A&P Pratical 1 - UGA
1/336
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
337 Terms
posterior (dorsal)
describes the back or direction toward the back of the body
superior (cranial)
describes a position above or higher than another part of the body
inferior (caudal)
describes a position below or lower than another part of the body
lateral
describes the side or direction toward the side of the body
medial
describes the middle or direction toward the middle of the body
proximal
describes a position in a limb that is nearer to the point of attachment or the trunk of the body
distal
describes a position in a limb that is farther from the point of attachment or the trunk of the body
superficial
describes a position closer to the surface of the body
deep
describes a position farther from the surface of the body
contralateral
describes structures found on opposite sides of the body (right vs. left side)
ipsilateral
describes structures found on the same side of the body
midsagittal
divides the body or an organ vertically into right and left sides; vertical plane runs directly down the middle of the body
parasagittal
divides the body or an organ vertically into right and left sides; vertical plane divides the body into unequal right and left sides
frontal
divides the body or an organ into an anterior (front) portion and posterior (rear) portion
transverse
divides the body or organ horizontally into upper and lower portions
oblique
diagonal section between longitudinal and horizontal and can produce uneven sections
cranial and vertebral
Cavities found in the dorsal body cavity:
thoracic and abdominopelvic
Two cavities that make up the ventral cavity
right hypochondriac region
right lateral region of the abdomen just below the ribs
epigastric region
abdomen region located about the stomach; top middle
left hypochondriac region
left upper region of abdomen below the rib cartilage
right lumbar region
right middle region near the waist
umbilical region
The centermost region, which includes the umbilicus
left lumbar region
left middle region near the waist
Right iliac Region
bottom right region above the pelvis
hypogastric region
inferior to the umbilical region
left iliac region
bottom left region above the pelvis
atom
simplest building block of matter made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons
molecule
two or more atoms combines; chemical building blocks of all body strucutures
cell
the smallest independently functioning unit of a living organism
tissue
a group of multiple similar cells that work together to perform a specific function
organ
an anatomically distinct structure of the body composed of two or ore tissue types that performs one or more specific functions
organ system
a group of organs that work together to perform major functions to meet physiological needs of the body
superior
The eyes are __________ to the mouth.
posterior
The spinal column is ___________ to the sternum
anterior
The toes are found on the __________ portion of the foot.
inferior
The pelvis is _________ to the abdomen
lateral
The thumb is _______ to the other digits
medial
The big toe is the most _________ toe.
proximal
The upper arm is _________ to the wrist
distal
The foot is _______ to the thigh
superficial
The skin is ____________ to the bones.
deep
The brain is _________ to the skull
contralateral
The right foot is _________________ to the left arm.
ipsilateral
The right hand and right shoulder are ________________
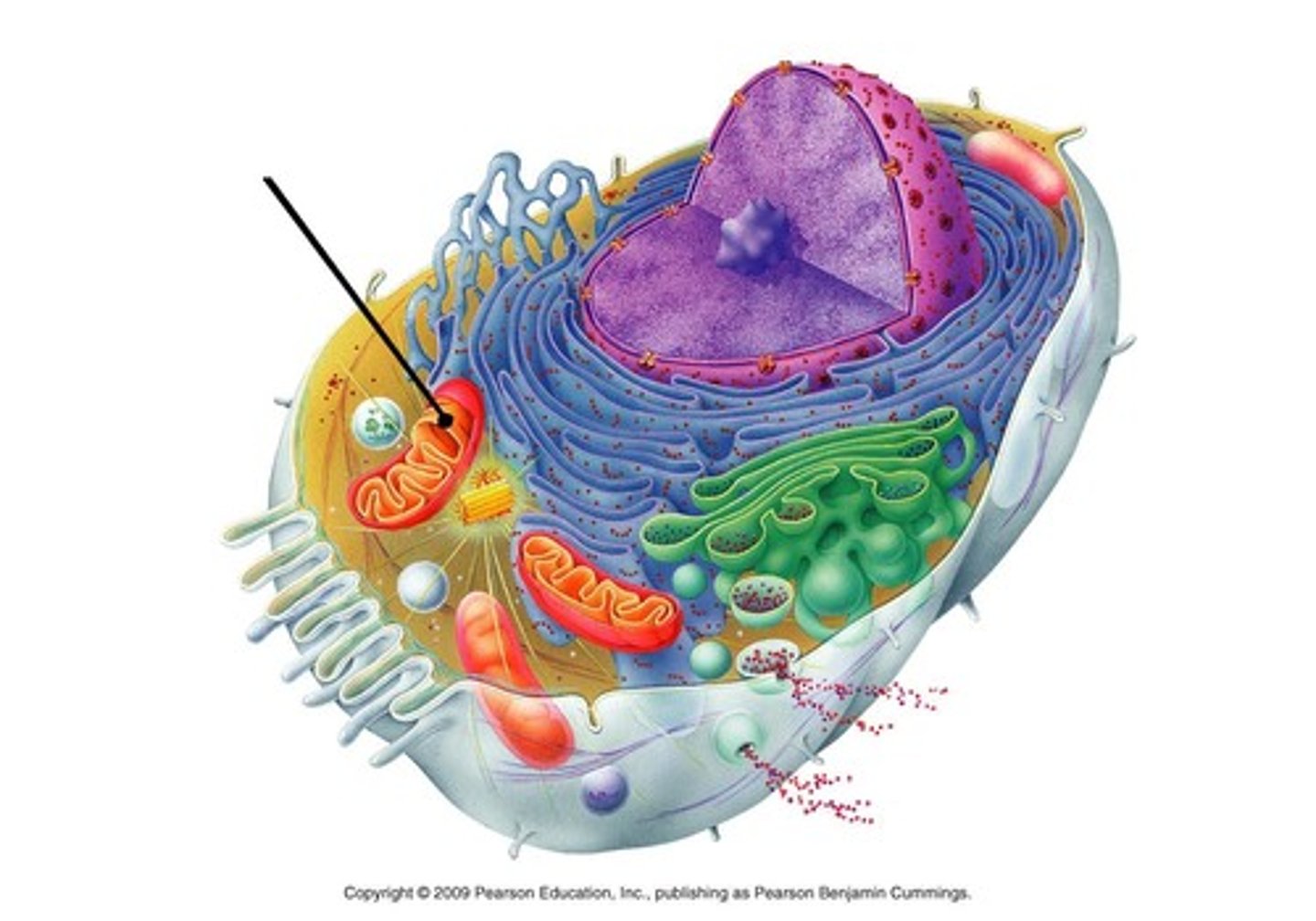
mitochondria
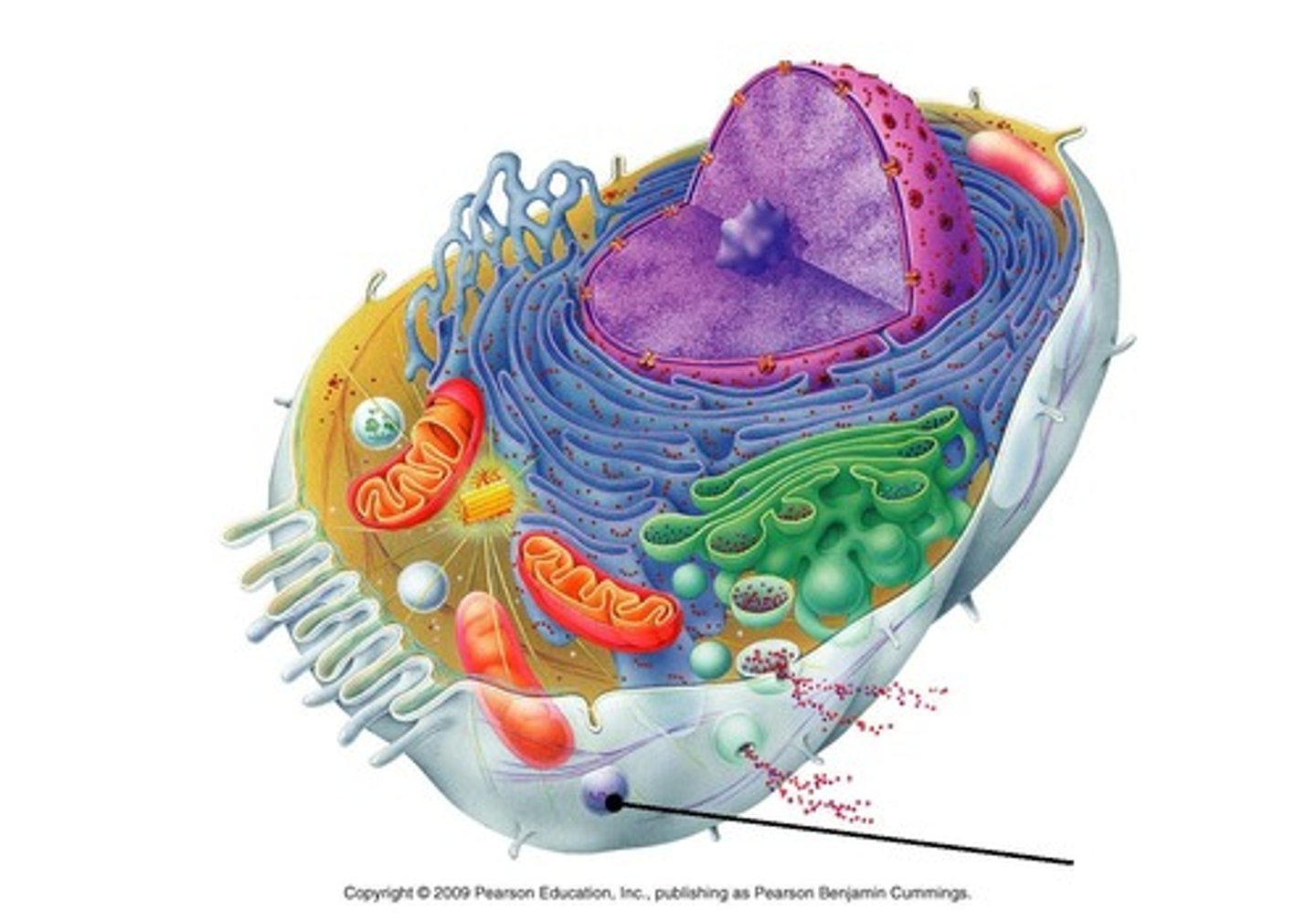
peroxisome
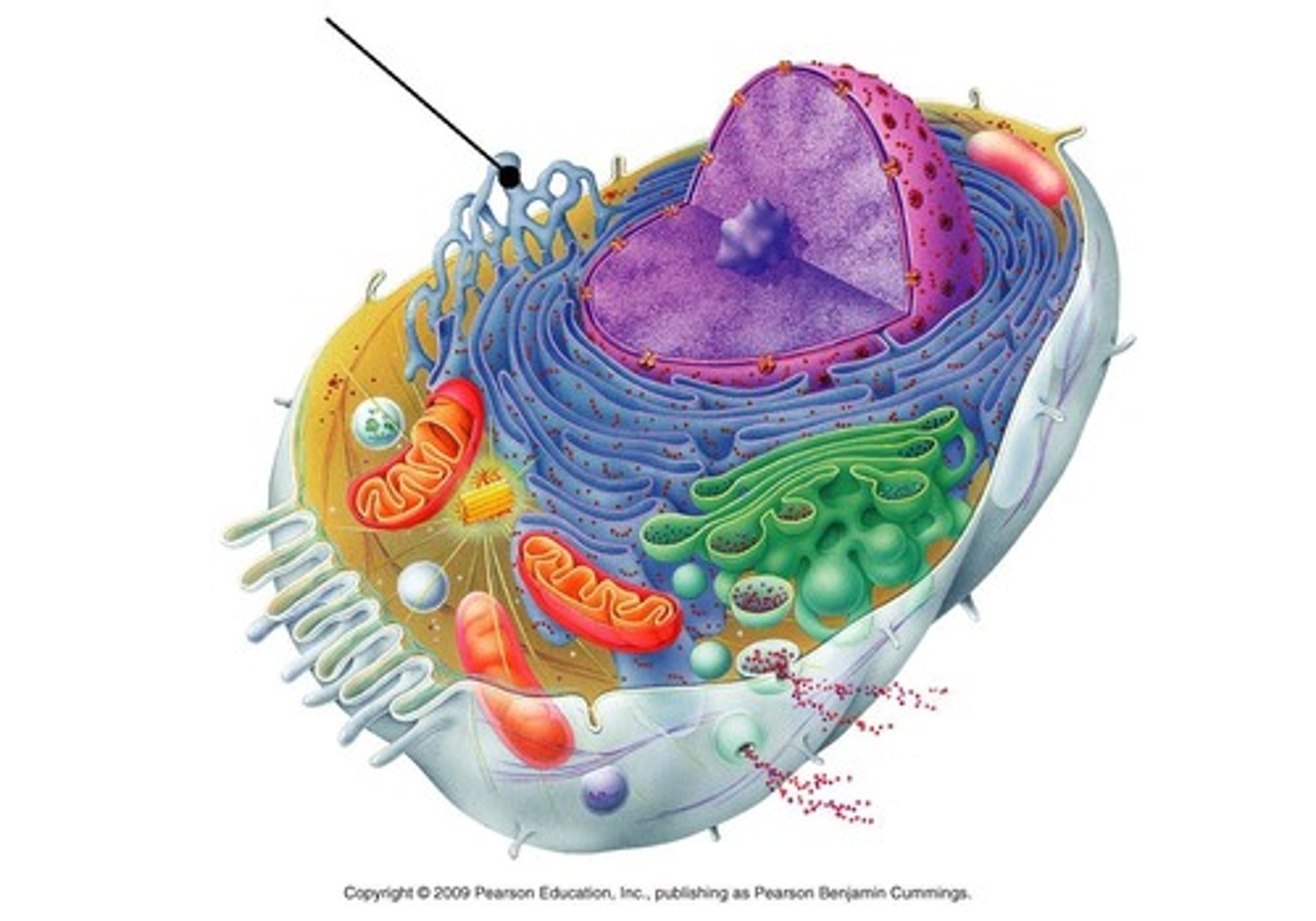
smooth ER
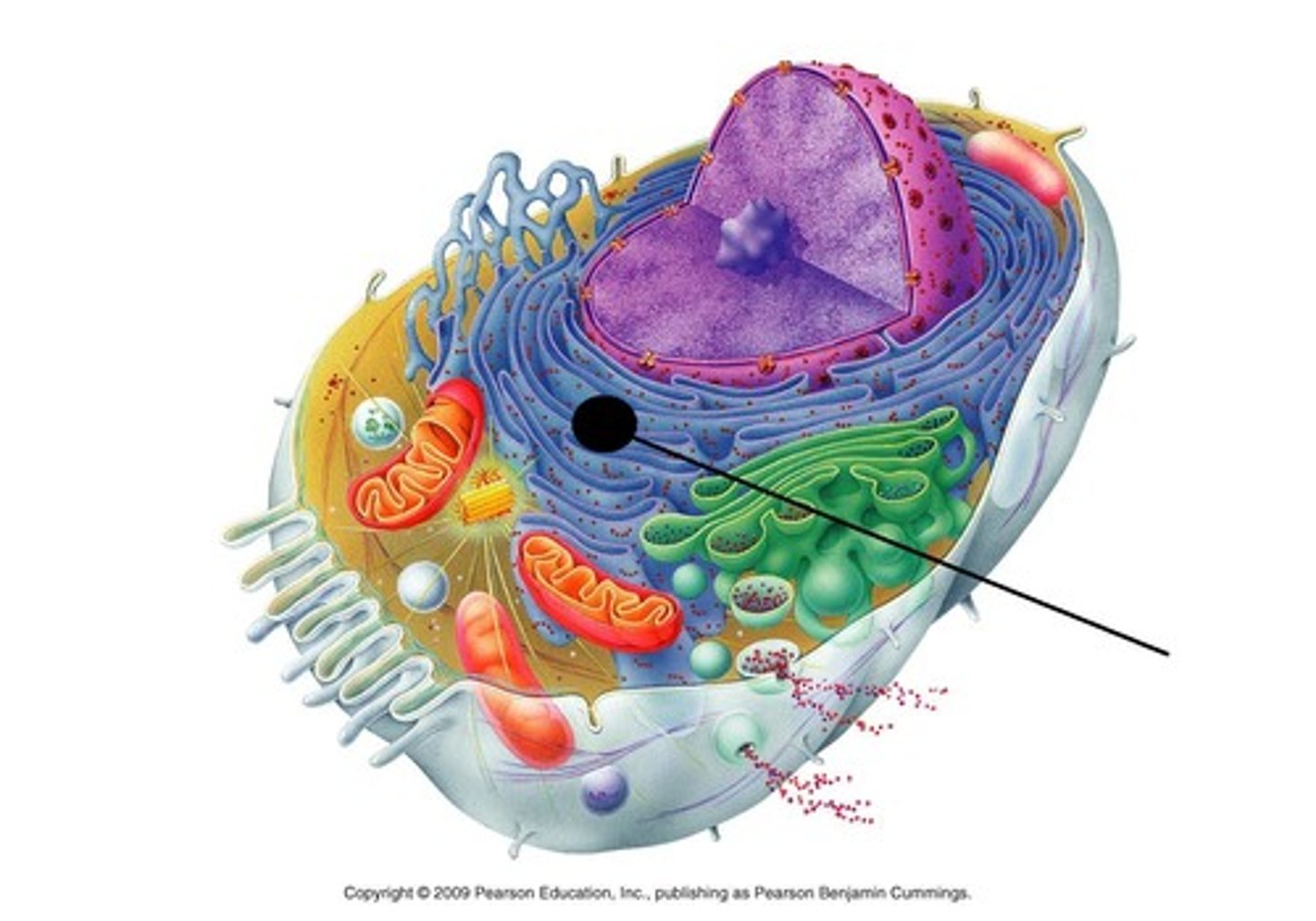
lysosome
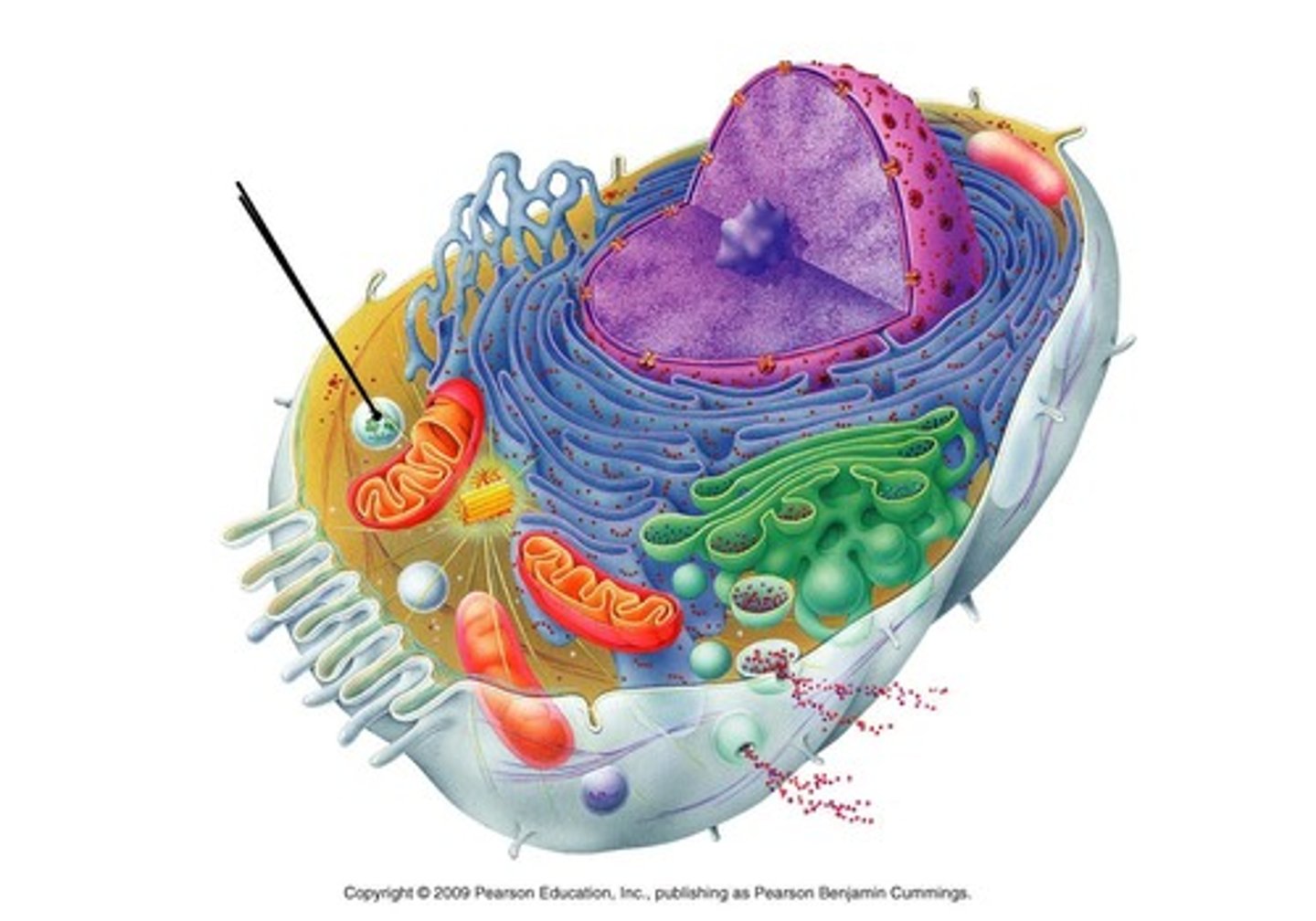
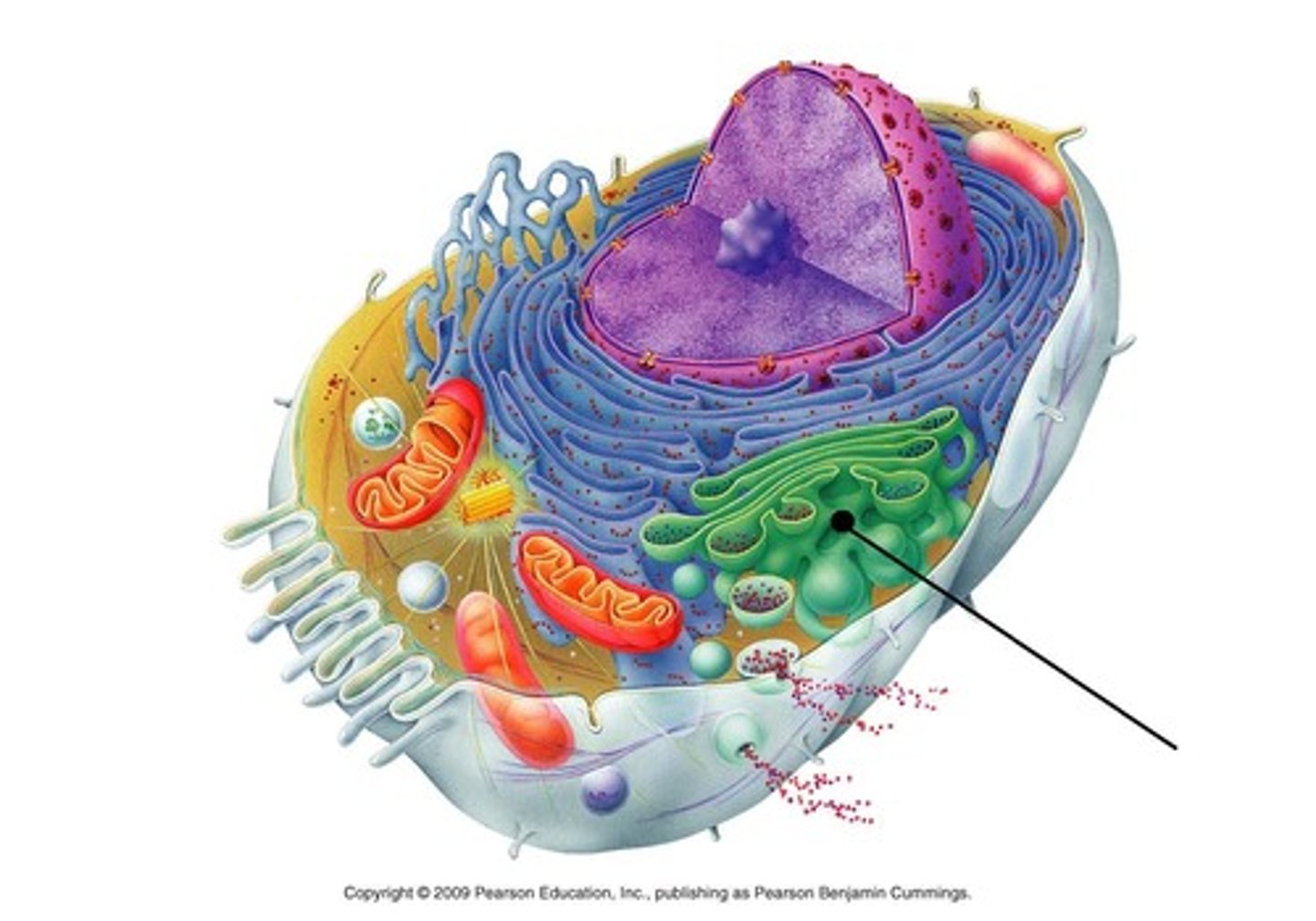
Golgi apparatus
nucleus
rough ER
ribosome
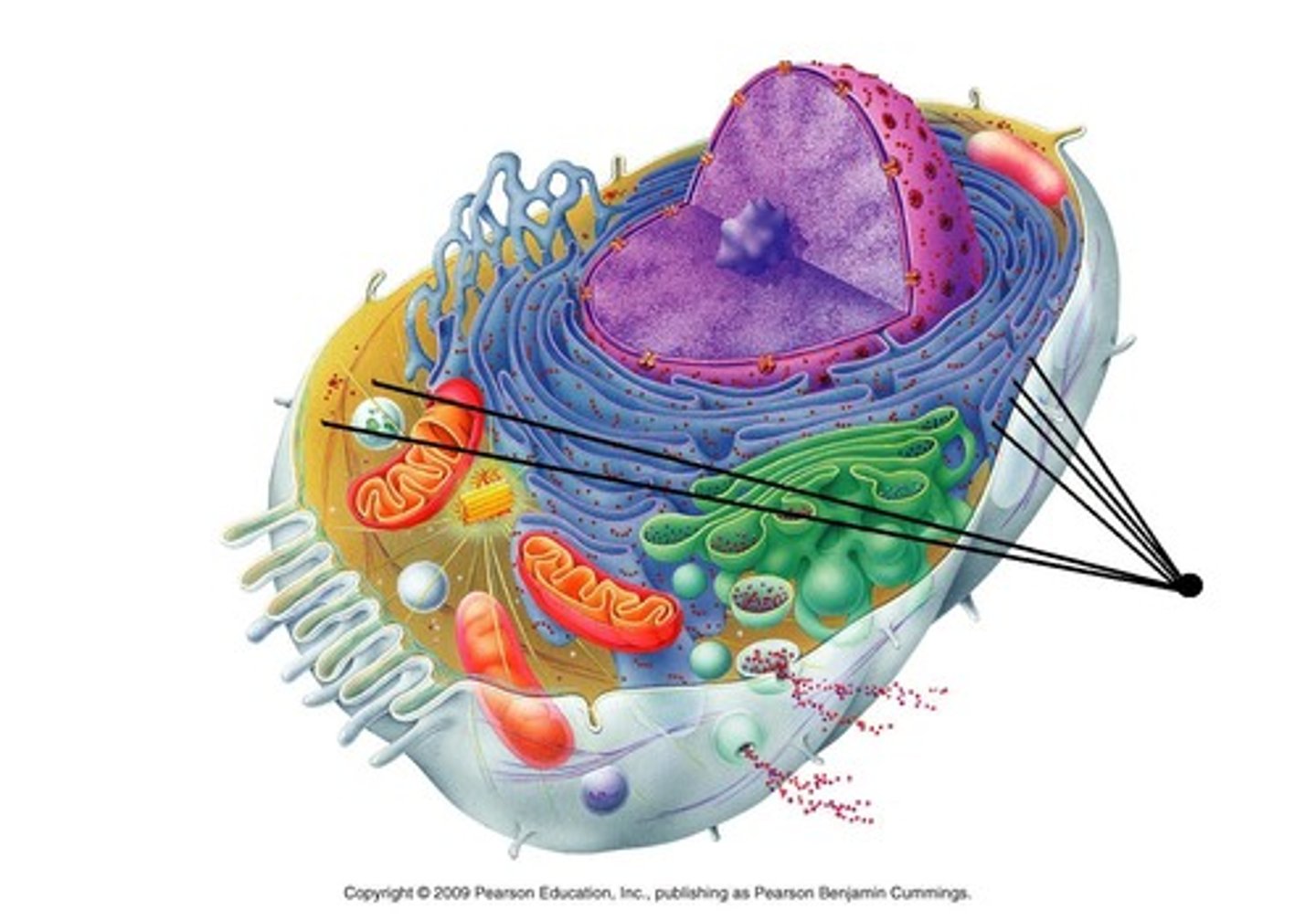
Mitochondria
Converts energy storage molecules into the major energy molecule, ATP, to power cellular function
peroxisome
Contains enzymes key for lipid metabolism and chemical detoxification
Smooth ER
lipid synthesis
lysosome
Contains digestive enzymes to break down materials
Golgi apparatus function
Sorts, modifies, and ships products from the endoplasmic reticulum
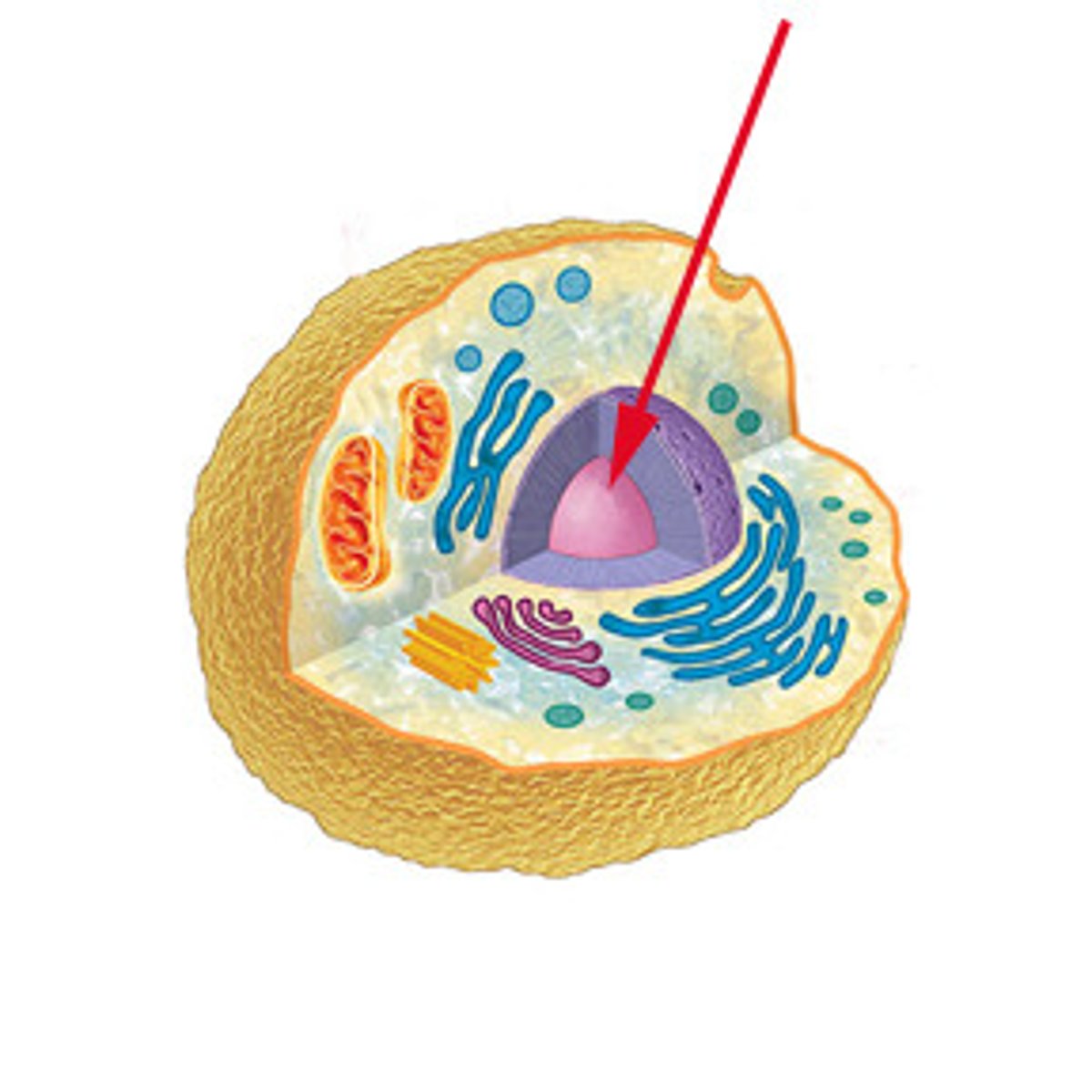
nucleus
Contains the cell's DNA and directs cellular functions.
Rough ER
includes ribosomes for the synthesis and modification of proteins
Ribosome
protein synthesis
G1 phase
the first gap, or growth, phase in the cell cycle and is the phase that varies the most in terms of duration; maybe couple hours or many days
S phase
replication of DNA; 8-10 hours
G2 phase
second phase, during which the cell continues to grow and makes the necessary preparations for mitosis; ~5 hours
prophase
-chromosomes condense and become visible
-spindle fibers emerge from the centrosomes
-nuclear envelope breaks down
-centrosomes move toward opposite poles
prophase
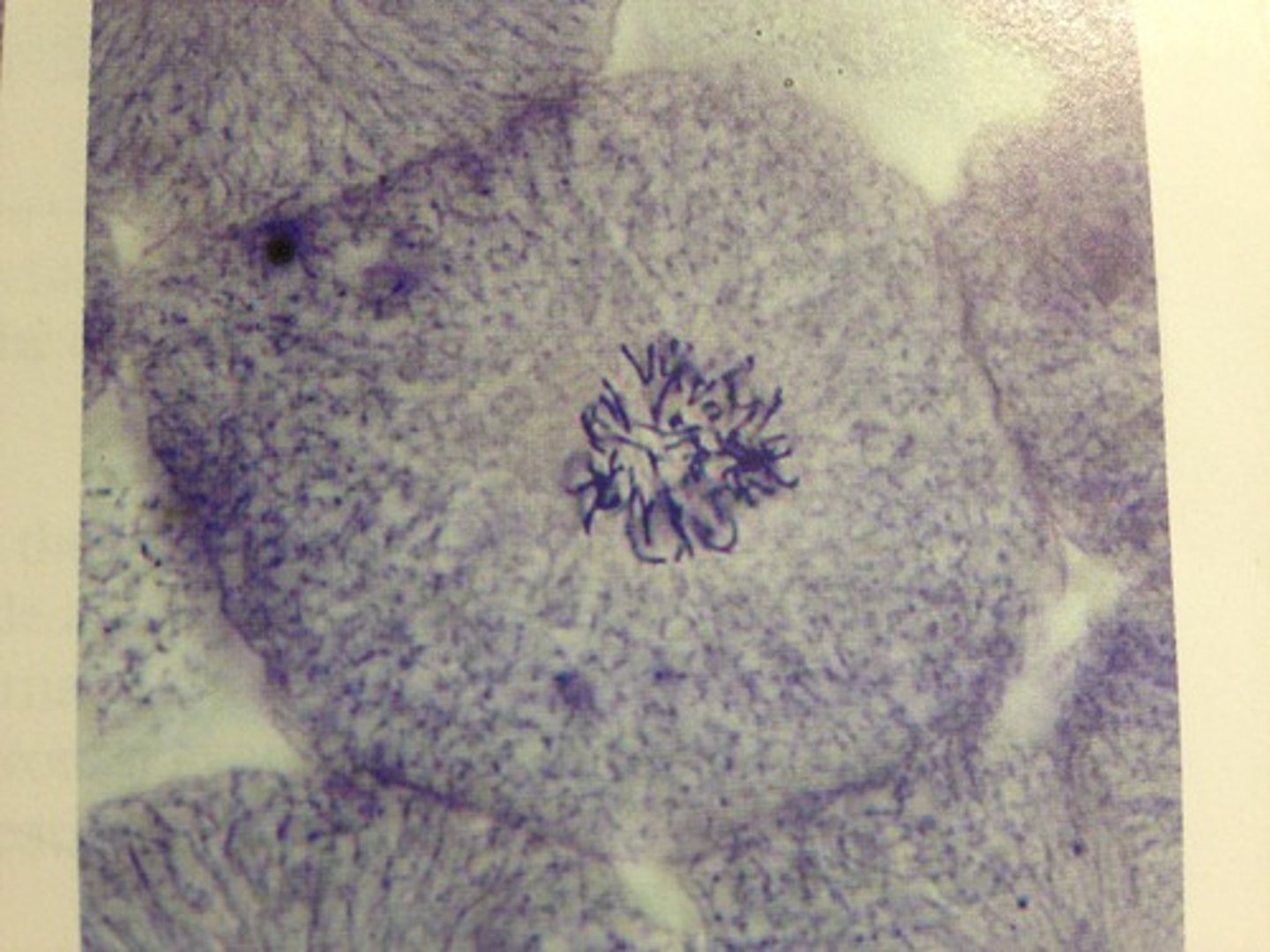
prometaphase
-chromosomes continue to condense
-kinetochores appear at the centromeres
-mitotic spindle microtubules attach to kinetochores
prometaphase
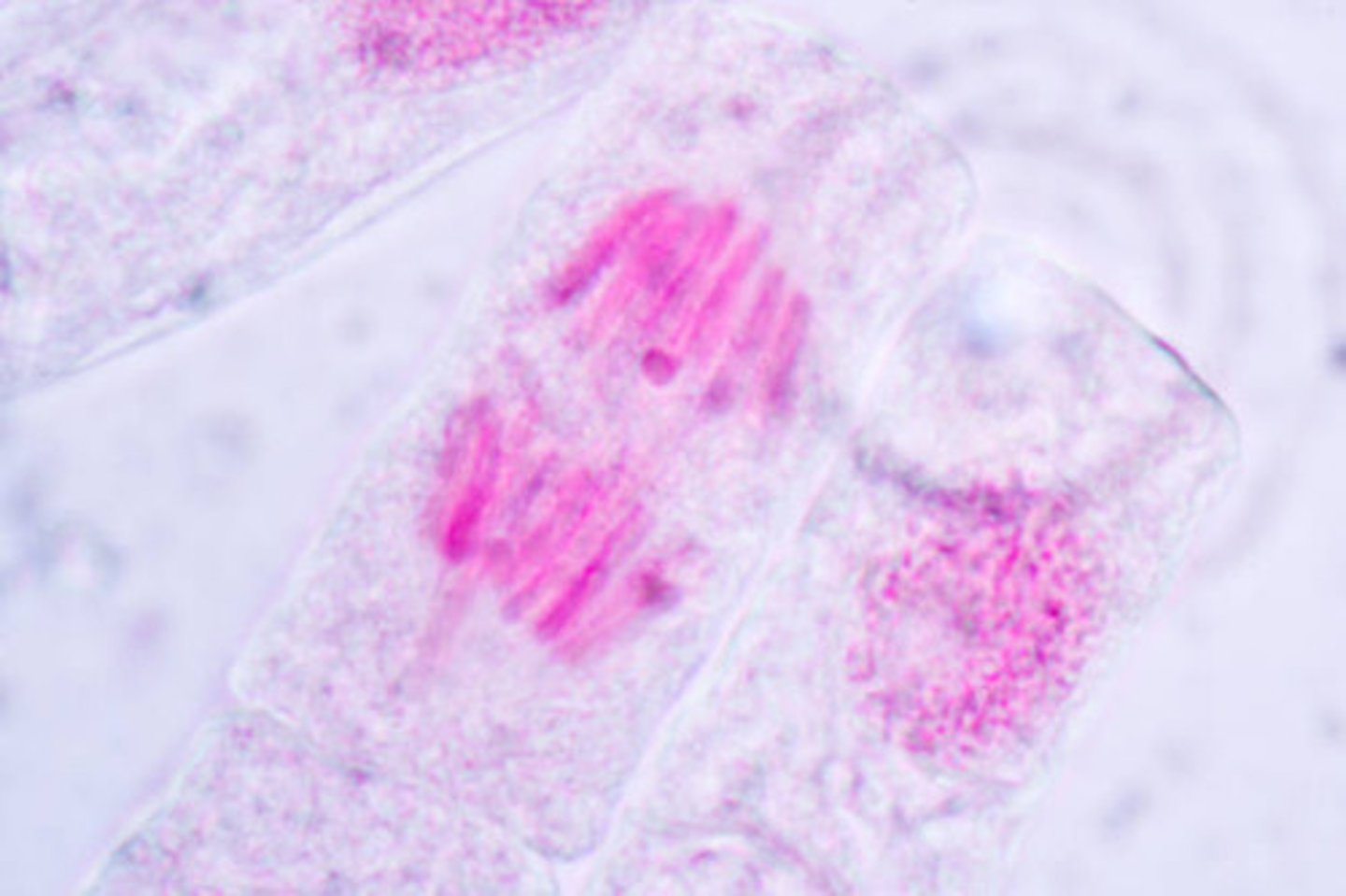
metaphase
-chromosomes are lined up at the metaphase plate
-each sister chromatid is attached to a spindle fiber originating from opposite poles
metaphase
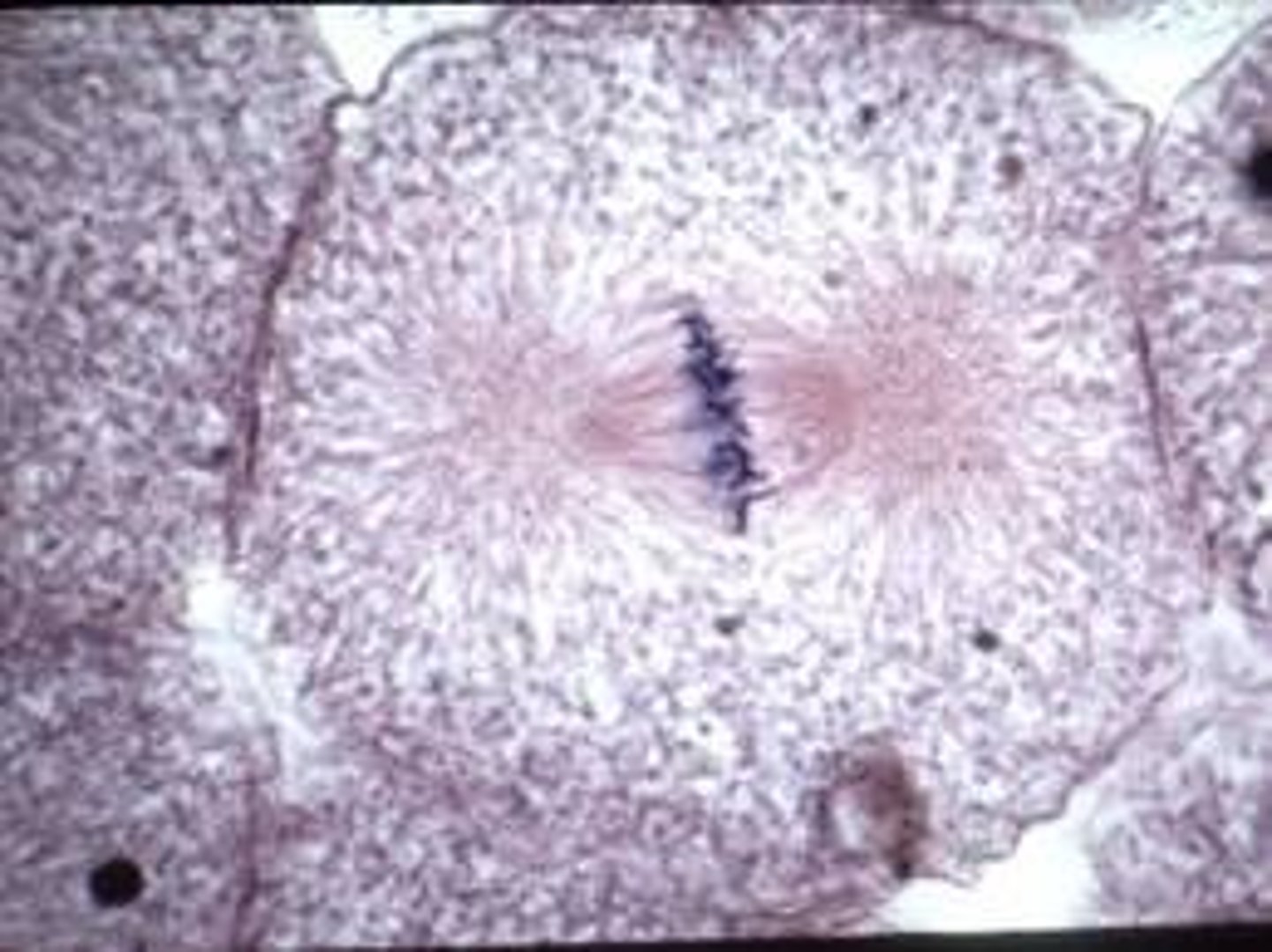
anaphase
-centromeres split into two
-sister chromatids (now called chromosomes) are pulled toward opposite poles
-certain spindle fibers begin to elongate cell
anaphase
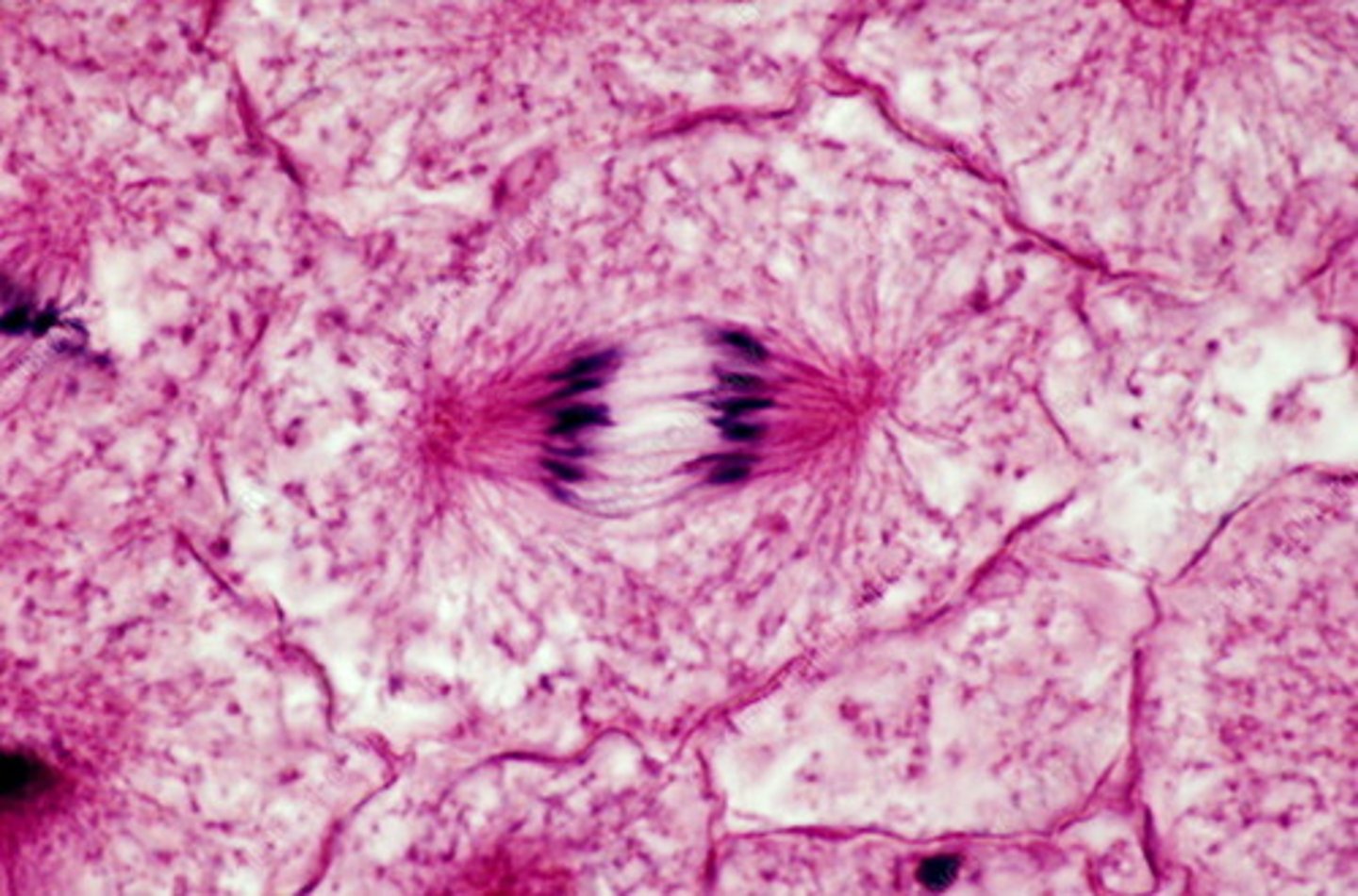
telophase
-chromosomes arrive at opposite poles and begin to decondense
-nuclear envelope material surrounds each set of chromosomes
-the mitotic spindle breaks down
-spindle fibers continue to push poles apart
telophase
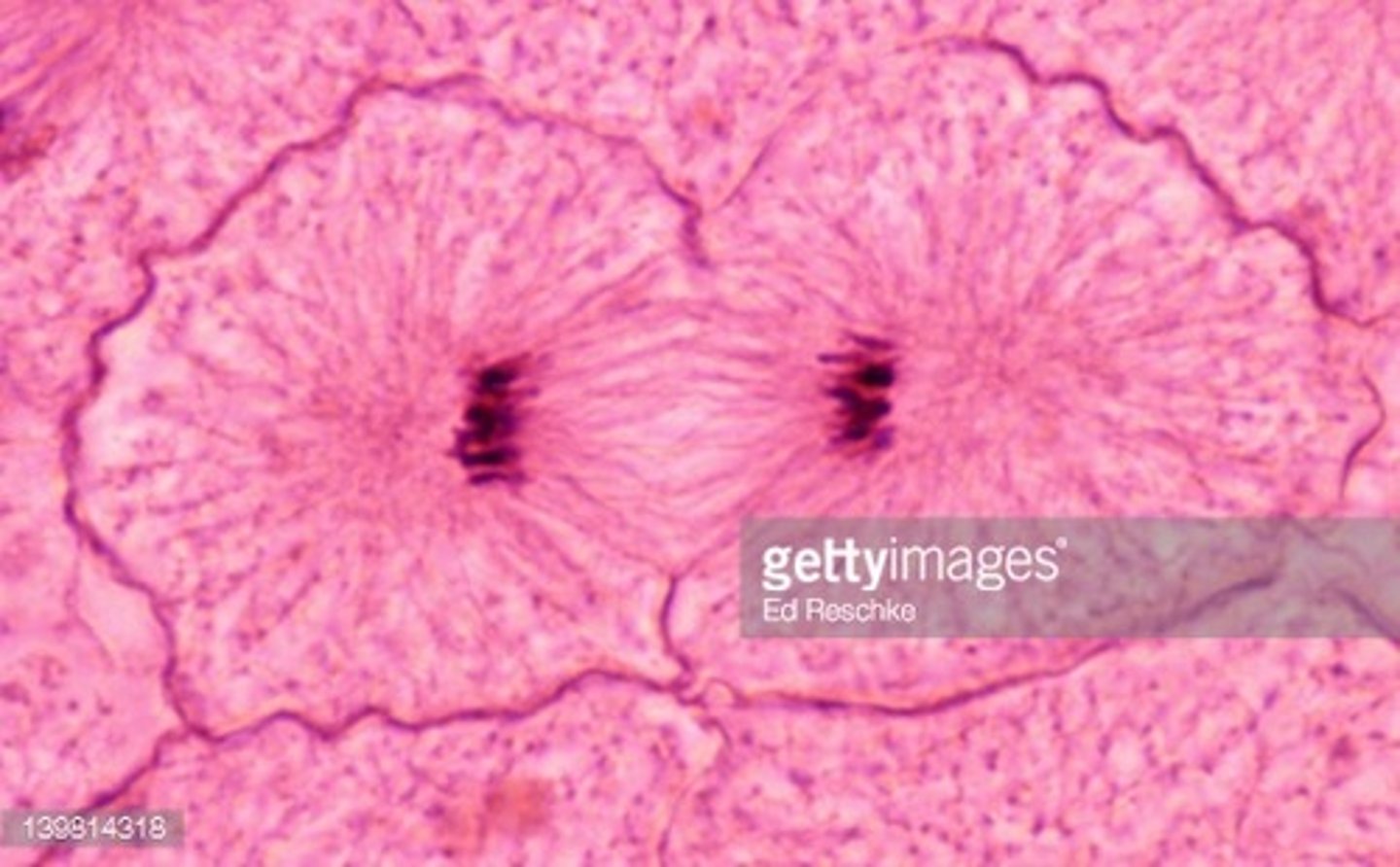
cytokinesis
-animal cells: a cleavage furrow separates the daughter cells
-plant cells: a cell plate, the precursor to a new cell wall, separates the daughter cells
cytokinesis
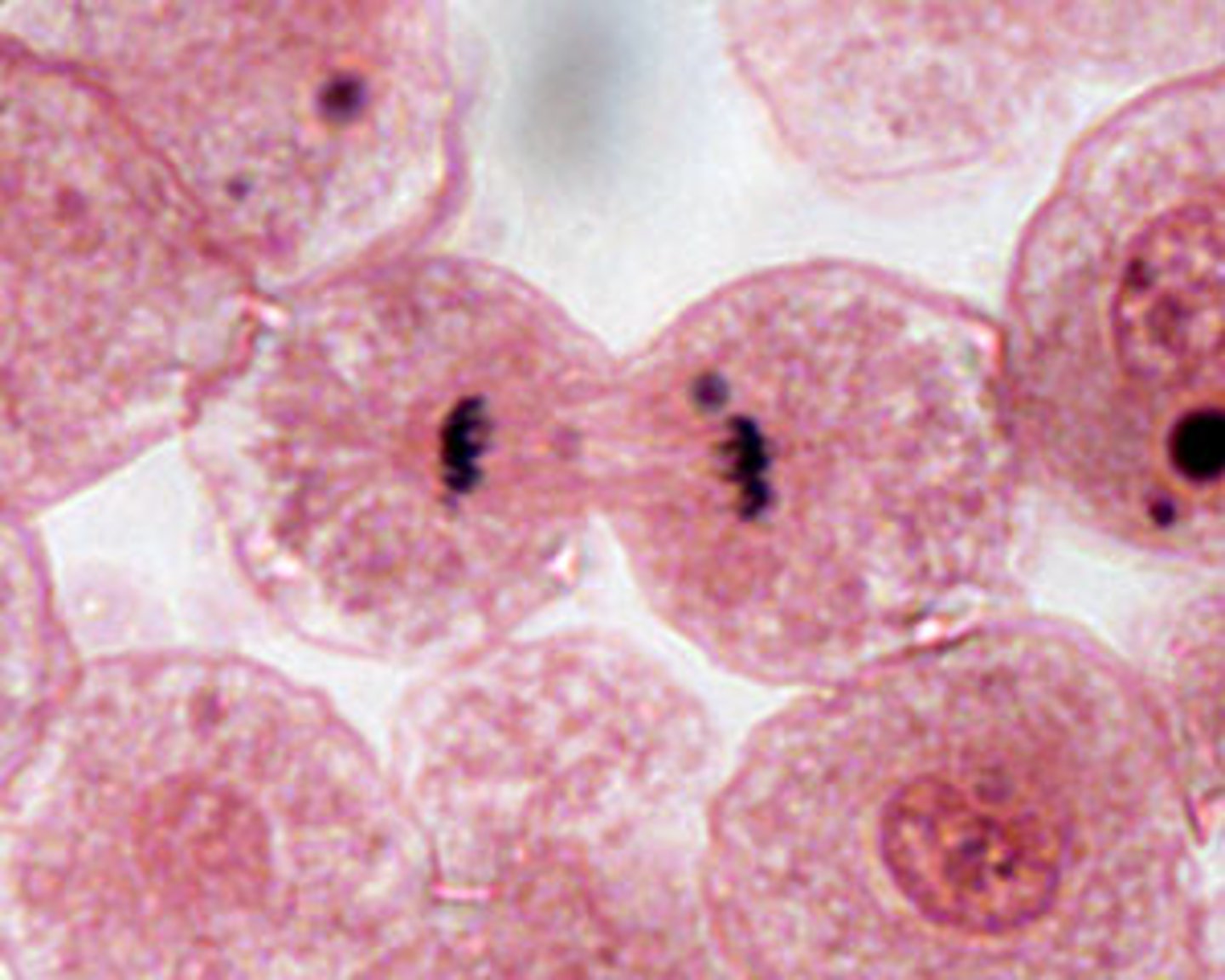
anaphase
sister chromatids are pulled to opposite poles
metaphase
sister chromatids line up at middle of cell
telophase
chromosomes de-condense and nuclear envelopes reform
cytokinesis
cleavage furrow separates daughter cells
interphase
significant cell growth to prepare for mitosis
interphase
replication of DNA
prophase
condensation of chromosomes
interphase
cells are not dividing
connective, muscle, nervous, epithelial
What are the 4 types of tissue?
epithelial
covers all exterior surfaces of the body
nervous
communication tissue
connective
support and protection tissue
connective
tissue that binds cell and organs together
epithelial
tissue that forms glands
muscle
tissue for movement
simple squamous epithelium
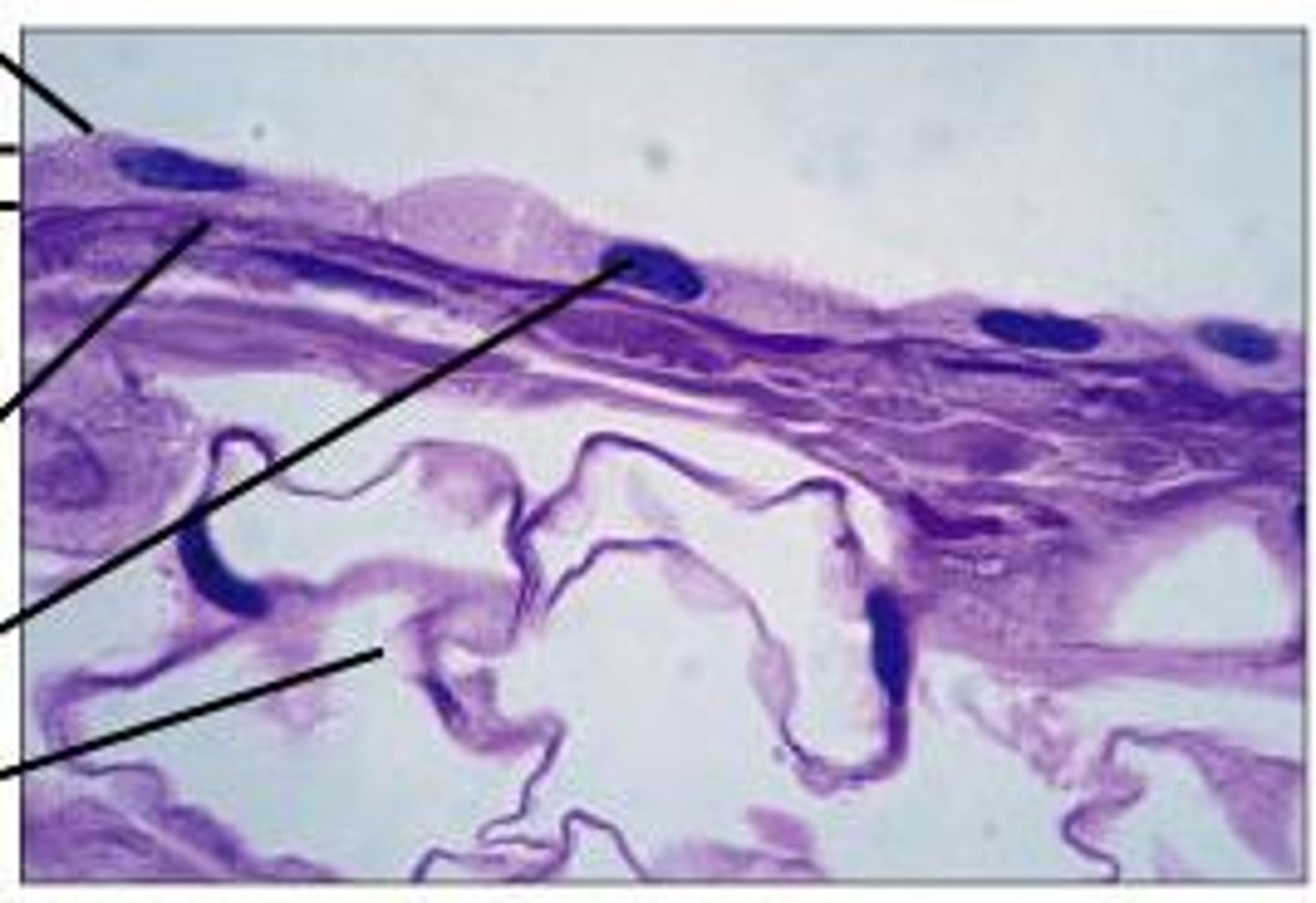
simple columnar epithelium
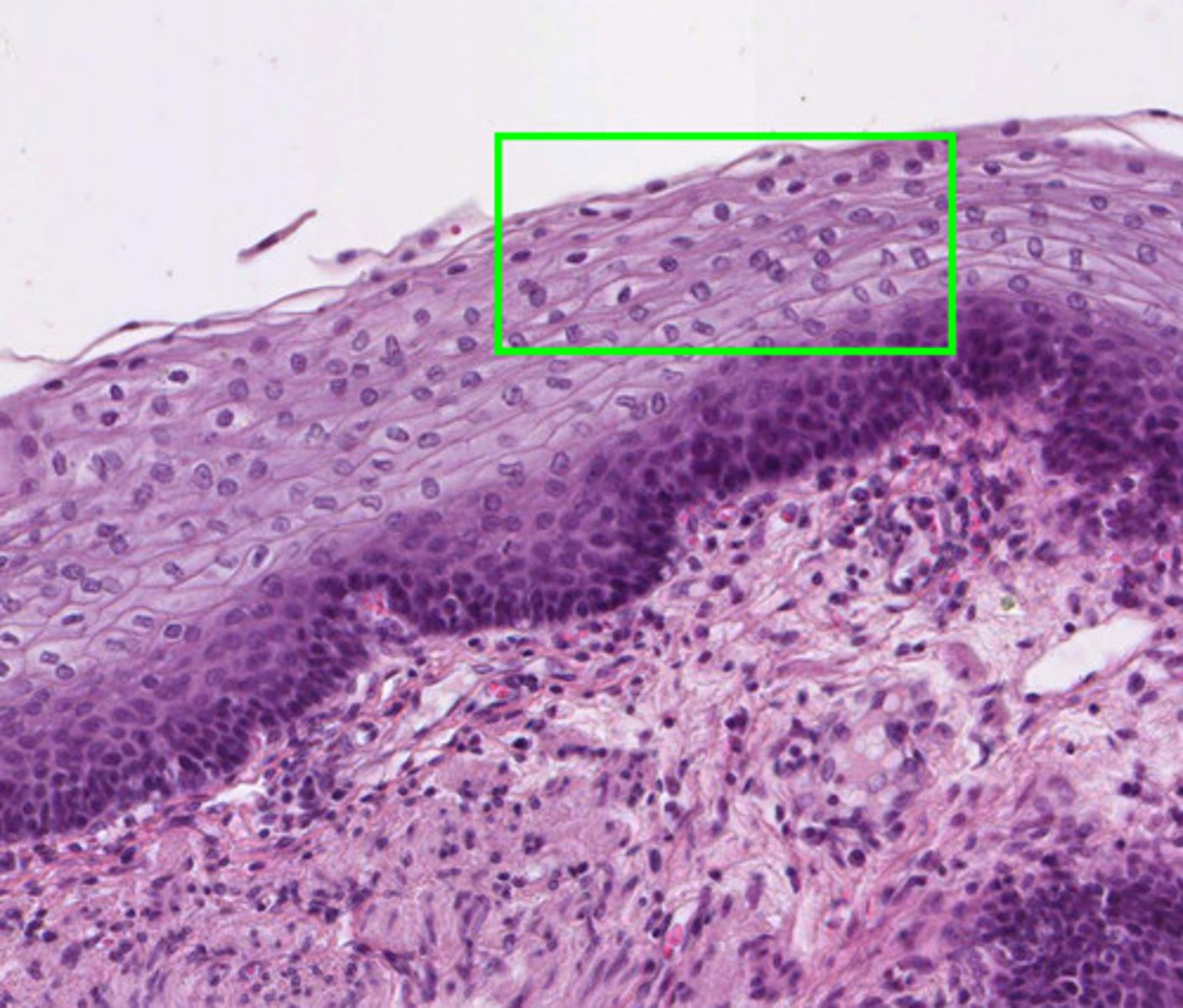
non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
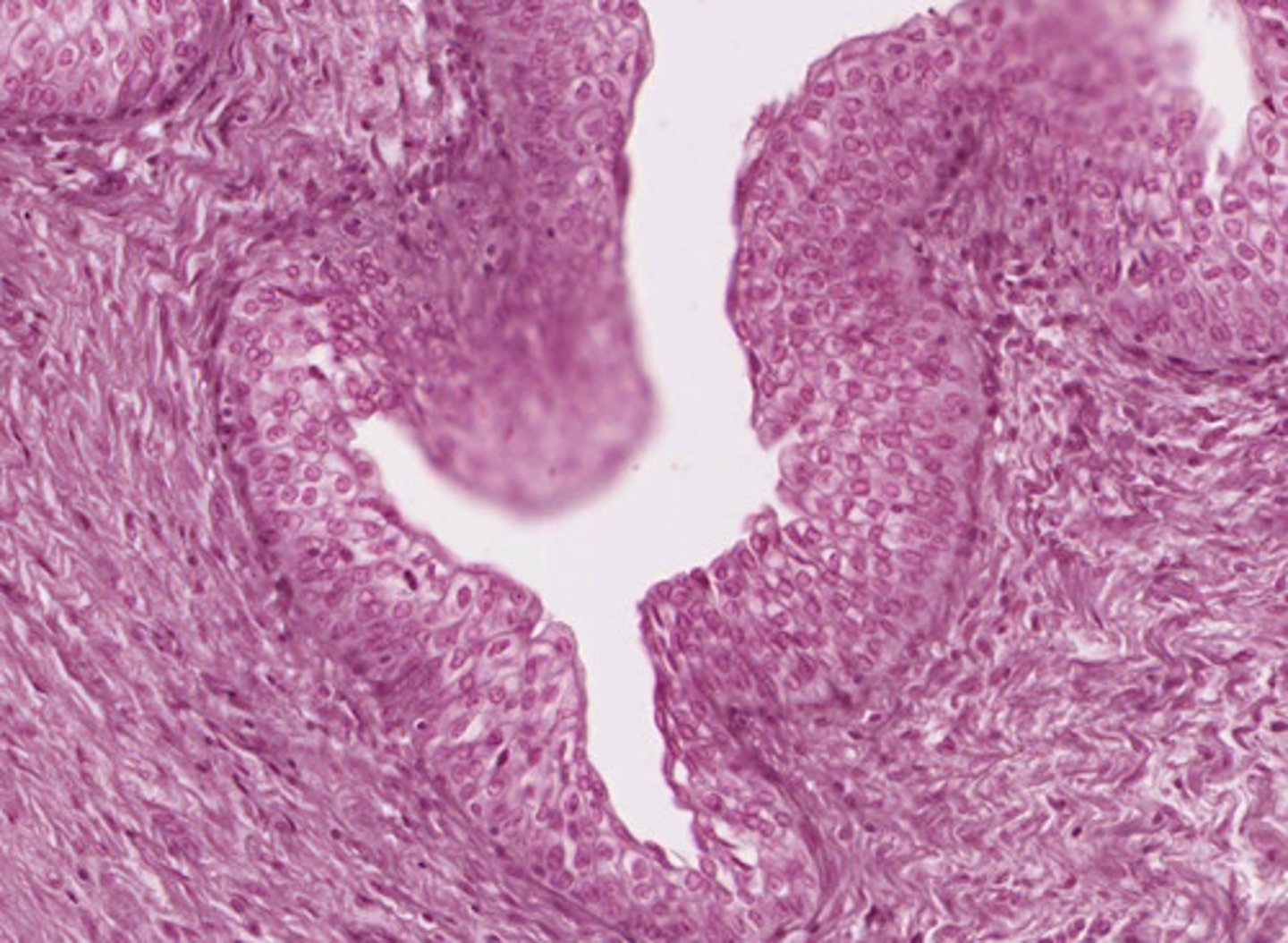
transitional epithelium, non-distended
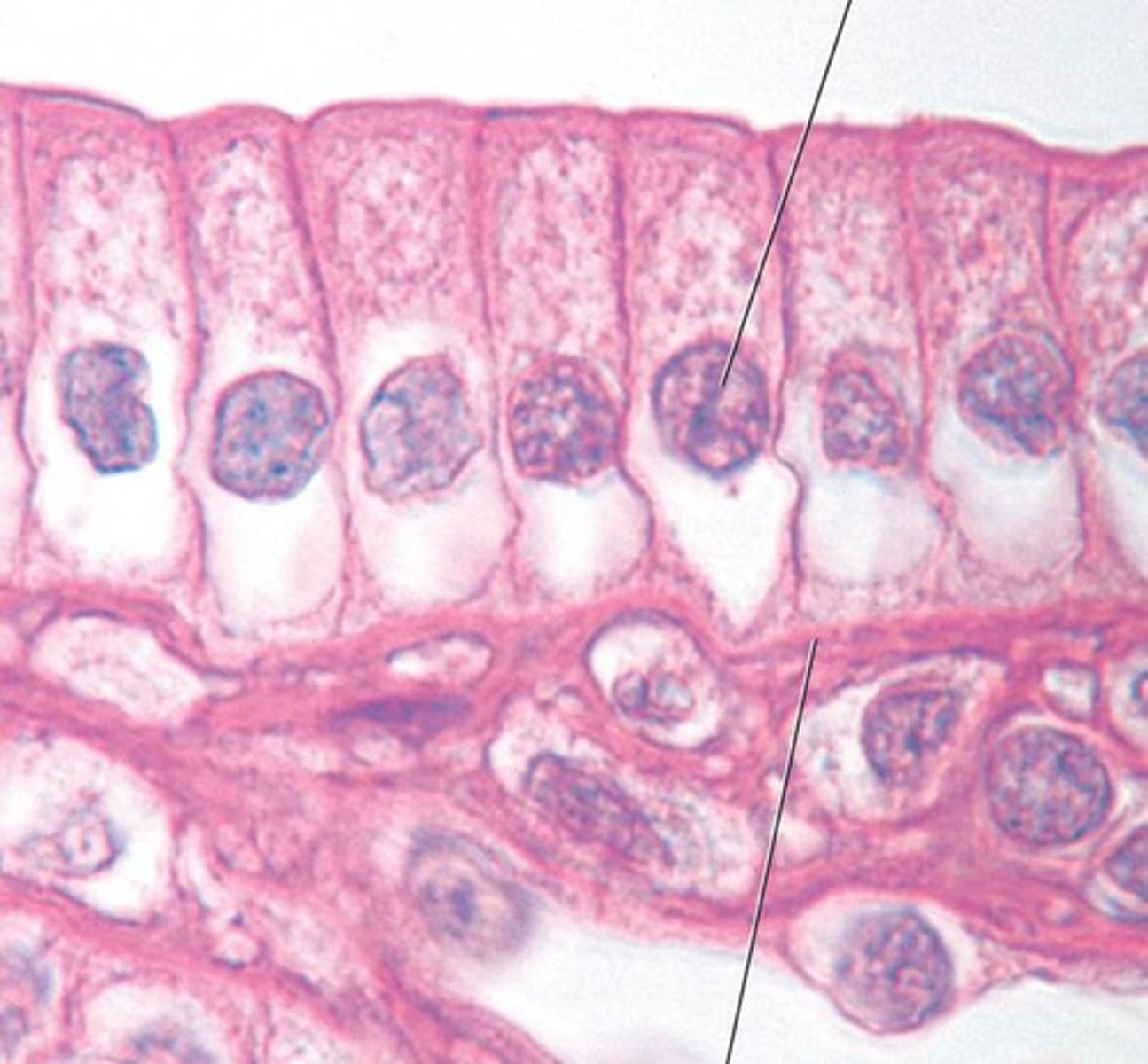
simple cuboidal epithelium
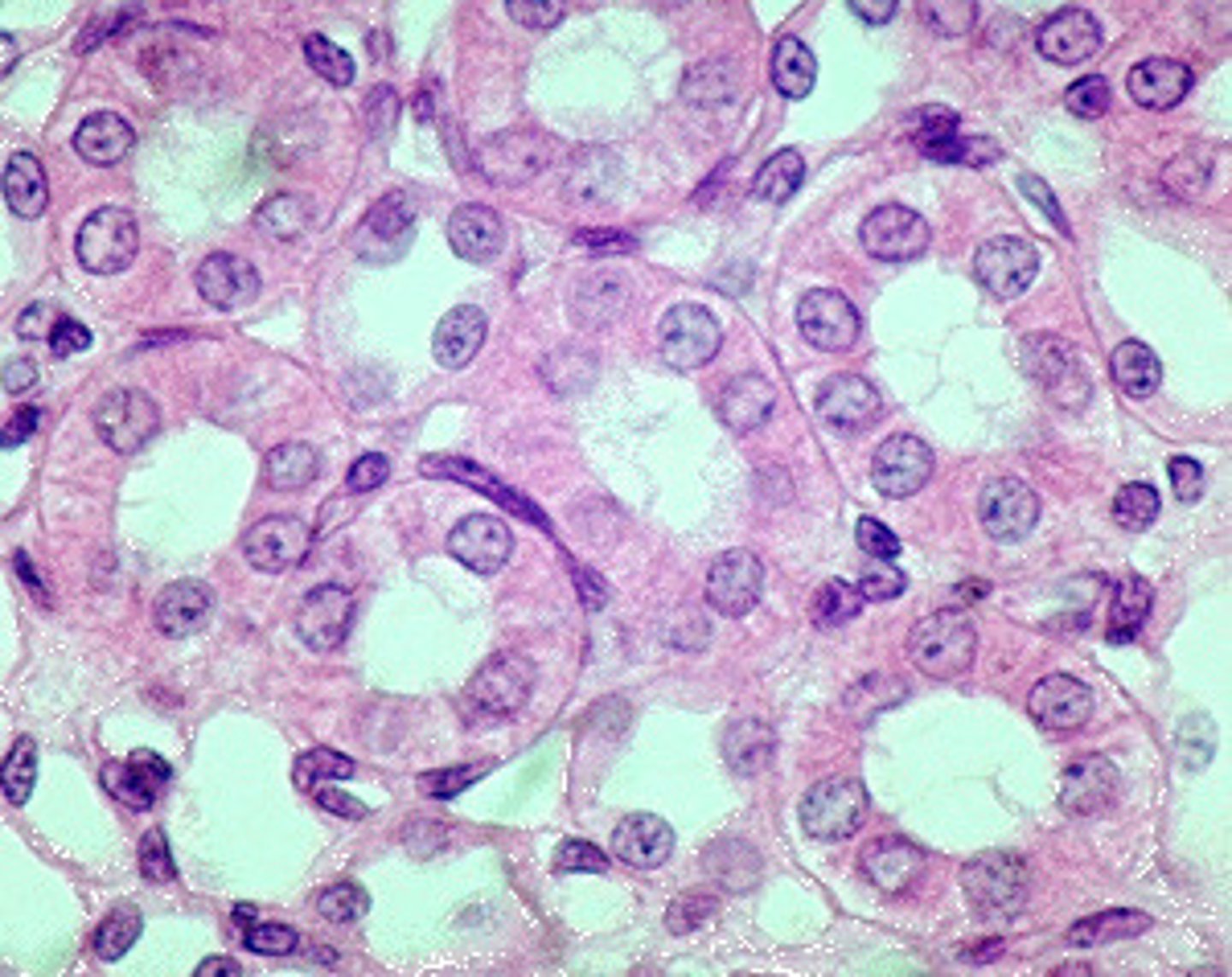
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
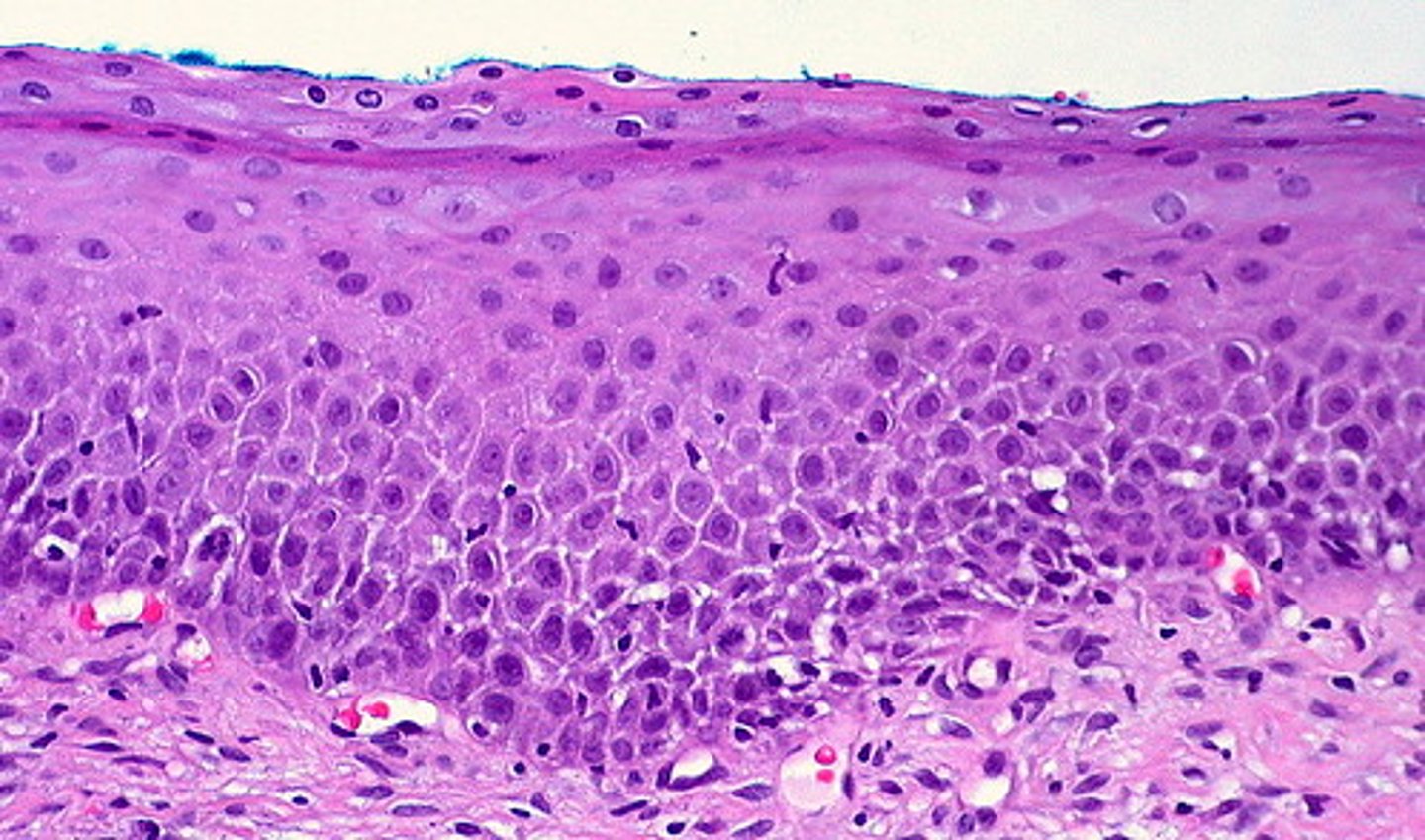
pseudostratified epithelium
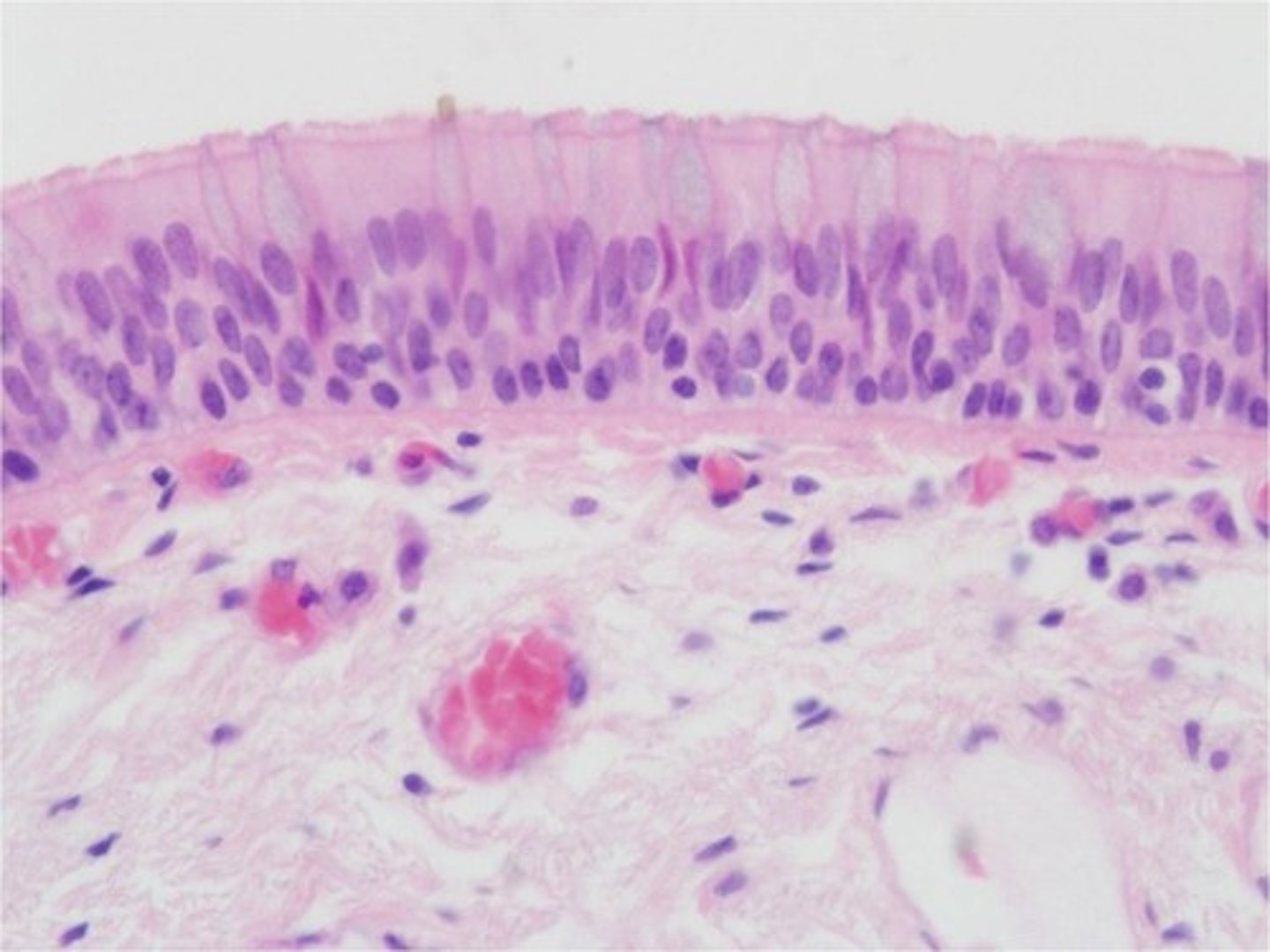
transitional epithelium, distended
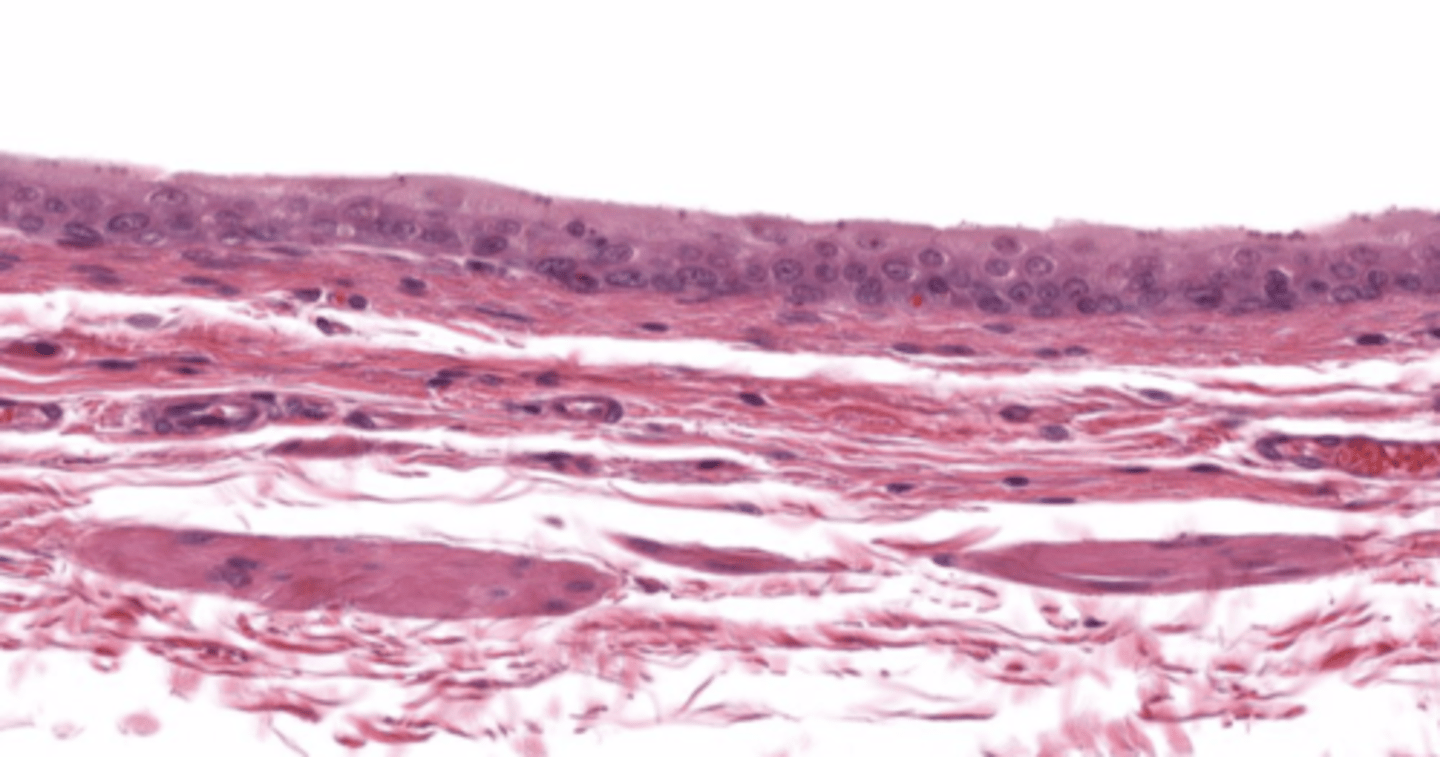
loose connective tissue