Heart Anatomy and Cardiac Circuit
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
pulmonary circuit
starts: right ventricle
ends: left
pumps oxygen poor blood to the lungs
systemic circuit
starts: left ventricle
ends: right atrium
pumps oxygen rich blood into the systemic tissues and removes CO2 waste
sulci
grooves separating chambers
contain important vessels that provide oxygen and nutrients to heart tissue and drains waste products and oxygen poor blood from heart tissue
coronary sulcus
yellow; atrioventricular sulcus
border between atria and ventricles
contain: coronary arteries and sinus
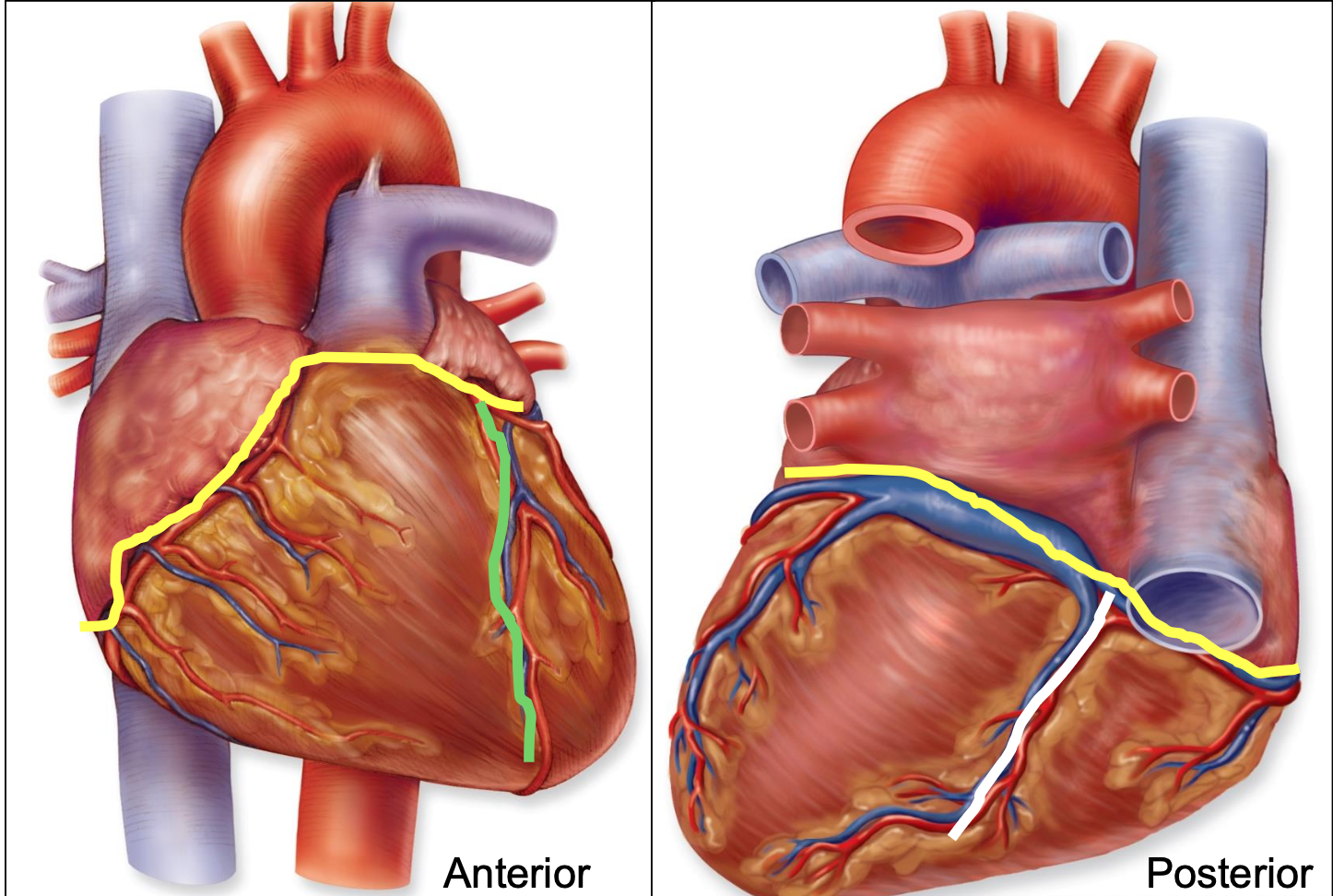
anterior interventricular sulcus
green; border between right and left ventricles on anterior surface
contain: anterior interventricular artery and great cardiac vein
posterior interventricular sulcus
white; border between right and left ventricles on posterior surface
contain: posterior interventricular artery and middle cardiac vein
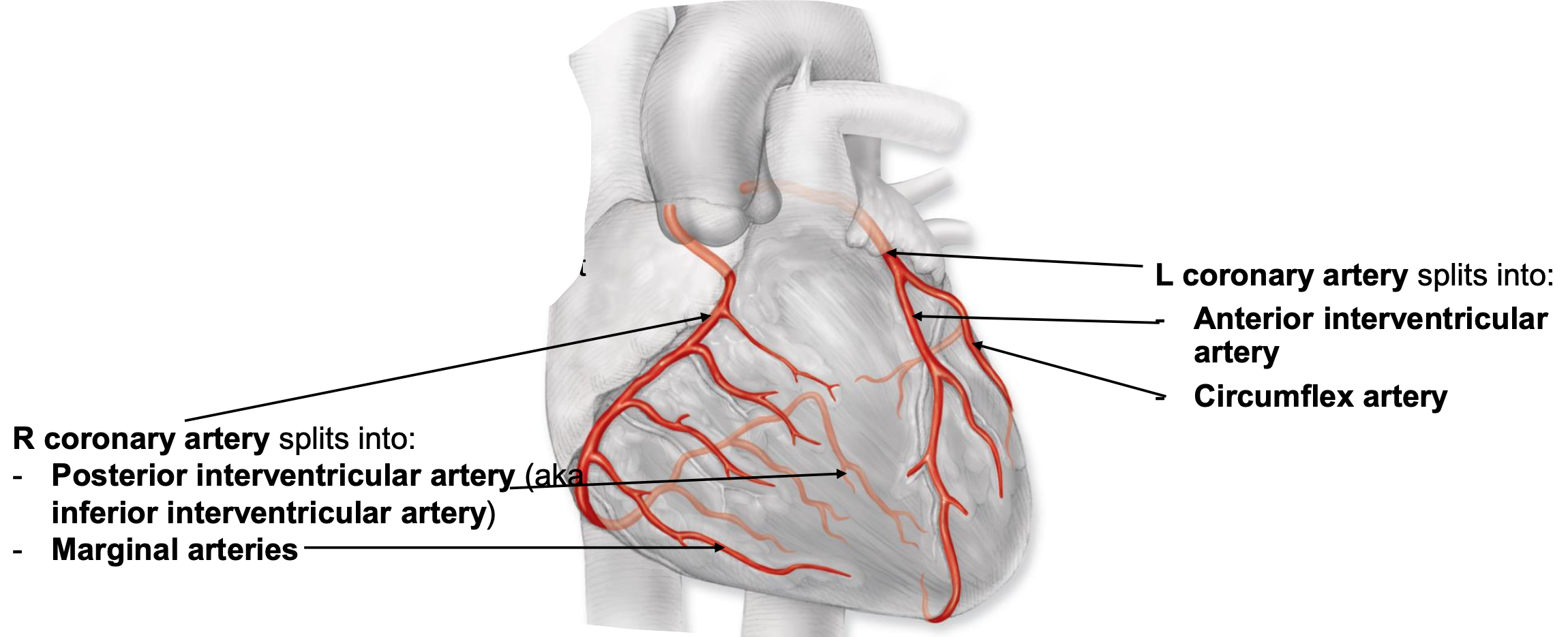
coronary arteries
supply blood to heart
starts at base of aorta and encircle heart in atrioventricular groove
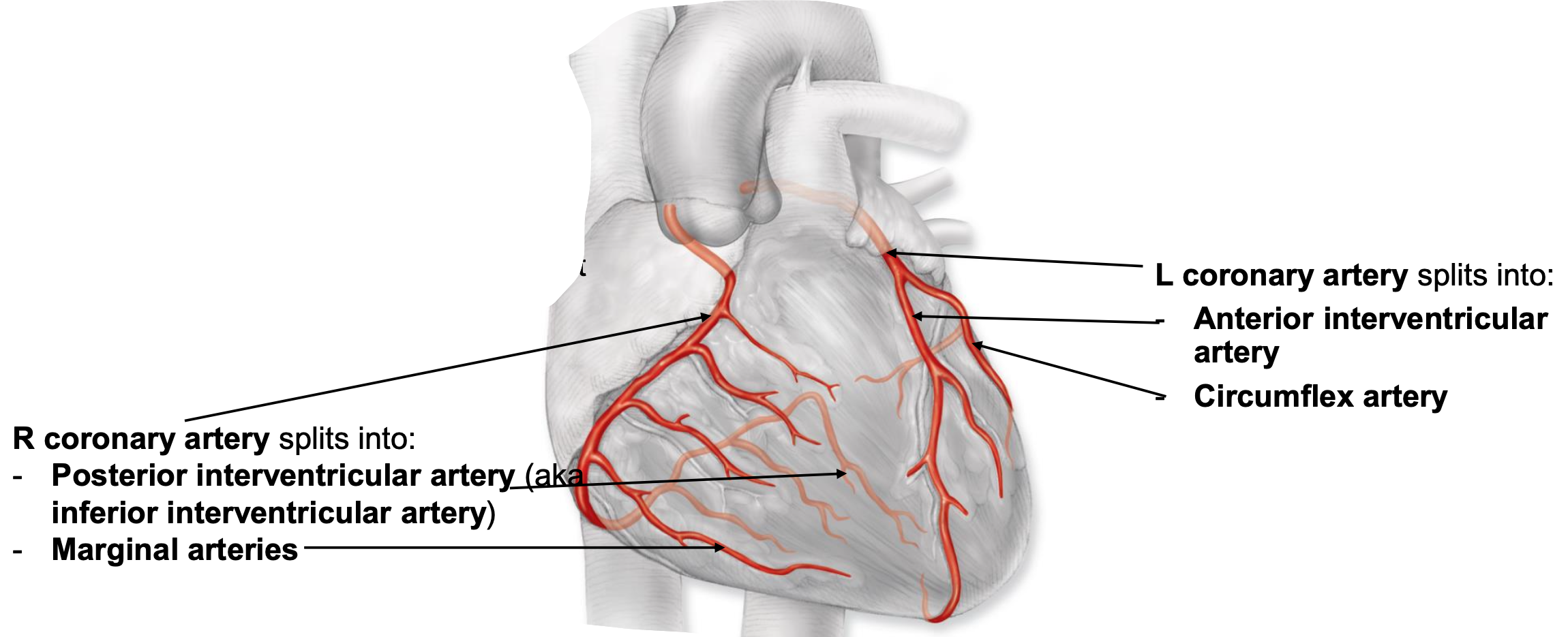
right coronary artery
feeds right atrium, majority of right ventricle, portion of left ventricle, portion of interventricular septum
splits into:
posterior interventricular artery
marginal arteries
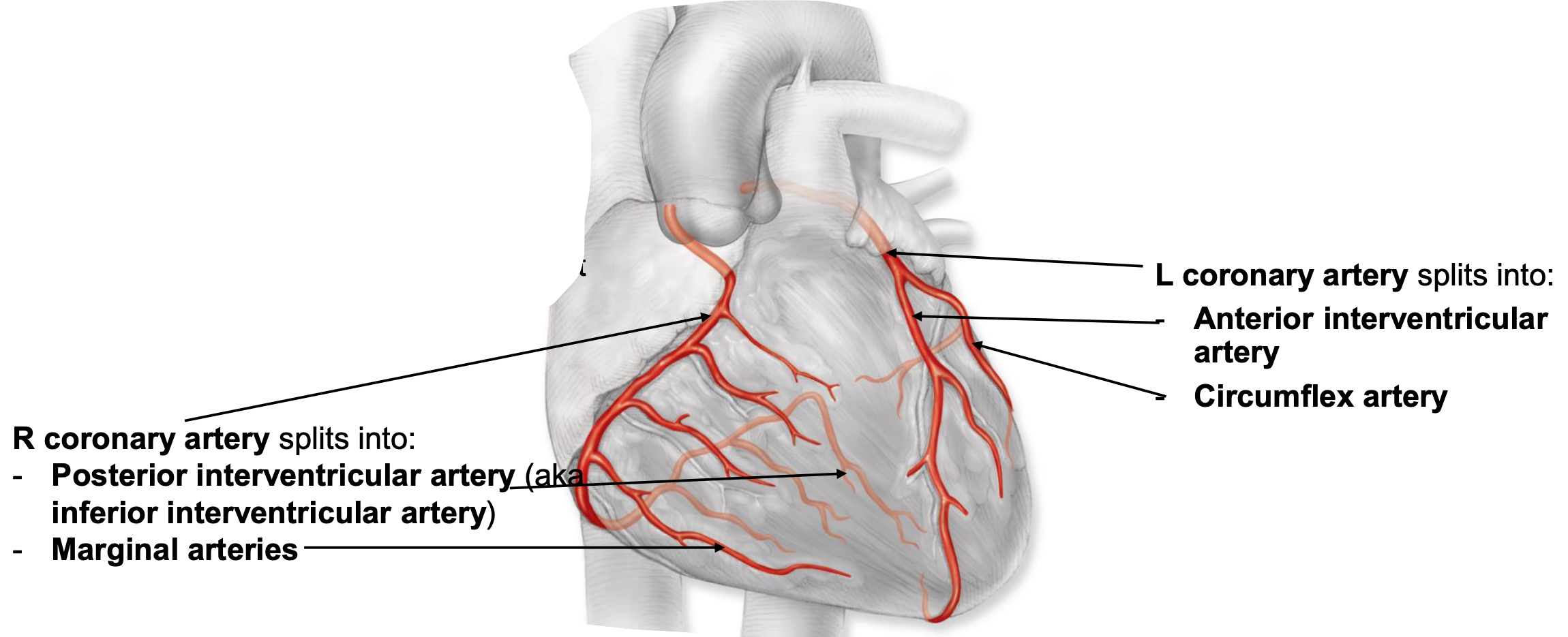
left coronary artery
feeds left atrium, majority of left ventricle, portion of right ventricle, portion of interventricular septum
splits into:
anterior interventricular artery
circumflex artery
coronary veins
return blood to the circulation; empty into the coronary sinus and blood flows directly into the right atrium from the coronary sinus (via opening of coronary sinus)
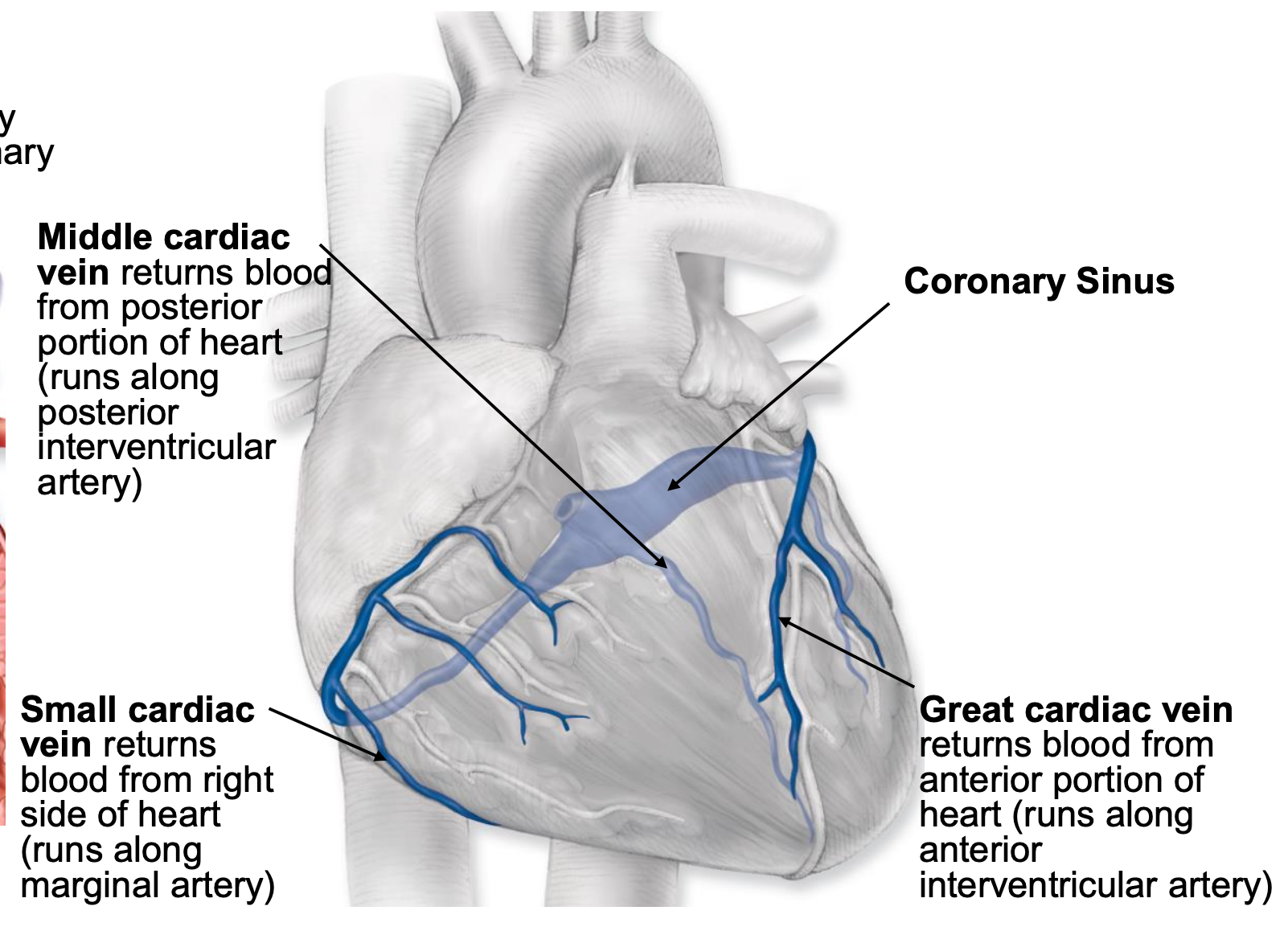
middle cardiac vein
returns blood from posterior portion of heart (runs along posterior interventricular artery)
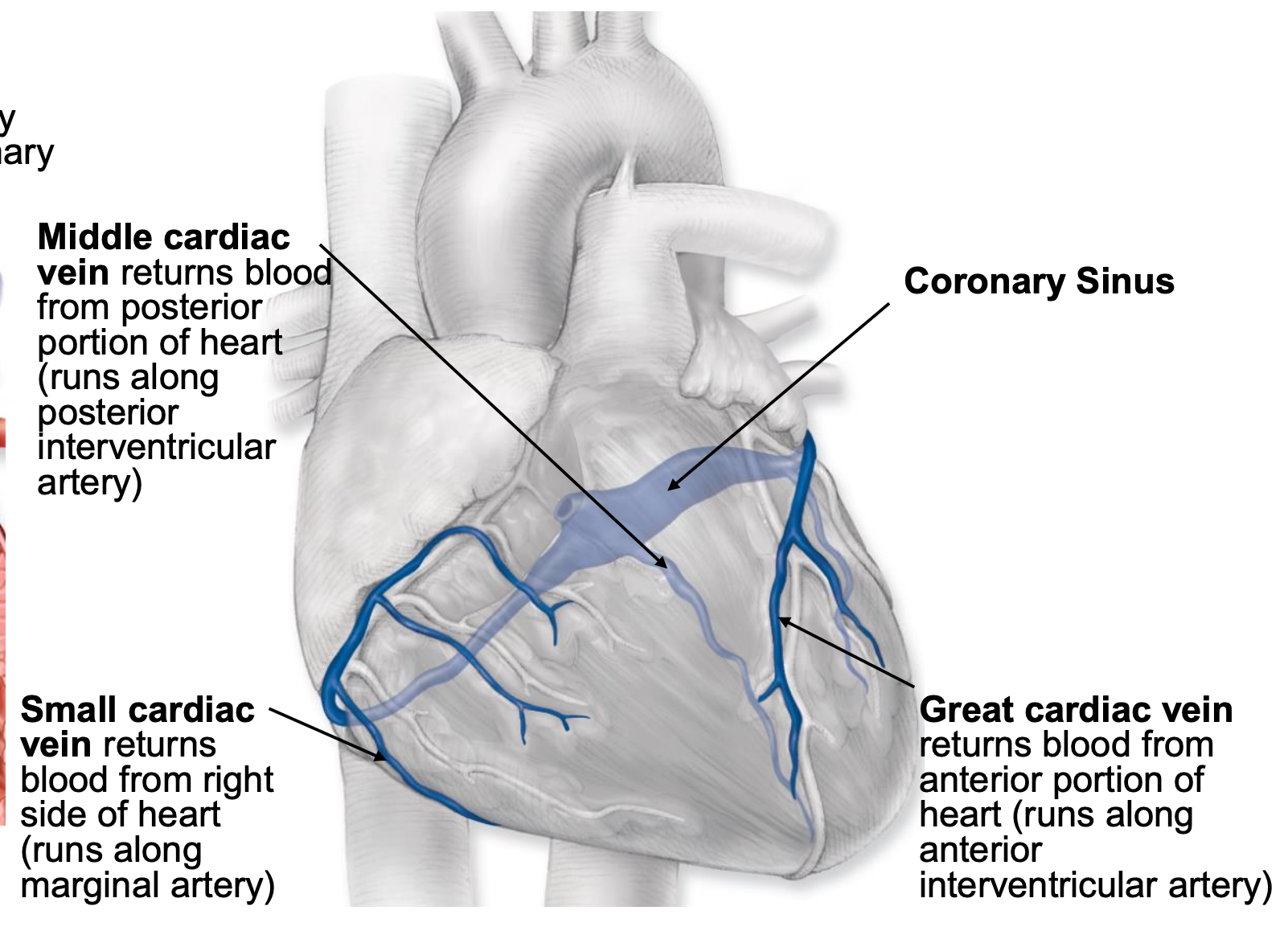
small cardiac vein
returns blood from right side of heart (runs along marginal artery)
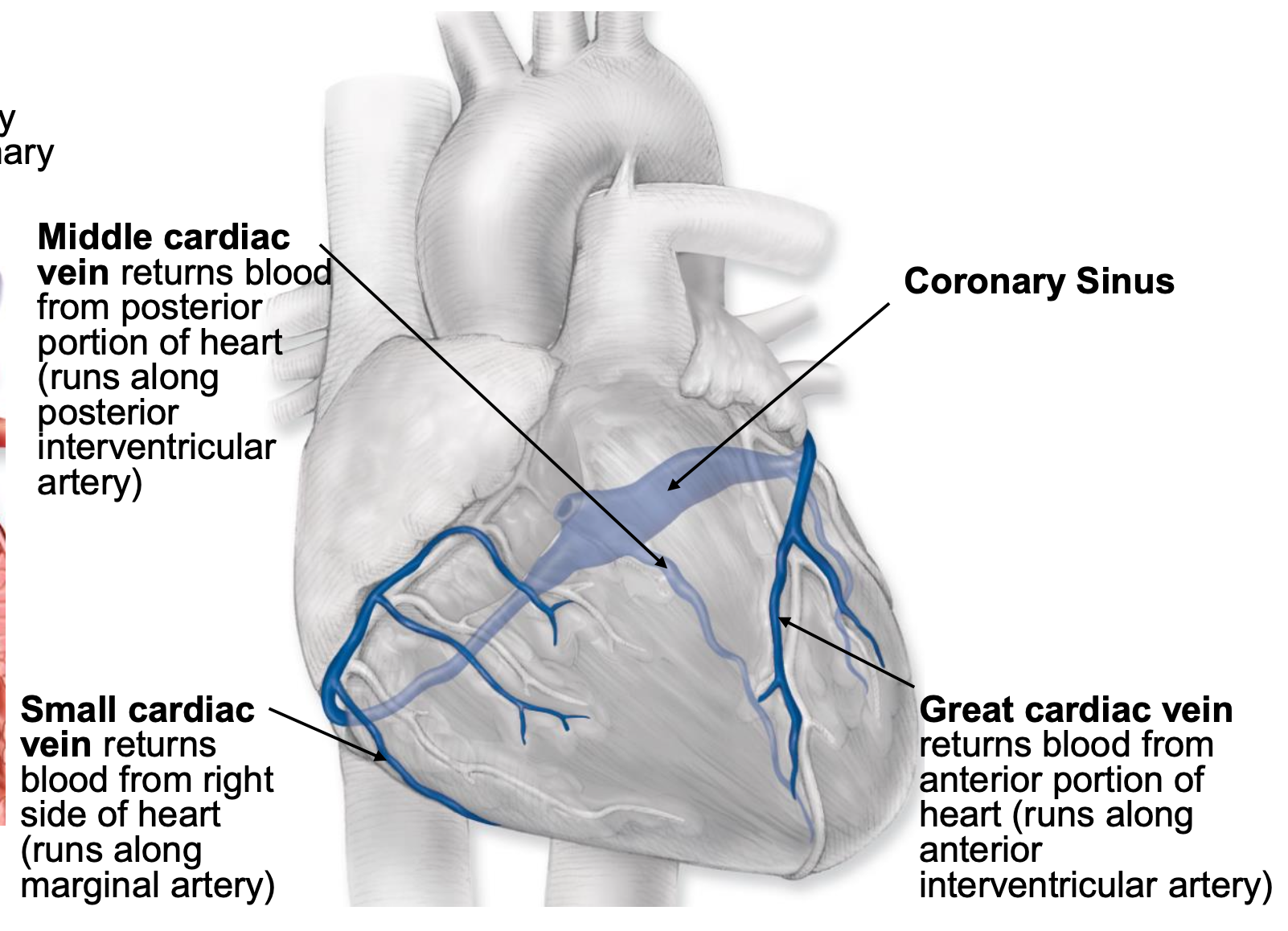
great cardiac vein
returns blood from anterior portion of heart (runs along anterior interventricular artery)
widow maker
massive heart attack caused by blockage of the anterior interventricular artery
reperfusion
restoring blood flow to an organ from which it has been blocked
myocardial ischemia
blood flow to the heart is reduced from blockage of the coronary arteries
transient flow interruption = mid/mild occlusion
angina pectoris- pain due to spasm of cardiac muscle
if flow blockage is complete and prolonged
myocardial infarction
death of tissue
dead muscle can’t be replaced
occlusion of R or L main coronary artery can mean instant death
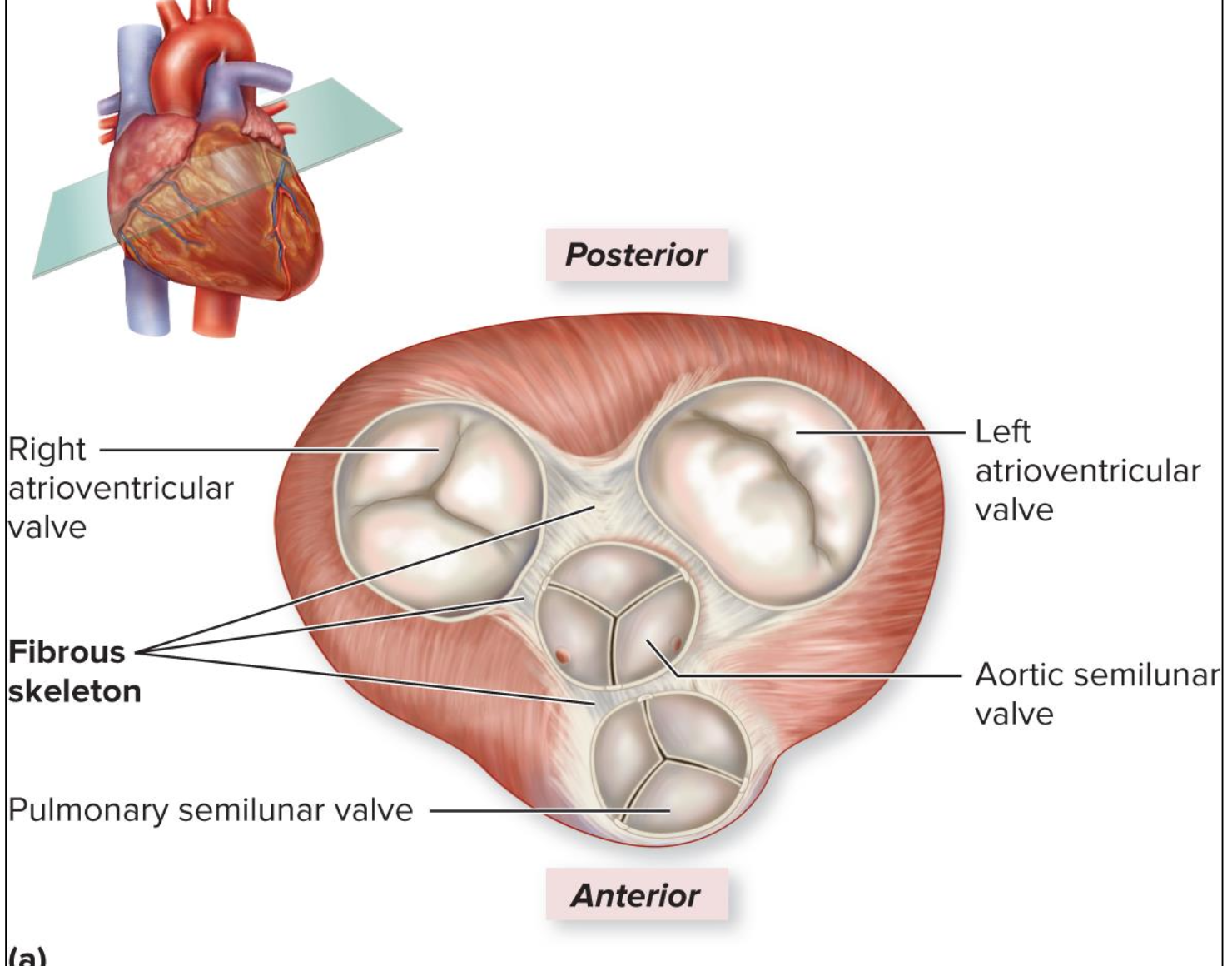
fibrous skeleton
anchors heart valves
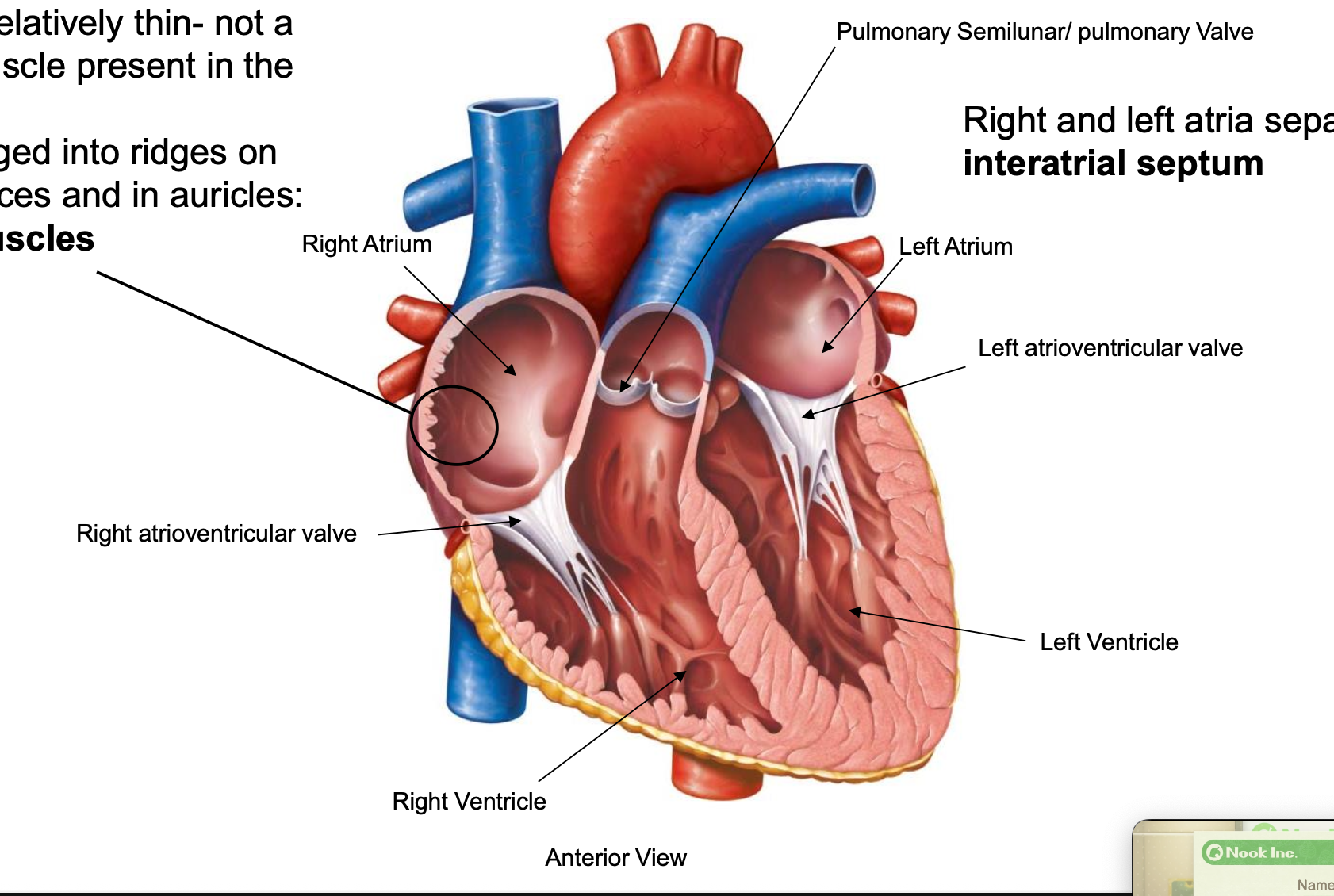
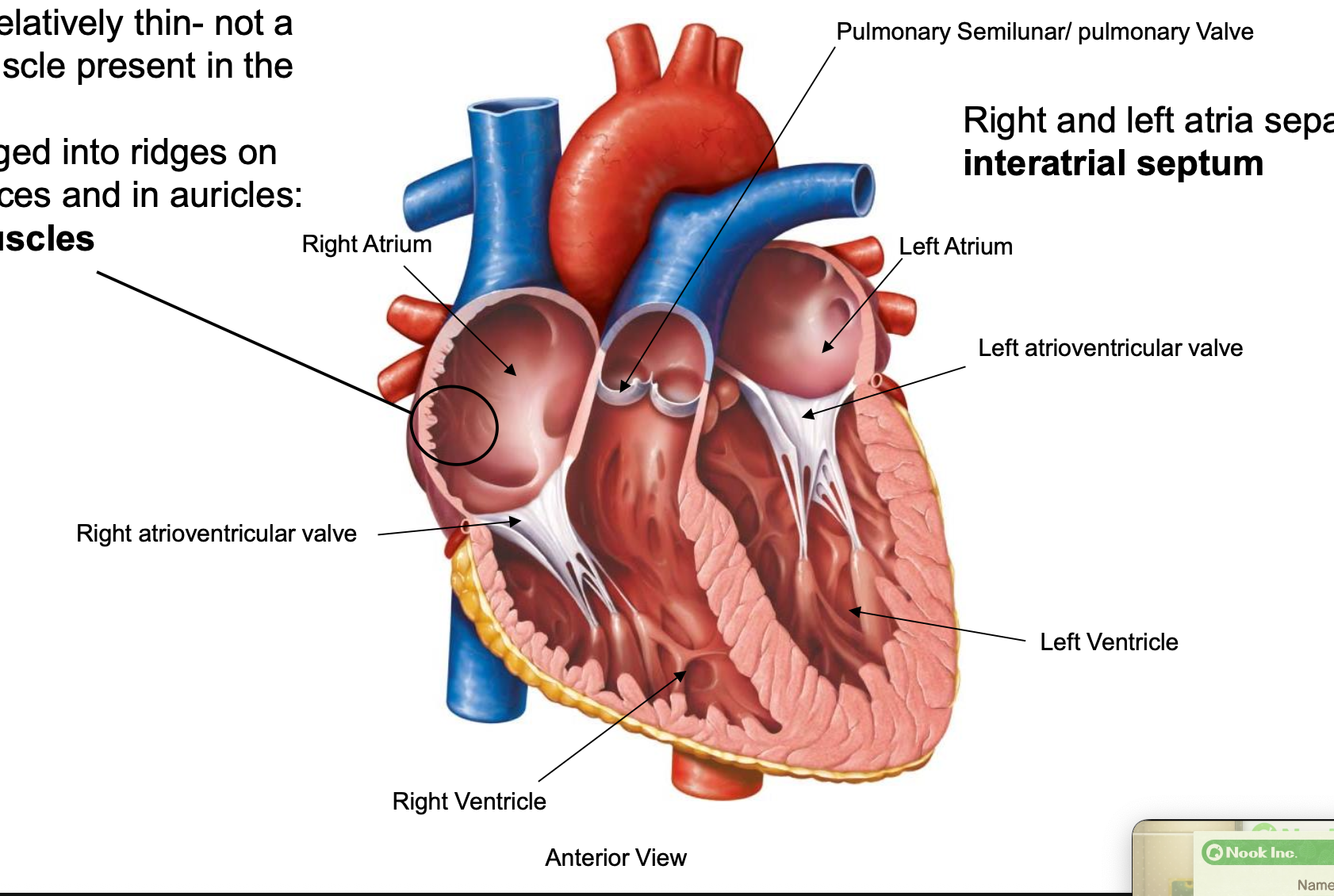
pectinate muscles
muscle arranged into ridges on anterior surfaces and in auricles
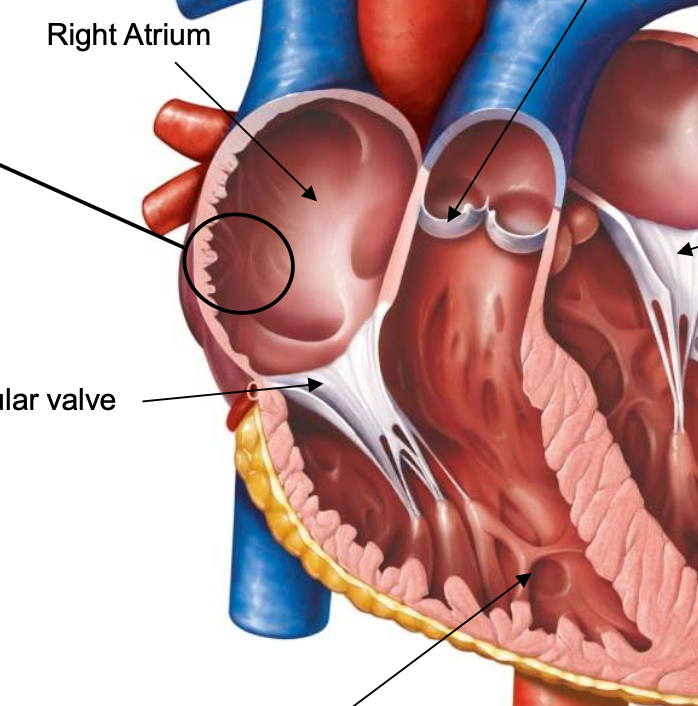
interatrial septum
separate left and right atria
internal structures of ventricles
conus arteriosus, trabeculae carneae, papillary muscles, chordae tendineae, interventricular septum
conus arteriosus
smooth region that directs blood out of right ventricle; no trabeculae
trabeculae carneae
ridges of myocardium in ventricle; prevent walls of ventricles from sticking together during contraction
papillary muscles
thickened extensions of trabeculae; numbers correcpond to leaflets in valve (each attaches to multiple leaflets)
chordae tendineae
attach valves to papillary muscles; prevent backflow of blood into atria when ventricles contract
what drives movement of blood
cardiac muscle contractions and pressure changes; valves prevent backflow
atrioventricular valves
open when ventricle is filling; close when ventricle is pushing blood out to body; moves from atria to valve
semilunar valves
open when ventricle is emptying; close when ventricle is filling; from ventricle to artery (push blood out of heart)
progression of blood flow through the heart
SVC + IVC → right atrium
right atrium → right ventricle (right atrioventricular valve)
right ventricle → pulmonary circuit (pulmonary trunk, pulmonary semilunar valve)
pulmonary veins → left atrium
left atrium → left ventricle (left atrioventricular valve)
left ventricle → systemic circuit (aorta, aortic semilunar valve)
heart murmur
occurs when a valve is slightly leaky; some blood regurgitates backward creating turbulence; some are innocent
diastolic murmur
heart is filling with blood (relaxed); right atrium
systolic murmur
heart is emptying; atrioventricular valve closed
continuous murmur
throughout the heartbeat; all the time
prolapse
occurs when valve is very leaky due to improper closure; blood regurgitates leading to congestion in circuit
stenosis
difficult to open a valve usually due to scar tissue formation
valve tissue becomes stiff and is constricted by scar tissue making valve hard to open
may lead to backup in circuit
produce whistling sound