Cytochrome P450 enzyme and drug metabolism 1
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What is phase 1 metabolism
Functionalisation
Activation of drugs
Add hydroxy groups e.g. oxidation to increase solubilisation
Which reactions does CYP450 usually undergo
Oxidation
What is phase 2
Conjugation for detoxification and excretion
What enzymes are involved in phase 2
UDP-glucuronic acid transferases
Glutathione-s-transferases
What can occur In phase 2 reactions
several metabolic pathways
one can predominate
What happens to the enzyme doing the reaction
Metabolises several drugs even if no structural similarity
Not very specific
effects drug-drug interactions and tolerance
Name a primary metabolic enzyme
Xanthine oxidase
Involved in metabolism of DNA/RNA bases
What does xanthine oxidase metabolise
Metabolises theophylline
theobromine
caffeine
how can metabolic rate vary
T1/2 in humans for caffeine can vary
Phase 1 reactions
oxidation
hydrolysis
Hydroxylation of aromatic rings and aliphatic groups
hydration
dethioacetylation
isomerisation
reduction: rare
Where are CYP450 found
In endoplasmic reticulum in the liver
membrane bound- metabolises lipophilic drugs
What does the reaction require
NADPH, O2, NADPH cytochrome P450 reductase
Selective oxygenases
selective oxygenanases for steroids present in mitochondriaLidocaine
Properties of CYP450 metabolism
stereoselective- one isomer often metabolised
reactions are regiospeciyfic- particular carbon is hydroxylated
exact details depends on enzymes
Metabolism of chiral drugs
different stereoisomers of drugs are different drugs
Therefore different kinetics, different products at different rate with varying enzymes
Enzymes are built from chiral molecules
What group is found in cyp450
Haem group
contains iron
What is required to initiate the reaction
Dioxygen from air
NADPH
Auxillary enzyme e.g. reduCtase
negative catalysis
ØEnzymes catalyse their reactions by negative catalysis (the enzyme generates a highly reactive chemical species and suppresses the reactions which are not required).

Structure of CYP450
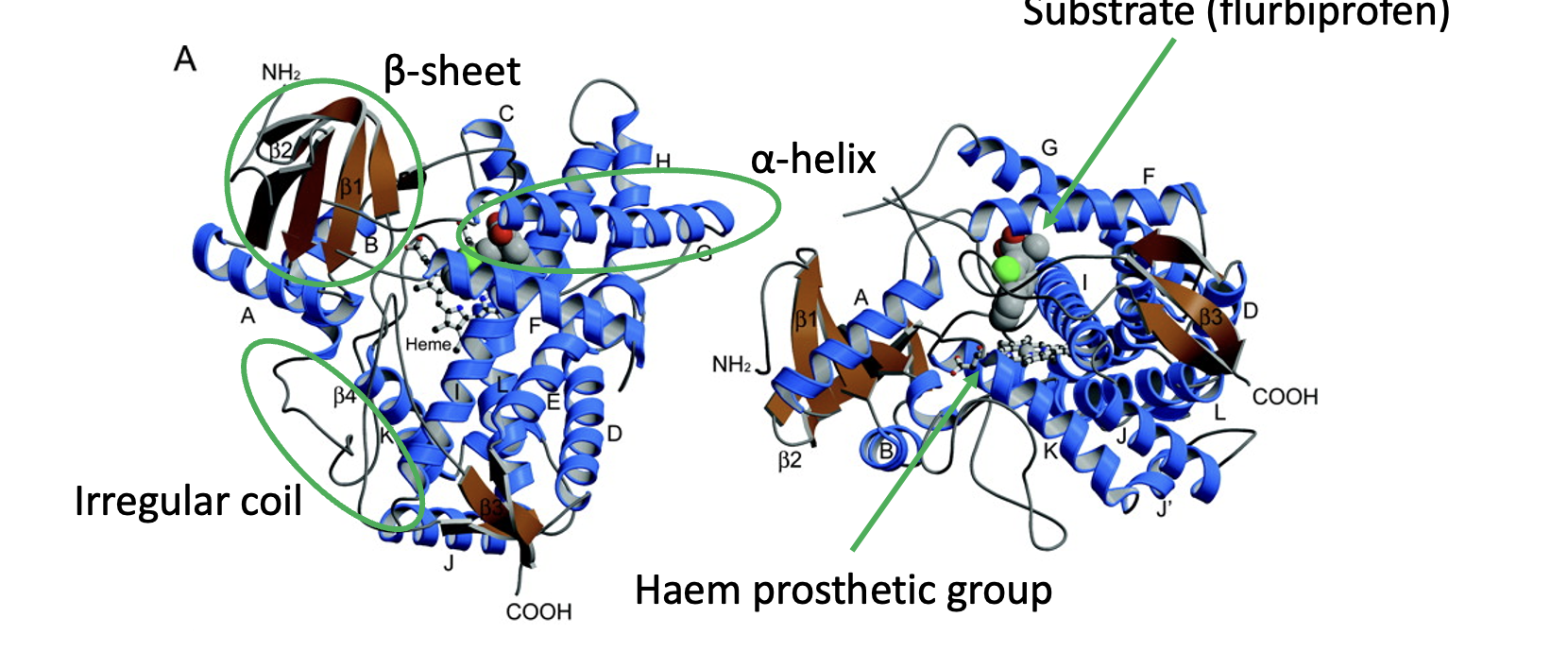
CYP450 MOA
Haem cofactor is non-covalently bound to the enzyme;
Reactivity of the haem centre depends on iron ligands;
Example is CYP2C9 with flurbiprofen bound

Explain the catalytic cycle
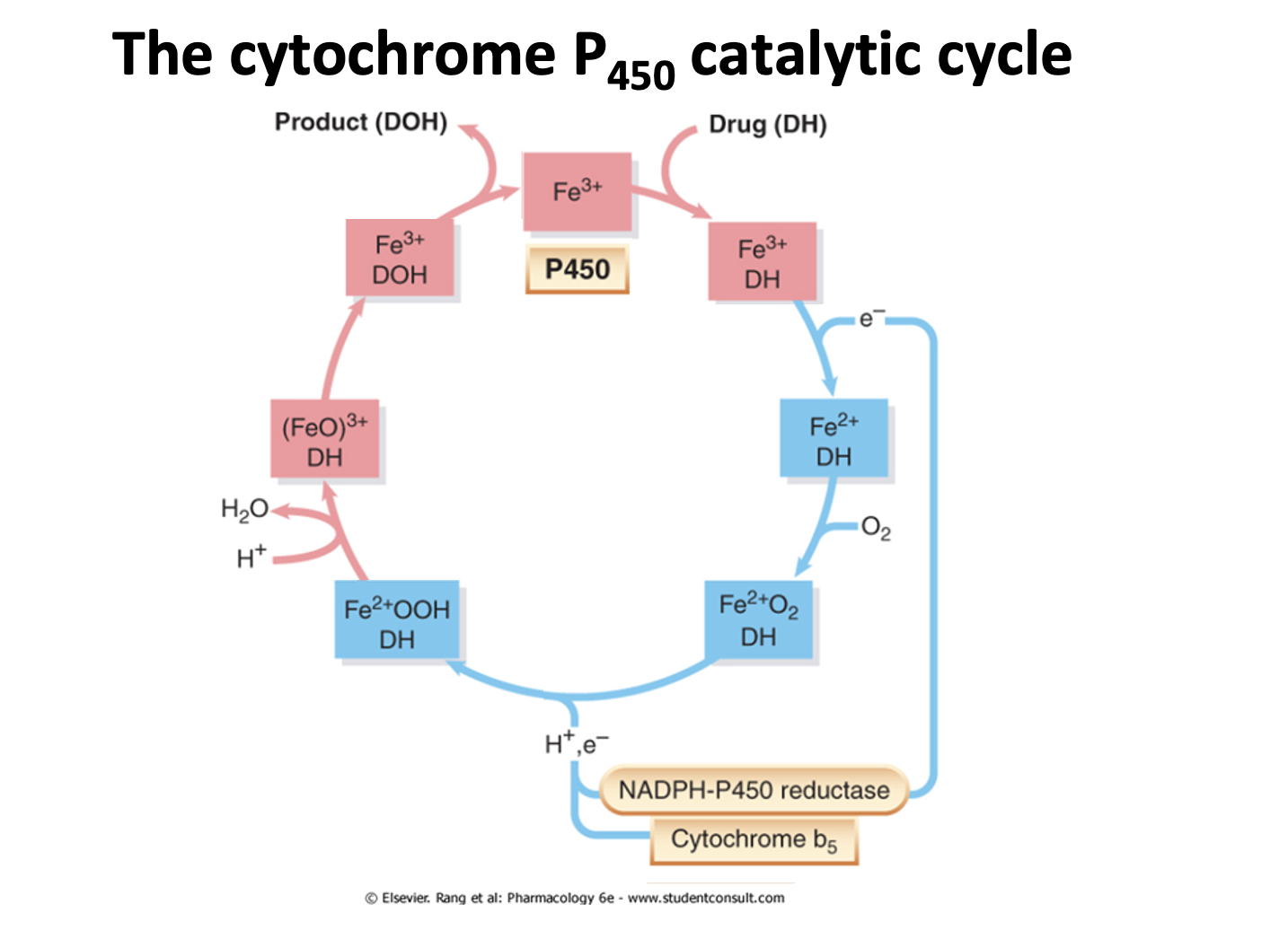
What happens to iron in catalytic cycle
Substrate binding to protein causes iron low spin to high spin change
Hydroxylation mechanisms
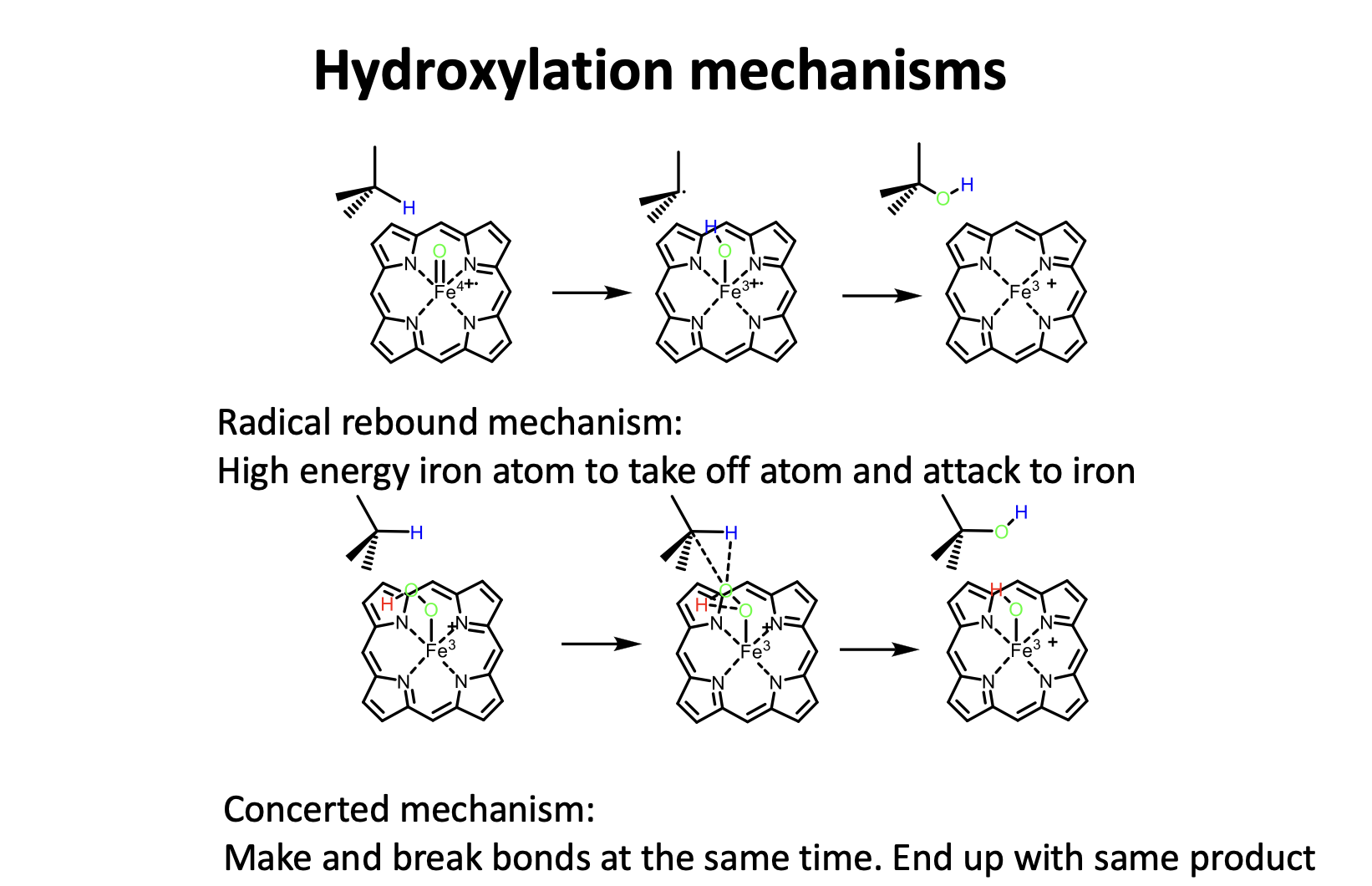
Explain uncoupled reactions
Dioxygen and NADPH are consumed but substrate is not oxidised;
Under most conditions uncoupled reactions are small proportion of catalytic cycles;
Product is reduced oxygen (hydrogen peroxide);
Source of H2O2 is unclear, but results from an abortive catalytic cycle;
P450 enzymes can also function as organic peroxidases.

super-family

The whole group of enzymes that catalyse the same or a similar type of reaction using a similar mechanism and are related by primary sequence homology or identity

What are the 3 super families
CYP enzymes (various oxidative reactions);
UDP-glucuronosyl transferases (‘glucuronidation’);
Glutathione-S-transferases (‘glutathione conjugation’).

Homology

when sequences are aligned an amino acid in a particular position is conserved by type

Identity
Identity means that when sequences are aligned an amino acid in a particular position is always the same
How do we classify enzymes
Classification of enzymes is based on amino acid primary sequence identity.

Inducibility
These enzymes are inducible (increased expression) by small molecules/drugs – results in faster metabolism of all drugs processed by the same enzyme.

Metabolism
Levels of CYP3A4 expression vary 100-fold between individuals – results in differences in metabolism & pharmacokinetics.

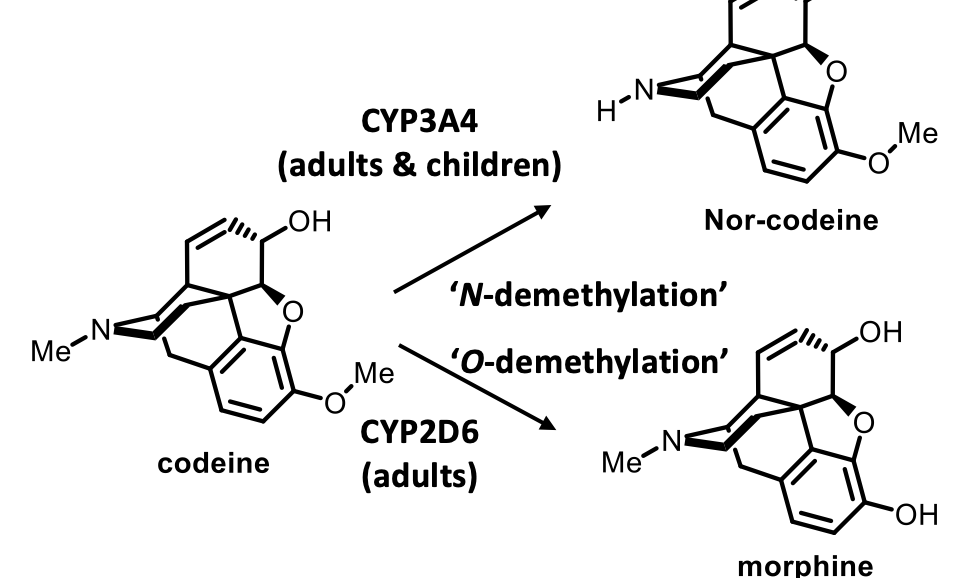
Expression in children
age of patient matters as metabolism varies between children and adults
Drugs with very different structures can be metabolised by the same enzyme