lecture 18 & 19: HIV and AIDS
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
gag
HIV gene that codes for structural proteins, including matrix capsid and nucleocapsid
pol
HIV gene that codes for enzymes, including protease, reverse transcriptase, and integrase
env
HIV gene that codes for for structural proteins and envelope proteins, including GP120 and GP41
tat
main HIV gene that codes for regulatory proteins
9
HIV genome contains _______ genes encoding 15 viral proteins
Tat
HIV virulence factor that is a transactivator of transcription
-enhances viral transcription and immune regulation
reverse transcriptase
HIV enzyme encoded by pol that •convert RNA genome into DNA to be integrated
integrase
HIV enzyme encoded by pol that integrates viral DNA into host DNA
protease
HIV enzyme encoded by pol that cleaves polyproteins into functional viral proteins
-primary infection 2-4 weeks with flu like symptoms
-latency with steady increase of anti-HIV ab and decrease of CD4 over 6-10 years
-full blown AIDs
clinical progression/timeline of HIV
gp160, also called Env gene
what is the viral attachment protein of HIV
receptor: CD4
coreceptor: CCR5 (on T cells, macs, DCs)
receptor and co-receptor of HIIV
CD4 T cells, macrophages, and DCs
target cells of HIV virus
1. gp120 binds CD4 and CCR5
2. conformational change exposes fusion peptide
3. capsid is released into cytoplasms and uncoated
4. The 2 ssRNA genomes are copied into 2 dsDNA molecules by reverse transcriptase that copies, then degrades, viral RNA
5. dsDNA is tranpsorted to nucleus and integrated into host cell by integrase
6/ proviral DNA is transcribed into genomiic RNA
7. viral proteinss are sysntehsized
8. viral particles are assembled and released by budding
steps of HIV-1 replication
gp120 and gp41 cmplex
protein on the HIV viral envelope that attaches to the CD4 cell
zidovudine
HIV med that competitively inhibits nucleotide binding to reverse transcriptase
Efanvirenz
HIV med that binds to and inhibits reverse transcriptase at different site than nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors
indinavir
HIV med that prevents cleavage of the polypeptide products of HIV mRNAinto their functional parts--> prevents maturation of new viruses
Raltegravir
HIVI med that inhibits HIVI integration into host cell DNA
Enfuvirtide
HIV med that binds gp41--->inhibits viral entry into host cell
maraviroc
HIV med that binds CCR6---> inhibits initeraction with gp120--> prevents viral biniding
proofreading capability---> extremely high error rate during synthesis
-error rate leads to emergence of strains with changes in antigenicity--> drug resistance to ART
unlike other polymerases, reverse transcriptase lacks
Viral RT is error-prone (no proof-reading), high mutation rate leads to drug resistance to ART (anti-retroviral therapy).
what has led to the resistance to anti-retroviral therapy?
-→ reduced Th activity (esp. IL-2 and IFN-γ production), so reduced CD8 and mac function
the impact on immune system placed by loss of CD4 cells
<200 (TH1 most affected, TH2 predominant cytokine profile)
CD4 count diagnostis of AIDS
1.Flu-like (acute)
2.Feeling fine (latent)
3.Falling count
4.Final crisis
what are the 4 stages of untreated HIV iinfectioiin
CD4 >500
CD4 count associated with acute phase, peak of virus that declines, non-specific "flu-like" symptoms to asymptomatic
latent stage of HIV
no detectable viral DNA; in late stage, CD4 T cell count of 200-500 cells/u
– CD4 T cell count <200 cells/ul and appearance of at least 1 “indicator” disease (neoplasm, opportunistic infection, dementia
define criteria of full blownn AIDS
generation of viral diversity via mutation and recombination--> life long infection
how does HIV evade the immune system?
Step 1: Antibodies to gag and env proteins - immunoassay
Step 2: Confirm with detection of p24 core Antigen - acute and end-stage/AIDS
Step 3: NAAT (RT-PCR) for HIV RNA
steps to diagnosing HIV
antiretroviral therapy
reduces plasma viremia and reduces transmission
condoms, ART, less risky sexual practices
how to decrease risk of contracting HIV
take ART, avoid breastfeeding (delivery method depends on viral load)
•Also prophylaxis the baby
avoiding perinatal transmission of HIV via
-less likely to transmit HIV to partner
-fewer incidences of TB, severe bacterial infection
the benefits of early treatment of HIV
post-exposure prophylaxis
the taking of ART as son as suspected exposure occurred
-begin within 72 hours of exposure
2-3 antiretroviral meds taken for 28 days
what does PEP consist of?
•For HIV- & at high risk for infection
ex: ongoing relationoship with infected partner, not mutually monogomous, MSM, STD in last 6 months, IVDU in last 6 months
pts indicated to take PrEP
every 3 months
how often are pts who take PrEP tested for HIV
tenofovir & emtricitabine
the two meds in PrEP
•Acute mononucleosis-like symptoms correlates to virus disseminating through lymphoid tissue
•Generalized lymphadenopathy, fever, fatigue, rash, pharyngitis, HA, arthralgia, myalgia
primary sympptoms of HIV infection
8-10 years
Avg time from acquisition to a CD4 <200 cells/μL is approximately
•Majority asymptomatic, but will often have generalized lymphadenopathy
symptoms of latent stage of HIV
thrush, vaginal candidiasis, oral hairy leukopplakia, herpes zoster , const. symptoms for more than one month
symptomatic illnesses associated with chronic HIV infection without AIDS
•HIV + & CD4 count < 200/μL or HIV+ w/ certain infections
definition of AIDs
grade A
screen ages 15-65 for HIV at least once in their lifetime or more
-screen all pregnant women
-if risk factors, test annually
USPSTF recommendation fo HIV screening
every 3-6 months
how often to screen gay and bisexual men for HHIV
•screen with a highly sensitive initial test and confirm reactive results with a different test that is both sensitive and highly specific
what is the general principle of HIV testing
IgG-sensitive HIV-1/2 antibody differentiation supplemental assay
-shortest window period of positivity
confirm initial Ag/Ab test with this test for HIV
•2 step testing (EIA + Confirmatory IgG sensitive assay) is sensitive 99.5 % and specificity of 99.9%. If ELISA (EIA) negative, then HIV is neg unless acute infection.
define the 4th generation testing of HIV and its efficacy
between 2 - 6 weeks; median window is 18 days after exposure with 99% of HIV-infected persons detectable within 44 days of exposure
-can due 4th gen testing
when is HIV detectable (outside window period)
4th generation tests
•Detect both HIV antibodies and the HIV-1 p24 antigen, but do not differentiate between them.
5th generation tests
•Detect both HIV antibodies and the HIV-1 p24 antigen, and provide separate results for each. Can differentiate between HIV-1 and HIV-2 antibodies. Detects the same biomarkers as 4th, but it is about being able to independently confirm each one separately
-HIV drug resistance testing
-may defer ART initiation til after this tests results, unless early infection or pregnant
initial testing in confirmed HIV + pt
pregnancy test
test in women before initiating ART
DTG based regimen
is one of the recommended options for persons of childbearing potential initiating ART
nucleoside, nucleotide, and non nucleoside inhibitors
what are the 3 types of reverse transcriptase inhibitors?
integrase inhibitors
suffix -gravir indicates this HIV drug
protease inhibitors
-exception: lenacapavir is a capsid inhibitor
suffix -avir indicates this HIV drug
•Zidovudine
•Stavudine
•Lamivudine
•Emtricitabine
VUDINE
list the pyrimidine analogs of NRTI
•Didanosine
•Abacavir
•Tenofovir
list the purine analogs of NRTI
darunavir
what is the most commonly used protease inhibitor
protease inhibitors
HIV drug class that renders the virus immature and noninfectious
Lenacapavir (capsid inhibitor)
indication: for adult patients living with HIV-1 in whom other available treatments have been unsuccessful due to resistance, intolerance, or safety considerations.
capsid inhibitor
-Capsid inhibitors are a class of drugs that interfere with HIV capsid, a protein shell that protects HIV's genetic material and enzymes needed for replication. Capsid inhibitors can disrupt HIV capsid during multiple stages of the viral life cycle
MOA of lenacapavir
4 hours post dose
-ppeak plasma concentrations of lenacapavir happen when?
Binds to the HIV integrase active site and blocks the strand transfer step of retroviral DNA integration which is essential for HIV replication
MOA of integrase strand transfer inhibitors (--gravir)
Maraviroc
A CCR5 inhibitor always used in combination with other HIV medicines
-tropism test must be performed prior to use
•Selectively binds to the human CCR5 chemokine co-receptor present on the cell membrane which prevents the interaction of HIV-1 gp120 and CCR5 for HIV to enter CD4 cells.
MOA of maraviroc
•increased liver enzymes, muscle/joint pain, cough
side effects of maraviroc
Enfuviritide
entry inhibitor inndicated inn pts whose infection is not well controlled by ongoing treatment with other HIV meds
Binds to the gp41 glycoprotein subunit of the viral envelope to prevent conformational changes needed for fusion of viral and cellular membranes and entry of HIV into CD4 cells.
MOA of enfuvirtide, a entry inhibitor
-2 NRTIs + (NNRTI or integrasae inhibitor or protease inhibitor) + PK enhancer (cobicistat + ritonavir)
-3 ARV + 2 booster
initial combination antiretroviral regimen for people with HIV
-tenofovir alafennamide OR tenofovir fumarate
-emtricitabine
-a --gravir
what are the 3 drugs initiated for most naive HIV + pts
HIV-infected women on cART with HIV RNA ≤ 1000 copies/mL late in pregnancy/near delivery date
IV zidovudine is not required for this woman late in pregnancy/near delivery date
HIV RNA >1000
HIV RNA number necessitating mother get IV zidovudine near delivery
at onset of labor or 3 hours piror to scheduled C-section until delivery of infant
at what point of pregnancy should IV zidovudine be administered?
-zidovudine syrup given as soon as possible (6-12 hours of delivery) until 6 weeks of age
-can lessen to 4 weeks if mother consistently on cART during pregnancy with suppressed viral load and reliable adherence
management of newborn baby whose mother has received HAART during pregnancy
add nevirapine suspension to zidovudine syrup regimen
management of newborn baby whos mother has not received HAART during pregnancy
38%
___% of people living with HIV are still not accessing ART
set as targets that by 2020, 90% of all people with HIV will know their HIV status, 90% of all people who know their status will be on ART, and 90% of all people receiving ART will have viral suppression
what is UNAIDS 90-90-90 goal?
immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome
•Inflammatory disorders associated with paradoxical worsening of preexisting infectious processes following the initiation of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) in HIV-infected individuals.
-unmasked by host's regained capacity to mount an inflammatory response
continue ART, treat opportunistic infections mostly with steroids
management of immune reconstitution inflammatory synndrome
coronary artery disease due too increased cholesterols due to ART
HIV pts are at risk for this heart disease
HCV, HBV
pts with HIV have an increased risk for cirrhosis esp with co-infection oof
HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder (HAND)
HIV associated CNS disorder characterized by memory and psychomotor impairment, depressive symptoms, movement disorders
-can progress to AIDS demention
10%
HIV wasting syndrome is a condition that occurs when a person with HIV loses more than ___% of their body weight, along with experiencing diarrrhea, weakness, or fever for at least 30 days
-ART, appetite stimulatnts, cytokine inhibitors, anabolic agents, human growth hormone (effectss don't last long)
-nutrition, exercise
treatments of HIV wasting syndrome innclude
cervical cancer, anal cancer
cancer to test for yearly in pts with HIV
breast, colon prostate
cancers that have normal screening recommendations for pts with HIV
200
avoid giving live virus vaccines if CD4 is below
herpes zoster
TB
opportunistic infection associated with CD4 over 500
mucocutaneous
______ infections tend to present first in pts with HIV
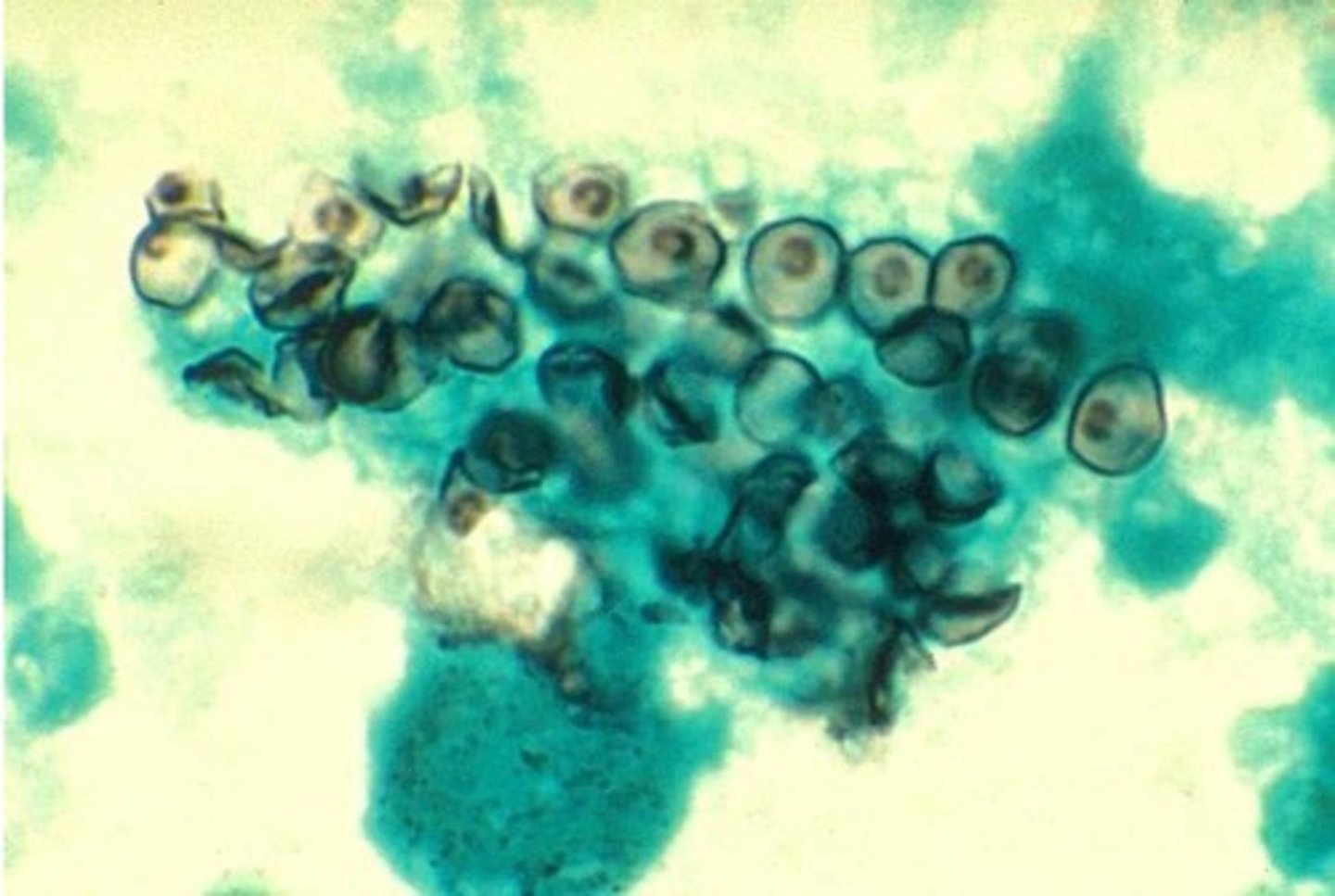
•unicellular fungus Pneumocystis jiroveci
-previously called pneumocystis carinii
pneumocystis pneumonia is caused by
airborne
transmission of pneumocystis pneumonia
-subacute progressive dyspnea
-hypoxemia and rales on PE
signs of pneumocystis pneumonia
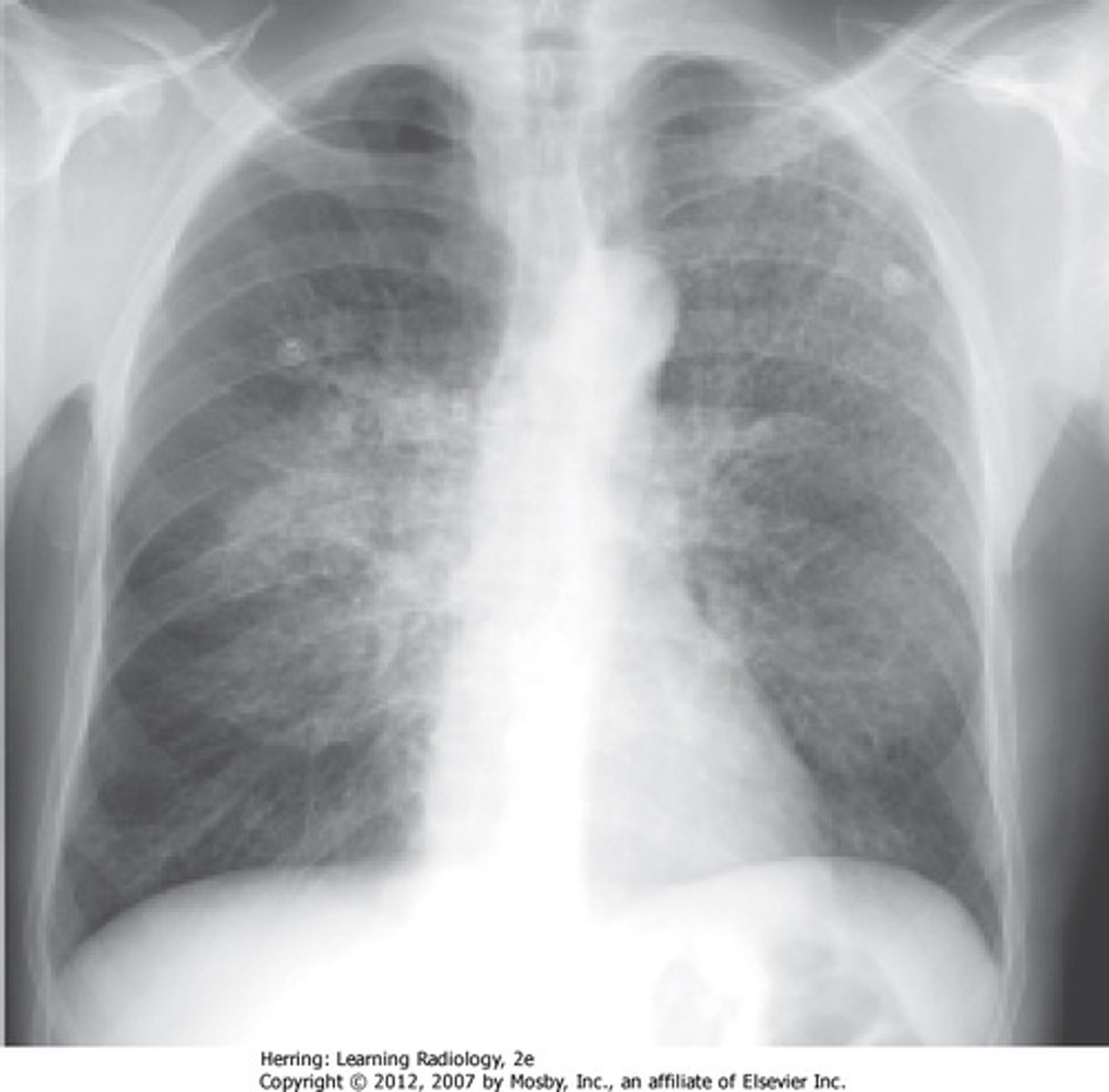
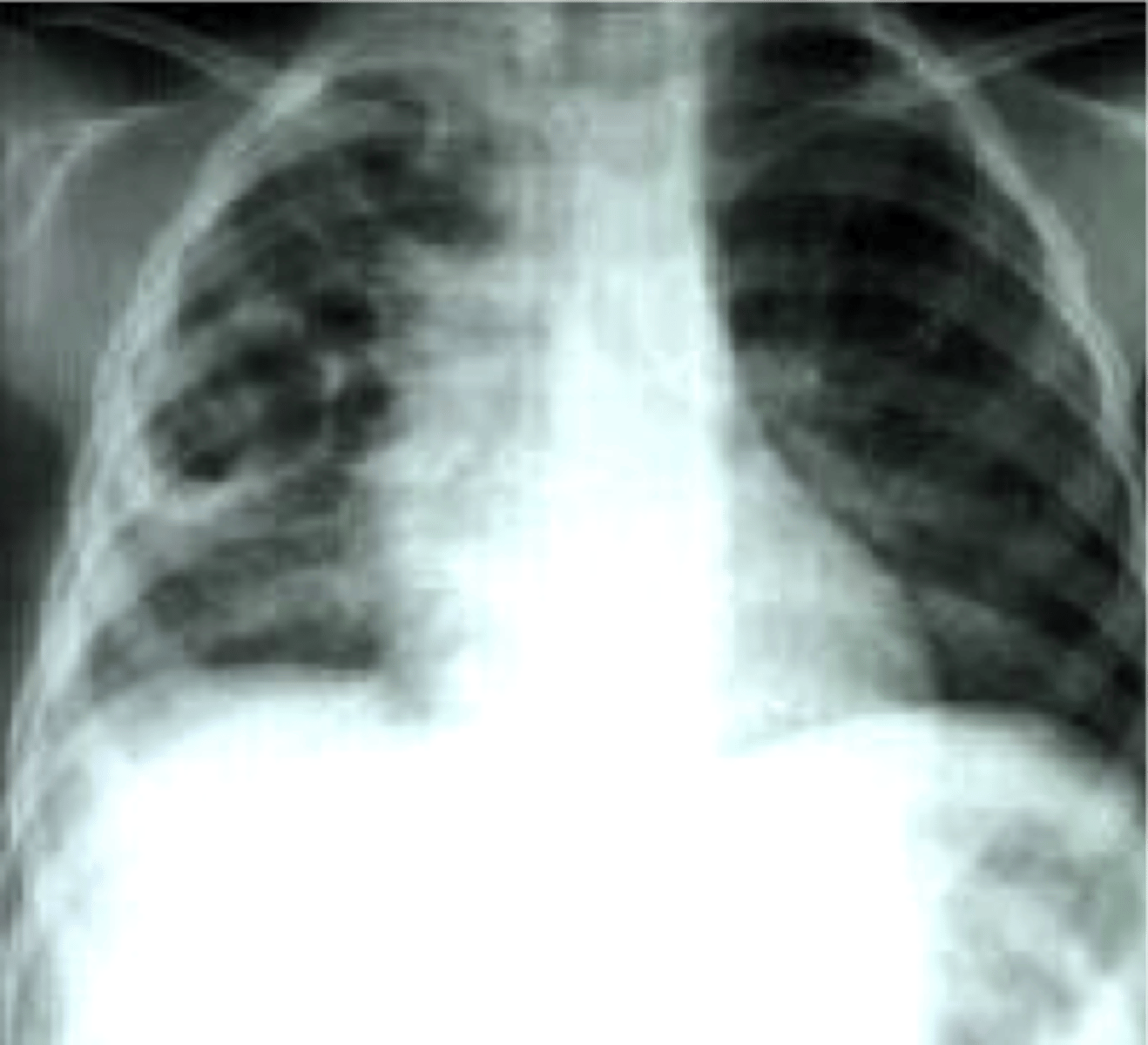
pneumocystis pneumonia
CXR shows •diffuse, bilateral, symmetrical interstitial infiltrates emanating from the hila in a butterfly pattern
-CT shows patchy areas of ground glass attenuation
•Tx: TMP-SMX + steroids (if hypoxemic) x 21 days
•Prevention: TMP-SMX daily for CD4 < 200
tx and prevention of pneumocystis pneumonia
pneumatoceles
air-filled cysts that may form abcesses; associated with pneumocystis pneumonia
Pneumocystis jiroveci
found on silver stain