Chemistry Thermodynamics - Test 7
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
state
energy is a ____ function
state function
means that it does not matter how we get there (independent of pathway)
1st law
energy cannot be created or destroyed
1st law
any change in energy of a system must be balanced by a transfer of energy either into or out of the system
q
heat symbol
heat
transfer of thermal energy between 2 objects at different temperatures
T
temperature symbol
temperature
measure of the particle motion in a system
temperature
proportional to the kinetic energy of the particles
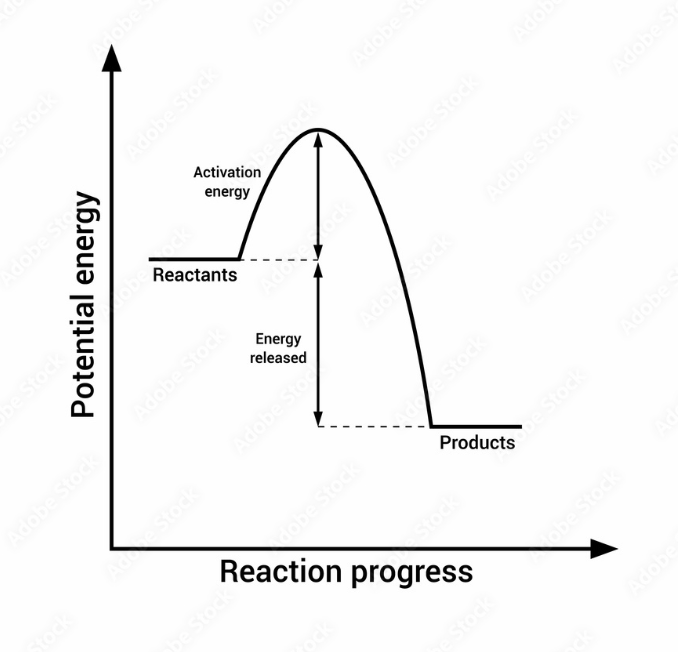
endothermic
addition of energy is required (products have more energy)
+H
temperature will go down
-H
temperature will go down
exothermic
energy is released (products have less energy)
-H
endothermic (enthalpy)
+H
exothermic (enthalpy)
heat, work
2 ways to transfer energy
+q
endothermic (heat symbol)
-q
exothermic (heat symbol)
endothermic
heat added to the system
exothermic
heat released from the system
+w
work done on system
-w
work done by system
E
= q + W
W
work
+E
+q + w
-q - w
-E
+q - w
-q + w
E
= qp = H
enthalpy
flow of heat at constant pressure
heat
you can view ____ as a reactant/product
exothermic
reactants —> products + heat = ____ reaction
endothermic
reactants + heat → products = _____ reaction
endothermic
ice —> water —> steam
exothermic
stream —> water —> ice
vaporization
_____ > H fusion
vaporize
it takes more energy to ____ because IMFs (H bonds_ are completely broken
endothermic
expanding solute, separating cations are ions:
-H1
endothermic
expanding solvent/separate H2O molecules (weakens H bonds):
+H2
exothermic
allow solute and solvent to interact/H2O molecules solvate ions:
-H3
hot to cold
heat will flow from ______ until temperatures are the same
q
is the heat transferred
H
is the heat transferred per mole
calorimetry
a process of measuring heat based on observing temperature change
specific heat capacity
energy required to raise the temperature of 1g by 1C
4.184 J/gxC
H2o C
up
q is less than zero when temp goes ___
exothermic
down
q is greater than zero, temp goes ____
endothermic
m
mass (g)
c
specific heat capacity (J/gxC)
T
change in temperature
enthalpy of fusion
energy required to melt a substance, or energy given off when you freeze a substance
KJ/mol, KJ/g
units for enthalpy of fusion/vaporization
enthalpy of vaporization
energy required to vaporize a substance or to condense a substance
specific heat capacity
energy required to heat a substance, usually given in J/gxC
endothermic
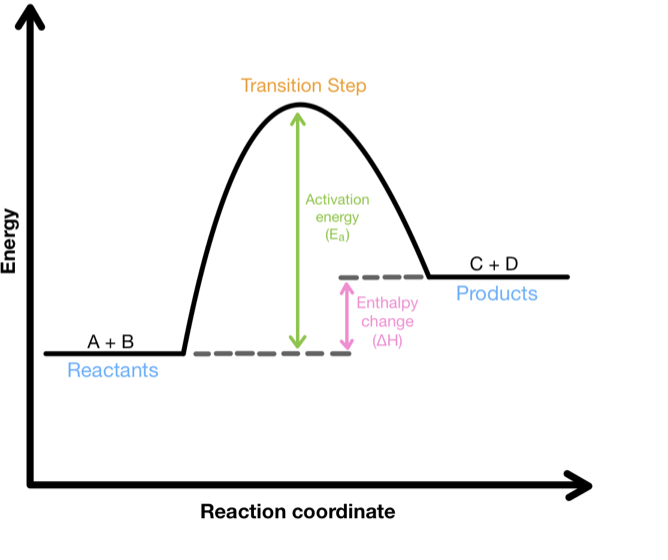
exothermic