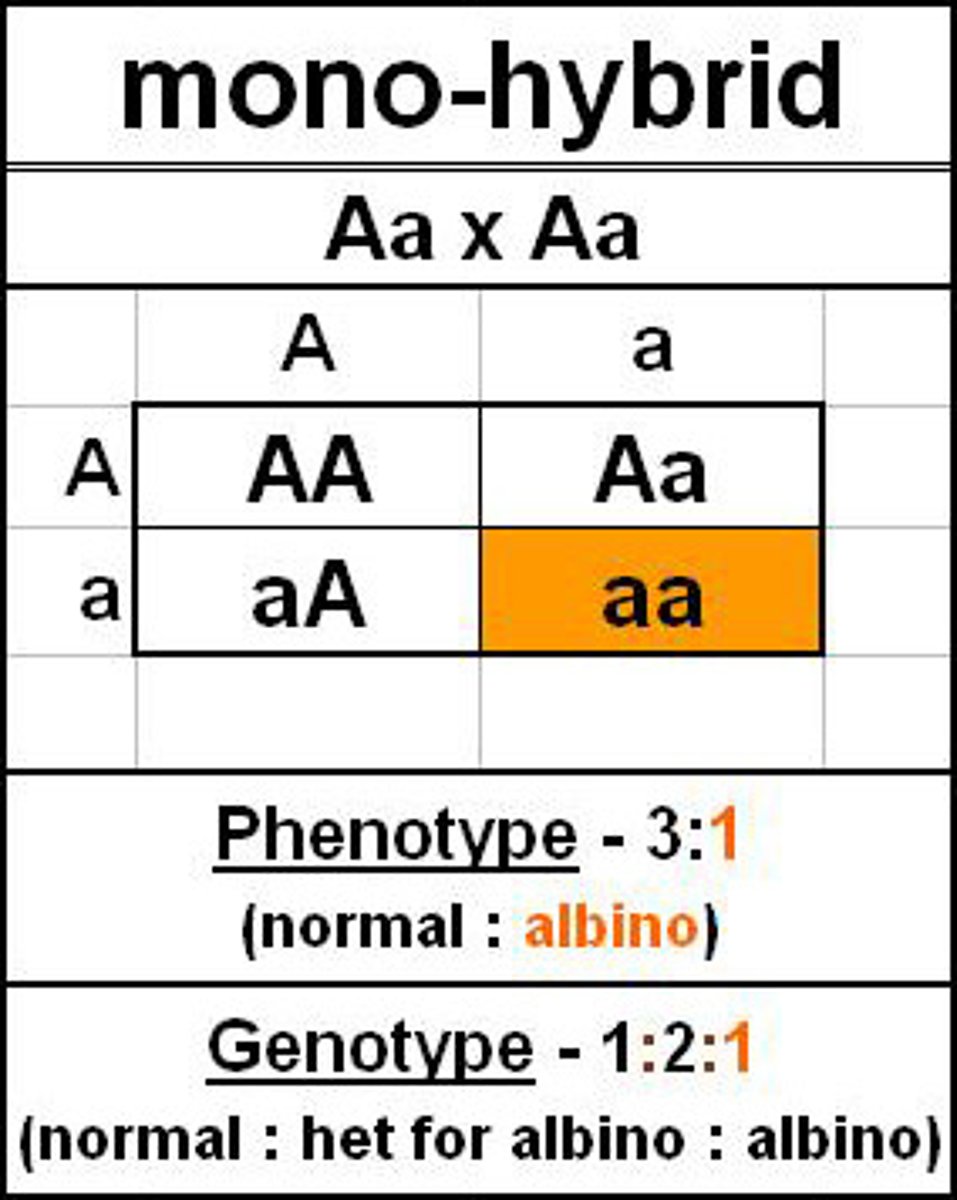
Monohybrid inheritance
The study of how the alleles of just one gene are passed from parents to offspring. Specifically in a cross between two heterozygotes
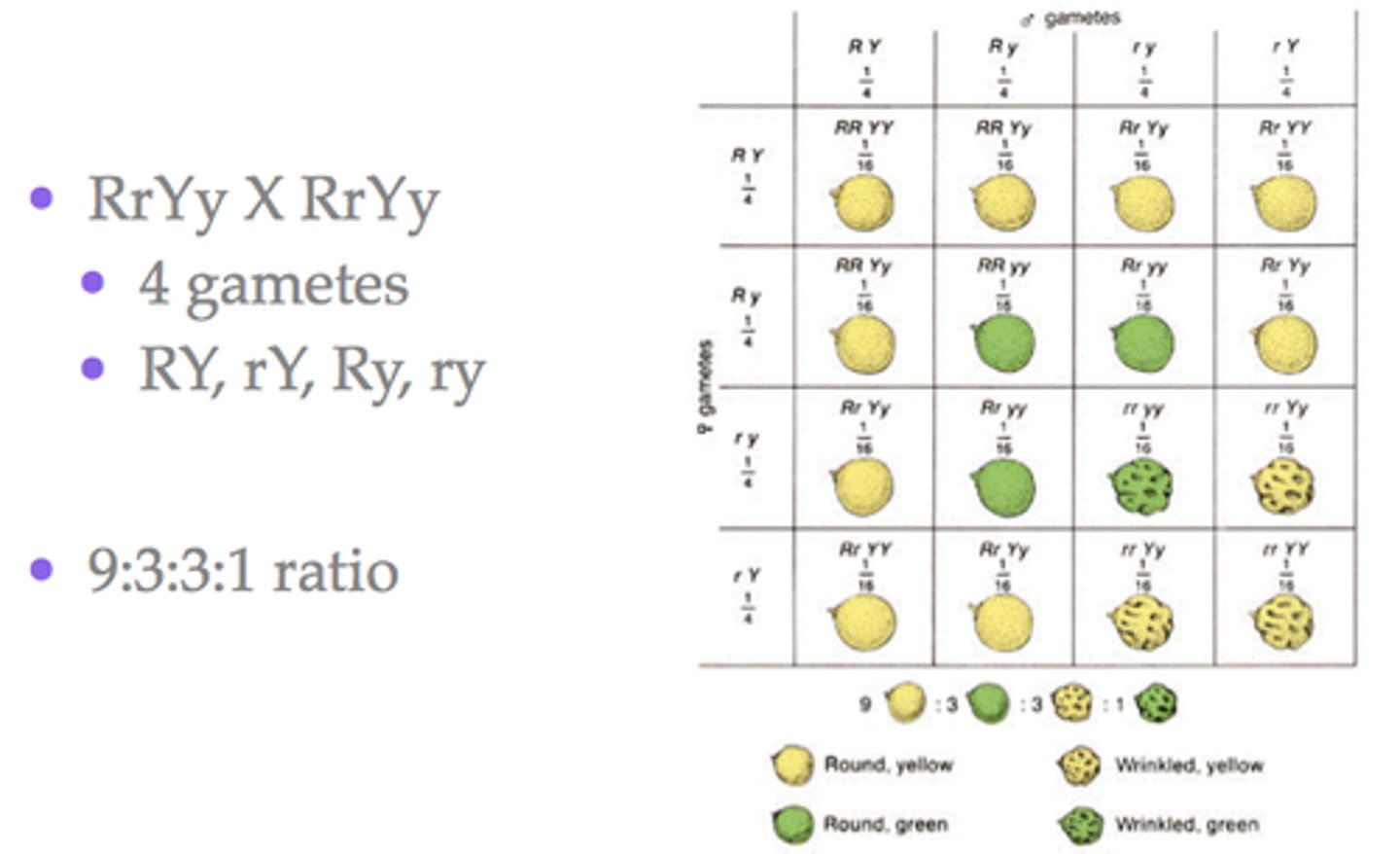
Dihybrid Inheritance
The inheritance of two characteristics which are controlled by different genes. Specifically in a cross between parents that are heterozygous for both traits.
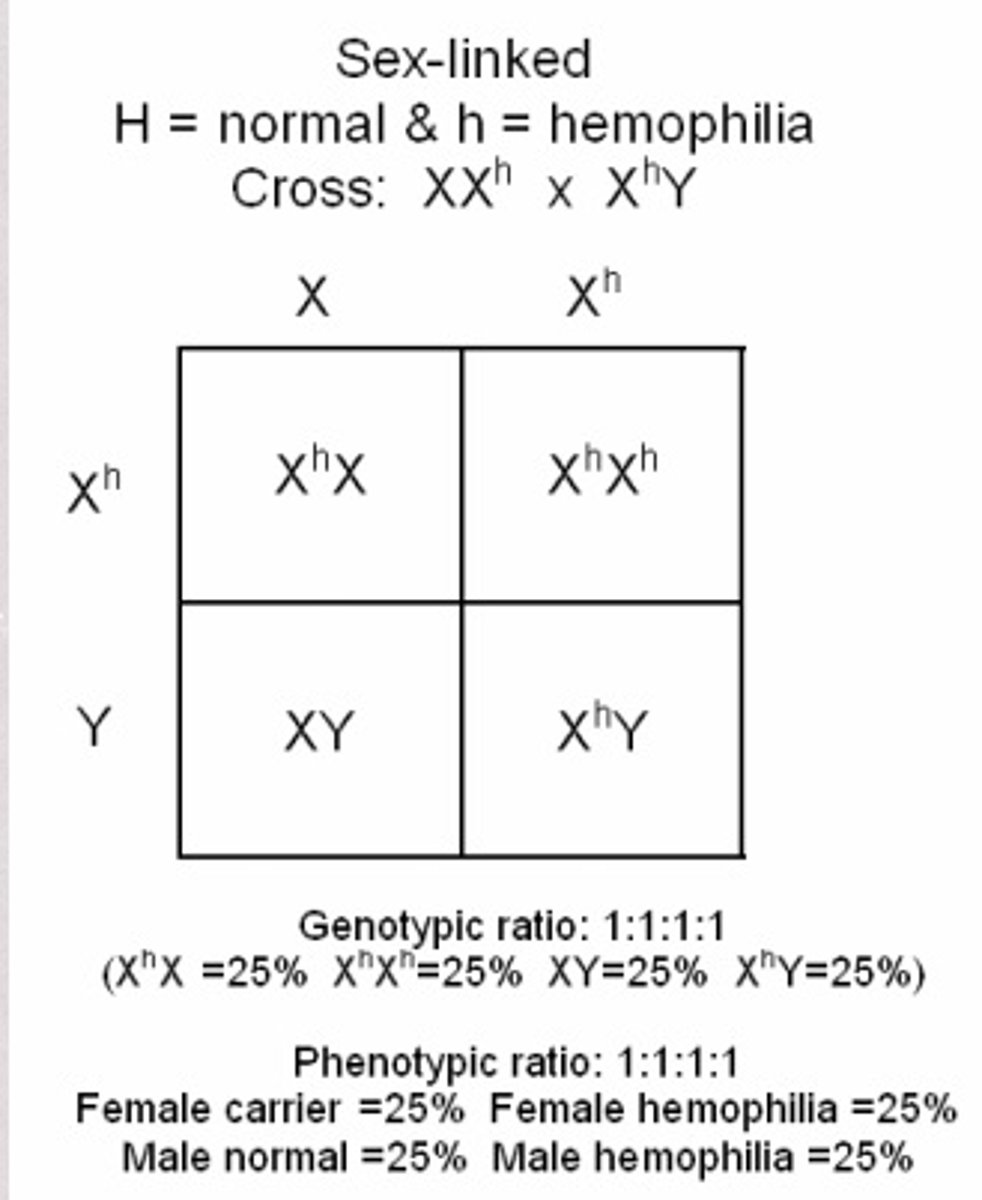
Sex-linked Inheritance
pattern of inheritance in which certain characteristics carried on the X chromosome inherited from the mother are transmitted differently to her male and female offspring
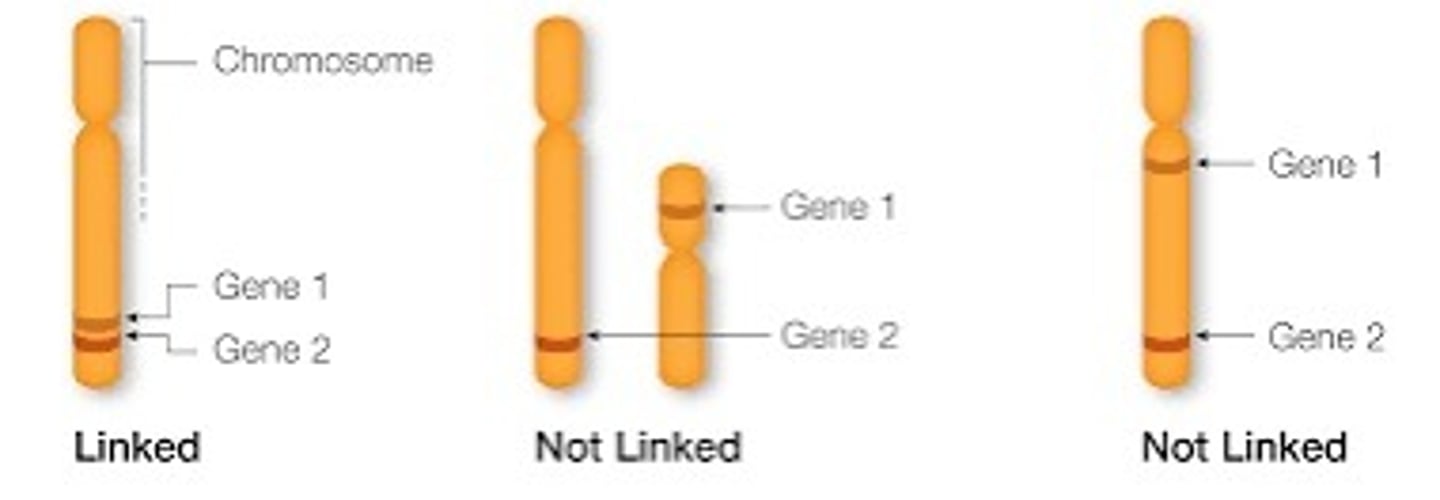
Gene Linkage
Traits that tend to be inherited together as a consequence of their genes being on the same chromosome
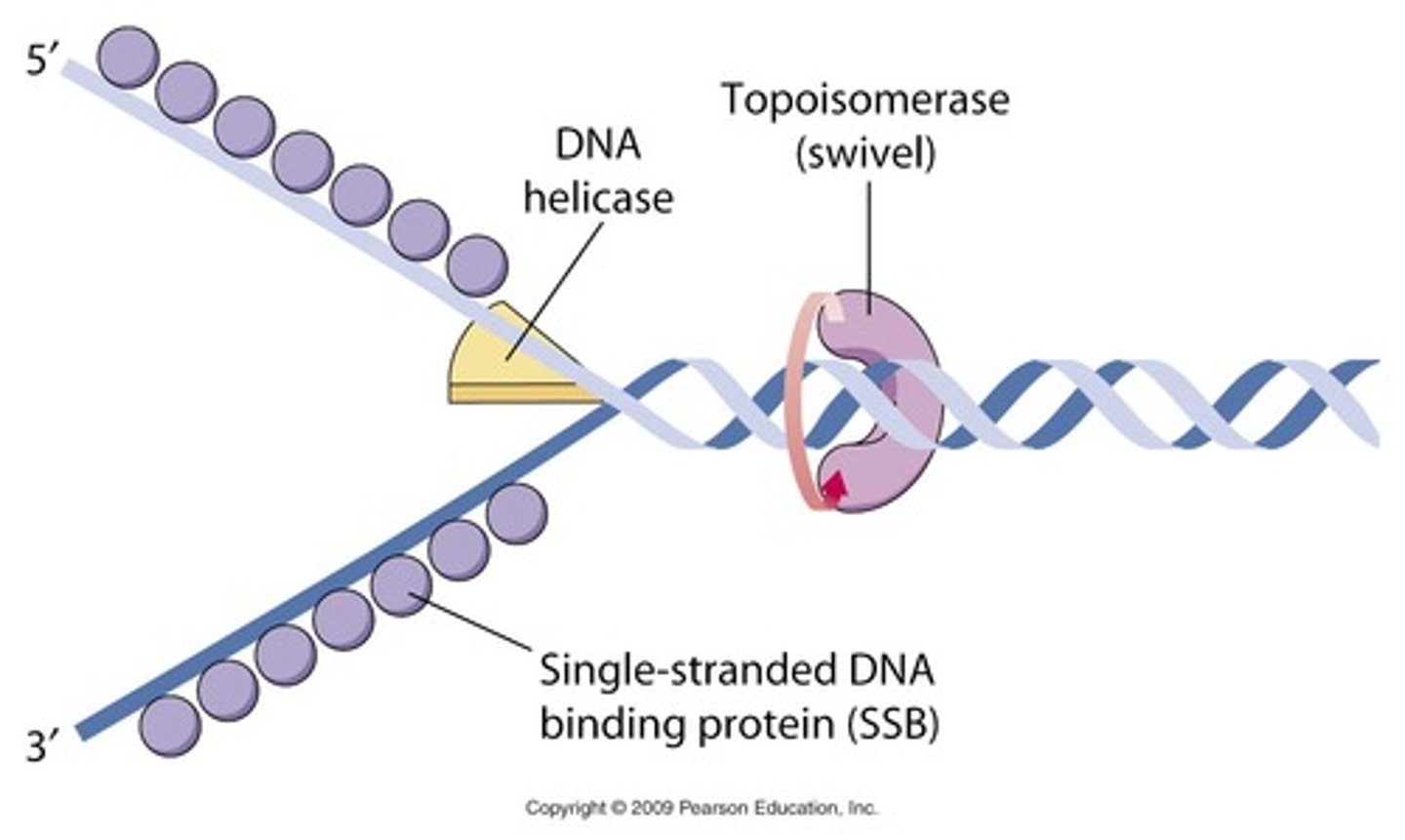
Helicase
An enzyme that untwists the double helix of DNA to prepare for replication
Topoisomerase
Enzyme that functions in DNA replication, helping to relieve strain in the double helix ahead of the replication fork.
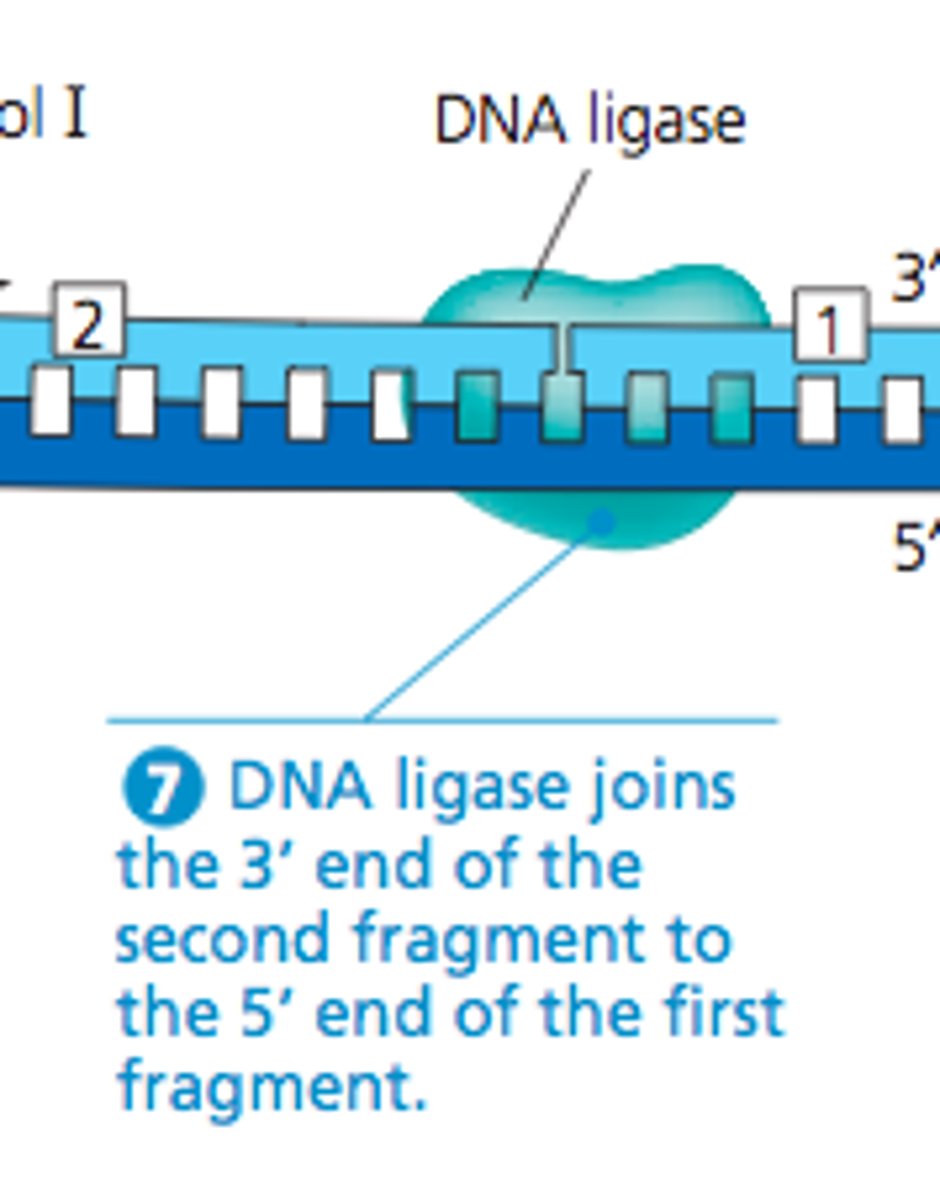
Ligase
An enzyme that connects two fragments of DNA to make a single fragment
mRNA
messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome
rRNA
ribosomal RNA; type of RNA that makes up part of the ribosome
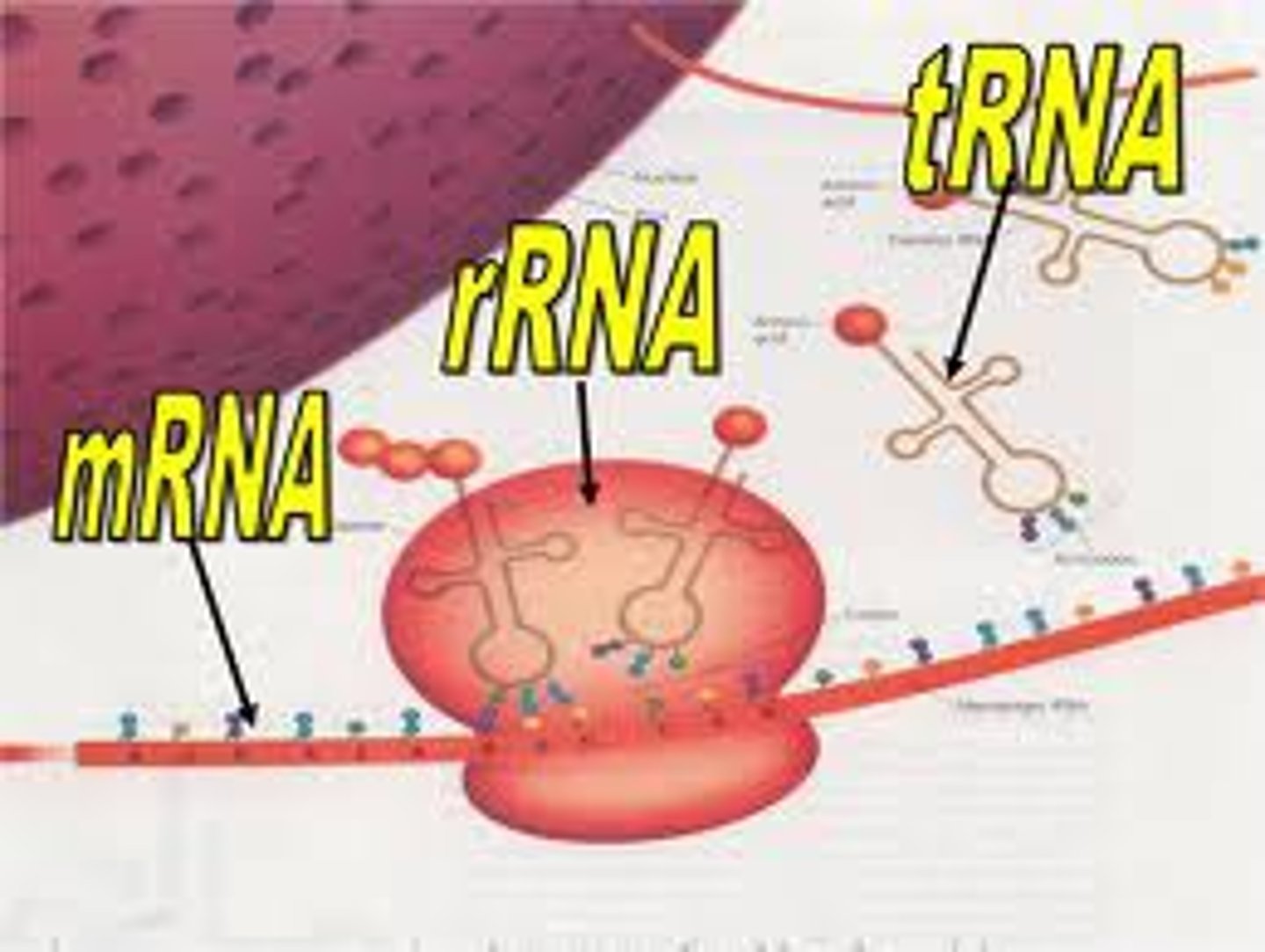
tRNA
transfer RNA; type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome
Poly-A tail
Modified end of the 3' end of an mRNA made up of a chain of adenine molecules
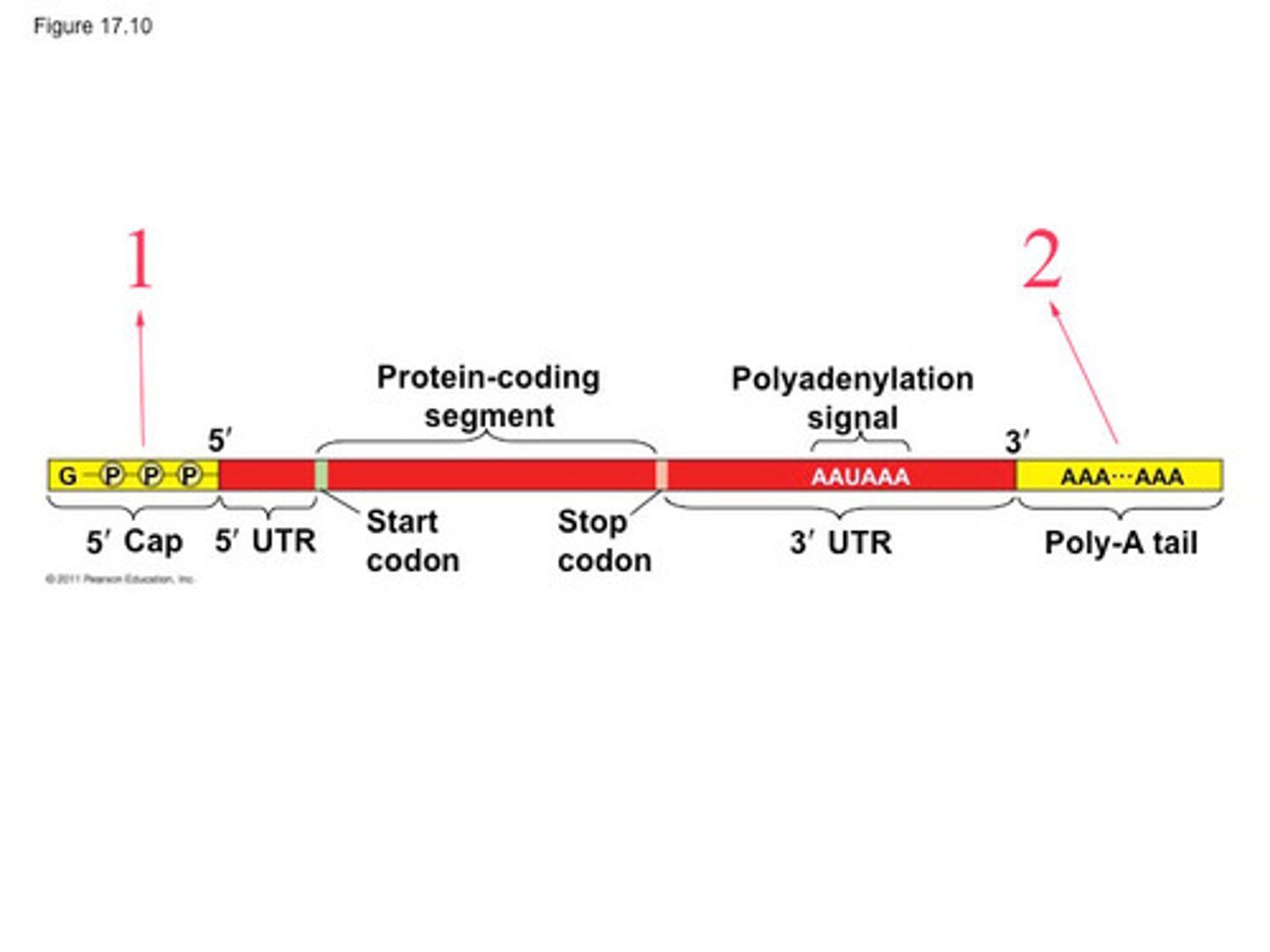
GTP cap
a molecule that is attached to the 5' head of the mRNA after transcription
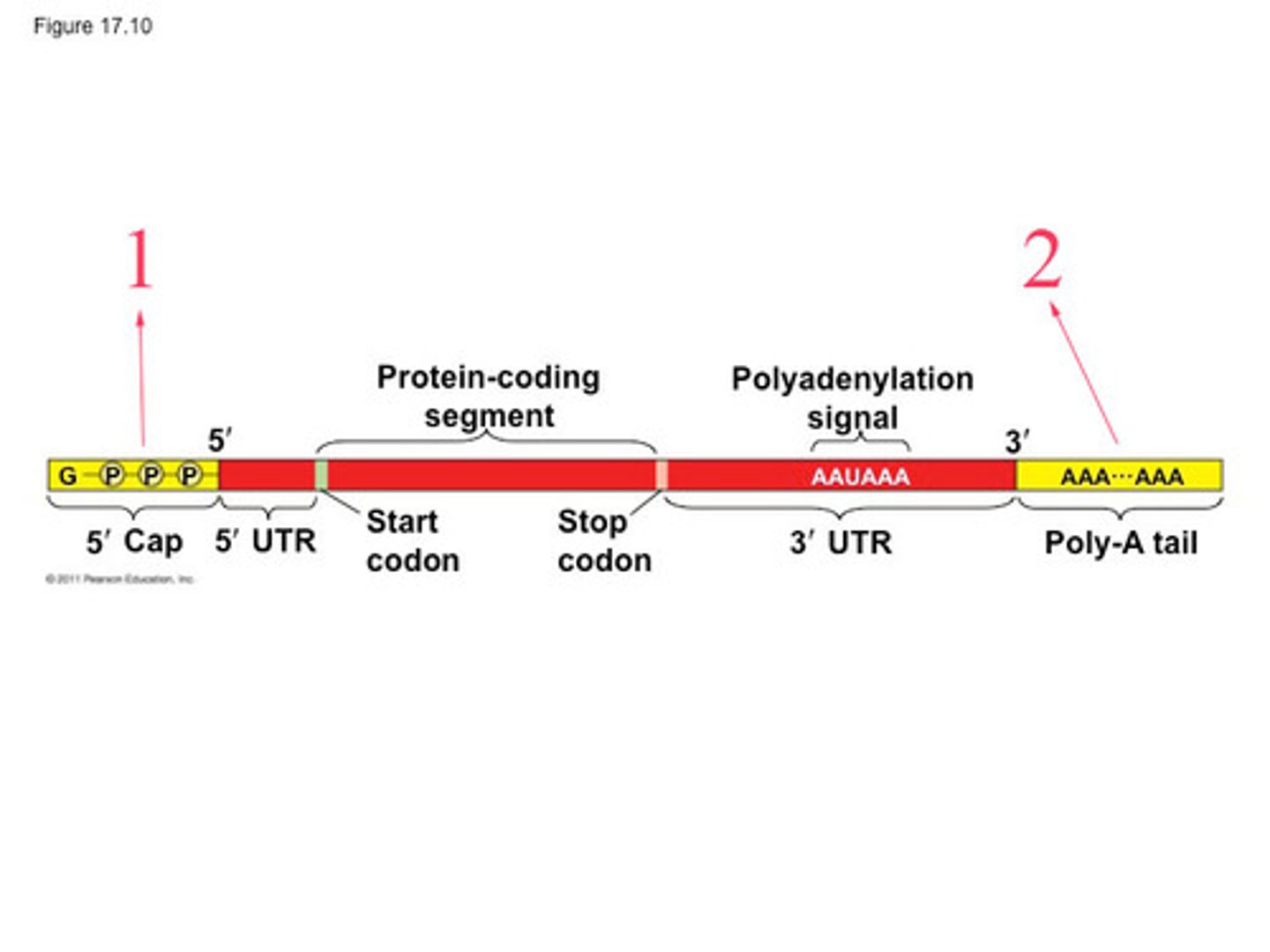
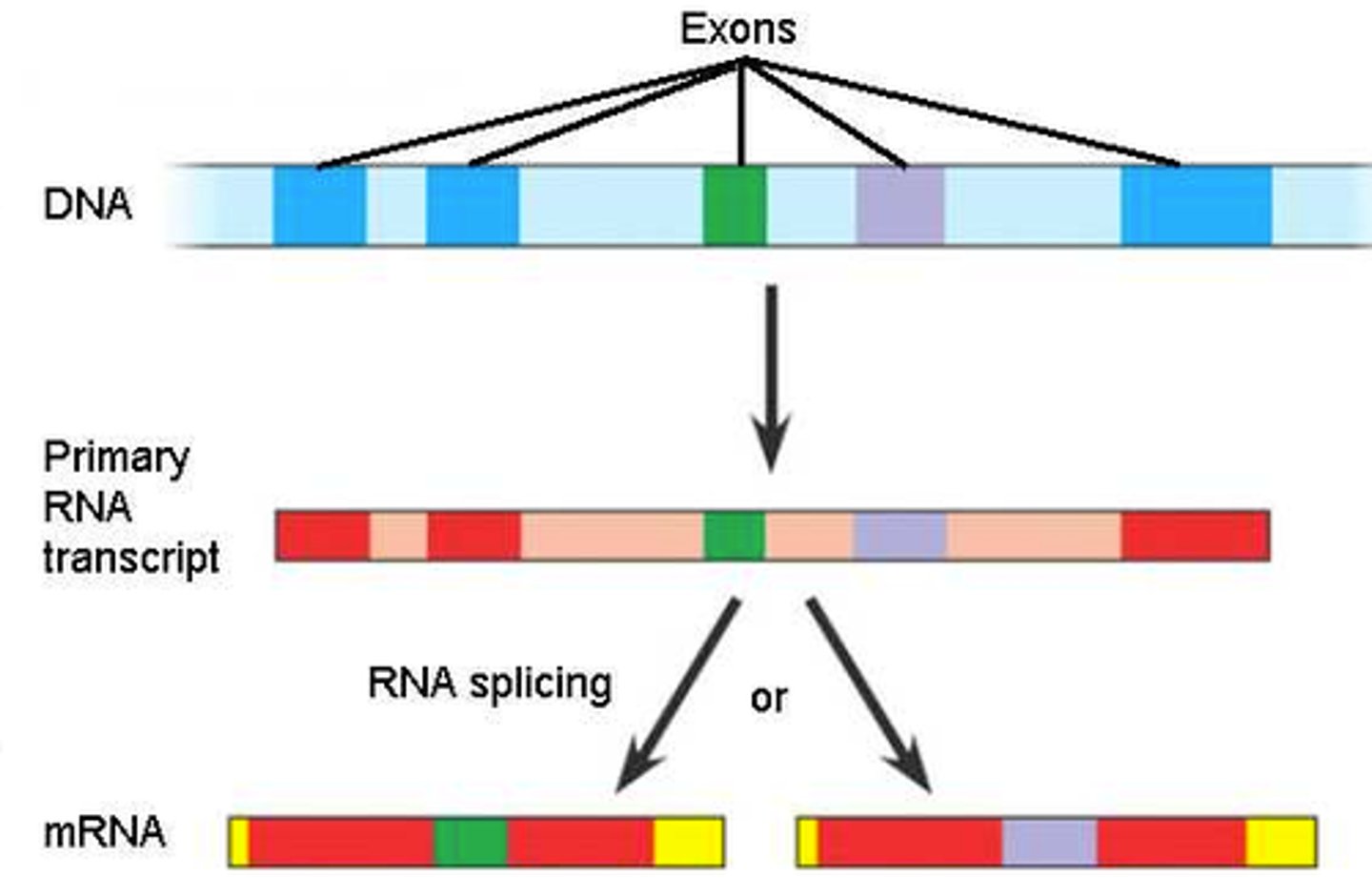
Intron
sequence of DNA that is not involved in coding for a protein
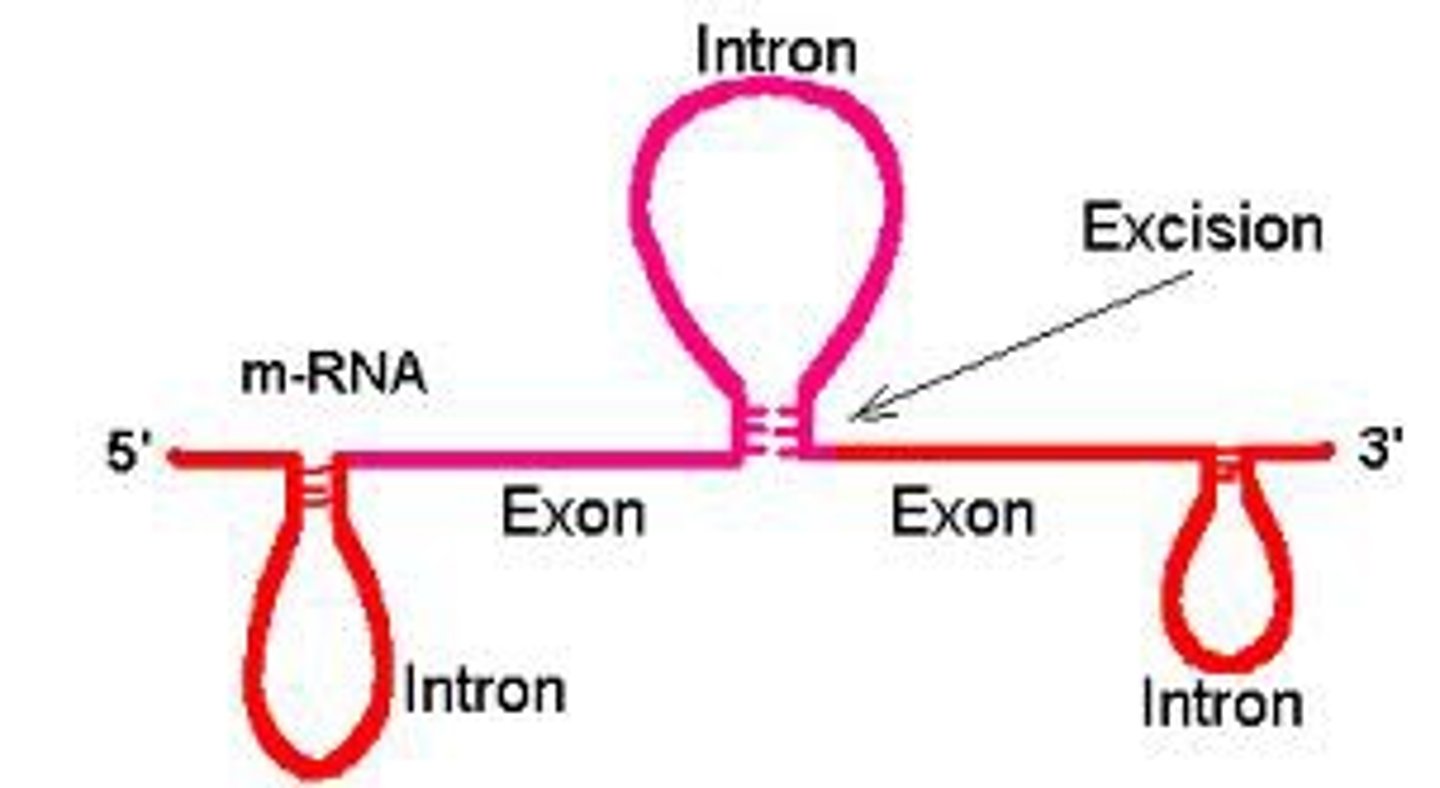
Exon
expressed sequence of DNA; codes for a protein
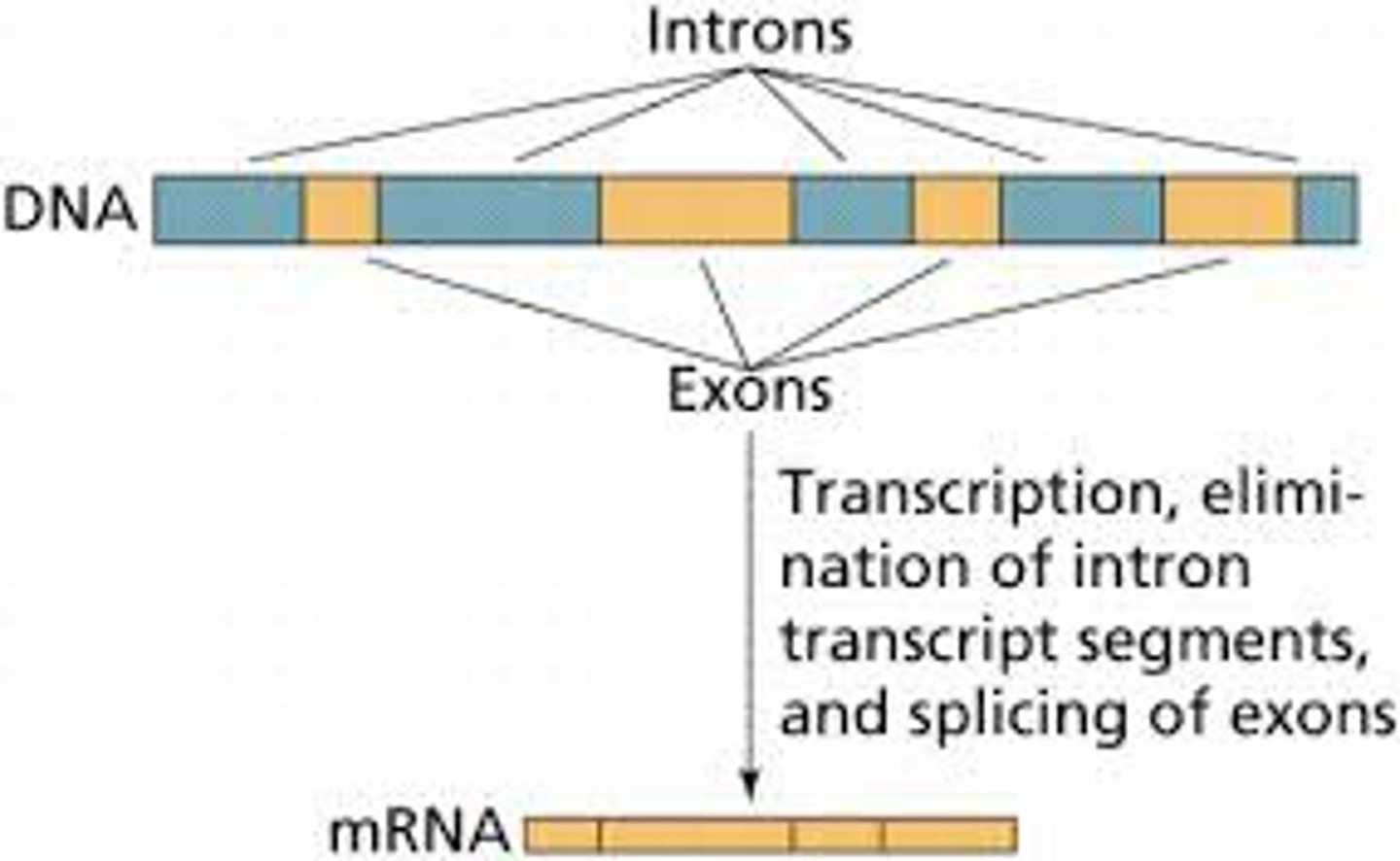
Alternative Splicing
Removal of introns in a pre-mRNA that occurs in different ways, leading to different mRNAs that code for different proteins. Increases the diversity of proteins.
Operon
group of genes operating together
Promoter
specific region of a gene where RNA polymerase can bind and begin transcription