Biology 171 - Exam 3 Practice Questions
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Independent assortment of chromosomes is a result of which of the following processes?
a. The random way each pair of homologous chromosomes lines up at the metaphase plate during meiosis I.
b. The random combinations of eggs and sperm during fertilization.
c. The random distribution of the sister chromatids to the two daughter cells during anaphase II.
d. The diverse combination of alleles that may be found within any given chromosome.
a. The random way each pair of homologous chromosomes lines up at the metaphase plate during meiosis I.
During which of the following processes does independent assortment of chromosomes occur?
a. in meiosis I only
b. in meiosis II only
c. in mitosis and meiosis I
d. in mitosis and meiosis II
a. in meiosis I only
Which of the following statements describes one characteristic of each chromosome in a cell during the entire process of meiosis I?
a. Each chromosome is paired with a homologous chromosome.
b. Each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids joined by a centromere.
c. Each chromosome consists of a single strand of DNA.
d. Each chromosome is joined with its homologous pair to form a synaptonemal complex.
b. Each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids joined by a centromere.
Which of the following processes occurs in meiosis but not in mitosis?
a. chromosome replication
b. synapsis of chromosome
c. alignment of chromosomes at the metaphase plate
d. condensation of chromosomes
b. synapsis of chromosome
Which of the following processes occur during meiosis but not mitosis?
a. Haploid cells fuse to form diploid cells.
b. Haploid cells multiply into more haploid cells.
c. Diploid cells form haploid cells.
d. A diploid cell combines with a haploid cell.
c. Diploid cells form haploid cells.
Which of the following events happens at the conclusion of meiosis I?
a. Homologous chromosomes of a pair are separated from each other.
b. The chromosome number per cell remains the same.
c. Sister chromatids are separated.
d. Four daughter cells are formed.
a. Homologous chromosomes of a pair are separated from each other.
Gene S controls the sharpness of spines in a type of cactus. Cactuses with the dominant allele, S, have sharp spines, whereas homozygous recessive ss cactuses have dull spines. At the same time, a second gene, N, determines whether or not cactuses have spines. Homozygous recessive nn cactuses have no spines at all. The relationship between genes S and N is an example of _____.
a. incomplete dominance
b. epistasis
c. pleiotropy
d. codominance
b. epistasis
Radish flowers may be red, purple, or white. A cross between a red-flowered plant and a white-flowered plant yields all-pink offspring. The flower color trait in radishes is an example of which of the following inheritance patterns?
a. a multiple allelic system
b. sex linkage
c. codominance
d. incomplete dominance
d. incomplete dominance
Which of the following phenotypes is an example of polygenic inheritance?
a. pink flowers in snapdragons
b. flower color in hydrangeas
c. white and purple flower color in peas
d. skin pigmentation in humans
d. skin pigmentation in humans
Which of the following statements explains the observation that closely linked genes are typically inherited together?
a. The genes are located close together on the same chromosome.
b. The genes undergo nondisjunction in either meiosis I or meiosis II.
c. Alleles are paired together during meiosis.
d. Crossing over between identical copies can’t be detected because it regenerates the original genotype.
a. The genes are located close together on the same chromosome.
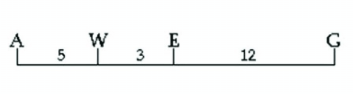
Use the following map of four genes on a chromosome to answer the question.
When collecting data from genetic crosses which gene pair is most likely to show the highest frequency of recombination?
a. A and W
b. E and G
c. A and E
d. A and G
d. A and G
Which of the following statements regarding gene linkage is correct?
a. The closer two genes are on a chromosome, the lower the probability that a crossover will occur between them.
b. The observed frequency of recombination of two genes that are far apart from each other has a maximum value of 100%.
c. Unlinked genes do not follow the law of equal segregation.
d. Linked genes are found on different chromosomes.
a. The closer two genes are on a chromosome, the lower the probability that a crossover will occur between them.
A (hypothetical. diploid organism has different genes that control wing color and wing length. A female of this species has a paternal chromosome set containing one orange-wing allele and one long-wing allele and a maternal set containing one blue-wing allele and one short-wing allele. Which of the following types of eggs would she be expected to produce after meiosis?
a. All eggs will have maternal types of gene combinations.
b. All eggs will have paternal types of gene combinations.
c. Half the eggs will have maternal and half will have paternal combinations.
d. Each egg has a one-fourth chance of having either blue long, blue short, orange long, or orange short combinations.
d. Each egg has a one-fourth chance of having either blue long, blue short, orange long, or orange short combinations.
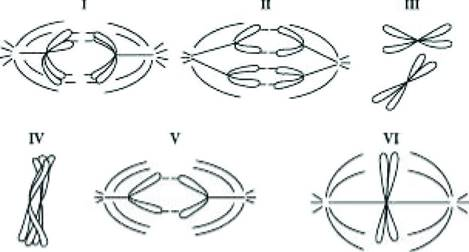
Cells from a diploid protist with n=1 are followed through mitosis and meiosis. The drawings in the figure below represent the chromosomes. Refer to the drawings and answer the following question(s).
Which diagram represents anaphase II of meiosis?
a. I
b. III
c. IV
d. V
d. V
In the case of Mendel’s pea plants where PP is a purple flowered plant and pp is a white flowered plant, P and p are:
a. different alleles for the same age
b. different genes for the same trait
c. different genotypes
d. different loci
a. different alleles for the same age
Which of the following statements correctly describes how Mendel accounted for the observation that traits had disappeared in the F1 generation and then reappeared in the F2 generation?
a. New mutations were frequently generated in the F2 progeny, causing traits that had been lost in the F1 to reappear in the F2.
b. The mechanism controlling the appearance of traits was different between the F1 and the F2 plants.
c. Traits can be dominant or recessive, and the traits were “hidden” by the dominant ones in the F1.
d. Members of the F1 generation had only one allele for each trait, but members of the F2 had two alleles for each trait.
c. Traits can be dominant or recessive, and the traits were “hidden” by the dominant ones in the F1.
Which of the following statements about the law of independent assortment is correct?
a. It describes the inheritance of different genes relative to one another.
b. It describes the inheritance of different alleles relative to one another.
c. It is the consequence of having two copies of each chromosome in somatic cells and one copy in gametes.
d. It is the reason that dominant alleles are visible in the organism’s phenotype.
a. It describes the inheritance of different genes relative to one another.
Which of the following best summarizes the law of segregation?
a. It describes the inheritance of different genes relative to one another.
b. It explains how codominant alleles each affect the phenotype in separate ways.
c. It describes the inheritance of different chromosomes relative to one another.
d. It describes situations where either genotype or environment affect phenotype, but not both.
c. It describes the inheritance of different chromosomes relative to one another.
A particular organism has 46 chromosomes in its karyotype. Which of the following statements is correct regarding this organism?
a. It must be human.
b. It must be an animal.
c. It reproduces asexually.
d. It produces gametes with 23 chromosomes.
d. It produces gametes with 23 chromosomes.
Which of the following processes best describes the mechanism of gamete production in plants?
a. sporophytes produce gametes by meiosis
b. gametophytes produce gametes by mitosis
c. gametophytes produce gametes by meiosis
d. sporophytes produce gametes by mitosis
b. gametophytes produce gametes by mitosis
Which of the following statements about reproduction is correct?
a. Asexual reproduction, but not sexual reproduction, is characteristic of only plants and fungi.
b. In sexual reproduction, individuals transmit half of their nuclear genes to each of their offspring.
c. In asexual reproduction, offspring are produced by fertilization without meiosis.
d. Asexual reproduction produces only haploid offspring.
b. In sexual reproduction, individuals transmit half of their nuclear genes to each of their offspring.
Which of the following individuals will inherit an X-linked allele from a male parent who carries the allele?
a. all of his daughters
b. half of his daughers
c. all of his sons
d. all of his children
a. all of his daughters
Which of the following events results in X-inactivation in female mammals?
a. Activation of the XISTI gene on the X chromosome that will become the Barr body.
b. Activation of the BARR gene on one X chromosome, which then becomes inactive.
c. Inactivation of the XIST gene on the X chromosome derived from the male parent.
d. Attachment of methyl (-CH3) groups to the X chromosome that will remain active.
a. Activation of the XISTI gene on the X chromosome that will become the Barr body.
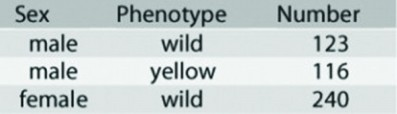
In a Drosophila experiment a homozygous wild-type female was crossed with a yellow-bodied male. All of the resulting F1 flies were phenotypically wild type. Crossing the F1 flies resulted in F2 flies having the characteristics shown in the figure. Which of the following statements best describes the location of the yellow body locus?
a. It is on an autosome.
b. It is X-linked.
c. It is inherited by X inactivation.
d. It is Y-linked.
b. It is X-linked.
In cats, an X-linked locus is responsible for fur color. There are two known alleles at this locus. One results in black fur color; the other results in orange fur color. A heterozygote animal has patches of orange and black fur (tortoiseshell). Which coat color phenotypes are expected from the cross of a black female and an orange male?
a. tortoiseshell females; tortoiseshell males
b. black females; orange males
c. tortoiseshell females; black males
d. orange females; black males
c. tortoiseshell females; black males
Male sex determination in mammals is in large part due to the SRY gene found on the Y chromosome. Which of the following scenarios will result in a person with an XX karyotype developing a male phenotype?
a. the loss of the SRY gene from an autosome during gamete formation
b. translocation (the moving) of SRY to an X chromosome during gamete formation
c. the presence of an extra autosomal chromosome after fertilization
d. nondisjunction of the X chromosome during meiosis
If cell Q enters meiosis, and nondisjunction of one chromosome occurs in one of its daughter cells during meiosis II, how will this affect the gametes at the completion of meiosis?
a. All the gametes descended from cell Q wll be diploid.
b. Half of the gametes descended from cell Q will be n+1, and half will be n-1.
c. One-quarter of the gametes descended from cell Q will be n+1, one-quarter will be n-1, and half will be n.
d. Two of the four gametes descended from cell Q will be haploid, and two will be diploid.
c. One-quarter of the gametes descended from cell Q will be n+1, one-quarter will be n-1, and half will be n.
Which of the following statements correctly describes what happens to a chromosome after a nonreciprocal translocation?
a. A Philadelphia chromosome is generated.
b. A duplication of part of the chromosome occurs.
c. Nondisjunction of pairs of homologous occurs.
d. A chromosome transfers a fragment but receives none in return.
d. A chromosome transfers a fragment but receives none in return.
Which of the following correctly describes a Philadelphia chromosome?
a. A human chromosome 22 that has had a specific translocation from chromosome 9.
b. A human chromosome 9 that is found only many types of cancer.
c. A chromosome found only in mitochondria.
d. A chromosome with a point mutation that increases cell division.
a. A human chromosome 22 that has had a specific translocation from chromosome 9.
Amber body color in fruit flies (B. is dominant to black body color (b.. Red eyes (R. are dominant to pink eyes (r.. What fraction of the progeny of crosses BbRr × BBrr will be expected to have amber bodies and pink eyes?
a. 3/16
b. 9/16
c. ½
d. all of them
c. ½
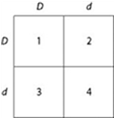
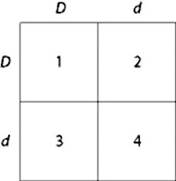
In a particular plant, leaf color is controlled by gene locus D. Plants with at least one allele D have dark green leaves, and plants with the homozygous recessive dd genotype have light green leaves. A true-breeding, dark-leaved plant is crossed with a light-leaved one, and the F1 offspring is allowed to self-pollinate. The predicted outcome of the F2 is diagrammed in the Punnett square shown in the figure, where 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the genotypes corresponding to each box within the square. Which of the boxes marked 1-4 correspond to plants with dark leaves?
a. 1 only
b. 2 and 3
c. 4 only
d. 1, 2, and 3
d. 1, 2, and 3
Use the figure to answer the question:
In a bird throat color is controlled by gene locus D. Birds with at least one allele D have dark brown throats, and birds with the homozygous recessive dd genotype have red throats. A true-breeding, dark-throated bird is crossed with a red-throated one, and the F1 offspring are mated. The predicted outcome of the F1 cross is diagrammed in the Punnett square shown in the figure, where 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the genotypes corresponding to each box within the square.
a. 1 only
b. 4 only
c. 1, 2, and 3
d. 2, 3, and 4
Black fur in mice (B. is dominant to brown fur (b.. Short tails (T. are dominant to long tails (t.. What fraction of the progeny of crosses BbTt × BBtt will be expected to have black fur and long tails?
a. 1/16
b. 3/8
c. ½
d. 9/16
c. ½
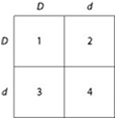
Use the figure and the following description to answer the question. Which of the boxes marked 1-4 correspond to plants that will be true-breeding?
a. 1 and 4 only
b. 2 and 3 only
c. 1, 2, 3, and 4
d. 1 only
a. 1 and 4 only
When Thomas Hunt Morgan crossed red-eyed F1 generation flies to each other, the F2 generation included both red- and white-eyed flies, but all the white-eyed flies were male. Which of these best explains Morgan's result?
a. The gene involved is located on the Y chromosome.
b. The gene involved is located on the X chromosome.
c. The gene involved is located on an autosome, but only in males.
d. Other male-specific factors influence eye color in flies.
b. The gene involved is located on the X chromosome.
Red-green color blindness is an X-linked recessive trait in humans. Two people with normal color vision have a son with colorblindness. Given this information, the genotypes of the parents are ________.
X^XNn and X^NY
A recessive allele on the X chromosome is responsible for red-green color blindness in humans. A woman with normal vision whose father is color blind has children with a color-blind male. What is the probability that this couple's first son will be color blind?
½
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PD) is inherited as an X-linked recessive allele in humans. A woman whose father had G6PD is planning a family with a man who has no history of the disease. What proportion of their sons are expected to have the disease?
a. 100%
b. ¼
c. ½
d. 0
c. ½
In cats, an X-linked locus is responsible for fur color. There are two known alleles at this locus. One results in black fur color; the other results in orange fur color. A heterozygote animal has patches of orange and black fur (tortoiseshell). Which of the following explains the patches of color in female heterozygote cats?
a. Incomplete dominance of the black fur color allele.
b. Fur color is codominant at the organism level.
c. Imprinting at the fur color locus.
d. Random X inactivation affects fur color.
d. Random X inactivation affects fur color.
Which of the following inheritance patterns describes the ability of a single allele to have multiple phenotypic effects?
a. incomplete dominance
b. multiple alleles
c. pleiotropy
d. epistasis
c. pleiotropy
Mendal studied characters that could be classified on an either-or basis, such as purple versus white flower color. But many characters, such as human skin color and height are not one of two discrete characters. This is referred to as…
a. Variation
b. Pedigree analysis
c. Polygenic inheritance
d. Incomplete dominance
c. Polygenic inheritance
Many diploid organisms produce haploid gametes for reproduction. Which of the following best describes how the diploid number of chromosomes is restored in the offspring of these organisms?
a. DNA replication creates homologous chromosomes.’
b. Independent assortment in meiosis allows random combinations of chromosomes.
c. Synapsis during prophase of meiosis I creates random combinations of alleles.
d. Fertilization combines chromosomes from each parent into resulting zygote.
d. Fertilization combines chromosomes from each parent into resulting zygote.
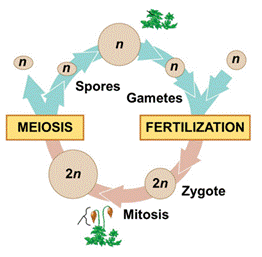
Referring to a plant sexual life cycle (picture to the right), which of the following terms describes the process that leads directly to the formation of gametes?
a. Spore meiosis
b. Spore mitosis
c. Zygote meiosis
d. Gamete mitosis
e. Alternation of generations
d. Gamete mitosis
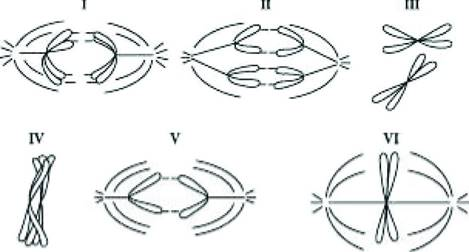
Cells from a diploid protist with n=1 are followed through mitosis and meiosis. The drawings in the figure below represent the chromosomes. Refer to the drawings and answer the following question(s)…
Which diagram represents anaphase I of meiosis?
I
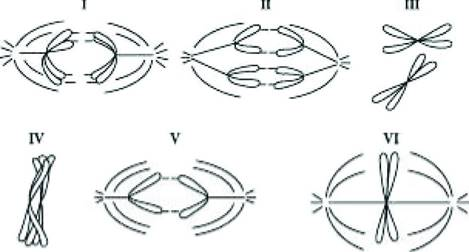
Cells from a diploid protist with n=1 are followed through mitosis and meiosis. The drawings in the figure below represent the chromosomes. Refer to the drawings and answer the following question(s)…
Which diagram represents metaphase of mitosis?
VI
How do cells at the completion of meiosis compare with cells that are in prophase of meiosis I?
a. The cells have half the number of chromosomes and half the amount of DNA.
b. The cells have the same number of chromosomes and half the amount of DNA.
c. The cells have half the number of chromosomes and one-fourth the amount of DNA.
d. The cells have half the amount of cytoplasm and twice the amount of DNA.
c. The cells have half the number of chromosomes and one-fourth the amount of DNA.
Which of the following processes has just occurred when chiasmata can first be viewed under a microscope?
a. meiosis II
b. anaphase II
c. prophase I
d. the separation of homologs
c. prophase I
Which of the following statements describes a major difference between meiosis II and mitosis in a diploid animal?
a. Homologous chromosomes align on the metaphase plate in meiosis II but not in mitosis.
b. Sister chromatids separate in mitosis, and homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis II.
c. Meiosis II occurs in a haploid cell, while mitosis occurs in diploid cells.
d. Crossing over of chromosomes take place in meiosis II but not in mitosis.
c. Meiosis II occurs in a haploid cell, while mitosis occurs in diploid cells.
A couple has a child with Down syndrome. Which of the following is the most probable cause of the child's condition?
a. The man’s family has a predisposition for Down syndrome.
b. The woman’s genome has a chromosomal duplication.
c. One member of the couple underwent nondisjunction in somatic cell production.
d. One member of the couple underwent nondisjunction during meiosis.
d. One member of the couple underwent nondisjunction during meiosis.
The chromosomal alteration that results from a chromosome fragment joined to a nonhomologous chromosome is called a ________.
a. deletion
b. inversion
c. translocation
d. duplication
c. translocation
Which of the following pairs of processes make the greatest contribution to genetic diversity between generations of a diploid insect?
a. random fertilization and cytokinesis
b. alternation of generations and crossing over
c. independent assortment and random fertilization
d. gametophyte fusion and mitotic division
c. independent assortment and random fertilization
Which of the following results when homologous chromosomes cross over in meiosis?
a. Two sister chromatids get tangled, resulting in one re-sequencing its DNA.
b. Two sister chromatids exchange identical pieces of DNA.
c. Corresponding segments of non-sister chromatids are exchanged.
d. DNA repair machinery alters maternal alleles, so they match paternal ones.
c. Corresponding segments of non-sister chromatids are exchanged.
Why did all of the F1 offspring of Mendel's classic pea cross always look like one of the two parental varieties?
a. No genes interacted to produce the parental phenotype.
b. Each allele affected phenotype expression.
c. The traits blended together during fertilization.
d. One allele was dominant.
d. One allele was dominant.
Which of the following statements is correct in describing the terms monohybrid cross and dihybrid cross?
a. A monohybrid cross involves a single parent, whereas a dihybrid cross involves two parents.
b. A dihybrid cross involves organisms that are heterozygous for two characters that are being studied, and s monohybrid cross involves organisms that are heterozygous for only one character being studied.
c. A monohybrid cross is performed for one generation, whereas a dihybrid cross is performed for two generations.
d. A monohybrid cross results in a 9:3;3;1 ratio, whereas a dihybrid cross gives a 3:1 ratio.
b. A dihybrid cross involves organisms that are heterozygous for two characters that are being studied, and s monohybrid cross involves organisms that are heterozygous for only one character being studied.
In the case of flower color in pea plants, PP and Pp have the same ___________ but different __________.
a. phenotypes, characters
b. genotypes, phenotypes
c. characters, phenotypes
d. phenotypes, genotypes
d. phenotypes, genotypes
Which of the following sentences state a significant conclusion that Gregor Mendel drew from his experiments with pea plants?
a. There is no considerable genetic variation in garden peas.
b. Traits are inherited in discrete units and are not the result of “blending”.
c. Recessive genes occur more frequently in the F1 generation than do dominant ones.
d. Genes are composed of DNA.
b. Traits are inherited in discrete units and are not the result of “blending”.
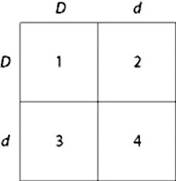
Use the figure to answer the question:
In a bird throat color is controlled by gene locus D. Birds with at least one allele D have dark brown throats, and birds with the homozygous recessive dd genotype have red throats. A true-breeding, dark-throated bird is crossed with a red-throated one, and the F1 offspring are mated. The predicted outcome of the F1 cross is diagrammed in the Punnett square shown in the figure, where 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the genotypes corresponding to each box within the square.
Which of the boxes marked 1-4 correspond to birds that will be true-breeding?
a. 1 and 4 only
b. 2 and 3 only
c. 1, 2, 3, and 4
d. 1 only
a. 1 and 4 only
In a plant, green seed color is dominant to red. If two plants with green seeds were crossed and resulted in 424 green and 0 red seed plants, which of these was the most probable genotype of each parent?
Gg x Gg
Gray seed color in peas is dominant to white. Assume that Mendel conducted a series of experiments where plants with gray seeds were crossed among themselves, and the following progeny were produced: 302 gray and 98 white. What is the most probable genotype of each parent?
a. GG x gg
b. Gg x Gg
c. GG x Gf
d. gg x Gg
b. Gg x Gg
Which of the following phrases correctly defines one genetic map unit?
a. the physical distance between any two linked genes
b. the physical distance between two genes that results in 1% frequency of recombination.
c. one nanometer of distance between two genes
d. the recombination freuqncy between two independently assorting genes.
b. the physical distance between two genes that results in 1% frequency of recombination.
What is the greatest benefit of using a testcross to determine an unknown genotype?
a. The homozygous recessive parent is obvious to the naked eye.
b. The homozygous parent is the only one whose crossovers make a difference.
c. A progeny’s phenotype reflects the contribution from the heterozygous parent.
d. All of the progeny will be heterozygous.
c. A progeny’s phenotype reflects the contribution from the heterozygous parent.
Which of the following reasons explains why map units on a chromosome linkage map are not reliable measures of physical distances?
a. The frequency of crossing over varies along the length of chromosome.
b. The relationship between recombination frequency and map units is different in every individual.
c. Physical distances between genes change during the course of the cell cycle.
d. The gene order on the chromosomes is slightly different in every individual.
a. The frequency of crossing over varies along the length of chromosome.
A testcross performed with F1 dihybrid flies results in more parental-type offspring than recombinant-type offspring. Which of the following statements best explains this result?
a. The two genes are linked on the same chromosome.
b. The two genes are linked but on different chromosomes.
c. Recombination did not occur in the cell during meiosis.
d. Both of the characters are controlled by more than one gene.
a. The two genes are linked on the same chromosome.
Which of the following statements describes an example of alternation of generations?
a. A grandparent and grandchild each have dark hair, but the parent has blond hair.
b. A diploid plant (sporophyte) produces a spore by meiosis that gives rise to a multicellular, haploid pollen grain (gametophyte).
c. A diploid animal produces gametes by meiosis, and the gametes undergo fertilization to produce a diploid zygote.
d. A haploid plant produces gametes by meiosis and the gametes fuse to produce a new plant.
b. A diploid plant (sporophyte) produces a spore by meiosis that gives rise to a multicellular, haploid pollen grain (gametophyte).
Which of the following statements is true of a species that has a chromosome number of 2n = 16?
a. The species is diploid and has 32 chromosomes per cell.
b. The species has 16 sets of chromosomes per cell.
c. Each diploid cell has eight homologous pairs of chromosomes.
d. A gamete from this species has four chromosomes.
c. Each diploid cell has eight homologous pairs of chromosomes.
A (hypothetical. diploid organism has different genes that control wing length and wing color.
A female of this species with short blue-colored wings has a chromosome pair with two short-wing alleles and a second chromosome pair with one blue-wing allele and one orange-wing allele. The eggs from this individual will have which of the following combinations of alleles?
a. all of the eggs will have alleles for short blue-colored wings.
b. all of the eggs will have alleles for short orange-colored wings.
c. 1/2 of the eggs will have alleles for short blue-colored wings and ½ will have alleles for short orange-colored wings.
d. 3/4 of the eggs have alleles for short blue-colored wings and ¼ of the eggs have alleles for short orange-colored wings.
c. 1/2 of the eggs will have alleles for short blue-colored wings and ½ will have alleles for short orange-colored wings.
Which of the following statements correctly describes the chromosome theory of inheritance as it was understood in the early 20th century?
a. Individuals inherit particular chromosomes attached to genes.
b. Mendelian genes are at specific loci on the chromosome and, in turn, segregate during meiosis.
c. No more than a single pair of chromosomes can be found in a healthy normal cell.
d. Natural selection acts on certain chromosome combinations rather than on genes.
b. Mendelian genes are at specific loci on the chromosome and, in turn, segregate during meiosis.
Why did all of the F1 offspring of Mendel's purple and white flowered pea cross always look like one of the two parental varieties?
a. No genes interacted to produce a new unique phenotype.
b. Each allele affected phenotypic expression.
c. The traits blended together during fertilization.
d. One allele was dominant.
d. One allele was dominant.
Amber body color in fruit flies (B. is dominant to black body color (b.. Red eyes (R. are dominant to pink eyes (r.. What fraction of the progeny of crosses BbRr × BBrr will be expected to have amber bodies and pink eyes?
a. 3/16
b. 9/16
c. ½
d. all of them
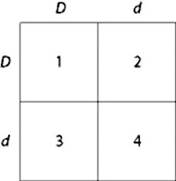
Use the figure to answer the question:
In a bird throat color is controlled by gene locus D. Birds with at least one allele D have dark brown throats, and birds with the homozygous recessive dd genotype have red throats. A true-breeding, dark-throated bird is crossed with a red-throated one, and the F1 offspring are mated. The predicted outcome of the F1 cross is diagrammed in the Punnett square shown in the figure, where 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the genotypes corresponding to each box within the square.
Which of the boxes marked 1 - 4 correspond to birds with dark brown throats?
a. 1 only
b. 4 only
c. 1,2, and 3
d. 2, 3, and 4
Pea plants produce either purple or white flowers with purple showing complete dominance. A gardener was given plants with purple flowers. Which of the following types of crosses would best allow her to determine the genotype of her plant in one generation?
a. A monohybrid cross
b. A dihybrid cross
c. A testcross
d. Self-pollination
c. A testcross
Amber body color in fruit flies (B. is dominant to black body color (b.. Red eyes (R. are dominant to pink eyes (r.. What fraction of the progeny of crosses bbRR × BBRr will be expected to have amber bodies and red eyes?
a. all of them
b. 3/16
c. ½
d. 9/16
For the following question, match the key event of meiosis with the stages listed below.
I. Prophase I V. Prophase II
II. Metaphase I VI. Metaphase II
III. Anaphase I VII. Anaphase II
IV. Telophase I VIII. Telophase II
Cohesins at centromeres of sister chromatids breakdown.
a. III
b. IV
c. V
d. VII
d. VII
For the following question, match the key event of meiosis with the stages listed below.
I. Prophase I V. Prophase II
II. Metaphase I VI. Metaphase II
III. Anaphase I VII. Anaphase II
IV. Telophase I VIII. Telophase II
Haploid cells form containing joined sister chromatids.
a. III
b. IV
c. VII
d. VIII
During which of the following processes do homologous pairs of chromosomes align adjacent to one another at the metaphase plate of a cell?
a. metaphase of mitosis
b. metaphase I of meiosis
c. telophase II of meiosis
d. metaphase II of meiosis
b. metaphase I of meiosis
During which of the following phases of meiosis do centromeres split and sister chromatids migrate to opposite poles of the cell?
a. anaphase I
b. telophase I
c. anaphase II
d. telophase II
c. anaphase II
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a serious condition caused by a recessive allele of a gene on the human X chromosome. The patients' muscles weaken over time because they have a lack or decreased levels of dystrophin, a muscle protein. Which of the following correctly predicts the probability of muscular dystrophy in female children?
a. Females can never have this condition.
b. One-fourth of the daughters of an affected man would have this condition.
c. One-half of the daughters of an affected man and a carrier woman would have this condition.
d. One-half of the daughters of an unaffected man and a carrier woman would have this condition.
c. One-half of the daughters of an affected man and a carrier woman would have this condition.
Males are more often affected by X-linked traits than are females because ________.
a. Imprinting is more likely to occur on X chromosomes inherited from the mother than on Y chromosomes inherited from the father.
b. X inactivation occurring in male effectively shuts down expression of any X chromosome genes.
c. X chromosomes in males generally have more mutations than X chromosomes in females.
d. Males are hemizygous genes on the X chromosomes.
d. Males are hemizygous genes on the X chromosomes.
In cats, an X-linked locus is responsible for fur color. There are two known alleles at this locus. One results in black fur color; the other results in orange color. A heterozygote animal has patches of orange and black fur (tortoiseshell). Which of the following outcomes represents all of the possible offspring from the cross provided. Assume all cats have two sex chromosomes.
| Cross | Female offspring | Male offspring |
A | black female x orange male | tortoiseshell | tortoiseshell |
B | orange female x black male | tortoiseshell | black |
C | tortoiseshell female x orange male | black or orange | black or orange |
D | tortoiseshell female x black male | black or tortoiseshell | black or orange |
A
B
C
D
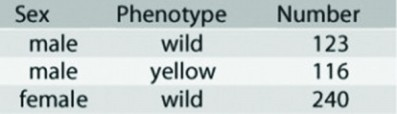
Use the following information to answer the question:
In a Drosophila experiment a homozygous wild-type female was crossed with a yellow-bodied male. All of the resulting F1 flies were phenotypically wild type. Crossing the F1 flies resulted in F2 flies having the characteristics shown in the figure. Which of the following statements best describes the location of the yellow body locus?
a. It is on an autosome.
b. It is X-linked.
c. It is inherited by X activation.
d. It is Y-linked.
b. It is X-linked.
A testcross performed with F1 dihybrid flies results in more parental-type offspring than recombinant-type offspring. Which of the following statements best explains this result?
a. Recombination did not occur in the cell during meiosis.
b. Both of the characters are controlled by more than one gene.
c. The two genes are linked on the same chromosome.
d. The two genes are linked but on different chromosomes.
c. The two genes are linked on the same chromosome.
Why did all of the F1 offspring of Mendel's purple and white flowered pea cross always look like one of the two parental varieties?
a. No genes interacted to produce a new unique phenotype.
b. Each allele affected phenotypic expression.
c. The traits blended together during fertilization.
d. One allele was dominant.
d. One allele was dominant.
Amber body color in fruit flies (B. is dominant to black body color (b.. Red eyes (R. are dominant to pink eyes (r.. What fraction of the progeny of crosses BbRr × BBrr will be expected to have amber bodies and pink eyes?
a. 3/16
b. 9/16
c. ½
d. all of them
c. ½
Which of the following statements describes a major difference between mitosis and meiosis I in a diploid organism?
a. Only meiosis I results in daughter cells that contain identical genetic information.
b. Sister chromatids separate in mitosis, while homologous pairs of chromosomes separate in meiosis I.
c. DNA replication takes place prior to mitosis, but not before meiosis I.
c. Sister chromatids separate in mitosis, while homologous pairs of chromosomes separate in meiosis II.
b. Sister chromatids separate in mitosis, while homologous pairs of chromosomes separate in meiosis I.
In birds, sex is determined by ZW chromosome inheritance. Males are ZZ and females are ZW. Within pigeon populations there is a recessive, Z-linked allele that is lethal in embryos. What is the expected sex ratio in the offspring of a cross between a male that is heterozygous for the lethal allele and a wildtype female?
2:1
A homozygous tomato plant with red fruit and yellow flowers was crossed with a homozygous tomato plant with golden fruit and white flowers. The F1 had red fruit and yellow flowers. F1 plants were testcrossed (crossing them to homozygous recessive individuals), and the following offspring were obtained:
Red fruit and yellow flowers–41
Red fruit and white flowers–7
Golden fruit and yellow flowers–8
Golden fruit and white flowers–44
15
Asexual reproduction occurs during which of the following processes?
a. meiosis
b. mitosis
c. fertilization
d. the exchange of chromosomes between organisms of different species
b. mitosis
Two different species of protists living in a tide pool. Species A reproduces both sexually and asexually, and Species B reproduce only asexually. The pool gradually becomes infested with disease-causing viruses. Which species are more likely to survive in the changing environment?
specis A
If a pair of homologous chromosomes fails to separate during meiosis I, select the choice that shows the chromosome number of the four resulting gametes with respect to the normal haploid number (n)?
a. n + 1; n + 1; n; n
b. n - 1; n - 1; n; n
c. n + 1; n - 1; n; n
d. n + 1; n + 1; n - 1; n - 1
e. n + 1; n - 1; n - 1; n - 1
d. n + 1; n + 1; n - 1; n - 1
A phenotypically normal couple seeks genetic counseling because the man's karyotype showed that his chromosomes had a reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 4 and 12. Because the translocation is reciprocal there was no genetic information lost and he is healthy; however, he and his wife want to know the probability that his sperm cells will be abnormal. Which fraction of his sperm cells is predicted to carry at least one chromosome with a translocation?
Which of the following statements best describes homologous chromosomes?
carry for same GENE
Somatic cells of roundworms have four individual chromosomes per cell. How many chromosomes would you expect to find in an ovum from a roundworm?
two
Which of the following statements correctly describes a karyotype?
organized image
Which of the following statements is correct regarding the human X chromosomes?
A) It is present in every somatic cell of males and females.
B) It is the same size as other chromosomes and has the same number of genes.
C) It carries genes that determine an individual's biological sex.
D) It is referred to as an autosome.
C) It carries genes that determine an individual's biological sex.
Which of the following statements describes the most likely result of a defect in meiosis that results in the failure of spindle microtubules to bind some kinetochores?
New microtubules with more effective binding capabilities to kinetochores will be synthesized to compensate for the defect.
Excessive cell divisions will occur resulting an increase in the chromosome number known as polyploidy.
The defect will be bypassed in order to ensure normal chromosome distribution in the new cells.
The resulting cells will not receive the correct number of chromosomes in the gametes, a condition known as aneuploidy.
The resulting cells will not receive the correct number of chromosomes in the gametes, a condition known as aneuploidy. |
Abnormal chromosomes are frequently found in malignant tumors. Errors such as translocations may place a gene in close proximity to different control regions that could result in which of the following events?
inappropriate
In Drosophila melanogaster, wing-size and body-color genes are linked. Vestigial wings and black body color are both recessive traits. A researcher crossed black-bodied, normal-winged females and gray-bodied, vestigial-winged males. The F1 were all gray bodied, normal winged. A test cross was performed with F1 females. The researcher calculated a map distance of 17 map units. Which of the following information is correct about the testcross progeny?
black-bodied, normal-winged flies plus gray-bodied, vestigial-winged flies = 17% of the total
If the parent or offspring genotypes or phenotypes are known, the pattern of inheritance can be predicted. Two organisms, with genotypes BbDD and BBDd, are mated. Assuming independent assortment of the two loci, which of the following ge…
✓ 1BBDD: 1 BbDD: 1 BBDd: 1 BbDd
During which of the following phases of meiosis do homologous chromosomes separate?
anaphase I
Quaking aspen trees usually reproduce by extending underground stems that then push aboveground and grow into trees. Sexual reproduction is not as common, but when it does happen, the haploid gametes have 19 chromosomes. How many chromosomes are in the cells of the underground stems?
38