🫀UNIT 1 BIO 3U: BODY SYSTEMS
1/139
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
140 Terms
What is the heart made of?
Muscle (myocardium)
What is the sheath SURROUNDING the heart called?
Pericardium
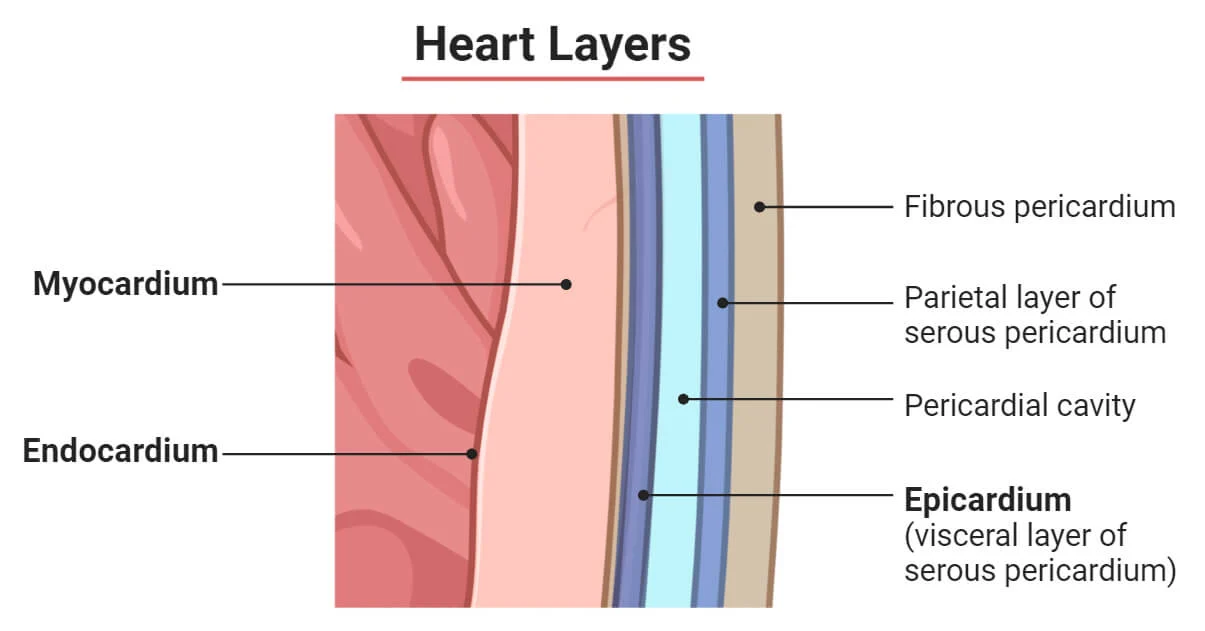
What is the INSIDE LINING of the heart’s chambers called?
The endocardium.
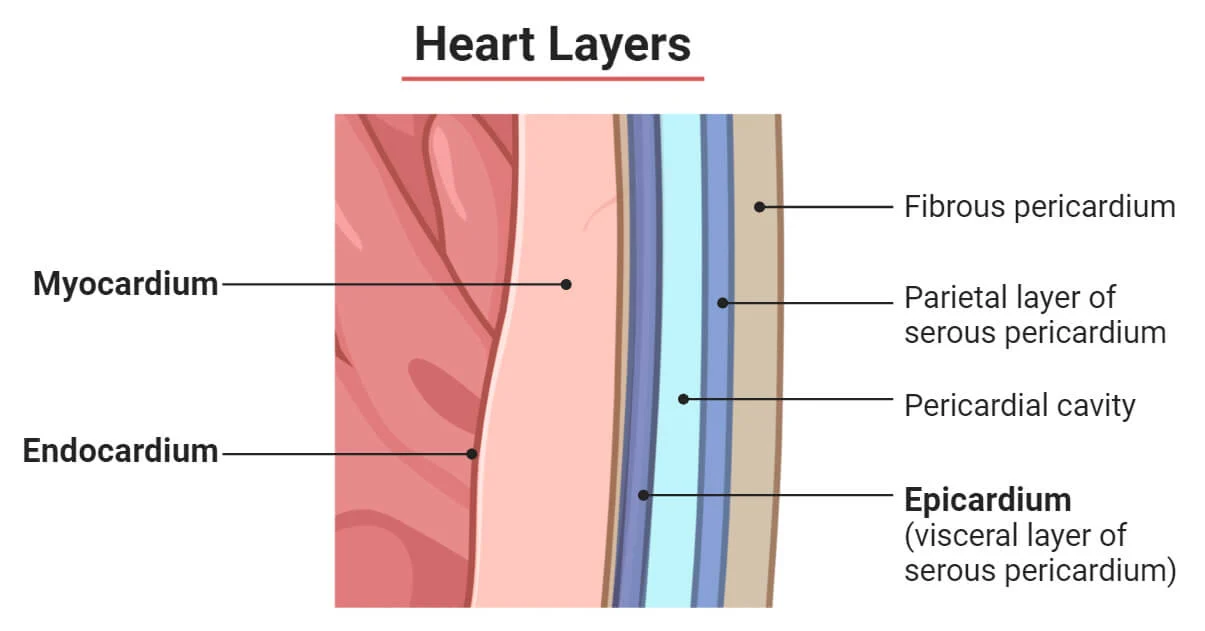
What are the ATRIA?
Chambers where blood is RECIEVED.
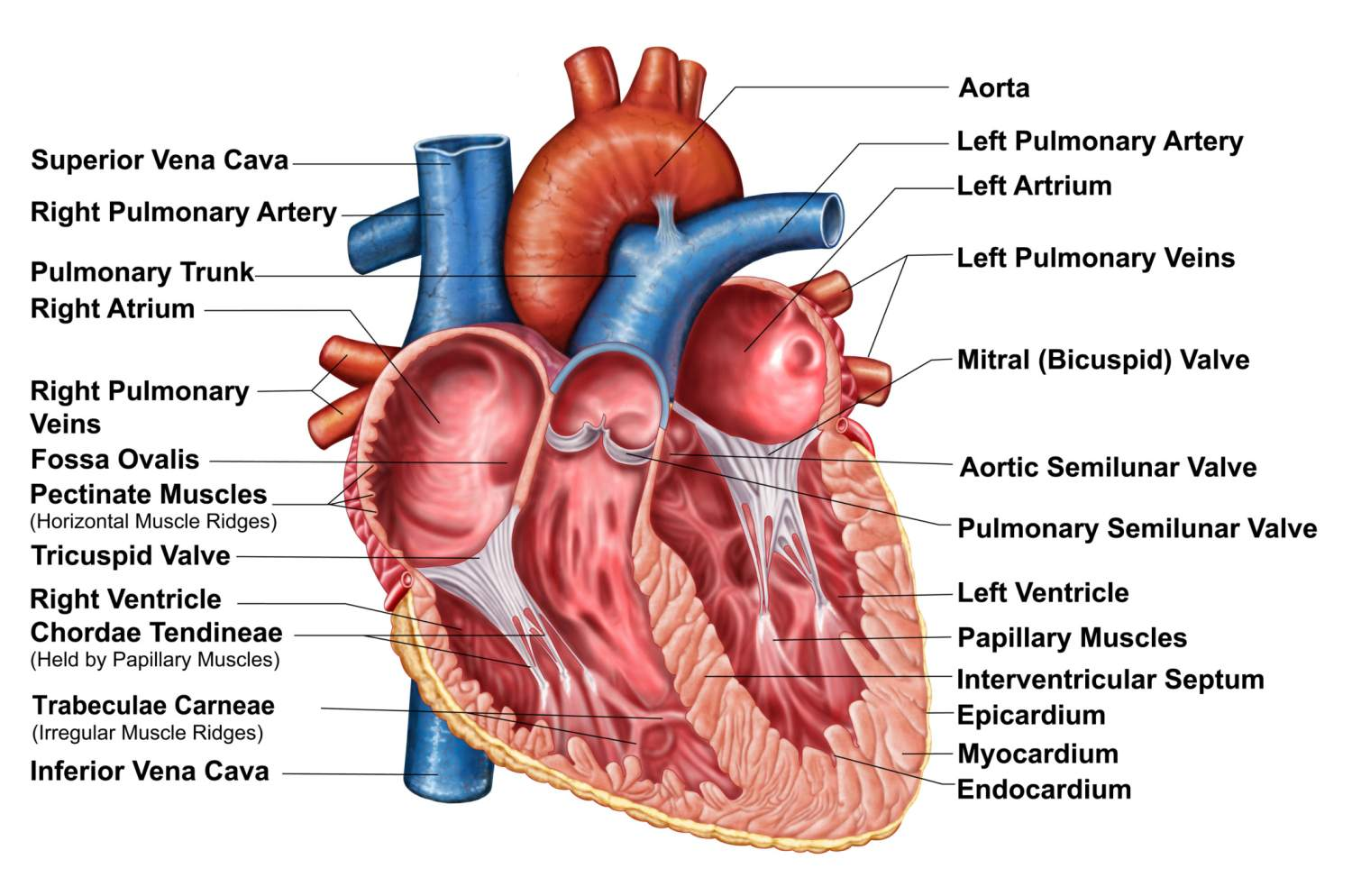
What are the VENTRICLES?
Chambers where blood is PUMPED.
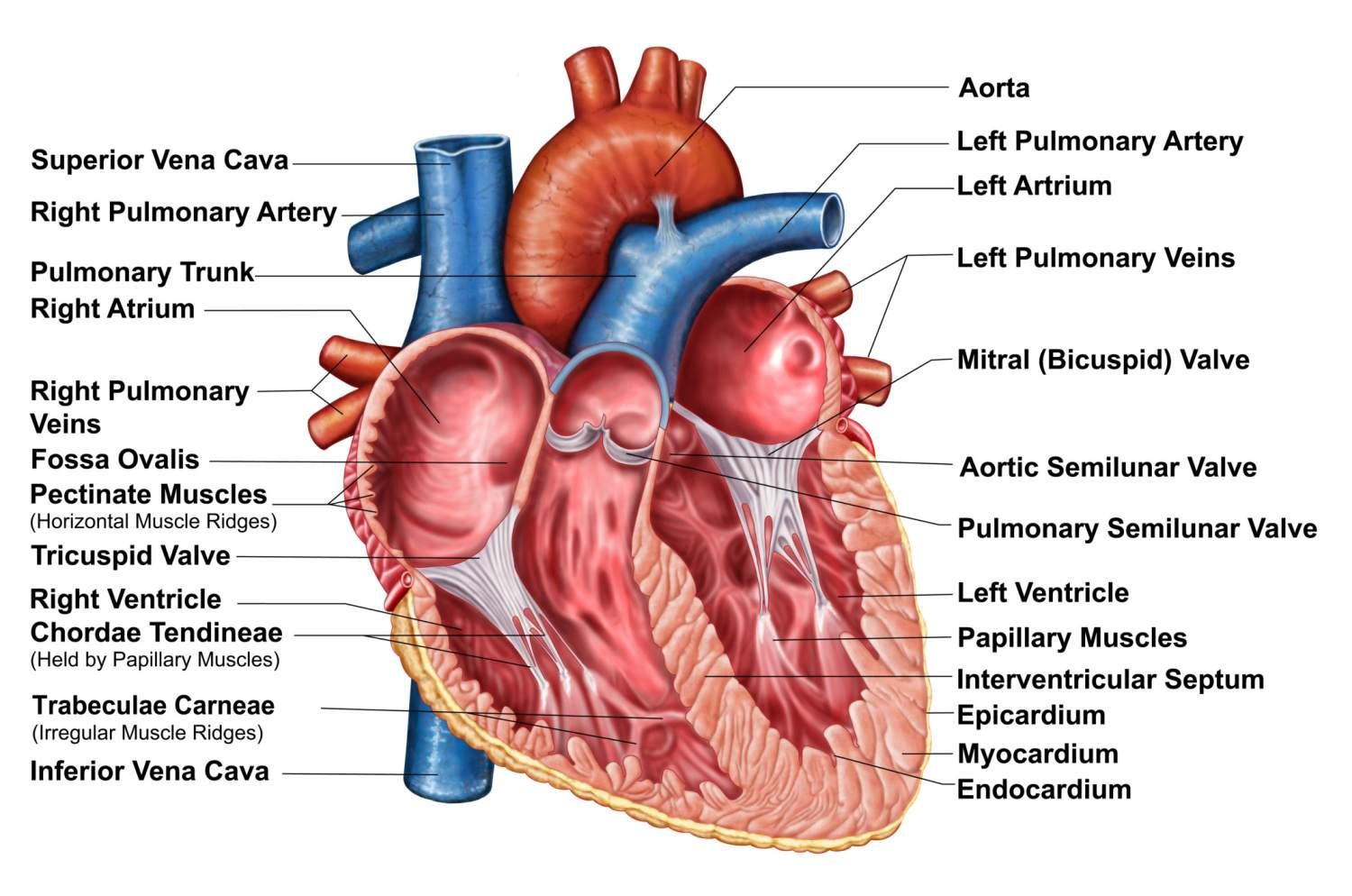
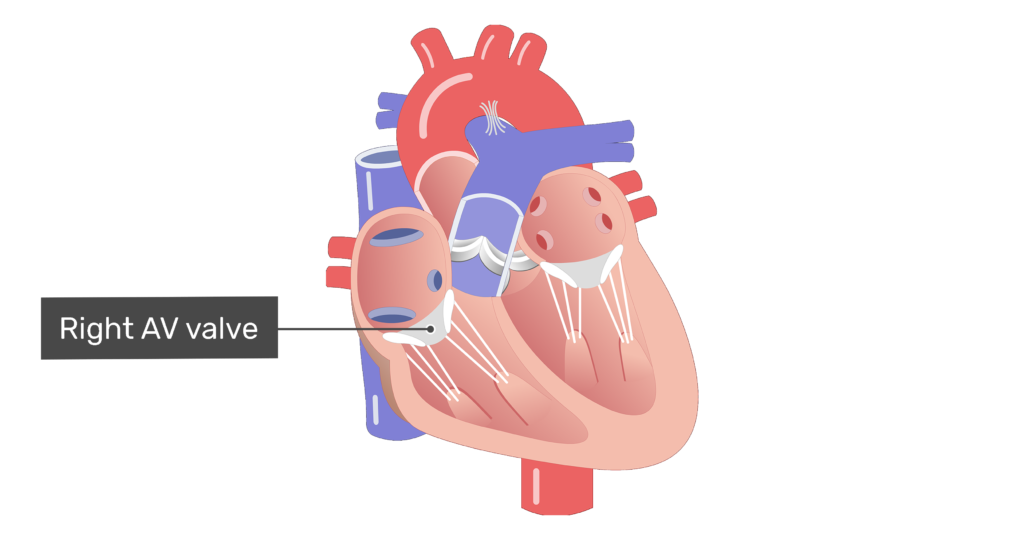
How are the atria and ventricles separated?
A-V valves.
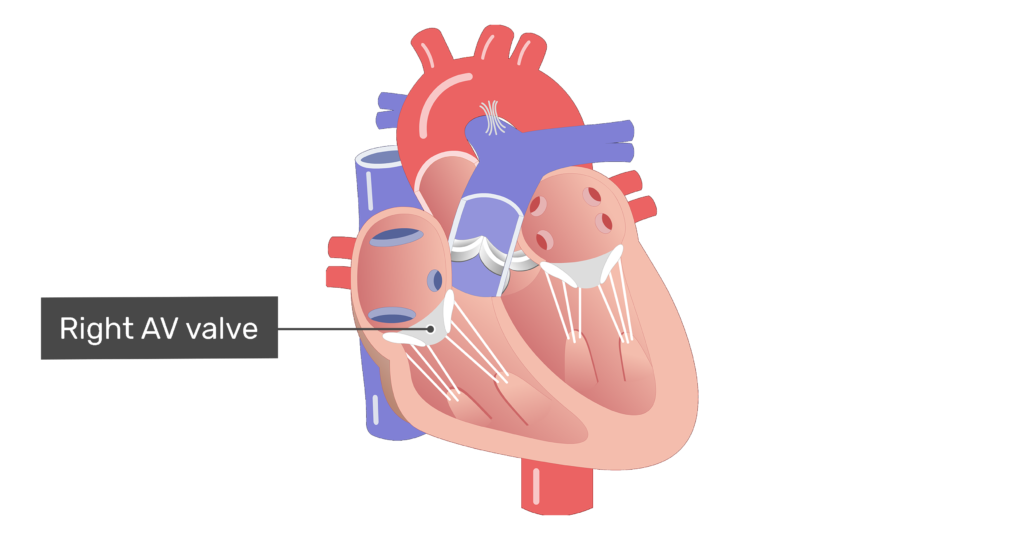
What separates the left and right sides of the heart?
The septum.
What are the four main functions of the circulatory system?
Transportation of O2 and CO2
Distribution of nutrients and transporting wastes
Maintenance of body temperature
Circulation of hormones
What are the three primary cycles of the circulatory system?
Cardiac circuit (Route taken by blood within the heart)
Pulmonary circuit (Heart to lungs and back)
Systemic circuit (Heart to rest of body)
What is systole?
State of the heart when it is beating.
What is diastole?
State of the heart in between beats.
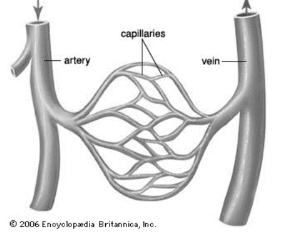
What blood vessels carry blood AWAY from the heart(ventricle)?
Arteries and arterioles
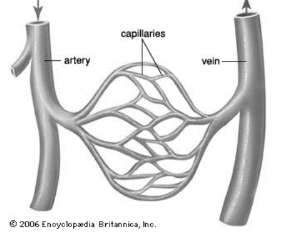
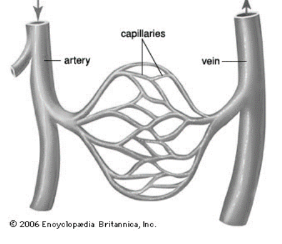
What blood vessels carry blood TOWARDS the heart (atria)?
Veins and verules.
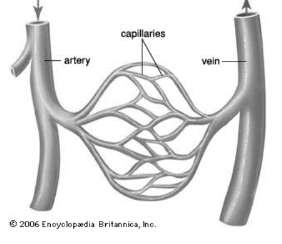
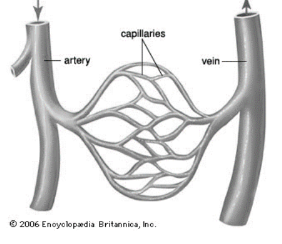
Which blood vessels exchange substances such as gasses with cells?
Capillaries.
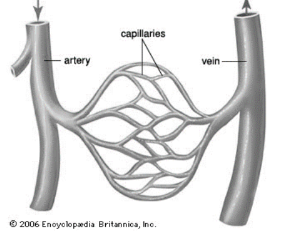
Do arteries or veins have more pressure? Why?
Arteries. Because they are going away from the heart, more pressure needs to be exerted for the blood to go where it needs to go.
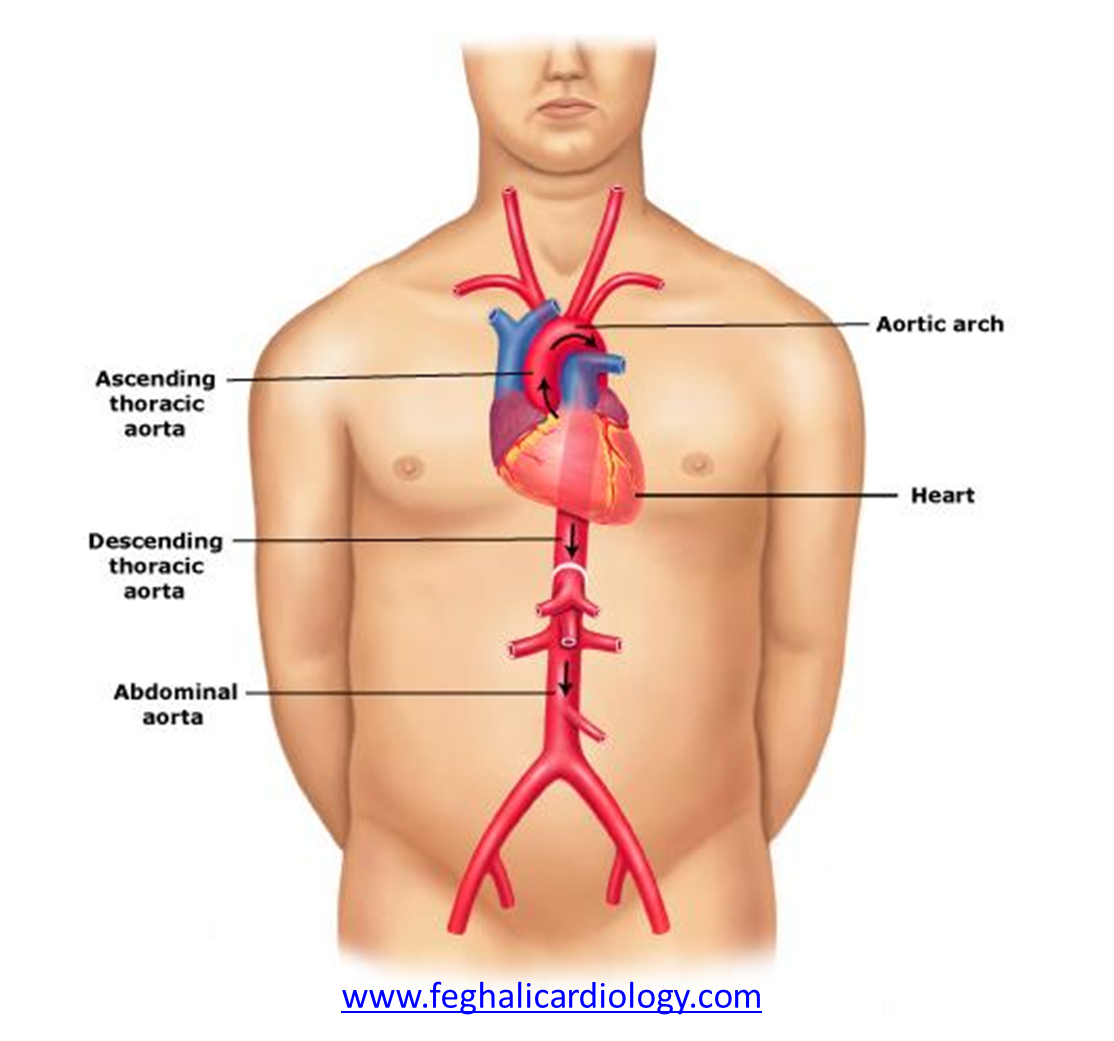
What is the largest artery?
The aorta.
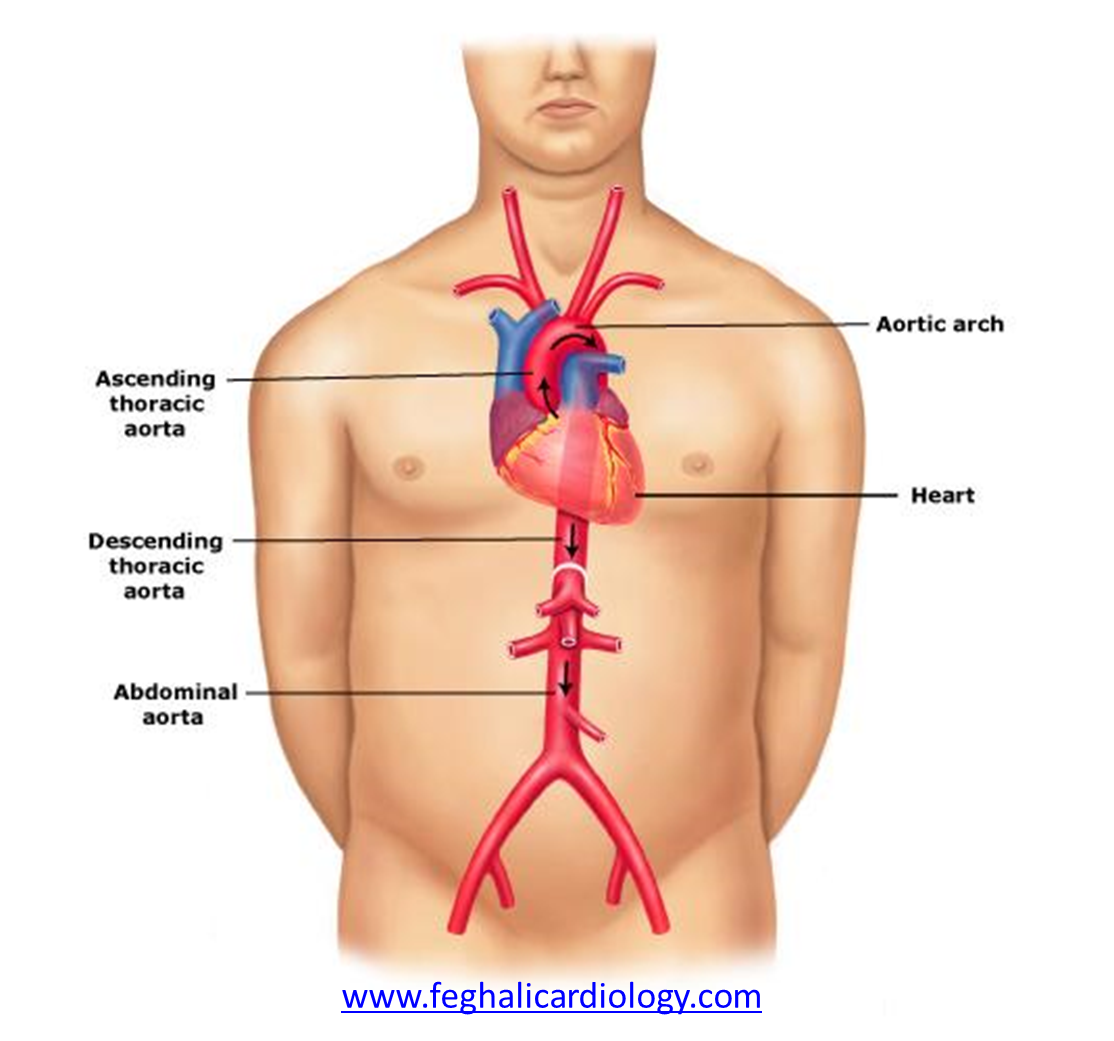
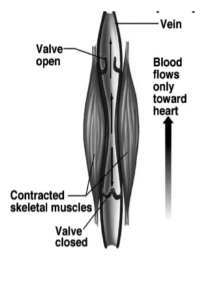
What do large veins contain, to help prevent backflow?
Valves.
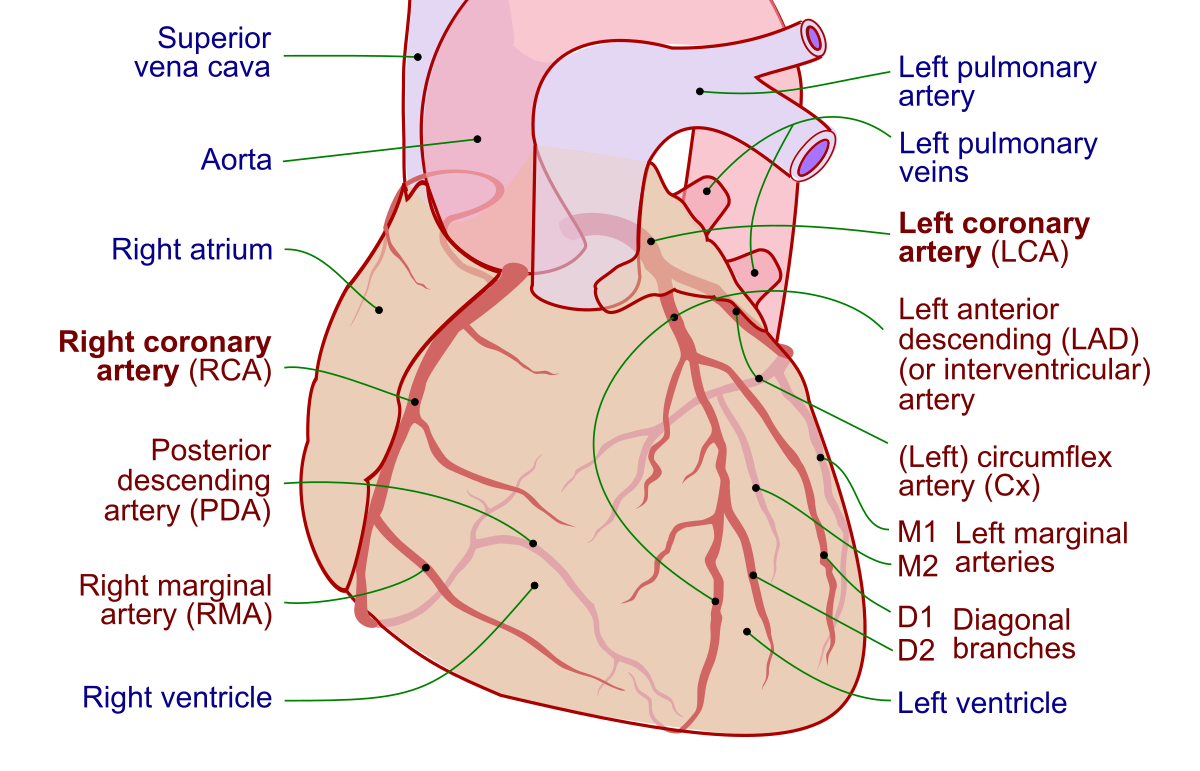
What is the function of coronary arteries?
They supply the tissue cells of the heart with oxygen.
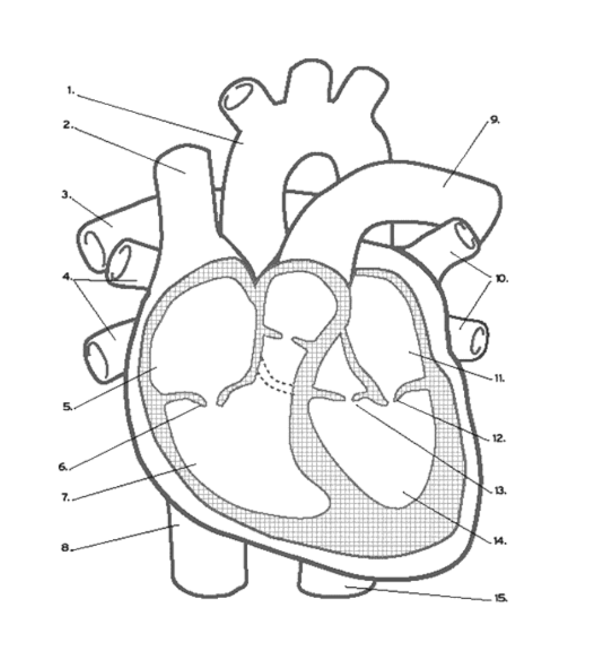
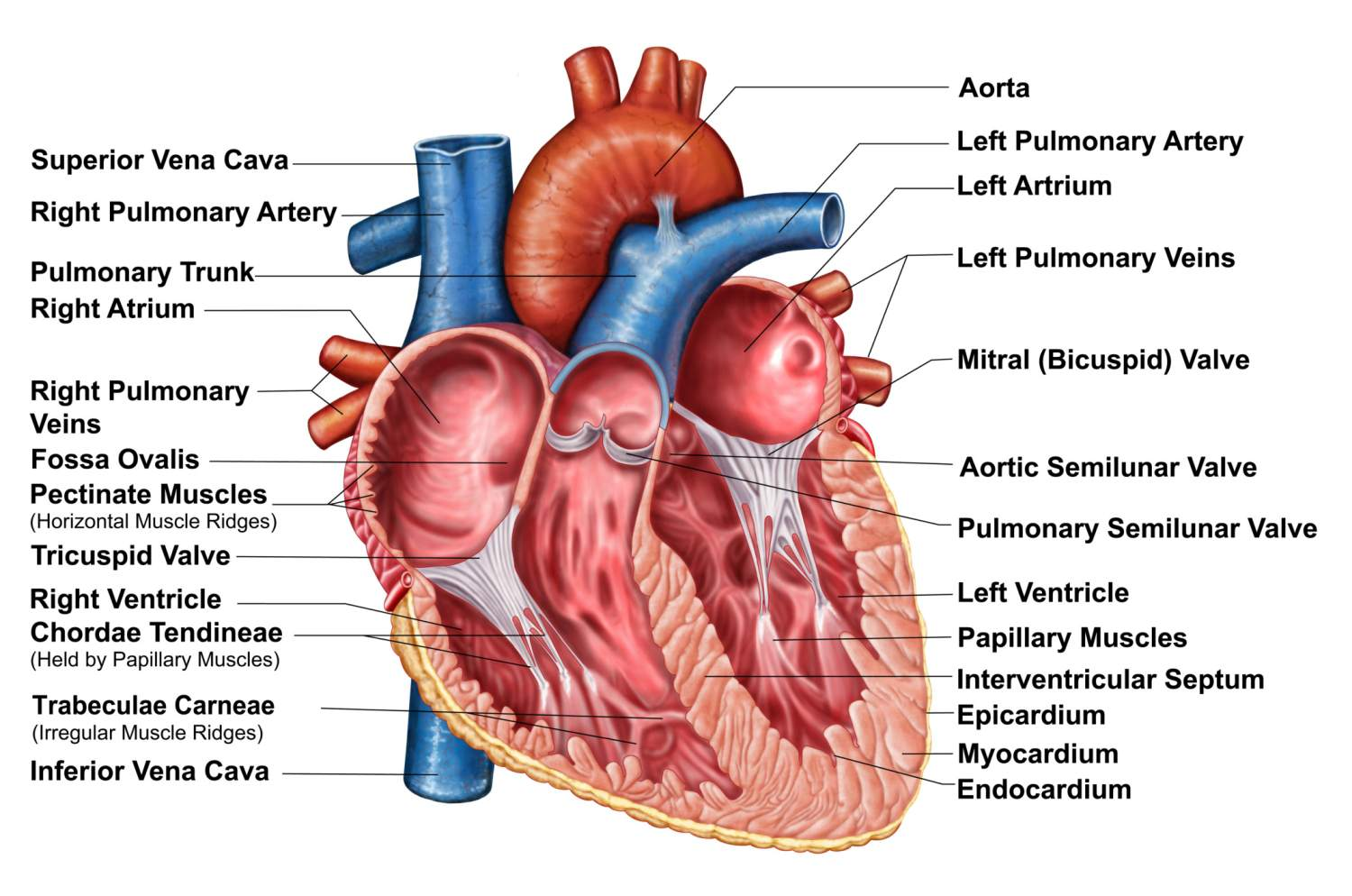
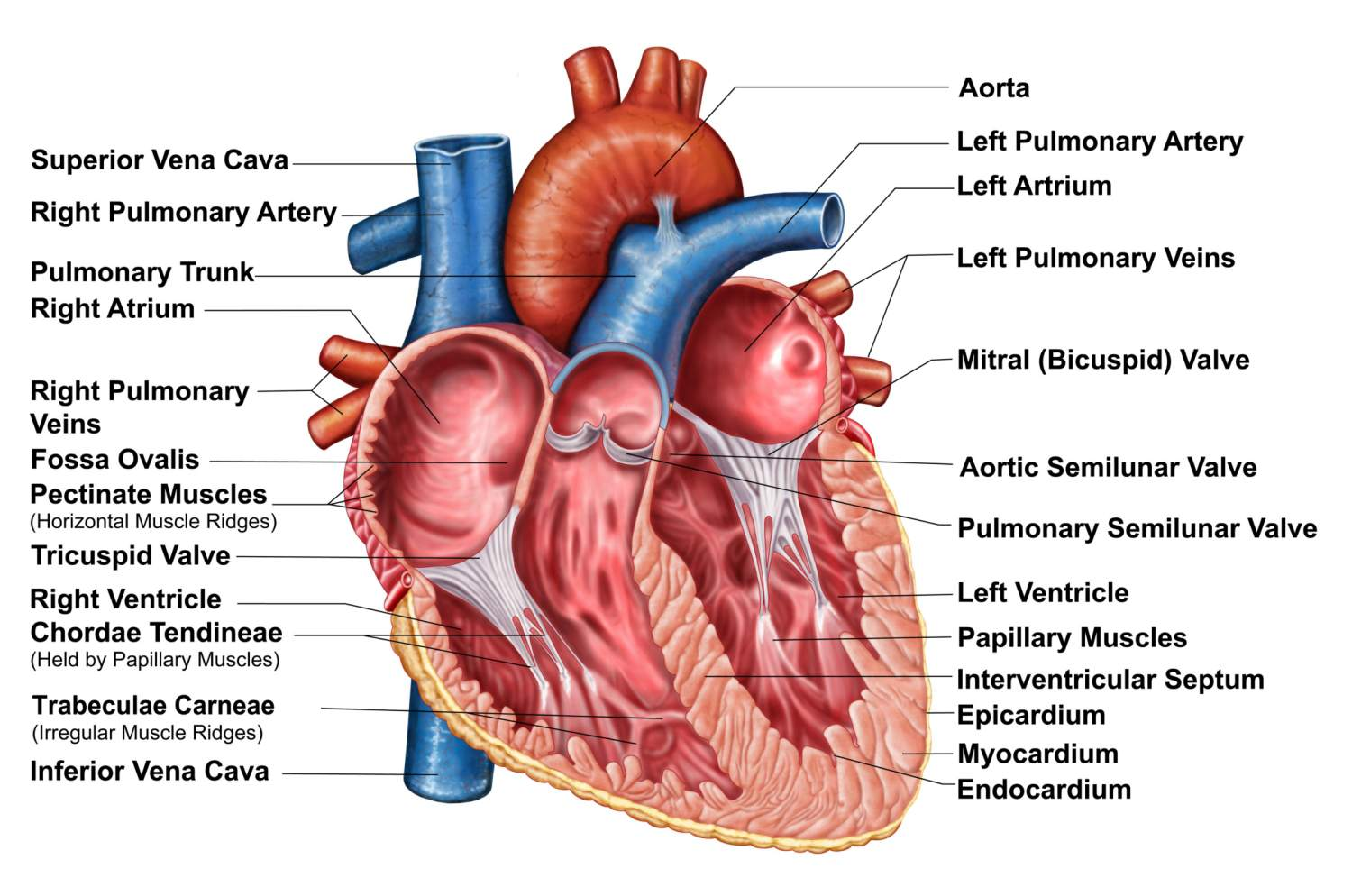
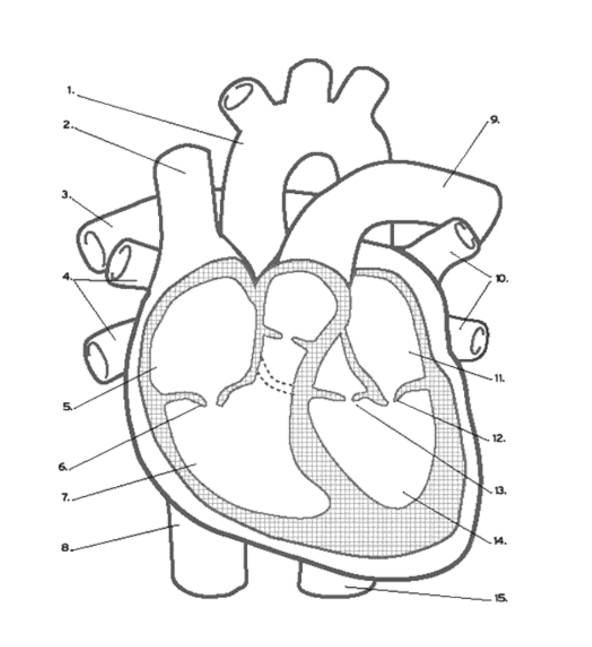
What valve is found at 16 (middle)?
Pulmonary (Semi-lunar) Valve
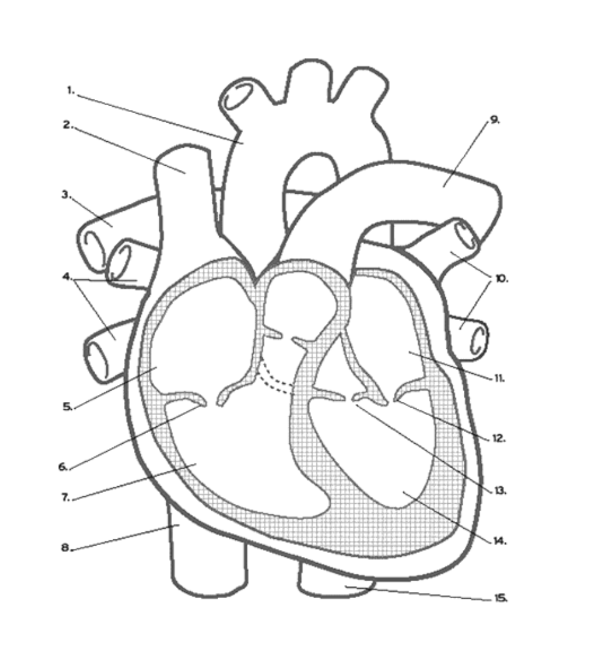
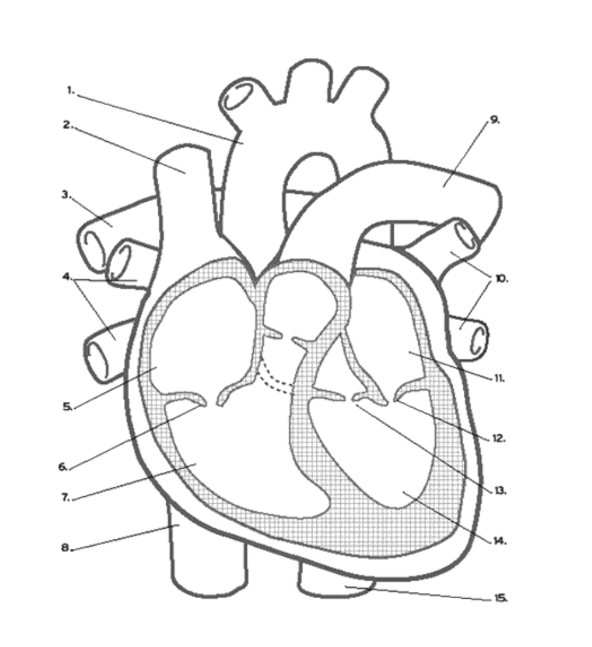
What valve is found at 6?
the Tricuspid (AV) Valve
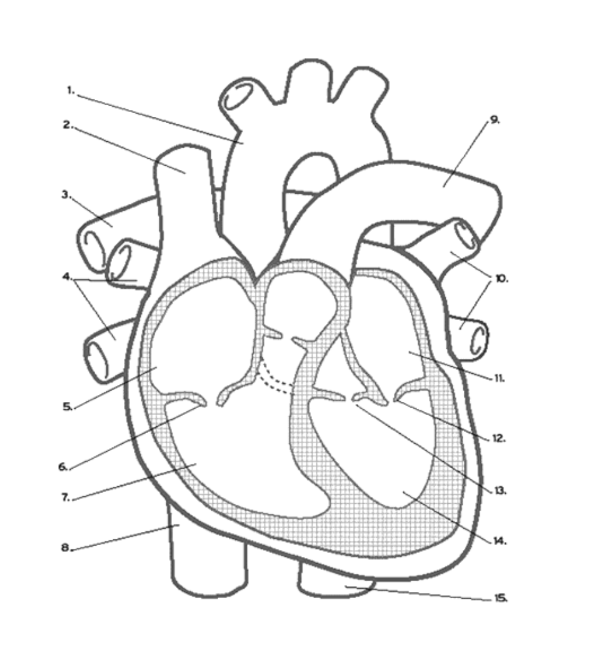
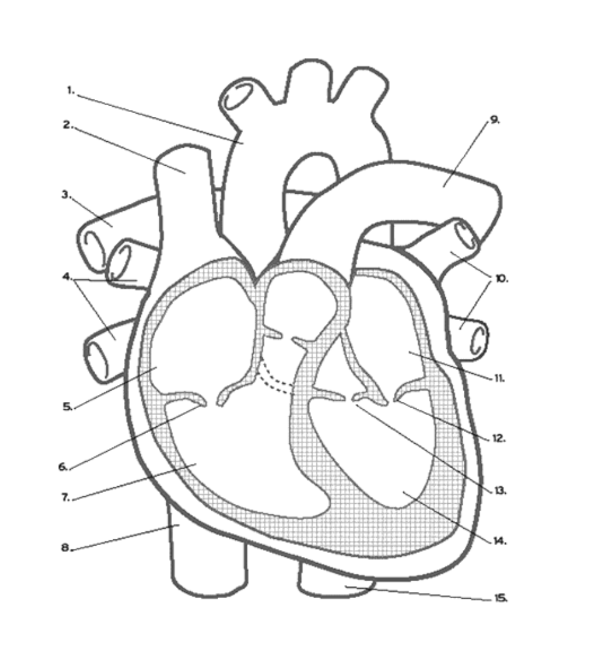
What valve is found at 13?
the Aortic (Semi-Lunar) Valve
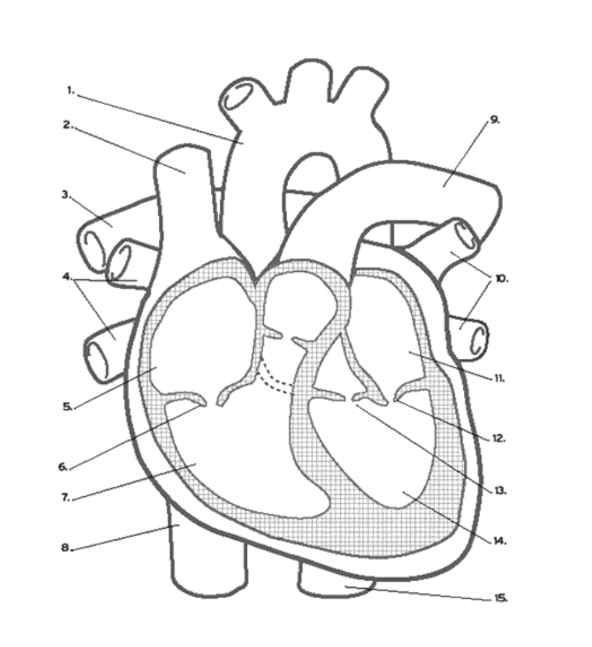
Which valve is found at 12?
the Mitral (AV) Valve
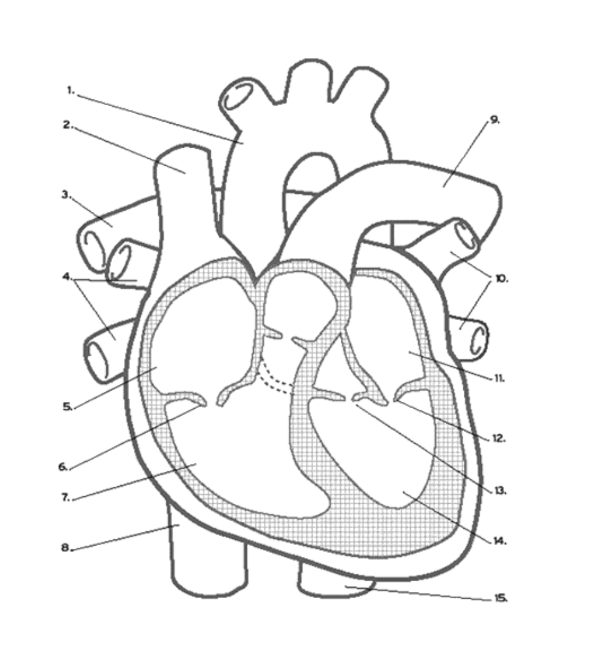
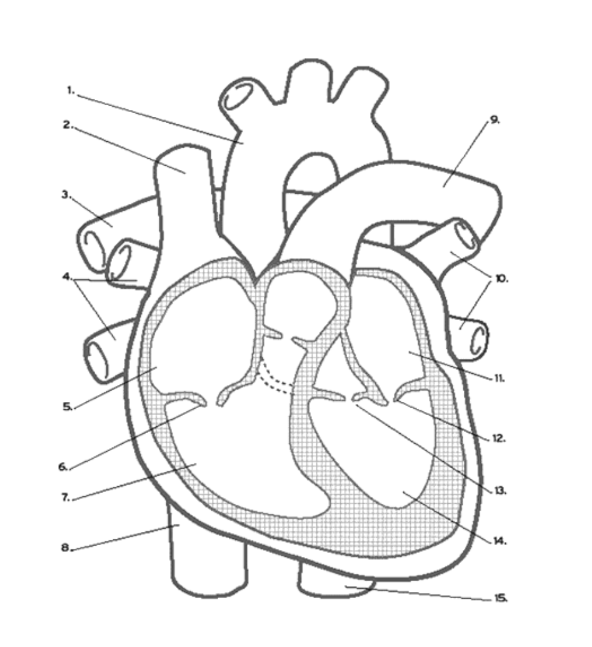
Where is the RIGHT VENTRICLE?
7
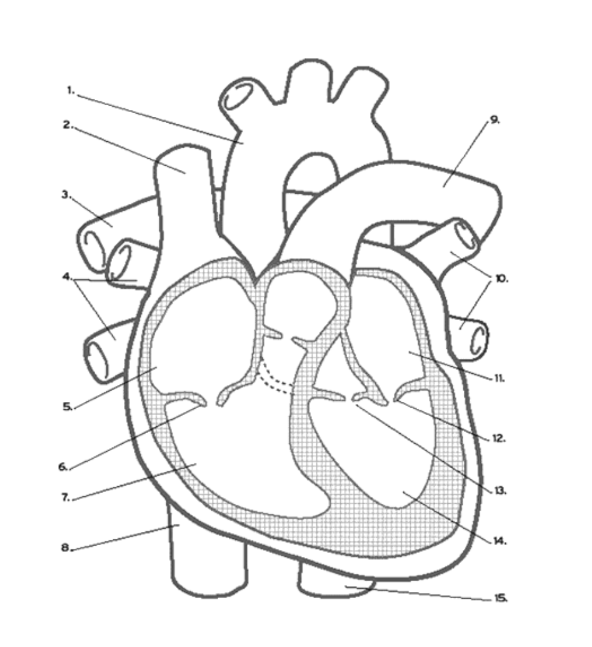
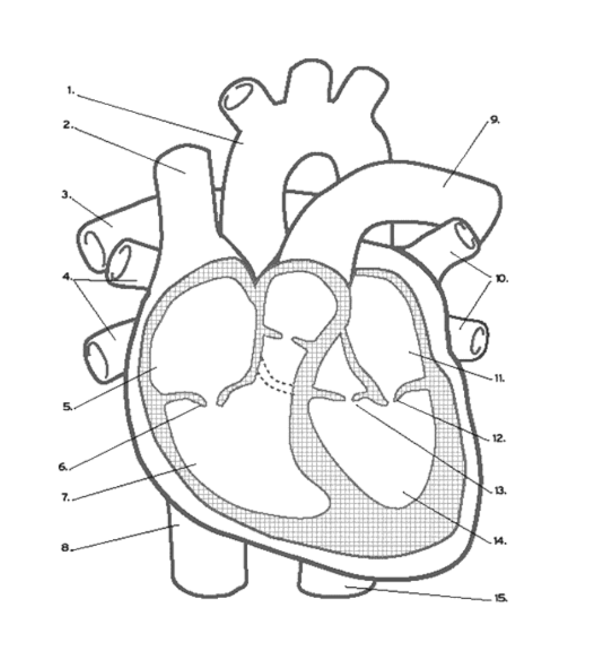
Where is the LEFT PULMONARY VEINS?
10
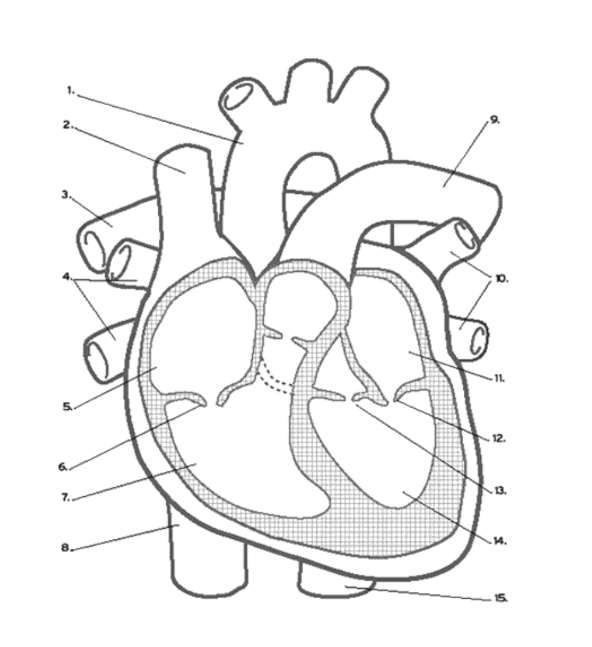
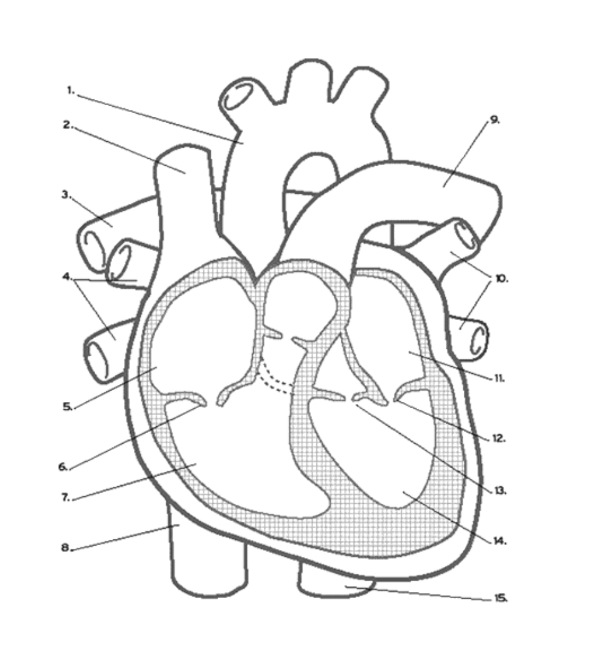
Where are the ATRIA?
5 and 11
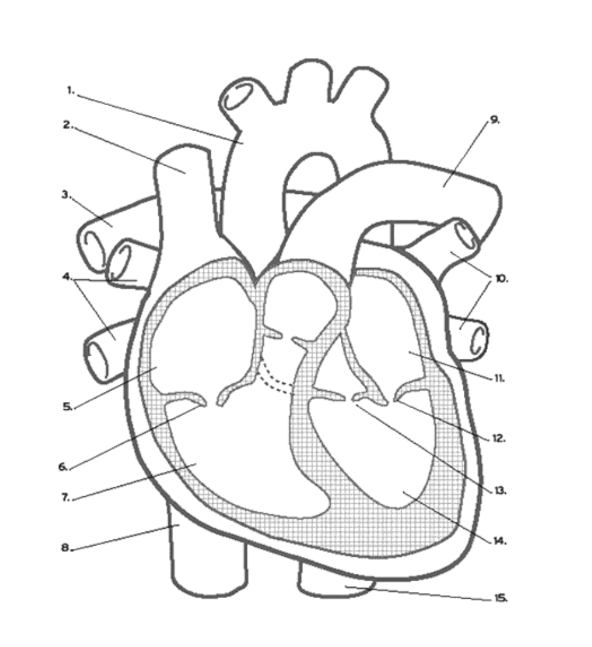
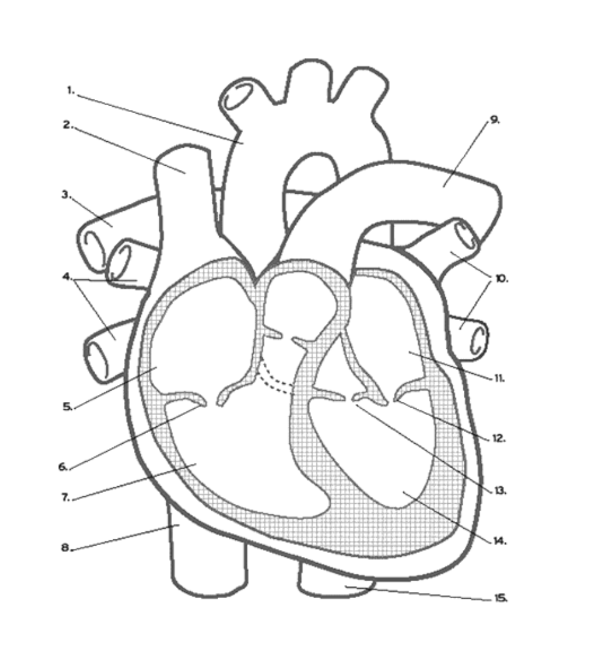
Name the vein at #2
Superior Vena Cava
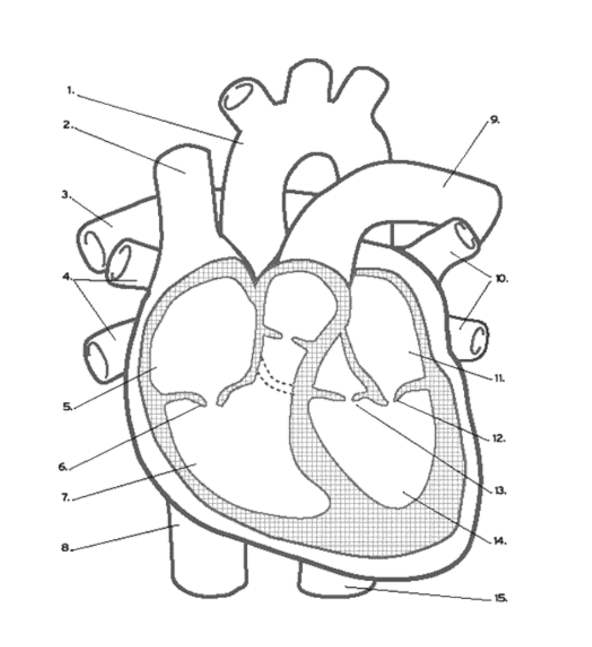
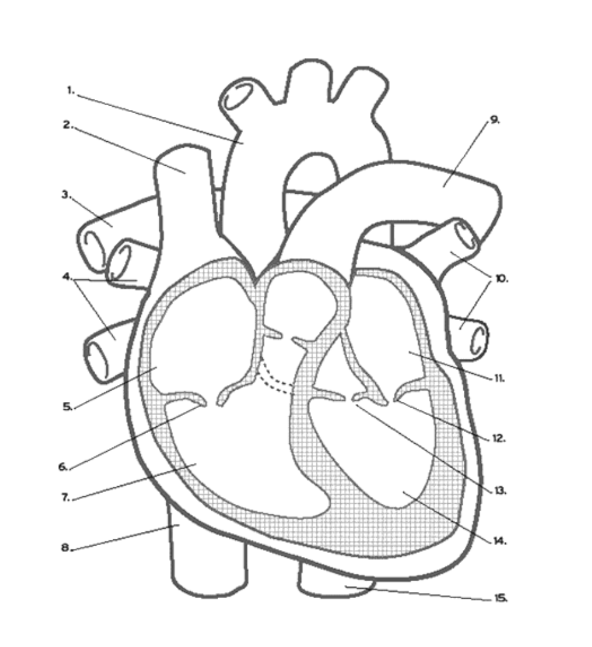
Name the vein at #8
Inferior Vena Cava
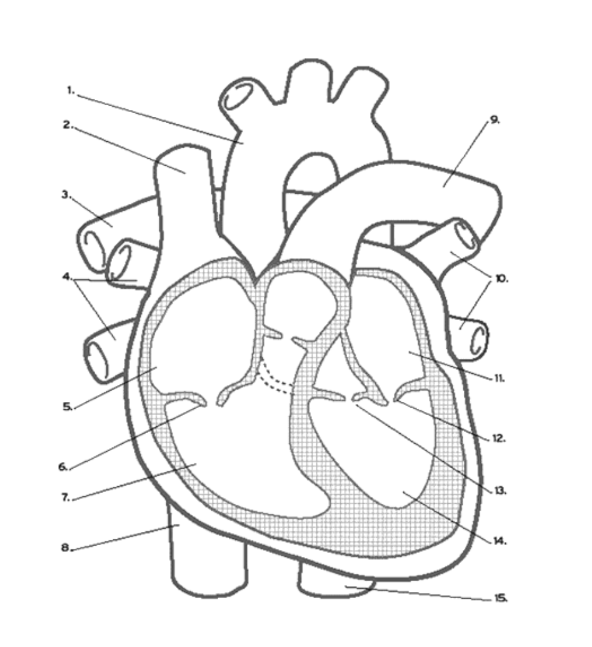
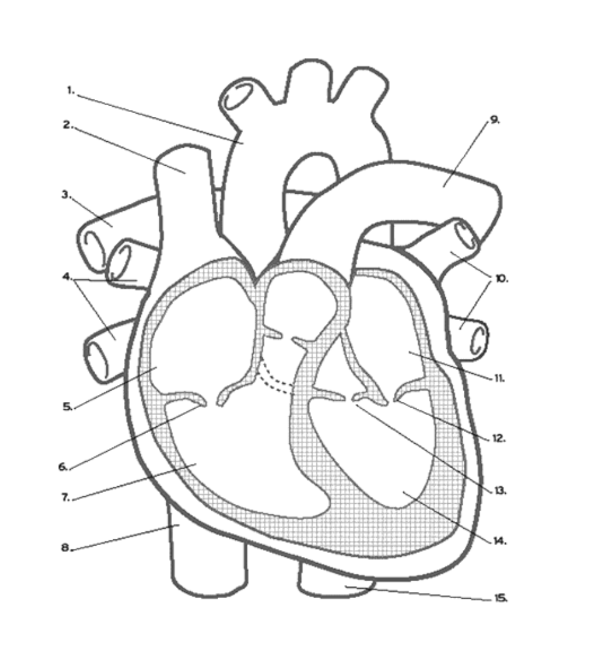
Where does DE-OXYGENATED blood enter the heart?
(Superior/Inferior) Vena Cava
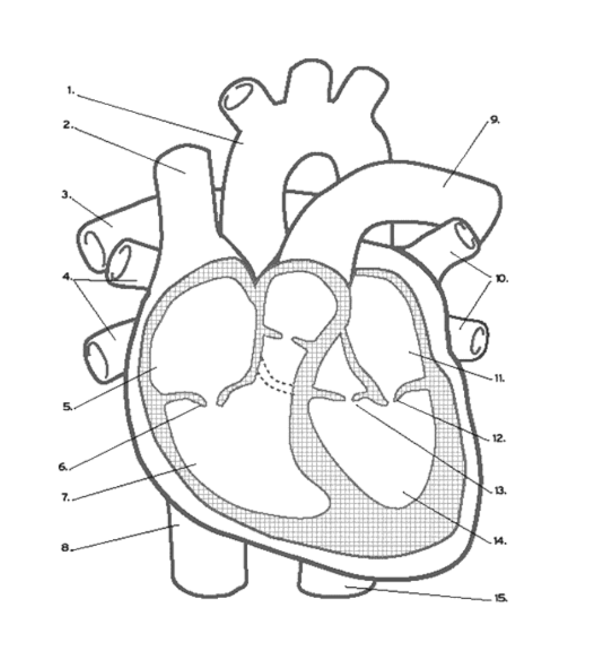
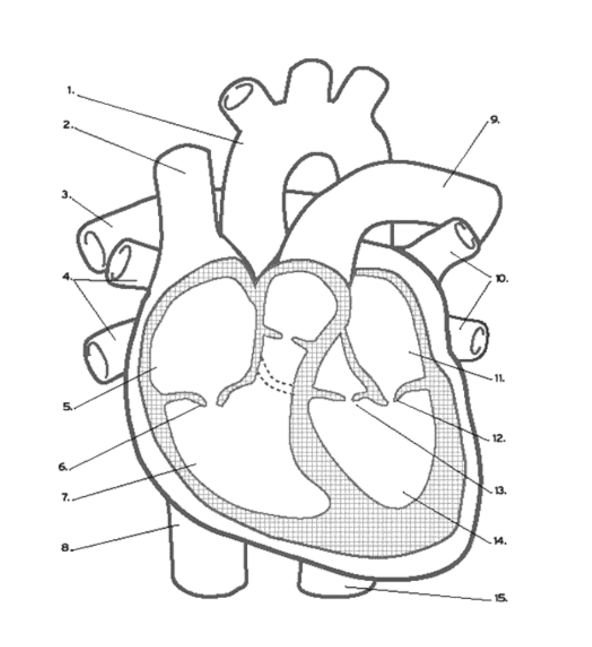
Where does de-oxygenated blood EXIT the heart?
The pulmonary ARTERY
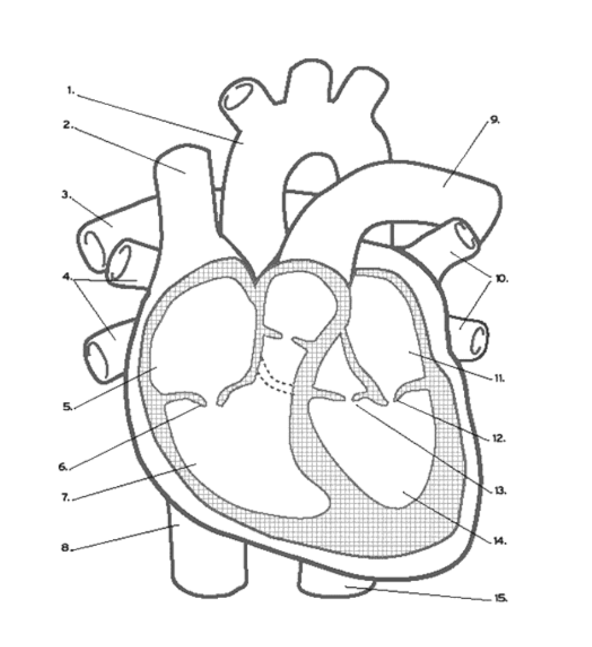
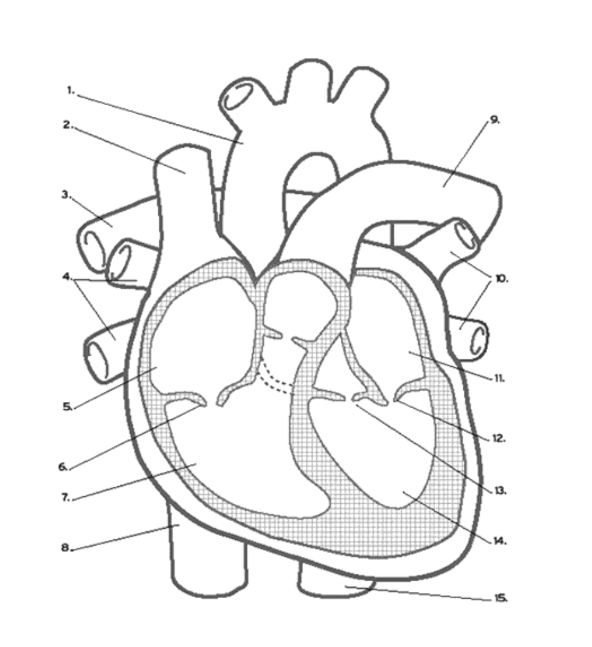
Where does oxygenated blood ENTER the heart?
Pulmonary VEINS
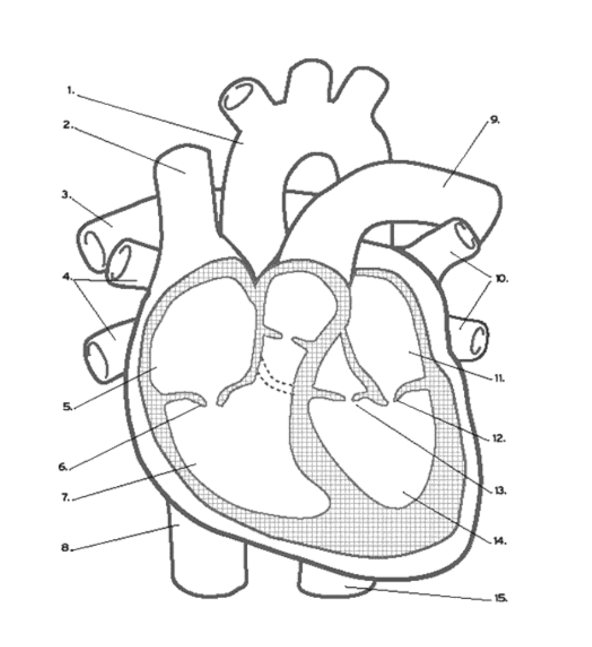
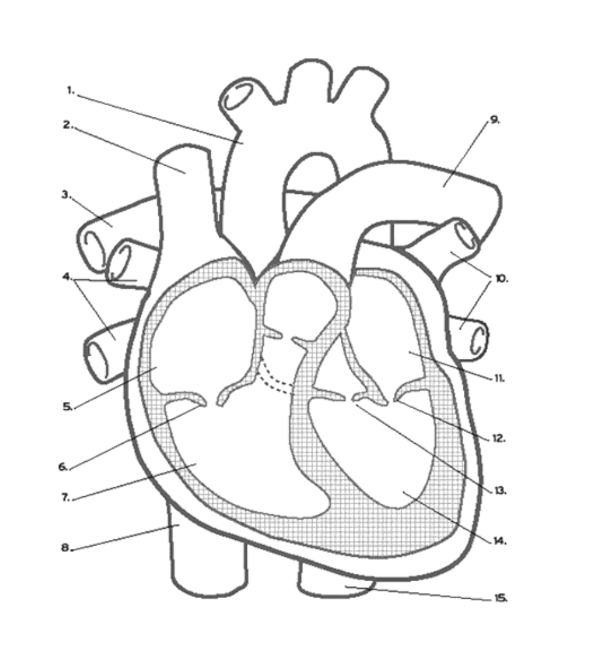
Where does oxygenated blood EXIT the heart?
The aorta
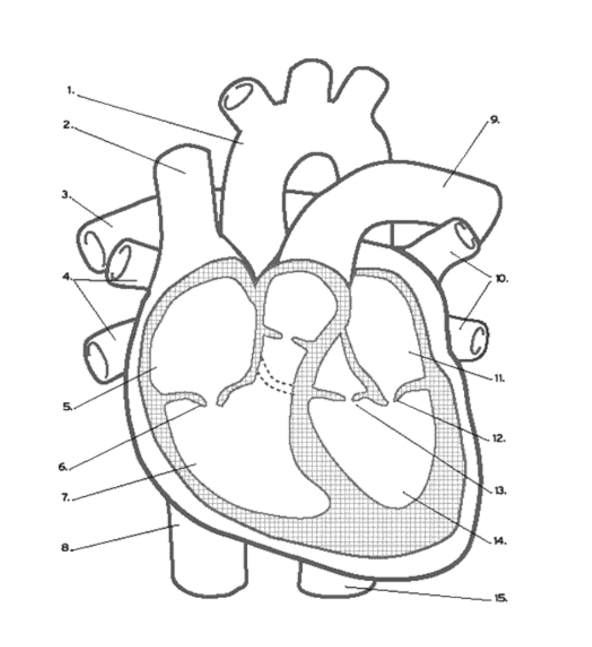
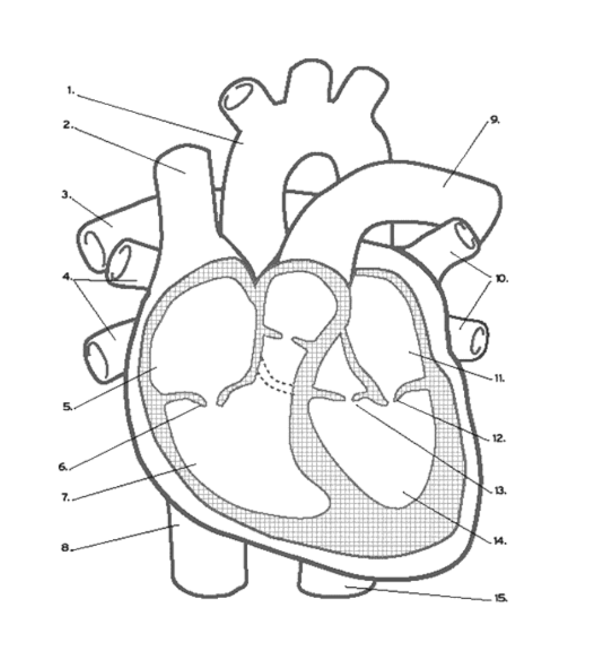
Which valves does de-oxygenated blood pass through?
Tricuspid, pulmonary
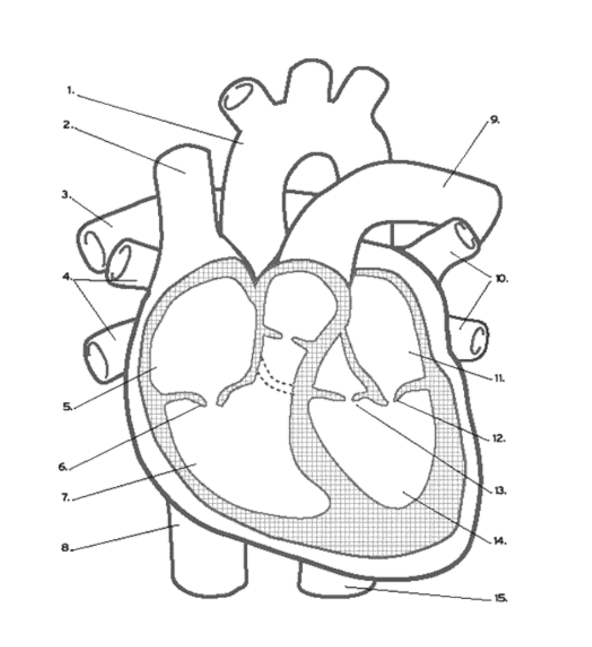
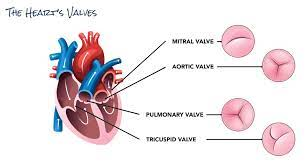
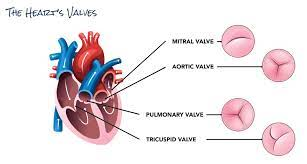
What makes the sounds of the heart?
“Lub” - Caused by closure of mitral and tricuspid valves
“Dub” - Caused by closure of aortic and pulmonary valves
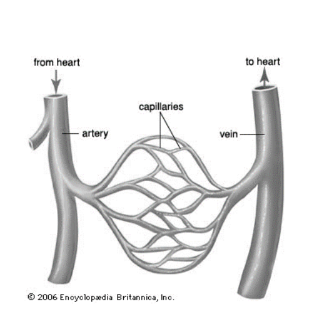
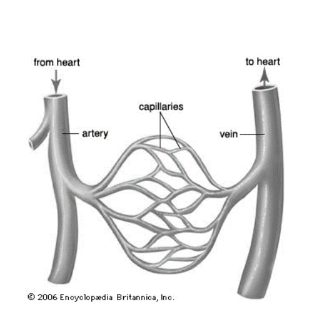
Where are capillaries located (In relation to other blood vessels?)
In between arteries and veins.
Why are red blood cells biconcave discs, as opposed to spheres?
The shape gives more surface area than a sphere.
What is blood plasma?
A protein-rich liquid that is 90% water.
What is hemoglobin?
A molecule carried in blood cells that allows them to carry more oxygen.
What mineral is hemoglobin rich in?
Iron(Fe)
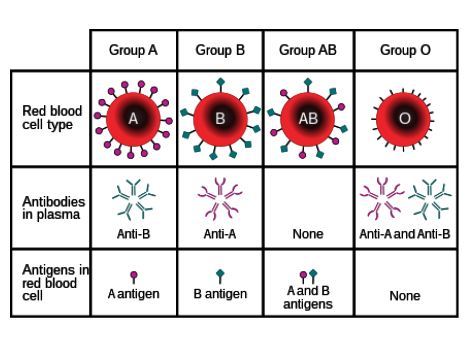
What antibodies do individuals with type A blood have?
Anti-B
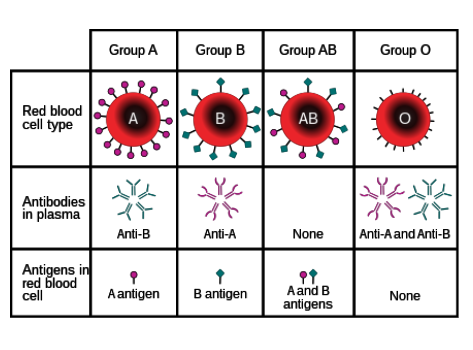
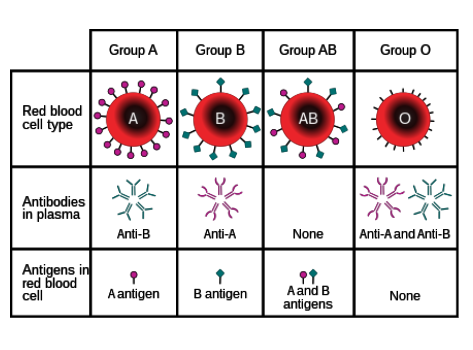
Where are antibodies found?
In blood plasma
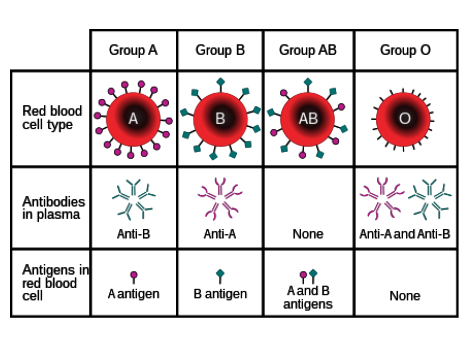
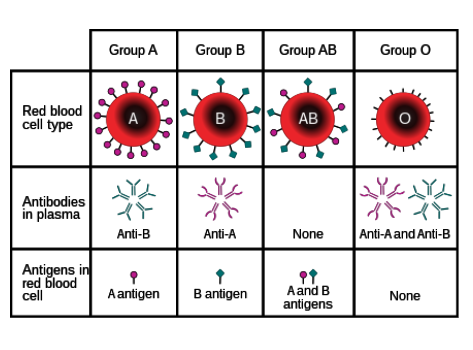
What are antigens?
Protein markers found on red blood cells that determine blood type
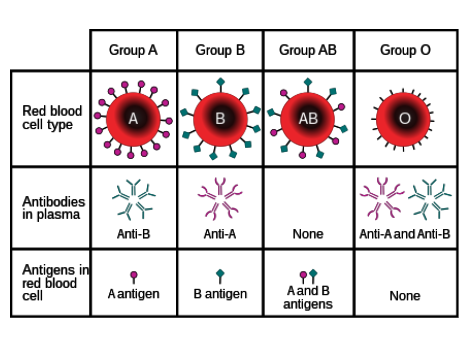
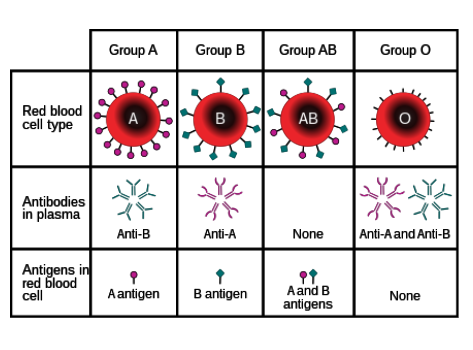
What types of antigens are there?
A and B
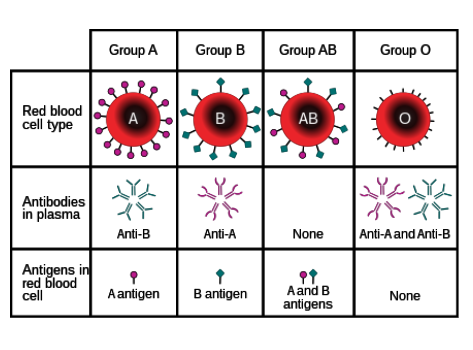
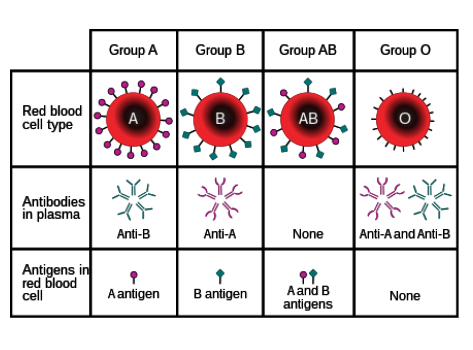
What types of antibodies are there?
Anti-A and anti-B
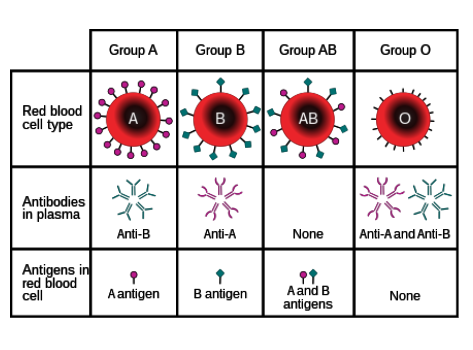
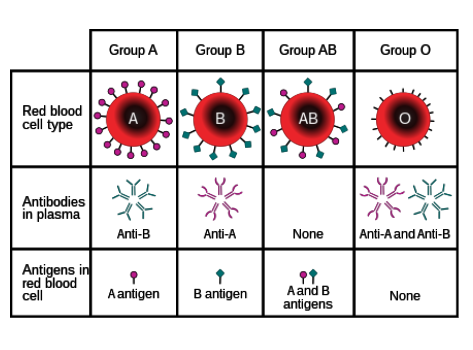
Which types of antigens do people with type O blood have?
None.
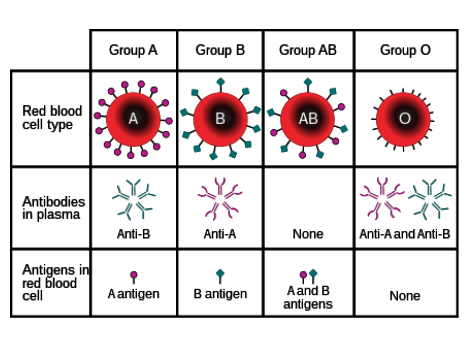
What determines positivity/negativity of blood type?
Rhesus factor- Whether the individual has the protein on their blood cells or not.
What unit is used for Blood pressure?
mmHg (mm of mercury)
What is atherosclerosis?
Buildup of substances in and on artery walls.
What is coronary artery disease?
When there is a blockage in the coronary arteries.
Myocardial infarction (Heart Attack)
Decreased/blockage of blood flow to the myocardium.
Cardiac Arrest
When the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops pumping.
Heart Failure
Occurs when the heart muscle doesn’t pump blood as well as it should. This can cause blood to back up in the lungs and legs.
how many layers does an artery have?
3
What is the purpose of the digestive system?
To break down food into nutrients.
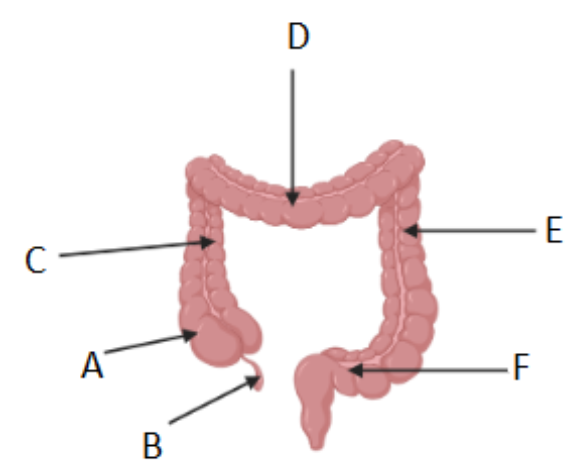
Where is the cecum/caecum (Area where S. intestine empties into L. intestine) ?
A
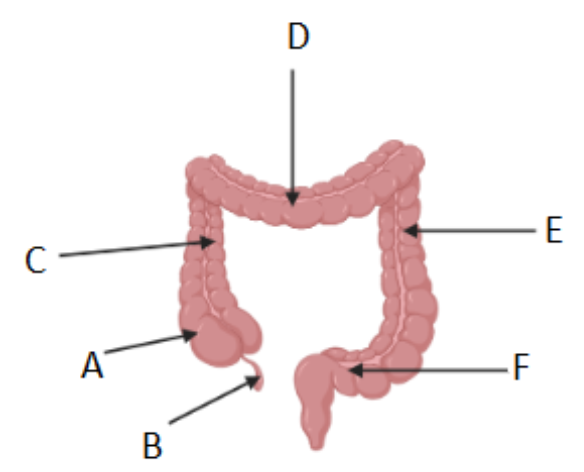
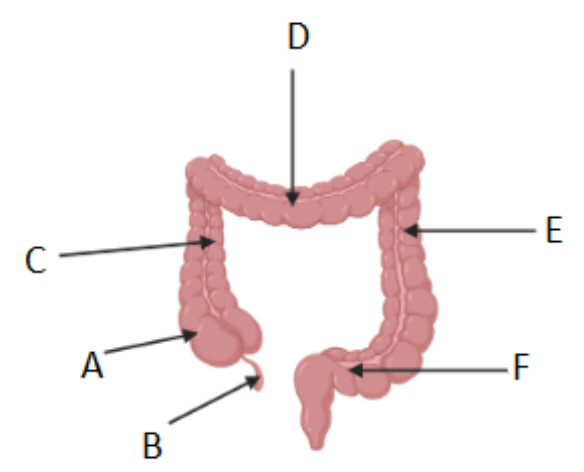
Which letter corresponds to the appendix?
B
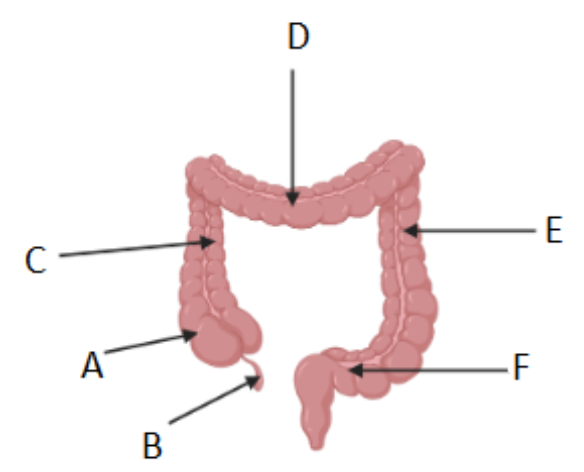
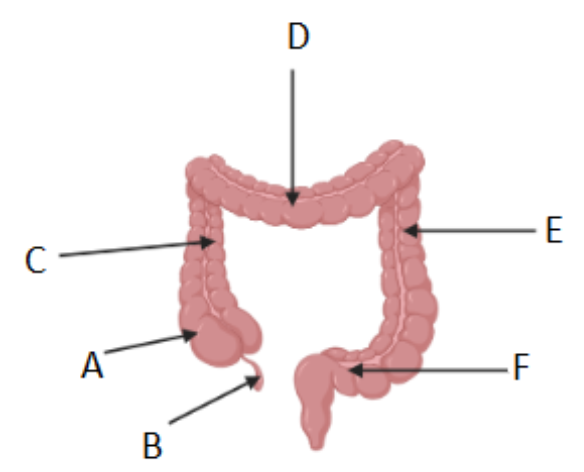
What is region C called?
Ascending colon
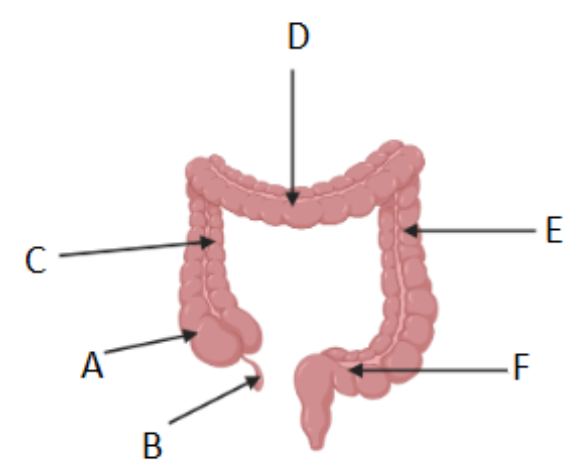
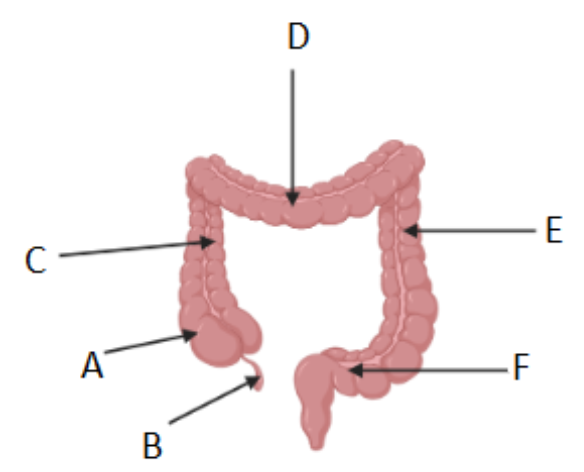
What is region D called?
Transverse colon
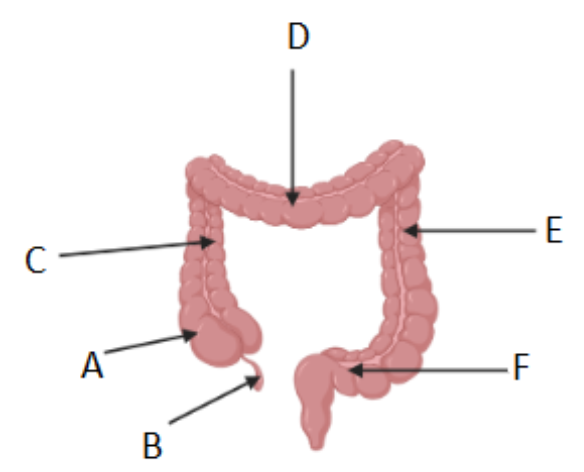
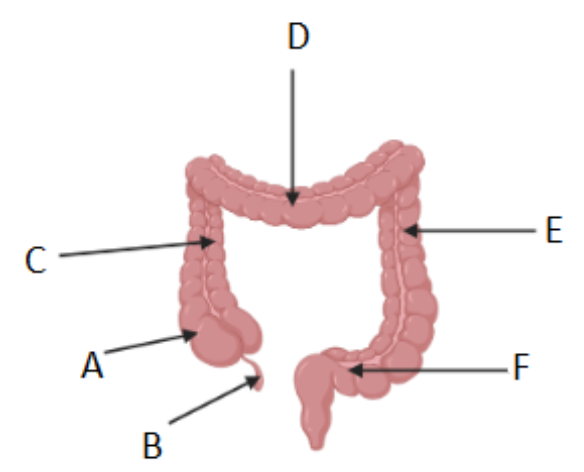
What is region F called?
Sigmoid colon
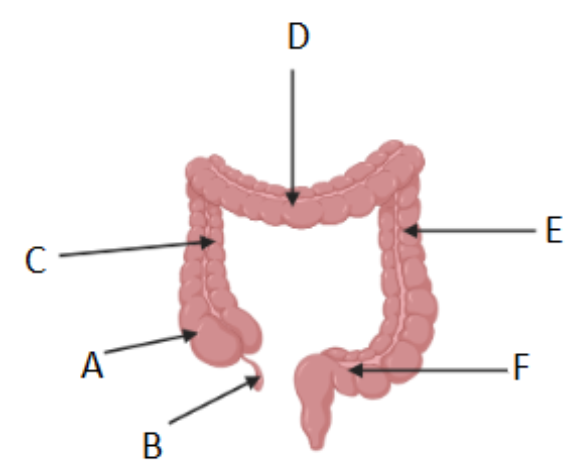
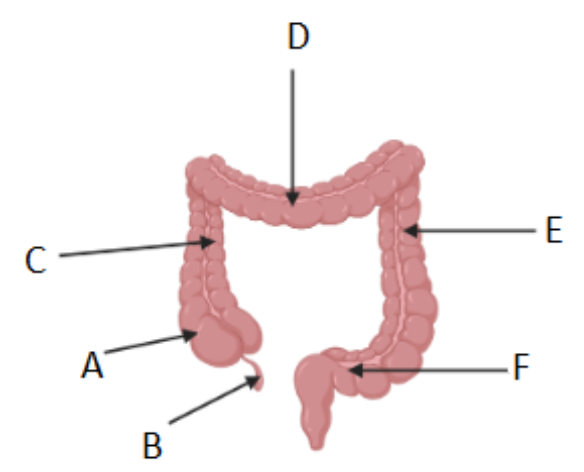
What is region E called?
Descending colon
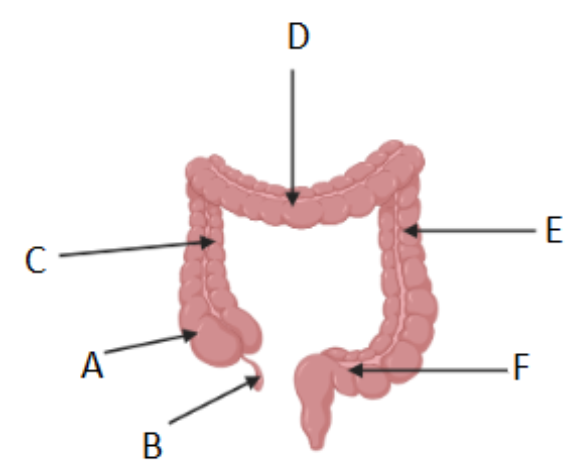
What is the purpose of bile?
to EMULSIFY(mix) fats, making them easier to break down
Where is bile made?
the liver
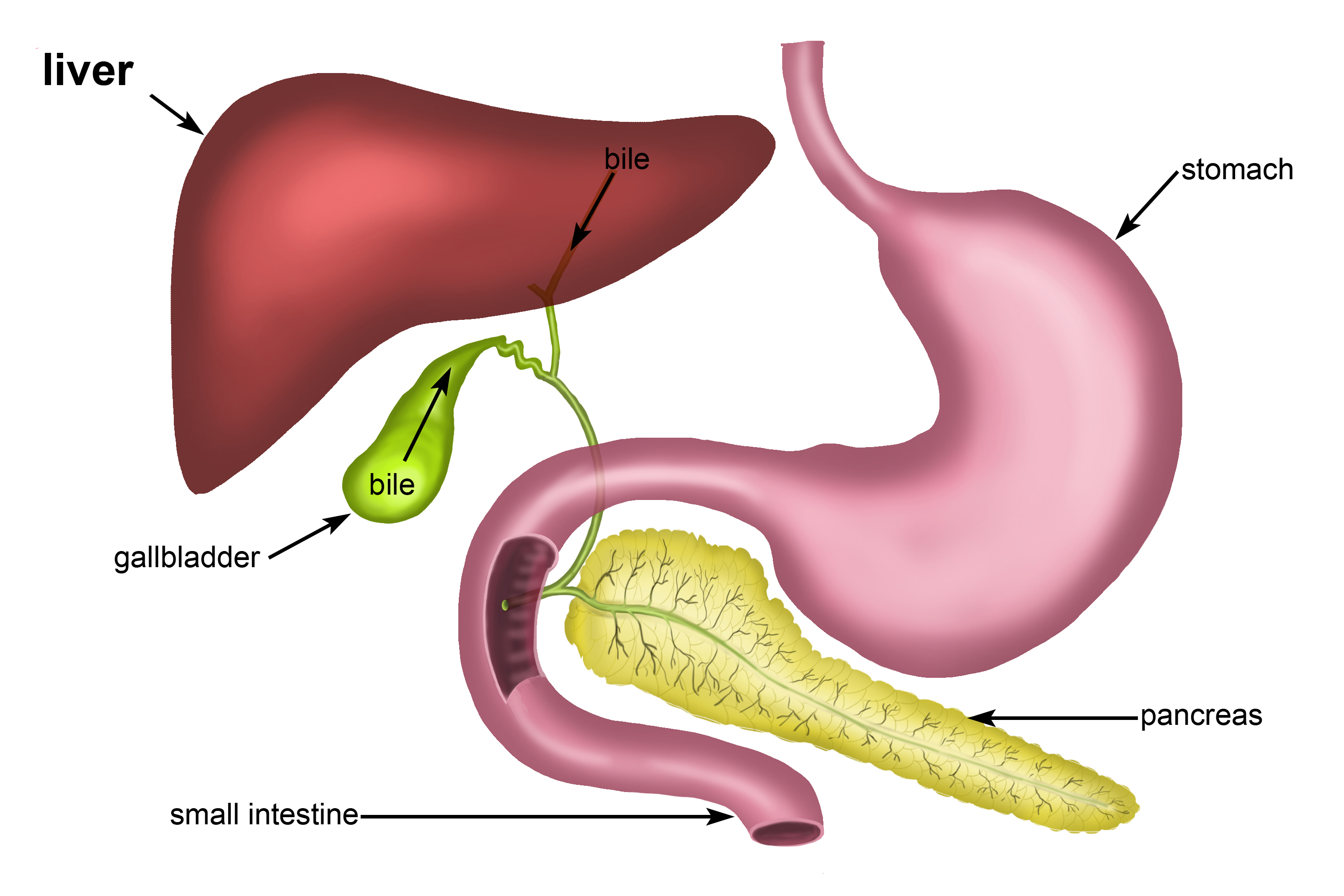
Where is bile stored?
The gallbladder
What is the purpose of the pancreas?
Produce enzymes that leave through the small intestine.
How many pairs of salivary glands do you have?
3
What is the function of the epiglottis?
Closes upon the trachea to prevent choking.
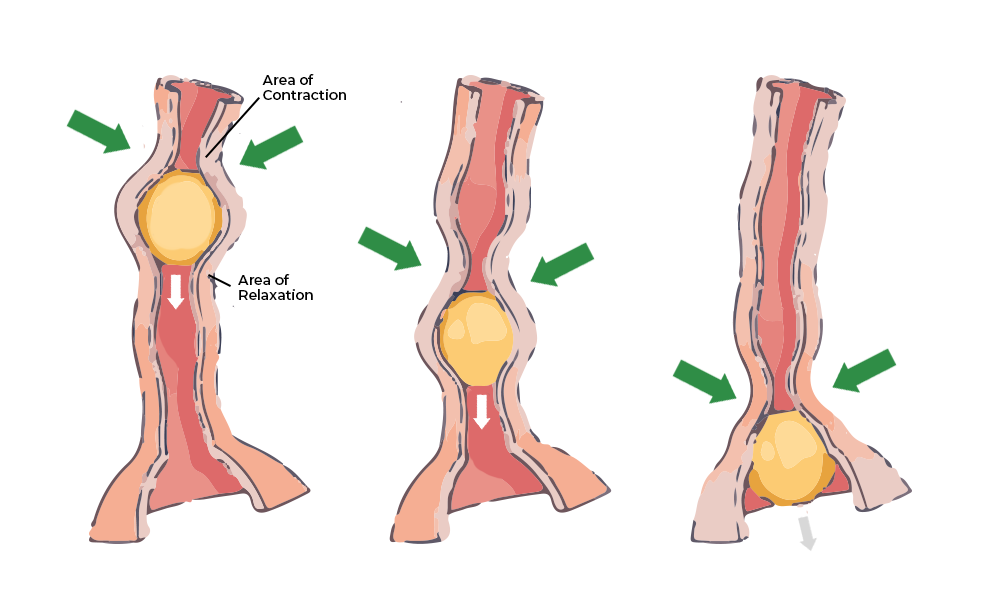
What is peristalsis?
Muscular contractions that help push food down the esophagus.
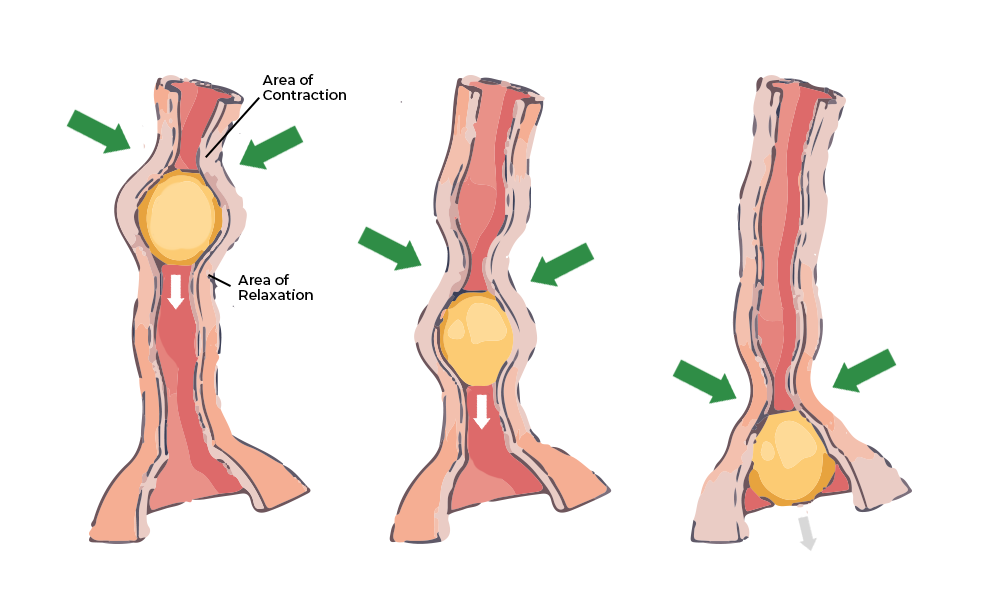
After passing through the stomach, a bolus becomes ________
Chyme
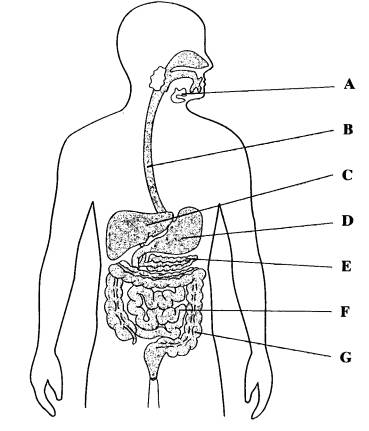
Which organ absorbs water?
G (Large intestine)
What acid is located in the stomach?
HCl (Hydrochloric acid)
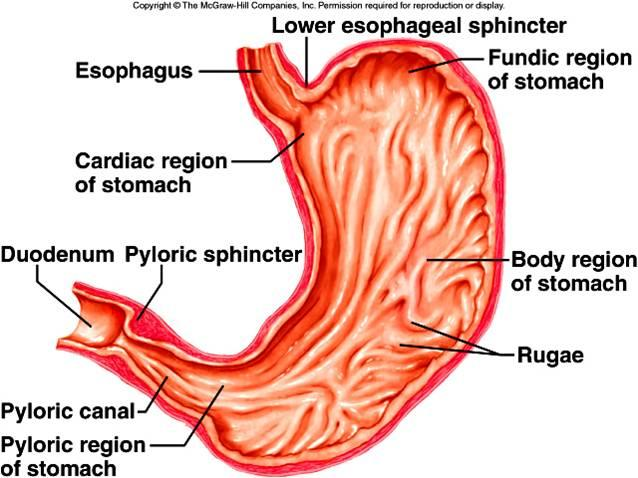
Name given to folds in the stomach lining that increase its surface area and allows for expansion when it gets full.
Rugae
What is the function of the small intestine?
To chemically break down food
A lipid breaks down into a ______
Fatty acid
Enzyme that breaks down lipids
Lipase
Where is lipase produced?
the stomach
What chemical (found in the stomach) is responsible for digesting protein?
Pepsin
where does chemical digestion start?
In the mouth (with saliva)
Does amylase (enzyme that breaks carbs into maltose/lactose) work in the stomach?
No. It’s not acidic enough to work in a pH of 2
What organ is responsible for producing maltase and lactase?
The small intestine.
What enzyme is released by the pancreas into the s. intestine for the purpose of digesting proteins?
trypsin
What role does an enzyme play in a chemical reaction?
Catalyst.
What are carbohydrates broken down into?
Simple sugars.
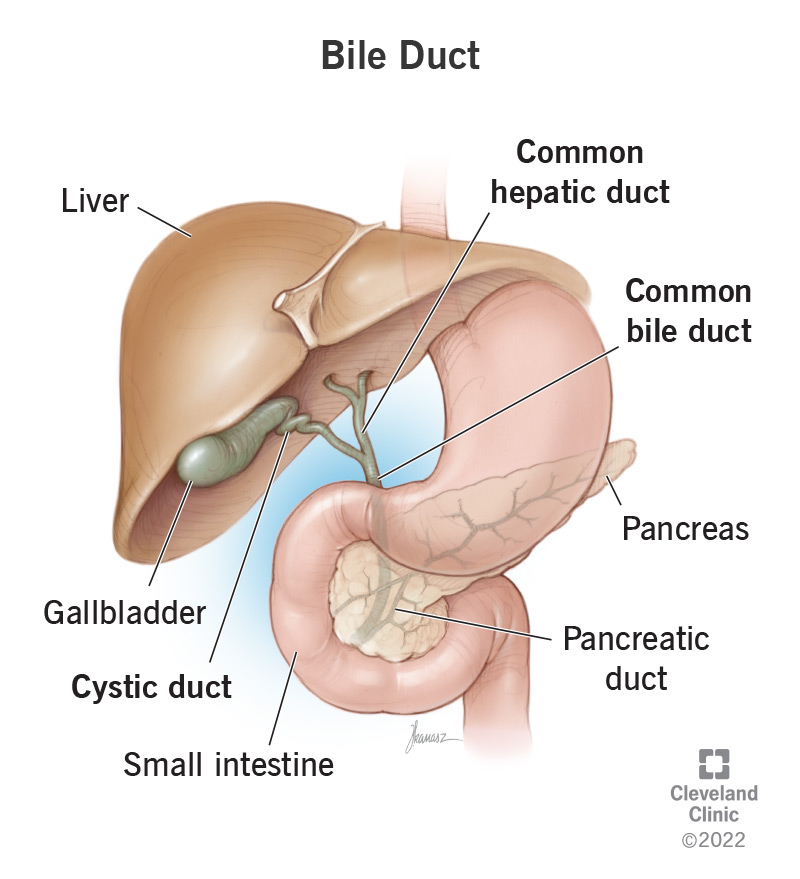
How do enzymes produced in the pancreas travel to the duodenum?
The common bile duct.
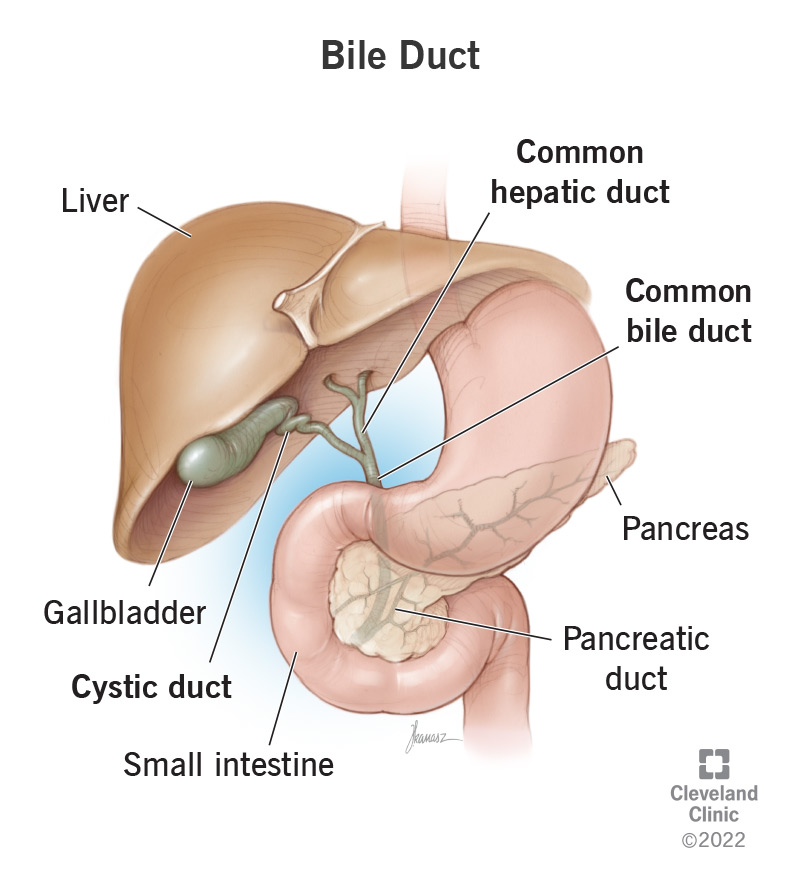
What reacts with HCl to form pepsin?
pepsinogen
Where is amylase produced?
The saliva and pancreas
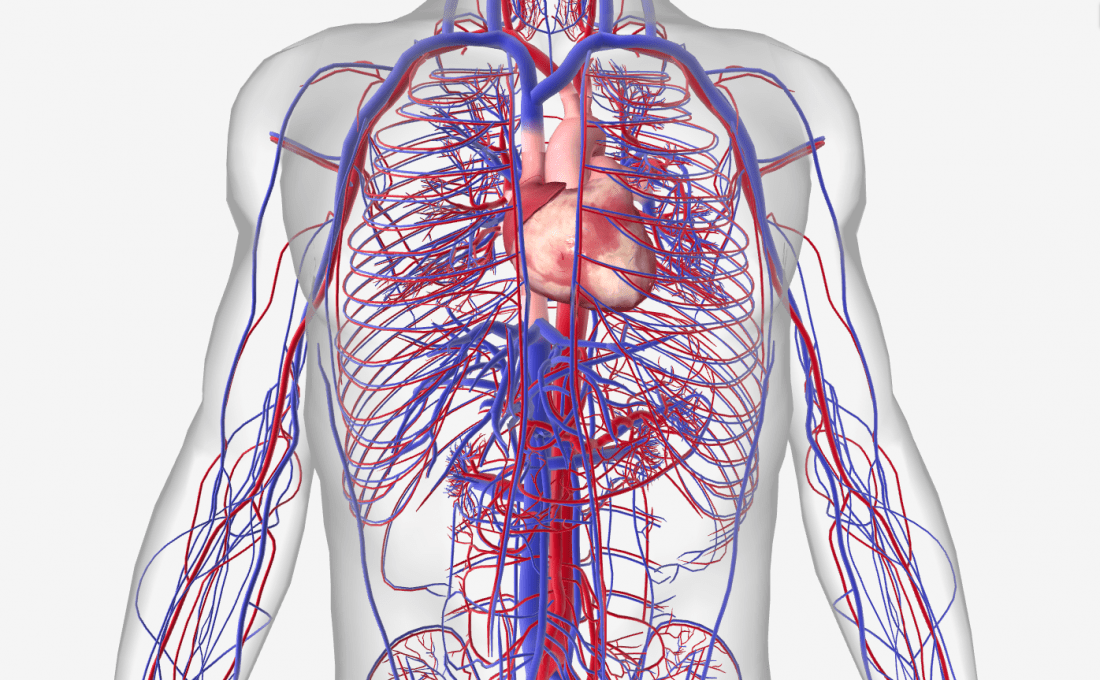
How are nutrients transported around the body?
the circulatory system.
What type of tissue is the tongue?
Muscle.
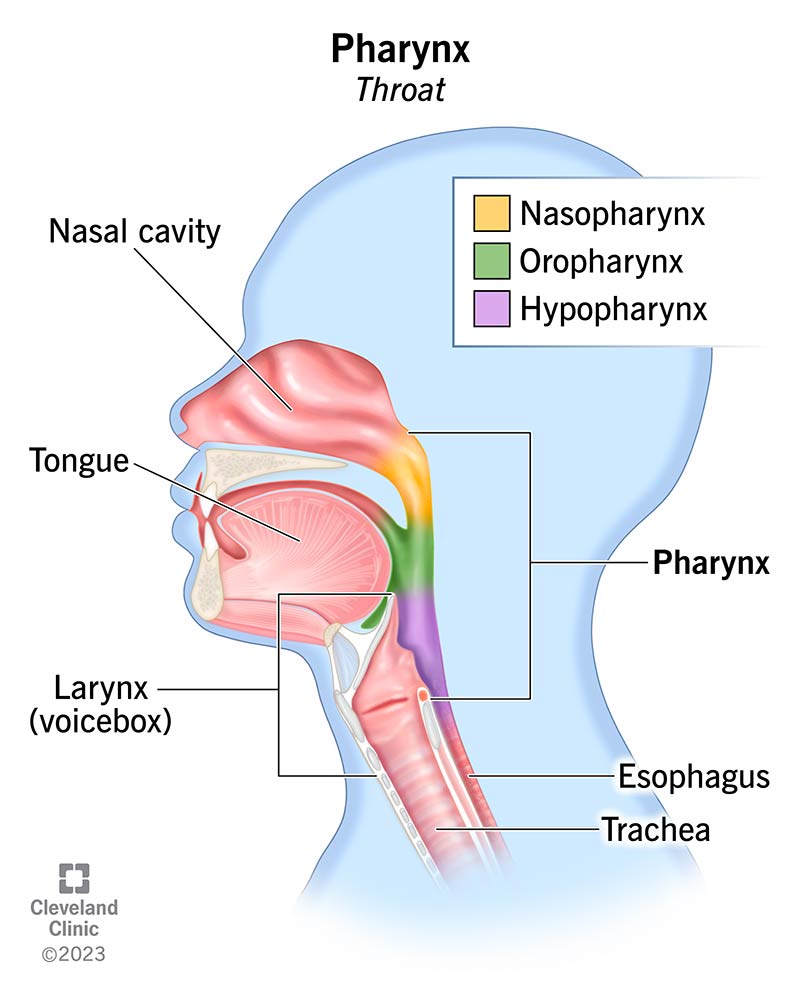
Where is the pharynx located?
At the back of the throat.
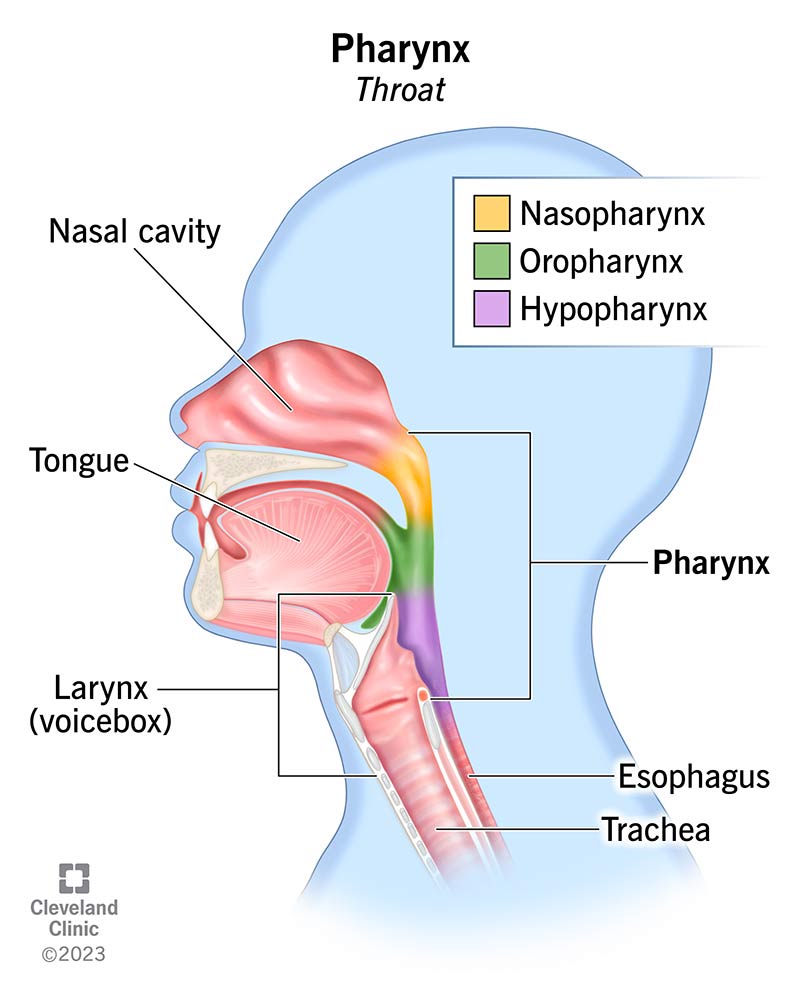
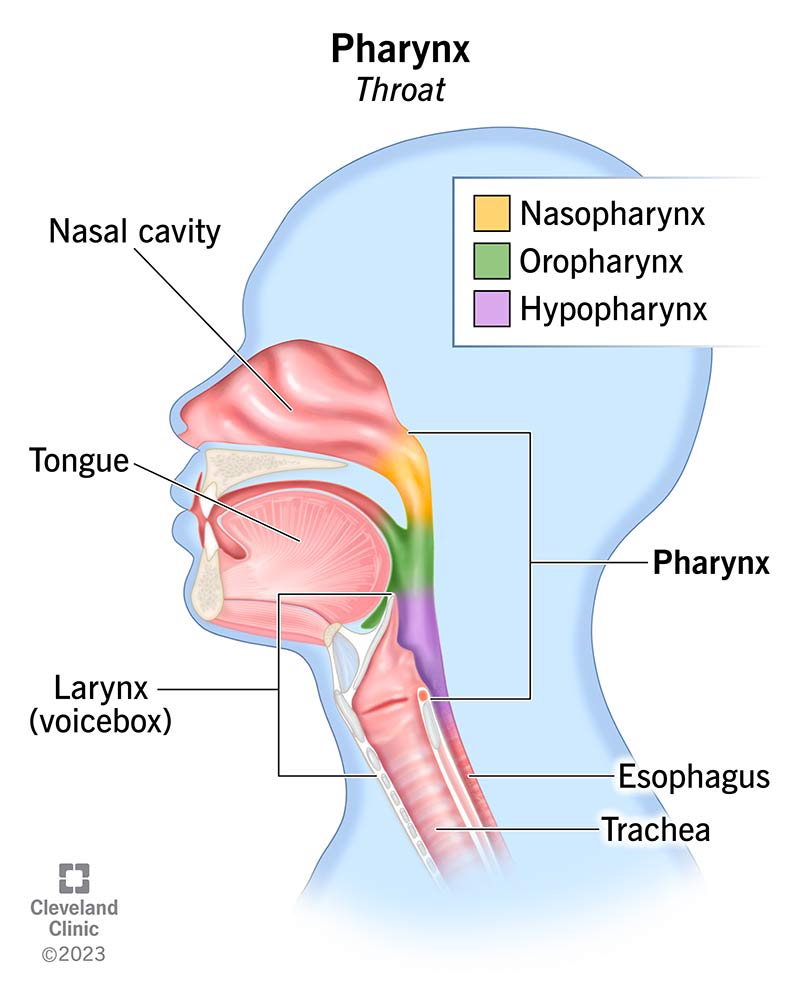
What is the purpose of the pharynx?
To guide the food into the esophagus from the oral cavity.
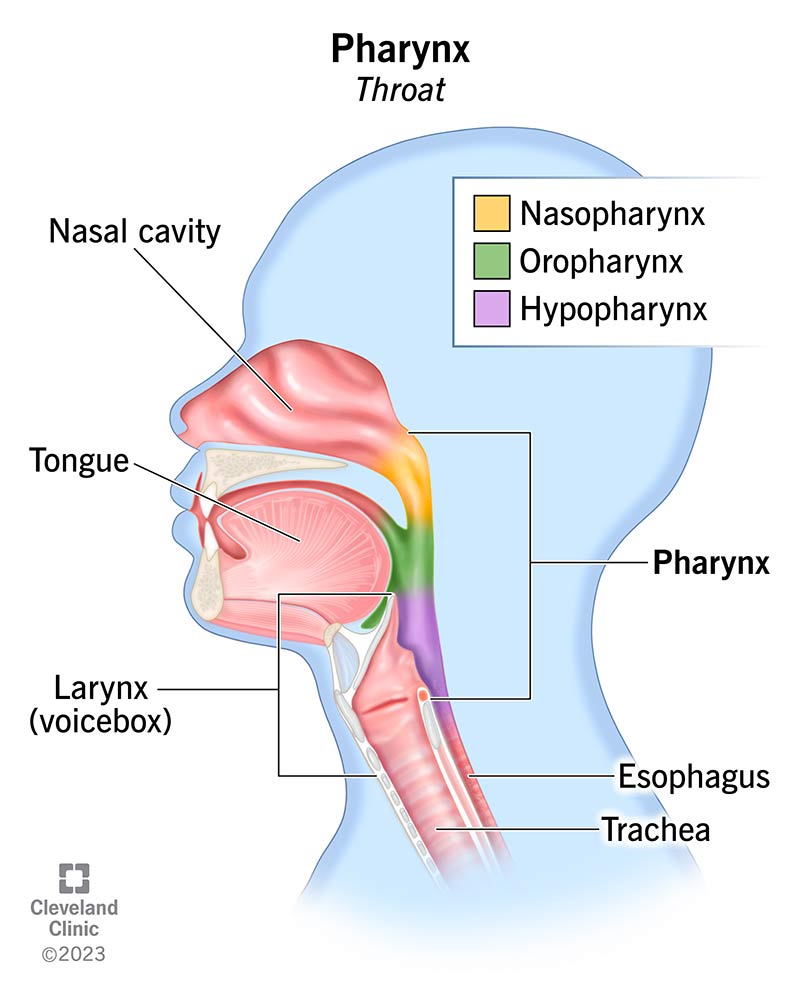
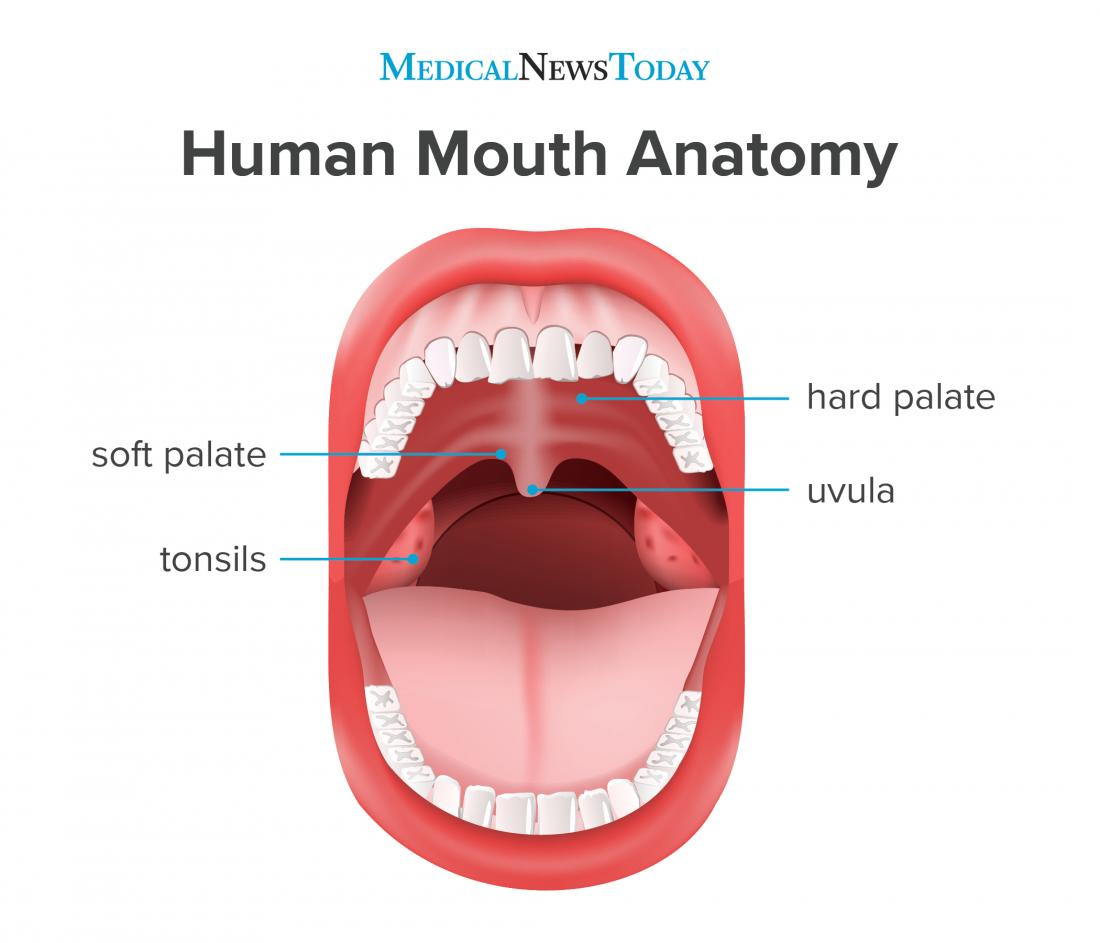
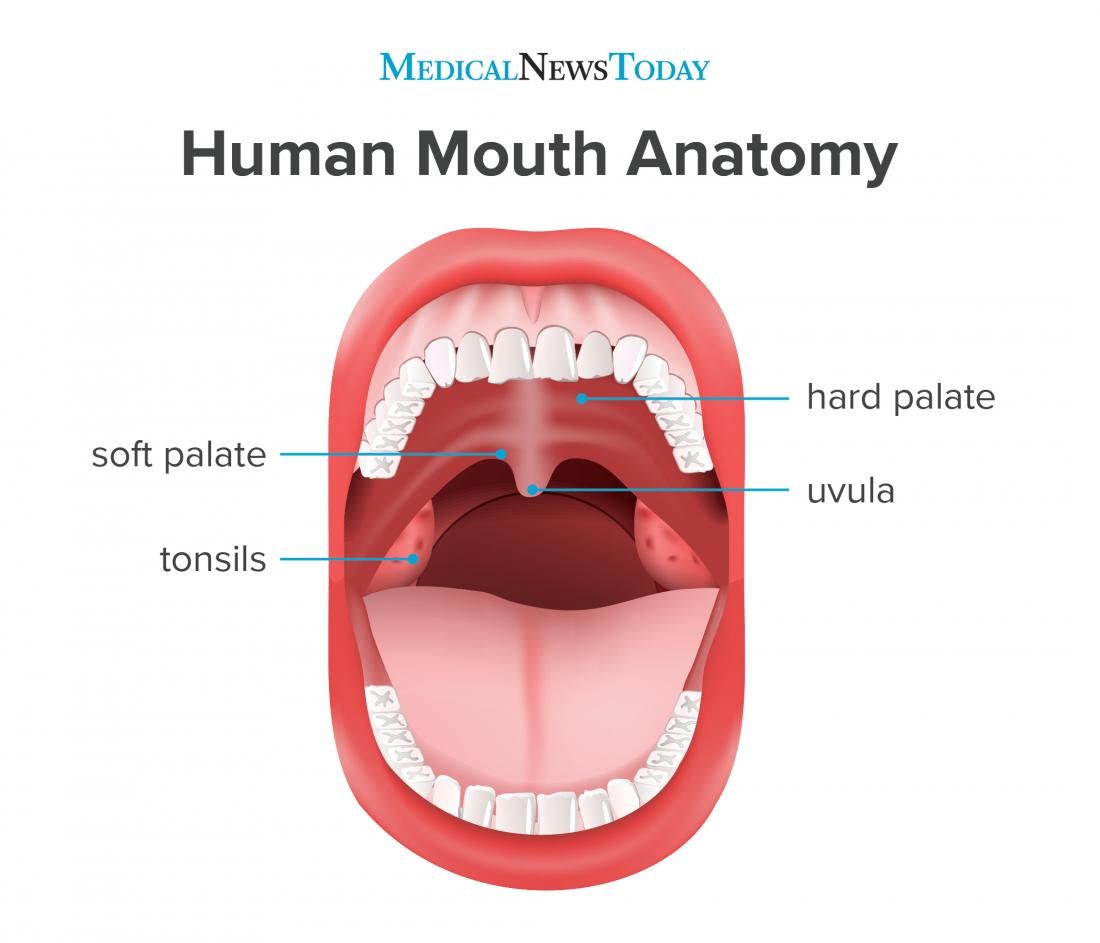
What closes over the nasal cavity during swallowing?
The uvula and soft palate
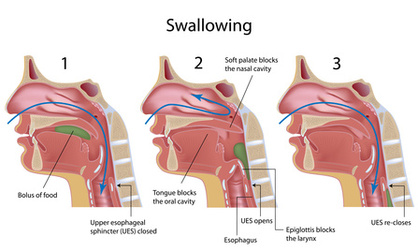
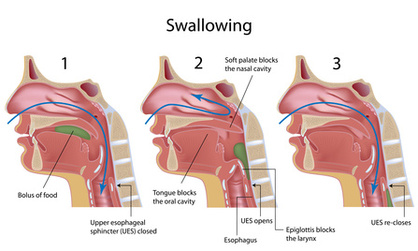
What closes over the trachea during swallowing?
Epiglottis
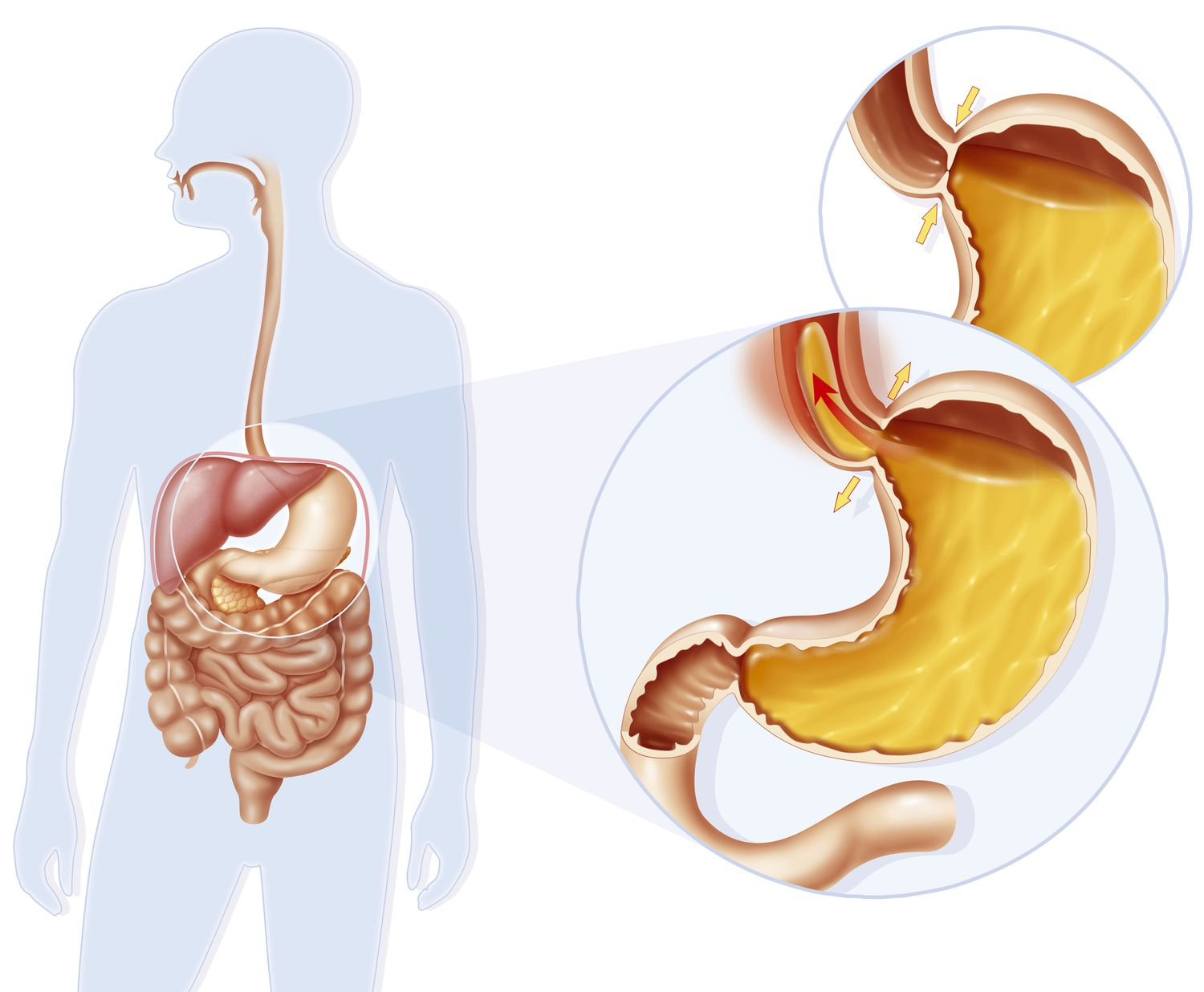
What is a sphincter?
A ring-shaped muscle that relaxes/tightens to open/close passages in the body.
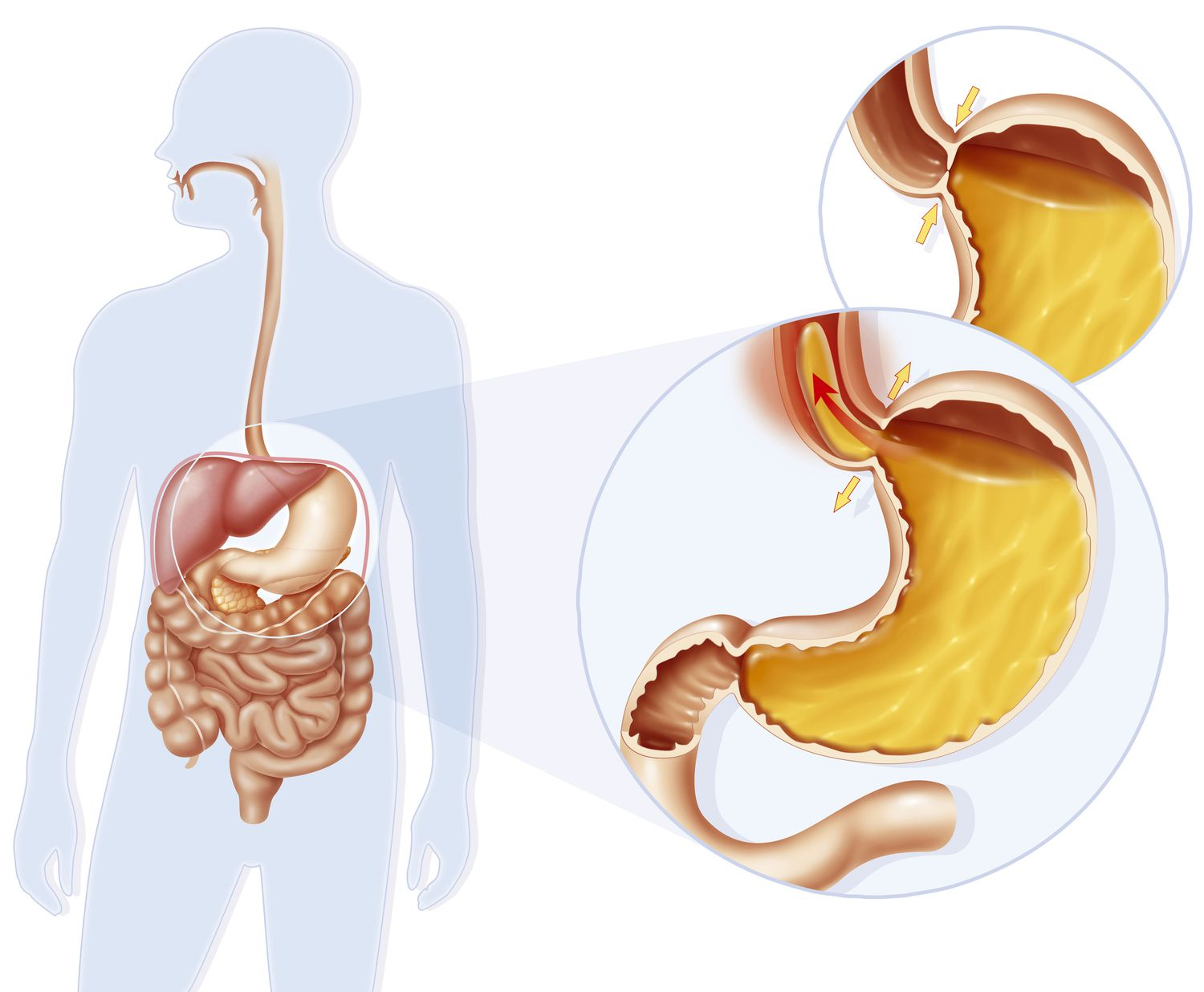
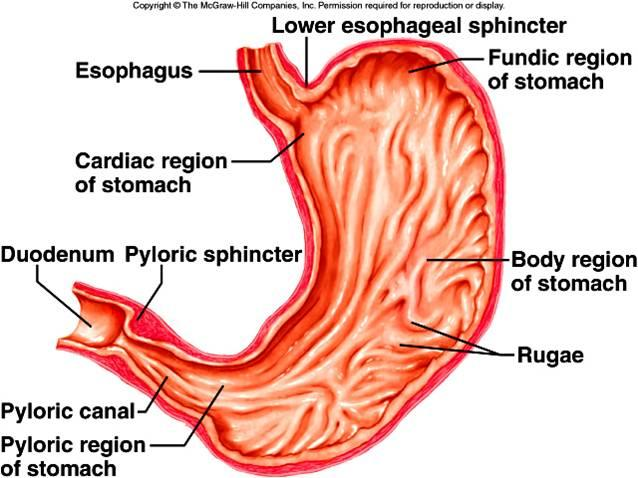
(T/F) The pyloric sphincter is located between the esophagus and stomach.
False. It is located between the duodenum and the stomach.
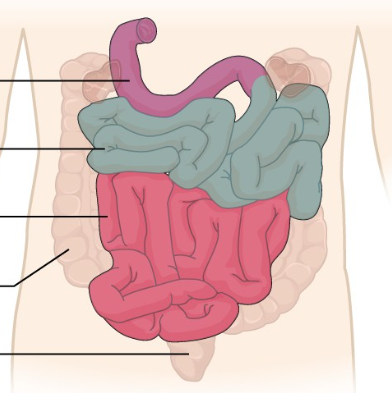
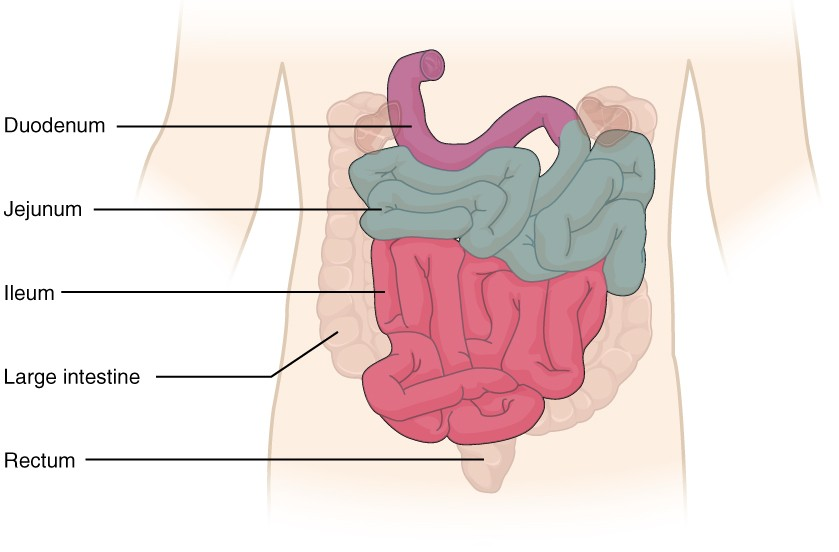
What is the purple region?
The duodenum.
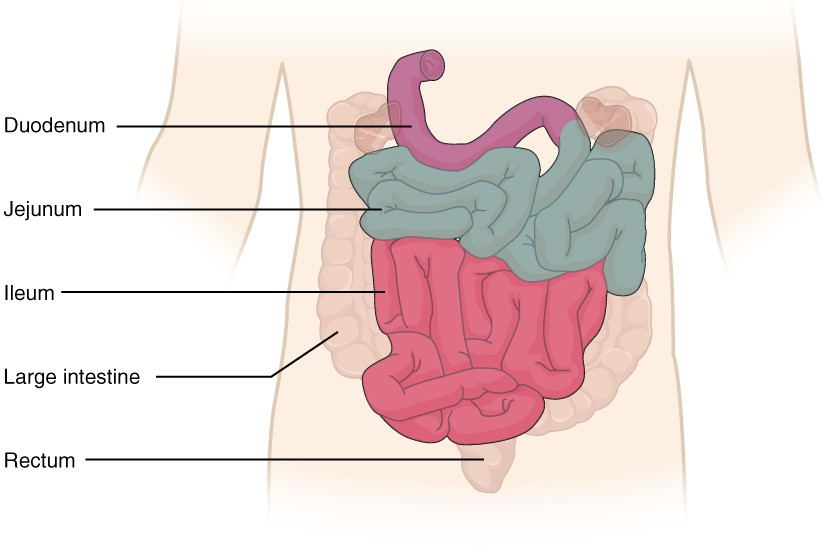
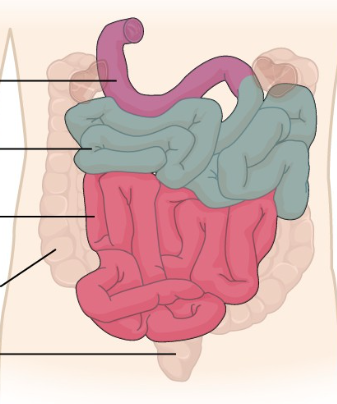
What is the blue region?
The jejunum
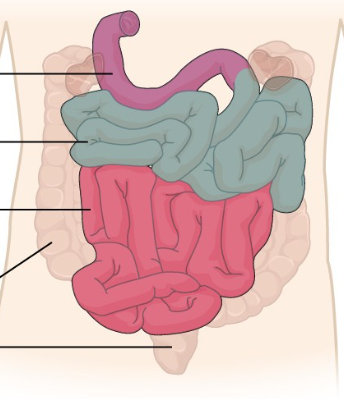
What is the pink region?
The Ileum
What do bacteria in the large intestine produce?
Vitamins B-12, K and amino acids
What are the 4 stages of digestion?
Ingestion, digestion, absorption, and egestion.
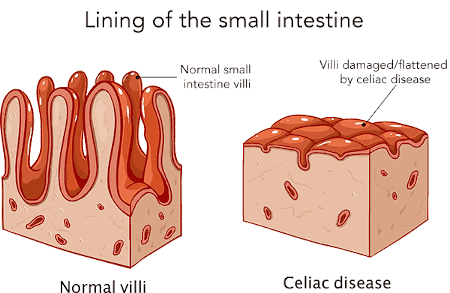
What is celiac?
A disorder in which the immune system attacks the body when gluten is ingested.
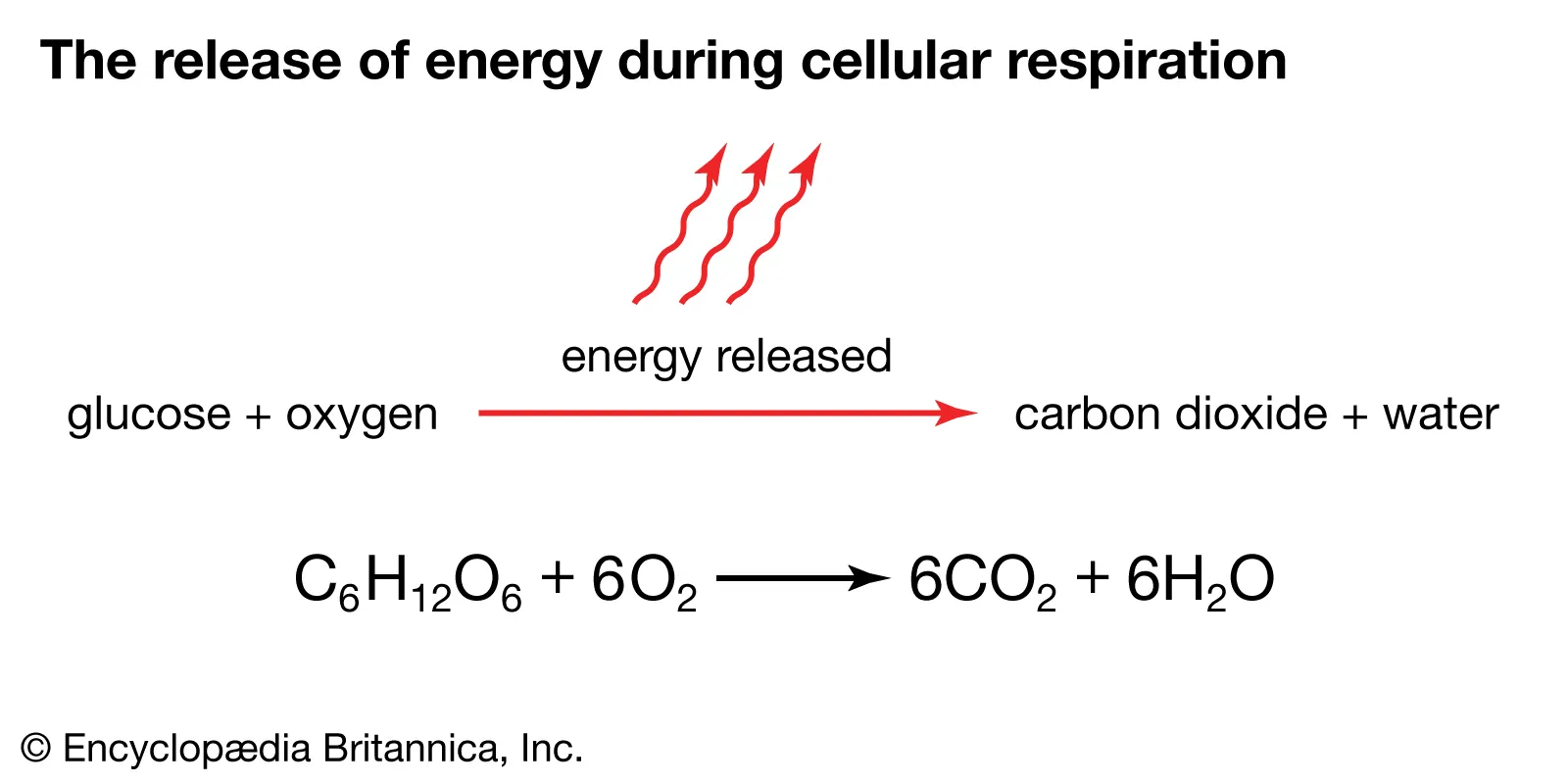
What is cellular respiration?
When oxygen reacts with glucose to fuel a cell.
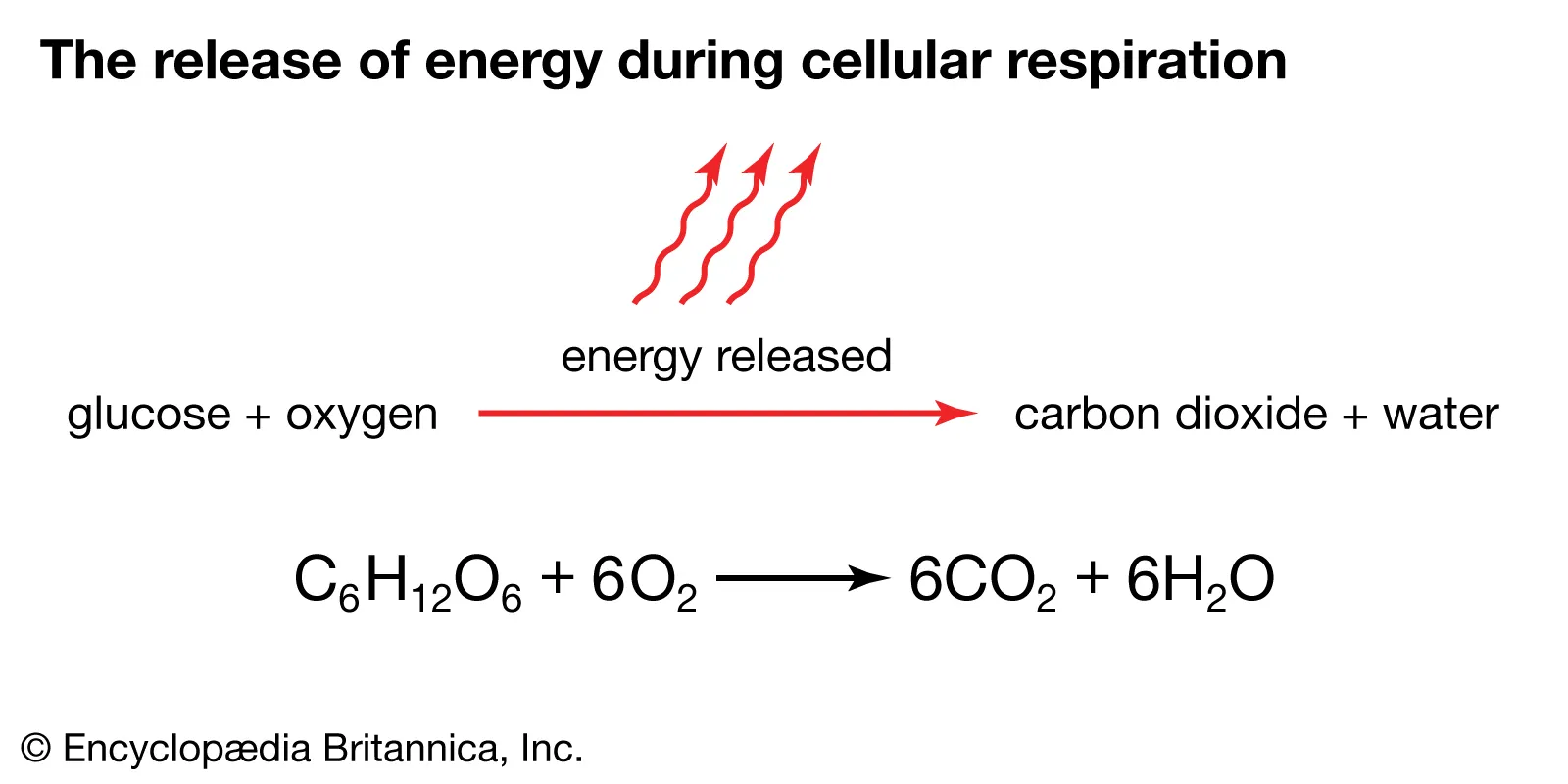
The balanced equation for cellular respiration.
C6H12O6 + 6O2 = 6CO2 + 6H2O