Chemistry Ch. 2 - Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Atomic Force Microscopy
A way to see atoms using a sharp tip with lasers
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy
Another way to see atoms using an electron beam
Dalton’s Atomic Theory and the 4 Postulates
1) Everything is made of Atoms
2) All atoms of 1 element are identical, but different elements have different atoms
3) One elemental atom (like oxygen) cannot be changed into a differnt elemental atom (like nitrogen)
4) Several elemental atoms can come together to make compounds and a specific compound will always be made in the same composition
Law of Constant Composition
Based on postulate 4. The composition of a compound will never change; it will always have the same percentages of elements
Ex) any water molecule will always have one oxygen and two hydrogens
Law of Conservation of Mass
Based on postulate 3. Mass is never lost or gained, total mass does not change in chemical reactions.
Law of Multiple Proportions
Based on all postulates. The same elements can form more than one compound
Ex) With just hydrogen and oxygen, you can make water (H2O) or hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
Who discovered Protons?
Ernest Rutherford
Who discovered Electrons?
J.J. Thompson
Who discovered Neutrons?
James Chadwick
What makes up the volume of electrons
The electron cloud
What is the electron mass
9.1 × 10-28
What do protons do and their relative charge?
Determine the identity of the atoms, +1 amu
What do neutrons do?
They glue/keep the atom together
What do electrons do and their relative charge?
They determine the reactivity, -1 amu
How to find the mass number?
Protons + Neutrons
Where is mass number, atomic number, and charge located on an elements periodic table
Mass number is on top, atomic number on bottom, and charge on the top right.
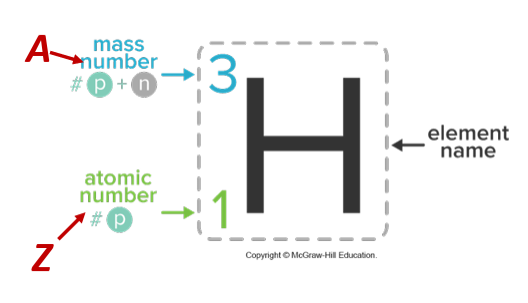
Isotope
Different versions of the same element due to different number of neutrons.
Groups
Vertical columns with the same physical and chemical properties
Periods
Horizontal rows
Where are the main groups and transition metals on the periodic table
The main group includes the two tall columns on each side and the transition metals in the middle and bottom
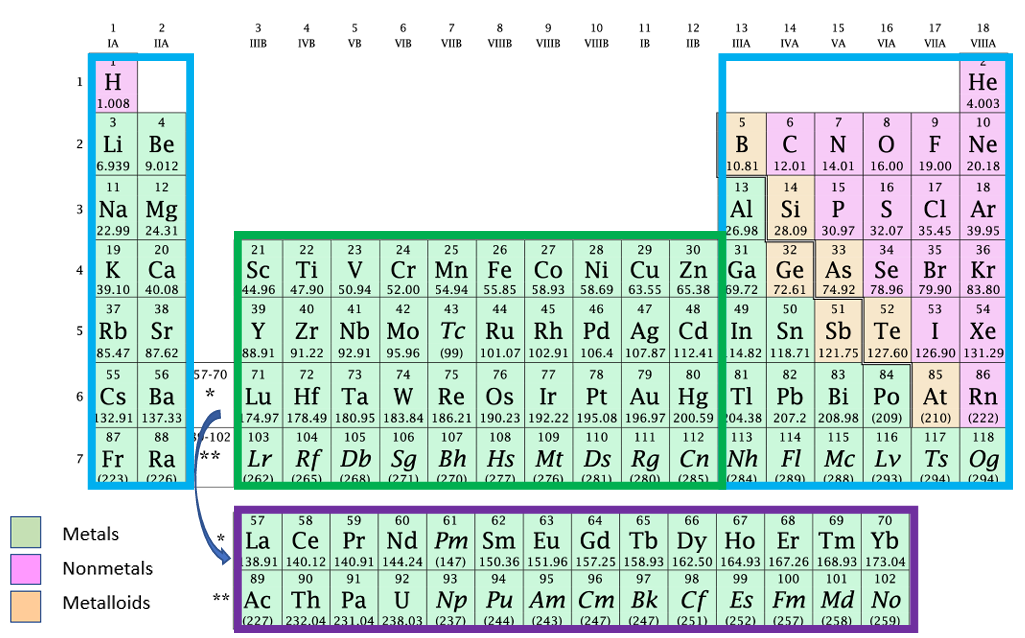
Properties of Metals
Shiny, conductive, lustrous, malleable, solids at room temperature, high melting point, high malleability, lose electrons easily (low ionization energy, low electronegativities)
Properties of Nonmetals
Most are gases at room temperature, hard and brittle, low/no luster, low melting points, gains electrons easily (high ionization energies, high electronegativities), good insulators (because theyre poor conductors)
Metalloids
They are good semiconductors
Molecular Compounds
Almost always nonmetals
Covalent Bonding
C.C. = Caring Covalent, covalent bonding shares electrons
Molecular Formulas
The exact number of atoms in each element
Ex) C6H12O6
Empirical Formula
The lowest whole number ratio of atoms in each element
Ex) CH2O
Polyatomic Ions
Compounds with a net charge
Ex) SO3-2 is Sulfite