L4 - Amino Acids and Proteins
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What are essential amino acids
obtained from food sources
cant be made by body
e.g. Leucine + Isoleucine
What are non-essential Amino Acids?
Made by the body
not obtained from food source
e.g. alanine + aspartate
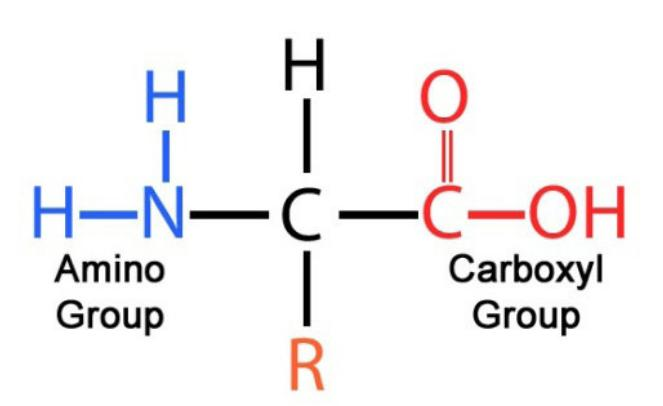
The general structure of a protein
Where do plants amino acids from?
From nitrates in the soil which is converted
Amino acids are joined together using what reaction
Condensation reactions, bonded with peptide bonds and releases water
What are polypeptides?
Proteins consisting on one or more polypeptide chains folded into a very specific 3D shape.
What are the 4 types of structure in Proteins?
Primary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary
What is the primary structure in proteins?
The order of amino acids according to bonds
amino acids held together by peptide bonds
What is the secondary structure in proteins?
It is the coiling/folding of the amino acid chain.
it is due to the hydrogen bonded between amino acids.
Forms either:
Alpha Helix
Beta Pleated Sheet
What determines if the Amino acid chain is alpha helix?
Coiled structure
Intra-chain hydrogen bonds within the same chain
What determines if the Amino acid chain is Beta Pleated Sheet?
Pleated/folded structure.
hydrogen bonds form between different sections of the chain (or different chains), forming sheet-like layers.
What is the Tertiary structure of a protein?
The overall 3D shape of a single polypeptide chain.
formed by further folding of secondary structure
What kind of different bonds occur in Tertiary Structure of proteins?
Stabilised by interactions between R Groups:
Disulphide bonding
Ionic Bonding
Hydrogen Bonding
Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic
Explain Disulphide bonds in Tertiarty Structure
Cysteine contains sulphur
if two cysteine are close together, a strong covalent bond forms
Explain Ionic Bonds in Tertiarty Structure
Positive and negative part of R groups can form ionic bonds.
Explain Hydrogen Bonds in Tertiarty Structure
Hydrogen bonds can form between polar parts of the R group.
Explain Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic interactions in Tertiarty Structure
Some parts of R-group are hydrophobic, some are hydrophilic
In water based environment, hydrophobic areas will cluster together.
What is the Quaternary Structure?
The quaternary structure is the association of two or more polypeptide chains into a functional protein.
What holds the quaternary structure together
Interactions between R groups, including hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulfide bonds, and hydrophobic interactions.
Do all proteins have a quaternary structure?
No, only proteins made of more than one polypeptide chain have quaternary structure.
Give an example of a protein with quaternary structure
Haemoglobin, which has four polypeptide chains (haem groups)
What are the 2 Types of Proteins?
Globular - Insulin, Catalase, Haemoglobin
Fibrous - Collagen, Keratin
Properties of Globular Proteins?
Spherical shape - tightlty folded polypeptide chains.
3 Types:
transport proteins (haemoglobin)
enzymes (catase)
Hormones (insulin)
Properties of Insulin
Globular Protein
Hormone secreted by pancreas
Quaternary structure - two polypeptide chains
Insulin soluble - hormone that travels in blood plasma
Properties of Haemoglobin
Globular protein
Four polypeptide chains
Each chain wrapped around atoms called haem groups (type of prosthetic group)
Prosthetic group - parts of proteins not made up of amino acids
Holds Fe2+ ion in the centre
Each ion is able to bond with 1 oxygen molecule
4 Haem groups x O2 = 8 Oxygen Atoms per Hb
What are proteins that have Prosthetic groups called?
Conjugated proteins (e.g. haemoglobin)
Properties of Catalase?
Globular protein
Common enzyme in nearly all living organisms
Catalyses decomposition of hydrogen peroxide → water + oxygen
Contains 4 polypeptide chains and 4 haem prosthetic groups
Properties of Fibrous proteins?
Formed from parallel polypeptide chains held by cross links
Generally insoluble in water.
Examples:
Elastin, Silk, Collagen and Keratin.
Properties of Keratin?
Fibrous protein
Group of Fibrous proteins found in hair, skin and nails
The degree of sulphide bonds determines flexibility.
Hair would have more sulphide bonds than nails
Properties of Collagen?
Fibrous protein
Found in connective tissues (e.g. skin, muscles, tendons)
Consists of 3 helical polypeptide chains that twist around eachother.
1 in every 3 Amino acids is Glycine to allow the chains to pack closely together.
Huge tensile strength - can withstand pulling pressure.
Glycine (amino acid type) forms a high proportion of the collagen molecule.