APHG Unit 6
1/57
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Urban Hearths
The original ancient centers of civilization
Where large cities first existed
Locations that could grow food and be defensible
Example: Mesopotamia
Urbanization
Movement of people from rural areas to cities
10 million
A how much population does a city need to be considered a megacity
semi periphery city
large cities in between average and mega city, often caused by rural to urban migration and high birth rates
20 million
A how much population does a city need to be considered a metacity
periphery countries
the least developed and least powerful nations; often exploited by the core countries as sources of raw materials, cheap labor, and markets
semiperiphery countries
nations ranking in between core and periphery countries, with some attributes of the core countries but with less of a central role in the global economy
core country
According to world systems theory, the most advanced industrial countries, which take the lion's share of profits in the world economic system.
core city
According to world systems theory, the most advanced industrial cities, which take the lion's share of profits in the country’s economic system.
Suburbanization
Movement of upper and middle-class people from urban core areas to the surrounding outskirts to escape pollution as well as deteriorating social conditions (perceived and actual)
urban sprawl
The process of urban areas expanding outwards, usually in the form of suburbs, and developing over fertile agricultural land. Often uncontrolled and unplanned
Edge City
Cities that are located on the outskirts of larger cities and serve many of the same functions of urban areas, but in a sprawling, decentralized suburban environment. Often contains office & retail space.
Exurbs
areas of new development beyond the suburbs that are more rural but on the fringe of urbanized areas - low population density
Boomburb
A city with more than 100,000 residents located within a metropolitan area but that is not the central city and that has maintained a strong growth rate in recent years.
World Cities
A group of cities that form an interconnected, internationally dominant system of global control of finance and commerce. Ex: NY, London, Tokyorank-size rule
rank-size rule
A pattern of settlements in a country, such that the nth largest settlement is 1/n the population of the largest settlement. Ex. Major city: 12 million, next largest city: 6 million, next largest city: 4 million, next largest city: 3 million, etc.
primate city
The largest settlement in a country, if it has more than twice as many people as the second-ranking settlement. Ex. Mexico City, Paris
Gravity Model
A model that predicts the interaction between two places based on their population size and distance. It suggests that larger cities attract more people and services than smaller ones.
Christaller's Central Place Theory
explains how towns and cities are spaced out to provide services to people based on how far they’re willing to travel for them through using hexagons because it helps everyone have access to what they need without leaving gaps

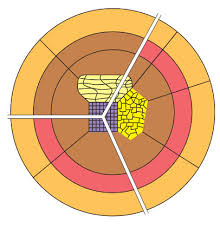
burgess concentric zone model
a model that describes urban land use in concentric circles, with the central zone representing businesses and the outer zones housing different socioeconomic groups as distance from the center increases.
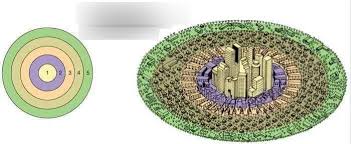
1
CBD in Burgess Concentric Zone Model
2
old homes, factories, sometimes poorer housing in Concentric Zone Model
3
Working-Class Homes (small homes, close to factories) in concentric zone model
4
middle-class suburbs in concentric zone model
5
commuter zone - rich suburbs in concentric zone model
Hoyt Sector Model
the theory of urban structure that a city develops in a series of certain sectors, instead of rings.
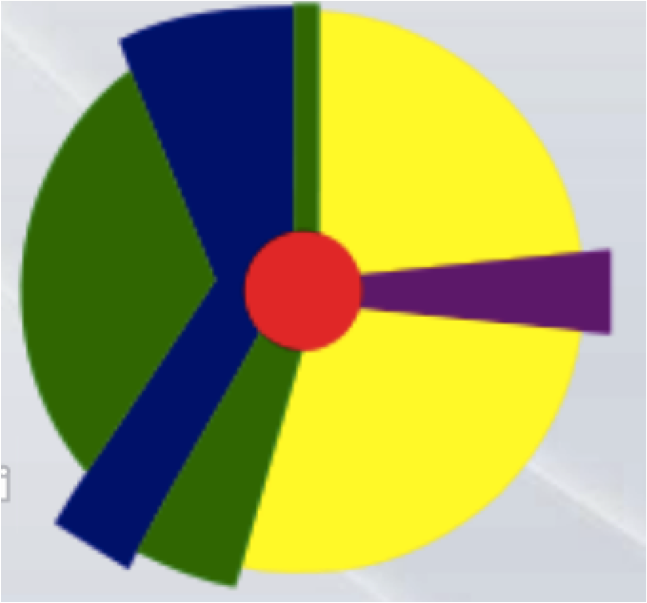
Multiple Nuclei Model
Model developed for a North American city, shows loss of dominance of CBD; the traditional influence of the CBD is decentralized and moved to multiples nodes around the city
Galactic (peripheral) City Model
represents the post-industrial city with its several, dispersed business districts. This model represents a distinct decentralization of the commercial urban landscape as the economy has transitioned to services as the leading form of production. Manufacturing has declined significantly and become specialized.
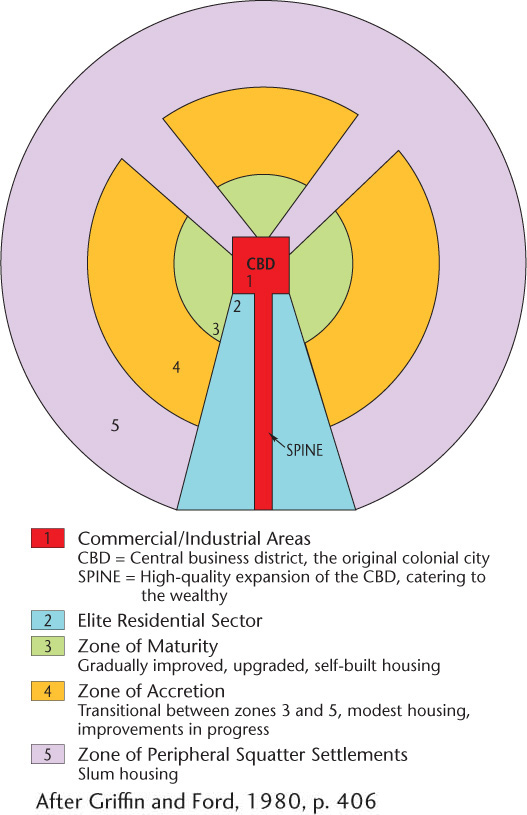
Latin American City Model
Developed by Ernst Griffin and Larry Ford. Blends traditional Latin American culture with the forces of globalization. The CBD is dominant; it is divided into a market sector and a modern high-rise sector. The elite residential sector is on the extension of the CBD in the "spine". The end of the spine of elite residency is the "mall" with high-priced residencies. The further out, less wealthy it gets. The poorest (disamenity sectors) are on the outer edge.
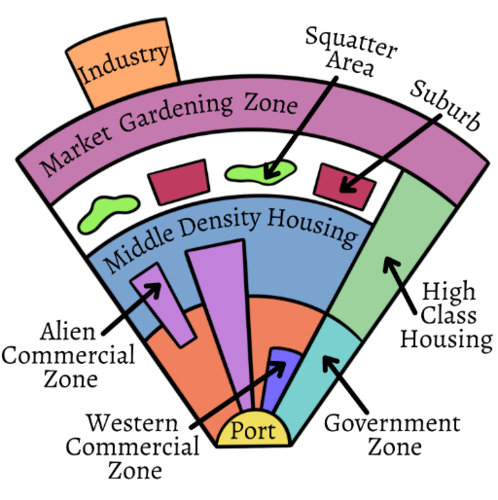
Southeast Asian City Model
McGee developed a model showing similar land-use patterns among medium sized cities of Southeast Asia. Its focal point is the old colonial port zone. The model also does not find any CBD in Asia, but rather he found elements of the CBD present as separate clusters surrounding the port zone.
African City Model
model that suggests that African cities have more than one CBD; often a traditional CBD, a CBD that reflects the colonial era; and a modern CBD
Interdependence
A relationship between countries (or cities) in which they rely on one another for resources, goods, or services
Bid rent theory
a chart explaining land costs getting cheaper as you move away from the CBD
mixed land use
More than one type of zoning, such as a condominium that has residential and commercial units. Part of Smart Growth and New Urbanism.
smart growth policies
an urban planning theory that concentrates walkable city areas to prevent urban sprawl. Features include, mixed use and compact design.
New Urbanism
emphasizes walkable, mixed-use neighborhoods with accessible public spaces, aiming to create human-scaled urban environments and reduce reliance on cars
housing discrimination
During the postwar suburban boom, federal agencies continued to insure mortgages that barred resale of houses to non-whites, thereby financing housing segregation.
Redlining
A discriminatory real estate practice in North America in which members of minority groups are prevented from obtaining money to purchase homes or property in predominantly white neighborhoods.

Blockbusting
A process by which real estate agents convince white property owners to sell their houses at low prices because of fear that persons of color will soon move into the neighborhood
Disamenity Zones
areas not connected to city services and under the control of drug lords and gangs; often found in Latin American cities
Zones of Abandonment
Areas that no longer have value to investors and are abandoned by businesses
Squatter Settlement
An area within a city in a less developed country in which people illegally establish residences on land they do not own or rent and erect homemade structures.
Inclusionary Zoning
zoning regulations that create incentives or requirements for affordable housing development
urban renewal
Program in which cities identify blighted inner-city neighborhoods, acquire the properties from private members, relocate the residents and businesses, clear the site, build new roads and utilities, and turn the land over to private developers.
Gentrification
A process of converting an urban neighborhood from a predominantly low-income renter-occupied area to a predominantly middle-class owner-occupied area.
Brownfields
a former industrial or commercial site where future use is affected by real or perceived environmental contamination.
farmland protection policy
governmental policies meant to protect agricultural lands surrounding a city to avoid suburbanization
field studies
a method that involves observing everyday activities as they happen in a natural setting
de facto segregation
the separation of different racial or ethnic groups that occurs not by law but by social norms and practices.
Slow-growth cities
urban communities where the planners have put into place smart growth initiatives to decrease the rate at which the city grows horizontally to avoid the adverse affects of sprawl
Greenbelts
A ring of land maintained as parks, agriculture, or other types of open space to limit the sprawl of an urban area.
transportation-oriented development
a type of urban development that seeks to maximize access to public transport, encouraging sustainable and efficient land use.
zoning laws
laws in a city or town that designate certain areas, or zones, for residential and business use
urban infill
new development that is sited on vacant or undeveloped land within an existing community, and that is enclosed by other types of development.
high-density housing
Housing that accommodates a large number of people relative to the land area, for example, high-rise apartments
Medium Density Housing
Subdivision or suburban neighborhood
low-density housing
typically made up of single- family homes that are detached with green space between properties- typically owned by the residents
range and threshold
the maximum distance people are willing to travel to use a service (range) and the minimum number of people needed to support the service (threshold)